Effects of Rejuvenator Dosage, Temperature, RAP Content and Rejuvenation Process on the Road Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Testing Method
2.2.1. Optimum Dosage of Rejuvenator Test
- Traditional laboratory tests of asphalt
- 2.
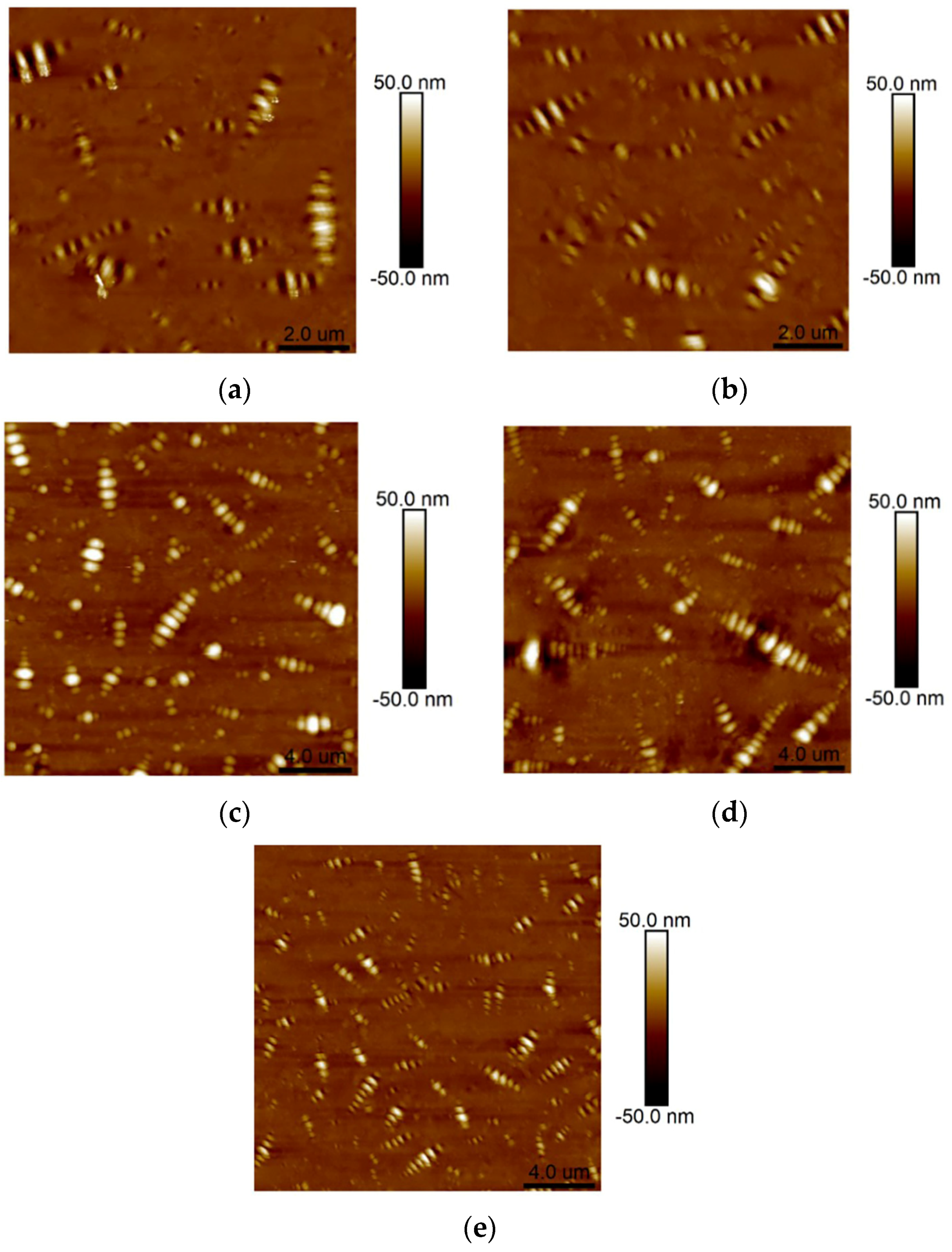
- Atomic force microscopy (AFM) test
2.2.2. Temperature Control Test
- Milling temperature control test
- 2.
