Abstract
The purpose of this study is to reveal the impact of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity (GTFP) to provide a reference for promoting green development in China. Based on the economic-growth objective-management perspective, this paper takes panel data of 249 cities in China from 2006 to 2019 as a sample, using the directional distance function and the Malmquist–Luenberger Productivity Index to measure GTFP, and then using the dual fixed-effect model to empirically analyze the impact and intrinsic mechanism of economic-growth pressure on GTFP. The results show that (1) economic-growth pressure significantly inhibits GTFP and has a significant inhibitory effect on both green-technology progress and green-technology efficiency. However, the marginal negative effect on green-technology progress is stronger. (2) The inhibition effect of economic-growth pressure on GTFP is characterized by heterogeneity of economic-growth-pressure intensity, economic-development degree, and marketization level. The greater the economic-growth-pressure intensity, the higher the economic-development degree, the lower the marketization level, and the stronger the inhibition effect of economic-growth pressure on GTFP, green-technology progress, and green-technology efficiency. (3) The pressure of economic growth significantly inhibits patent innovation of green inventions and hinders the improvement of green technological innovation, leading to stagnation or retreat of green technological progress and the obstruction of GTFP improvement. The research conclusion of this paper has certain theoretical and practical significance. Based on the findings of the study, suggestions on promoting green development via economic-growth targets are given in three aspects: reforming the promotion-assessment system of officials, rationalizing the setting of economic-growth targets, and green-invention–patent-innovation-driven development.
1. Introduction
Productivity is the main driving force for economic growth [1]. Green total factor productivity (GTFP) is the integration of productivity improvement and environmental protection [2]. Since the reform and opening-up, China’s economy has made remarkable achievements [3]. As shown in Figure 1, in 1978, China’s GDP was only CNY 37 trillion. In 2020, China’s GDP exceeded CNY 100 trillion for the first time, reaching about CNY 101.60 trillion. In addition, per-capita GDP grew at an average annual rate of 8.2% from CNY 39 thousand in 1979 to CNY 72,000 in 2020. However, China’s traditional economic-development mode of high investment and high pollution has worsened the relationship between economic development and environmental protection. The problem of environmental pollution is very serious [4,5,6], and China urgently needs to transform the economic-development mode to high-quality development [7,8]. Since the 18th Party Congress, China has always taken the construction of ecological civilization as a fundamental plan for the sustainable development of the Chinese nation, adhered to the concept of green water and mountains as wealth, and made efforts to promote the comprehensive green transformation of economic and social development. The report of the 19th Party Congress clarifies that China’s economy has changed from a high-speed growth stage to a high-quality development stage. The report of 20th Party Congress emphasizes that we should adhere to the theme of promoting high-quality development fully, accurately, and comprehensively implement the new development concept, as well as strive to raise total-factor productivity and promote green development. Therefore, in the new development stage, GTFP, which takes environmental protection into account, has become the engine of new economic growth. Improving GTFP is the root cause of China’s green economic transformation.
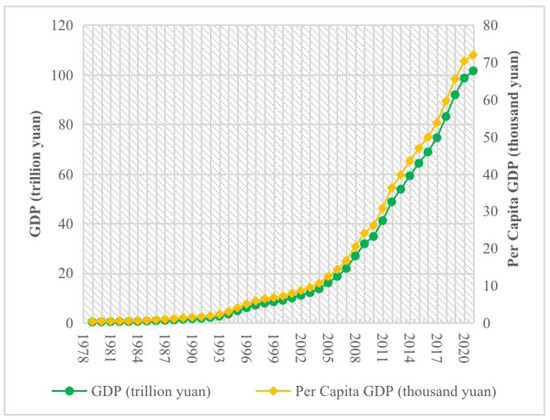
Figure 1.
China’s GDP and per-capita GDP over the years.
Economic-growth-target management plays a key role in promoting economic growth [5]. The miracle of China’s economic development is naturally inseparable from the role of proactive government, and governments at all levels in China have taken active and reasonable interventions to protect the economic development. Local governments at all levels often hold government work meetings at the beginning of each year to clarify annual economic-growth targets and manage macroeconomic regulation and control through economic-growth-target management. In the process of economic-development-stage change, the economic-growth target makes rational adjustment, increasing the interval value and approximate target as well as adjusting the target value downward. To a certain extent, it tends to guide and plan the local economic development. However, China’s economic development is still a catch-up economy, and it is still in the critical period of climbing from low- and middle-income economies to high-income economies. The economic-growth rate is still a key indicator for governments at all levels concerned. Even though the performance-appraisal targets are becoming more diversified, the GDP growth rate, which can be easily measured, is still the most important appraisal indicator for officials’ promotion. This GDP-only performance-appraisal system undoubtedly creates important incentives for local officials, resulting in local officials facing appraisal pressure mainly from the pressure of economic growth in their jurisdictions. Local officials will take measures to promote economic growth in order to achieve the set economic-growth target, such as policy tools and resource instruments [9]. However, when faced with economic-growth pressure, local officials may adopt misguided economic policies for the sake of their political career, resulting in low resource utilization and unreasonable allocation, causing waste of resources and environmental pollution, which is not conducive to economic-efficiency improvement and even affects economic-growth performance, and thus may inhibit GTFP and go against sustainable economic development [1].
What exactly is the influence of economic-growth pressure on GTFP? This research empirically discusses the effect of economic-growth pressure on GTFP and the intrinsic mechanism of action using a double fixed-effects model with a panel data sample of 249 cities from 2006 to 2019. The possible innovations of this article mainly include the following three points: (1) As far as research is concerned, there are still some deficiencies in the study of influencing factors of GTFP from the perspective of economic-growth-target management. This paper discusses how economic-growth pressure affects GTFP, which just makes up for this deficiency. (2) In terms of mechanism analysis, this paper decomposes green-technology innovation into patent types and then discusses the influence of green-technology innovation of different patent types on GTFP, green-technology progress, and green-technology efficiency. Finally, it clarifies the inner mechanism of the negative influence of economic-growth pressure on GTFP. (3) In terms of research significance, the research on the impact of economic-growth pressure on GTFP has certain policy implications for the management of economic-growth targets and the promotion and assessment of officials, which is conducive to promoting China’s green development.
2. Literature Review
This research focuses on the influence of economic-growth pressures on GTFP and covers two main types of literature: economic-growth targets and green total factor productivity.
2.1. Economic-Growth-Target-Related Literature
Economic-growth-target management has been practiced for a long time in different economies around the world. Since 1950, 49 countries have announced or successively announced economic-growth targets, including developed countries such as the United Kingdom and Germany and developing countries such as China and India [10]. There is relatively little literature on economic-growth pressure, which is mainly concentrated in literature on economic-growth targets. Chinese governments at all levels set GDP growth targets in advance every year and spend the entire year trying to accomplish them [11,12]. The Chinese government uses investment tools to manage economic-growth targets, which directly affect economic growth [13]. When the economy encounters adverse shocks, government expenditure increases with the increase in the economic-growth target, and increasing government expenditure to stabilize economic growth is a global phenomenon [14]. Although the management of economic-growth targets can lead and stabilize economic growth, economic-growth targets and economic-growth pressure also cause a series of problems worth paying attention to. The government’s economic-growth targets have significantly inhibited spending on public services such as education and science and technology, resulting in a stagnation of human capital and technological progress that will constrain China’s long-term economic growth [15]. In China, top officials use economic-growth targets to convey the importance of economic growth and to motivate subordinates, leading to economic-growth targets being scaled up from the level of jurisdiction. Local governments are also more likely to set higher targets than higher authorities in order to show their competence to higher authorities [16]. However, the top-down amplification of economic-growth targets significantly inhibits regional green-technology innovation and affects the capacity-utilization rate of enterprises, which is not conducive to the development of regional economy and local enterprises [17,18,19]. In addition, economic-growth target negatively affects environmental performance and constrain sustainable development [20]. Hao et al. [21] found an inverted U-shaped relationship between economic-growth targets and eco-efficiency. Economic-growth targets with increased foreign direct investment may lead to increased air pollution [22], affect energy consumption [23], inhibit the improvement of energy efficiency, and increase carbon emissions [24,25,26]. An increase in economic growth targets weakens the intensity of environmental regulation [27]. When economic-growth targets are too high, local governments come under intense economic-growth pressure, prompting local officials to relax environmental regulations and companies to cut back on environmental investment [28].
