The Embedded Agroecology of Coffee Agroforestry: A Contextualized Review of Smallholder Farmers’ Adoption and Resistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
“man’s economy, as a rule, is submerged in his social relationships. He does not act so as to safeguard his individual interest in the possession of material goods; he acts so as to safeguard his social standing, his social claims, his social assets. He values material goods only in so far as they serve this end.”[15] (p. 48).
“It is governed by laws of its own, the so-called laws of supply and demand, and motivated by fear of hunger and hope of gain. Not blood-tie, legal compulsion, religious obligation, fealty or magic creates the sociological situations which make individuals partake in economic life but specifically economic institutions such as private enterprise and the wage system.”[16] (p. 60).
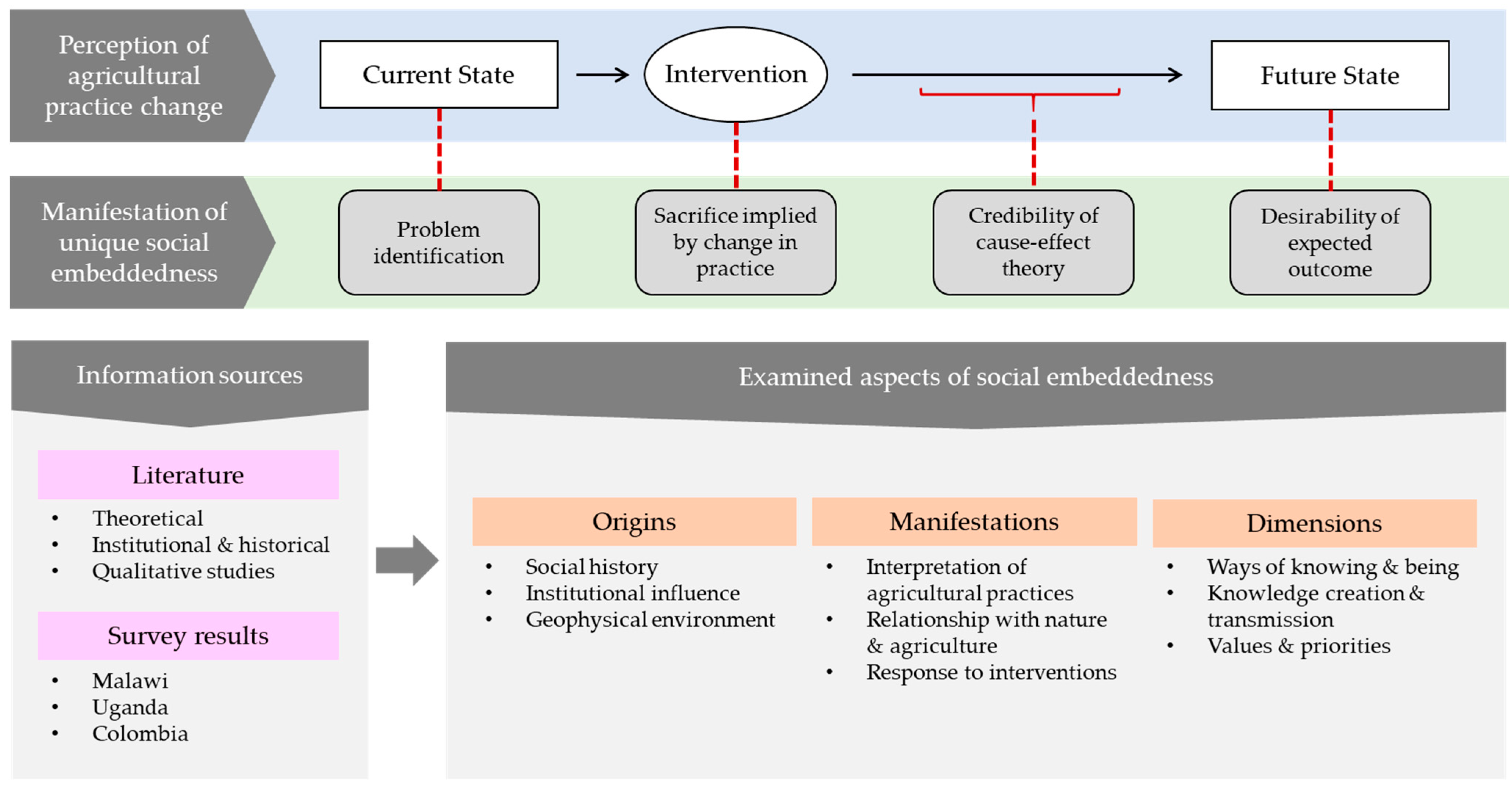
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review Methods
2.2. Insights from Focus Groups under the Slow Food Coffee Coalition Agroforestry Program
2.3. Colombia Smallholder Interviews
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Literature Review
3.1.1. Opportunities of Coffee Agroforestry
3.1.2. Ecosystem Service Provision via Coffee Agroforestry
3.1.3. Agricultural Benefits of Coffee Agroforestry
3.1.4. Socio-Economic Benefits of Coffee Agroforestry
3.1.5. Producers’ Challenges
3.1.6. Epistemological Embeddedness of Coffee Agroecology
3.1.7. Historical Epistemological Processes
“the effectiveness of tree planting programs and activities will be largely determined by the degree to which we understand and address the factors which encourage or discourage farmers to plant trees. It is essential to comprehend how farmers perceive the benefits and challenges associated with tree planting in order to explain the current extent of tree planting in Malawi and scale up these efforts in the future. To accomplish this, it is important to understand the decision-making process of farmers who plant trees on their land. In addition to the beliefs farmers hold with regards to the possible positive and negative outcomes of tree planting activities, their decisions are also influenced by the opinions and behaviour of relevant others in their surroundings as well as the practical possibilities they have to plant trees.”[53] (p. 2).
3.1.8. Farmers’ Relationships with Land
3.1.9. Non-Economic Rationalities
4. Historical Embeddedness
4.1. Legacy of Past Intervention
4.2. Institutional Embeddedness and Agency
4.2.1. Transnational Companies
4.2.2. Multilateral Organizations
4.2.3. Producer Country Governments
4.2.4. Consumer Country Governments
4.2.5. The Aid Complex
4.3. Resistance to Agroforestry
4.3.1. Practical Resistance to Agroforestry
4.3.2. Resistance to the Means
4.4. Capabilities
4.4.1. Access to Resources
4.4.2. Economic Challenges
4.5. Participatory and Socially Inclusive Efforts
4.6. Malawi and Uganda Focus Groups
4.7. Uganda
4.7.1. Conflicting Interventions
4.7.2. Coffee Agroforestry Is Viewed Favorably, but the Means Are Unclear
4.7.3. Non-Economization of Ecosystem Services
4.8. Malawi
4.9. Colombia Interviews
4.9.1. Favorability of Shade Trees
4.9.2. Advantages of Agroforestry
