Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Based on Hybrid Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- The regeneration of battery capacity was eliminated through CEEMDAN, and the accuracy of the prediction model was improved.
- (2)
- The weights of the initial population, control factor, and wolf group in the traditional GWO were improved to enhance the diversity and iteration speed of the population.
- (3)
- IGWO was used to improve the parameters of neurons, dropout rate, batch size, etc. in the neural network. The universality of RUL prediction was improved for IMF components at different frequencies.
2. Methodology
2.1. Battery Remaining Useful Life
2.2. Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise
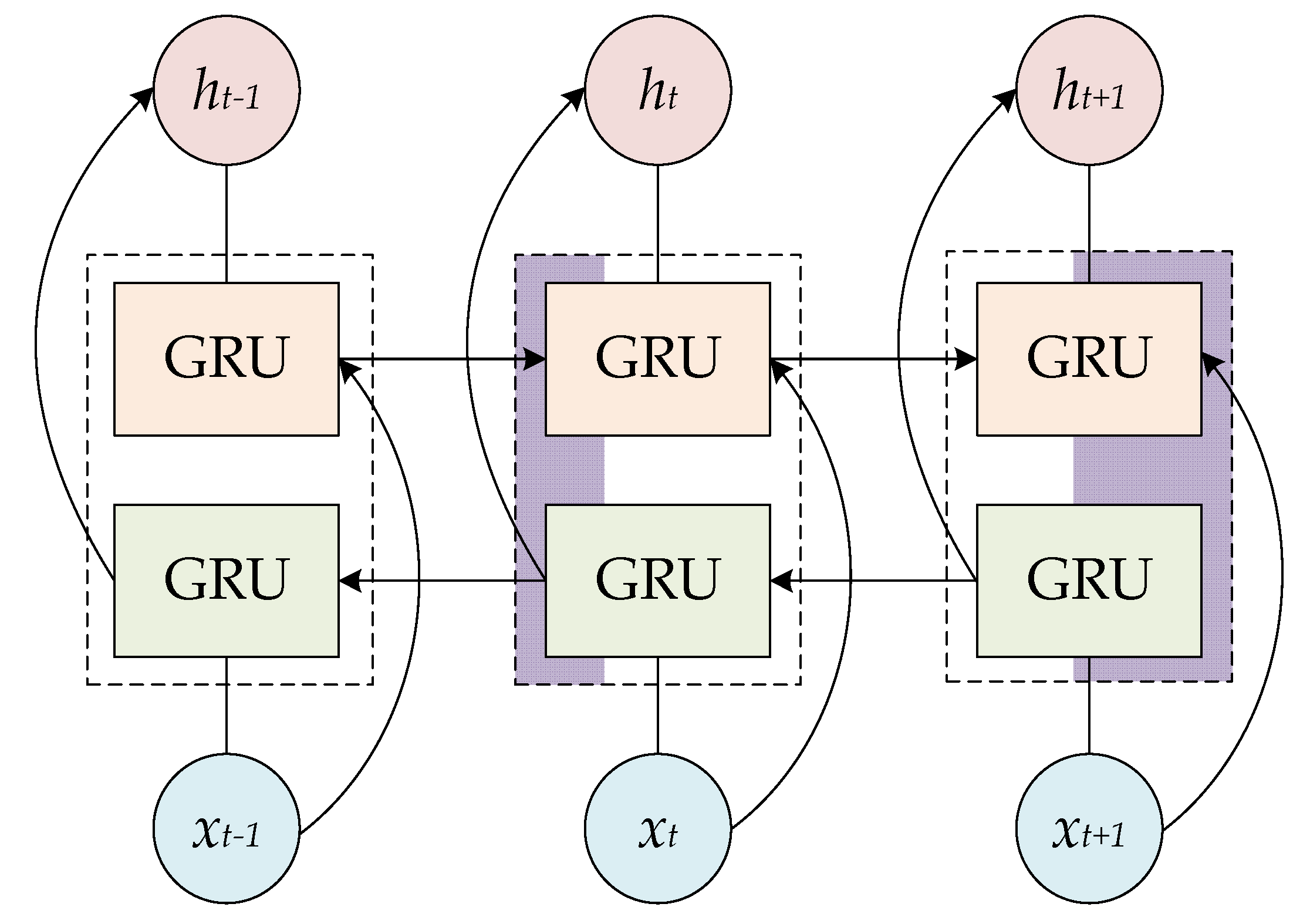
2.3. Bidirectional Gate Recurrent Unit
2.4. The Grey Wolf Optimizer
2.5. Improved Grey Wolf Optimizer
2.5.1. Population Initialization
2.5.2. Optimize Control Parameters α
2.5.3. Dynamic Weight
3. Experiment
3.1. Data Sets
3.2. Evaluation Criteria
3.3. Structure of the RUL Prediction Model
4. Results and Discussion
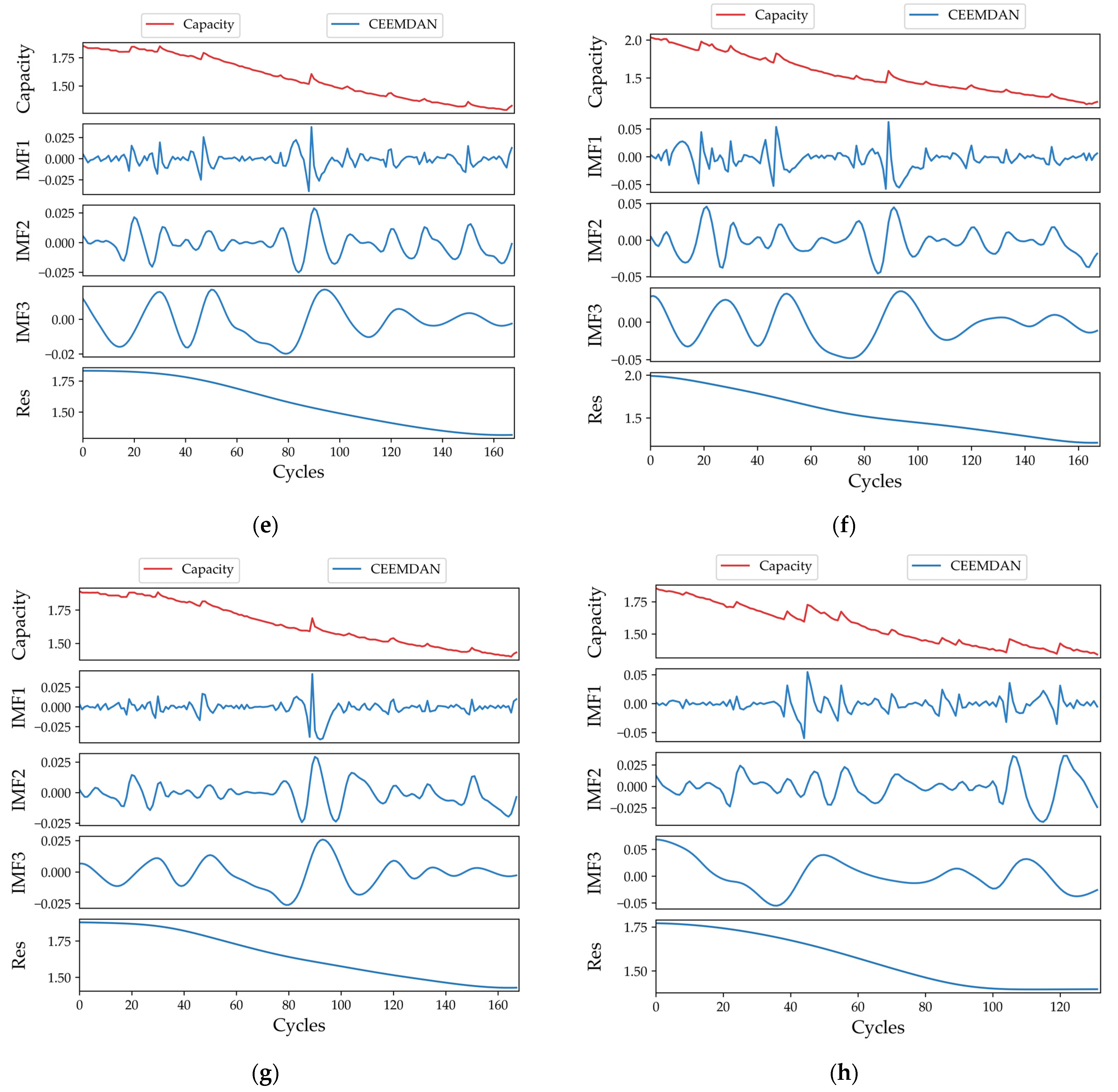
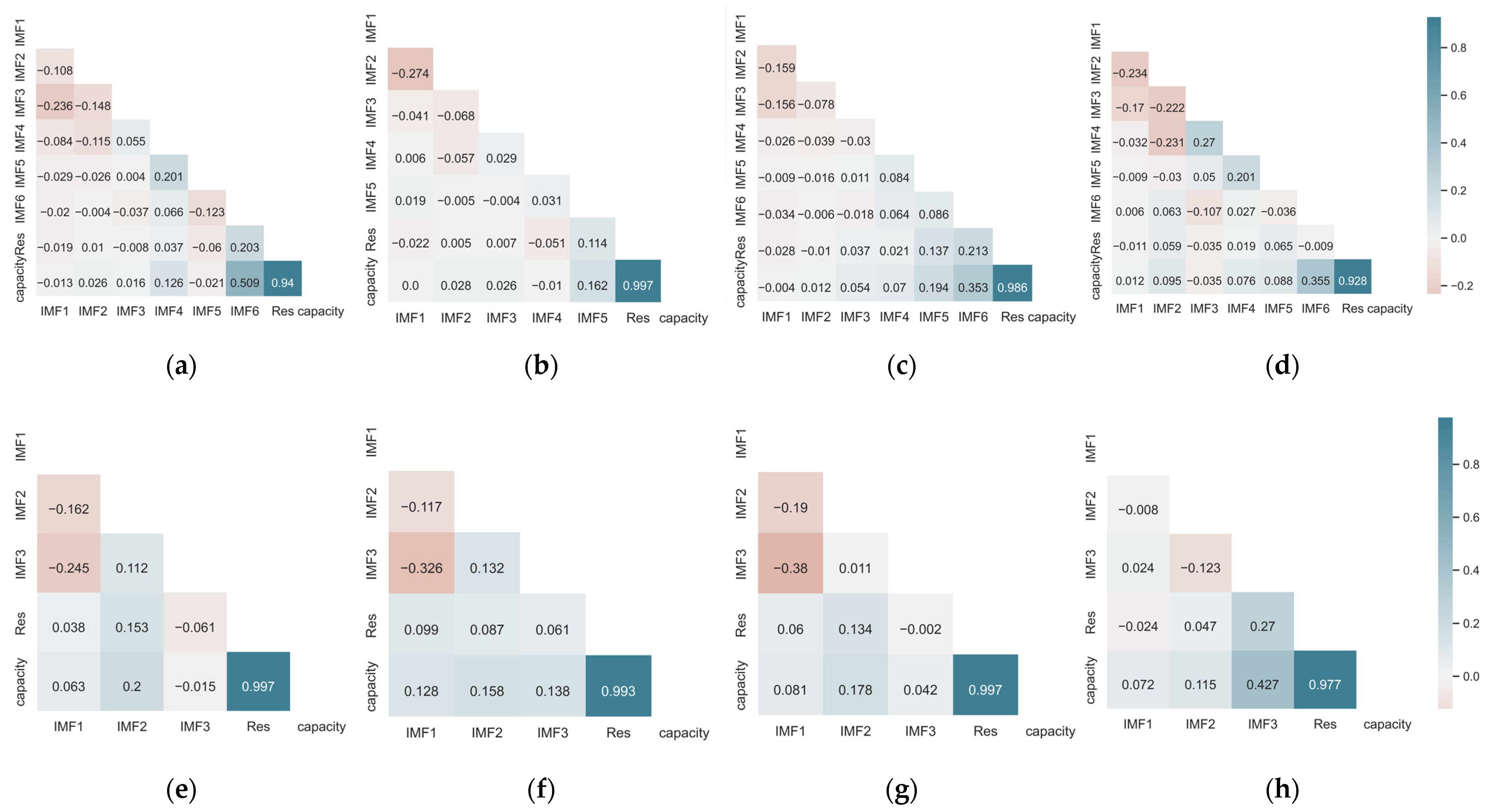
4.1. Results of CEEMDAN
4.2. Results of IGWO–BiGRU
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Larcher, D.; Tarascon, J.M. Towards greener and more sustainable batteries for electrical energy storage. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, S.M.; Sanad, M.M.S.; Mattar, T.; El-Shahat, M.F.; Rossignol, C.; Dessemond, L.; Zaidat, K.; Obbade, S. The Structural, Thermal and Electrochemical Properties of MnFe1−x−yCuxNiyCoO4 Spinel Protective Layers in Interconnects of Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs). J. Alloy. Compd. 2022, 923, 166351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbaoui, D.; Sanad, M.M.S.; Rossignol, C.; Hlil, E.K.; Amdouni, N.; Zaidat, K.; Obbade, S. Effect of Divalent Transition Metal Ions on Physical, Morphological, Electrical and Electrochemical Properties of Alluaudite Phases Na2M2 + 2Fe3+(PO4)3 (M = Mn, Co and Ni): Cathode Materials for Sodium-Ions Batteries. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 901, 163641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Lipu, M.H.; Hussain, A.; Mohamed, A. A review of lithium-ion battery state of charge estimation and management system in electric vehicle applications: Challenges and recommendations. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 78, 834–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaguemont, J.; Boulon, L.; Dubé, Y. A comprehensive review of lithium-ion batteries used in hybrid and electric vehicles at cold temperatures. Appl. Energy 2016, 164, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Feng, X.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Ouyang, M. A review on the key issues of the lithium ion battery degradation among the whole life cycle. ETransportation 2019, 1, 100005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Tang, X.; Dai, H.; Yang, Y.; Wu, W.; Wei, X.; Huang, Y. Building safe lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles: A review. Electrochem. Energy Rev. 2020, 3, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.; Ma, X.; Chen, B.; Arsenault, R.; Karlson, P.; Simon, N.; Wang, Y. Recycling end-of-life electric vehicle lithium-ion batteries. Joule 2019, 3, 2622–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makuza, B.; Tian, Q.; Guo, X.; Chattopadhyay, K.; Yu, D. Pyrometallurgical options for recycling spent lithium-ion batteries: A comprehensive review. J. Power Sources 2021, 491, 229622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.; Patra, A. State of health estimation of lithium-ion batteries using capacity fade and internal resistance growth models. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2017, 4, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severson, K.A.; Attia, P.M.; Jin, N.; Perkins, N.; Jiang, B.; Yang, Z.; Braatz, R.D. Data-driven prediction of battery cycle life before capacity degradation. Nat. Energy 2019, 4, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, R.; Cao, J.; Yu, Q.; He, H.; Sun, F. Critical review on the battery state of charge estimation methods for electric vehicles. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 1832–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, M.M.; Meselhy, N.K.; El-Boraey, H.A.; Toghan, A. Controllable engineering of new ZnAl2O4-decorated LiNi0· 8Mn0· 1Co0· 1O2 cathode materials for high performance lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 