Research on the Sustainable Development Path of Regional Economy Based on CO2 Reduction Policy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Correlation Analysis between Carbon Emission Reduction Policy and SD RE
2.1. Correlation Analysis between GTFP and RE Sustainability
2.2. Correlation Analysis of Carbon Reduction Policies and GTFP
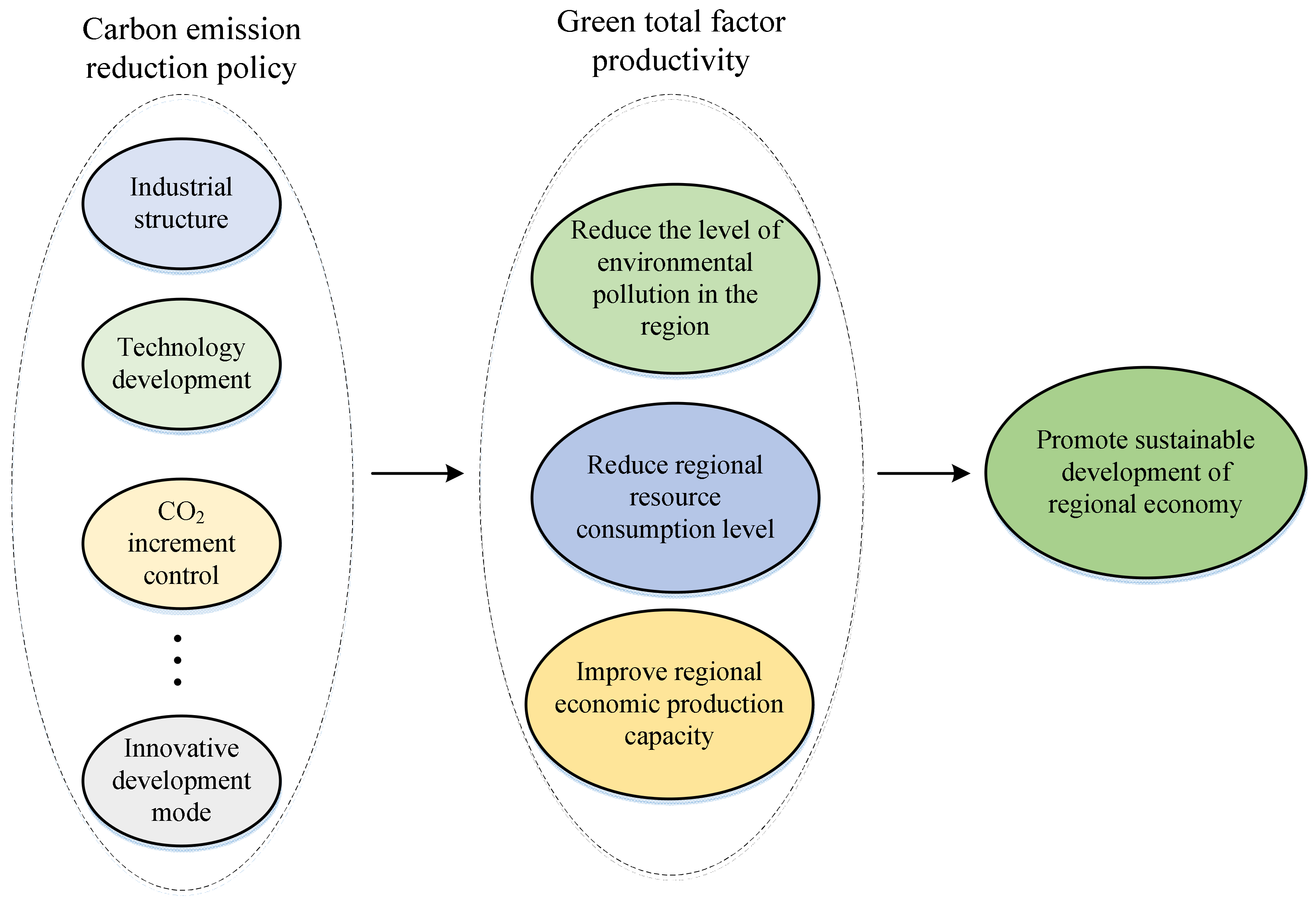
2.3. Analysis of the Impact of CRPs on the SD of a Regional Economy
3. Empirical Study of CO2 Emissions in Various Regions
3.1. Emission Measurement Model Construction for Each Region’s CO2
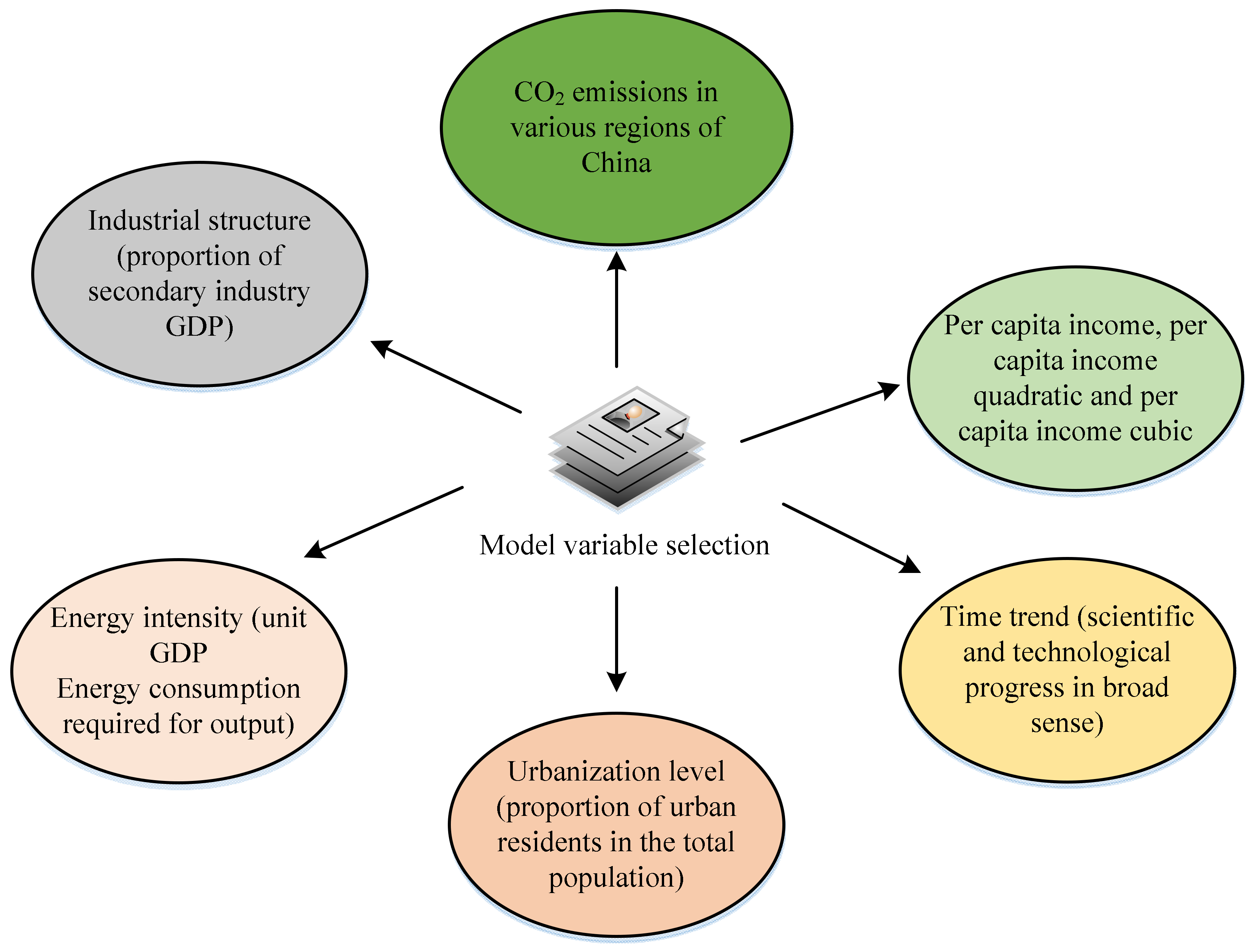
3.2. Model Variable Selection
3.3. Econometric Model Results and Regression Analysis
4. Measurement and Analysis of GTFP Efficiency Values
4.1. Selection of Efficiency Measurement Model
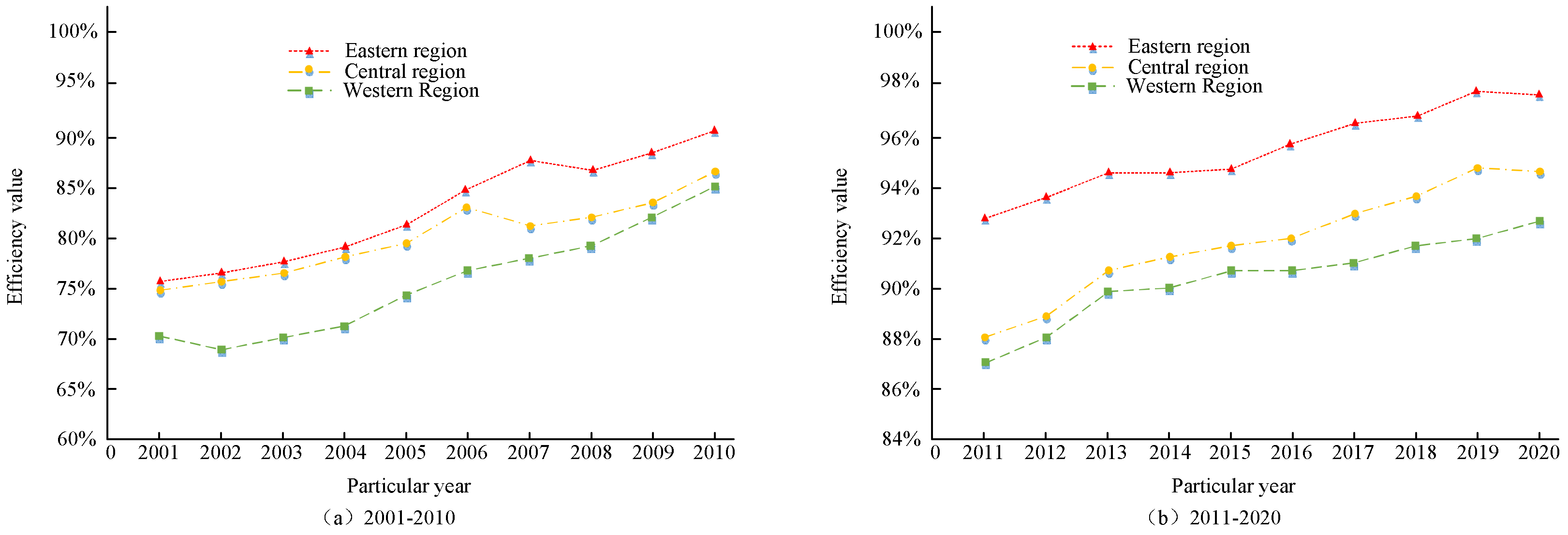
4.2. Measurement of the GTFP Efficiency Value
4.3. Analysis of the Drivers of GTFP Efficiency Values
5. Accounting and Analysis of GTFP Growth Rate
5.1. Selection of Production Function
5.2. Regional GTFP Growth Rate Accounting
5.3. Analysis of the Factors Influencing the Growth Rate of GTFP
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, R. Is China’s economic growth decoupled from carbon emissions? J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 1194–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, A.; Kang, L.; Somerse, W.E.; Dixon, S. Venting in the comparative study of flexural ultrasonic transducers to improve resilience at elevated environmental pressure levels. IEEE Sens. J. 2020, 20, 5776–5784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callesen, G.M.; Pedersen, S.M.; Carolus, J.; Lopez, J.M.; Karrman, E.; Hjerppe, T.; Barquet, K. Recycling nutrients and reducing carbon emissions in the baltic sea region-sustainable or economically infeasible? Environ. Manag. 2022, 69, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallucci, M. The Ammonia Solution: Ammonia engines and fuel cells in cargo ships could slash their carbon emissions. IEEE Spectrum. 2021, 58, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Xu, M. Exploring the green total factor productivity of china’s metallurgical industry under carbon tax: A perspective on factor substitution. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 233, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; An, Q.; Ding, T.; Yin, P.; Liang, L. Carbon emission allocation in China based on gradually efficiency improvement and emission reduction planning principle. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 278, 123–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Xu, H.C.; Liu, W.W.; Wang, D.F.; Zheng, W.L. Influence of collaborative agglomeration between logistics industry and manufacturing on green total factor productivity based on panel data of china’s 284 cities. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 109196–109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayele, S.; Fayek, A.R. A framework for total productivity measurement of industrial construction projects. Can. J. Civil Eng. 2019, 46, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiao, Y.; Lei, X.; Kang, A.; Wang, M.; Liao, W.; Wang, H.; Ma, Y. A two-stage water allocation strategy for developing regional economic-environment sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyslova, O.Y.; Stroyev, P.V.; Nesterova, N.N. Mechanism of increasing the sustainability of socio-economic development of regions with using gis-technologies. Manag. Sci. 2019, 8, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q. Regional technological innovation and green economic efficiency based on dea model and fuzzy evaluation. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. Appl. Eng. Technol. 2019, 37, 6415–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kong, L.; Wang, W.; Xie, J. Motivating individual carbon reduction with saleable carbon credits: Policy implications for public emission reduction projects. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2022, 122, 1268–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunerhjelm, P. The Influence of Agglomeration on Large Firms’ Investments—Evidence from Swedish Foreign Direct Investment; Spring: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Pang, S.; Hmani, I.; Hmani, I.; Li, C.; He, Z.; Welford, R. Towards sustainable development: How does technological innovation drive the increase in green total factor productivity? Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Nadarajah, S. A note on ‘Parameter estimation for bivariate Weibull distribution using generalized moment method for reliability evaluation’. Qual. Reliab. Eng. Int. 2019, 35, 732–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forghani, D.; Ibrahim, M.D.; Daneshvar, S. Improving weak efficiency frontier in a variable returns to scale stochastic data envelopment analysis model. RAIRO—Oper. Res. 2022, 56, 2159–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omrani, H.; Amini, M.; Babaei, M.; Shafaat, K. Use Shapley value for increasing power distinguish of data envelopment analysis model: An application for estimating environmental efficiency of industrial producers in Iran. Energy Environ. 2020, 31, 656–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.K.; Cao, F.F.; Dennis, B. Does the China-korea free trade area promote the green total factor productivity of china’s manufacturing industry? J. Korea Trade 2019, 23, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q. Which factors stimulate industrial TFP growth rate in China? An industrial aspect. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, D. A general equilibrium impact study of the emissions reduction fund in australia by using a national environmental and economic model. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 216, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Ye, Q.; Zhen, Z. A new assessment model of social cost of carbon and its situation analysis in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Khan, M.A.; Husnain, M. Searching appropriate system boundary for accounting india’s emission inventory for the responsibility to reduce carbon emissions. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 295, 112907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yang, G.; Li, X. Modeling the evolutionary nexus between carbon dioxide emissions and economic growth. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oblasov, N.V.; Goncharov, I.V.; Derduga, A.V.; Kunitsyna, I.V. Geochemistry and carbon isotope characteristics of associated gases from oilfields in the nw greater caucasus, russia. J. Pet. Geol. 2022, 45, 325–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprów, M.; Machnik, J.; Otulakowski, U.; Dworak, A.; Trzebicka, B. Thermoresponsive p(hema-co-oegma) copolymers: Synthesis, characteristics and solution behavior. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 40966–40974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehouse, L.J.; Farihi, J.; Howarth, I.D.; Mancino, S.; Walters, N.; Swan, A.; Wilson, T.G.; Guo, J. Carbon-enhanced stars with short orbital and spin periods. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2021, 506, 4877–4892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Yang, B.; Lu, Y.; Guo, X.; Zu, G.; Huang, J. Detection of electrolyte leakage from lithium-ion batteries using a miniaturized sensor based on functionalized double-walled carbon nanotubes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 6760–6765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numata, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Takasu, H.; Kato, Y. Carbon dioxide reduction on a metal-supported solid oxide electrolysis cell. ISIJ Int. 2019, 59, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, W. Potential impacts of coal substitution policy on regional air pollutants and carbon emission reductions for china’s building sector during the 13th five-year plan period. Energy Policy 2019, 131, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, B.W.; Niemeier, D. Quantifying greenhouse gas emissions and the marginal cost of carbon abatement for residential buildings under california’s 2019 title 24 energy codes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12121–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emodi, N.V.; Chaiechi, T.; Beg, A.R.A. Are emission reduction policies effective under climate change conditions? A backcasting and exploratory scenario approach using the leap-osemosys model. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 1183–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, T.; Ali, S.F.; Gillich, A. Opportunities to decarbonize heat in the uk using urban wastewater heat recovery. Build. Serv. Eng. Res. Technol. 2021, 42, 715–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.P.; Xue, J.J.; Shi, X.P.; Wang, K.Y.; Qi, S.Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, C. A dynamic and continuous allowances allocation methodology for the prevention of carbon leakage: Emission control coefficients. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al, A.; Djaj, A.; El, B. Negative Co2 emissions—An analysis of the retention times required with respect to possible carbon leakage. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control. 2019, 87, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhou, X.; Li, G. Does the internet promote green total factor productivity? empirical evidence from china. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, L.; Huang, G.H.; Niu, D.X.; Cai, Y.P.; Yin, J.G. A stochastic optimization model for carbon-emission reduction investment and sustainable energy planning under cost-risk control. J. Environ. Inform. 2020, 36, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, S.; Wu, F. Research on carbon emission reduction benefit of wind power project based on life cycle assessment theory. Renew. Energy 2020, 155, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, L. Green total factor productivity and its decomposition of chinese manufacturing based on the mml index: 2003–2015. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 222, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Li, J. Towards a green world: How do green technology innovations affect total-factor carbon productivity. Energy Policy 2019, 131, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Region | Province | Total Carbon Emissions | Carbon Emission Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Value/10,000 t | Average/(t·1000 USD−1) | ||
| Central region | Henan | 50,215.08 | 0.38 |
| Shanxi | 70,213.21 | 1.05 | |
| Anhui | 29,366.27 | 0.85 | |
| Hubei | 31,187.19 | 0.88 | |
| Jiangxi | 17,356.38 | 1.49 | |
| Hunan | 26,032.23 | 0.58 | |
| Western Region | Shanxi | 30,957.62 | 0.89 |
| Sichuan | 27,513.62 | 0.60 | |
| Yunnan | 19,585.07 | 0.28 | |
| Guizhou | 21,978.53 | 1.11 | |
| Guangxi | 16,935.68 | 0.64 | |
| Gansu | 17,215.43 | 0.40 | |
| Qinghai | 3796.38 | 0.35 | |