4.9.3. Tree Species Selection
4.9.4. Sources of Knowledge
5. Conclusions
Summary of Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rolo, V. Agroforestry for Sustainable Food Production. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Aguilera, J.N.; Conrad, J.M.; Gómez, M.I.; Rodewald, A.D. The Economics and Ecology of Shade-Grown Coffee: A Model to Incentivize Shade and Bird Conservation. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 159, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponte, S. Standards and Sustainability in the Coffee Sector; International Institute for Sustainable Development: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Beer, J.; Muschler, R.; Kass, D.; Somarriba, E. Shade Management in Coffee and Cacao Plantations. Agrofor. Syst. 1997, 38, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, C. Confronting the Coffee Crisis: Can Fair Trade, Organic, and Specialty Coffees Reduce Small-Scale Farmer Vulnerability in Northern Nicaragua? World Dev. 2005, 33, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinion, A.; Chirwa, P.W.; Akinnifesi, F.K.; Ajayi, O.C. Do Agroforestry Technologies Improve the Livelihoods of the Resource Poor Farmers? Evidence from Kasungu and Machinga Districts of Malawi. Agrofor. Syst. 2010, 80, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Bacon, C.M.; Philpott, S.M.; MÉndez, V.E.; LÄderach, P.; Rice, R.A. Shade Coffee: Update on a Disappearing Refuge for Biodiversity. BioScience 2014, 64, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volsi, B.; Telles, T.S.; Caldarelli, C.E.; da Camara, M.R.G. The Dynamics of Coffee Production in Brazil. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemal, O.M.; Callo-Concha, D.; van Noordwijk, M. Coffee Agroforestry and the Food and Nutrition Security of Small Farmers of South-Western Ethiopia. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 608868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, C.; Owen, C.T.; Melzi, S.; Beaucage, P. Biodiversity and Modernization in Four Coffee-Producing Villages of Mexico. Ecol. Soc. 2005, 10, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndihokubwayo, S.; Havyarimana, T.; Windbühler, S.; Niragira, S.; Habonimana, B.; Kaboneka, S.; Megerle, H.E. Farmers’ Perception of Coffee Agroforestry Systems in an Area Targeted for Organic Certification in Burundi. East Afr. J. For. Agrofor. 2021, 3, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Pinto, L.; Perfecto, I.; Castillo-Hernandez, J.; Caballero-Nieto, J. Shade Effect on Coffee Production at the Northern Tzeltal Zone of the State of Chiapas, Mexico. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 80, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara Estrada, L.D. Efectos de La Altitud, Sombra, Producción y Fertilización Sobre La Calidad Del Café (Coffea arabica L. Var. Caturra) Producido En Sistemas Agroforestales de La Zona Cafetalera Norcentral de Nicaragua; Centro Agronómico Tropical de Investigación y Enseñanza (CATIE): Turrialba, Costa Rica, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- De Leijster, V.; Santos, M.J.; Wassen, M.W.; Camargo García, J.C.; Llorca Fernandez, I.; Verkuil, L.; Scheper, A.; Steenhuis, M.; Verweij, P.A. Ecosystem Services Trajectories in Coffee Agroforestry in Colombia over 40 Years. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 48, 101246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polanyi, K. The Great Transformation: Economic and Political Origins of Our Time; Rinehart: New York, NY, USA, 1944. [Google Scholar]