2.2. Literature on Green Total Factor Productivity
In recent years, China’s green development has been a hot topic in the academic circle, and improving green total factor productivity is the key to promoting green development. In early studies on total factor productivity, scholars only considered traditional input factors (labor and capital) and expected output (total output) but did not consider resource input and environmental factors (non-expected output), resulting in biased productivity-measurement results [29]. GTFP, which fully considers non-expected output such as pollution emissions, is more in line with the new concept of green development in the new era [30]. Considering environmental protection and economic development, GTFP is an important comprehensive indicator of green-development ability [31], which is conducive to sustainable economic development [1]. To promote green development, China has introduced a series of policies. Studies have shown that green-credit policy [32], low-carbon city-pilot policy [33,34], and smart-city policy [35] all have a significant positive impact on China’s GTFP. In addition, China has also formulated corresponding environmental laws and regulations to constrain the behavior of all parties to better promote green development. The relationship between environmental regulations and China’s GTFP is not linear but a U-shaped relationship, and China is still in the left half of the U-shaped curve [36]. However, both command-and-control (regulatory) environmental regulations and market-based environmental regulations can contribute to the growth of industrial GTFP [37]. Different types of environmental regulations have different impacts on GTFP. Command-and-control environmental regulations improve GTFP, whereas market-based environmental regulations and voluntary environmental regulations both have negative impacts on GTFP [38]. In general, environmental regulation has a significant positive impact on GTFP, which is mainly promoted through green-technology innovation [39]. The “innovation dividend” based on green innovation is the key to improving GTFP [40]. Green innovation improves the GTFP of enterprises, but there are differences in patent types and enterprise characteristics [41]. Environment-induced R&D has effectively improved GTFP, whereas traditional R&D has no significant effect on GTFP [42]. Innovation investment has significantly promoted the GTFP of countries along the Belt and Road [43]. The development of the Internet has had a direct and indirect positive impact on GTFP [44]. The digital economy has not only significantly enhanced the growth of GTFP in the manufacturing industry [45] but also has a spatial spillover effect on the impact of GTFP [46]. Input digitization significantly improves low-carbon GTFP, and this effect is higher in middle-income countries than in high-income countries [47]. AI has a significant U-shaped effect on GTFP. For areas with abundant resources, improving the AI level can promote the growth of GTFP and break the “resource curse” [48]. The application of robots helps to improve GTFP [49,50]. In addition, foreign direct investment [51], the increase in industrial electricity prices [52], and the opening of high-speed railways [53] all significantly promote the improvement of GTFP. The GTFP-growth advantage of big cities is increasingly significant [54], and the GTFP growth of export enterprises is higher than that of non-export enterprises [55]. However, the transformation of energy consumption has a nonlinear impact on GTFP, and it cannot effectively improve GTFP if it is too high or too low [56]. Improper allocation of land resources directly reduces urban GTFP and hinders the development of GTFP in surrounding cities [57].
Although there is a lot of literature on the influencing factors of GTFP, there is still a lack of research on how economic-growth pressure affects GTFP from the perspective of economic-growth-target management. Therefore, in order to make up for this deficiency, this study empirically analyzes the influence of economic-growth pressure on GTFP by taking the data of 249 cities from 2006 to 2019 as samples in order to provide relevant policy suggestions for promoting green development in China.
3. Theoretical Basis and Research Hypothesis
This section constructs a conceptual framework between economic-growth pressure and green total factor productivity. Figure 2 demonstrates the conceptual framework and research hypotheses of this paper.
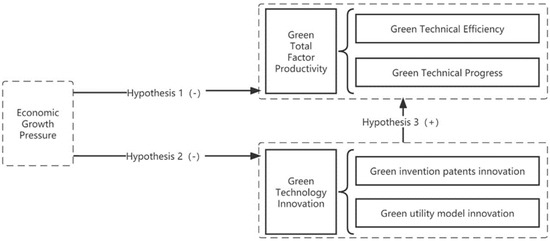
Figure 2.
The conceptual framework of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity. Note: The framework diagram includes this study’s main research questions and hypotheses.
To a certain extent, economic-growth targets have contributed to economic growth [58]. In China, the promotion of local government officials is significantly correlated with the economic performance of their jurisdictions. To a certain extent, the level of local economic development represents the performance and ability of officials. The better the economic development, the more likely the officials will stand out and be recognized and promoted by the superior leaders. Therefore, local GDP growth is still an important core indicator for local government officials to focus on. Under the GDP growth-based promotion-tournament mechanism, local government officials tend to set high economic-growth targets in order to send positive signals about their abilities to higher authorities. However, there is a short-term conflict between economic growth and environmental protection. Higher economic-growth targets may deviate from the economic growth achievable with regional resource endowments, and local officials are thus under greater pressure to grow economically. At higher levels of economic development, the potential for regional economic growth is insufficient. In order to achieve or exceed the economic-growth targets set by local governments, local officials often implement short-term economic behaviors and intervene in the market, resulting in many issues that are not directly related to short-term economic growth, such as environmental protection and pollution control being ignored [59], leading to the reduction of public-service expenditures and the stagnation of human capital and technological progress, hindering green economic development [15]. In addition, local governments tend to implement relatively lax environmental regulations in order to ensure the achievement of economic-growth goals, leading to weakened environmental supervision [27], which in turn leads to reduced investment in environmental protection by enterprises [1], thus increasing environmental pollution [22] and hindering green total factor productivity growth. Thus, this paper proposes hypothesis 1:
Hypothesis 1.
Economic-growth pressure inhibits green total factor productivity growth.
The setting of economic-growth targets and top-down decentralization can have a significant inhibiting effect on green-technology innovation [18]. When economic-growth targets are set too high, local governments face high pressure for growth and usually introduce strong economic policies to achieve the preset economic-growth targets, which may distort government-resource allocation, crowd out corporate R&D expenditures, and harm economic efficiency. Due to the high risk, large investment, long cycle, and low investment returns in the short term of R&D activities, enterprises tend to follow government policies and choose to invest in “short and quick” projects in order to obtain higher investment returns, thus crowding out R&D investment in green-technology innovation and leading to the reduction of resources in the field of green innovation, which in turn has a disincentive effect on green-technology innovation. However, green-technology innovation aims to achieve environmental benefits, clean production, and reduced pollution emissions through green-product innovation, green-process innovation, and end-of-pipeline-treatment technology innovation, and the undesired output (environmental pollutants) is thus reduced. In addition, the promotion and application of green patents can compensate for the R&D cost of green-technology innovation of enterprises, which in turn enhances green total factor productivity. Based on this, this paper argues that economic-growth pressure may inhibit green-technology innovation, whereas green-technology innovation can promote green total factor productivity, and eventually economic-growth pressure may hinder green total factor productivity improvement by inhibiting green-technology innovation. Thus, this paper proposes hypothesis 2, hypothesis 3, and hypothesis 4.
