Abstract
Interpretive structural modeling (ISM) is widely used to understand the complex connections between different components. This study presents a bibliometric overview of ISM research, with a focus on its linkages to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the impact of COVID-19. The study analyzed 1988 publications on ISM published between 2012 and 2021, of which 1202 were directly mapped to the SDGs and 59 were related to COVID-19. The study identified key authors, institutions, countries, and journals involved in the research and their linkages to the SDGs. The results showed that ISM research is strongly linked to SDG 12 (on responsible consumption and production) and SDG 9 (on industry, innovation, and infrastructure). We also identified influential SDGs on the basis of centrality measures such as betweenness and eigenvector. The top four countries contributing to ISM publications were India, China, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The most frequently cited journals were Benchmarking: An International Journal, Sustainability, the Journal of Modelling in Management, and the Journal of Cleaner Production. Four main clusters were identified in the ISM research, including (1) integration with AHP and fuzzy logic for promoting sustainability alignment, (2) ISM-based strategy development for various stakeholders, (3) ISM-based decision-making in various fields, and (4) ISM-based risk evaluation. For the first time, studies that used the ISM approach to understand the epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 were identified, and their key findings were discussed. The study also identified several emerging topics for future ISM research, such as blockchain and IoT, environmental management systems, climate change adaptation, smart cities, and humanitarian logistics and their potential linkages to the SDGs.
1. Introduction
In today’s academic, industrial, and research fields, people and organizations often face complex problems due to rising digitalization, increased information access, advancing technology, networked societies, and cross-cultural differences, among other factors. These individuals deal with large amounts of complex, ill-defined, or basic information that they struggle to manage with their current tools. As a result, multiple solutions can be generated for a single issue, requiring a shared framework for similar interpretations. To address this, interpretive structural modeling (ISM) helps people understand the intricate connections between these pieces from a common perspective. ISM transforms a poorly defined model into a systematic and well-articulated model by establishing relationships between its elements.
J.N. Warfield established ISM as a potent tool for organizing complex problems []. Warfield developed a mathematical dialect relevant to many complicated issues, given that they can be evaluated from the perspective of sets of components and relations, relying on discrete or finite mathematics. The created structural models are presented to the client as a collection of words and digraphs, where the mathematics are concealed in a computer program []. ISM entails conducting a thorough, systematic, and complete review of the literature on a subject at hand, speaking with specialists in the field about it first hand, breaking down a complicated problem into smaller ones, and then creating an extensive multilevel structured model [,]. This technique has the added benefit of MICMAC analysis, which allows researchers to understand the forces that drive and depend on the factors that they are studying [].
In contrast to ISM, total interpretive structural modeling (TISM) employs nodes and linkages to illustrate the relationships. ISM and TISM are interpretive methods used to clarify poorly organized mental models such that they become structured, hierarchical ones. Both scholars and practitioners use them as tools in theory development []. These interpretive techniques address important questions in theory development, such as what, how, and why. While ISM successfully answers the first two questions, those of what and how, TISM goes further, by also addressing the question why and adding more explanatory power in theory development. The m-TISM model is utilized to categorize these linkages because ISM alone is insufficient to explain the interdependencies of components. Paired comparison is then employed to lessen the cognitive load during model construction. The MICMAC method is beneficial for analyzing indirect linkages [].
A group of 17 goals and 169 targets, known as the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), were established by the UN General Assembly in 2015 as a component of the 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda. These goals provide a universal framework for sustainable development and aim to end poverty, protect the planet, and ensure peace and prosperity for all. The SDGs are integrated and indivisible, recognizing that economic growth, social development, and environmental protection are interdependent and mutually reinforcing. ISM is a research method that can analyze the interconnections and interdependencies between different elements in a system. In the context of the SDGs, ISM can be used to understand the interrelationships between the various SDGs and their associated targets and to identify the key drivers and barriers to achieving these goals. This information can then inform decision-making and prioritize actions to achieve the SDGs. In addition, ISM can also be used to analyze the relationships between stakeholders involved in achieving the SDGs, such as governments, businesses, and civil society organizations.
ISM can also be used to prioritize actions to achieve specific SDG targets. For example, ISM can be used to prioritize actions to achieve SDG 7 Target 7.2 (access to affordable, reliable, sustainable, and modern energy for all). This can involve identifying the key drivers of energy access, such as the availability of renewable energy sources, the level of investment in energy infrastructure, and the level of political commitment to energy access. ISM can also be used to identify the key drivers and barriers to achieving SDG 3 Target 3.8 (universal health coverage), such as the availability of healthcare resources, the quality of healthcare infrastructure, and the level of political commitment to health. Recent bibliometric studies have analyzed research topics such as green hydrogen, female entrepreneurship, virtual learning environments, and their SDG mappings [,,].
The scope of ISM has also been expanded to include identifying obstacles to knowledge management in engineering institutions. The study suggested that the ISM method could benefit these contexts by developing approaches for integrating technology and capturing and developing knowledge []. Furthermore, the ISM approach is increasingly being used in chemical laboratories to support the instruction of students in knowledge-based settings []. ISM is used in the service sector, which includes the healthcare industry, startups, and higher education [,,,], to discover enablers for effective management. This model has generated crucial inputs for government officials to improve their policies for enhancing these service sectors. Risk interrelations play a significant part in green building projects, another trend in the construction sector currently receiving a great deal of attention []. Apart from these studies, ISM has been employed in the current pandemic situation, COVID-19. This approach is used to solve various issues from COVID-19 and to make the organization more resilient and agile in the present scenario [,,,,,].
The following discourse will examine ISM-related research work in various contexts. Authors from various fields have employed the ISM technique in multiple contexts. [] looked into the issue of creating a welcoming environment for intercultural communication. In the context of rural India, [] pinpointed the main difficulties that common service centers face and established their hierarchical relationships by using ISM. According to the research, the main difficulties faced by the common service centers in rural India include “higher travel distances and transaction costs”, “poor digital literacy”, and “low awareness” of e-government services. In a study in India by [], the ISM method was used to identify the 26 challenges to implementing green supply chain management in 10 auto parts manufacturing companies in Tamil Nadu. After conducting a literature review and obtaining input from business professionals and industry leaders, the study identified the main obstacles as a lack of consumer knowledge, skepticism about environmental principles, insufficient green infrastructure, and poor supplier obligations. The ISM approach has also been used to improve the efficiency of inventory and manufacturing control systems. For example, by working together, a company could enhance its clustering algorithms and other classification technologies []. Additionally, the ISM method combined the information systems of Indian Railways and Indian Airlines. The study showed how the method could improve communication in these organizations by displaying detailed information structures and using digraphs [].
An approach to identifying the key success factors of encouragement and motivation for the effective implementation of sustainable supply-chain-management practices in Indian oil and gas sectors was provided by []. The mutual links between the drivers were established by using the ISM method, which not only aids in understanding the relative relationship between the critical success factors but also helps to build their interdependence while implementing sustainability. A MICMAC analysis was also used to determine the significance of critical success factors in sustainability on the basis of their driving and dependency power. In addition, thanks to governmental regulations and growing public awareness of environmental protection and waste reduction, the return of old goods is becoming a crucial logistical operation []. ISM and fuzzy techniques are used to prioritize orders on the basis of how closely they resemble the ideal solution.
The critical components for applying knowledge management in engineering businesses have been examined to produce an ISM, which demonstrates the interrelationships of the variables and their levels, in the study published by []. Organizations need to have a strong capacity to develop, organize, and use their knowledge assets in this era of globalization if they want to thrive. In addition, in a lean manufacturing company, [] employed ISM to pinpoint various wastes. The study aided in the discovery of the interconnectedness of various wastes in a manufacturing organization by using the ISM tool.
Even during the current COVID-19 scenario, the ISM technique is used to solve various issues, such as studies conducted by [,,,,,,] and many others. The study conducted by [] emphasized the interdependencies of the factors affecting artificial intelligence in the healthcare sector during COVID-19. The paper offered an interpretive structural model to broaden the skeleton of intricate relationships and significance among the crucial pieces that have been uncovered. [] integrated an enhanced “type-2 fuzzy TISM” with a Bayesian network to create an integrated model to assess medical waste transportation risk during COVID-19.
Because management practices are the foundation of every business, their importance to the success of renewable energy organizations cannot be understated. Energy companies are dealing with serious environmental problems, so the industry eventually needs to engage in environmentally friendly production. This can be accomplished only by implementing concurrent management methods, as slow management practices result in dormancy and poor performance. The study conducted by [] looked into the new management techniques that will allow the market’s current demands to be met by the renewable energy industry, especially in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic’s emergence. On the side of the consumer, because they could not make offline payments for purchases in India, because of the COVID-19 pandemic, [] concentrated on identifying crucial impediments to the adoption of mobile payment systems.
