Towards SDGs 4 and 8: How Value Co-Creation Affecting Entrepreneurship Education’s Quality and Students’ Entrepreneurial Intention
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Background
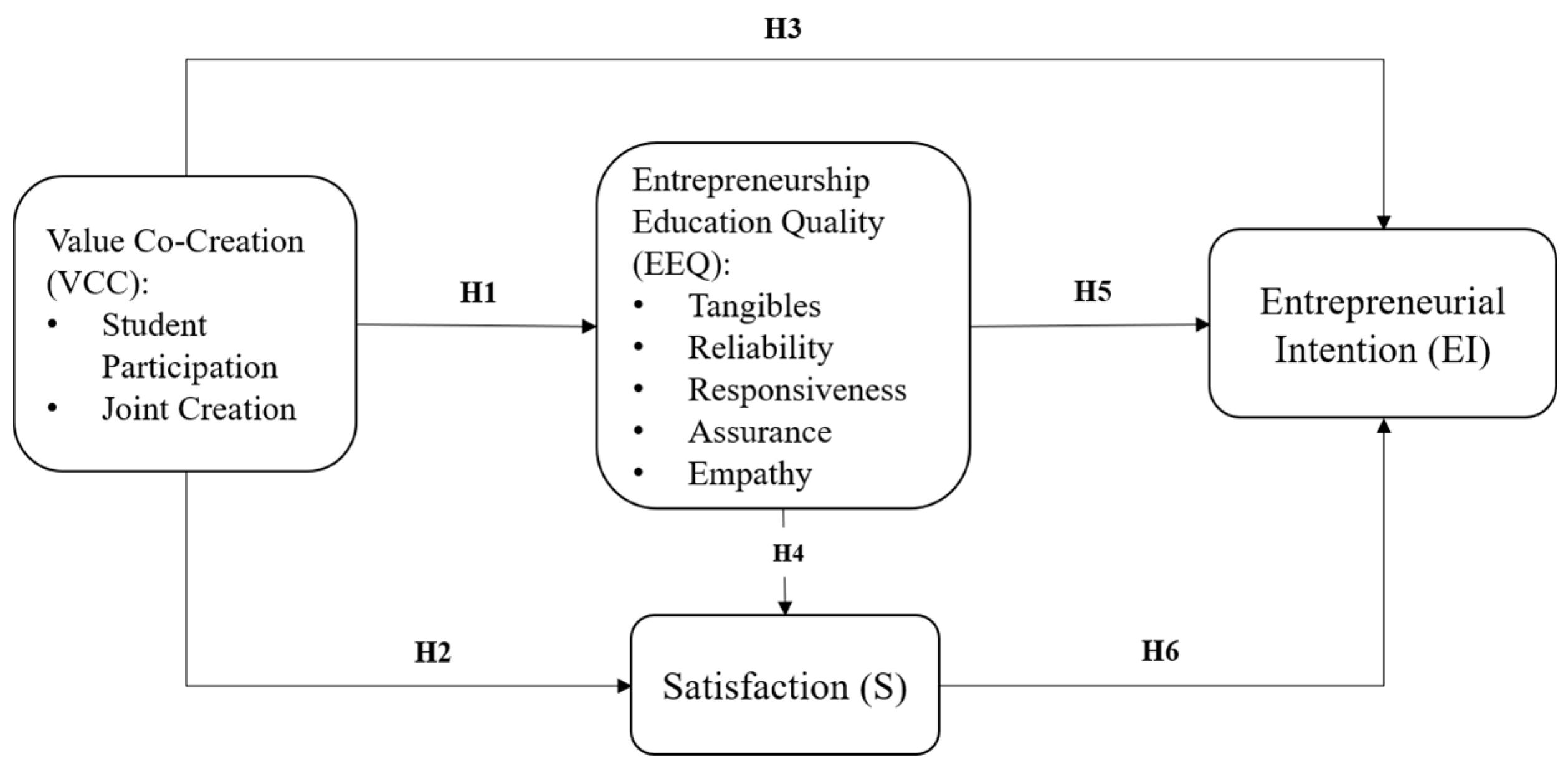
2.2. Effect of Value Co-Creation on Entrepreneurship Education Quality, Satisfaction, and Entrepreneurial Intention
2.3. Effect of Entrepreneurship Education Quality on Satisfaction and Entrepreneurial Intention
2.4. Effect of Satisfaction on Entrepreneurial Intention
3. Research Methodology
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Stage One: Analysis of the LOC Measurement Model
4.2. Stage Two: Analysis of the HOC Measurement Model
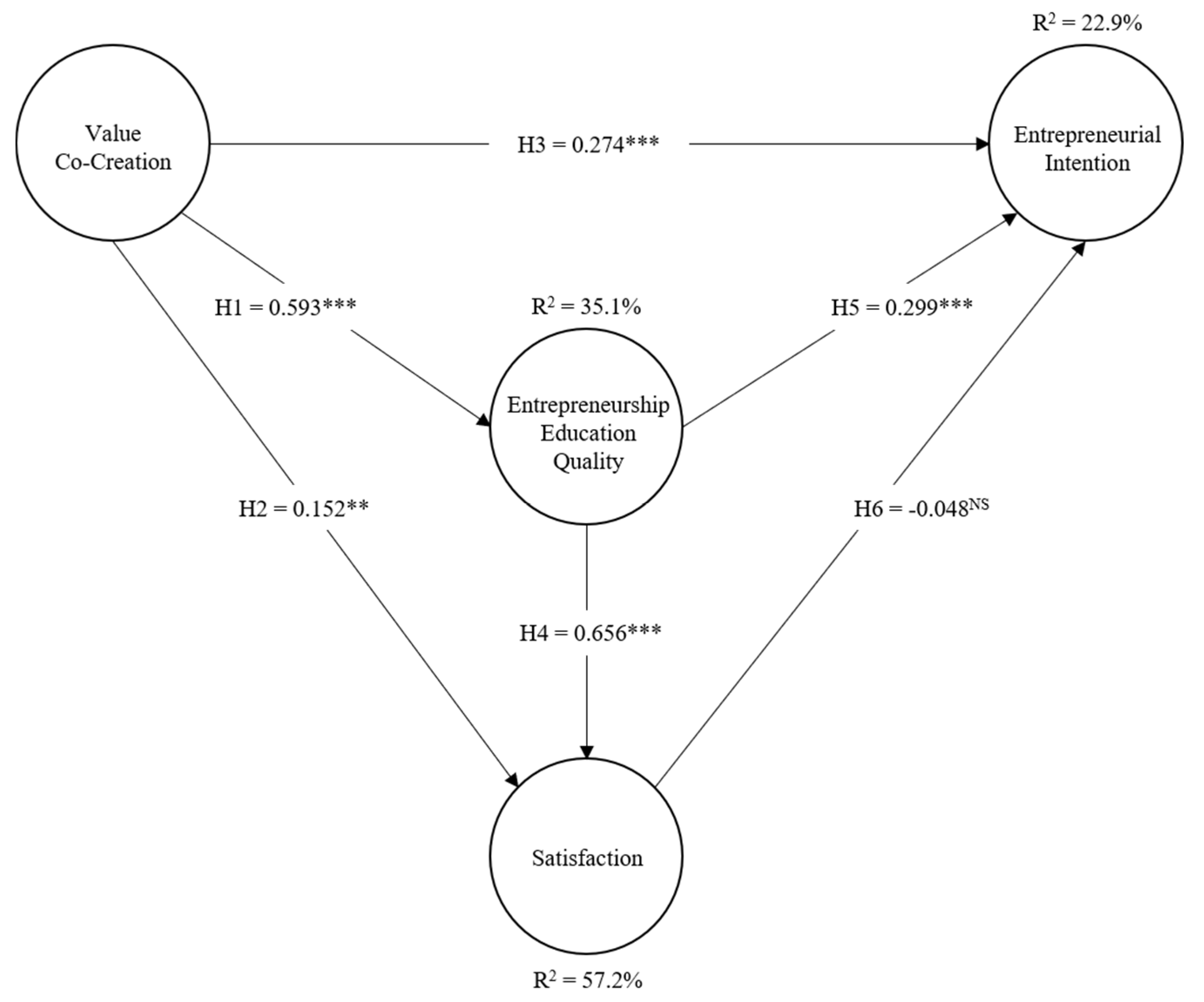
4.3. Results of the Structural Model
4.4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Limitations
5.1. Theoretical Contribution
5.2. Managerial Implication for the School and Government
5.3. Limitation and Future Research Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chazan, B. What Is “Education”? In Principles and Pedagogies in Jewish Education; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, G.S. Human Capital; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1964. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, L. Entrepreneurship Education and Sustainable Development Goals: A Literature Review and a Closer Look at Fragile States and Technology-Enabled Approaches. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. SDG 4: Ensure Inclusive and Equitable Quality Education and Promote Lifelong Learning Opportunities for All. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal4 (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Dewi, S.S.; Sudira, P. The Contribution of Teaching Factory Program Implementation on Work Readiness of Vocational High School Students in Makassar. J. Educ. Sci. Technol. (EST) 2018, 4, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supardi, E.; Islamy, F.J.; Muhidin, S.A.; Sutarni, N. How to Educate Student Become Competent Entrepreneurs. J. Cakrawala Pendidik. 