Hypothesis 2.
Economic-growth pressure will inhibit green-technology innovation.
Hypothesis 3.
Green-technology innovation can promote green total factor productivity enhancement.
Hypothesis 4.
Economic-growth pressure inhibits green total factor productivity growth by suppressing green-technology innovation.
4. Model Setting and Variable Description
4.1. Econometric-Model Setting
In order to better empirically test the impact of economic growth target on GTFP, the following double-fixed effect model is constructed.
where the subscript i denotes the city and t denotes the year. GTFPit is the green total factor productivity of city i in year t, EGPit denotes the economic-growth pressure of city i in year t, CONTROLit is a series of control variables, λi denotes the control-city fixed effect, µt denotes the control-year fixed effect, and εit denotes the random-disturbance term. δ is the coefficient of most interest in this paper. If δ > 0 and is significant, it indicates that the increase in economic-growth pressure is beneficial to improve green total factor productivity; if δ < 0 and is significant, it indicates that the increase in economic-growth pressure is not beneficial to improving green total factor productivity; and if δ = 0, it indicates that there is no direct relationship between economic-growth pressure and green total factor productivity. Therefore, based on hypothesis 1, δ should be less than 0 in this paper.
4.2. Description of Variables
4.2.1. Explained Variables
Green total factor productivity (GTFP). The directional distance function (DDF) seeks to maximize desired output, minimize undesired output, and reduce the amount of factor inputs, which is consistent with the concept of green production and green development. Based on this, this paper used the method of combining DDF with the Malmquist–Luenberger Productivity Index (MLPI) to measure China’s urban GTFP.
Assuming that x is the input vector, y is the expected output vector, and b is the unexpected output vector, the output set form [60] can be expressed as:
In Equation (2), p(x) represents the production possibility set of desired output (y) and non-desired output (b) produced by input factor x(). There are three assumptions to be satisfied by the environmental-production technology: First, input factor x and desired output y have strong disposability; second, non-desired output b has joint weak disposition; and third, desired output y and non-desired output b satisfy the zero-combination assumption.
The set of production possibilities provided by environmental-production technologies is the basis for measuring GTFP. Each city in this study represents a production decision-making unit (DMU), and the DDF can calculate the relative-efficiency value of each DMU, as in Equation (3).
In Equation (3), g is the direction vector, set , indicates the direction vector of the desired output y increase, and indicates the direction vector of the non-desired output b decrease. β is the distance-function value, which means that the original input vector x remains unchanged, and the output vector (y, b) can be extended to the maximum multiple along the direction vector . β reflects the value of the distance between the DMU and the effective-production-frontier surface. The greater the β value, the farther away the DMU is from the effective production frontier and the lower the production efficiency of the DMU is. A β value of 0 indicates that the DMU is located on the frontier of effective production and the production efficiency of this DMU is optimal.
In Equation (4), N denotes the use of N input factors and , S denotes the production of S desired outputs and , M denotes the production of M non-desired outputs and . k = 1, 2,…,K denotes the Kth decision unit, t = 1, 2,…,T denotes the Tth period, and denotes the weight of each cross-sectional observation.
According to Chung et al.’s [61] definition of productivity change in period t and period t + 1, the MLPI productivity index in output perspective is:
The MLPI index can be further decomposed into the green technical efficiency (GEFFCH) index and the green technical progress (GTECH) index. GEFFCH is the output growth due to the change in intra-producer efficiency, whereas GTECH indicates the output growth caused by the green technical progress. The specific formula is as follows.
In this paper, the MLPI index was used to represent the green total factor productivity. In the model, the expected-output index is the actual GDP of each prefecture-level city based on 2000; the unexpected-output index includes industrial wastewater, industrial sulfur dioxide, industrial soot, and PM2.5; and the input-factor index includes labor input, capital input, and energy input. Among them, the capital input is measured by the actual capital stock of each city calculated by the perpetual-inventory method, the labor input is expressed by the sum of the number of employees in each city at the end of the year and the number of private individual employees, and the energy input is the total energy consumption of each city. At the same time, GTFP is decomposed into GEFFCH and GTECH.
The labor input is expressed by the sum of the number of unit employees and the number of private and individual employees at the end of each city. The energy input is the total energy consumption of each city. At the same time, GTFP is decomposed into GEFFCH and GTECH.
In this paper, the MLPI index was used to characterize green total factor productivity. In the model, the expected output index is the real GDP of each prefecture-level city in the base period of 2000. The expected output index includes PM2.5, industrial dust, industrial wastewater, and industrial sulfur dioxide. The input-factor index includes labor, capital, and energy. Among them, capital factor is measured by the perpetual-inventory method, measuring real capital-stock metrics for each city [62]. The labor factor is expressed by the sum of the number of unit employees and the number of private and individual employees at the end of each city. The energy factor is the total energy consumption of each city. At the same time, GTFP is decomposed into GEFFCH and GTECH.
4.2.2. Core Explanatory Variables
Economic growth pressure (EGP). When a city’s economic-growth target is higher than its actual economic-growth rate, it indicates that the economic growth that the city can achieve with natural resource-endowment conditions cannot reach the set economic-growth target, and the high economic-growth target will undoubtedly put economic-growth pressure on the local government and officials. Therefore, this paper used the difference between the city’s economic-growth-target value and the actual economic-growth-rate value of that year to represent the economic-growth pressure.
4.2.3. Control Variables
Level of economic development (LED). Government investment in R&D varies depending on the level of economic development, which affects GTFP. In this study, the logarithm of per-capita real GDP is used to represent the level of urban economic development. Financial agglomeration (FAG). Financial agglomeration can enhance productivity through optimizing resource allocation and alleviating credit constraints, which in turn affects GTFP, so this paper used the share of financial-industry employees in total employment. Human capital (HCA). The level of human capital is conducive to improving the skill level and knowledge structure of the local labor force and promoting the improvement of GTFP, and this paper used the logarithm of college students per 10,000 workers to represent the level of HCA. In addition, financial autonomy (FAU), which is expressed as the ratio of budgeted revenue to budgeted expenditure, and investment in education and technology (IET), which is measured by the ratio of expenditure on science and education expenditure to GDP, are also used as control variables.
The municipal people’s congress meeting is usually held at the beginning of each year to discuss and decide on major matters such as economic development and environmental-resource protection within the jurisdiction, and to announce the expected GDP growth rate, i.e., the economic-growth target, to be achieved within the jurisdiction in the current year. Therefore, the original data of economic-growth targets in this paper were mainly collected and compiled from the work reports of municipal governments by hand. The target expressions with modifiers such as “about,” “around,” “above,” “not less than”, etc., are based on specific figures; the average value was taken for the interval target. The data of green patents were collected from the international patent green list published by the World Intellectual Property Organization by conducting patent searches related to environmentally friendly technologies at the China National Intellectual Property Administration (China National Intellectual Property Administration: https://www.cnipa.gov.cn/ (accessed on 1 February 2023)), and the original data of the remaining indicators mainly came from the China City Statistical Yearbook, China Energy Statistical Yearbook, China Environmental Statistical Yearbook (China City Statistical Yearbook, China Energy Statistical Yearbook, China Environmental Statistical Yearbook come from CNKI: https://www.cnki.net/ (accessed on 1 February 2023), CSMAR Database (CSMAR Database: https://www.gtarsc.com/ (accessed on 1 February 2023), CEI Database (CEI Database: https://ceidata.cei.cn/ (accessed on 1 February 2023), EPS Database (EPS Database: https://www.epsnet.com.cn/ (accessed on 1 February 2023), and the official websites of the statistical bureaus of each city. A total of 249 cities were selected based on data availability and data integrity. For missing sample data, the moving average method was used to complete the data. In addition, the research software of this paper was stata16.1. Table 1 shows the descriptive statistics of each variable.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistical table.