In light of the COVID-19 issue, the automotive industry has been unstable and unpredictable. Automotive firms need to properly manage their agile supply chains if they want to thrive in this new market. The discovery of the agile drivers driving the supply chain is the major determinant of this management. [] employed a MICMAC analysis after an ISM technique to determine the link between these enablers. [] utilized the ISM method to create a structural model and examine digital learning drivers. The COVID-19 pandemic introduced numerous difficulties to human life. The practice of teaching and learning is one of these difficulties. Although digital media are a part of teaching and learning, digitizing the educational system is necessary. In light of this, the study conducted by [] examined the factors influencing digital learning in the COVID-19 and potential post-COVID-19 contexts.
The recent COVID-19 pandemic has negatively impacted the pharmaceutical supply chain, particularly in emerging economies that are most vulnerable because of their insufficient resources. Identifying any potential obstacles keeping supply chains from sustainably performing in a post-COVID-19 environment has become crucial. To aid decision makers, [] looked into and analyzed the obstacles that the pharmaceutical supply chain of a growing country faces in its pursuit of sustainability. [] identified and classified the major difficulties associated with applying industry 4.0 technology in the medical device sector. Global industry executives are overcoming obstacles as their firms undergo a digital transition following COVID-19. When developing a strategy for industry 4.0 transformation and ensuring they get off to a good start, medical device manufacturing businesses may use the industry 4.0 implementation problems found and categorized in their research as a reference.
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic has further emphasized the significance of researching ISM and its linkages to the SDGs. Both new and exacerbated difficulties to sustainable development have been brought up by the pandemic. ISM can assist in identifying and ranking the important elements that are essential to achieving the SDGs while accounting for the pandemic’s effects. ISM can support decision-making processes and aid in identifying more-effective and more-efficient solutions by modeling the relationships and trade-offs between the many SDGs and associated variables. Therefore, understanding ISM and how it relates to the SDGs is essential in light of the COVID-19 pandemic because it can promote sustainable development initiatives that are sensitive to changing global issues. Despite the widespread use, the existing literature on ISM techniques has yet to fully explore its potential, specifically its linkages to SDGs and the impact of COVID-19. To address this gap, further research using bibliometrics and science-mapping analysis is necessary to comprehensively examine the literature, covering a wider range of years.
Our study has identified the following research questions (RQs):
RQ1: How has the area of study on ISM transformed in terms of publications, citations, source titles, countries, institutions, etc., and how well do they map to the various SDGs?
RQ2: How well does ISM research map to the various SDGs?
RQ3: What themes have emerged in ISM research?
RQ4: How has COVID-19 impacted ISM research?
2. Study Methods
Our study employed quantitative statistical analysis by using a reliable data set of peer-reviewed publications from various academic and geographical areas. The Dimensions database was chosen for its trustworthy data integrity and field-normalized citation scores, which were determined by using a field categorization scheme []. The validity of this database has been reinforced by other research studies [].
Science-mapping tools are a fundamental aspect of bibliometrics. Bibliographic coupling, the most widely used citation-based method in science mapping, is especially useful for analyzing the growth of new research fields and tracking recent research trends [,]. This method is well suited for capturing emerging patterns in a field because it is forward-looking [,]. The present study combined country and journal bibliographies to determine the similarity between the cited articles, and it applied a network analysis to identify research hot spots and changes over time and to gain insights into new research areas []. The visualization tool VOSviewer was utilized to map and highlight the temporal and structural features of the corpus of scientific research, and it has been commonly used for science-mapping purposes [,,,,].
This study is organized by initially describing the protocol used for the literature review. With SDG mappings in context, the results and discussion are focused on the overall trend of publications and citations, the top contributing nations and their bibliographic couplings, the most productive institutions and authors, the frequently cited journals, keyword co-occurrence analysis, and the impact of COVID-19. The final section includes the conclusions and future research directions.
2.1. SPAR-4-SLR Protocol
A systematic literature review requires a protocol to ensure careful planning, consistent execution, and transparency for replicability []. However, few protocols exist for conducting a comprehensive literature review []. The commonly used PRISMA protocols are used primarily by researchers performing systematic literature reviews []. While these protocols enable researchers to present their studies in an organized and consistent manner, they provide limited support for conclusions and justifications []. To address these limitations, an alternative protocol was suggested, namely the SPAR-4-SLR protocol, specifically created for systematic literature reviews []. Figure 1 shows the SPAR-4-SLR protocol used in this study.
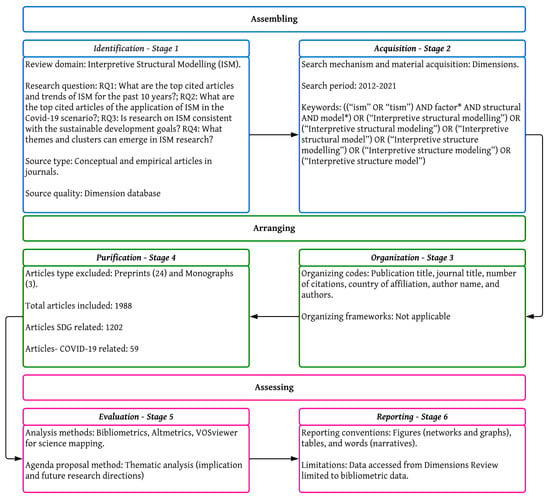
Figure 1.
SPAR-4-SLR protocol framework.
2.1.1. Assembling
The first step in the process is called “assembling” and involves gathering publications for review. In this study, the Dimension database was used for this purpose. The search was conducted by using the search term provided in Figure 2 in the title and abstract on 29 November 2022. The search resulted in a list of 1988 publications from 2012 to 2021.
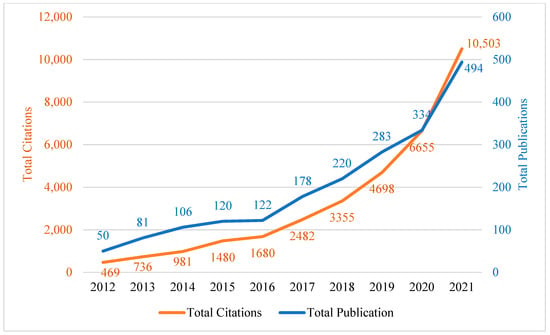
Figure 2.
Publications and citations trends.
2.1.2. Arranging
The next step in the process is “arrangement”, which involves organizing and cleaning up the publications by using inclusion and exclusion criteria. The search data for the publications were coded by using standard bibliometric characteristics, such as the publication title, journal title, number of citations, country of affiliation, and author name. The filtering process excluded monographs and preprints.
2.1.3. Assessing
The “evaluation” section of the article discusses the analysis method and the study constraints. The primary tool used for analysis was the VOSviewer. No additional ethics clearance was required, because the study utilized secondary data accessible to anyone with access to the Dimension database.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Publications and Citations Trends
The growth of ISM-related publications over the years reflects the field’s dynamic and rapidly evolving nature. Figure 2 displays the number of publications and citations received each year. To answer RQ1, we analyzed the publication patterns in the ISM literature between 2012 and 2021 by using the data collected for the number of total publications and citations. The results show a yearly increase in both the number of publications and the number of citations. The highest number of publications, 494, was recorded in 2021, and the most citations, 10,503, were received in the same year, surpassing the number of citations received in 2020 (6655 citations). These findings highlight that 2021 was a particularly productive year for research in the field of ISM.
3.2. Most-Influential Authors
This study uses Table 1 to list the most influential authors in the field of ISM and interdisciplinary topics relevant to ISM from 2012 to 2021. The author with the most publications is M. Suresh (TP: 41), but with a citation of 997, followed by Sushil (TP: 36; TC: 1578) and Rakesh D Raut (TP: 30; TC: 1068). Suresh’s article “Factors influencing the epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 pandemic: A TISM approach” received the most citations and used TISM to identify the factors influencing the spread of the pandemic. The findings suggest that a country’s susceptibility to the virus can be predicted on the basis of its geographic location and future meteorological conditions. These factors are important in supporting the virus’s life span and airborne dispersion. The authors suggest that addressing the issue should prioritize the connection elements, such as changes in host behavior and the number of contacts, identified in the paper.

Table 1.
Top-10 most-influential authors in terms of publications.
3.3. Mapping ISM Research to SDGs
Figure 3 shows ISM research publications mapped to the SDG, where the top five are SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production, TP: 277), SDG 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure, TP: 206), SDG 7 (affordable and clean energy, TP: 82), SDG 11 (sustainable cities and communities, TP: 66), and SDG 2 (zero hunger, TP: 56), according to the total number of publications.
