Abstract
Groundwater is regarded as the primary source of agricultural and drinking water in semi-arid and arid regions. However, toxic substances released from sources such as landfills, industries, insecticides, and fertilizers from the previous year exhibited extreme levels of groundwater contamination. As a result, it is crucial to assess the quality of the groundwater for agricultural and drinking activities, both its current use and its potential to become a reliable water supply for individuals. The quality of the groundwater is critical in Egypt’s Sohag region because it serves as a major alternative source of agricultural activities and residential supplies, in addition to providing drinking water, and residents there frequently have issues with the water’s suitability for human consumption. This research assesses groundwater quality and future forecasting using Deep Learning Time Series Techniques (DLTS) and long short-term memory (LSTM) in Sohag, Egypt. Ten groundwater quality parameters (pH, Sulfate, Nitrates, Magnesium, Chlorides, Iron, Total Coliform, TDS, Total Hardness, and Turbidity) at the seven pumping wells were used in the analysis to create the water quality index (WQI). The model was tested and trained using actual data over nine years from seven wells in Sohag, Egypt. The high quantities of iron and magnesium in the groundwater samples produced a high WQI. The proposed forecasting model provided good performances in terms of average mean-square error (MSE) and average root-mean-square error (RMSE) with values of 1.6091 × 10−7 and 4.0114 × 10−4, respectively. The WQI model’s findings demonstrated that it could assist managers and policymakers in better managing groundwater resources in arid areas.
1. Introduction
Egypt is regarded as a country with a scarcity of water [1]. The Nile River regulates Egypt’s water supplies, with a fixed portion of 55.5 BCM/year [2]. Groundwater in Egypt is regarded as a secondary water resource for domestic use as well as irrigation in various parts of the country. The amount of water withdrawn from the aquifer is estimated to be around 7–8 BCM/year [2,3]. The sources of groundwater in Egypt’s Nile Valley aquifers are canal seepage and deep percolation from irrigated agriculture [4]. The demand for groundwater has considerably increased because of an increase in population, human activities, industrialization, and urbanization that is occurring at an accelerated rate [5,6]. Due to man-made activities such as overuse and improper disposal of waste (industrial, agricultural, and household) into groundwater reservoirs, the quality, quantity, and availability of groundwater are being severely impacted at an alarming rate [7]. Therefore, the current agricultural activities, especially in connection to the excessive use of fertilizers, improper ways of releasing wastewater to groundwater, and filthy circumstances in groundwater recharge, pose a major threat to human health [8]. The underlying environment, seasonal fluctuations, dissolved salts that have been leached, and water depth all affect the quality of groundwater [9]. About 80% of human illness is water-related, as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO) [10]. When groundwater gets contaminated, it is challenging to restore and maintain its appropriateness quality by removing the pollutants from the sources. Therefore, it is essential to check the quality of groundwater and devise strategies for keeping it free of contaminants. Different biological, physical, and chemical aspects of water are used to determine groundwater quality [11]. These could be considered assessment tools for the groundwater’s cleanliness and quality concerning the demand for and use in human consumption [12].
The assessment of groundwater quality is critical for agriculture and drinking, as well as industrial activities. Many researchers have assessed groundwater quality for irrigation and drinking using geographic information systems (GISs), water quality indicators [13,14,15,16], multivariate statistical analysis [17], and machine learning models [18,19,20,21]. El Bilali et al. [18] used different machine learning methods for forecasting the irrigation water quality indexes using Adaboost, Support Vector Regression (SVR), Random Forest (RF), and ANN models. In addition, Hanoon et al. [19] used various machine learning (ML) models, such as Gaussian process regression (GPR), tree regression (TR), SVM, linear regression (LR), and ensembles of regression trees (ER). Kouadri et al. [20] applied different machine learning models for irrigation parameters such as long short-term memory (LSTM), multi-linear regression (MLR), and artificial neural network (ANN). El Yousfi et al. [21] developed a model based on PCA and ANN that can predict WQI. All of the literature is focused on developing a machine-learning model, and no research focuses on deep learning.
One of the assessment tools for evaluating groundwater quality is the Water Quality Index (WQI). The WQI is therefore an essential instrument for evaluating the quality of groundwater, including chemical, biological, and physical characterizations, and how it is managed in a particular area. It also aids in the selection of an economically viable treatment, desalination, or purification method to address the water quality issues at hand [22,23]. Furthermore, it communicates water quality information to legislative decision-makers and the public, demonstrating the aggregate influence of several water quality metrics. The WQI could also assist the decision-makers in developing sound legislation and implementing the government’s water quality programs [24,25].
According to the above, all prior models offered to provide improved prediction of groundwater quality. They concentrated on predicting groundwater quality using previously measured data over a specified period. In addition, just a few parameters were considered in each inquiry. Based on the preceding discussion, it should address some concerns, such as the evaluation of long-term field data, the creation of enhanced machine learning technology systems to give reliable models, and the examination of more factors in groundwater quality.
More trustworthy and effective forecasting algorithms for all forms of comparable and challenging data are required in the literature due to a shortage of groundwater quality time series forecasting models. This research was conducted in an attempt to address some of the difficulties raised above. The WQI was developed using ten groundwater quality parameters, including Turbidity, pH, Magnesium, Iron, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chloride, Total Dissolved Solids (TDSs), Total Coliform, and Total Hardness (TH). A deep neural network model was used to forecast nine groundwater quality metrics (Turbidity, Magnesium, Iron, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chloride, TDS, TH, and water quality indexing (WQI)) connected with seven wells in the Sohag district of Egypt. The new Deep Learning Time Series Techniques (DLTS) network structure has been enhanced to produce better outcomes. To produce more precise results, the model was built on data from nine years. For groundwater quality forecasting, the method uses DLTS with the long short-term memory (LSTM) network.
The purpose of this research was to analyze and forecast groundwater quality for drinking intentions using principal factor analysis [13,26] to identify the key factors that influence the water quality and DLTSF, along with water quality indexing (WQI) related to significant biological, chemical, and physical constraints of the groundwater from the district of Sohag, Egypt. This work will assist officials in drinking water and wastewater companies in making decisions to improve the efficiency and quality of used water, which will be reflected in the health of people who use this water.
2. Study Area Description
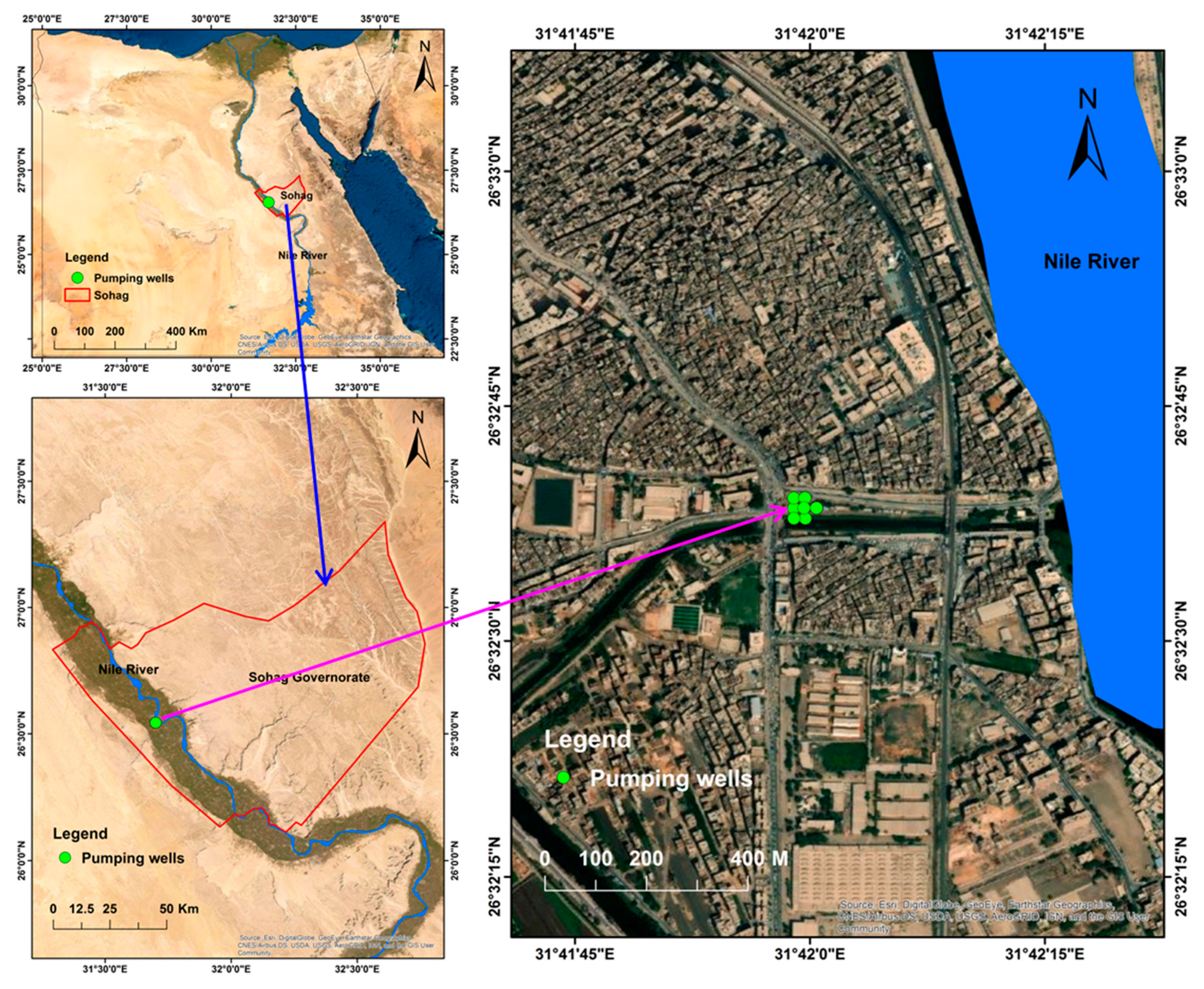
The study area is situated in a small city, Sohag Governorate, on the west bank of the Nile River in Egypt. Sohag is located at 26°33′26.8″ N and 31°41′39.0″ E. It is located nearly 471 km south of Cairo. Sohag is located on a productive agricultural plain along the western bank of the Nile. It has a population of 600,000. The samples were collected from the wells pump station (26°32′38.5″ N 31°41′59.7″ E) at Sohag First, Sohag Governorate. These wells supply 175 L/sec of water, mainly for drinking water uses; see Figure 1.
