Pollution and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Rivers in a Northeastern Chinese City: Implications for Continuous Rainfall Events
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
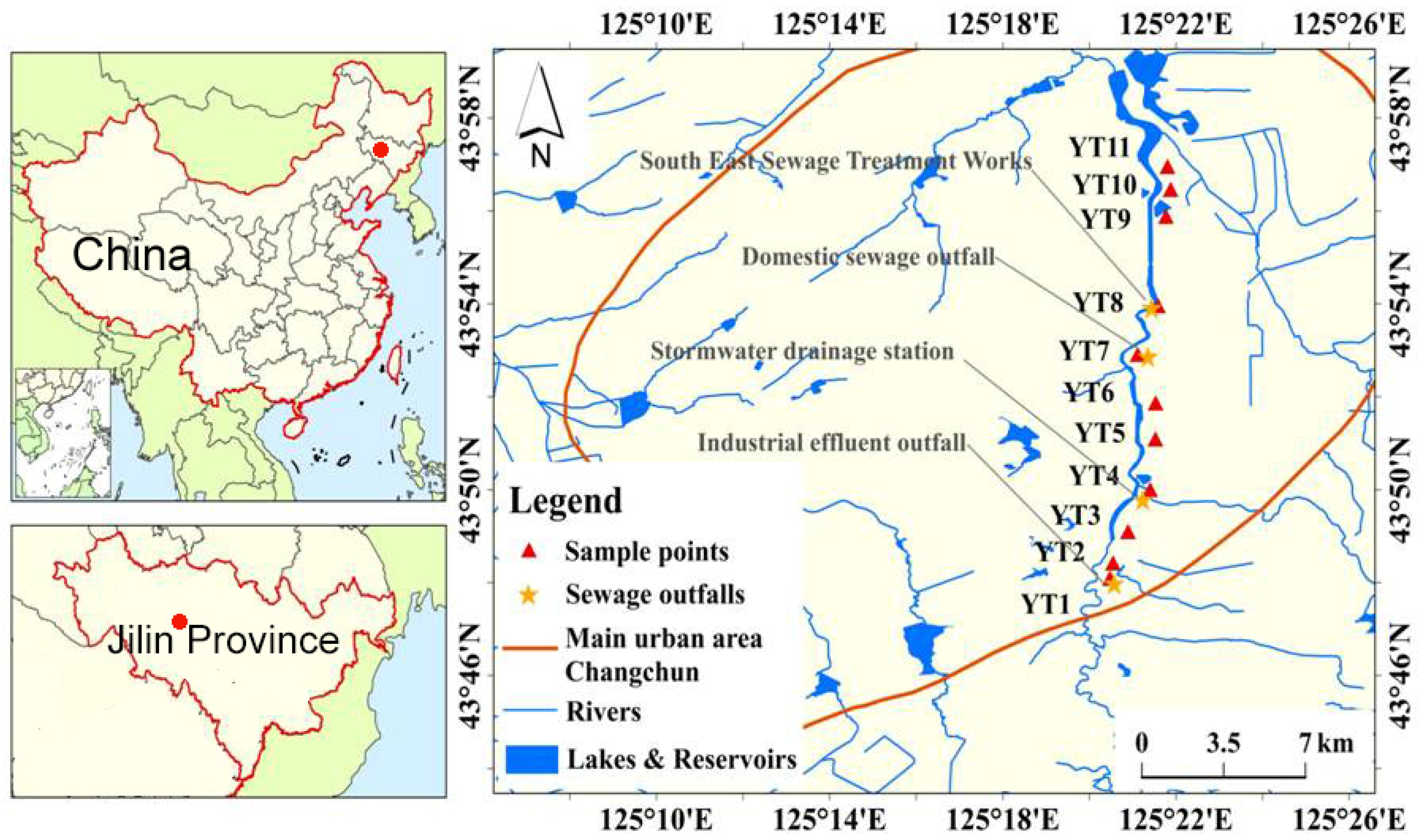
2.1. Location of Study
2.2. Instruments and Reagents
2.3. In Situ Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Extraction of PAHs
2.5. GC–MS Analysis and Quality Control
2.6. Toxic Equivalent Quantity for Human Risk
2.7. Risk Index for Ecological Risk
2.8. Statistic Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Occurrence of PAHs in Riverine Samples
3.2. Characteristics of 16 PAH Concentrations in Samples of Rainfall
3.3. Spatial Distributions of PAHs in Riverine Samples
3.4. Identification of PAH Sources
3.4.1. Sources by Diagnostic Ratios of Selected PAHs
3.4.2. Sources by PCA
3.5. Environmental Risk Assessment
3.5.1. Human Health Risk Assessment
3.5.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
3.6. PAHs Characteristics and Risk before and after Typhoon
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, C.C.; Chen, C.S.; Wang, Z.X.; Tien, C.J. Polycyclic hydrocarbons in 30 river ecosystems, Taiwan: Sources, and ecological and human health risks. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambade, B.; Sethi, S.S. Health risk assessment and characterization of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon from the hydrosphere. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2021, 25, 05020008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastral, A.M.; Callen, M.S. A review on polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) emissions from energy generation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 3051–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Qu, X.; Lin, D.; Yang, K. Octanol-water partition coefficient (logKow) dependent movement and time lagging of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) from emission sources to lake sediments: A case study of Taihu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojiri, A.; Zhou, J.L.; Ohashi, A.; Ozaki, N.; Kindaichi, T. Comprehensive review of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water sources, their effects and treatments. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 696, 133971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, J.R.; Dachbrodt-Saaydeh, S.; Kudsk, P.; Messéan, A. Toward a reduced reliance on conventional pesticides in European agriculture. Plant Disease 2016, 100, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fleming, L.E.; Broad, K.; Clement, A.; Dewailly, E.; Elmir, S.; Knap, A.; Pomponi, S.A.; Smith, S.; Gabriele, H.S.; Walsh, P. Oceans and human health: Emerging public health risks in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2006, 53, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.; Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, C.; Ren, M. Distribution, source and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in groundwater in a coal mining area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, W.; Lei, T.; Jingxin, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hongqin, Z.; Dong, L.; Lin, W. Distribution, sources and toxicity of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Liuxi River, China. Chem. Ecol. 2022, 38, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lu, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, P.; Cao, X.; Cui, H.; Zhang, M.; Du, D. Effects of urbanization on the distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in China’s estuarine rivers. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 301, 119001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C. The distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in shallow groundwater from an alluvial-diluvial fan of the Hutuo River in North China. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 13, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Xia, X.; Shen, Z.; Zhou, Z. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in Wuhan section of the Yangtze River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 133, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xia, X.; Yang, Z.; Wang, R.; Voulvoulis, N. Distribution and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 144, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, P.; Guo, W.; Dai, S.; Sun, H. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the surface sediments from Yellow River, China. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.H.; Wang, G.L.; Chai, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, J.; Feng, J. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in Henan reach of the Yellow River, Middle China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2009, 72, 1614–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.L.; Liu, L.Y.; Qi, H.; Zhang, Z.F.; Song, W.W.; Shen, J.M.; Chen, Z.L.; Ren, N.Q.; Grabuski, J.; Li, Y.F. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water, sediment and soil of the Songhua River Basin, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 8399–8409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Chang, Y.; Yan, G.; Chu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, T. Distributions, compositions, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydro-carbons and phthalic acid esters in surface sediment of Songhua river, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lai, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Yang, W.; Mai, Y.; Wang, C. Occurrence, source identification, and ecological risk assessment of polycyclic aromatic hydro-carbons in sediments of the Pearl River Delta, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 170, 112666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Wang, H.; Zhan, H.; Wu, C.; Huang, Y.; Yang, B.; Mosa, A.; Ling, W. Catalyzed degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by recoverable magnetic chitosan immobilized laccase from Trametes versicolor. Chemosphere 2022, 301, 134753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremina, N.; Paschke, A.; Mazlova, E.A.; Schüürmann, G. Distribution of polychlorinated biphenyls, phthalic acid esters, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and organochlorine substances in the Moscow River, Russia. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 210, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Dai, Y.; Han, M.; He, H.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Xian, Q.; Yang, S.; Sun, C. Nitrated and parent PAHs in the surface water of Lake Taihu, China: Occurrence, distribution, source, and human health risk assessment. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 102, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Q.; Wang, K.Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.C.; Wang, X.J. Characterization and sources of PAHs in an urban river system in Beijing, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 31, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, N.; Kong, X.-Z.; He, W.; He, Q.-S.; Liu, W.-X.; Xu, F.-L. Dustfall-bound polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) over the fifth largest Chinese lake: Residual levels, source apportionment, and correlations with suspended particulate matter (SPM)-bound PAHs in water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 55388–55400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Q.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Li, P.; Xia, S.; Huang, Q. Contamination of 16 priority polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in urban source water at the tidal reach of the Yangtze River. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 6122–61235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, R.; Sun, P.; Xia, H.; He, T. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the soils of the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration, China: Influence of land cover types and urbanization. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 715, 137011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Jiménez, J.; Berrojalbiz, N.; Wollgast, J.; Dachs, J. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Mediterranean Sea: At-mospheric occurrence, deposition and decoupling with settling fluxes in the water column. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 166, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dachs, J.; Eisenreich, S.J.; Baker, J.E.; Ko, F.-C.; Jeremiaso, J.D. Coupling of phytoplankton uptake and air−water exchange of persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 3653–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, J.A.; Mondon, J.; Mitchell, B.D.; Kidd, T.; Eshelman, B. Urban stormwater inputs to an adapted coastal wetland: Role in water treatment and impacts on wetland biota. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Xu, J.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Meng, W. Spatial and temporal distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in surface water from Liaohe River Basin, northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 7088–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekhavhambe, T.J.; Van Ree, T.; Fatoki, O.S. Determination and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in rivers, surface runoff, and sediments in and around Thohoyandou, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Water 2014, 40, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, A.; Verma, P.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, K.P. Distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in water and bed sediments of the Gomti River, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2010, 172, 529–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, M.; He, J.; Zheng, Z. Black-odor water analysis and heavy metal distribution of Yitong River in Northeast China. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wu, G.; Wang, C.; Lu, N.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, X. Pollution characteristics of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance of coliform bacteria in the Yitong River, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Tang, Z.; Zhao, T.; Teng, M.; Liang, W.; Wang, J.; Niu, L. Using deterministic and probabilistic approaches to assess the human health risk assessment of 7 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 331, 129811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.L.; Jing, X.; Chang, W.J.; Chen, Z.X.; Zeng, H. Cumulative health risk assessment of halogenated and parent polycyclic aromatic hydro-carbons associated with particulate matters in urban air. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisbet IC, T.; Lagoy, P.K. Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, S.; Zhang, T.; Jin, B.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhou, J.; et al. A review on occurrence and risk of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in lakes of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalf, D.F.; Crommentuijn, T.; van de Plassche, E.J. Environmental quality objectives for 10 polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 1997, 36, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Wade, T.L.; Sweet, S.T. Atmospheric deposition of PAHs, PCBs, and organochlorine pesticides to Corpus Christi Bay, Texas. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 1707–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S. The distribution variation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons between fresh snow and seasonal snowpack in campus in Changchun City, Northeast China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileshi, A.; Awoke, A.; Beyene, A.; Stiers, T.; Triest, L. Water purifying capacity of natural riverine wetlands in relation to their ecological quality. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merino, P.; Švec, M.; Martinez, J.I.; Jelinek, P.; Lacovig, P.; Dalmiglio, M.; Lizzit, S.; Soukiassian, P.; Cernicharo, J.; Martin-Gago, J.A. Graphene etching on SiC grains as a path to interstellar polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons formation. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bateganya, N.L.; Mentler, A.; Langergraber, G.; Busulwa, H.; Hein, T. Carbon and nitrogen gaseous fluxes from subsurface flow wetland buffer strips at mesocosm scale in East Africa. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 85, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, R.K.; Baker, J.E. Source apportionment of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the urban atmosphere: A comparison of three methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, M.B.; Macdonald, R.W.; Vingarzan, R.; Mitchell, R.H.; Goyette, D.; Sylvestre, S. PAHs in the Fraser River basin: A critical appraisal of PAH ratios as indicators of PAH source and composition. Org. Geochem. 2002, 33, 489–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masclet, P.; Cachier, H.; Liousse, C.; Wortham, H. Emissions of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by savanna fires. J. Atmos. Chem. 1995, 22, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofowote, U.M.; McCarry, B.E.; Marvin, C.H. Source apportionment of PAH in Hamilton Harbour suspended sediments: Com-parison of two factor analysis methods. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 6007–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobbins, R.A.; Fletcher, R.A.; Benner, B.A., Jr.; Hoeft, S. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in flames, in diesel fuels, and in diesel emissions. Combust. Flame 2006, 144, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, S. Partial nitrification-anammox (PNA) treating sewage with intermittent aeration mode: Effect of influent C/N ratios. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.; Su, G.; Wei, S.; Liu, H.; Cheng, S.; Yu, H. Identification of trace organic pollutants in freshwater sources in Eastern China and estimation of their associated human health risks. Ecotoxicology 2011, 20, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doong, R.-A.; Lin, Y.-T. Characterization and distribution of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminations in surface sediment and water from Gao-ping River, Taiwan. Water Res. 2004, 38, 1733–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W.; Wu, B.; Han, F.; Lin, Z.; Wamg, X. Enrichment behavior and transport mechanism of soil-bound PAHs during rainfall-runoff events. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 171, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekpo, B.O.; Oyo-Ita, O.E.; Oros, D.R.; Simoneit, B.R. Distributions and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in surface sediments from the Cross River estuary, SE Niger Delta, Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Cai, H.; Van Gelder, P.; Luo, P.; Liu, F.; Yang, Q. Dynamics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in water column of Pearl River estuary (China): Seasonal pattern, environmental fate and source implication. Appl. Geochem. 2018, 90, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Duan, X.; Qin, N.; Lv, J.; Wu, G.; Wei, F. Health risk from dietary exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in a typical high cancer incidence area in southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Wade, T.L.; Sweet, S. Atmospheric Deposition of Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) and Pesticides to Galveston Bay. 1999. Available online: https://tamug-ir.tdl.org/handle/1969.3/25859 (accessed on 23 December 2022).