- Polanyi, K. Dahomey and the Slave Trade: An Analysis of an Archaic Economy; University of Washington Press: Seattle, WA, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Méndez, V.E.; Bacon, C.M.; Cohen, R. Agroecology as a Transdisciplinary, Participatory, and Action-Oriented Approach. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2013, 37, 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Gliessman, S.R. Agroecology: The Ecology of Sustainable Food Systems, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, C.A.; Conforti, P.; Ergin, I.; Gennari, P. Defining Small-Scale Food Producers to Monitor Target 2.3. of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. FAO Stat. Work. Pap. Ser. 2017, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- HLPE Investing in Smallholder Agriculture for Food Security. A Report by the High Level Panel of Experts on Food Security and Nutrition of the Committee on World Food Security; Committees on World Security: Rome, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Guhl, A. Coffee Production Intensification and Landscape Change in Colombia, 1970–2002. In Land-Change Science in the Tropics: Changing Agricultural Landscapes; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- IDH Sustainable Trade. Coffee Production in the Face of Climate Change: Country Profiles; IDH Sustainable Trade: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Daviron, B.; Ponte, S. The Coffee Paradox; Zed Books: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, R.H. Open-Economy Politics; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, J.M. Grounds for Agreement: The Political Economy of the Coffee Commodity Chain; Rowman & Littlefield Publishers: Lanham, ML, USA, 2004; ISBN 0742526291. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations. UN Comtrade; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Market Research & Intelligence Unit Coffee Board. Database on Coffee; Market Research & Intelligence Unit Coffee Board: Bangaluru, India, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Nolte, G.E. Peru Coffee Annual: Peru’s Coffee Production Continues Recovering; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sood, D. India Coffee Annual; New Delhi; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gerencia General Federación. Ensayos Sobre Economía Cafetera; Gerencia General Federación: Bogotá, Colombia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Gmünder, S.; Toro, C.; Rojas Acosta, J.M.; Rodríguez-Valencia, N. Huella Ambiental Del Café En Colombia; Quantis: Zurich, Switzerland, 2020; ISBN 9789588368146. [Google Scholar]