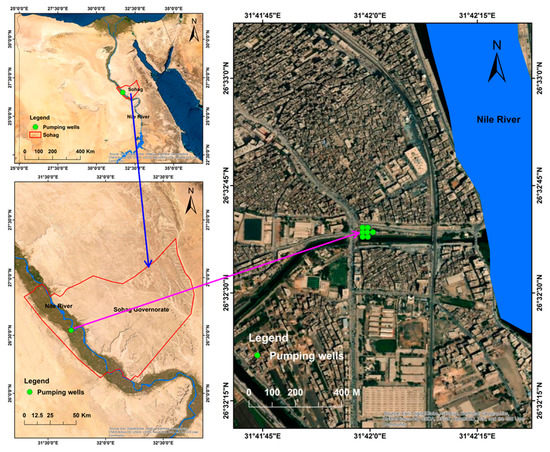
Figure 1.
Map of the study area and sample locations.
The research region is part of Egypt’s Nile Valley geological system. A diverse range of sediments dating from the Lower Eocene to more recent deposits [27] distinguishes the exposed sedimentary successions in the area. The Lower Eocene Thebes Formation is mostly composed of limestone, with flint nodules visible on the western plateau’s surface. The Muneiha Formation (Early Pliocene) is constituted of fluvial sediments of clays with quartz grains that serve as the Quaternary aquifer’s foundation [28]. The Qena Formation of the Early Pleistocene consisted of coarse and medium-grained sand and gravel sediments and served as the area’s primary aquifer unit [13]. The Kom Ombo, Ghawanim, and Dandara Formations are Pleistocene-aged cross-bedded fluvial sediments that get smaller with depth. It is constituted of cross-bedded sand with gravel intercalation, gradually going down to medium and fine to very fine sands [29].
The groundwater in the study area comes from the Quaternary and Plio–Pliestocene aquifer, which is composed of successive layers of fluvial sands and gravels with clay lenses. The Quaternary aquifer is semi-confined in the Nile Valley due to the silt–clay top layer over all of the aquifer, whereas it is phreatic in the western fringes of the Sohag district. This aquifer is mostly sand, with clay lenses intercalated at different depths. Plio–Pleistocene sediments dominate the foot slopes of the limestone plateau along the desert fringes. The aquifer’s surface is composed of coarse sand, clay, and limestone, while the subsurface is dominated by silty sand beds. The Pliocene clay, which represents the aquifer’s base, generally supports the Quaternary aquifer. The aquifer thickness ranges from 20 m west of the plateau to 80 m in the west of the Nile Valley area [29]. The only source of recharge for the Quaternary aquifer is surface water, specifically irrigation canals [2,4].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Analysis of Collected Samples
Between 2013 and 2021, the groundwater quality in the Sohag Governorate, Egypt, was examined. A total of 117 groundwater samples were collected from seven different well pump stations. Polyethylene vessels that were acid-cleaned and primed were used for sampling. The distances between the wells were 50 m apart. At each location, the seven wells’ GPS coordinates were recorded; see Figure 1. The gathered water samples were evaluated for pH, Turbidity, Total Hardness (TH), Magnesium, Chloride, Iron, Total Dissolved Solids (TDSs), Nitrates, Sulfate, and Total Coliform by using these common strategies, which are presented by the “American Public Health Association” [30,31,32,33]. The results were assessed using drinking water quality standards set forth by Egyptian Health Ministry Law (EHML) no. 458 for 2007 and the World Health Organization (WHO).
3.2. Water Quality Index (WQI) Calculation
In 1965, the WQI was created using weighted arithmetic calculations [34]. Based on weighing and grading numerous parameters for water quality that are produced using the weighted arithmetic method, several researchers developed several WQI models. The WQI is a number without dimensions, with scores ranging from 0 to 300 [35]. Based on several water quality metrics, the WQI is a distinctive expression that indicates the overall quality condition of the water, such as excellent, good, or bad, at a certain location and time. Three steps of WQI were estimated by weighing the index of arithmetic methodologies [35]. To assess the drinking water quality, wi (weight) of 10 selected water quality parameters was assigned [36,37,38,39], as indicated in Table 1. Because of their large contributions to WQI, the parameters Turbidity and Nitrate each received a maximum weight of five. The minimal weight for total hardness was two because it cannot be damaging to human health. The formula below was utilized to calculate RWi (relative weight):
where the number of water quality parameters shown is n, Wi defines the weight of each selected water quality parameter, and the relative weight is represented by RWi. The computed RWi (relative weight) values for each water quality indicator are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Assigned weight and RWi calculated for selected parameters considering EHML and WHO [36,37,38,39].
Then, using the Egyptian drinking water standards from 2007 (EHML), the quality rating scale (qi) was determined for each water quality indicator separately, where the measured value was divided in the relevant water sample by the associated standard. The outcome was then multiplied by one hundred using the formula below:
where qi stands for quality rating, Ci is the individual parameter concentration in mg/I for each sample of water, and Si is the Egyptian drinking water standard for the individual parameter concentration in mg/I as per the EHML no. 458 for 2007 (EHML).
After that, for calculating the WQI of each study parameter, SI was estimated by multiplying quality rating (qi) by relative weight (wi). In the end, the WQI was equal to the total sum of the sub-index (SIi), as shown in the following equations:
Five classifications of water were created based on the WQI values: unsuitable for drinking, very poor, poor, good, and excellent [38].