2022, 41, 170–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CNN Indonesia. Lulusan SMK Banyak Menganggur, Menteri Bambang Anggap Anomali. Available online: https://www.cnnindonesia.com/ekonomi/20190403134803-92-383168/lulusan-smk-banyak-menganggur-menteri-bambang-anggap-anomali (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Alika, R. Mendikbud Lihat Lulusan SMK Banyak Menganggur Karena Masalah Industri—Makro Katadata. Available online: https://katadata.co.id/marthathertina/finansial/5e9a5598a6f9e/mendikbud-lihat-lulusan-smk-banyak-menganggur-karena-masalah-industri (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Oebaidillah, S. Ini Penyebab Tingginya Pengangguran SMK. Available online: https://mediaindonesia.com/humaniora/160233/ini-penyebab-tingginya-pengangguran-smk (accessed on 28 April 2021).
- Lu, G.; Song, Y.; Pan, B. How University Entrepreneurship Support Affects College Students’ Entrepreneurial Intentions: An Empirical Analysis from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegalajar-Palomino, M.d.C.; Burgos-García, A.; Martinez-Valdivia, E. What Does Education for Sustainable Development Offer in Initial Teacher Training? A Systematic Review. J. Teach. Educ. Sustain. 2021, 23, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Progress on Education for Sustainable Development and Global; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kementerian Riset, Teknologi, dan Pendidikan Tinggi. Panduan Sekolah Pencetak Wirausaha; Kementerian Riset, Teknologi, dan Pendidikan Tinggi: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2018.
- Handayati, P.; Wulandari, D.; Soetjipto, B.E.; Wibowo, A.; Narmaditya, B.S. Does Entrepreneurship Education Promote Vocational Students’ Entrepreneurial Mindset? Heliyon 2020, 6, e05426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priowirjanto, G.H.; Amat; Suryatno, I.; Novathalia, Y. Sekolah Pencetak Wirausaha Kalimantan Utara. 2021. Available online: https://www.scribd.com/document/554590117/Spw-Kalimantan-Utara-1 (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Badan Pusat Statistik Tingkat Pengangguran Terbuka Berdasarkan Tingkat Pendidikan 2015–2021. Available online: https://www.bps.go.id/indicator/6/1179/1/tingkat-pengangguran-terbuka-berdasarkan-tingkat-pendidikan.html (accessed on 8 March 2022).