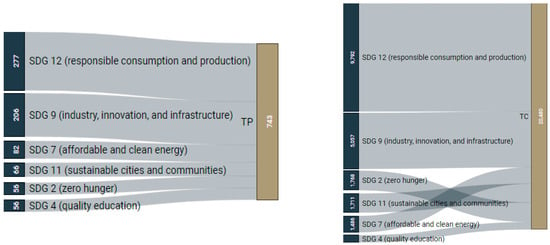
Figure 3.
ISM research publications mapped to SDGs.
SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production, TC: 9792), SDG 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure, TC: 5057), SDG 2 (zero hunger, TC: 1768), SDG 11 (sustainable cities and communities, TC: 1711), and SDG 7 (affordable and clean energy, TC: 1486) are the most mapped ISM research topics in terms of the total number of citations.
Table 2 shows the frequently cited publications from the top-three SDGs: SDG12, SDG 9, and SDG 7

Table 2.
Frequently cited publications mapped to SDGs.
The top-cited study by [] focuses on the barriers to implementing green supply-chain management, making it relevant to SDG 12’s target of “responsible consumption and production”. The study aims to identify the dominant obstacle to implementing the green supply-chain-management concept, to make it easier for companies to adopt it. The study results show that green supply-chain-management challenges vary among different sectors in India that produce auto components, and they show that the vendor hurdle is the dominant obstacle, particularly in promoting environmental awareness. By eliminating the dominant obstacle, the study’s results will aid companies in implementing green supply-chain management, contributing to SDG 12’s target of sustainable management and the efficient use of natural resources (Target 12.2).
The study by [] has received 454 citations and is the most significant SDG 9 mapped publication that focuses on the sustainability roles of Industry 4.0 and adds to the body of research on sustainability. This is relevant to SDG 9, which aims to “build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation”. The study methodically defines the sustainability roles of Industry 4.0 by first explaining its design and architecture and second analyzing key design concepts and technological trends. This research can help stakeholders in the private and public sectors, businesspeople, and academics to better understand the sustainability potential of the digital age and promote closer collaboration to ensure that Industry 4.0 efficiently, equitably, and effectively achieves its sustainability objectives worldwide.
The most significant SDG 7 mapped publication was the article by [], which received 142 citations. The article addresses the rapidly increasing demand for electricity on a global scale and the need for more cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and socially responsible energy supplies, consumption, and technologies. The study focuses on the need to improve grid operations and resource availability to meet the rising energy demands in an economical, effective, and environmentally responsible way. The study also examines the barriers to implementing smart grid technology and identifies ways to improve its deployment. This study is relevant to SDG 7 as it addresses the need for affordable and clean energy, which is crucial in addressing climate change and reducing radiative forcing.
In our study, a cocitation network was created to reveal the linkages between the SDGs as measured by citations (Figure 4). The proximity between the SDGs on the network indicates their similarity in terms of cocitation occurrence, meaning that publications from the two SDGs are often cited together in the same set of publications. The nodes’ sizes reflect the SDG frequency in terms of overall publications, and the thickness of the edges shows how often these SDGs are cocited. Two clusters of SDGs were identified: Cluster 1 (red) includes SDGs that have a strong industrial and economic growth orientation, such as SDG 12 (responsible production), SDG 9 (industry and innovation), SDG 11 (sustainable cities), and SDG 8 (economic growth). Cluster 2 (green) groups SDG 7 (clean energy) and SDG 13 (climate action), possibly focusing on the environmental aspects, along with linkages to SDG 3 (health) and SDG 4 (education).
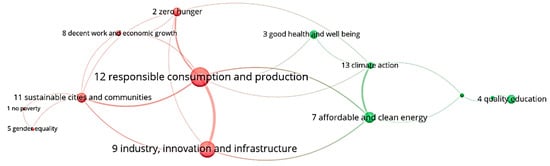
Figure 4.
Cocitation network showing SDG linkages.
We analyzed the SDG network by using two network analysis measures: betweenness and eigenvector. The betweenness centrality of an SDG node measures its significance as a connecting point in the flow of information within the network. This is determined by counting how many times the node lies on the shortest path between two other SDG nodes. An SDG node with high betweenness centrality serves as a bridge between different sections of the network. Eigenvector centrality is another metric used in social network analysis to measure a node’s influence within a network []. This considers the number of connections a node has and the centrality of the nodes it is connected to. In other words, the importance of a node is determined by the number of important nodes it is connected to. SDG nodes with high eigenvector centrality in SDG networks will be considered key centers of attention.
Figure 5 displays the three SDGs with the highest betweenness centrality in the field of ISM research. The thickness of the links between the two goals on the map represents the strength of the connection between the two SDGs. The strongest links are between health and peace (SDG 3, 16), between health and hunger (SDG 3, 2), between education and life below water (SDG 4, 14), and between health and industry (SDG 3, 9). The figure highlights the central role of SDGs 2, 6, and 3 in the network.

Figure 5.
ISM research and SDG linkages (betweenness centrality).
In Figure 6, SDG 3 (good health) is seen as the network leader, having the highest eigenvector centrality value. SDG 9 (industry innovation) and SDG 2 (zero hunger) are the second-most-influential SDG in the eigenvector network.
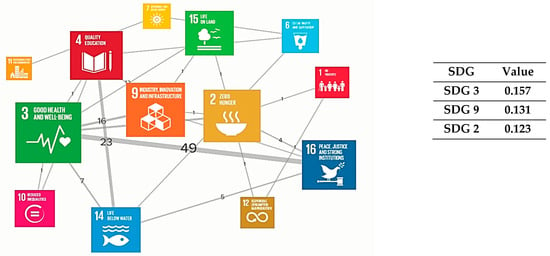
Figure 6.
ISM research and SDG linkages (eigenvector centrality).
3.4. Top Contributing Countries and Their SDG Mappings
Table 3 shows that India, China, and Iran are the top contributing countries in the field of ISM, with 32%, 11%, and 4% of total publications, respectively. These three countries have a total of 1210 publications, which represents 47% of all ISM publications in the review corpus. The authors of ISM publications in the review corpus came from 67 countries.

Table 3.
Top contributing countries in terms of publications and citations.
The citation mean (TC/TP), calculated to understand the quality and impact of the publications from each country, shows that Denmark received the highest TC/TP, of 109.6, despite having only 22 publications. Uruguay received 59 citations for one publication, with a TC/TP of 59, while France had a TC/TP of 52.9 with 846 citations. In terms of the total number of citations (TC), India ranked first with 21,507 citations, followed by China (TC: 4905), the United Kingdom (TC: 3382), and the United States (TC: 3083). These rankings reflect the quality and impact of each country’s contributions to the field of ISM.
The bibliographic coupling analysis in Figure 7 highlights the collaboration and exchange of ideas in the field of ISM among different countries. It shows various countries’ contributions to the ISM field in different years. In 2016, Japan, Taiwan, and Denmark made notable contributions. India, China, the United States, Indonesia, the United Arab Emirates, and France dominated the field in 2017 and 2018. The number of publications from countries such as the United Kingdom, Australia, Iran, Pakistan, Italy, and Bangladesh increased in 2019. The graph shows strong connections between India and China, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Australia in ISM studies. India also seems to have connections with France, Canada, Thailand, Malaysia, Italy, and other countries. This information provides an understanding of international collaboration in the field of ISM.
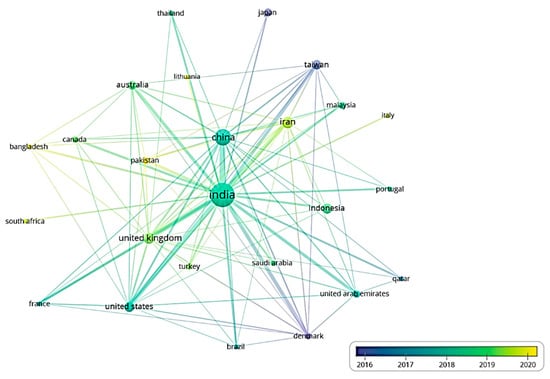
Figure 7.
Bibliographic coupling of countries.
According to Figure 8, India has the highest number of publications mapped to the highest number of SDGs. SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production) and SDG 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure) are the most frequently mapped SDGs among the top contributing countries.