3.3. Deep Learning Time Series Techniques
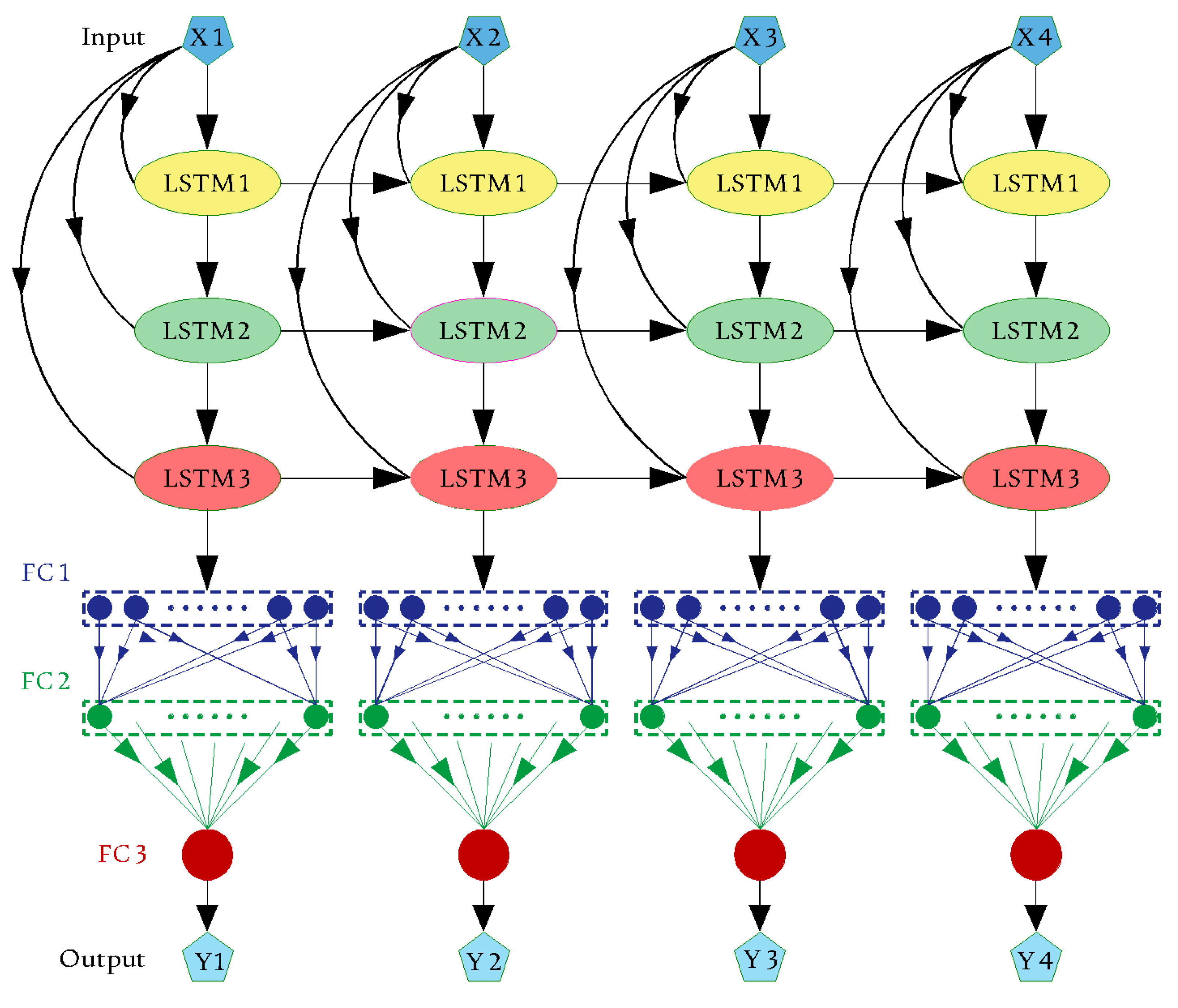
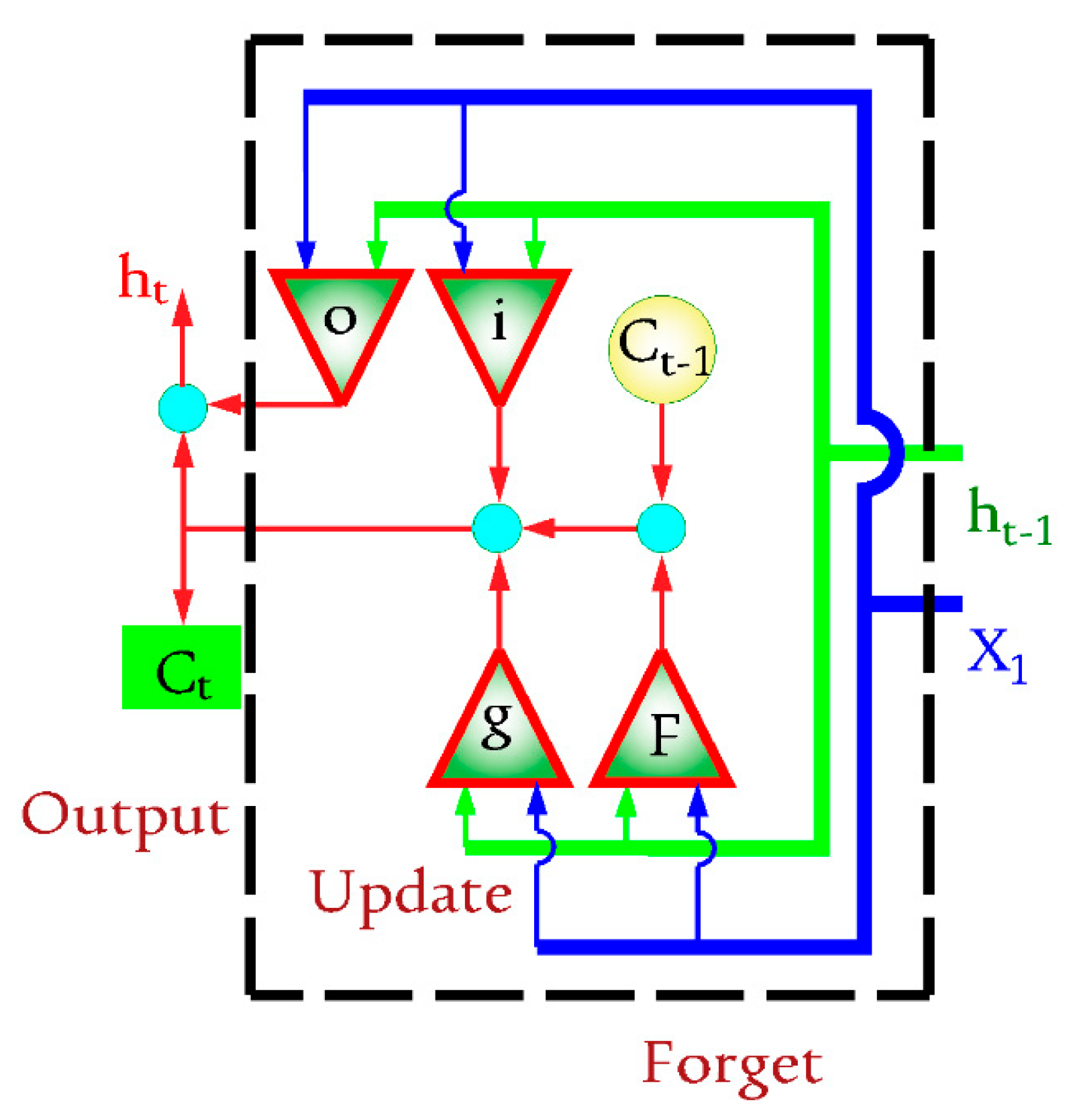
The data were separated into three groups before running the recommended networks: training, validation, and verification test (40%, 20%, and 40% of the dataset, respectively). A DLTSF was suggested for simulating the groundwater quality parameters using an LSTM-based design. LSTM is used in a variety of Hochreiter and Schmidhuber applications [5]. The layers of the network are an input layer followed by three LSTM layers linked with three fully connected (FC) layers and ending with a regression layer (see Figure 2). RNN is an LSTM-based architecture whose evolution state is determined by the entries for the current and previous time steps. The LSTMs learn from previous encounters by using strategies that correlate to the computer’s memory stored data. A network cell has the ability to read, write, and store data. Furthermore, this design aids in limiting the propagation of faults over several layers over time. Because of this technology, the network may extend its learning process over a variety of periods [11]. Figure 3 depicts the gate’s ignoring, updating, and yielding of the cell and hidden states. The cell state equation is as follows:
where ⊙ denotes the element-wise multiplication of vectors. i denotes the input gate. f denotes the forget gate. g denotes the cell candidate. o denotes the output gate. The hidden state at time step t is given as follows:
where σc denotes the state activation function.
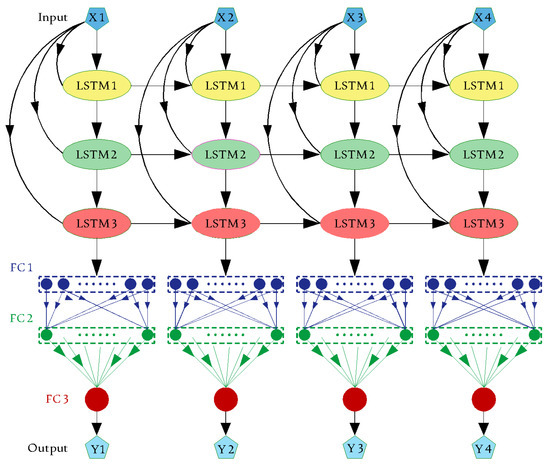
Figure 2.
Proposed DLTSF model structure.
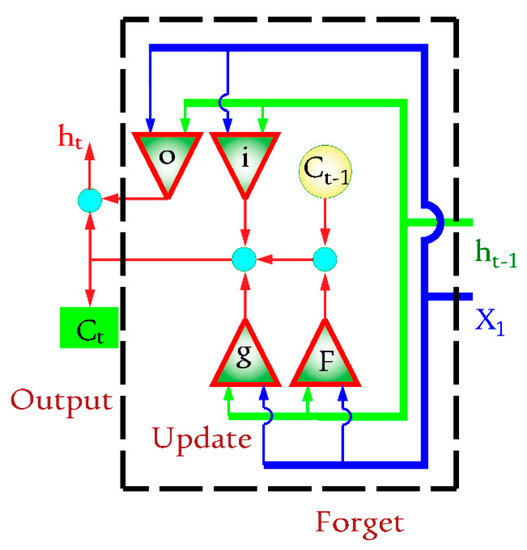
Figure 3.