- Arias, M.A.; Ibáñez, A.M.; Zambrano, A. Agricultural Production amidst Conflict: The Effects of Shocks, Uncertainty and Governance of Non-State Armed Actors; IDS OpenDocs: Birghton, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Navarrete-Cruz, A.; Birkenberg, A.; Birner, R. Factors Influencing the Development of Rural Producer Organizations in Post-War Settings. The Case of Coffee Growers Associations in Southern Tolima, Colombia. Int. J. Commons 2020, 14, 692–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Rodríguez, J.S. Replication Data for: Party Politics amid Civil War: Brutality, Narcotrafficking and Corruption in Colombia’s Transition; Harvard Dataverse: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Gliessman, S.R. Agroecología: Procesos Ecológicos En Agricultura Sostenible; CATIE: Turrialba, Costa Rica, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Calo, M.; Wise, T. A Revaluing Peasant Coffee Production: Organic and Fair Trade Markets in Mexico; Global Development and Environment Institute: Medford, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Octavia, D.; Suharti, S.; Murniati; Dharmawan, I.W.S.; Nugroho, H.Y.S.H.; Supriyanto, B.; Rohadi, D.; Njurumana, G.N.; Yeny, I.; Hani, A.; et al. Mainstreaming Smart Agroforestry for Social Forestry Implementation to Support Sustainable Development Goals in Indonesia: A Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griscom, B.W.; Adams, J.; Ellis, P.W.; Houghton, R.A.; Lomax, G.; Miteva, D.A.; Schlesinger, W.H.; Shoch, D.; Siikamäki, J.V.; Smith, P.; et al. Natural Climate Solutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 11645–11650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraphan, P.; Jirawan, K. Estimating Benefits of Forest Ecosystem Service to Support Payments for Ecosystem Services in Mae Sa Watershed, Chiang Mai, Thailand. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2019, 15, 613–624. [Google Scholar]
- Bacon, C.M. Quality Revolutions, Solidarity Networks, and Sustainability Innovations: Following Fair Trade Coffee from Nicaragua to California. J. Polit. Ecol. 2013, 20, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, L.C.; Bianchi, F.J.J.A.; Cardoso, I.M.; Fernandes, R.B.A.; Filho, E.I.F.; Schulte, R.P.O. Agroforestry Systems Can Mitigate the Impacts of Climate Change on Coffee Production: A Spatially Explicit Assessment in Brazil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 294, 106858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topik, S.; Marichal, C.; Frank, Z. From Silver to Cocaine: Latin American Commodity Chains and the Building of the World Economy, 1500–2000; Duke University Press: Durham, UK, 2006; ISBN 978-0-8223-3766-9. [Google Scholar]
- Akinnifesi, F.K.; Ajayi, O.C.; Sileshi, G.; Chirwa, P.W.; Chianu, J. Fertiliser Trees for Sustainable Food Security in the Maize-Based Production Systems of East and Southern Africa. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 30, 615–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanto, H.W.; Lo, K.-A.; Toiba, H.; Rahman, M.S. Does Agroforestry Adoption Affect Subjective Well-Being? Empirical Evidence from Smallholder Farmers in East Java, Indonesia. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voluntary Service Overseas. Improving Market Access for the Poor—Malawi Coffee Co-Operatives. Available online: https://www.vso.ie/fighting-poverty/where-we-fight-poverty/malawi/improving-market-access-poor-malawi-coffee-co (accessed on 26 October 2022).
