Effect of Temperature on Co-Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure and Empty Fruit Bunch: A Kinetic Parametric Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Feedstock Materials
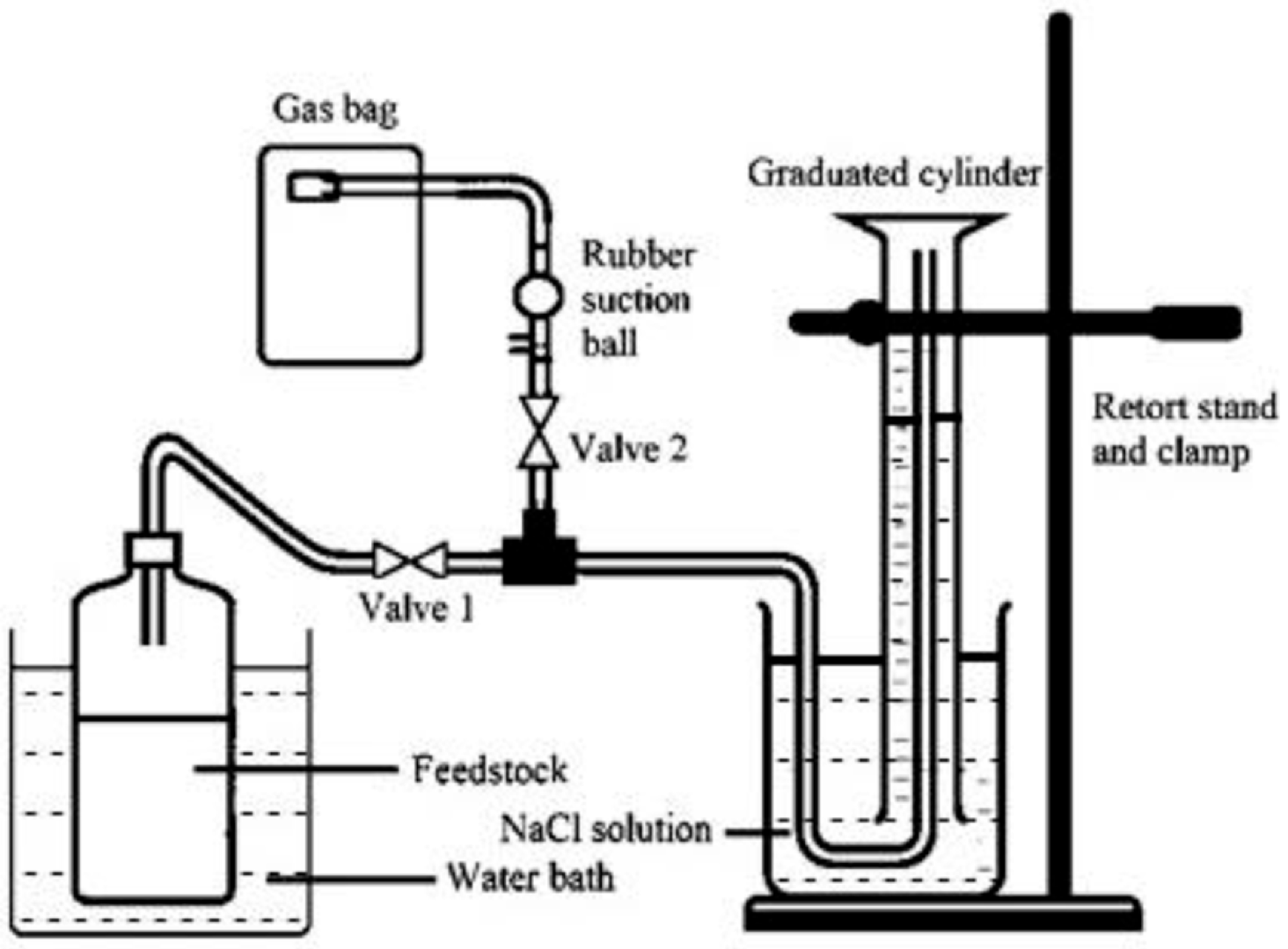
2.2. Batch Digester Setup and Experimental Design
2.3. Biogas Volume and Composition Analysis
2.4. Kinetic Modelling and Statistical Indicators
3. Results
3.1. Biogas and Methane Generation
3.2. Kinetic Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chijioke, N.O.; Uddin Khandaker, M.; Tikpangi, K.M.; Bradley, D.A. Metal uptake in chicken giblets and human health implications. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 85, 103332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, E.M.M.; Herrera, A.M.N.; Esteves, V.P.P.; Morgado, C.d.R.V. Life cycle assessment of manure biogas production: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeshahian, P.; Lim, J.S.; Ho, W.S.; Hashim, H.; Lee, C.T. Potential of biogas production from farm animal waste in Malaysia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 714–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, A.; Sürmeli, R.Ö.; Çalli, B. Dry anaerobic digestion of chicken manure coupled with membrane separation of ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 816–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, S.Q.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Umar, M. Leachate characterization in semi-aerobic and anaerobic sanitary landfills: A comparative study. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2608–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manogaran, M.D.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Yusoff, M.H.M.; Lay, M. An overview on available treatment processes of poultry manure in Malaysia. AIP Conf. Proc. 2022, 2610, 040005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manogaran, M.D.; Shamsuddin, R.; Mohd Yusoff, M.H.; Lay, M.; Siyal, A.A. A review on treatment processes of chicken manure. Clean. Circ. Bioecon. 2022, 2, 100013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Johari, S.A.; Aqsha, A.; Osman, N.B.; Shamsudin, M.R.; Ameen, M.; Dol, S.S. Enhancing biogas production in anaerobic co-digestion of fresh chicken manure with corn stover at laboratory scale. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, H.Y.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Aqsha, A. Anaerobic Treatment of Chicken Manure Co-digested with Sawdust. In Advances in Manufacturing Engineering; Emamian, S.S., Awang, M., Yusof, F., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 741–748. [Google Scholar]
- Chuenchart, W.; Logan, M.; Leelayouthayotin, C.; Visvanathan, C. Enhancement of food waste thermophilic anaerobic digestion through synergistic effect with chicken manure. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 136, 105541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsuddin, R.; Singh, G.; Kok, H.Y.; Hakimi Rosli, M.; Dawi Cahyono, N.A.; Lam, M.K.; Lim, J.W.; Low, A. Palm Oil Industry—Processes, By-Product Treatment and Value Addition. In Sustainable Bioconversion of Waste to Value Added Products; Inamuddin, Khan, A., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 121–143. [Google Scholar]
- Cahyono, N.A.D.; Shamsuddin, M.R.; Ayoub, M.; Mansor, N.; Isa, N.H.M.; Gunny, A.A.N. Anaerobic co-digestion of chicken manure with energy crop residues for biogas production. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 765, 012044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; He, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wu, D.; Wang, X.; Peng, X. Anaerobic digestion of food waste: Correlation of kinetic parameters with operational conditions and process performance. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 130, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y. Bioaugmentation improves batch psychrophilic anaerobic co-digestion of cattle manure and corn straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Zhu, A.; Sun, B.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y.