LSTM data flow.
4. Results and Discussion
The water quality index determination is important to evaluate water quality for drinking and irrigation uses. The majority of unabsorbed fertilizers, pesticides, and other toxins in sewer systems, landfills, hazardous waste disposal sites, and agricultural areas are the principal contributors to groundwater pollution.
4.1. Statistical Analysis and Water Quality Index
The outcomes of a statistical evaluation of the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of groundwater samples from the Sohag region, including the parameters of the standard deviation, mean, minimum, and maximum, are shown in Table 2. The physical, chemical, and biological aspects of the groundwater analysis result have been evaluated in comparison to WHO recommendations and Egyptian drinking water regulations.

Table 2.
Statistical analysis of water quality parameters.
Interconnected chemical processes that either consume hydrogen ions or release them regulate pH in water [40]. Although pH value normally has no direct impact on human health, it is one of the most crucial limitations on the quality of water [38]. The pH determines the acidity and alkalinity of freshwater. The amount and chemical makeup are primarily monitored for both organic and inorganic compounds in groundwater [41]. In this research, all pH samples were between 7.20 and 7.80, within the permissible limits of EHML.
Turbidity, which prevents light from passing through water, is brought on by suspended particles, such as plankton, organic and inorganic substances, clay, silt, colloidal matter, or other tiny organisms [42]. Turbidity can only be measured below 4 NTU with measuring devices; however, over 4 NTU, a murky suspension, which is white, brown, or black, may be visible. Another important aesthetic aspect of water quality is turbidity, which affects the appearance and appropriateness of drinking water for end users [43,44]. The turbidity of studied groundwater samples ranged between 0.16 and 1.3 NTU. The allowed limit of turbidity is 1 NTU, as stated in EHML [36]. The turbidity of most collected samples was within a permissible limit, and all samples had a turbidity of less than 1.3, which is considered acceptable. Since turbidity exceeding 5 NTU is undesirable, it should be avoided. To maintain ideal drinking water quality, turbidity levels should be kept between 1 and 5 NTU [45].
Total hardness (TH) is how much magnesium and calcium have been dissolved in the water. As water flows through rock and soil, it disintegrates naturally existing minerals and transports them into groundwater. Water is a powerful solvent for magnesium and calcium. Total hardness ranged between 210 and 420.10 mg/L, which falls within the acceptable Egyptian range (1000 mg/L). Human kidney stones and heart problems have been connected to the high amounts of TH in groundwater [46].
Total dissolved solids (TDSs), which is calculated by weighing the residue after an evaporating water sample reaches a dry state, was then expressed. Sulfate, chloride, magnesium, sodium, potassium, carbonate, and bicarbonate were the main components. It varied from 400 to 774 mg/L (<1000 mg/L TDS as acceptable drinking water per EHML).
Iron poisoning of groundwater is frequently caused by weathering of iron-bearing rocks and minerals [47]. The iron is present in the aquifer in normal conditions of decreased Fe2+; however, its dissolution raises the quantity of iron present in groundwater. Since iron is soluble in this condition, there is typically little health risk. When the Fe state interacts with oxygen from the air or when iron-related bacteria produce insoluble hydroxides in groundwater, the Fe state is changed to the Fe’t state. Iron concentrations in groundwater are frequently higher than those in surface water as a result. The iron concentration in this study ranged from 0.06 to 0.46 mg/L, indicating that several samples exceeded the allowed limit of 0.3 mg/L. This could return to the nature of the minerals and rocks of the underground layers [48,49].
In groundwater, magnesium (Mn) naturally occurs, especially in anaerobic conditions. The chemistry of the rainfall, the lithology of the aquifer, the geochemical environment, the flow pathways and residence times of the groundwater, etc. all affect the concentrations of Mn in the groundwater, and these factors can change dramatically over time and place. It may be released through the leaching of underlying rocks, soils, and minerals in addition to being leached from the minerals of the aquifer itself in groundwater. In this research, the minimum value of magnesium was 0.05 mg/L, within the Egyptian permissible limit (0.40 mg/L). However, the highest magnesium level was 0.86, which is higher than the Egyptian allowable limit. This level needs groundwater purification to reduce the magnesium level to within the acceptable drinking water quality range.
Nitrate is a crucial nutrient for plants and is typically present in the terrestrial environment. Numerous agricultural and related activities, particularly the excessive use of manures, inorganic nitrogenous fertilizers, and wastewater dumping by uncontrolled industries, can result in high nitrate concentrations in groundwater as well as surface water [50]. Nitrates are significantly added to the water as a result of nitrogenous waste degradation found in human or animal excrement, for instance, the septic tank. Nitrate concentrations in surface water can rise quickly as a result of surface washing, phytoplankton absorption, and bacterial nitrate denitrification, although nitrate concentrations in groundwater normally vary slowly. Additionally, nitrate pollution of groundwater due to leaching from organic vegetation is possible [51]. Nearly all instances of excessive nitrate buildup in shallow groundwater were brought on by surface water’s downward leaching of nitrogen [52]. In the Sohag area, for this research, the concentration of nitrate samples was between 0 and 1.82 mg/L, which is way less than the acceptable value of the Egyptian drinking water standard (45 mg/L). This confirms the safety of the groundwater from any nitrate contamination in the studied area.
Sulfate is a naturally occurring compound found in several minerals and is utilized commercially, primarily in the chemical industries. Gypsum, iron sulfides, and other sulfur-bearing compounds are found in rocks, where they are dissolved and leached to sulfate. In the current study, it was significantly below the EHML permissible level of 250 mg/L, ranging from 7.49 to 105.26 mg/L.
Chloride (Cl) varied in the current study from 33.90 to 156.00 mg/L, which is less than the permitted limit (250 mg/L). Groundwater could be dangerous to human health because of the increased concentration of chlorine in it [53]. Chlorine in groundwater is primarily derived from windborne rainwater, saltwater, saline brines, and evaporite deposits. Furthermore, the chlorine concentration in groundwater can be linked to wastewater pollution. As a result, the existence of chlorine is regarded as a sign of contamination. Furthermore, excessive chlorine concentrations in water may hasten the corrosion of metal parts in the water distribution system. A large concentration of chlorine in water poses a health risk. Epidemiological studies have found a link between water chlorination and different types of human cancer [53].
Total coliforms were utilized to measure bacterial contamination from feces. The total coliform rule for the surface water treatment regulation [54] requires community water systems to do total coliform monitoring. Testing for E. coli or fecal coliforms is required for all samples that test positive for total coliforms, since there are maximum contamination levels (MCLs) for total coliforms. No more than 5% of monthly samples in water systems with at least 40 analyses per month may test positive for total coliforms. One sample at most may test positive for all coliforms in systems that analyze less than 40 samples per month [55]. These requirements serve as a benchmark for the public-health acceptability of drinkable water. In this research, none of the samples were positive for total coliforms, which indicates no sewage leakage contamination within groundwater in the study area.
All units other than pH are in mg/L if not included in the table. Min (Minimum), Max (Maximum). EHML no. 458 for 2007 and WHO [36,37,38,39].
One of the greatest tools for displaying information on the quality of groundwater or any water body is the WQI [56]. To determine if groundwater in the Sohag area is suitable for domestic human purposes, the WQI value was calculated. The present research showed that 27.4% of groundwater samples were of excellent quality, and 72.6% of samples had good water quality; see Table 3.

Table 3.
Sohag groundwater quality classification based on WQI value [57].
The matrix of correlations for the ten major parameters of groundwater quality, including pH, Turbidity, Total Hardness, Magnesium, Nitrates, TDS, Iron, Chloride, Sulfate, and Total Coliform, was calculated and generated through MS Excel. Out of these, some parameters, such as TDS, Total Hardness, and Sulfate, were strongly correlated, displaying a correlation value of over 0.50 (Table 4). Further, TDS vs. Total Hardness, Sulfate vs. TDS, and Total Hardness as CaCO3 demonstrate that the most pertinent correlation, more so than any other important indicators, has a considerable influence on the overall evaluation of groundwater quality. The vast majority of quality indicators, however, have a low positive correlation with one another. A thorough examination of the correlation matrix for the heavy metal parameters under study reveals that Iron is positively correlated with pH, Turbidity, Total Hardness, and TDS. Similarly, Magnesium has a positive relationship with pH, Total Hardness, TDS, and Iron. In addition, chemical parameters including Nitrates, Sulfate, and Chloride are correlated positively with pH, Turbidity, Total Hardness, TDS, and Iron. Meanwhile, Total Coliform has a negative correlation coefficient with most studied parameters, including pH, Total Hardness, Turbidity, TDS, Iron, Nitrates, Sulfate, and Chloride.