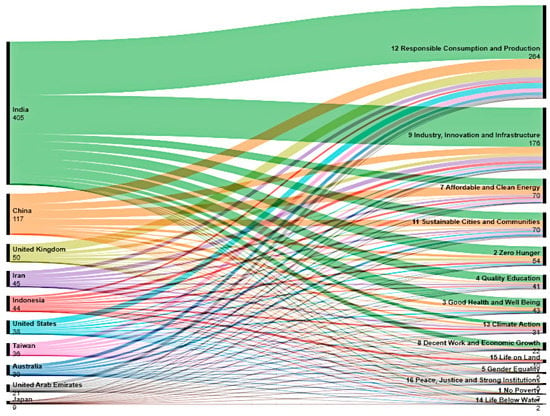
Figure 8.
Mapping publications to SDGs on the basis of countries.
3.5. Frequently Cited Journals and Their SDG Mappings
Determining the most frequently cited journal sources is important because it will help future scholars focus their research on these journals. Table 4 lists the top-cited journals on ISM research, led by Benchmarking: An International Journal (TP: 54) and the Journal of Cleaner Production with the highest citations (TC: 3999).

Table 4.
Top-cited journals in terms of number of publications and citations.
The overlay visualization of the most frequently cited journals in the ISM field is presented in Figure 9. This figure displays the similarity between different journals on the basis of the ISM publications that they cite. The closer the journal nodes, the more similar their cited ISM publications. The figure shows a strong connection between Sustainability and the Journal of Cleaner Production, the International Journal of Production Research, Benchmarking: An International Journal, and the Journal of Modelling in Management. Additionally, a large number of ISM-related publications appeared in the journal Sustainability post-2020, as well as in Benchmarking between 2017 and 2019. These findings highlight the strong connections between certain ISM journals and indicate where future research in this field may be directed.
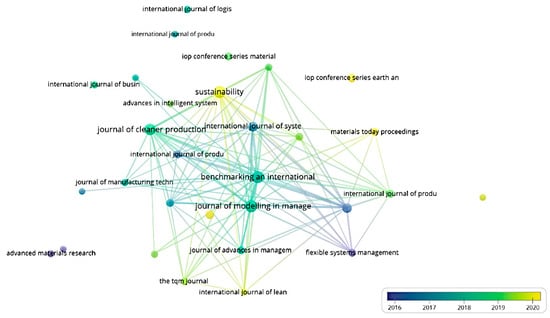
Figure 9.
Overlay visualization of top journals.
According to Figure 10, the Journal of Cleaner Production has the highest number of publications mapped to 12 SDGs. Among the top-cited journals, SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production) and SDG 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure) are the most frequently mapped SDGs.
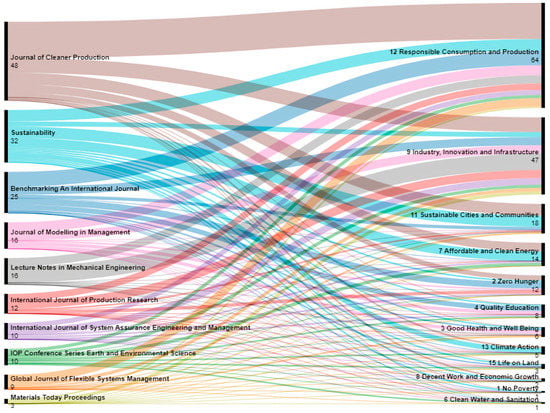
Figure 10.
Mapping publications to SDGs on the basis of journals.
3.6. Most-Productive Institutions and Their SDG Mappings
Table 5 presents the most productive institutions in terms of ISM publications. The top 10 institutions are in India, China, Iran, the United Kingdom, Taiwan, the United States, Indonesia, Australia, Japan, and Pakistan. India is the leading country, with 122 institutions contributing to the field; followed by China, with 81 institutions; and followed by the United Kingdom, with 27 institutions. The Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, stands out as the top contributor, with 130 publications; followed by Amity University, with 48 publications; and followed by Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham University, with 44 publications.

Table 5.
Most-productive academic institutions in terms of number of publications.
As seen in Figure 11, the Indian Institute of Technology Delhi has the highest number of publications mapped to SDGs, where SDG 12 has the most. Among the top-cited journals, SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production), SDG 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure) are the most frequently mapped SDGs.
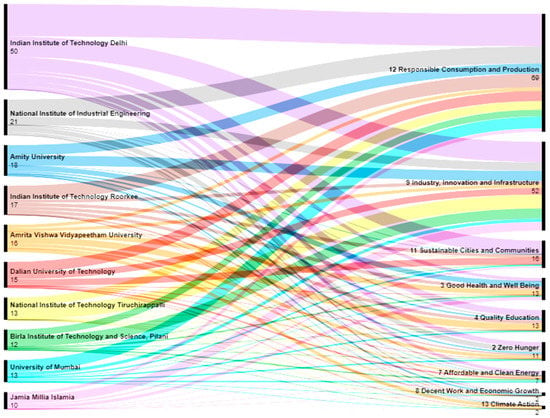
Figure 11.
Mapping publications to SDGs on the basis of institutions.
3.7. Co-occurrence Analysis Based on Keywords
The visualization in Figure 12 shows the connection between different keywords and the topics related to ISM. The keywords are grouped on the basis of their relationship and frequency of occurrence in the literature. The size of each node represents the frequency of occurrence, while the strength of the connection between nodes represents the co-occurrence relationship. The keywords related to ISM can be seen as clusters, where the strongest connections are in the center of the network. This information provides a clear picture of the main topics and subtopics related to ISM and their relationships. By visualizing the keywords network, researchers can obtain an understanding of the research structure and the trends in the ISM field.
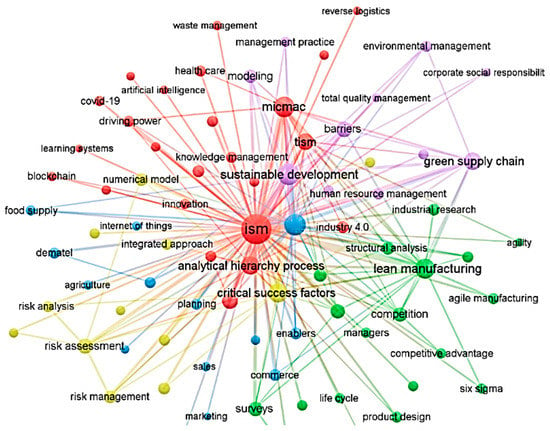
Figure 12.
Co-occurrence network of keywords.
Table 6 displays the clusters of keywords on the map of ISM research on the basis of their co-occurrence network. Each cluster comprises keywords that frequently appear together in the same research articles. The table shows the size of each cluster, the number of publications, and the main keywords representing the cluster. The thematic mapping of the keywords provides insights into the structure and connections of the research topics in ISM. It helps identify the research areas that are most prominent in the field.

Table 6.
Overview of clusters based on keyword co-occurrence analysis.
3.7.1. Cluster 1 (Red): Integration of ISM with MICMAC/TISM/AHP/Fuzzy Logic and Alignment to Sustainability
The first cluster, shown in red, focuses on integrating ISM with other methods and aligning it with sustainability. This cluster has the highest number of publications (1434) and citations (29,335) but has a lower TC/TP ratio (20.5) compared with other clusters. The top-three-cited articles are shown in Table 7.

Table 7.
Top-cited articles in Cluster 1.
The frequently cited article by [] explores the challenges to implementing green supply-chain management and uses ISM to analyze the 26 identified obstacles. It highlights that the main barrier is the supplier and calls for proper consideration of the client and distribution network in supply-chain management, including green supply-chain management. The second-most-frequently-cited article in the red cluster is “Industry 4.0, digitization, and opportunities for sustainability”, by []. The study sheds light on the potential of Industry 4.0 to contribute to sustainability despite the radical changes brought about by digital transformation. Additionally, it further identifies the sustainability roles of Industry 4.0 and helps stakeholders, including government entities, business owners, and academics, to better understand the opportunities for sustainable development presented by the technological age. They aim to ensure that Industry 4.0 efficiently, equitably, and equivalently meets its sustainability goals throughout the world. The third-most-frequently-cited article in this cluster is “Analysis of Third-Party Reverse Logistics Provider Using ISM”, by []. The article examines how a corporation can participate in reverse-logistics activities by employing a third-party logistics provider in a complex business environment. The study highlights the importance of selecting the right suppliers for reverse logistics as the idea and practice of reverse logistics matures [].
3.7.2. Cluster 2 (Purple): Framing Strategies for Various Stakeholders by Using the ISM Technique
The second cluster contains 282 publications that use the ISM approach to develop strategies for various stakeholders. The ISM approach effectively identifies decision-making factors, with 6724 citations and a TC/TP of 23.8. Table 8 shows the top-three-cited articles in this cluster.