-Y. Methanogenic treatment of dairy product wastewater by thermophilic anaerobic membrane bioreactor: Ammonia inhibition and microbial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 357, 127349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Qiao, W.; Xiong, L.; Ricci, M.; Adani, F.; Dong, R. Effects of organic loading rate on anaerobic digestion of chicken manure under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Renew. Energy 2019, 139, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T.E.; Khan, M.U.; Tian, H.; Ee, A.W.L.; Lim, E.Y.; Dai, Y.; Tong, Y.W.; Ahring, B.K. Improving methane yield of oil palm empty fruit bunches by wet oxidation pretreatment: Mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion conditions and the associated global warming potential effects. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 225, 113438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, G.; Carotenuto, C.; Di Cristofaro, F.; Papa, S.; Morrone, B.; Minale, M. Does the C/N ratio really affect the Bio-methane Yield? A three years investigation of Buffalo Manure Digestion. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2016, 49, 463–468. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Lin, J.; Zuo, J.; Li, P.; Li, X.; Guo, X. Effects of free ammonia on volatile fatty acid accumulation and process performance in the anaerobic digestion of two typical bio-wastes. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 55, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanatamskul, C.; Manpetch, P. Comparative assessment of prototype digester configuration for biogas recovery from anaerobic co-digestion of food waste and rain tree leaf as feedstock. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanimu, M.I.; Ghazi, T.I.M.; Harun, R.M.; Idris, A. Effect of carbon to nitrogen ratio of food waste on biogas methane production in a batch mesophilic anaerobic digester. Int. J. Innov. Manag. Technol. 2014, 5, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Cioabla, A.E.; Ionel, I.; Dumitrel, G.-A.; Popescu, F. Comparative study on factors affecting anaerobic digestion of agricultural vegetal residues. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2012, 5, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakimi, M.; Shamsuddin, R.; Pendyala, R.; Siyal, A.A.; AlMohamadi, H. Co-anaerobic digestion of chicken manure with the addition of Cymbopogan citratus, Mentha piperita and Citrus sinensis as fly deterrent agents: Biogas production and Kinetic study. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2021, 15, 100748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheri, A.N.; Ndiweni, S.N.; Belaid, M.; Muzenda, E.; Hubert, R. Optimising biogas production from anaerobic co-digestion of chicken manure and organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akindolire, M.A.; Rama, H.; Roopnarain, A. Psychrophilic anaerobic digestion: A critical evaluation of microorganisms and enzymes to drive the process. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 161, 112394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ona, J.I.; Halling, P.J.; Ballesteros, M. Enzyme hydrolysis of cassava peels: Treatment by amylolytic and cellulolytic enzymes. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2019, 37, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rajagopal, R.; Bellavance, D.; Rahaman, M.S. Psychrophilic anaerobic digestion of semi-dry mixed municipal food waste: For North American context. Proc. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 105, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayrakdar, A.; Molaey, R.; Sürmeli, R.Ö.; Sahinkaya, E.; Çalli, B. Biogas production from chicken manure: Co-digestion with spent poppy straw. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 119, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.M.; Westerholm, M.; Qiao, W.; Bi, S.J.; Wandera, S.M.; Fan, R.; Jiang, M.M.; Dong, R.J. An explanation of the methanogenic pathway for methane production in anaerobic digestion of nitrogen-rich materials under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 264, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Takemura, Y.; Kubota, K.; Li, Y.Y. Comparing mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of chicken manure: Microbial community dynamics and process resilience. Waste Manag. 