1528–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeiyazdi, I.; Rezaei-Zare, A.; Shokrzadeh, S. State of charge prediction of EV Li-ion batteries using EIS: A machine learning approach. Energy 2021, 223, 120116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Dong, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, L.; Deen, M.J. A data-driven auto-CNN-LSTM prediction model for lithium-ion battery remaining useful life. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 3478–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Lithium-ion battery capacity and remaining useful life prediction using board learning system and long short-term memory neural network. J. Energy Storage 2022, 52, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; He, W.; Wu, Y.; Ding, F.; Meng, D. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries using a hybrid model. Energy 2022, 248, 123622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Shang, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Widanage, W.D. A data-driven approach with uncertainty quantification for predicting future capacities and remaining useful life of lithium-ion battery. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 3170–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, H.; Hou, L. State of health monitoring and remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries based on temporal convolutional network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 53307–53320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Wang, X.; He, Y. Remaining useful life and state of health prediction for lithium batteries based on empirical mode decomposition and a long and short memory neural network. Energy 2021, 232, 121022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, X. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion battery with optimal input sequence selection and error compensation. Neurocomputing 2020, 414, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, Z.; Li, J. Financial time series forecasting model based on CEEMDAN and LSTM. Phys. A: Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2019, 519, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, Z.; Qin, W.; Shi, W.; Ping, P. State-of-health prediction for lithium-ion batteries based on a novel hybrid approach. Energies 