Table 8.
Top-cited articles in Cluster 2.
Ref. [] article has the highest number of citations, at 276. This study aimed to investigate the obstacles to Industry 4.0 adoption in manufacturing companies and provide insights into the key barriers, their short-term and long-term effects, and their driving forces. This information can assist professionals and policymakers in overcoming the challenges of a successful digital manufacturing platform. The second-most-frequently-cited article in Cluster 2 is “Barriers in green lean six sigma product development process: An ISM approach”, by [], which has a citation count of 169. The article explores the use of ISM to identify barriers to implementing green lean six sigma, a strategy aimed at reducing costs, optimizing processes, and promoting sustainability in product development. The study highlights the strategic value of this approach in the highly competitive business environment. The third-most-frequently-cited article in Cluster 2 is “Strategic response to Industry 4.0: an empirical investigation on the Chinese automotive industry”, by [], with 145 citations. This study investigates the strategies adopted by the Chinese automotive industry toward Industry 4.0 and identifies the key factors for successful adoption. The findings suggest that factors other than company size and nature positively impact technological deployment but do not necessarily lead to the use of advanced production methods.
3.7.3. Cluster 3 (Green): Decision-Related Matters Using the ISM Technique in Various Fields
The third cluster consists of 425 publications that use ISM to make informed decisions across various fields. With 13,475 citations, this cluster has the highest TC/TP ratio, of 31.7. Table 9 shows the top-three-cited articles in this cluster.

Table 9.
Top-cited articles in Cluster 3.
Agriculture in specific was studied in the current investigation by various researchers, but businesses in this field are often globally focused and face numerous issues. The ISM method can simultaneously address these problems, making it a valuable tool for conducting regular business. It is believed that the implementation of blockchain technology in the agriculture supply chain will bring about a transformation in the way transactions are conducted, reducing the number of intermediaries, late payments, and long process lead times. India, a developing country facing sustainability challenges in the agriculture supply chain, needs this technology to meet its expanding population’s growing food security demands []. Businesses are under pressure from customers, international competitiveness, and government regulations to adopt sustainable practices, which has led to a focus on environmental performance over economic success []. Organizations must develop resilient supply chains to mitigate risk and gain a competitive advantage in a changing business environment. The research into supply-chain resilience has helped firms quantify and evaluate the resilience of their supply chains, aiding decision-making and potentially making it easier to manage supply-chain disruptions in dynamic settings [].
3.7.4. Cluster 4 (Yellow): Evaluation of Various Risks by Using the ISM Approach
The fourth cluster of the publication studies focuses on risk elimination through the application of ISM. There are 265 publications, with 5322 citations and a TC/TP ratio of 20.1. Table 10 shows the top-three-cited articles in this cluster.

Table 10.
Top-cited articles in Cluster 4.
The increased vulnerability of supply chains to risks from unpredictable demand, global economic integration, accelerating product life cycles, and complex international supply network relationships has led to the need for effective risk-management techniques. Companies today need to adopt innovative supply-chain-management strategies, such as “lean”, “green”, and “resilient” practices, to remain competitive. However, these practices face challenges in terms of incorporating essential issues. Therefore, senior management must concentrate on identifying the crucial “lean”, “green”, and “resilient” techniques to enhance the efficiency of automotive supply chains []. As unpredictability increases, the supply chain becomes increasingly vulnerable to risks. This is especially true for businesses that rely heavily on outsourcing and have complex international supply network relationships. To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to understand the sources of risk and how they interact [].
3.8. ISM Research and COVID-19
Studying the relationship between ISM research and the COVID-19 pandemic is important. The pandemic has caused significant concerns and speculation because of its rapid global spread, the high number of deaths, the lack of treatment, the emergence of various variants, and the reliance on social media as a source of information and communication. Using the SPAR-4-SLR framework, COVID-19 was filtered in the title and abstract of a sample of 1988 publications, resulting in 59 articles from 34 countries, the majority coming from India, Pakistan, and South Africa. The author with the most publications on the topic was M. Suresh, with 11 publications, followed by Tehmina Fiaz Qazi and Abdul Aziz Khan Niazi, each with six publications (Table 11).

Table 11.
Top authors based on number of publications.
The top-cited articles related to the ISM method and COVID-19 are shown in Table 12.

Table 12.
Top-cited articles related to COVID-19.
The top-cited article is titled “Improving supply chain sustainability in the context of COVID-19 pandemic in an emerging economy: Exploring drivers using an integrated model”. This research aims to study the drivers of sustainable supply chains in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic in Bangladesh and proposes a method that is based on a Pareto analysis, fuzzy theory, and TISM to improve supply-chain sustainability. Findings from this study suggest that financial support and policy development focused on health protocols and automation are necessary for long-term sustainability in supply chains. The MICMAC analysis also clusters drivers to provide insights into supply-chain sustainability. These findings can help industrial managers, supply-chain partners, and government policymakers address sustainability in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic []. The second-most-cited article is titled “Factors influencing the epidemiological characteristics of pandemic COVID-19: A TISM approach”. This research uses the TISM approach to identify and categorize the sociobiological and climatic factors influencing the global spread of COVID-19. The MICMAC analysis of these factors found that air temperature, humidity, age, airflow, and ventilation can increase the mortality rate of COVID-19 compared with other epidemics. The model also predicts the susceptibility of countries on the basis of their geographic location and upcoming climatic conditions. The study suggests that host behavior and the number of contacts can be targeted to address the spread of the virus, as these factors can be altered by human intervention. This is the first study to use the TISM approach to understand the epidemiological characteristics of COVID-19 [].
This is followed by another article, “What can we learn from previous pandemics to reduce the frequency of emerging infectious diseases like COVID-19?”—which is the third-most-frequently-cited article. Climate change is a leading global risk, according to the 2020 Global Risks Report. In recent decades, the frequency of new infectious diseases has increased, and rapidly mutating viruses, epidemics, and climate-sensitive vector-borne diseases are expected to increase and intensify. Susceptible disease hosts, human activities, and environmental changes contribute to the “adaptive evolution” of infectious agents. Mathematical modeling tools were used to identify and rank risk factors, including TISM and MICMAC. Immediate action is needed to address the factors contributing to the evolution of pathogens and the frequent emergence of pandemics because we are not prepared for another pandemic outbreak like COVID-19 [].
4. Future Research Directions
The results of this study suggest several research topics for further study. We arrived at future research topics on the basis of the prominence percentile from SciVal. Prominence, a measure of a field’s momentum, is used to order the topics. Topic prominence will help answer the following questions []: “Which are the topics with high momentum that are likely to be well funded and thus have higher grant success rates?”; “Who else is active and publishing research on a similar topic to mine, whom I could partner and coauthor with?”; “What are some related topics adjacent to mine with a lot of momentum, where I could focus my research attention?” The prominence percentile, which measures the topic’s popularity and dynamism, is derived from the number of citations, Scopus view, and journal CiteScore. Identifying themes with a high prominence percentile might be helpful for academics and policymakers because topic prominence is positively correlated with research funding and grants []. Table 13 shows the top topics ranked by prominence percentile.

Table 13.
Emerging research topics related to ISM.
4.1. Blockchain; Internet of Things; Cloud Computing
This topic has the highest prominence percentile, of 99.982. One of the most potential emerging economy innovations is “blockchain technology”. The enormous market opportunity from blockchain technology has captured the interest of scholars and business professionals, taking the corporate world by storm []. ISM can be used to understand the relationships between stakeholders, such as miners, developers, users, and regulators, and how they influence the functioning and evolution of the blockchain. It can also be used to analyze the dependencies between different components of the blockchain, such as the network infrastructure, consensus mechanisms, and smart contracts. Developing intriguing new technologies such as cloud computing, big data, machine learning, and cognitive computing promise to fundamentally alter how businesses operate []. Industry and technological attempts should be heavily concentrated on “enhancing regulatory clarity”, “fostering industry collaboration”, “creating a rich ecosystem”, “creating industry standards”, “investing in blockchain technology”, and, last but not least, “engaging and educating leaders on blockchains’ capability and applications” to accomplish the consistent success of blockchain-based cloud services []. Through the use of ISM methods, the hierarchical structure can be developed to lead sustainable organizations. The studies can also suggest fostering new business prospects with intelligent technology to create a predictable business climate by enhancing administrative effectiveness, openness, economic mobility, and infrastructural services. The corporate sectors are trying to adopt advanced technologies to sustain themselves in the VUCA world. ISM can help identify the potential benefits and challenges of integrating these technologies into sustainable development strategies and can be used to prioritize actions to achieve specific SDG targets.