- Winarno, A. Intensi Kewirausahaan: Perspektif Karakteristik Kepribadian, Pembelajaran Dan Jaringan Sosial (Studi Pada Mahasiswa Program Akademik Dan Vokasi UM). J. Ekon. Bisnis 2012, 17, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Winarno, A. Entrepreneurship Education in Vocational Schools: Characteristics of Teachers, Schools and Risk Implementation of the Curriculum 2013 in Indonesia. J. Educ. Pract. 2016, 7, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Anggraini, F.; Sukardi, S. Pengembangan Modul Pembelajaran Kewirausahaan Model Student Company Di SMK Negeri 1 Godean. J. Pendidik. Vokasi 2016, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alifah, S.; Narsih, D.; Widiyarto, S. Pengaruh Metode Partisipatori Dan Minat Belajar Terhadap Kemampuan Berwirausaha Siswa SMK. Lect. J. Pendidik. 2019, 10, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasisto, E. Pendidikan Kewirausahaan Melalui Pembinaan Karakter Bagi Siswa Sekolah Kejuruan Di Kota Surakarta. ProBank 2017, 2, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatari, W.; Hariyanto, V.L. Upaya Pembelajaran Kewirausahaan Di SMK Potret Komitmen Terhadap Standar Nasional Proses Pendidikan Dan Pembelajaran. J. Pendidik. Teknol. Dan Kejuru. 2013, 21, 285–293. [Google Scholar]
- Dangnga, T.; Mustari, M.; Sahabuddin, R. Pembelajaran Kewirausahaan Dan Komitmen Individu Pengaruhnya Terhadap Motivasi Berprestasi Dan Minat Usaha Bagi Siswa SMK Di Kota Makassar. In Proceedings of the Seminar Nasional LP2M UNM, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 29 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Peterman, N.E.; Kennedy, J. Enterprise Education: Influencing Students’ Perceptions of Entrepreneurship. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2003, 28, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmons, J.A.; Spinelli, S. New Venture Creation: Entrepreneurship for the 21st Century, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill/Irwin: Boston, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Wafudu, S.J.; Kamin, Y.b.; Marcel, D. Validity and Reliability of a Questionnaire Developed to Explore Quality Assurance Components for Teaching and Learning in Vocational and Technical Education. Hum. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2022, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargo, S.L.; Lusch, R.F. Service-Dominant Logic 2025. Int. J. Res. Mark. 2017, 34, 46–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovill, C.; Cook-Sather, A.; Felten, P. Students as Co-creators of Teaching Approaches, Course Design, and Curricula: Implications for Academic Developers. Int. J. Acad. Dev. 2011, 16, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasnakoğlu, B.T.; Mercan, H. Co-Creating Positive Outcomes in Higher Education: Are Students Ready for Co-Creation? J. Mark. High. Educ. 2020, 32, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grönroos, C.; Voima, P. Critical Service Logic: Making Sense of Value Creation and Co-Creation. J. Acad. Mark Sci. 2013, 41, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasnakoğlu, B.T. Antecedents and Consequences of Co-Creation in Credence-Based Service Contexts. Serv. Ind. J. 2016, 36, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldfield, B.M.; Baron, S. Student Perceptions of Service Quality in a UK University Business and Management Faculty. Qual. Assur. Educ. 2000, 8, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, M.; Palmer, A. Survey Timing and Consumer Perceptions of Service Quality: An Overview of Empirical Evidence. Manag. Serv. Qual. Int. J. 2001, 11, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell-Stuart, R.; Taheri, B.; Paterson, A.S.; O’Gorman, K.; Jackson, W. Working Together to Increase Student Satisfaction: Exploring the Effects of Mode of Study and Fee Status. Stud. High. Educ. 2016, 43, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, P.; Wong, H.Y. How Service Quality Affects University Brand Performance, University Brand Image and Behavioural Intention: The Mediating Effects of Satisfaction and Trust and Moderating Roles of Gender and Study Mode. J. Brand Manag. 2018, 26, 332–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjua, Q.R.; Ramay, M.I. The Effect of Co-Creation of Value on Service Quality-Customer Loyalty Chain and the Role of Relationship Quality in Higher Education Institutions. J. Bus. Econ. 2020, 12, 125–147. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.T.K.; Lin, T.M.Y.; Lam, H.P. The Role of Co-Creating Value and Its Outcomes in Higher Education Marketing. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak-Kwit, S.; Wiścicka-Fernando, M.; Fernando, K.S.D. The Symbiotic Mutualism between Co-Creation and Entrepreneurship. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Qinghua, Z.; Landström, H. Entrepreneurship Research in Three Regions-the USA, Europe and China. Int. Entrep. Manag. J. 2015, 11, 861–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzaro, E. Linking the Creative Economy with Universities’ Entrepreneurship: A Spillover Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Entrepreneurship 2020 Action Plan: Reigniting the Entrepreneurial Spirit in Europe; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. SMEs, Entrepreneurship, and Innovation; OECD: Paris, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- World Economic Forum. Enhancing Europe’s Competitiveness. Fostering Innovation-Driven Entrepreneurship in Europe; WEF: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- World Economic Forum. The Global Competitiveness Report 2016–2017; WEF: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Castro, M.P.; Scheede, C.R.; Zermeño, M.G.G. The Impact of Higher Education on Entrepreneurship and the Innovation Ecosystem: A Case Study in Mexico. Sustainability 2019, 11, 5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bărbulescu, O.; Constantin, C.P. Sustainable Growth Approaches: Quadruple Helix Approach for Turning Brașov into a Startup City. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, B.A.; Audretsch, D.B.; McDougall, P.P. The Emergence of Entrepreneurship Policy. Small Bus. Econ. 2004, 22, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundström, A.; Stevenson, L.A. Entrepreneurship Policy: Theory and Practice; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. The Impact of the Global Crisis on SME and Entrepreneurship Financing and Policy Responses; OECD: Paris, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, D.S.; Wessner, C. Universities and the Success of Entrepreneurial Ventures: Evidence from the Small Business Innovation Research Program. J. Technol. Transf. 2012, 37, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, A.; Magalhães, A.; Amaral, A. Disentangling Policy Convergence within the European Higher Education Area. Eur. Educ. Res. J. 2019, 18, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seikkula-Leino, J.; Salomaa, M.; Jónsdóttir, S.R.; McCallum, E.; Israel, H. EU Policies Driving Entrepreneurial Competences—Reflections from the Case of EntreComp. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toutain, O.; Mueller, S. The Outward-Looking School and Ecosystem. OECD Econ. Stud. 2015, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Warnecke, T. Social Entrepreneurship in China: Driving Institutional Change. J. Econ. Issues 2018, 52, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashari, H.; Abbas, I.; Abdul-Talib, A.