5. Empirical Analyses
5.1. Baseline Regression
The results of the baseline regression based on Equation (1) are shown in Table 2. Column 1 in Table 2 reports the regression results controlling only for city and time fixed effects, with a regression coefficient of −0.213 for economic-growth pressure, which passes the 5% significance-level test. In order to minimize the potential endogeneity affecting the robustness of the regression results, columns 2–6 in Table 2 report the regression results with the addition of control variables (economic-development level, financial agglomeration, human capital, fiscal autonomy, and investment in education and technology) in turn. It was found that the regression results did not change essentially, and only the absolute value of the regression coefficient of EGP decreased slightly. However, the regression coefficient still passed the statistical test of 5% significance level. The regression result in column 6, which controls all control variables, was considered as the baseline regression result. The regression coefficient of economic-growth pressure was −0.196, indicating that for every 1 unit increase in economic growth pressure green total factor productivity decreased by about 0.196 units, which is supported by the research conclusion of Chai et al. to some extent [22]. This may be because officials facing economic-growth pressure ignore issues such as environmental protection and pollution control [59] and the government weakens environmental supervision [27], which leads to an increase in non-desired output (environmental pollutants) in the jurisdiction [22] and hinders green development and a decrease in green total factor productivity. Hypothesis 1 is verified, as shown in Table 3.

Table 2.
Benchmark regression results.

Table 3.
Hypothesis supported or not.
Among the control variables, the level of economic development, financial agglomeration, human capital, and investment in education and science and technology were all significantly positive and the significance level was 1%, which are conducive to green total factor productivity growth. The investment in education and science and technology contributes to the improvement of the human-capital level and green-technology-innovation level, and the improvement of HCA level also contributes to the improvement of green-technology innovation. A high economic-development level and high degree of financial agglomeration can optimize resource allocation and ensure R&D investment, thus improving green technological innovation and GTFP. The regression coefficient of fiscal autonomy was non-significant but positive, indicating that there was a non-significant positive contribution of fiscal autonomy to the improvement of green total factor productivity.
5.2. Robustness Tests
5.2.1. Replacement of Core Variables
In this study, the measurement methods of core explanatory variables (EGP) and explained variables (GTFP) were changed to test the robustness of baseline regression. Column 1 of Table 4 measures economic-growth pressure as the ratio of the city’s economic-growth target to its actual growth rate for the year; the regression coefficient of economic-growth pressure was −0.002, and it passed the 5% significance-level test, indicating that economic-growth pressure inhibits the improvement of green total factor productivity. Currently, the main indices used to measure green total factor productivity are the MLPI index and the GMLPI (Global Malmquist–Luenberger Productivity Index) index. The baseline regression used the MLPI index to measure green total factor productivity, and column 2 of Table 4 used the re-measured green total factor productivity of the GMLPI index as the explained variable; the results show that the coefficient of EGP was −0.175 and was significant at the 5% level, which shows that the benchmark regression results are robust.

Table 4.
Robustness tests.
5.2.2. Split-Sample Regression
In order to prevent the different administrative levels of Beijing, Tianjin, Shanghai, and Chongqing and other prefecture-level cities from affecting the robustness of the regression results, the regressions were conducted again by excluding the samples of the four municipalities directly under the central government. In column 3 of Table 4, we can see that the coefficient value of economic-growth pressure was −0.195, and it passed the 5% significance-level test, which is not significantly different from the benchmark regression results, indicating that the benchmark regression results are stable and reliable.
5.2.3. System GMM
In order to reduce the potential endogeneity problem affecting the robustness of the regression results, this paper used a two-stage systematic GMM model to re-run the regression. The results of the AR 1 and AR 2 tests showed that the original hypothesis of no autocorrelation of the disturbance term could be accepted and passed the autocorrelation test; the p-value of the Hansen test was 0.235, which is greater than 0.1, indicating that the original hypothesis of the validity of the instrumental variable cannot be rejected, so the estimation results of the two-stage systematic GMM model are consistent and reliable. The regression results in column 4 of Table 4 indicate that economic-growth pressure still significantly inhibited the growth of green total factor productivity, which again proves the robustness of the baseline regression results.
5.3. Further Analysis
GTFP can be further decomposed into GTECH and GEFFCH. In order to explore in which component the inhibitory effect of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity is mainly manifested, the impact of EGP on green technological progress and green technological efficiency was further analyzed. Column 1 of Table 5 and Table 6 show the regression results when there was only one core explanatory variable, and columns 2–6 show the regression results when one control variable was added gradually. Regardless of the addition and number of control variables, economic-growth pressure always significantly inhibited green technological progress at the 10% level and always significantly inhibited green technological efficiency at the 5% level. Similarly, using the regression results in column 6 with all control variables added in Table 5 and Table 6 as the benchmark for the analysis, the green-technology progress and green-technology efficiency decreased by 0.147 units and 0.054 units, respectively, for each unit of economic-growth pressure.

Table 5.
Regression results of green technological progress.

Table 6.
Regression results of green technological efficiency.
The absolute value of the impact coefficient of economic-growth pressure on green technological progress was significantly larger than its absolute value on green technological efficiency, indicating that the marginal negative impact effect of economic-growth pressure on green technological progress was stronger, which indicates that the inhibitory effect of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity is more reflected in its hindering green technological progress.
5.4. Heterogeneity Analysis
The heterogeneity test in this paper adopted a split-sample regression approach, aiming to examine the impact of EGP on GTFP under different conditions so as to deeply analyze the characteristic laws behind it.
5.4.1. Intensity of Economic-Growth Pressure
When faced with different intensities of economic-growth pressures, there will be differences in the measures taken by local governments to boost economic growth and the economic policies introduced, which may have a differential impact on green total factor productivity. Therefore, in order to examine the effects of different intensities of economic-growth pressure on GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH, this paper grouped the samples according to the intensity of regional economic-growth pressure. The prefecture-level cities with economic-growth targets higher than their actual economic-growth rates in the current year were considered as the high-economic-growth-pressure group, otherwise they were considered the low-economic-growth-pressure group. The results of columns 1–3 in Table A1 in Appendix A show that high economic-growth pressure significantly inhibited green total factor productivity with a coefficient value of −0.310 and passed the 5% significance-level test, whereas in its decomposition term, high economic-growth pressure only had a significant negative effect on green technological efficiency and no significant negative effect on green technological progress. Columns 4–6 in Table A1 in Appendix A show that low economic-growth pressure had a negative effect on green total factor productivity and its decomposition term, but none of them were significant. Comparing the absolute values of EGP coefficients of high economic-growth pressure, low economic-growth pressure, and full-sample benchmark regression, we found that high economic-growth pressure > full-sample benchmark regression > low economic-growth pressure, indicating that the negative effect of increasing EGP on GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH increased. One possible reason is that when governments face high EGP, they implement strong economic policies that distort resource allocation and crowd out green-innovation resources, which leads to EGP significantly inhibiting GTFP.