Table 4.
Correlation coefficients of ten hydrogeochemical parameters for Sohag groundwater water quality characteristics.
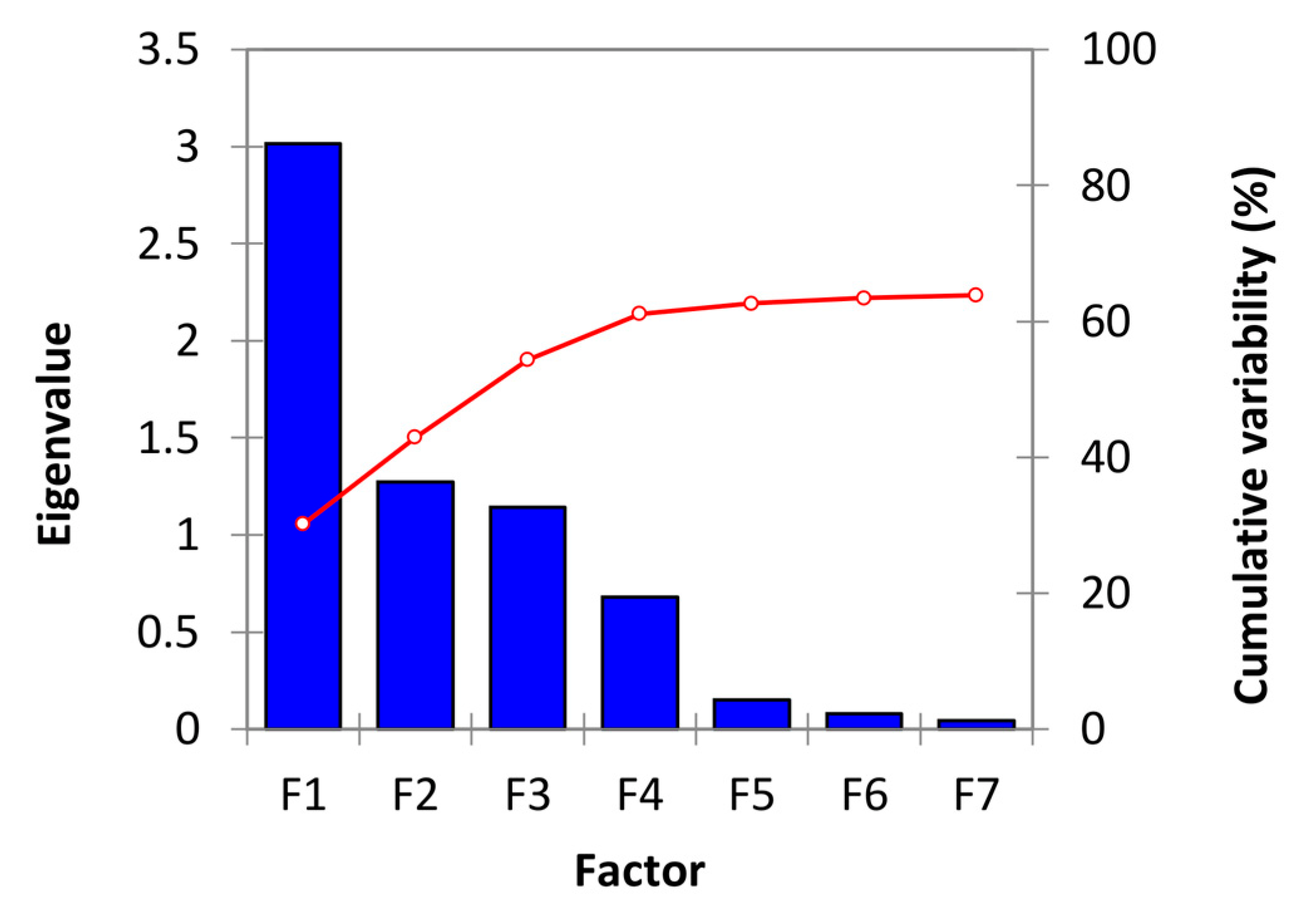
Principal factor analysis was used to identify the key factors that influence the water quality at the seven pumping wells at the Sohag water station. Factor analysis is a multivariate statistical technique for reducing the number of variables to examine and determining their relationships. Using factor analysis, we can explain the correlation coefficient between variables and factors [13,28]. The water quality factors were considered in this study in seven different factors, as shown in Figure 4. According to Table 5, all ten parameters are present in the four factors with the highest variability.
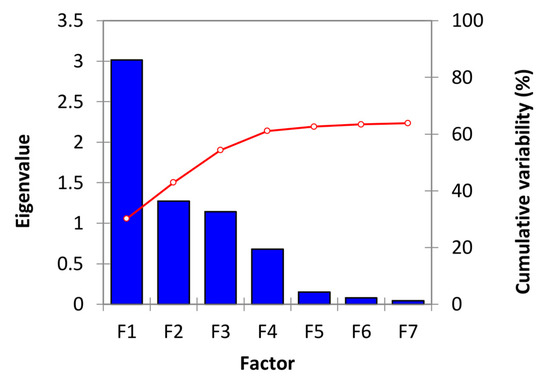
Figure 4.
Scree plot with the eigenvalues and cumulative variability (%) of seven factors that affect water quality.

Table 5.
Factor analysis of the seven water quality variables at the seven pumping wells in the study area.
Total Hardness, TDS, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chlorides, and Total Coliform, with loading values of 0.570, 0.935, 0.520, 0.881, 0.589, and −0.183, respectively, explain approximately 30.16% of the total variance. As a result of agricultural practices such as the extensive use of fertilizers and the application of lime, these ions are becoming more abundant. Factor 2 accounts for approximately 12.723% of total variance and contains only pH with a loading value of 0.653. Factor 3 accounts for approximately 11.41% of the total variance and contains only Magnesium with a loading value of −0.811. Finally, Factor 4 accounts for approximately 6.82 % of the total variance and includes Turbidity and Iron, which have loading values of −0.398 and −0.620, respectively. According to the result in Table 5, the ions in solution mainly deal with carbonates (Total Hardness), Sulfate, and Chlorides.