2015, 43, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G. Effect of ammonia on methane production, methanogenesis pathway, microbial community and reactor performance under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appels, L.; Baeyens, J.; Degrève, J.; Dewil, R. Principles and potential of the anaerobic digestion of waste-activated sludge. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 2008, 34, 755–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.H. An overview of empty fruit bunch from oil palm as feedstock for bio-oil production. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 62, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, Z.J.; Bashir, M.J.K.; Ng, C.A.; Sethupathi, S.; Lim, J.W.; Show, P.L. Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Development in Malaysia: Appraisal of Environmental, Financial, and Public Issues Related with Energy Recovery from Municipal Solid Waste. Processes 2019, 7, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaka, M.; Walvekar, R.; Rasheed, A.K.; Khalid, M. A review on Malaysia’s solar energy pathway towards carbon-neutral Malaysia beyond Covid’19 pandemic. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 273, 122834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Qin, W.; Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Wen, X. Long-term performance and microbial community characteristics of pilot-scale anaerobic reactors for thermal hydrolyzed sludge digestion under mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 720, 137566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.L.; Lin, Z.; Sun, Z.Y.; Gou, M.; Xia, Z.Y.; Tang, Y.Q. A comparative study of mesophilic and thermophilic anaerobic digestion of municipal sludge with high-solids content: Reactor performance and microbial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, A.; Braguglia, C.M.; Gianico, A.; Montecchio, D.; Pagliaccia, P. Kitchen waste valorization through a mild-temperature pretreatment to enhance biogas production and fermentability: Kinetics study in mesophilic and thermophilic regimen. J. Environ. Sci. 2020, 89, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, M.; Zeshan; Zeeshan, M.; Nawaz, I.; Hassan, M. Effect of low levels of oxytetracycline on anaerobic digestion of cattle manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 349, 126894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wang, R.; Xing, H.; Yu, M.; Shen, S.; Zhao, L.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. Effects of different low temperature conditions on anaerobic digestion efficiency of pig manure and composition of archaea community. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 86, 1181–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wan, L.; Li, D. The screening of early warning indicators and microbial community of chicken manure thermophilic digestion at high organic loading rate. Energy 2021, 224, 120201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, A.; Parajuli, A.; Dangol, S.; Thapa, B.; Sapkota, L.; Carmona-Martínez, A.A.; Ghimire, A. Effect of the Substrate to Inoculum Ratios on the Kinetics of Biogas Production during the Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste. Energies 2022, 15, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pečar, D.; Goršek, A. Kinetics of methane production during anaerobic digestion of chicken manure with sawdust and miscanthus. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 143, 105820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Xiao, X.; Feng, L.; He, Y.; Liu, G. Evaluating Methane Production from Anaerobic Mono- and Co-digestion of Kitchen Waste, Corn Stover, and Chicken Manure. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahboubi, N.; Kerrou, O.; Karouach, F.; Bakraoui, M.; Schüch, A.; Schmedemann, K.; Stinner, W.; El Bari, H.; Essamri, A. Methane production from mesophilic fed-batch anaerobic digestion of empty fruit bunch of palm tree. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 12, 3751–3760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Kim, S.H. Conditions of lag-phase reduction during anaerobic digestion of protein for high-efficiency biogas production. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 143, 105813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, S.K.; Suja, F.B.; Porhemmat, M.; Pramanik, B.K. Performance and Kinetic Model of a Single-Stage Anaerobic Digestion System Operated at Different Successive Operating Stages for the Treatment of Food Waste. Processes 2019, 7, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| First Order Kinetic Model | ||||||||