5.4.2. Degree of Economic Development
Different degrees of economic development imply that local governments face different economic-growth potentials. Therefore, in order to dissect whether economic-growth pressure has different effects on GTFP under different degrees of economic development, this paper used the mean of the logarithm of real GDP per capita as the cutoff point, with samples above the mean being those with high degrees of economic development and those below the mean being those with low degrees of economic development. The results in columns 1–3 in Table A2 in Appendix A show that when the degree of economic development was high, economic-growth pressure significantly inhibited green total factor productivity at the 1% level with a marginal negative effect of 0.420, which mainly stems from the fact that economic-growth pressure hinders green technological progress. The results in columns 4–6 in Table A2 in Appendix A show that when the degree of economic development was low, economic-growth pressure only had an inhibitory effect on green technological efficiency at the 10% significance level, which still negatively affected green total factor productivity, albeit insignificantly, whereas it had a non-significant positive effect on green technological progress. In addition, the absolute value of the economic-growth-pressure coefficient at a high degree of economic development was significantly larger than the absolute value of the economic-growth-pressure coefficient at a low degree of economic development, which indicates that the higher the degree of economic development, the stronger the negative effect of economic-growth pressure on GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH. At a lower degree of economic development, the local economy still had more room for growth under the condition of natural-resource endowment, which weakened the negative effect of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity. However, at higher levels of economic development, the local economy had limited room for growth, which strengthened the negative effect of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity.
5.4.3. Level of Marketization
The degree of local government intervention in economic development was limited by the difference in marketization level. Therefore, in order to clarify whether the impact of economic-growth pressure on GTFP differs under different marketization levels, this paper considered the group above the average marketization level as the high marketization level and the group below the average marketization level as the low marketization level. In this paper, the Fangang index was used to measure the marketization level, and Table A3 in Appendix A reports the results of the heterogeneity test of marketization level. At a high marketization level, economic-growth pressure inhibited green total factor productivity, green technical progress, and green technical efficiency, but only green technical efficiency passed the significance level test of 10%. However, at a low marketization level, the marginal negative effect of economic-growth pressure on GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH increased, with both green total factor productivity and green technical efficiency passing the statistical test at the significance level of 5%. In conclusion, the lower the level of marketization, the stronger the inhibitory effect of economic-growth pressure on GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH. When the level of marketization is low, the more likely the government is to intervene in the market. When local governments face higher economic-growth pressure, excessive intervention in market behavior may lead to distorted resource allocation, inefficient market, and increased environmental pollution, thus inhibiting GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH.
5.5. Mechanism Analysis
The previous regression results confirmed that economic growth pressure is negatively related to green total factor productivity. Therefore, this paper attempted to explore the inner mechanism of the effect, emphasizing the green-technology innovation channel.
The amount of patent acquisition is a more stable and real measure of a region’s technological-innovation level, so this paper chose per-capita green-patents granted (PGPG) to characterize a region’s green-technological-innovation level. Green patents are divided into green-invention patents and green-utility-model patents, according to different types of patents, and since invention patents are mainly for innovation and utility-model patents are mainly for technical improvement, this paper used per-capita green-invention patents granted (PGIPG) to represent the level of innovation of green-invention patents and used per-capita green-utility-model patents granted (PGUPG) to represent the level of regional green-utility-model innovation.
This paper used a two-step regression method to test the mechanism of green-technology innovation. The first step was to test the effects of economic-growth pressure on green technological innovation, green-invention-patent innovation, and green-utility-model innovation, that is, economic-growth pressure was the core explanatory variable and green technological innovation, green-invention-patent innovation, and green-utility-model innovation were the explained variables; the second step was to test the effects of green technological innovation, green-invention-patent innovation, and green-utility-model innovation on GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH, respectively. The effects of green-technology innovation, green-invention-patent innovation, and green-utility innovation on green total productivity, green technological progress, and green technological efficiency, respectively, i.e., green-technology innovation, green-invention-patent innovation, and green-utility innovation, were the core explanatory variables, and GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH were the explained variables.
5.5.1. Green-Technology-Innovation Mechanism
Column 1 in Table 7 takes economic-growth pressure as the core explanatory variable and green-technology-innovation level as the explained variable; columns 2–4 have green-technology-innovation level as the core explanatory variable and GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH as the explained variables, in turn. The regression results in column 1 indicate that economic-growth pressure inhibited the level of green-technology innovation at a significance level of 10%, and the level of green-technology innovation decreased by 0.097 units for every unit increase in economic-growth pressure, which is supported by the research conclusions of Wang et al. [58] and Shen et al. [18] to some extent. The coefficient value of green-technology-innovation level in column (2) was 0.066 and it passed the 5% significance-level test, which shows that every unit increase in green-technology-innovation level was beneficial to the increase in green total factor productivity by 0.066 units. Green technology not only improves the economy’s response to global climate change and environment [63] but also positively correlates with environmental productivity [64]. Green innovation can increase environmental productivity [65]. Green-technology advancement can improve the utilization rate of natural resources, reduce production costs, and improve ecological efficiency [66], which are conducive to improving green total factor productivity and promoting green economic development. The results of the two-step regression in column 1 and column 2 show that economic-growth pressure inhibited green-technology-innovation level, thus preventing the positive effect of green-technology innovation on green total factor productivity, and eventually economic-growth pressure would have a negative effect on green total factor productivity. In addition, column 3 shows that green technological innovation promoted green technological progress at the 1% significance level with a coefficient value of 0.076, and column 4 shows that green technological innovation negatively affected green technological efficiency but not significantly. Thus, it is shown that economic-growth pressure inhibits green total factor productivity improvement mainly in terms of inhibiting green technological progress.

Table 7.
Green-technology innovation-mechanism test.
5.5.2. Heterogeneity of Patent-Type Mechanism
Column 1 of both Table 8 and Table 9 take economic-growth pressure as the core explanatory variable and green-invention-patent innovation and green-utility-model innovation as the explained variables; columns 2–4 of both Table 8 and Table 9 take GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH as the explained variables, in turn, among which Table 8 takes green-invention-patent innovation as the core explanatory variable and Table 9 takes green-utility-model innovation as the core explanatory variable. The results in column 1 of Table 8 and Table 9 show that economic-growth pressure had different degrees of negative effects on green-invention-patent innovation level and green-utility-model innovation level, and its marginal-effect coefficient value on the level of green-invention-patent innovation was −0.028 and significant at the 5% level, whereas the negative effect on the level of green-utility-model innovation was not significant, indicating that the economic-growth pressure mainly inhibited the green-invention-patent innovation, which is more difficult to develop and thus had a significant inhibitory effect on green-technology innovation. The results in columns 2–4 in Table 8 show that the level of green-invention-patent innovation effectively promoted green total factor productivity at the 10% significance level, and for every percentage-point increase in the level of green-invention-patent innovation, green total factor productivity increased by 0.177 percentage points. In the green total factor decomposition term, green-invention-patent innovation only significantly promoted green technological progress at the level of 10% and had a non-significant inhibitory effect on green technological efficiency, with green technological progress increasing by 0.197% for every 1% increase in green-invention-patent innovation. The results show that the promotion effect of green-invention patents on GTFP was mainly reflected in its favorable effect on green technological progress. The regression results in columns 2–4 in Table 9 show that green-utility-model innovation promoted green total factor productivity and green technological progress at the 1% significance level, with marginal positive effects of 0.086 and 0.100, respectively. Like the level of green-invention-patent innovation, its marginal effects on green technological efficiency were also negative and insignificant. Economic-growth pressure mainly inhibited green technological progress by negatively affecting green-invention and patent innovation, thus hindering green total factor productivity improvement.