-N.; Mohd Zamani, S.N. Entrepreneurship and Sustainable Development Goals: A Multigroup Analysis of the Moderating Effects of Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial Intention. Sustainability 2022, 14, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belitski, M.; Heron, K. Expanding Entrepreneurship Education Ecosystems. J. Manag. Dev. 2017, 36, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.; Galloway, L. Refocusing—Building a Future for Entrepreneurial Education and Learning. Ind. High. Educ. 2014, 28, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlay, H. Entrepreneurship Education in the UK: A Critical Analysis of Stakeholder Involvement and Expectations. J. Small Bus. Enterp. Dev. 2009, 16, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oganisjana, K.; Matlay, H. Entrepreneurship as a Dynamic System: A Holistic Approach to the Development of Entrepreneurship Education. Ind. High. Educ. 2012, 26, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, A. A Conceptual Framework for Entrepreneurship Education Policy: Meeting Government and Economic Purposes. J. Bus. Ventur. 2013, 28, 546–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Fenton, M.; Barry, A. Entrepreneurship Education: Ireland’s Solution to Economic Regeneration? Ind. High. Educ. 2012, 26, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.C.; McNally, J.J.; Kay, M.J. Examining the Formation of Human Capital in Entrepreneurship: A Meta-Analysis of Entrepreneurship Education Outcomes. J. Bus. Ventur. 2013, 28, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliemel, M.J. Lessons Learned from an Inside-out Flip in Entrepreneurship Education. Small Enterp. Res. 2014, 21, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval-Couetil, N. Assessing the Impact of Entrepreneurship Education Programs: Challenges and Approaches. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2013, 51, 394–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maritz, A.; Jones, C.; Shwetzer, C. The Status of Entrepreneurship Education in Australian Universities. Educ. Train. 2015, 57, 1020–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neck, H.M.; Greene, P.G. Entrepreneurship Education: Known Worlds and New Frontiers. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2011, 49, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkel, D.; Vanevenhoven, J.; Drago, W.A.; Clements, C. The Structure and Scope of Entrepreneurship Programs in Higher Education around the World. J. Entrep. Educ. 2013, 16, 15–29. [Google Scholar]
- St-Jean, E.; Audet, J. Factors Leading to Satisfaction in a Mentoring Scheme for Novice Entrepreneurs. Int. J. Evid. Based Coach. Mentor. 2009, 7, 148–161. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, R. Entrepreneurial Learning and Mentoring. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2000, 6, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, E.A.; Sørheim, R. Action-Based Entrepreneurship Education. Technovation 2006, 26, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, A.Y.; Kolb, D.A. Experiential Learning Theory: A Dynamic, Holistic Approach to Management Learning, Education and Development. In The SAGE Handbook of Management Learning, Education and Development; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2009; pp. 42–68. [Google Scholar]
- Politis, D. The Process of Entrepreneurial Learning: A Conceptual Framework. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2005, 29, 399–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, D.A. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Fayolle, A.; Gailly, B.; Lassas-Clerc, N. Assessing the Impact of Entrepreneurship Education Programmes: A New Methodology. J. Eur. Ind. Train. 2006, 30, 701–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.; Hill, F.M.; Leitch, C.M. The Effectiveness of Training for New Business Creation: A Longitudinal Study. Int. Small Bus. J. Res. Entrep. 2004, 22, 249–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khotimah, P.C.; Kantun, S.; Widodo, J. Pengaruh Hasil Belajar Mata Pelajaran Produk Kreatif Dan Kewirausahaan Terhadap Minat Berwirausaha Siswa Di SMK Negeri 7 Jember (Studi Kasus Pada Kelas XII Program Keahlian Multimedia Semester Gasal Tahun Ajaran 2019/2020). J. Pendidik. Ekon. J. Ilm. Ilmu Pendidik. Ilmu Ekon. Dan Ilmu Sos. 2020, 14, 357–360. [Google Scholar]
- Goda, K.; Kijima, K. Modeling Service Ecosystems Innovation. J. Bus. Manag. Sci. 2015, 3, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aicha, D. Co-Creation Strategy, New Challenges in Entrepreneurship Education. GATR J. Bus. Econ. Rev. 2021, 6, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kijima, K.; Arai, Y. Value Co-Creation Process and Value Orchestration Platform. In Global Perspectives on Service Science—Japan; Kwan, S.K., Spohrer, J.C., Sawatani, Y., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 137–154. [Google Scholar]
- Etzkowitz, H.; Ranga, M.; Benner, M.; Guaranys, L.; Maculan, A.M.; Kneller, R. Pathways to the Entrepreneurial University: Towards a Global Convergence. Sci. Public Policy 2008, 35, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Kulturel-Konak, S.; Konak, A. Key Elements and Their Roles in Entrepreneurship Education Ecosystem: Comparative Review and Suggestions for Sustainability. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novela, S.; Syarief, R.; Fahmi, I.; Arkeman, Y. Creating a University-Based Entrepreneurial Ecosystem in Indonesia. Acad. J. Interdiscip. Stud. 2021, 10, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. Entrepreneurial Ecosystems around the Globe and Company Growth Dynamics; WEF: Davos, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brush, C.G. Exploring the Concept of an Entrepreneurship Education Ecosystem. In Innovative Pathways for University Entrepreneurship in the 21st Century (Advances in the Study of Entrepreneurship, Innovation and Eco-nomic Growth); Kuratko, D.F., Hoskinson, S., Eds.; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2014; Volume 24, pp. 25–39. [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg, D.J. Applying the Ecosystem Metaphor to Entrepreneurship. Antitrust Bull. 2016, 61, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regele, M.D.; Neck, H.M. The Entrepreneurship Education Subecosystem in The United States: Opportunities to Increase Entrepreneurial Activity. J. Bus. Entrep. 2012, 23, 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Stam, E. Entrepreneurial Ecosystems and Regional Policy: A Sympathetic Critique. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2015, 23, 1759–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruns, K.; Bosma, N.; Sanders, M.; Schramm, M. Searching for the Existence of Entrepreneurial Ecosystems: A Regional Cross-Section Growth Regression Approach. Small Bus. Econ. 2017, 49, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.N.; Reboud, S.; Toutain, O.; Ballereau, V.; Mazzarol, T. Entrepreneurial Education: An Entrepreneurial Ecosystem Approach. J. Manag. Organ. 2021, 27, 694–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badan Perencanaan Pembangunan Daerah Kabupaten Buleleng Pembangunan Indonesia Dan Permasalahannya|Badan Perencanaan Pembangunan Daerah. Available online: https://bappeda.bulelengkab.go.id/informasi/detail/artikel/pembangunan-indonesia-dan-permasalahannya-44 (accessed on 16 March 2022).