| Ningxia | 13,816.08 | 2.18 | |
| Xinjiang | 28,958.31 | 0.69 | |
| Inner Mongolia | 54,529.76 | 1.51 | |
| Chongqing | 11,127.35 | 0.52 | |
| Liaoning | 60,348.19 | 0.45 | |
| Heilongjiang | 31,219.56 | 0.82 | |
| Jilin | 23,065.46 | 2.16 | |
| Hainan | 3708.56 | 0.94 | |
| Guangdong | 50,489.46 | 0.83 | |
| Eastern Region | Hebei | 69,518.35 | 3.76 |
| Beijing | 13,158.49 | 0.75 | |
| Tianjin | 16,236.35 | 0.99 | |
| Shandong | 93,527.15 | 0.49 | |
| Jiangsu | 59,872.59 | 1.37 | |
| Shanghai | 24,926.73 | 0.67 | |
| Zhejiang | 37,654.28 | 0.42 | |
| Fujian | 20,368.18 | 0.95 |
| Explanatory Variable | Static Model | Dynamic Model |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 emissions in the previous period | / | 0.46 *** (0.06) |
| Per capita income logarithm | 12.28 *** (0.08) | 10.19(0.07) |
| Quadratic power of logarithm of per capita income | 1.19 ** (0.68) | 1.08 (1.12) |
| Cubic power of logarithm of per capita income | −0.091 ** (0.48) | −0.61 ** (0.75) |
| Industrial structure | 0.32 ** (0.17) | 0.09 ** (0.18) |
| Energy intensity | −0.14 ** (0.04) | −0.41 ** (0.24) |
| Foreign investment | 0.12 * (0.13) | 0.37 * (1.18) |
| Urbanization level | 1.61 * (0.49) | 1.99 ** (0.24) |
| Time | −0.06 ** (0.02) | −0.06 ** (0.02) |
| Square of time | 0.11 ** (0) | 0.10 ** (0) |
| Constant term | −0.21 | 0.04 ** (0.25) |
| Estimation method | Generalized least squares | Generalized moment estimation |
| Arellano | / | −3.38 * |
| Sargan test | / | 57.46 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.78 | 0.93 |
| AIC | −3.58 | −4.03 |
| BIC | −3.49 | −4.47 |
| Variable | Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Constant term | 0.7779 *** (0.2132) |
| Marketization variables | 0.0148 *** (0.0056) |
| Per capita years of education | 0.0853 *** (0.0201) |
| Research and development investment | 0.0718 *** (0.0182) |
| The logarithm of foreign expenditure | 0.0096 *** (0.0031) |
| Foreign investment | −1.0559 *** (0.3565) |
| Industrial structure | −0.5796 *** (0.1406) |
| / | MAR | Edu | ln Ftech | ln R&D | FDI | SEC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAR | 1 | 0.5638 | 0.6394 | 0.5412 | 0.7369 | 0.4956 |
| Edu | 0.5638 | 1 | 0.3965 | 0.5139 | 0.4863 | 0.3697 |
| ln Ftech | 0.6394 | 0.3965 | 1 | 0.5528 | 0.6321 | 0.4863 |
| ln R&D | 0.5412 | 0.5139 | 0.5528 | 1 | 0.4965 | 0.5932 |
| FDI | 0.7369 | 0.4863 | 0.6321 | 0.4965 | 1 | 0.6231 |
| SEC | 0.4956 | 0.3697 | 0.4863 | 0.5932 | 0.6231 | 1 |
| Variable | Coefficient | Variable | Coefficient |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant term | 8.5475 *** (0.9683) | LnK × lnE | 0.0441 *** (0.0232) |
| t | 0.1308 *** (0.0269) | LnK × lnC | 0.0028 *** (0.0191) |
| (1/2)t2 | 0.0027 *** (0.0004) | t × lnC | −0.0029 *** (0.0041) |