4.2. Forecasting Model Results
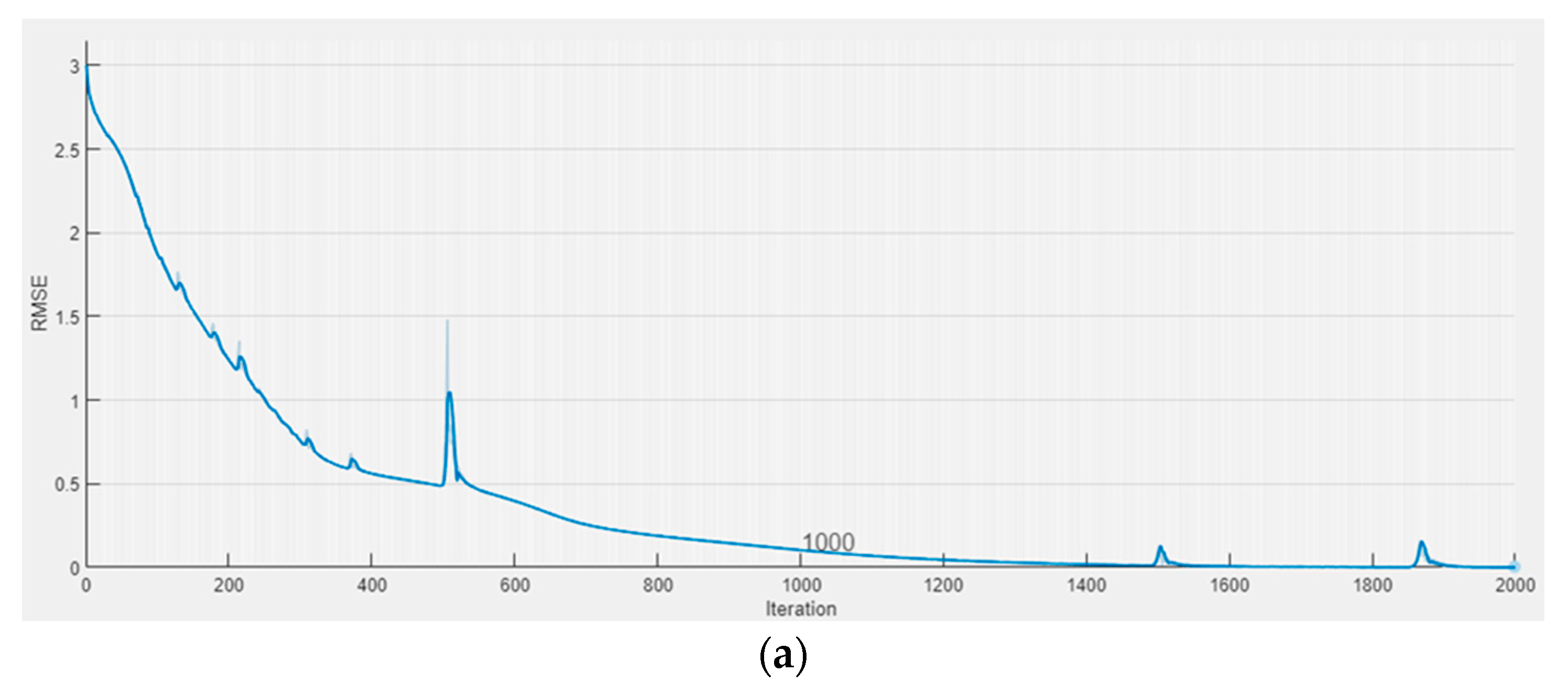
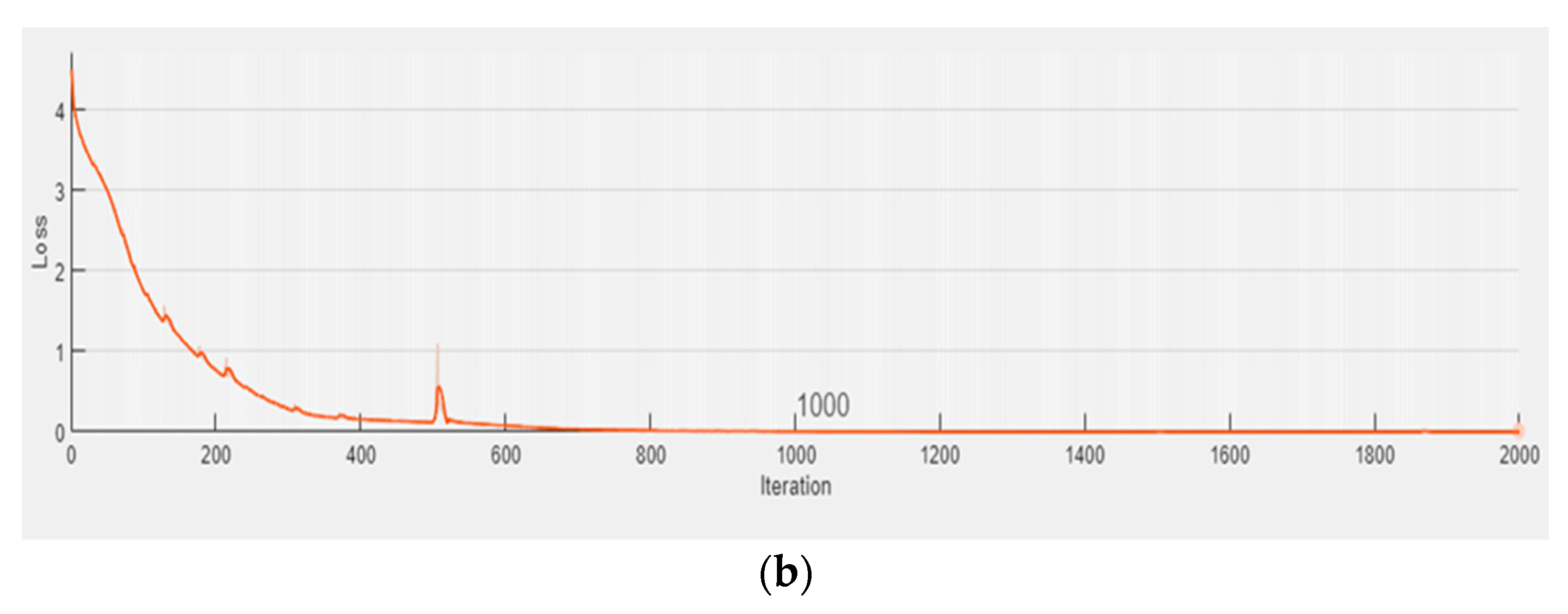
The major purpose of this part is to understand the DLTSF efficiency for projecting the future condition of groundwater quality. Data from 117 samples collected from seven wells in Egypt’s Sohag area were used. The data were split into two parts: 70 samples were for training and validation, while the remaining 47 samples were for testing. The DLTSF training for Turbidity, Magnesium, Iron, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chloride, TDS, Total Hardness, and WQI demonstrated that the proposed model fits and uses the training and validation data successfully (see Figure 5).
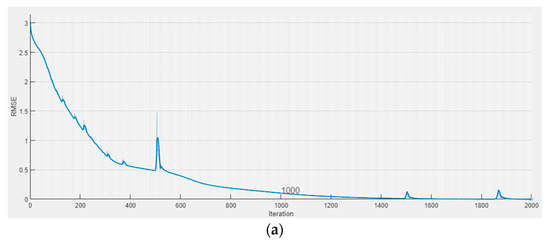
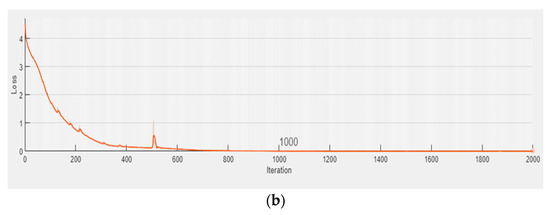
Figure 5.
(a) Training and (b) validation of DLTSF Model.
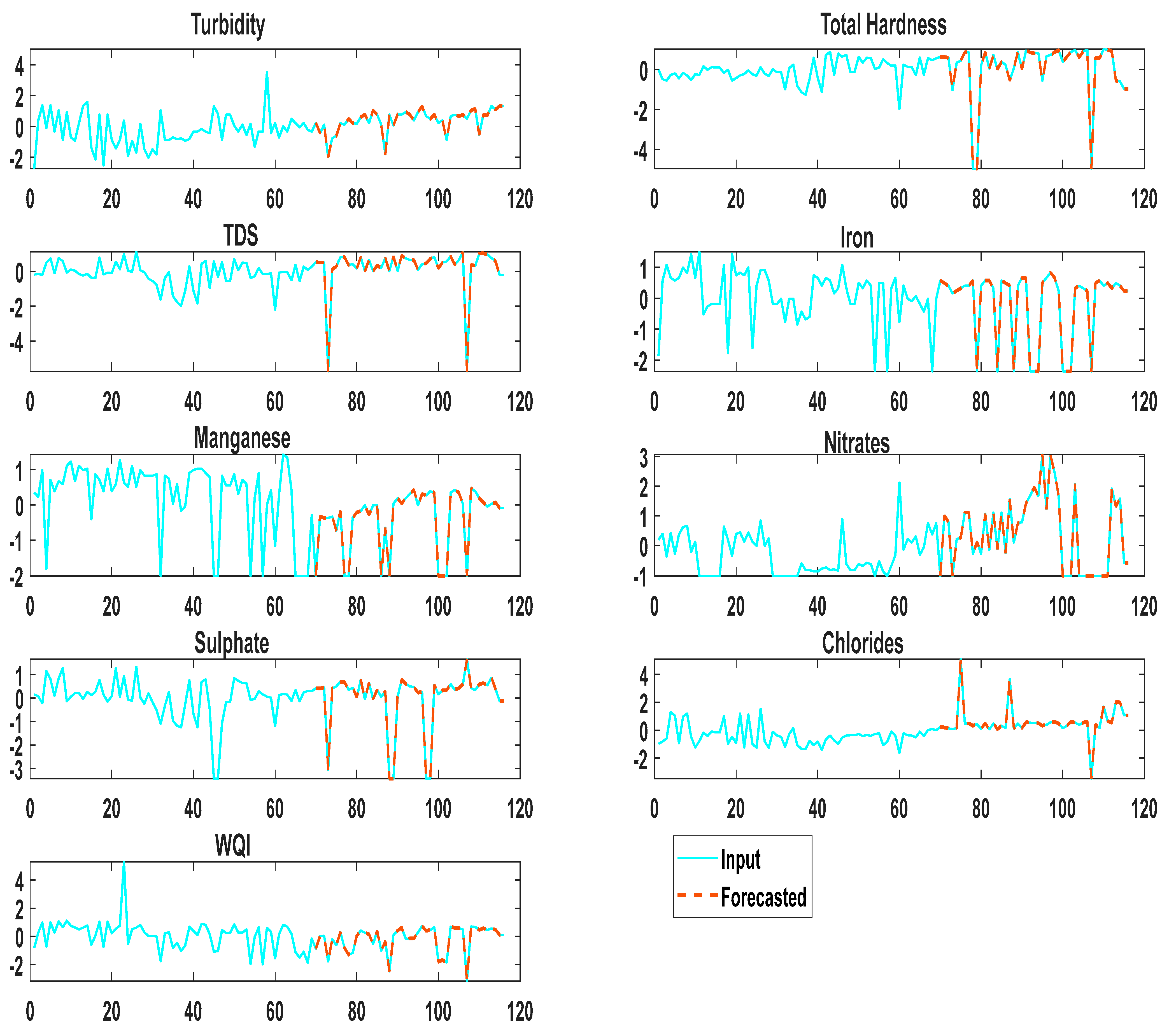
Figure 6 depicts the observed and DLTSF-predicted findings for Turbidity, Magnesium, Iron, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chloride, TDS, Total Hardness, and water quality indexing (WQI). According to the statistics, the forecasting of Turbidity, Magnesium, Iron, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chloride, TDS, Total Hardness, and WQI in groundwater quality exhibits sufficient competence and accuracy. Notably, the DLTSF-predicted output data matched the measured dataset from the seven wells in the Sohag district of Egypt for all the groundwater quality parameters. The model’s capacity to estimate future groundwater quality parameters is proven. The RMSE evaluates the DLTSF model for each parameter, as shown in Table 5. The average MSE value for all groundwater quality parameters (Turbidity, Magnesium, Iron, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chloride, TDS Total Hardness, and WQI) is 4.0114 × 10−4. Furthermore, the average MSE for all groundwater quality parameters (Turbidity, Magnesium, Iron, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chloride, TDS, TH, and WQI) is 1.6091 × 10−7. Table 6 shows a comparison of the presented model to previous similar studies in the literature. The table clearly shows that the performance of the current proposed models performs better than similar previous research studies (Table 6).