- Optimum mixing and compaction temperature test
2.2.3. Road Performance Test
2.2.4. Effect of Rejuvenation Process on Road Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixture
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Optimum Dosage of Rejuvenator
3.1.1. Rejuvenator Content
3.1.2. Nano-Morphology of Asphalt Sample
3.2. Effect of Temperature Control
3.2.1. Milling Temperature Control
3.2.2. Optimum Mixing and Compaction Temperature
3.3. Effect of RAP Content on Road Performance
3.3.1. High-Temperature Stability
3.3.2. Moisture Susceptibility
3.3.3. Low-Temperature Crack Resistance
3.4. Effect of Rejuvenation Process
4. Conclusions
- As the content of the rejuvenator increases, the softening point of the recycled asphalt increases, the penetration and ductility decrease and the indexes of , and gradually decrease. Based on the penetration, ductility, softening and Nanomorphology analysis of recycled asphalt, the optimum rejuvenator content is 4%.
- The damage of aggregate can be reduced by milling the pavement under high temperature and ensure the uniformity of the original pavement gradation. For every 10% increase in RAP content, the average mixing and compaction temperature of hot recycled asphalt mixture decreases by 2–6 °C.
- As the RAP content increases, the high-temperature stability of the hot recycled asphalt mixture increases, the moisture-induced damage and the low-temperature crack resistance decrease. The strain performance density of 10 KJ/m3 is proposed as the index to evaluate the low-temperature performance of recycled asphalt mixture. From comprehensive road performance results, the optimum percentage of RAP is 30%.
- High moisture-induced damage and high-temperature stability can be obtained by using RAP + rejuvenator co-heating construction process for recycled asphalt mixture. High low-temperature crack resistance can be obtained by using a RAP + rejuvenator not-heating construction process.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nosetti, A.; P’erez-Madrigal, D.; P’erez-Jim’enez, F.; Martínez, A.H. Effect of the recycling process and binder type on bituminous mixtures with 100% reclaimed asphalt pavement. Construct. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.G. Situation and development of hot in-place recycling technology of asphalt pavement. J. China Foreign Highw. 2019, 39, 50–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Frank, R. 100% recycled hot mix asphalt: A review and analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2014, 92, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, S.; Santos, J.; Oreškovi´c, M.; Losa, M. A comparative environmental impact analysis of asphalt mixtures containing crumb rubber and reclaimed asphalt pavement using life cycle assessment. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milad, A.; Taib, A.M.; Ahmeda, A.G.F.; Solla, M.; Yusoff, N.I.M. A Review of the use of reclaimed asphalt pavement for road paving applications. J. Teknol. 2020, 82, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanbakhsh, H.; Karimi, M.M.; Naseri, H.; Nejad, F.M. Sustainable asphalt concrete containing high reclaimed asphalt pavements and recycling agents: Performance assessment, cost analysis, and environmental impact. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 244, 118837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Frank, R. 100% hot mix asphalt recycling: Challenges and benefits. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 3493–3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dughaishi, H.A.; Lawati, J.A.; Bilema, M.; Babalghaith, A.M.; Mashaan, N.S.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Milad, A. Encouraging sustainable use of RAP materials for pavement construction in Oman: A Review. Recycling 2022, 7, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.P.; Lee, N. A sensitivity study of RAP cost and performance on its life cycle benefits. Trans. Tech. Publ. 2013, 723, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Influences of preheating temperature of RAP on properties of hot-mix recycled asphalt mixture. J. Test. Eval. 2016, 44, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.J.; Leng, Z.; Hsu, S.C. Comparative eco-efficiency analysis on asphalt pavement rehabilitation alternatives: Hot in-place recycling and milling-and-filling. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.T.; Polaczyk, P.; Zhang, M.M.; Xiao, R.; Jiang, X.; Huang, B.S. Comparative study of pavement rehabilitation using hot in-place recycling and hot-mix asphalt: Performance evaluation, pavement life prediction, and life cycle cost analysis. Transp. Res. Record. 