4.2. Sustainability; Environmental Management Systems
This topic has the second-highest prominent percentile, of 99.947. There is a trend among businesses to adopt green practices as part of their strategic agendas to reduce their environmental impacts and potentially improve their performance. Using environmental management systems (EMSs) can give organizations a competitive edge as market rivalry rises. Owing to the growing consumer understanding of environmental concerns and market concern for the environment, EMS use is rising across many industries. Although there is a wealth of literature on the advantages of EMS implementation, more attention should be paid to the difficulties []. Green human resource management is currently a popular topic. Still, the literature on this subject lacks a clear definition of green human-resource-management practices and a lack of theoretical contributions to the concept of “greening” the workforce []. Future research could explore the factors that help organizations implement green human-resource-management practices, referred to as antecedents. These antecedents may include prerequisites that encourage enterprises’ green human-resource-management practices []. By considering the interconnections between EMS and specific SDG targets, ISM can support the development of integrated and effective strategies for environmental management and the achievement of the 2030 Sustainable Development Agenda.
4.3. Technology Management; Innovation; Productivity
Innovation plays a crucial role in firms’ obtaining a competitive advantage in the quickly evolving commercial sector. The extant literature covers various issues related to technology management and business innovations. Therefore, it is necessary to close these gaps in ways that contribute to organizational innovations []. Companies are putting more effort into finding novel collaborations and methods thanks to their adopting open innovation forms to better detect outside knowledge. Despite the significance of knowledge-sharing practices for businesses, only a few studies have considered how open innovation arrangements can improve knowledge-sharing practices []. How can ISM be used to identify potential barriers to technological innovation and productivity within an organization, and how can these barriers be overcome? How do external factors, such as regulations or market condition changes, affect an organization’s technological innovation and productivity? For example, ISM can be used to analyze the potential impact of technology management and innovation on SDG Target 9.5 (improve the technological capacity of the industrial sectors in all countries, especially those that are developing).
4.4. Climate Change Adaptation; Urban Climate; Resilience
Global pandemics such as COVID-19 harm people’s physical and emotional health []. To improve community resilience, particularly within the cities and our communities, ISM could be used to understand the interdependencies between adaptation strategies, such as green infrastructure, early warning systems, and disaster risk reduction measures, and understand how they influence each other. There is much focus on how cities should prepare for and recuperate from such catastrophes, and resilience has become crucial. How do external factors, such as regulations or funding changes, affect urban areas’ adaptation and resilience to climate change? Future researchers can determine the variables that affect resilience and investigate their causal relationships in order to assist in managing the risks related to COVID-19, drawing on research on resilience. ISM can be used to analyze the potential effect of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable land use on SDG Target 13.3 (boosting institutional and human capability for advance detection, impact mitigation, adaptation, and reduction of climate change).
4.5. Smart Cities; Sustainable Development
Smart cities are seen as the model for how the economy of the country would flourish in the future. Over the past 20 years, this idea has grown in significance. Thanks to their access to cutting-edge technology, robust resources, and efficient city-planning techniques, industrialized nations find it easier to construct smart cities. However, existing smart cities are helpful in that they guide future developments []. Smart cities offer suggestions for future urban development and building orientations thanks to the constant change in technology and society. The smart city includes and engages with human and social capital, in addition to just integrating innovative infrastructure and technology or the efficient transmission of information among tall buildings []. In the context of smart cities and sustainable development, ISM can be used to identify the key drivers of sustainable development and the factors that influence the adoption and implementation of smart city technologies. For example, it could be used to understand the interdependencies between smart city technologies, such as intelligent transportation systems, smart energy systems, and smart waste management systems, and understand how they influence each other. ISM could be used to understand the relationships between the various elements contributing to achieving the SDGs in a smart city. For example, ISM could be used to understand the relationships between different technologies, infrastructure, policies, and other factors that influence the progress toward the SDGs in the smart city context.
4.6. Information Modeling; Facilities Management; Construction Industry
The complexity of the construction business can be attributed to operational inefficiency, uncertainty, and dependency, which have led to a growth in the industry’s complexity. “Total quality management (TQM)”, “lean practices”, “sustainability”, “partnering”, and “building information modeling (BIM)”, among others, have all been suggested as solutions. These are directed at enhancing the procedures used in the construction sector. However, only BIM has had a significant impact on the entire industry. The introduction of BIM presents novel chances to maximize the effectiveness of prefabricated construction. A significant line of “integration” offered by BIM, a digital depiction of a built facility, is also essential for delivering prefabricated buildings []. The information and data made accessible by the BIM may be easily changed, duplicated, and distributed with the project stakeholders, improving interoperability throughout different stages of the undertaking [].
4.7. Humanitarian Logistics; Disaster Management; Big Data
Researchers can look into the humanitarian logistics aspect by using the ISM approach, especially in disaster management using big data. The key components of commercial and humanitarian supply-chain-management systems are the delivery of the “right suppliers” at the “right time”, to the “right place”, in the “right quantities”, and to the “right people” []. Future studies might also examine the effect of combining blockchain and big data analytics in the humanitarian supply chain. Other academics should in the future devote more attention to “performance metrics” and “metrics in sustainable humanitarian supply chain management”. Using ISM, it is possible to investigate the effects of behavioral factors on the humanitarian structure, including leadership and culture. The humanitarian logistics and the supply-chain field have a rare chance to combine ecological footprints. A growing community, known as responsible humanitarian logistics and the supply chain, will also result from this []. Future research in this area seems highly promising and will be crucial in determining the obstacles to using solar energy in different nations and their relative importance []. ISM can be used to analyze the potential impact of efficient humanitarian logistics and disaster management on SDG Target 11.5 (with an emphasis on safeguarding the underprivileged and those in susceptible situations, considerably decreasing the number of fatalities, the number of those impacted, and the immediate economic losses as a percentage of the world’s gross domestic product by 2030).
5. Conclusions
This study provided a comprehensive examination of ISM tool usage in the literature. By analyzing 1988 publications from 2012 to 2021, the study used bibliometric analysis and visualization techniques to highlight research hot spots and address gaps in the existing literature to respond to RQ1. The rise in publications over time highlights the research community’s growing interest in and commitment to further understanding and promoting ISM. M. Suresh was identified as the most influential author in the field. India, China, the United Kingdom, and the United States were the top four countries contributing to ISM publications, and Benchmarking: An International Journal, Sustainability, the Journal of Modelling in Management, and the Journal of Cleaner Production were the most cited journals.
RQ2 aimed to determine how well ISM research maps to the SDGs. The findings suggested that ISM research maps to multiple SDGs, with a particular focus on SDG 12 (responsible consumption and production), SDG 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure), SDG 7 (affordable and clean energy), SDG 11 (sustainable cities and communities), and SDG 2 (zero hunger). The study identified four key clusters in ISM research, including the integration of ISM with AHP and fuzzy logic for sustainability alignment, ISM-based strategy formulation for various stakeholders, ISM-based decision-making in various fields, and ISM-based risk evaluation. These findings answer RQ3, on what clusters and themes exist in the current ISM literature. RQ4 examined the relationship between COVID-19 and ISM. Research on COVID-19 and ISM has been conducted in 58 countries, most of the publications coming from India, Pakistan, and South Africa.
Recognizing that no research is comprehensive and completely free from limitations is important. One potential limitation is that some publications may have been missed in the analysis of the keywords used to shortlist articles that were not explicitly stated in the title, abstract, or keywords of the publications. This could result in some inconsistencies in the statistical analysis. Additionally, the citation analysis technique used in this study considers only the importance of the referenced papers. It does not differentiate between articles that focus specifically on the SDGs and those that mention ISM and the SDGs in part. The current analysis also focused on peer-reviewed publications and excluded gray literature, such as government reports, which could affect the results. In this study, only published literature available in well-known databases such as Dimensions was considered. Additionally, the scope of the study was limited to 2012 to 2021, so any studies published outside these years were not included in the analysis.
Implications
The method known as ISM is used to examine and comprehend the connections between diverse system components, such as objects, thoughts, and ideas. ISM aims to visually depict the system’s structure so that users can make better-informed decisions. ISM can be used by researchers to provide practitioners with many implications. By identifying a system’s essential components, ISM can assist authors in determining which components of a system are most important and how they interact. This can aid readers in understanding the important aspects that affect a specific topic or situation. ISM can give a visual depiction of the intricate connections between the system’s various components. This can aid researchers or practicians in understanding the different interdependencies and cause-and-effect linkages between the elements. ISM can assist researchers in finding the source of a problem by looking at all the elements that factor into the problem. This can aid readers in comprehending the issue’s root causes and developing workable remedies. ISM can aid researchers in assessing alternative solutions to the problem by examining how they might affect the various system components. This can aid practitioners in better understanding the potential effects of various solutions and aid them in making better-informed choices. Therefore, ISM can be a helpful tool for researchers to help practitioners comprehend complex systems and make better judgments in general. Researchers can assist practitioners in recognizing important elements, outlining relationships, identifying the core cause, and assessing potential remedies by presenting a visual picture of a system’s structure.