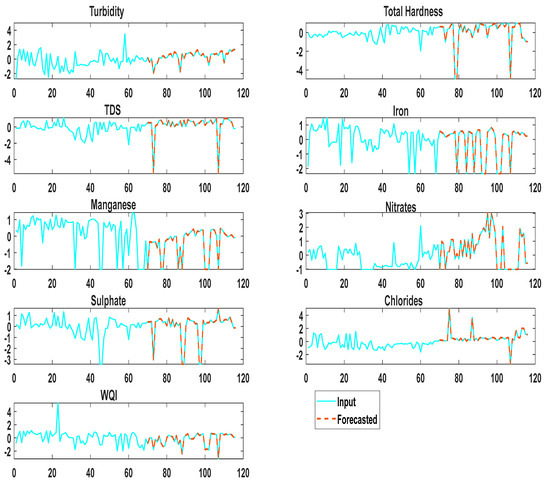
Figure 6.
Observed and DLTSF forecasting output.

Table 6.
Comparison between the presented model and previous similar studies in the literature.
5. Conclusions
The evaluation of groundwater quality is important for agricultural, drinking, and development activities. Groundwater quality is critical in Egypt’s Sohag region since it serves as a key alternative source of residential supplies in addition to supplying drinking water, and inhabitants regularly complain about the water’s fitness for human use. In the Sohag area, Egypt, the groundwater quality and whether it is fit for human water consumption have been assessed.
Ten groundwater quality parameters (pH, Turbidity, Total Hardness, TDS, Iron, Magnesium, Nitrates, Sulfate, Chlorides, and Total Coliform) from seven pumping wells in Sohag, Egypt were used in the current study to assess water quality. Principal factor analysis was used to identify the key factors that influence the water quality at the seven pumping wells in the study area. The WQI was computed and analyzed. According to the WQI results, approximately 27.4% of the water samples have excellent water quality, while 72.6% have good water for drinking. It is recommended that a suitable water purification system could be used to enhance the water quality for drinking uses. The groundwater quality parameters and the WQI were forecasted using Deep Learning Time Series Techniques (DLTS) and LSTM. The proposed model predicts the WQI as well as the top eight groundwater quality metrics. The model was trained and evaluated over a nine-year period using real-world data from seven wells. Because of the high levels of iron and magnesium in the groundwater samples, the WQI was high. The developed forecasting model demonstrated good agreement between model and measurement results, with an average RMSE of 4.0114 × 10−4. Finally, the current study has shown that Deep Learning Time Series Techniques can be used to evaluate and forecast groundwater quality effectively. Furthermore, the findings can help managers and policymakers manage groundwater resources more effectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.A.A., M.E.-R., M.K.A.-E. and A.M.I.; methodology, A.K.A.A., M.E.-R., M.K.A.-E. and A.M.I.; software, A.K.A.A., M.E.-R., M.K.A.-E. and A.M.I.; validation, M.K.A.-E.; formal analysis, M.E.-R.; investigation, A.K.A.A., M.E.-R., M.K.A.-E. and M.K.A.-E.; data curation, A.K.A.A., M.E.-R., M.K.A.-E. and A.M.I.; writing—original draft preparation, A.K.A.A., M.E.-R., M.K.A.-E. and A.M.I.; writing—review and editing, A.K.A.A., M.E.-R., A.M.I., N.A.-A. and A.M.I.; visualization, A.K.A.A., M.E.-R. and M.K.A.-E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available based on request from first author.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the journal editor and reviewers for their valuable comments and suggestions. Al-Arifi thanks the Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University for funding through the Vice Deanship of Scientific Research Chairs.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Luo, P.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, S.; Lyu, J.; Zhou, M.; Nakagami, K.; Takara, K.; Nover, D. Historical assessment and future sustainability challenges of Egyptian water resources management. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Abdalla, F.; El Alfy, M. Water Resources in Egypt. In The Geology of Egypt. Regional Geology Reviews; Hamimi, Z., El-Barkooky, A., Martínez Frías, J., Fritz, H., Abd El-Rahman, Y., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 687–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, S.A.; Arauzo, M.; Elnazer, A.A. Groundwater quality and vulnerability assessment in west Luxor Governorate, Egypt. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 8, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Makhloof, A.A.; Hashem, M.D.; Eltarabily, M.G. Groundwater management of quaternary aquifer of the Nile Valley under different recharge and discharge scenarios: A case study Assiut Governorate, Egypt. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdella Ahmed, A.K.; Ibraheem, A.M.; Abd-Ellah, M.K. Forecasting of municipal solid waste multi-classification by using time-series deep learning depending on the living standard. Results Eng. 2022, 16, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Rai, S.C.; Rai, S.P.; Ram, K. Impact of anthropogenic and geological factors on groundwater hydrochemistry in the unconfined aquifers of Indo-Gangetic plain. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2022, 127, 103109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.A.; Quraishi, S.B.; Newaz, M.A.; Sultana, J.; Bodrud-Doza, M.; Rahman, M.A.; Patwary, M.A.; Bhuiyan, M.A.H. Groundwater quality and human health risk assessment in selected coastal and floodplain areas of Bangladesh. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2022, 249, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, S.; Gogu, R. Groundwater Assessment and Management for Sustainable Water-Supply and Coordinated Subsurface Drainage: A Guidebook for Water Utilities & Municipal Authorities; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2022; p. 50. Available online: https://library.oapen.org/handle/20.500.12657/57565 (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Ha, K.; Lee, E.; An, H.; Kim, S.; Park, C.; Kim, G.-B.; Ko, K.-S. Evaluation of Seasonal Groundwater Quality Changes Associated with Groundwater Pumping and Level Fluctuations in an Agricultural Area, Korea. Water 2021, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality: Incorporating the First and Second Addenda. 2022. Available online: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/igo (accessed on 15 January 2023).