| Setup | Bo (mL/gvs) | k (1/day) | R2 | RMSE | Experimental CH4 Yield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Computed CH4 Yield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Percent Difference (%) | |
| PAD | 2.701 | 0.046 | 0.984 | 0.030 | 2.434 | 2.431 | 0.123 | |
| MAD | 47.277 | 0.006 | 0.882 | 0.391 | 12.845 | 12.357 | 3.799 | |
| TAD | 4.603 | 0.039 | 0.957 | 0.079 | 3.988 | 3.932 | 1.404 | |
| Monod Model | ||||||||
| Setup | Bo (mL/gvs) | k (1/day) | R2 | RMSE | Experimental CH4 Yield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Computed CH4 Yield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Percent Difference (%) | |
| PAD | 3.821 | 0.036 | 0.984 | 0.030 | 2.434 | 2.468 | 1.397 | |
| MAD | 78.270 | 0.004 | 0.882 | 0.391 | 12.845 | 12.309 | 4.173 | |
| TAD | 6.659 | 0.029 | 0.960 | 0.076 | 3.988 | 3.967 | 0.527 | |
| Cone Model | ||||||||
| Setup | Bo (mL/gvs) | k (1/day) | n | R2 | RMSE | Experimental CH4 Yield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Computed CH4 Yield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Percent Difference (%) |
| PAD | 3.070 | 0.056 | 1.277 | 0.975 | 0.031 | 2.434 | 2.422 | 0.493 |
| MAD | 150.259 | 0.001 | 0.852 | 0.840 | 0.415 | 12.845 | 11.996 | 6.610 |
| TAD | 7.078 | 0.026 | 0.960 | 0.933 | 0.084 | 3.988 | 3.979 | 0.226 |
| Modified Gompertz Model | ||||||||
| Setup | Bo (mL/gvs) | Rb (mL/gvs day) | λ (Days) | R2 | RMSE | Experimental CH4 Dield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Computed CH4 Dield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Percent Difference (%) |
| PAD | 2.373 | 0.088 | −0.278 | 0.970 | 0.040 | 2.434 | 2.334 | 4.108 |
| MAD | 52.569 | 0.330 | 11.100 | 0.897 | 0.365 | 12.845 | 12.962 | 0.911 |
| TAD | 3.968 | 0.120 | −1.435 | 0.935 | 0.096 | 3.988 | 3.813 | 4.388 |
| Logistics Function Model | ||||||||
| Setup | Bo (mL/gvs) | Rb (mL/gvs day) | λ (Days) | R2 | RMSE | Experimental CH4 Yield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Computed CH4 Yield at Day 50 (mL/gvs) | Percent Difference (%) |
| PAD | 2.299 | 0.086 | −0.137 | 0.951 | 0.051 | 2.434 | 2.290 | 5.916 |
| MAD | 29.205 | 0.336 | 10.906 | 0.895 | 0.369 | 12.845 | 13.139 | 2.289 |
| TAD | 3.837 | 0.112 | −1.797 | 0.913 | 0.112 | 3.988 | 3.771 | 5.441 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Manogaran, M.D.; Hakimi, M.; Basheer Ahmad, M.H.N.; Shamsuddin, R.; Lim, J.W.; M Hassan, M.A.; Sahrin, N.T. Effect of Temperature on Co-Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure and Empty Fruit Bunch: A Kinetic Parametric Study. Sustainability 2023, 15, 5813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075813
Manogaran MD, Hakimi M, Basheer Ahmad MHN, Shamsuddin R, Lim JW, M Hassan MA, Sahrin NT. Effect of Temperature on Co-Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure and Empty Fruit Bunch: A Kinetic Parametric Study. Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):5813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075813
Chicago/Turabian StyleManogaran, M. Devendran, Mohd Hakimi, Mohammad Harith Nizam Basheer Ahmad, Rashid Shamsuddin, Jun Wei Lim, Muzamil Abdalla M Hassan, and Nurul Tasnim Sahrin. 2023. "Effect of Temperature on Co-Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure and Empty Fruit Bunch: A Kinetic Parametric Study" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 5813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075813
APA StyleManogaran, M. D., Hakimi, M., Basheer Ahmad, M. H. N., Shamsuddin, R., Lim, J. W., M Hassan, M. A., & Sahrin, N. T. (2023). Effect of Temperature on Co-Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure and Empty Fruit Bunch: A Kinetic Parametric Study. Sustainability, 15(7), 5813. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15075813