Table 8.
Green-invention-patent innovation-mechanism test.

Table 9.
Green-utility-model innovation-mechanism test.
6. Discussion
EGP has an important negative effect on the growth of green total factor productivity. The greater the pressure on economic growth, that is, the higher the target value of economic growth is than the actual economic-growth rate of the year, the more detrimental it is to the improvement of local green total factor productivity and green development. First of all, when the pressure of economic growth is too great, local governments tend to invest in short-term projects to promote economic growth in order to achieve economic-growth targets, while environmental protection projects and innovative projects are often ignored [59]. Secondly, if the pressure on economic growth is too great, local governments will also reduce public expenditure [15] and weaken the intensity of environmental regulation [27], resulting in the reduction of environmental-protection funds, which will lead to the worsening of environmental pollution. Third, if the EGP is extraordinary, local governments will reduce the expenditure on technological innovation, which is not conducive to the improvement of the green-technological-innovation level, which makes it difficult to support the growth of green total factor productivity [39]. Fourth, when the level of economic development is high, the local economic-growth potential is limited due to the local resource-endowment conditions. When the local government is under great pressure of economic growth, local officials pay little attention to environmental protection [28], technological innovation, and other aspects, and are bent on achieving the economic-growth goals of the year at the expense of green total factor productivity. Finally, when the level of marketization is low, the ability of enterprises to raise funds independently is insufficient and the development goals and positioning of enterprises depend on the will of local governments, which leads to a decline in enterprises’ independent-innovation capability. However, the decline of enterprises’ independent-innovation capability is damaged to the improvement in enterprises’ green-technological-innovation level and green transformation, which leads to a decrease in local overall green total factor productivity and ultimately is harmful to the green development of China’s economy.
7. Conclusions and Recommendations
7.1. Conclusions
Green total factor productivity is a new economic-growth engine that takes environmental protection into account, which is important for China to practice the new development concept and promote green development. This paper focused on the impact of urban economic-growth pressure on GTFP and its internal mechanism of action based on the perspective of economic-growth-target management. This research adopted the difference between the target value of economic growth in each local government work report and its actual economic-growth rate in that year to measure the economic-growth pressure. Based on 249 cities’ panel data from 2006–2019, this study empirically analyzed the influence of economic-growth pressure on GTFP and the mechanism of green-technological-innovation action, etc., using a double fixed-effect model and drew the following conclusions.
(1) Economic-growth pressure significantly inhibited green total factor productivity growth, which to some extent is supported by the research conclusion of Chai et al. [22]. Further analysis by decomposing green total factor productivity revealed that economic-growth pressure inhibited not only green technological progress but also green technological efficiency with significance levels of 10% and 5%, but the marginal negative effect of economic-growth pressure on green technological progress was stronger. The conclusion still held after robustness tests.
(2) There was heterogeneity in the inhibitory effect of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity in terms of the intensity of economic-growth pressure, the degree of economic development, and the level of marketization. The higher the intensity of economic-growth pressure, the higher the degree of economic development, and the lower the level of marketization, the stronger the inhibitory effect of economic-growth pressure on GTFP, GTECH, and GEFFCH.
(3) Economic-growth pressure inhibited green total factor productivity growth by suppressing the improvement in green technological innovation, which to some extent is supported by the research conclusions of Wang et al. [58] and Shen et al. [18]. The mechanism of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity is that economic-growth pressure inhibited the level of green technological innovation, and improving the level of green-technology innovation can significantly promote the growth of green total factor productivity. After the decomposition of GTFP, it was found that green-technology innovation mainly improved GTFP through significantly positive influence on green-technology progress. Therefore, the mechanism of economic-growth pressure on green total factor productivity is that economic-growth pressure inhibited green technological innovation and hindered green technological progress, which eventually affected green total factor productivity negatively. Based on the decomposition of green-patent types, it was found that economic-growth pressure significantly inhibited green-invention-patent innovation, although it also had a negative effect on green-utility-model innovation, albeit not significantly. Therefore, the inner mechanism of the negative effect of economic-growth pressure on GTFP is that the economic-growth pressure significantly inhibited green-invention-patent innovation, which led to the slow increase or decrease in green-technology-innovation level, and then hindered green-technology progress, resulting in the obstruction of green total factor productivity growth.
7.2. Recommendations
Based on the above research findings, this paper briefly proposes three recommendations for economic-growth targets to boost green development.
(1) Reform the official promotion-assessment system. Weaken the proportion of GDP indicators in officials’ promotion appraisal and appropriately increase the proportion of environmental protection, substantial innovation, and other related indicators in the appraisal to avoid local governments and officials from setting excessive economic-growth targets for career advancement, which hinders the development of China’s green development.
(2) Rationalization of economic-growth-target setting. Since there are differences in the level of economic development and marketization in each place, and the natural resource-endowment conditions and economic-growth potential are also different, each place should set its economic-growth target according to the differences in the level of economic development, marketization, resource-endowment conditions and economic-growth potential in its jurisdiction, instead of following the general trend or setting economic-growth targets too high, so as to prevent each place from facing high pressure of economic growth due to unreasonable economic-growth-target setting.
(3) Innovation-driven development of green inventions and patents. During the critical period when China’s economy is transforming its development mode and dynamic energy conversion, it should help improve the innovation level of invention patents in all aspects and in multiple measures, especially the innovation level of green-invention patents that can substantially improve the efficiency of green-production technology and focus on the quality rather than the quantity of innovation so as to compensate for the negative impact of economic-growth pressure on the level of green-technology innovation, better promote the improvement of GTFP, and effectively promote the overall green transformation of the development of the economy and society.
Although this research has important theoretical and practical value, there are still some deficiencies that cannot be ignored. First, due to data limitations, the study did not include all prefecture-level cities in China but selected 249 prefecture-level cities with relatively complete data. Second, a comparative analysis of economic-growth pressure on total factor productivity and GTFP was not carried out in this study. If a comparative analysis is done, it may better explain the environmental pollution caused by economic-growth pressure and the inhibition of GTFP. Third, the mechanism analysis of this study only discusses the impact of economic-growth pressure on GTFP through green-technology innovation and lacks the verification of other mechanisms. Therefore, future research should focus on the comparative analysis of economic-growth pressure on total factor productivity and GTFP and the mechanism of enriching eco-nomic-growth pressure on g GTFP.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W. and J.L.; data curation, N.W.; formal analysis, N.W.; funding acquisition, J.L.; methodology, J.L.; project administration, X.W.; supervision, J.L.; writing—original draft, X.W. and J.L.; writing—review and editing, X.W. and J.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71964032), the Social Science Foundation of Xinjiang (19BJL028), and the Natural Science Foundation of Xinjiang (2018D01C052).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Test for heterogeneity of economic-growth pressure.
Table A1.