- Wei, S.H.I.; Zhang, X.N.; JIA, H.B.; Feng, S.D.; Yang, Z.X.; Zhao, O.Y.; Li, Y.L. Effective remediation of aged HMW-PAHs polluted agricultural soil by the combination of Fusarium sp. and smooth bromegrass (Bromus inermis Leyss). J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 199–209. [Google Scholar]




| PAHs | TEF | NCs (ng/L) | MPCs (ng/L) | PAHs | TEF | NCs (ng/L) | MPCs (ng/L) |
| Nap | 0.001 | 12 | 1200 | BaA | 0.1 | 0.1 | 10 |
| Acy | 0.001 | 0.7 | 70 | Chr | 0.01 | 3.4 | 340 |
| Ace | 0.001 | 0.7 | 70 | BbF | 0.1 | 0.1 | 10 |
| Flu | 0.001 | 0.7 | 70 | BkF | 0.1 | 0.4 | 40 |
| Phe | 0.001 | 3 | 300 | BaP | 1 | 0.5 | 50 |
| Ant | 0.01 | 0.7 | 70 | DahA | 0.1 | 0.5 | 50 |
| Fla | 0.001 | 3 | 300 | InP | 1 | 0.4 | 40 |
| Pyr | 0.001 | 0.7 | 70 | BghiP | 0.001 | 0.3 | 30 |
| ∑16PAHs | -- | 27.2 | 2720 |
| Samples Collected Before Bavet | Samples Collected Before Metsak and After Bavet | Samples Collected Before Poseidon and After Metsak | Samples Collected After-Poseidon | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAP | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.92 | 0.24 |
| ANY | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| ANAA | n.d. | 0.31 | n.d. | n.d. |
| FLU | 9.50 | 3.29 | 1.10 | 0.32 |
| PHE | 40.47 | 31.23 | 16.47 | 10.16 |
| ANT | n.d. | 1.18 | 0.45 | 1.6 |
| FLT | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| PYR | 5.57 | 6.03 | 4.95 | 3.65 |
| BaA | 3.97 | 4.37 | 4.57 | 4.20 |
| CHR | 3.33 | 3.32 | 3.20 | 3.09 |
| BbF | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| BkF | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| BaP | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| IPY | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| DBA | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| BPE | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Sampling Time | PAHs | TEQ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Children | ||
| Before Bavet (first sampling) | NAP | 3.99 × 10−5 | 4.53 × 10−5 | 1.09 × 10−5 |
| ANAA | -- | -- | -- | |
| FLU | 1.89 × 10−3 | 2.15 × 10−3 | 5.17 × 10−4 | |
| PHE | 8.07 × 10−3 | 9.17 × 10−3 | 2.20 × 10−3 | |
| ANT | -- | -- | -- | |
| PYR | 1.10 × 10−3 | 1.26 × 10−3 | 3.03 × 10−4 | |
| BaA | 7.88 × 10−2 | 8.97 × 10−2 | 2.16 × 10−2 | |
| CHR | 6.62 × 10−3 | 7.55 × 10−3 | 1.81 × 10−3 | |
| After Bavet (second sampling) | NAP | 7.59 × 10−5 | 8.61 × 10−5 | 2.07 × 10−5 |
| ANAA | 6.18 × 10−5 | 7.02 × 10−5 | 1.69 × 10−5 | |
| FLU | 6.56 × 10−4 | 7.45 × 10−4 | 1.79 × 10−4 | |
| PHE | 6.23 × 10−3 | 7.08 × 10−3 | 1.70 × 10−3 | |
| ANT | 2.35 × 10−3 | 2.67 × 10−3 | 6.43 × 10−4 | |
| PYR | 1.19 × 10−3 | 1.37 × 10−3 | 3.29 × 10−4 | |
| BaA | 8.69 × 10−2 | 9.90 × 10−2 | 2.38 × 10−2 | |
| CHR | 6.60 × 10−3 | 7.52 × 10−3 | 1.80 × 10−3 | |
| After Metsak (third sampling) | NAP | 1.84 × 10−4 | 2.08 × 10−4 | 5.01 × 10−5 |
| ANAA | -- | -- | -- | |
| FLU | 2.19 × 10−4 | 2.49 × 10−4 | 5.99 × 10−4 | |
| PHE | 3.29 × 10−3 | 3.73 × 10−3 | 8.97 × 10−4 | |
| ANT | 8.96 × 10−4 | 1.01 × 10−3 | 2.45 × 10−4 | |
| PYR | 9.85 × 10−4 | 1.04 × 10−3 | 2.69 × 10−4 | |
| BaA | 9.09 × 10−2 | 0.104 | 2.49 × 10−2 | |
| CHR | 6.36 × 10−3 | 7.25 × 10−3 | 1.74 × 10−3 | |