6. Recommended Approaches
ISM is a valuable tool for understanding the complex interrelationships among the elements. ISM can be used in the future by taking various approaches. Experts and stakeholders can be involved in the ISM process. This collaborative approach can help ensure that the model accurately reflects the interrelationships among the elements and that the results are meaningful and actionable. Multiple perspectives can be considered when developing ISM. Different stakeholders may have different views on the relationships among the elements, and these perspectives should be taken into account to develop a comprehensive model. Various software tools can be utilized to facilitate the creation and analysis of ISM. ISM can be continuously evaluated and refined as new data and information become available. Systems are dynamic and constantly evolving, and ISM should be updated to reflect changes in the system. ISM can be integrated into other analytical methods, such as fuzzy TOPSIS-ISM [], DEMATEL-ISM [], ISM and fuzzy ANP [], ISM and type-2 fuzzy [], and many more, to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the system. In conclusion, ISM is a valuable tool for understanding complex systems, and its use should be informed by taking a collaborative, multiperspective approach and should use software tools. The ongoing evaluation and the ongoing refinement of ISM are critical for ensuring that it accurately reflects the evolving nature of the system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.S. and S.M.; Methodology, S.M. and R.R.R.; Data curation, A.S., P.N. and R.R.R.; Writing—original draft, A.S. and S.M.; Writing—review & editing, P.N., V.R.S. and R.R.R.; Visualization, R.R.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Janes, F.R. Interpretive structural modelling: A methodology for structuring complex issues. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control. 1988, 10, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, R.; Dev, N.; Sharma, V. Interpretive structural modelling (ISM) approach: An overview. Res. J. Manag. Sci. 2013, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar]
- Mathiyazhagan, K.; Govindan, K.; NoorulHaq, A.; Geng, Y. An ISM approach for the barrier analysis in implementing green supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 47, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Goel, P. Exploring the domain of interpretive structural modelling (ISM) for sustainable future panorama: A bibliometric and content analysis. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 29, 2781–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sushil. Incorporating polarity of relationships in ISM and TISM for theory building in information and organization management. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 43, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, S.; Dhir, S. Modeling of strategic thinking enablers: A modified total interpretive structural modeling (TISM) and MICMAC approach. Int. J. Syst. Assur. Eng. Manag. 2020, 11, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Nair, V.K.; Prakash, V.; Patwardhan, A.; Nedungadi, P. Green-hydrogen research: What have we achieved, and where are we going? Bibliometrics analysis. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 9242–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, R.; Subramaniam, N.; Nair, V.K.; Shivdas, A.; Achuthan, K.; Nedungadi, P. Women entrepreneurship and sustainable development: Bibliometric analysis and emerging research trends. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achuthan, K.; Nair, V.K.; Kowalski, R.; Ramanathan, S.; Raman, R. Cyberbullying research—Alignment to sustainable development and impact of COVID-19: Bibliometrics and science mapping analysis. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2022, 140, 107566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, R.; Narain, R.; Agarwal, A. An interpretive structural modeling of knowledge management in engineering industries. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 2003, 1, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Suresh, M. Assessment of COVID-19 prevention and protection measures in hospitals. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 7, 100440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaishnavi, V.; Suresh, M.; Dutta, P. Modelling the readiness factors for agility in healthcare organization: A TISM approach. Benchmarking Int. J. 2019, 26, 2372–2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, A.; Suresh, M.; Panduro, J.A.T. Modelling the resilience of start-ups during COVID-19 pandemic. Benchmarking: Int. J. 2022. (ahead-of-print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Suresh, M. Factors influencing organizational agility in higher education. Benchmarking Int. J. 2020, 28, 307–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Abbasi, A.; Ryan, M.J. Analyzing green building project risk interdependencies using Interpretive Structural Modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badhotiya, G.K.; Soni, G.; Jain, V.; Joshi, R.; Mittal, S. Assessing supply chain resilience to the outbreak of COVID-19 in Indian manufacturing firms. Oper. Manag. Res. 2022, 15, 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Raut, R.D.; Sharma, M.; Choubey, V.K.; Paul, S.K. Enablers for resilience and pandemic preparedness in food supply chain. Oper. Manag. Res. 2022, 15, 1198–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poduval, A.; Ayyagari, M.S.; Malinda, M.; KEk, V.; Kumar, A.; Kandasamy, J. Barriers in repurposing an existing manufacturing plant: A total interpretive structural modeling (TISM) approach. Oper. Manag. Res. 2022, 15, 1315–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilevari, N.; Shiva, M.V. Country-wide resilience model for the health system: A case study on iran, under coronavirus outbreak. Iran. J. Public Health 2021, 50, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi Priyadarsini, S.; Suresh, M. Factors influencing the epidemiological characteristics of pandemic COVID-19: A TISM approach. Int. J. Healthc. Manag. 2020, 13, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harikumar, P.; Saleeshya, P.G. Suitability and adaptability of Lean manufacturing in Indian pharmaceutical sector. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 390, p. 012050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broome, B.J.; Derk, I.; Razzante, R.J.; Steiner, E.; Taylor, J.; Zamora, A. Building an inclusive climate for intercultural dialogue: A participant-generated framework. Negot. Confl. Manag. Res. 2019, 12, 234–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Metri, B.; Dwivedi, Y.K.; Rana, N.P. Challenges common service centers (CSCs) face in delivering e-government services in rural India. Gov. Inf. Q. 2021, 38, 101573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenradee, P.; Dangton, R. Implementation sequence of engineering and management techniques for enhancing the effectiveness of production and inventory control system. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2000, 38, 2689–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanungo, S.; Bhatnagar, V.V. Beyond generic models for information system quality: The use of interpretive structural modeling (ISM). Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2002, 19, 531–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, R.D.; Narkhede, B.; Gardas, B.B. To identify the critical success factors of sustainable supply chain management practices in the context of oil and gas industries: ISM approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, G.; Haq, A.N.; Sasikumar, P.; Arunachalam, S. Analysis and selection of green suppliers using interpretative structural modelling and analytic hierarchy process. Int. J. Manag. Decis. Mak. 2008, 9, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Saleeshya, P.G.; Harikumar, P. A combined AHP and ISM-based model to assess the leanness of a manufacturing company. Int. J. Bus. Perform. Manag. 2017, 18, 403–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, R.; Aich, S.; Tripathy, S.; Kim, H.C. Artificial intelligence is reshaping healthcare amid COVID-19: A review in the context of diagnosis & prognosis. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W. COVID-19 medical waste transportation risk evaluation integrating type-2 fuzzy total interpretive structural modeling and Bayesian network. Expert Systems Appl. 2022, 213, 118885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, M.; Naz, S.; Martins, J.M.; Mata, M.N.; Mata, P.N.; Maqbool, S. A study on emerging management practices of renewable energy companies after the outbreak of COVID-19: Using an interpretive structural modeling (ISM) approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Singh, P. Identifying consumer resistance of mobile payment during COVID-19: An interpretive structural modeling (ISM) approach. Bus. Manag. Econ. Eng. 2022, 20, 258–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Asim, Z.; Ahmed, Z.; Moosa, S. Exploring and establishing the barriers to sustainable humanitarian supply chains using fuzzy interpretive structural modeling and fuzzy MICMAC analysis. Soc. Responsib. J. 2021, 18, 1463–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamtam, F.; Tourabi, A. Interpretive structural modeling of supply chain leagility during COVID-19. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2021, 54, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Wankhede, V.A.; Nair, R.S. Analysis of Drivers of Digital Learning in COVID-19 and Post-COVID-19 Scenario Using an ISM Approach. J. Inst. Eng. Ser. B 2021, 102, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liza, S.A.; Chowdhury, N.R.; Paul, S.K.; Morshed, M.; Morshed, S.M.; Bhuiyan, M.A.T.; Rahim, M.A. Barriers to achieving sustainability in pharmaceutical supply chains in the post-COVID-19 era. Int. J. Emerg. Mark. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, S.; Puppala, H.; Kumar, A.; Frederico, G.F.; Dwivedy, M.; Prakash, S.; Talwar, V. Applicability of industry 4.0 technologies in the adoption of global reporting initiative standards for achieving sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 305, 127141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Large-scale comparison of bibliographic data sources: Scopus, Web of Science, Dimensions, Crossref, and Microsoft Academic. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2021, 2, 20–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belussi, F.; Orsi, L.; Savarese, M. Mapping business model research: A document bibliometric analysis. Scand. J. Manag. 