- Chirwa, E.W.; Dorward, A.; Kydd, J. Reforming the Smallholder Coffee Sector in Malawi: A Case Study of Smallholder Commercialisation; Future Agriculture: Potsdam, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Oxfam International. Unearthed: Land, Power and Inequality in Latin America; Oxfam International: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Dekens, J.; Bagamba, F. Promoting an Integrated Approach to Climate Adaptation: Lessons from the Coffee Value Chain in Uganda; International Institute for Sustainable Development: Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Nsibirwa, R.W. Coffee Yield [Productivity] and Production in Uganda: Is It Only a Function of GAP1and Diseases? Africa Coffee Academy: Kampala, Uganda, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bro, A.S. Climate Change Adaptation, Food Security, and Attitudes toward Risk among Smallholder Coffee Farmers in Nicaragua. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Dávila, J.P.; Casanova-Pérez, L. Epistemic and Conceptual Orphanhood in the Sustainability of Agroecosystems. In Sustainability of Agroecosystems; BoD: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Meshesha, A.T.; Birhanu, B.S.; Bezabih Ayele, M. Effects of Perceptions on Adoption of Climate-Smart Agriculture Innovations: Empirical Evidence from the Upper Blue Nile Highlands of Ethiopia. Int. J. Clim. Change Strateg. Manag. 2022, 14, 293–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meijer, S.S.; Catacutan, D.; Sileshi, G.W.; Nieuwenhuis, M. Tree Planting by Smallholder Farmers in Malawi: Using the Theory of Planned Behaviour to Examine the Relationship between Attitudes and Behaviour. J. Environ. Psychol. 2015, 43, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobar, A. Encountering Development: The Making and Unmaking of the Third World; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- West, P. From Modern Production to Imagined Primitive; Duke University Press Books: Durham, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hoogvelt, A. Globalization and the Postcolonial World, 2nd ed.; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Neilson, J. Value Chains, Neoliberalism and Development Practice: The Indonesian Experience. Rev. Int. Polit. Econ. 2014, 21, 38–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellinga, M. Globalization and Neoliberalism: Economy and Society in Latin America. Iberoam.–Nord. J. Lat. Am. Caribb. Stud. 2002, 32, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales-Martínez, V.; Martínez-Dávila, J.P.; Casanova-Pérez, L. Coffee Agroecosystem in Mexico: Productive Culture between Tradition and Change. Agro Product. 2020, 13, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, E.B. The Poverty of Progress, 1st ed.; University of California Los Angeles: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, R.A. A Place Unbecoming: The Coffee Farm of Northern Latin America. Geogr. Rev. 1999, 89, 554–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.M.; Molnar, J.J.; Fazio, R.A.; Sydnor, E.; Lowe, M.J. Barriers to Adoption of Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Change Agent Perspectives. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2009, 24, 60–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, H. Why Development Is More Complex than Growth: Clarifying Some Confusions. Rev. Soc. Econ. 2003, 61, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwyn, B. Poverty Chains and Global Capitalism. Compet. Chang. 2019, 23, 71–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, D. The Impacts of Coffee Production on Local Producers; California Polythechnic State University: San Luis Obispo, CA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Quentin, D.; Campling, L. Global Inequality Chains: Integrating Mechanisms of Value Distribution into Analyses of Global Production. Glob. Netw. 2018, 18, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, S.B. Derivatives and Development: A Political Economy of Global Finance, Farming, and Poverty; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, T.; Vorley, B. Small Producers: Constraints and Challenges in the Global Food System. In Ethical Sourcing in the Global Food System; Routledge: Abingdon-on-Thames, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ricci, A. Unequal Exchange in the Age of Globalization. Rev. Radic. Political Econ. 2019, 51, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwyn, B.; Leyden, D. Oligopoly-Driven Development: The World Bank’s Trading for Development in the Age of Global Value Chains in Perspective. Compet. Chang. 2021, 26, 174–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charveriat, C. Bitter Coffee: How the Poor Are Paying for the Slump in Coffee Prices; Oxfam GB: Oxford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Fitter, R.; Kaplinsky, R. Who Gains from Product Rents as the Coffee Market Becomes More Differentiated? A Value-Chain Analysis. IDS Bull. 2001, 32, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, S.A. Financialization and Changes in the Social Relations along Commodity Chains: The Case of Coffee. Rev. Radic. Political Econ. 2009, 41, 539–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richey, L.A.; Ponte, S. Brand Aid and Coffee Value Chain Development Interventions: Is Starbucks Working Aid out of Business? World Dev. 2021, 143, 105193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronemeyer, M. Helping. In The Development Dictionary: A Guide to Knowledge as Power; Sachs, W., Ed.; Zed Books: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Maizels, A.; Bacon, R.; Mavrotas, G. Commodity Supply Management by Producing Countries; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- UNCTAD Commodities at a Glance—Special Issue on Coffee in East Africa; The United Nations Conference on Trade and Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Humphrey, J.F.; Memedović, O. Global Value Chains in the Agrifood Sector; United Nations [UN] Industrial Development Organization: Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kiptot, E.; Hebinck, P.; Franzel, S.; Richards, P. Adopters, Testers or Pseudo-Adopters? Dynamics of the Use of Improved Tree Fallows by Farmers in Western Kenya. Agric. Syst. 2007, 94, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladkikh, T.M.; Collazo, J.A.; Torres-Abreu, A.; Reyes, A.M.; Molina, M. Factors That Influence Participation of Puerto Rican Coffee Farmers in Conservation Programs. Conserv. Sci. Pract. 2020, 2, e172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atlani-Duault, L.; Dozon, J.-P. Colonization, Development, Humanitarian Aid: Towards a Political Anthropology of International Aid. Ethnol. Française 2011, 41, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, H.V.; Nielson, D.L.; Findley, M. Which Devil in Development? A Randomized Study of Citizen Actions Supporting Foreign Aid in Uganda. 2013. Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2134409 (accessed on 24 October 2022).