- Okwita, A. Wacana Dan Ketidakmeratan Pembangunan Di Indonesia (Inequallity of Discourse and Development in Indonesia). Cahaya Pendidik. 2016, 2, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmelseed, A.M.M. Quality Assurance Practices in Public Technical and Vocational Education and Training Institutions in the Khartoum State-Sudan. J. Educ. Soc. Res. 2021, 11, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oviawe, J.I. Technical Education Lecturers’ Knowledge of Students’ Engagement in Application of Interactive Instructional Strategies. J. Technol. Humanit. 2020, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Darling-Hammond, L.; Flook, L.; Cook-Harvey, C.; Barron, B.; Osher, D. Implications for Educational Practice of the Science of Learning and Development. Appl. Dev. Sci. 2020, 24, 97–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, C.D.D.A. Avaliação da Qualidade Percebida Em Serviços: Aplicação Em Um Colégio Privado de Ensino Fundamental e Médio. Master’s Dissertation, Universidade Federal de Santa Catarina, Florianópolis, Brazil, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, O.J.D.; Ferreira, E.C. Adaptation and Application of the SERVQUAL Scale in Higher Education. In Proceedings of the POMS 20th Annual Conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 1–4 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- De Mello, S.C.B.; Dutra, H.F.D.O.; Oliveira, P.A.S. Avaliando a Qualidade de Serviço Educacional Numa IES: O Impacto Da Qualidade Percebida Na Apreciação Do Aluno de Graduação. Organ. Soc. 2001, 8, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. A Conceptual Model of Service Quality and Its Implications for Future Research. J. Mark. 1985, 49, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. SERVQUAL: A Multiple-Item Scale for Measuring Consumer Perceptions of Service Quality. J. Retail. 1988, 16, 12–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, C. Perception of Quality in Higher Education. In Proceedings of the Australian Universities Quality Forum; AUQA Occasional Publication: Melbourne, Australia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, S.M.Z.; Shoeb, M.Z.H. Measuring Service Quality of a Public University Library in Bangladesh Using SERVQUAL. Perform. Meas. Metr. 2009, 10, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Nawaz, M.M.; Ahmad, Z.; Ahmad, Z.; Shaukat, M.Z.; Usman, A.; Rehman, W.; Ahmed, N. Does Service Quality Affect Students’ Performance? Evidence from Institutes of Higher Learning. Afr. J. Bus. Manag. 2010, 4, 2527. [Google Scholar]
- Abili, K.; Thani, F.N.; Mokhtarian, F.; Rashidi, M.M. Assessing Quality Gap of University Services. Asian J. Qual. 2011, 12, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchroen, K. Literature Review: Service Quality in Educational Institutions. ABAC J. 2004, 24, 14–25. [Google Scholar]
- Prahalad, C.K.; Ramaswamy, V. Co-Opting Customer Competence. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2000, 78, 79–90. [Google Scholar]
- Astin, A.W. Student Involvement: A Developmental Theory for Higher Education. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 1984, 25, 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Prahalad, C.K.; Ramaswamy, V. Co-creating Unique Value with Customers. Strategy Leadersh. 2004, 32, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nysveen, H.; Pedersen, P.E. Influences of Co-Creation on Brand Experience: The Role of Brand Engagement. Int. J. Mark. Res. 2014, 56, 807–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook-Sather, A.; Luz, A. Greater Engagement in and Responsibility for Learning: What Happens When Students Cross the Threshold of Student–Faculty Partnership. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2015, 34, 1097–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, G.R.; Rillo, A.P. Structural Equation Modeling of Co-Creation and Its Influence on the Student’s Satisfaction and Loyalty towards University. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 2016, 291, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nystrand, M.; Gamoran, A. Instructional Discourse, Student Engagement, and Literature Achievement. Res. Teach. Engl. 1991, 25, 261–290. [Google Scholar]
- Sutarso, Y.; Halim, R.E.; Balqiah, T.E.; Tjiptoherijanto, P. The Role of Co-Creation Activities, Trust and Gender on Higher Education Marketing Performance. Eur. Res. Stud. J. 2017, 20, 825–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunasz, M. Determinants of Selection of the Moment of Starting Running Own Business. Manag. Bus. Adm. Cent. Eur. 2014, 22, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chenet, P.; Tynan, C.; Money, A. Service Performance Gap. J. Bus. Res. 1999, 46, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeithaml, V.A. Consumer Perceptions of Price, Quality, and Value: A Means-End Model and Synthesis of Evidence. J. Mark. 1988, 52, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, H.; Raposo, M. Conceptual Model of Student Satisfaction in Higher Education. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2007, 18, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultan, P.; Wong, H.Y. An Integrated-Process Model of Service Quality, Institutional Brand and Behavioural Intentions. Manag. Serv. Qual. 2014, 24, 487–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-Ferrer, C.M. Quality of University Services: Dimensional Structure of SERVQUAL VS. ESQS. Serv. Sci. 2010, 2, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.; Refai, D. Creating Meaningful Entrepreneurial Practice: Crafting Pedagogical Awareness. Entrep. Educ. 2017, 7, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westhead, P.; Solesvik, M.Z. Entrepreneurship Education and Entrepreneurial Intention: Do Female Students Benefit? Int. Small Bus. J. Res. Entrep. 2016, 34, 979–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresch, D.; Harms, R.; Kailer, N.; Wimmer-Wurm, B. The Impact of Entrepreneurship Education on the Entrepreneurial Intention of Students in Science and Engineering versus Business Studies University Programs. Technol. Soc. Chang. 2016, 104, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayolle, A.; Gailly, B. The Impact of Entrepreneurship Education on Entrepreneurial Attitudes and Intention: Hysteresis and Persistence. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2015, 53, 75–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinnar, R.S.; Hsu, D.K.; Powell, B.C.; Zhou, H. Entrepreneurial Intentions and Start-Ups: Are Women or Men More Likely to Enact Their Intentions? Int. Small Bus. J. Res. Entrep. 2018, 36, 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harini, C.; Yulianeu, Y. Faktor-Faktor Yang Mempengaruhi Minat Berwirausaha Pada Remaja Karang Taruna Wijaya Kusuma Kelurahan Kramas Kecamatan Tembalang Kota Semarang. J. Disprotek 2018, 9, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Idris, M.M.; Mukhadis, A.; Pali, M.; Akbar, A. The Contribution of Entrepreneurial Learning towards Entrepreneurial Passion and Entrepreneurial Action Choice of Vocational Students. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1028, 012082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noviasari, D.; Haryono, A.T.; Fathoni, A. Analisis Pengaruh Kualitas Pembelajaran Kewirausahaan, Kreativitas Inovasi, Dan Modal Sosial Terhadap Minat Wirausaha Dengan Efikasi Diri Sebagai Variabel Intervening (Studi Pada Siswa SMKN 3 Semarang). J. Manag. 2018, 1, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, K.M.; Healy, M.A. Key Factors Influencing Student Satisfaction Related to Recruitment and Retention. J. Mark. High. Educ. 2001, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.C.; Murdoch, N.; Mertova, P. Benchmarking the Student Experience: The Offshore Campus Experience. TQM J. 2011, 23, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helgesen, Ø.; Nesset, E. What Accounts for Students’ Loyalty? Some Field Study Evidence. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2007, 21, 126–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.R. Individual Entrepreneurial Intent: Construct Clarification and Development of an Internationally Reliable Metric. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2009, 33, 669–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armitage, C.J.; Conner, M. Efficacy of the Theory of Planned Behaviour: A Meta-Analytic Review. Br. J. Soc. Psychol. 2001, 40, 471–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C. Entrepreneurship Education and Research: Emerging Trends And Concerns. J. Glob. Entrep. 2011, 1, 13–25. [Google Scholar]
- Saeed, S.; Yousafzai, S.Y.; Yani-De-Soriano, M.; Muffatto, M. The Role of Perceived University Support in the Formation of Students’ Entrepreneurial Intention. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2015, 53, 1127–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.S.A. Entrepreneurship Education in an Engineering Curriculum. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2016, 35, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotty, M.J. The Foundations of Social Research; Sage Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, M.N.K.; Lewis, P.; Thornhill, A.; Bristow, A. Understanding Research Philosophy and Approaches to Theory Development. In Research Methods for Business Students; Saunders, M.N.K., Lewis, P., Thornhill, A., Eds.; Pearson Education: Harlow, UK, 2015; pp. 122–161. [Google Scholar]
- Neuman, W.L. Social Research Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative Approaches, 7th ed.; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2014; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Petropoulos, F.; Apiletti, D.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Babai, M.Z.; Barrow, D.K.; ben Taieb, S.; Bergmeir, C.; Bessa, R.J.; Bijak, J.; Boylan, J.E.; et al. Forecasting: Theory and Practice. Int. J. Forecast. 2022, 38, 705–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM); Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sarstedt, M.; Hair, J.F.; Cheah, J.H.; Becker, J.M.; Ringle, C.M. How to Specify, Estimate, and Validate Higher-Order Constructs in PLS-SEM. Australas. Mark. J. 2019, 27, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan. Statistik Sekolah Menengah Kejuruan (SMK) Tahun 2020–2021; Kementerian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2021.
- Tosupedia 13 Cabang Dinas Di Dinas Pendidikan Provinsi Jawa Barat. Available online: https://www.tosupedia.com/2018/05/13-cabang-dinas-di-dinas-pendidikan-provinsi-jawa-barat.html (accessed on 27 April 2022).