Test for heterogeneity of economic-growth pressure.
| Variables | High Economic-Growth Pressure | Low Economic-Growth Pressure | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTFP | GTECH | GEFFCH | GTFP | GTECH | GEFFCH | |
| EGP | −0.310 ** | −0.225 | −0.094 *** | −0.146 | −0.122 | −0.017 |
| (−2.30) | (−1.65) | (−2.82) | (−0.76) | (−0.61) | (−0.28) | |
| LED | 0.337 *** | 0.384 *** | −0.026 ** | 0.054 | 0.059 | −0.007 |
| (6.73) | (7.53) | (−2.07) | (0.84) | (0.89) | (−0.37) | |
| FAG | 0.513 ** | 0.514 ** | 0.009 | 1.215 ** | 1.198 ** | 0.024 |
| (2.56) | (2.51) | (0.17) | (2.12) | (2.01) | (0.13) | |
| HCA | 0.041 * | 0.048 * | −0.006 | 0.065 *** | 0.058 ** | 0.005 |
| (1.65) | (1.91) | (−0.92) | (2.78) | (2.38) | (0.74) | |
| FAU | 0.001 | 0.007 | −0.011 | 0.027 | 0.019 | 0.007 |
| (0.01) | (0.13) | (−0.83) | (0.66) | (0.44) | (0.55) | |
| IET | 0.332 *** | 0.562 *** | −0.123 *** | −0.304 | −0.328 | 0.011 |
| (4.26) | (7.08) | (−6.35) | (−1.24) | (−1.30) | (0.15) | |
| Constant | −0.489 ** | −0.711 *** | 1.132 *** | 0.623 ** | 0.623 ** | 1.015 *** |
| (−2.21) | (−3.15) | (20.52) | (2.28) | (2.20) | (11.93) | |
| N | 1885 | 1885 | 1885 | 1601 | 1601 | 1601 |
| F | 33.43 | 35.28 | 29.13 | 35.34 | 43.87 | 36.29 |
| R2 | 0.282 | 0.293 | 0.255 | 0.335 | 0.384 | 0.341 |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Note: t-statistics in parentheses, * p < 0.10, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01.

Table A2.
Test for heterogeneity of economic-development levels.
Table A2.
Test for heterogeneity of economic-development levels.
| Variables | High Level of Economic Development | Low Level of Economic Development | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTFP | GTECH | GEFFCH | GTFP | GTECH | GEFFCH | |
| EGP | −0.420 *** | −0.383 *** | −0.054 | −0.046 | 0.019 | −0.061 * |
| (−3.19) | (−2.86) | (−1.63) | (−0.41) | (0.16) | (−1.81) | |
| LED | 0.228 *** | 0.262 *** | −0.041 ** | 0.311 *** | 0.372 *** | −0.037 ** |
| (3.38) | (3.81) | (−2.46) | (6.34) | (7.30) | (−2.46) | |
| FAG | 2.469 *** | 2.185 *** | 0.293 * | 1.350 ** | 1.556 ** | −0.211 |
| (3.53) | (3.07) | (1.68) | (2.28) | (2.53) | (−1.17) | |
| HCA | 0.102 *** | 0.106 *** | −0.007 | −0.004 | −0.008 | 0.004 |
| (3.31) | (3.40) | (−0.96) | (−0.21) | (−0.37) | (0.68) | |
| FAU | 0.061 | 0.075 | −0.016 | −0.005 | −0.025 | 0.018 |
| (1.18) | (1.43) | (−1.29) | (−0.12) | (−0.56) | (1.38) | |
| IET | −0.171 | −0.213 | 0.002 | 0.323 *** | 0.569 *** | −0.136 *** |
| (−0.18) | (−0.22) | (0.01) | (4.49) | (7.60) | (−6.20) | |
| Constant | −0.296 | −0.469 | 1.218 *** | −0.224 | −0.462 ** | 1.136 *** |
| (−0.91) | (−1.41) | (15.00) | (−1.12) | (−2.21) | (18.57) | |
| N | 1695 | 1695 | 1695 | 1791 | 1791 | 1791 |
| F | 38.09 | 41.46 | 37.91 | 34.60 | 41.19 | 32.79 |
| R2 | 0.330 | 0.349 | 0.329 | 0.297 | 0.335 | 0.286 |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Note: t-statistics in parentheses, * p < 0.10, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01.

Table A3.
Heterogeneity test of marketization level.
Table A3.
Heterogeneity test of marketization level.
| Variables | High Level of Marketability | Low Level of Marketability | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTFP | GTECH | GEFFCH | GTFP | GTECH | GEFFCH | |
| EGP | −0.109 | −0.060 | −0.059 * | −0.243 ** | −0.172 | −0.078 ** |
| (−0.77) | (−0.41) | (−1.85) | (−2.27) | (−1.56) | (−2.18) | |
| LED | 0.354 *** | 0.431 *** | −0.043 *** | 0.245 *** | 0.280 *** | −0.042 ** |
| (6.57) | (7.75) | (−3.59) | (3.78) | (4.19) | (−1.96) | |
| FAG | 0.406 ** | 0.460 ** | −0.040 | 0.789 | 0.838 | −0.073 |
| (2.04) | (2.24) | (−0.90) | (0.96) | (0.99) | (−0.27) | |
| HCA | 0.122 *** | 0.113 *** | 0.011 | 0.030 | 0.032 | −0.004 |
| (4.20) | (3.76) | (1.62) | (1.20) | (1.23) | (−0.52) | |
| FAU | −0.010 | −0.021 | 0.006 | 0.003 | 0.004 | −0.001 |
| (−0.17) | (−0.37) | (0.45) | (0.08) | (0.08) | (−0.10) | |
| IET | 0.341 *** | 0.610 *** | −0.144 *** | −0.076 | 0.065 | −0.183 |
| (4.15) | (7.19) | (−7.82) | (−0.13) | (0.11) | (−0.92) | |
| Constant | −0.795 *** | −1.089 *** | 1.150 *** | −0.072 | −0.226 | 1.198 *** |
| (−3.17) | (−4.21) | (20.45) | (−0.26) | (−0.79) | (12.86) | |
| N | 1746 | 1746 | 1746 | 1740 | 1740 | 1740 |
| F | 34.95 | 36.60 | 32.19 | 38.29 | 47.11 | 31.42 |
| R2 | 0.309 | 0.319 | 0.292 | 0.330 | 0.377 | 0.287 |
| City | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Year | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Note: t-statistics in parentheses, * p < 0.10, ** p < 0.05, *** p < 0.01.