- Buyinza, J.; Nuberg, I.K.; Muthuri, C.W.; Denton, M.D. Why Farmers Are Hesitant to Adopt What Appears Good on the Basis of Science: Understanding Farmers’ Perceptions of Biophysical Research. J. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 15, 68–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, H.; Luedeling, E.; Whitney, C. Decision Analysis of Agroforestry Options Reveals Adoption Risks for Resource-Poor Farmers. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 40, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albers, H.J.; Brockmann, S.; Ávalos-Sartorio, B. Assessing Policies to Mitigate Abandonment of Shade-Grown Coffee Production in Forest Systems amid Low and Uncertain Prices. Environ. Dev. Econ. 2021, 26, 403–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, M.M.; Mahimba, M.B.; Mbe Mpie, P.M.; M’vubu, A.R.N.; Khasa, D.P. Adoption of Agroforestry Practices in and around the Luki Biosphere Reserve in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Angel-Perez, A.L.; Villagomez-Cortes, J.A. Environment Perceptions and Conservation Preferences along the Coatepec-La Antigua Watershed, México. J. Hum. Ecol. 2014, 46, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibale, B.; Kafakoma, R.; Shaba, A.; Macqueen, D. Trees On-Farm: Removing the Obstacles to Enterprise: A Review of Current Climate-Smart Tree-Based Experiences in Malawi; International Institute for Environment and Development: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Do, T.H.; Mulia, R. Constraints to Smallholder Tree Planting in the Northern Mountainous Regions of Viet Nam: A Need to Extend Technical Knowledge and Skills. Int. For. Rev. 2018, 20, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Ihli, H.J.; Gassner, A. Agroforestry, Indigenous Tree Cover and Biodiversity Conservation: A Case Study of Mount Elgon in Uganda. Eur. J. Dev. Res. 2021, 34, 1893–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangata, P.H.; Hildebrand, P.E.; Gladwin, C.H. Modeling Agroforesty Adoption and Household Decision Making in Malawi. Afr. Stud. Q. 2002, 6, 271–293. [Google Scholar]
- Potts, J. Building a Sustainable Coffee Sector Using Market-Based Approaches; IISD and UNCTAD: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Yesuf, M.; Bluffstone, R.A. Poverty, Risk Aversion, and Path Dependence in Low-Income Countries: Experimental Evidence from Ethiopia. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2009, 91, 1022–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, A.; Albers, H.; Ávalos-Sartorio, B.; Crooks, L. Deforestation and Shade Coffee in Oaxaca, Mexico: Key Research Findings; Discussion Paper; No. 1318-2016-103337; AEC: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Meyfroidt, P. Environmental Cognitions, Land Change and Social-Ecological Feedbacks: Local Case Studies of Forest Transition in Vietnam. Hum. Ecol. 2013, 41, 367–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borda-Rodriguez, A.; Vicari, S. Coffee Co-Operatives in Malawi: Building Resilience through Innovation. Ann. Public Coop. Econ. 2015, 86, 317–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, S.; Bacon, C.M.; Philpott, S.M.; Rice, R.A.; Méndez, V.E.; Läderach, P. A Review of Ecosystem Services, Farmer Livelihoods, and Value Chains in Shade Coffee Agroecosystems. In Integrating Agriculture, Conservation and Ecotourism: Examples from the Field; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pinard, F.; Aithal, A. Can Good Coffee Prices Increase Smallholder Revenue? Cah. d’Outre-Mer 2008, 61, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Production Country | Production Rank | World Share | Majority Agroforestry | Majority Smallholder | Coffee Share of Exports | Yield MT per ha | Yield 60 kg Bags per ha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil | 1 | 30% | No | No | 3.0% | 0.77 | 12.8 |
| Vietnam | 2 | 22% | No | Yes | 1.5% | 1.77 | 29.5 |
| Colombia | 3 | 10% | No | Yes | 7.0% | 0.83 | 13.8 |