- Mueller, S.L.; Thomas, A.S. Culture and Entrepreneurial Potential: A Nine Country Study of Locus of Control and Innovativeness. J. Bus. Ventur. 2001, 16, 51–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, S.; Indarti, N. Entrepreneurial Intention Among Indonesian and Norwegian Students. J. Enterprising Cult. 2004, 12, 55–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liñán, F.; Chen, Y. Development and Cross–Cultural Application of a Specific Instrument to Measure Entrepreneurial Intentions. Entrep. Theory Pract. 2009, 33, 593–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouselli, S.; Khalifa, B. Entrepreneurship in Crisis: The Determinants of Syrian Students’ Entrepreneurial Intentions. Bus. Manag. Educ. 2017, 15, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, M.L.; de Moraes, G.H.S.M.; Spatti, A.C. Do University Ecosystems Impact Student’s Entrepreneurial Behavior? BAR Braz. Adm. Rev. 2021, 18, e200079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, A.; Zeithaml, V.A.; Berry, L.L. Refinement and Reassessment of the SERVQUAL Scale. J. Retail. 1991, 67, 420–450. [Google Scholar]
- Tabachnick, B.G.; Fidell, L.S. Using Multivariate Statistics, 5th ed.; Pearson Allyn and Bacon: Boston, MA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Black, W.C.; Babin, B.J.; Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis, 7th ed.; Pearson: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Risher, J.J.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M. When to Use and How to Report the Results of PLS-SEM. Eur. Bus. Rev. 2019, 31, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM), 2nd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sinkovics, R.R. The Use of Partial Least Squares Path Modeling in International Marketing. In New Challenges to International Marketing (Advances in International Marketing); Sinkovics, R.R., Ghauri, P.N., Eds.; Emerald Group Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2009; Volume 20, pp. 277–319. [Google Scholar]
- Lusch, R.F.; Vargo, S.L. Service-Dominant Logic: Reactions, Reflections and Refinements. Mark. Theory 2006, 6, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, M.; Pillitu, D. Improving Entrepreneurship Education in Primary Schools: A Pioneer Project. Int. J. Educ. Manag. 2019, 33, 1148–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, T.; Brooks, I. Co-Creation of Value: A Customer-Integration Approach. In Strategic Brand Management in Higher Education; Nguyen, B., Melewar, T., Hemsley-Brown, J., Eds.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations SDG 8: Promote Sustained, Inclusive and Sustainable Economic Growth, Full and Productive Employment and Decent Work for All. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal8 (accessed on 1 October 2022).
- Bahrami, H.; Evans, S. Flexible Re-Cycling and High-Technology Entrepreneurship. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1995, 37, 62–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubini, P. The Influence of Motivations and Environment on Business Start-Ups: Some Hints for Public Policies. J. Bus. Ventur. 1989, 4, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnyawali, D.R.; Fogel, D.S. Environments for Entrepreneurship Development: Key Dimensions and Research Implications. Entrep. Theory Pract. 1994, 18, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennings, J.M. The Urban Quality of Life and Entrepreneurship. Acad. Manag. J. 1982, 25, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stam, E.; van de Ven, A. Entrepreneurial Ecosystem Elements. Small Bus. Econ. 2019, 56, 809–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Ven, H. The Development of an Infrastructure for Entrepreneurship. J. Bus. Ventur. 1993, 8, 211–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askun, B.; Yıldırım, N. Insights on Entrepreneurship Education in Public Universities in Turkey: Creating Entrepreneurs or Not? Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2011, 24, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Level of Education | Open Unemployment Rate by Educational Level (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
| Never Go to School/Not Graduated and Graduated from Elementary School | 2.71 | 2.95 | 2.62 | 2.40 | 2.39 | 3.61 | 3.61 |
| Junior High School | 6.24 | 5.84 | 5.52 | 4.77 | 4.72 | 6.46 | 6.45 |
| Senior High School | 10.27 | 8.63 | 8.32 | 7.90 | 7.87 | 9.86 | 9.09 |
| Vocational High School | 13.02 | 11.49 | 11.38 | 11.18 | 10.36 | 13.55 | 11.13 |
| Diploma I/II/III | 7.22 | 5.03 | 6.86 | 6.00 | 5.95 | 8.08 | 5.87 |
| University | 5.98 | 4.54 | 5.25 | 5.88 | 5.64 | 7.35 | 5.98 |
| Construct and Indicator | LOC’s | HOC’s | Descriptive Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loadings | CR | AVE | α | Outer Weights | Mean (%) | St.d. | ||
| Value Co-Creation (HOC)—Student Participation (LOC) | VCC. SP | 0.917 | 0.788 | 0.865 | 0.487 | 70.66 | 1.12 | |
| I often tell the teachers what I need from this entrepreneurship education | VCC. SP1 | 0.859 | 1.11 | |||||
| I often give suggestions how this entrepreneurship education can be improved | VCC. SP2 | 0.920 | 1.15 | |||||
| I participate in making decisions about how this entrepreneurship education should work | VCC. SP3 | 0.883 | 1.11 | |||||
| Value Co-Creation (HOC)—Joint Creation (LOC) | VCC. JC | 0.894 | 0.738 | 0.822 | 0.595 | 76.44 | 1.01 | |
| During the learning process, I often find solutions to my problems together with the teachers | VCC. JC1 | 0.885 | 1.00 | |||||
| I am actively involved when teachers composing this entrepreneurship education program | VCC. JC2 | 0.845 | 1.03 | |||||
| Teachers always involve students in evaluating and improving the learning process | VCC. JC3 | 0.846 | 0.91 | |||||
| Entrepreneurship Education Quality (HOC)—Tangibles (LOC) | EEQ. TAN | 0.821 | 0.435 | 0.741 | 0.229 | 71.02 | 1.48 | |