2020, 13, 4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Geng, M.; Xing, J.; Zio, E. A hybrid method for prognostics of lithium-ion batteries capacity considering regeneration phenomena. Energy 2022, 261, 125278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Liu, F.; Ma, Y.; Fan, J. A neural-network-based method for RUL prediction and SOH monitoring of lithium-ion battery. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 87178–87191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Tang, B.; Zeng, X.; Zhou, P.; Kang, P.; Long, H. Short-term wind speed forecasting based on long short-term memory and improved BP neural network. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2022, 134, 107365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karijadi, I.; Chou, S.Y. A hybrid RF-LSTM based on CEEMDAN for improving the accuracy of building energy consumption prediction. Energy Build. 2022, 259, 111908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Wang, W.; Zhu, T. Remaining Useful Life Prediction for Lithium-Ion Batteries Based on CS-VMD and GRU. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 89402–89413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Huang, X.; Shi, J.; Tai, Y.; Zhang, J. Hourly forecasting of solar irradiance based on CEEMDAN and multi-strategy CNN-LSTM neural networks. Renew. Energy 2020, 162, 1665–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014, 69, 46–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dokeroglu, T.; Sevinc, E.; Kucukyilmaz, T.; Cosar, A. A survey on new generation metaheuristic algorithms. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 137, 106040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abualigah, L.; Diabat, A.; Mirjalili, S.; Abd Elaziz, M.; Gandomi, A.H. The arithmetic optimization algorithm. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2021, 376, 113609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altan, A.; Karasu, S.; Zio, E. A new hybrid model for wind speed forecasting combining long short-term memory neural network, decomposition methods and grey wolf optimizer. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadimi-Shahraki, M.H.; Taghian, S.; Mirjalili, S. An improved grey wolf optimizer for solving engineering problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 166, 113917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, W.; Cai, S.; Jiao, J.; Xu, M.; Wu, T. A new hybrid algorithm based on grey wolf optimizer and cuckoo search for parameter extraction of solar photovoltaic models. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 203, 112243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.; Cai, Z.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y.; Hu, L. Chaos enhanced grey wolf optimization wrapped ELM for diagnosis of paraquat-poisoned patients. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 78, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Xu, L.; Lin, X.; Pecht, M. Battery lifetime prognostics. Joule 2020, 4, 310–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Cai, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tan, L. Remaining useful life prediction of lithium-ion batteries using CEEMDAN and WOA-SVR model. Front. Energy Res. 2022, 10, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, W.; Chen, G.; Zhang, T. An Adaptive Noise Reduction Approach for Remaining Useful Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries. Energies 2022, 15, 7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, M.; Wang, D.; Qiu, J. A GRU-RNN based momentum optimized algorithm for SOC estimation. J. Power Sources 2020, 459, 228051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, C.; Gao, M. A new hybrid neural network method for state-of-health estimation of lithium-ion battery. Energies 2022, 15, 4399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellit, A.; Pavan, A.M.; Lughi, V. Deep learning neural networks for short-term photovoltaic power forecasting. Renew. Energy 2021, 172, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, A.A.; Mirjalili, S.; Faris, H.; Aljarah, I.; Mafarja, M.; Chen, H. Harris hawks optimization: Algorithm and applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 97, 849–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, S.; Saremi, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Coelho, L.D.S. Multi-objective grey wolf optimizer: A novel algorithm for multi-criterion optimization. Expert Syst. Appl. 2016, 47, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Mao, S. Fractional multivariate grey Bernoulli model combined with improved grey wolf algorithm: Application in short-term power load forecasting. Energy 2023, 269, 126844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhou, J.; Pan, D.; Peng, Y.; Peng, X. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation with an optimized relevance vector machine algorithm with incremental learning. Measurement 2015, 63, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Guo, L.; Pecht, M. Lithium-ion battery remaining useful life estimation based on fusion nonlinear degradation AR model and RPF algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2014, 25, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Lu, N.; Wang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, B. Dynamic long short-term memory neural-network-based indirect remaining-useful-life prognosis for satellite lithium-ion battery. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




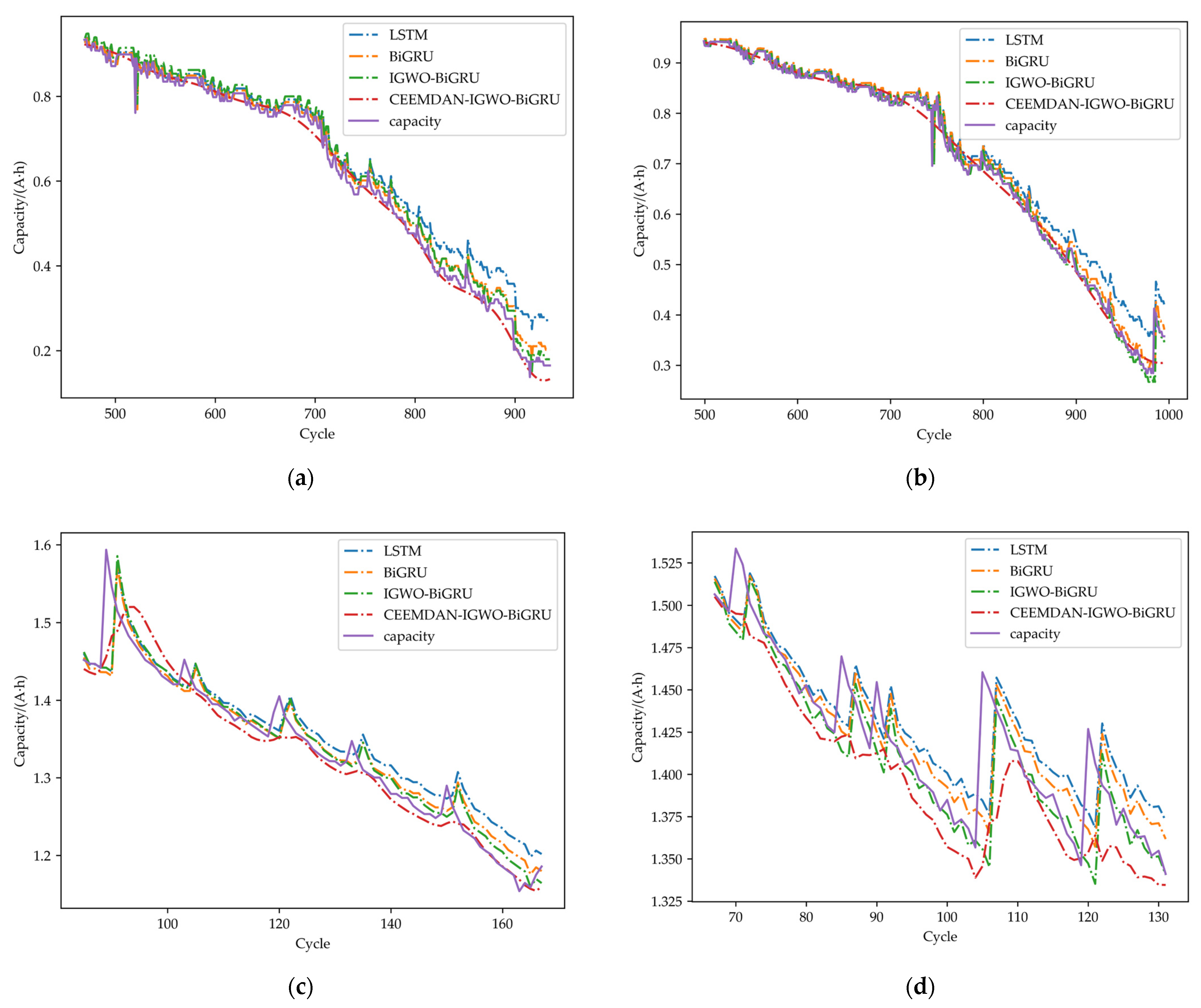

| Battery | Model | MAE (%) | MSE (%) | RMSE (%) | R2 (%) | e1 (%) | e2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS2_35 | LSTM | 5.63 | 0.60 | 7.73 | 88.92 | 11 | 1.74 |
| BiGRU | 4.50 | 0.39 | 6.31 | 92.61 | 11 | 1.74 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 2.73 | 0.12 | 3.47 | 97.77 | 9 | 1.43 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 1.35 | 0.04 | 2.58 | 98.96 | 4 | 0.63 | |
| CS2_36 | LSTM | 3.91 | 0.26 | 5.12 | 95.20 | 2 | 0.38 |
| BiGRU | 3.22 | 0.19 | 4.38 | 96.48 | 2 | 0.38 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 2.46 | 0.08 | 2.87 | 98.49 | 2 | 0.38 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 1.57 | 0.04 | 2.03 | 99.23 | 2 | 0.38 | |
| CS2_37 | LSTM | 4.19 | 0.33 | 5.72 | 93.12 | 18 | 2.57 |
| BiGRU | 3.72 | 0.28 | 5.33 | 94.03 | 18 | 2.57 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 2.51 | 0.12 | 3.46 | 97.47 | 12 | 1.71 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 1.36 | 0.04 | 1.92 | 99.06 | 12 | 1.71 | |
| CS2_38 | LSTM | 3.00 | 0.17 | 4.10 | 96.96 | 2 | 0.27 |
| BiGRU | 2.96 | 0.16 | 4.06 | 97.02 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 1.73 | 0.05 | 2.27 | 99.06 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 1.36 | 0.04 | 1.91 | 99.06 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| B0005 | LSTM | 4.24 | 0.24 | 4.91 | 87.64 | 78 | 12.36 |