| Indonesia | 4 | 5% | No | Yes | 0.6% * | 0.5 | 8.3 |
| Honduras | 5 | 5% | Yes | Yes | 20.0% | 0.7 | 11.7 |
| Uganda | 6 | 4% | Yes | Yes | 25.0% | 0.64 | 10.7 |
| India | 7 | 4% | Yes *** | Yes ** | 0.2% * | 0.64 | 10.7 |
| Peru | 8 | 3% | Yes | Yes | 2.6% | 0.72 *** | 12.0 |
| Ethiopia | 9 | 3% | Yes | Yes | 25.0% | 0.71 | 11.8 |
| Guatemala | 10 | 3% | Yes | Yes | 6.2% | 0.9 | 15.0 |
| Tree Presence | Uganda | Colombia |
|---|---|---|
| Native | 42% | 71% |
| Nitrogen-fixing | 22% | 34% |
| Edible-Fruit-Producing | 50% | 26% |
| Manifestation of Embeddedness | Point of Potential Dissonance | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Theory | Intervention | Problem & Outcome | |
| Epistemological Dissonance | Different expected benefits Interpretation of cause-effect relationship Sufficiency of context-relevant evidence and experience Credible knowledge transmitted through social networks | View that obedience of or collaboration with outsiders contributes to the loss of sovereignty Perceptions of unintended consequences | Resistance to economic rationalization of nature as a resource Outsiders’ diagnosis of differences as problems: imposed underdevelopment Prominence of individualistic desires |
| Values & Priorities | Moral environmental prioritization Focus on reciprocity over accumulation Lifestyle or routine change may not be worth the projected outcome | Social harmony, prioritization of community-wide beliefs and practices Social cost of increased integration with monetary economy Social factors such as status may outweigh the desire for a projected outcome Program governance structures incompatible with community organization (e.g. third-party certifications) | Different desirability of projected outcomes Individuality vs. collectivity; importance of externalities caused Importance of preserving traditional practices and aesthetics Perceived non-economic tradeoffs |
| Institutional & Historical Factors | Failed past interventions may undermine credibility of proposed theories History of prior interventions oppose adoption of conflicting/updated theories Private interests promote opposing theories, e.g. agrochemical sellers Lack of confidence in own ability to achieve projected outcome via intervention Suspicion of conflict of interest | Development program support that incentivizes “pseudo-adoption” Outsider demand for performance implies value, requiring compensation Land tenure: permission, expectation of continued access Resource constraints: inability to execute despite buy-in Disruption of status-quo & current distribution of power | Implanted view of inferiority, rejection of local knowledge, mistrust of community, and individualization Resource scarcity & prioritization (relative scale of problems) Limited access to basic social services Outcome attractiveness influenced by institutions (e.g. subsidies, market access, permissions) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wienhold, K.; Goulao, L.F. The Embedded Agroecology of Coffee Agroforestry: A Contextualized Review of Smallholder Farmers’ Adoption and Resistance. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086827
Wienhold K, Goulao LF. The Embedded Agroecology of Coffee Agroforestry: A Contextualized Review of Smallholder Farmers’ Adoption and Resistance. Sustainability. 2023; 15(8):6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086827
Chicago/Turabian StyleWienhold, Karl, and Luis F. Goulao. 2023. "The Embedded Agroecology of Coffee Agroforestry: A Contextualized Review of Smallholder Farmers’ Adoption and Resistance" Sustainability 15, no. 8: 6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086827
APA StyleWienhold, K., & Goulao, L. F. (2023). The Embedded Agroecology of Coffee Agroforestry: A Contextualized Review of Smallholder Farmers’ Adoption and Resistance. Sustainability, 15(8), 6827. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086827