- Balamurugan, P.; Kumar, P.S.; Shankar, K. Dataset on the suitability of groundwater for drinking and irrigation purposes in the Sarabanga River region, Tamil Nadu, India. Data Brief 2020, 29, 105255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, P.; Kumar, P.S.; Shankar, K.; Nagavinothini, R.; Vijayasurya, K. Non-carcinogenic risk assessment of groundwater in southern part of Salem district in Tamilnadu, India. J. Chil. Chem. Soc. 2020, 65, 4697–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Rawy, M.; Ismail, E.; Abdalla, O. Assessment of groundwater quality using GIS, hydrogeochemistry, and factor statistical analysis in Qena Governorate, Egypt. Desalin. Water Treat. 2019, 162, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadri, A.; Baouia, K.; Kateb, S.; Al-Ansari, N.; Kouadri, S.; Najm, H.M.; Mashaan, N.S.; Eldirderi, M.M.A.; Khedher, K.M. Assessment of Groundwater Suitability for Agricultural Purposes: A Case Study of South Oued Righ Region, Algeria. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, E.; El-Rawy, M.; Mauritsch, H. Evaluation of Groundwater Potential Zones Using Electrical Resistivity and Hydrogeochemistry in West Tahta Region, Upper Egypt. In Sustainability of Groundwater in the Nile Valley, Egypt; Earth and Environmental Sciences Library; Negm, A.M., El-Rawy, M., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, E.M.; Badr, A.M.; Abdelradi, F.; Negm, A.; Nosair, A.M. Detection of Groundwater Quality Changes in Minia Governorate, West Nile River. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negm, A.M.; Armanuos, A.M. GIS-based spatial distribution of groundwater quality in the Western Nile Delta, Egypt. In The Nile Delta; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Bilali, A.; Taleb, A.; Brouziyne, Y. Groundwater quality forecasting using machine learning algorithms for irrigation purposes. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanoon, M.S.; Ammar, A.M.; Ahmed, A.N.; Razzaq, A.; Birima, A.H.; Kumar, P.; Sherif, M.; Sefelnasr, A.; El-Shafie, A. Application of soft computing in predicting groundwater quality parameters. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 828251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouadri, S.; Pande, C.B.; Panneerselvam, B.; Moharir, K.N.; Elbeltagi, A. Prediction of irrigation groundwater quality parameters using ANN, LSTM, and MLR models. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 29, 21067–21091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Yousfi, Y.; Himi, M.; El Ouarghi, H.; Aqnouy, M.; Benyoussef, S.; Gueddari, H.; Ait Hmeid, H.; Alitane, A.; Chaibi, M.; Zahid, M.; et al. Assessment and Prediction of the Water Quality Index for the Groundwater of the Ghiss-Nekkor (Al Hoceima, Northeastern Morocco). Sustainability 2023, 15, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, M.H.; Chowdhury, M.A.T.; Bhuiyan, M.H.R.; Das, S.; Morshed, A.J.M.; Das, J.; Islam, S. Seasonal variation of drinking water quality in urban water bodies (UWBs) of Chittagong Metropolitan City, Bangladesh: Implications of higher water quality index (WQI) for the urban environment. Water Supply 2022, 22, 4934–4950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, V.; Ramesh, R.; Sreeja, P.; Jarin, T.; Kumar, P.S.; Ansar, S.; Ashraf, G.A.; Pandey, S.; Said, Z. Hybridization of long short-term memory with Sparrow Search Optimization model for water quality index prediction. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villada-Canela, M.; Muñoz-Pizza, D.M.; García-Searcy, V.; Camacho-López, R.; Daesslé, L.W.; Mendoza-Espinosa, L. Public Participation for Integrated Groundwater Management: The Case of Maneadero Valley, Baja California, Mexico. Water 2021, 13, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, J.; Mahmoud, A.; Alam, T.; Sanchez, A.; Jones, K.D.; Ernest, A. Collaborative Environmental Approach for Development of the Lower Laguna Madre Estuary Program Strategic Plan in South Texas. J. Environ. Inform. Lett. 2022, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.W.; Lin, K.H.; Kuo, Y.M. Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 313, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, R. The Nile in Egypt. The Geological Evolution of the River Nile; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1981; pp. 12–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seif, E.S.S.A. Geological evolution of Nile Valley, west Sohag, Upper Egypt: A geotechnical perception. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 11049–11072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.H.; Mustafa, A.R.A.; El-Sheikh, A.A. Geochemistry and spatial distribution of selected heavy metals in surface soil of Sohag, Egypt: A multivariate statistical and GIS approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omran, A. Integration of remote sensing, geophysics and GIS to evaluate groundwater potentiality—A case study in Sohag Region, Egypt. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Water Resources and Arid Environments and the 1st Arab Water Forum, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 16–19 November 2008; Available online: https://icwrae-psipw.org/papers/2008/Tech/10.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Lenore, S.C.; Arnold, E.G.; Andrew, D.E.; Mary, A.H. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA; American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA; World Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, S.P.; Reeta, K.; Suniti, P.; Basu, D.D.; Kamyotra, J.S. Guide Manual: Water and Wastewater Analysis; Central Pollution Control Board, Ministry of Environment & Forests, Government of India: New Delhi, India, 2011.
- Maiti, S.K. Handbook of Methods in Environmental Studies; ABD Publishers: Jaipur, India, 2003; Volume 2, pp. 110–121. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.K. An index number system for rating water quality. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1965, 37, 300–306. [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnaiah, C.R.; Sadashivaiah, C.; Ranganna, G. Assessment of water quality index for the groundwater in Tumkur Taluk, Karnataka State, India. E-J. Chem. 2009, 6, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.K. Handbook of Methods in Environmental Studies, Volume 1 (Water and Wastewater Analysis); Oxford Book Company: Oxford, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Gawad, S. Actualizing the right to water: An Egyptian perspective for an action plan. Int. J. Water Resour. Develop. 2007, 23, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, A.; Tiwari, S.K.; Pandey, H.K.; Chaurasia, A.K.; Singh, S.; Singh, Y.V. Groundwater quality assessment using water quality index (WQI) under GIS framework. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandge, K.P.; Patil, S.S. Spatial distribution of ground water quality index using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2022, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, B.; Muniraj, K.; Duraisamy, K.; Pande, C.; Karuppannan, S.; Thomas, M. An integrated approach to explore the suitability of nitrate-contaminated groundwater for drinking purposes in a semiarid region of India. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 45, 647–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurts, W.A.; Durborow, R.M. Interactions of pH, Carbon Dioxide, Alkalinity and Hardness in Fish Ponds. SRAC Publication No. 464. 1992, pp. 1–4. Available online: https://lee-phillips.org/Backyard/cache/464fs.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Sadat-Noori, S.M.; Ebrahimi, K.; Liaghat, A.M. Groundwater quality assessment using the Water Quality Index and GIS in Saveh-Nobaran aquifer, Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3827–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safar, Z.; Chassagne, C.; Rijnsburger, S.; Sanz, M.I.; Manning, A.J.; Souza, A.J.; van Kessel, T.; Horner-Devine, A.; Flores, R.; McKeon, M.; et al. Characterization and classification of estuarine suspended particles based on their inorganic/organic matter composition. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 896163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality. Incorporating the First Addendum; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254636/9789241550017-eng.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2023).
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, M.S.; Gutiérrez-López, A.; Iribarnegaray, M.A.; Weir, M.H.; Seghezzo, L. Long-Term Assessment of a Water Safety Plan (WSP) in Salta, Argentina. Water 2022, 14, 2948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, D.N.D.; Diyabalanage, S.; Dunuweera, S.P.; Rajapakse, S.; Rajapakse, R.M.G.; Chandrajith, R. Significance of Mg-hardness and fluoride in drinking water on chronic kidney disease of unknown etiology in Monaragala, Sri Lanka. Environ. Res. 2022, 203, 111779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.K.; Ghosh, G.C.; Ghosh, P.; Jahan, I.; Zaman, S.; Islam, M.S.; Hossain, M.R.; Habib, A.; Biswas, B.; Sultana, N.; et al. Arsenic, iron, and manganese in groundwater and its associated human health risk assessment in the rural area of Jashore, Bangladesh. J. Water Health 2022, 20, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desye, B.; Belete, B.; Asfaw Gebrezgi, Z.; Terefe Reda, T. Efficiency of treatment plant and drinking water quality assessment from source to household, gondar city, Northwest Ethiopia. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 9974064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Doula, M.K.; Aggelatou, V.; Zorpas, A.A. Removal of iron and manganese from underground water by use of natural minerals in batch mode treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 18, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdella, A.K.; Abdel-Aa, M.H. Iron Removal from Ground Water through Expanded Polystyrene Filter. J. Environ. Treat. Tech. 2021, 9, 657–666. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, T.; Sun, X.; Yang, T.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H. Major ions in drinking and surface waters from five cities in arid and semi-arid areas, NW China: Spatial occurrence, water chemistry, and potential anthropogenic inputs. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2020, 27, 5456–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Nitrate and Nitrite in Drinking Water; National Academies Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wei, S.; Liang, H.; Zheng, W.; Li, X.; Hu, C.; Currell, M.J.; Zhou, F.; Min, L. Nitrogen stock and leaching rates in a thick vadose zone below areas of long-term nitrogen fertilizer application in the North China Plain: A future groundwater quality threat. J. Hydro. 2019, 576, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhanardakani, S.; Taghavi, L.; Shahmoradi, B.; Jahangard, A. Groundwater quality assessment using the water quality pollution indices in Toyserkan Plain. Environ. Health Eng. Manag. 2017, 4, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Drinking water, national primary drinking water regulations, total coliforms (including fecal coliforms and E. coli); Final rule. Fed. Regist. 1989, 54, 27544–27568. [Google Scholar]
- Acrylamide, O.C. National Primary Drinking Water Regulations. Kidney 2009, 2, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.K.; Bharani, R.; Magesh, N.S.; Godson, P.S.; Chandrasekar, N. Hydrogeochemistry and groundwater quality appraisal of part of south Chennai coastal aquifers, Tamil Nadu, India using WQI and fuzzy logic method. Appl. Water Sci. 2014, 4, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).