2019, 35, 101048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, K.; Sangwan, K.S. Green supply chain management pressures, practices and performance: A critical literature review. Benchmarking: Int. J. 2021, 29, 1393–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyack, K.W.; Klavans, R. Co-citation analysis, bibliographic coupling, and direct citation: Which citation approach represents the research front most accurately? J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 2389–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thukral, S.; Shree, D.; Singhal, S. Consumer behaviour towards storage, disposal and recycling of e-waste: Systematic review and future research prospects. Benchmarking Int. J. 2022. (ahead-of-print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahimnia, B.; Sarkis, J.; Davarzani, H. Green supply chain management: A review and bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 162, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Citation-based clustering of publications using CitNetExplorer and VOSviewer. Scientometrics 2017, 111, 1053–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladinrin, O.T.; Arif, M.; Rana, M.Q.; Gyoh, L. Interrelations between construction ethics and innovation: A bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer. Constr. Innov. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzior, A.; Sira, M. A Bibliometric Analysis of Blockchain Technology Research Using VOSviewer. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, D.; Kaur, G. Bibliometric analysis of ecopreneurship using VOSviewer and RStudio Bibliometrix, 1989–2019. Library Hi Tech 2021, 39, 1001–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, E.; Dien, S.; Gonzales, A.; Chavez, M.; Hazen, B. Supply chain cost research: A bibliometric mapping perspective. Benchmarking Int. J. 2020, 28, 1083–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreenivasan, A.; Suresh, M. Future of healthcare start-ups in the era of digitalization: Bibliometric analysis. Int. J. Ind. Eng. Oper. Manag. 2022. (ahead-of-print). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Sahoo, S.; Lim, W.M.; Dana, L.P. Religion as a social shaping force in entrepreneurship and business: Insights from a technology-empowered systematic literature review. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 175, 121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harju, C. The perceived quality of wooden building materials—A systematic literature review and future research agenda. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2022, 46, 29–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, P.; Dhar, R.L. Impact of diversity training on employees and consumers: A review and research agenda. Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2022, 46, 1665–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, J.; Lim, W.M.; O’Cass, A.; Hao, A.W.; Bresciani, S. Scientific procedures and rationales for systematic literature reviews (SPAR-4-SLR). Int. J. Consum. Stud. 2021, 45, O1–O16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M. Industry 4.0, digitization, and opportunities for sustainability. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthra, S.; Kumar, S.; Kharb, R.; Ansari, M.F.; Shimmi, S.L. Adoption of smart grid technologies: An analysis of interactions among barriers. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 33, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, D.; Shneiderman, B.; Smith, M.A. Analyzing social media networks with NodeXL: Insights from a connected world. Int. J. Hum.-Comput. Interact. 2012, 27, 405–408. [Google Scholar]
- Govindan, K.; Palaniappan, M.; Zhu, Q.; Kannan, D. Analysis of third party reverse logistics provider using interpretive structural modeling. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 140, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Sharma, R. Analysis of the driving and dependence power of barriers to adopt industry 4.0 in Indian manufacturing industry. Comput. Ind. 2018, 101, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Luthra, S.; Govindan, K.; Kumar, N.; Haleem, A. Barriers in green lean six sigma product development process: An ISM approach. Prod. Plan. Control. 2016, 27, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Lee, C.K.; Lau, H.; Yang, Y. Strategic response to Industry 4.0: An empirical investigation on the Chinese automotive industry. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2018, 118, 589–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamble, S.S.; Gunasekaran, A.; Sharma, R. Modeling the blockchain enabled traceability in agriculture supply chain. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 52, 101967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, U.; Jain, V.; Kumar, S. Measuring supply chain resilience using a deterministic modeling approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2014, 74, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabat, A.; Kannan, D.; Mathiyazhagan, K. Analysis of enablers for implementation of sustainable supply chain management–A textile case. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 83, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Azevedo, S.G.; Carvalho, H.; Cruz-Machado, V. Lean, green and resilient practices influence on supply chain performance: Interpretive structural modeling approach. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 15–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabat, A.; Govindan, K.; Panicker, V.V. Supply chain risk management and its mitigation in a food industry. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 3039–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haleem, A.; Sushil; Qadri, M.A.; Kumar, S. Analysis of critical success factors of world-class manufacturing practices: An application of interpretative structural modelling and interpretative ranking process. Prod. Plan. Control. 2012, 23, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmaker, C.L.; Ahmed, T.; Ahmed, S.; Ali, S.M.; Moktadir, M.A.; Kabir, G. Improving supply chain sustainability in the context of COVID-19 pandemic in an emerging economy: Exploring drivers using an integrated model. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 26, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyadarsini, S.L.; Suresh, M.; Huisingh, D. What can we learn from previous pandemics to reduce the frequency of emerging infectious diseases like COVID-19? Glob. Transit. 2020, 2, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SciVal. (1 February 2022). Topic Prominence in Science FAQs—SciVal Support Center. Available online: https://service.elsevier.com/app/answers/detail/a_id/28428/supporthub/scival/p/10961/#panel20b (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Wang, J.; Shen, L.; Zhou, W. A bibliometric analysis of quantum computing literature: Mapping and evidences from scopus. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2021, 33, 1347–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.; Shankar, R.; Gupta, R.; Roy, S. A TISM modeling of critical success factors of Blockchain based cloud services. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 2018, 15, 434–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zhang, X. Analysis of the barriers in implementing environmental management system by interpretive structural modeling approach. Manag. Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 1316–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moktadir, M.A.; Dwivedi, A.; Ali, S.M.; Paul, S.K.; Kabir, G.; Madaan, J. Antecedents for greening the workforce: Implications for green human resource management. Int. J. Manpow. 2019, 41, 1135–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, R.D.; Gardas, B.; Luthra, S.; Narkhede, B.; Mangla, S.K. Analysing green human resource management indicators of automotive service sector. Int. J. Manpow. 2020, 41, 925–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, R.; Dhir, S. Technology management for innovation in organizations: An argumentation-based modified TISM approach. Benchmarking Int. J. 2020, 28, 1959–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crupi, A.; Del Sarto, N.; Di Minin, A.; Phaal, R.; Piccaluga, A. Open innovation environments as knowledge sharing enablers: The case of strategic technology and innovative management consortium. J. Knowl. Manag. 2020, 25, 1263–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xiang, L.; Proverbs, D.; Xiong, S. The influence of COVID-19 on community disaster resilience. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, G.; Mangla, S.K.; Luthra, S.; Rai, D.P. Developing a sustainable smart city framework for developing economies: An Indian context. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 47, 101462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Gao, Y.; Jin, M.; Liu, S. Sustainable development of the business environment in smart cities: A hierarchical framework. Kybernetes 2020, 50, 1426–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.; Chen, K.; Xue, F.; Lu, W. Barriers to Building Information Modeling (BIM) implementation in China’s prefabricated construction: An interpretive structural modeling (ISM) approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, A.B.; Chan, D.W.; Siu, F.M. Drivers of sustainable adoption of building information modelling (BIM) in the Nigerian construction small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Sustainability 2020, 12, 3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrudi, S.H.H.; Tavana, M.; Abdi, M. A comprehensive framework for analyzing challenges in humanitarian supply chain management: A case study of the Iranian Red Crescent Society. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2020, 42, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.K.; Barve, A. Modeling post-disaster challenges of humanitarian supply chains: A TISM approach. Glob. J. Flex. Syst. Manag. 2016, 17, 321–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, S.; Nehra, V.; Luthra, S. Identification and analysis of barriers in implementation of solar energy in Indian rural sector using integrated ISM and fuzzy MICMAC approach. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 62, 70–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, G.; Pokharel, S.; Kumar, P.S. A hybrid approach using ISM and fuzzy TOPSIS for the selection of reverse logistics provider. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2009, 54, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeri, H.; Khalilzadeh, M. Analysis of factors affecting project communications with a hybrid DEMATEL-ISM approach (A case study in Iran). Heliyon 2020, 6, e04430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, S.P. An integrated fuzzy-ANP and fuzzy-ISM approach using blockchain for sustainable supply chain. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2021, 34, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoosi, J.; Suratgar, A.A.; Menhaj, M.B.; Mosavi, A.; Mohammadzadeh, A.; Ranjbar, E. Modeling renewable energy systems by a self-evolving nonlinear consequent part recurrent type-2 fuzzy system for power prediction. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).