2022, 2677, 03611981221099907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Y.; Han, D.D.; Yang, T.; Tang, D.; Huang, Y.X.; Tang, N.X.; Zhao, Y.L. Field observations and laboratory evaluations of asphalt pavement maintenance using hot in-place recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 271, 121864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.T.; Wang, X.C.; Zhang, M.Y.; Chen, Z.; Meng, J.Q.; Shao, X.S. Morphology and properties changes of virgin and aged asphalt after fusion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 44, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Guo, Y.; Peng, L.; Guo, F.; Yu, H. Rejuvenating effect of soft bitumen, liquid surfactant, and bio-rejuvenator on artificial aged asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.T.; Hu, W.; Polaczyk, P.A.; Han, B.Y.; Xiao, R.; Zhang, M.M.; Huang, B.S. Rheological and aging characteristics of the recycled asphalt binders with different rejuvenator incorporation methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, G.; Jamal, A.; Almoshageh, M.; Alharbi, F.; Awan, H.H. Performance evaluation of aged asphalt pavement binder through rejuvenators. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Q.; Liu, G.Q.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, J.; Pan, Y.Y.; Zhou, J. Research on the aging and rejuvenation mechanisms of asphalt using atomic force microscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilema, M.; Bin Aman, Y.; Hassan, N.A.; Al-Saffar, Z.; Ahmad, K.; Rogo, K. Performance of aged asphalt binder treated with various types of rejuvenators. Civ. Eng. J. 2021, 7, 502–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Cao, L.P.; Fini, E.H.; Li, L.W.; Liu, Z.Y.; Dong, Z.J. Behaviors of asphalt under certain aging levels and effects of rejuvenation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.Y.; Shen, F.; Ding, Q.J. Micromechanism of the dispersion behavior of polymer-modified rejuvenators in aged asphalt material. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foroutan Mirhosseini, A.; Kavussi, A.; Tahami, S.A.; Dessouky, S. Characterizing temperature performance of bio-modified binders containing RAP binder. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04018176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, X.M.; Cao, J.W.; Feng, D.C.; Gao, L.B.; Hu, W.; Yi, J.Y. Performance evaluation of recycled asphalt mixtures with various percentages of RAP from the rotary decomposition process. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.W.; Yang, F.; Cheng, M.; Wang, Y.F.; Amirkhanian, S.; Wu, S.P.; Wei, M.H.; Xie, J. Multi-scale performance evaluation and correlation analysis of blended asphalt and recycled asphalt mixtures incorporating high RAP content. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 317, 128278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.H.; Koting, S.; Katman, H.Y.B.; Ibrahim, M.R.; Babalghaith, A.M.; Asqool, O. Performance of high content reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) in asphaltic mix with crumb rubber modifier and waste engine oil as rejuvenator. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.; Mokhtari, A.; Lee, H.D.; Tang, S.; Williams, C.; Schram, S. Effects of high reclaimed asphalt pavement content on the binder grade, fatigue performance, and mix design. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04016218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Gu, X.Y.; Wu, M.; Ni, F.J. Application of a high percentage of reclaimed asphalt pavement in an asphalt mixture: Blending process and performance investigation. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 753–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilema, M.; Aman, M.Y.; Hassan, N.A.; Memon, Z.A.; Omar, H.A.; Yusoff, N.I.M.; Milad, A. Mechanical performance of reclaimed asphalt pavement modified with waste frying oil and crumb rubber. Materials 2021, 14, 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Pan, B.F. Effect of RAP content on fatigue performance of hot-mixed recycled asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 328, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.Q.; Ma, T.; Fan, J.W.; Fang, Z.Y.; Chen, T.; Zhou, Y. Experimental study of high modulus asphalt mixture containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaumanis, M.; Arraigada, M.; Poulikakos, L.D. 100% recycled high-modulus asphalt concrete mixture design and validation using vehicle simulator. Construct. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.T.; Polaczyk, P.; Park, H.; Jiang, X.; Hu, W.; Huang, B.S. Performance evaluation of temperature effect on hot in-place recycling asphalt mixtures. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 277, 124093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Lv, X.C.; Zhou, Y.H.; You, Z.P.; Chen, Y.L.; Cui, Z.J.; Diab, A. Homogeneity evaluation of hot in-place recycling asphalt mixture using digital image processing technique. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 258, 120524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.X.; Rizvi, H.; Purdy, C.; Ali, A.; Mehta, Y. Effect of rejuvenator types and mixing procedures on volumetric properties of asphalt mixtures with 50% RAP. Construct. Build. Mater 2019, 218, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, H.N.; You, Z.P.; Wang, Y.X.; Jiang, X.; Gao, J.F. Effect of mixing sequence on compaction property of hot recycled asphalt mixtures. Eng. J. Wuhan Univ. 2019, 52, 317–323. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, Y.; Wang, H.N.; Ji, C.J.; You, Z.P. Effect of mixing sequence on high temperature performance of hot recycled asphalt mixture. J. Jiangsu Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 38, 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, C.H.; Li, Y.W.; Feng, L.; Huang, S. Performance development of polyurethane elastomer composites in different construction and curing environments. Construct. Build. Mater 2023, 365, 130047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Transport, M.O. Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Transport, M.O. Technical Specifications for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements; China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2004. [Google Scholar]









| Property Indices | Test Results | Test Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Viscosity at 60 °C (mm2/s) | 87 | T0619-2011 |
| Flash point (°C) | 238 | T0633-2011 |
| Saturates (%) | 7.3 | T0618-1993 |
| Aromatics (%) | 69.5 | T0618-1993 |
| Viscosity ratios before and after RTFOT | 2.3 | T0610-2011 T0619-2011 |
| Mass ratios before and after RTFOT | 1.5 | T0610-2011 |
| 15 °C Density (g/cm3) | 0.94 | T0603-2011 |
| Appearance | Black viscous liquid |
| Number | Rejuvenation Construction Process |
|---|---|
| Process I | RAP Heating + Rejuvenator |
| Process II | RAP + Rejuvenator Co-heating |
| Process III | RAP +Rejuvenator not heating |
| Rejuvenator Dosage (%) | Penetration (25 °C, 0.01 mm) | Softening Point (°C) | Ductility (10 °C, cm) | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24.6 | 70 | 8.7 | Permeable Rejuvenator |
| 3 | 30.8 | 66.3 | 12.2 | |
| 4 | 35.5 | 64.2 | 15.6 | |
| 5 | 41.2 | 60.9 | 18.7 |
| Sample Shape | Aged Asphalt | Asphalt Mixed with | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3% Rejuvenator | 4% Rejuvenator | 5% Rejuvenator | Virgin Asphalt | ||
| n | 34 | 38 | 76 | 59 | 79 |
| 118 | 108 | 98.6 | 115 | 82.1 | |
| 9.42 | 9.5 | 5.04 | 8.15 | 5.48 | |
| 5.68 | 7.58 | 2.68 | 4.82 | 2.93 | |
| RAP Content (%) | Mixing Temperature (°C) | Compaction Temperature (°C) | DS (Time mm−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value | Specification Requirement | |||
| 30 | 175 | 152 | 2872 | ≥800 |
| 40 | 170 | 150 | 3216 | |
| 50 | 165 | 144 | 3753 | |
| 60 | 155 | 139 | 3989 | |
| RAP Content (%) | Mixing Temperature (°C) | Compaction Temperature (°C) | TSR (%) | MS0 (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test Result | Specification Requirement | Test Result | Specification Requirement | |||
| 30 | 175 | 152 | 89.6 | ≥75 | 87.6 | ≥80 |
| 40 | 170 | 150 | 85.9 | 86.6 | ||
| 50 | 165 | 144 | 79.3 | 83.1 | ||
| 60 | 155 | 139 | 76.7 | 81.3 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, T.; Fan, Q.; Hou, M.; Mi, S.; Yan, X. Effects of Rejuvenator Dosage, Temperature, RAP Content and Rejuvenation Process on the Road Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixture. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043539
Jiang T, Fan Q, Hou M, Mi S, Yan X. Effects of Rejuvenator Dosage, Temperature, RAP Content and Rejuvenation Process on the Road Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixture. Sustainability. 2023; 15(4):3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043539
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Tingting, Qiaojuan Fan, Mingye Hou, Shuzhen Mi, and Xiaohui Yan. 2023. "Effects of Rejuvenator Dosage, Temperature, RAP Content and Rejuvenation Process on the Road Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixture" Sustainability 15, no. 4: 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043539
APA StyleJiang, T., Fan, Q., Hou, M., Mi, S., & Yan, X. (2023). Effects of Rejuvenator Dosage, Temperature, RAP Content and Rejuvenation Process on the Road Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixture. Sustainability, 15(4), 3539. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15043539