| After Poseidon (forth sampling) | NAP | 4.79 × 10−5 | 5.44 × 10−5 | 1.31 × 10−5 |
| ANAA | -- | -- | -- | |
| FLU | 6.38 × 10−5 | 7.25 × 10−5 | 1.74 × 10−5 | |
| PHE | 2.02 × 10−3 | 2.30 × 10−3 | 5.53 × 10−4 | |
| ANT | 3.18 × 10−3 | 3.63 × 10−3 | 8.72 × 10−4 | |
| PYR | 7.26 × 10−4 | 8.27 × 10−4 | 1.99 × 10−4 | |
| BaA | 8.35 × 10−2 | 9.51 × 10−2 | 2.29 × 10−2 | |
| CHR | 6.15 × 10−3 | 7.00 × 10−3 | 1.68 × 10−3 | |
| PAHs. | Samples Collected Before Bavet | Samples Collected Before Metsak and After Bavet | Samples Collected Before Poseidon and After Metsak | Samples Collected After Poseidon | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RQNCs | RQMPCs | RQNCs | RQMPCs | RQNCs | RQMPCs | RQNCs | RQMPCs | |
| Nap | 0.02 | 1.67 × 10−4 | 0.03 | 3.17 × 10−4 | 0.08 | 7.67 × 10−4 | 0.02 | 2 × 10−4 |
| Acy | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Ace | -- | -- | 0.44 | 4.40 × 10−3 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Flu | 13.57 | 0.14 | 4.70 | 0.05 | 1.57 | 0.02 | 0.46 | 4.57 × 10−3 |
| Phe | 13.49 | 0.13 | 10.41 | 0.10 | 5.49 | 0.05 | 3.39 | 0.03 |
| Ant | -- | -- | 1.69 | 0.02 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 2.29 | 0.02 |
| Fla | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| Pyr | 7.96 | 0.08 | 8.61 | 0.09 | 7.07 | 0.07 | 5.21 | 0.05 |
| BaA | 39.70 | 0.40 | 43.70 | 0.44 | 45.70 | 0.46 | 42.00 | 0.42 |
| Chr | 0.98 | 0.01 | 0.98 | 9.76 × 10−3 | 0.94 | 9.41 × 10−3 | 0.91 | 9.09 × 10−3 |
| BbF | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| BkF | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| BaP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| DahA | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| InP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| BghiP | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| ∑16PAHs | 75.72 | 0.76 | 68.87 | 0.69 | 60.85 | 0.61 | 51.99 | 0.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, G.; Bian, D.; Zou, M.; Wang, X.; Chen, F. Pollution and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Rivers in a Northeastern Chinese City: Implications for Continuous Rainfall Events. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5777. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075777
Mu G, Bian D, Zou M, Wang X, Chen F. Pollution and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Rivers in a Northeastern Chinese City: Implications for Continuous Rainfall Events. Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):5777. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075777
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Guangyi, Dejun Bian, Min Zou, Xuege Wang, and Fangfang Chen. 2023. "Pollution and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Rivers in a Northeastern Chinese City: Implications for Continuous Rainfall Events" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 5777. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075777
APA StyleMu, G., Bian, D., Zou, M., Wang, X., & Chen, F. (2023). Pollution and Risk Assessment of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Urban Rivers in a Northeastern Chinese City: Implications for Continuous Rainfall Events. Sustainability, 15(7), 5777. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075777