References
- Rusiawan, W.; Tjiptoherijanto, P.; Suganda, E.; Darmajanti, L. Assessment of green total factor productivity impact on sustainable Indonesia productivity growth. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, E.M. Green TFP intensity impact on sustainable east Asian productivity growth. Econ. Anal. Policy 2012, 42, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, J. Did the digital economy effectively promote energy conservation and CO2 reduction? China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2022, 32, 83–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.X. China is moving away the pattern of “develop first and then treat the pollution”. Energy Policy 2007, 35, 3547–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J. Pollution haven hypothesis and environmental impacts of foreign direct investment: The case of industrial emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) in Chinese provinces. Ecol. Econ. 2006, 60, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, H.; Zhou, Y. How does green trade affect the environment? Evidence from China. J. Econ. Anal. 2022, 1, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhanbayev, R.; Du, M. Does the internet development put pressure on energy-saving potential for environmental sustainability? Evidence from China. J. Econ. Anal. 2022, 1, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Cui, D.; Geng, C.; Xia, Z. The role of business environment optimization on entrepreneurship enhancement. J. Econ. Anal. 2022, 1, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.X.; Li, S.J.; Wang, X.B.; Bi, Q.M. Growth target choices: Ending Chinese collapse fallacy with high-quality development. World Econ. 2018, 10, 3–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Y. Economic growth target management. Econ. Res. J. 2017, 7, 18–33. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J. Governing by goals and numbers: A case study in the use of performance measurement to build state capacity in China. Public Adm. Dev. 2009, 29, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.C.; Olasehinde-Williams, G. Gasoline demand elasticities in the world’s energy gluttons: A time-varying coefficient approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64830–64847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Gao, Y. Growth target management and regional economic growth. J. Asia Pac. Econ. 2015, 20, 517–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Xu, X. Stabilizing economic growth: Growth target and government expenditure since World War II. China Econ. Q. Int. 2022, 2, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Xu, C.; Yu, Y.; Rong, K.; Zhang, J. Economic growth target, distortion of public expenditure and business cycle in China. China Econ. Rev. 2020, 63, 101373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Qian, Y.; Weingast, B.R. Regional decentralization and fiscal incentives: Federalism, Chinese style. J. Public Econ. 2005, 89, 1719–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latham, G.; Borgony, L.; Petitta, L. Goal setting and performance management in the public sector. Public Adm. Issues 2011, 11, 72–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Liu, B.; Luo, F.; Wu, C.; Chen, H.; Wei, W. The effect of economic growth target constraints on green technology innovation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Hou, Q.; Hu, M. Haste doesn’t bring success: Top-down amplification of economic growth targets and enterprise overcapacity. J. Corp. Financ. 2021, 70, 102059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yi, H. Target-setting, political incentives, and the tricky trade-off between economic development and environmental protection. Public Adm. 2022, 100, 923–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Huang, J.; Guo, Y.; Wu, H.; Ren, S. Does the legacy of state planning put pressure on ecological efficiency? Evidence from China. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022, 31, 3100–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Hao, Y.; Wu, H.; Yang, Y. Do constraints created by economic growth targets benefit sustainable development? Evidence from China. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 4188–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Wu, H.; Hao, Y. Planned economic growth and controlled energy demand: How do regional growth targets affect energy consumption in China? Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 185, 122068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Yan, J.; Zhao, J.; Shen, J.; Ran, Q. Analysis of the impacts of economic growth targets and marketization on energy efficiency: Evidence from China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Lin, B. Economic growth pressure and energy efficiency improvement: Empirical evidence from Chinese cities. Appl. Energy 2022, 307, 118275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhao, B.; Fan, T.; Zhang, J. Economic growth targets and carbon emissions: Evidence from China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, L. Economic growth target and environmental regulation intensity: Evidence from 284 cities in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 10235–10249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Wen, H.; Lee, C.C. How does economic growth target affect corporate environmental investment? Evidence from heavy-polluting industries in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanere, M.; Fraser, I.; Quazi, A.; D’Souza, C. Environmentally adjusted productivity measurement: An Australian case study. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Ouyang, H.; Fang, K.; Ye, L.; Zhang, J. Evaluation of regional environmental efficiencies in China based on super-efficiency-DEA. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 51, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Shao, T.; Lai, H.; Shen, M.; Li, Y. Total-factor eco-efficiency and its influencing factors in the Yangtze River delta urban agglomeration, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Du, Q. Can green credit policy promote green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 6891–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S. The policy outcomes of low-carbon city construction on urban green development: Evidence from a quasi-natural experiment conducted in China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.L.; Li, J.; Xu, R.Y.; Pang, S.Q.; Miao, Z.; Sun, H.P. The impact of low-carbon city pilot policy on green total-factor productivity in China’s cities. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 24299–24318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.L.; Pang, S.Q.; Zhang, F.Q.; Miao, Z.; Sun, H.P. The impact assessment of smart city policy on urban green total-factor productivity: Evidence from China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 94, 106756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Liao, J.; Sun, C.; Cao, Y. Measure is treasure: Revisiting the role of environmental regulation in Chinese industrial green productivity. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Kong, S. The effect of environmental regulation on green total-factor productivity in China’s industry. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 94, 106757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Feng, C. The internal-structural effects of different types of environmental regulations on China’s green total-factor productivity. Energy Econ. 2022, 113, 106246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Yang, P.; Li, Q. Impact of environmental regulation on green total factor productivity: A new perspective of green technological innovation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53785–53800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Nakonieczny, J.; Jabeen, F.; Shahzad, U.; Jia, W. Does green innovation induce green total factor productivity? Novel findings from Chinese city level data. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 185, 122021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xia, Q.; Li, Z. Green innovation and enterprise green total factor productivity at a micro level: A perspective of technical distance. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Cao, Y.; Feng, C.; Guo, K.; Zhang, J. How do heterogeneous R&D investments affect China’s green productivity: Revisiting the Porter hypothesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 825, 154090. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wu, H.; Irfan, M.; Ahmad, M. The role of innovation investment and institutional quality on green total factor productivity: Evidence from 46 countries along the “Belt and Road”. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16597–16611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Pang, J. The role of internet development on green total-factor productivity—An empirical analysis based on 109 cities in Yangtze River economic belt. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Bai, G.; Shen, Z.; Xia, L. Digital economy and its spatial effect on green productivity gains in manufacturing: Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J. How does digital economy affect green total factor productivity? Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Liao, F. Input digitalization and green total factor productivity under the constraint of carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, Y.; Sun, X. How does artificial intelligence affect green economic growth?—Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 834, 155306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, A.; Han, M.; Veglianti, E. Carbon emission reduction effects of industrial robot applications: Heterogeneity characteristics and influencing mechanisms. Technol. Soc. 2022, 70, 102034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Mai, Q. Robot adoption and green productivity: Curse or Boon. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Xiao, H. Can FDI facilitate green total factor productivity in China? Evidence from regional diversity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 49309–49321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Xiong, S.; Li, K.; Jia, P. Electricity price and industrial green productivity: Does the “low-electricity price trap” exist? Energy 2020, 207, 118239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Razzaq, A.; Kizys, R.; Bao, Q. High-speed rail and urban green productivity: The mediating role of climatic conditions in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 185, 122055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.E.; Cheng, K.M. Do large cities have a productivity advantage in China? From the perspective of green total factor productivity growth. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debbarma, J.; Choi, Y.; Yang, F.; Lee, H. Exports as a new paradigm to connect business and information technology for sustainable development. J. Innov. Knowl. 2022, 7, 100233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Zhang, B.; Wang, N. Non-linear relationship between energy consumption transition and green total factor productivity: A perspective on different technology paths. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 28, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, R.; Yao, S.; Han, F.; Zhang, Q. Does misallocation of land resources reduce urban green total factor productivity? An analysis of city-level panel data in China. Land Use Policy 2022, 122, 106353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Dong, Z.; Wang, S.; Cao, Z. The air pollution effect of government economic growth expectations: Evidence from China’s cities based on green technology. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 27639–27654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L. Governing China’s Local Officials: An Analysis of Promotion Tournament Model. Econ. Res. J. 2007, 7, 36–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S.; Pasurka, C.A., Jr. Environmental production functions and environmental directional distance functions. Energy 2007, 32, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.H.; Färe, R.; Grosskopf, S. Productivity and undesirable outputs: A directional distance function approach. J. Environ. Manag. 1997, 51, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J. The Estimation of China’s provincial capital stock: 1952–2000. Econ. Res. J. 2004, 10, 35–44. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Do neighboring prefectures matter in promoting eco-efficiency? Empirical evidence from China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 144, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisetti, C.; Quatraro, F. Green technologies and environmental productivity: A cross-sectoral analysis of direct and indirect effects in Italian regions. Ecol. Econ. 2017, 132, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xu, L.; Chen, Z. Environmental efficiency analysis of the Yangtze River Economic Zone using super efficiency data envelopment analysis (SEDEA) and tobit models. Energy 2017, 134, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Y.; Miao, C.L.; Yang, L. Ecological-economic efficiency evaluation of green technology innovation in strategic emerging industries based on entropy weighted TOPSIS method. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 73, 554–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).