| The available infrastructure supports my learning process in entrepreneurship | EEQ. TAN1 | 0.664 | 0.90 | |||||
| The available facilities support my learning process in entrepreneurship | EEQ. TAN2 | 0.719 | 0.87 | |||||
| The available teachers support my learning process in entrepreneurship | EEQ. TAN3 | 0.642 | 0.83 | |||||
| The available guest lecturers support my learning process in entrepreneurship (if unavailable, answer with value of 1) | EEQ. TAN4 | 0.699 | 1.63 | |||||
| The available seed funding supports my learning process in entrepreneurship (if unavailable, answer with value of 1) | EEQ. TAN5 | 0.597 | 1.70 | |||||
| The available assistance to market access supports my learning process in entrepreneurship (if unavailable, answer with value of 1) | EEQ. TAN6 | 0.627 | 1.68 | |||||
| Entrepreneurship Education Quality (HOC)—Reliability (LOC) | EEQ. REL | 0.880 | 0.553 | 0.838 | 0.246 | 75.78 | 1.34 | |
| The knowledge possessed by the teachers support my learning process in entrepreneurship | EEQ. REL1 | 0.806 | 0.78 | |||||
| The knowledge possessed by the guest lecturers support my learning process in entrepreneurship (if unavailable, answer with value of 1) | EEQ. REL2 | 0.636 | 1.65 | |||||
| The teachers’ ability in delivering material supports my learning process in entrepreneurship | EEQ. REL3 | 0.799 | 0.81 | |||||
| The guest lecturers’ ability in delivering material supports my learning process (if unavailable, answer with value of 1) | EEQ. REL4 | 0.622 | 1.63 | |||||
| The materials delivered are suitable with what I need in managing a business | EEQ. REL5 | 0.764 | 0.88 | |||||
| The applied learning methods support my learning process in entrepreneurship | EEQ. REL6 | 0.808 | 0.89 | |||||
| Entrepreneurship Education Quality (HOC)—Responsiveness (LOC) | EEQ. RES | 0.936 | 0.880 | 0.864 | 0.241 | 85.00 | 0.83 | |
| The teachers are responsive in helping students in the learning process | EEQ. RES1 | 0.941 | 0.85 | |||||
| The teachers are solution-oriented in helping students in the learning process | EEQ. RES2 | 0.936 | 0.81 | |||||
| Entrepreneurship Education Quality (HOC)—Assurance (LOC) | EEQ. AS | 0.953 | 0.801 | 0.938 | 0.233 | 83.60 | 0.83 | |
| The teachers give clear instructions | EEQ. AS1 | 0.882 | 0.84 | |||||
| The teachers provide clear standards | EEQ. AS2 | 0.911 | 0.81 | |||||
| The standard of the material provided guarantees good learning outcomes | EEQ. AS3 | 0.923 | 0.83 | |||||
| The standard of assignment given guarantees good learning outcomes | EEQ. AS4 | 0.880 | 0.82 | |||||
| The applied grading criteria guarantees good learning outcomes | EEQ. AS5 | 0.878 | 0.83 | |||||
| Entrepreneurship Education Quality (HOC)—Empathy (LOC) | EEQ. EM | 0.921 | 0.794 | 0.870 | 0.215 | 87.26 | 0.81 | |
| The teachers are always open for questions & answers and consultation in the learning process | EEQ. EM1 | 0.861 | 0.78 | |||||
| The teachers are always open to listen to students’ difficulties in the learning process | EEQ. EM2 | 0.921 | 0.79 | |||||
| The teachers always doing evaluation and improvement for the betterment of the learning process | EEQ. EM3 | 0.891 | 0.85 | |||||
| Satisfaction (HOC) | S | 0.929 | 0.814 | 0.886 | 82.84 | 0.86 | ||
| Overall, I am satisfied with the entrepreneurship education at VHS | S1 | 0.909 | 0.86 | |||||
| Overall, entrepreneurship education at VHS has fulfilled my needs in learning entrepreneurship | S2 | 0.895 | 0.89 | |||||
| Overall, entrepreneurship education in VHS is already good | S3 | 0.904 | 0.82 | |||||
| Entrepreneurial Intention (HOC) | EI | 0.916 | 0.686 | 0.885 | 86.06 | 0.89 | ||
| I am ready to be an entrepreneur | EI1 | 0.864 | 0.88 | |||||
| I will put forth every effort to start and run my own business | EI2 | 0.865 | 0.77 | |||||
| My professional aspiration is to be an entrepreneur | EI3 | 0.833 | 0.96 | |||||
| I am determined to create my own business in the near time | EI4 | 0.820 | 1.02 | |||||
| I am determined to create my own business in the future | EI5 | 0.754 | 0.71 | |||||
| EEQ.AS | EEQ.EM | EEQ.REL | EEQ.RES | EEQ.TAN | EI | S | VCC.JC | VCC.SP | |
| EEQ.AS | 0.895 | ||||||||
| EEQ.EM | 0.736 | 0.891 | |||||||
| EEQ.REL | 0.743 | 0.672 | 0.744 | ||||||
| EEQ.RES | 0.790 | 0.786 | 0.714 | 0.938 | |||||
| EEQ.TAN | 0.537 | 0.479 | 0.745 | 0.518 | 0.659 | ||||
| EI | 0.303 | 0.401 | 0.396 | 0.367 | 0.365 | 0.828 | |||
| S | 0.677 | 0.592 | 0.657 | 0.694 | 0.581 | 0.324 | 0.902 | ||
| VCC.JC | 0.506 | 0.470 | 0.596 | 0.491 | 0.597 | 0.388 | 0.550 | 0.859 | |
| VCC.SP | 0.432 | 0.290 | 0.411 | 0.414 | 0.417 | 0.399 | 0.439 | 0.706 | 0.887 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walidayni, C.T.; Dellyana, D.; Chaldun, E.R. Towards SDGs 4 and 8: How Value Co-Creation Affecting Entrepreneurship Education’s Quality and Students’ Entrepreneurial Intention. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054458
Walidayni CT, Dellyana D, Chaldun ER. Towards SDGs 4 and 8: How Value Co-Creation Affecting Entrepreneurship Education’s Quality and Students’ Entrepreneurial Intention. Sustainability. 2023; 15(5):4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054458
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalidayni, Carissa Tibia, Dina Dellyana, and Evy Rachmawati Chaldun. 2023. "Towards SDGs 4 and 8: How Value Co-Creation Affecting Entrepreneurship Education’s Quality and Students’ Entrepreneurial Intention" Sustainability 15, no. 5: 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054458
APA StyleWalidayni, C. T., Dellyana, D., & Chaldun, E. R. (2023). Towards SDGs 4 and 8: How Value Co-Creation Affecting Entrepreneurship Education’s Quality and Students’ Entrepreneurial Intention. Sustainability, 15(5), 4458. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15054458