| BiGRU | 4.25 | 0.24 | 4.88 | 87.78 | 72 | 11.41 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 2.65 | 0.14 | 3.79 | 92.60 | 26 | 4.12 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 2.53 | 0.12 | 3.46 | 93.86 | 11 | 1.74 | |
| B0006 | LSTM | 4.05 | 0.20 | 4.9 | 85.71 | 25 | 41.67 |
| BiGRU | 3.07 | 0.16 | 4.04 | 87.01 | 25 | 41.67 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 2.12 | 0.11 | 3.35 | 91.09 | 25 | 41.67 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 1.99 | 0.10 | 3.19 | 91.87 | 25 | 41.67 | |
| B0007 | LSTM | 4.05 | 0.24 | 4.95 | 85.71 | 4 | 3.25 |
| BiGRU | 3.73 | 0.22 | 4.66 | 87.29 | 5 | 4 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 2.28 | 0.15 | 3.89 | 91.14 | 3 | 2.44 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 2.47 | 0.14 | 3.68 | 92.08 | 7 | 5.69 | |
| B0018 | LSTM | 4.93 | 0.30 | 5.49 | 64.55 | 1 | 1.35 |
| BiGRU | 4.42 | 0.27 | 5.18 | 68.48 | 1 | 1.35 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 2.84 | 0.28 | 5.29 | 67.09 | 2 | 2.7 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 3.62 | 0.23 | 4.86 | 72.29 | 3 | 4.05 |
| Battery | Model | MAE (%) | MSE (%) | RMSE (%) | R2 (%) | e1 (%) | e2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CS2_35 | LSTM | 9.68 | 1.66 | 12.87 | 71.15 | 78 | 12.36 |
| BiGRU | 9.68 | 1.66 | 12.89 | 71.06 | 72 | 11.41 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 6.02 | 0.60 | 7.74 | 89.55 | 26 | 4.12 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 2.45 | 0.12 | 3.44 | 97.94 | 11 | 1.74 | |
| CS2_36 | LSTM | 17.18 | 4.56 | 21.36 | 29.28 | 2 | 0.27 |
| BiGRU | 15.58 | 4.11 | 20.27 | 36.29 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 9.44 | 1.48 | 12.15 | 77.11 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 3.74 | 0.22 | 4.73 | 96.54 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| CS2_37 | LSTM | 9.19 | 1.42 | 11.91 | 71.60 | 80 | 11.41 |
| BiGRU | 8.12 | 1.23 | 11.09 | 75.36 | 80 | 11.41 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 5.05 | 0.44 | 6.61 | 91.25 | 59 | 8.42 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 3.98 | 0.20 | 4.53 | 95.90 | 50 | 7.13 | |
| CS2_38 | LSTM | 5.65 | 0.61 | 7.78 | 89.43 | 2 | 0.27 |