| lnK | 0.0285 *** (0.1428) | t × lnK | 0.0043 ** (0.0021) |
| lnL | 0.3316 *** (0.1318) | t × lnL | 0.0019 (0.0019) |
| lnE | −0.8412 *** (0.2893) | t × lnE | −0.0118 ** (0.0049) |
| lnC | 0.0232 | (1/2)lnK2 | −0.0387 ** (0.0258) |
| lnL × lnE | −0.1172 ** (0.0388) | (1/2)lnL2 | 0.0288 ** (0.0197) |
| lnL × lnK | 0.0269 (0.0273) | (1/2)lnE2 | 0.2333 ** (0.1413) |
| lnL × lnC | −0.0646 ** (0.0886) | (1/2)lnC2 | 0.0425 (0.0536) |
| LnK × lnL | 0.0223 *** (0.1533) |
| Year/Region | Central Region | Western Region | Eastern Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 | −0.0386 | −0.0248 | 0.0008 |
| 2002 | −0.0208 | −0.0041 | −0.0165 |
| 2003 | −0.0382 | −0.0112 | −0.0297 |
| 2004 | −0.0247 | −0.0186 | −0.0385 |
| 2005 | −0.0263 | −0.0243 | −0.0513 |
| 2006 | −0.0051 | −0.0289 | −0.0402 |
| 2007 | −0.0004 | −0.0107 | −0.0367 |
| 2008 | −0.0121 | −0.0199 | −0.0152 |
| 2009 | −0.0431 | −0.0095 | −0.0459 |
| 2010 | −0.0403 | −0.0272 | −0.0477 |
| 2011 | −0.0426 | −0.0312 | −0.0493 |
| 2012 | −0.0448 | −0.0327 | −0.0562 |
| 2013 | −0.0369 | −0.0286 | −0.0483 |
| 2014 | −0.0421 | −0.0306 | −0.0532 |
| 2015 | −0.0397 | −0.0198 | −0.0426 |
| 2016 | −0.0458 | −0.0237 | −0.0517 |
| 2017 | −0.0357 | −0.0325 | −0.0467 |
| 2018 | −0.0296 | −0.0277 | −0.0396 |
| 2019 | −0.0318 | −0.0261 | −0.0457 |
| 2020 | −0.0353 | −0.0185 | −0.0367 |
| Variable | Coefficient |
|---|---|
| Constant term | −0.0738 (0.2548) |
| Marketization variables | 0.1889 *** (0.1227) |
| Education investment | 0.0833 *** (0.0251) |
| Research and development investment | 0.0477 *** (0.0273) |
| The logarithm of foreign expenditure | −0.0028 (0.0038) |
| Foreign investment | 0.2076 (0.5289) |
| Industrial structure | −0.0342 *** (0.1187) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, J.; Wang, S.; Lian, M. Research on the Sustainable Development Path of Regional Economy Based on CO2 Reduction Policy. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6767. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086767
Qiu J, Wang S, Lian M. Research on the Sustainable Development Path of Regional Economy Based on CO2 Reduction Policy. Sustainability. 2023; 15(8):6767. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086767
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Ju, Shumei Wang, and Meihua Lian. 2023. "Research on the Sustainable Development Path of Regional Economy Based on CO2 Reduction Policy" Sustainability 15, no. 8: 6767. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086767
APA StyleQiu, J., Wang, S., & Lian, M. (2023). Research on the Sustainable Development Path of Regional Economy Based on CO2 Reduction Policy. Sustainability, 15(8), 6767. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086767