| BiGRU | 5.54 | 0.58 | 7.61 | 89.89 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 3.74 | 0.27 | 5.18 | 95.33 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 2.56 | 0.10 | 3.13 | 98.29 | 2 | 0.27 | |
| B0005 | LSTM | 26.08 | 7.85 | 28.02 | -47.88 | 2 | 2 |
| BiGRU | 25.94 | 7.73 | 27.81 | -45.60 | 1 | 1 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 17.89 | 3.71 | 19.25 | 30.21 | 0 | 0 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 3.45 | 0.41 | 6.16 | 89.24 | 0 | 0 | |
| B0006 | LSTM | 8.78 | 0.90 | 9.50 | 63.92 | 5 | 6.37 |
| BiGRU | 8.39 | 0.84 | 9.18 | 66.34 | 5 | 6.37 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 5.53 | 0.38 | 6.18 | 84.73 | 2 | 3.1 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 2.88 | 0.12 | 3.46 | 95.20 | 2 | 3.1 | |
| B0007 | LSTM | 21.00 | 4.99 | 22.33 | -13.33 | 7 | 5.69 |
| BiGRU | 21.38 | 5.18 | 22.76 | -17.70 | 5 | 4.07 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 13.00 | 1.92 | 13.86 | 56.33 | 3 | 2.44 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 5.27 | 0.33 | 5.73 | 92.54 | 3 | 2.44 | |
| B0018 | LSTM | 6.72 | 0.62 | 7.84 | 84.44 | 4 | 5.41 |
| BiGRU | 6.39 | 0.58 | 7.62 | 85.31 | 4 | 5.41 | |
| IGWO–BiGRU | 5.10 | 0.43 | 6.54 | 89.20 | 2 | 2.7 | |
| CEEMDAN–IGWO–BiGRU | 3.57 | 0.40 | 6.30 | 89.97 | 2 | 2.7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, X.; Wan, H.; Wang, W.; Gu, M.; Wang, L.; Gan, L. Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Based on Hybrid Model. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6261. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076261
Tang X, Wan H, Wang W, Gu M, Wang L, Gan L. Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Based on Hybrid Model. Sustainability. 2023; 15(7):6261. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076261
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Xuliang, Heng Wan, Weiwen Wang, Mengxu Gu, Linfeng Wang, and Linfeng Gan. 2023. "Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Based on Hybrid Model" Sustainability 15, no. 7: 6261. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076261
APA StyleTang, X., Wan, H., Wang, W., Gu, M., Wang, L., & Gan, L. (2023). Lithium-Ion Battery Remaining Useful Life Prediction Based on Hybrid Model. Sustainability, 15(7), 6261. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15076261






