Manganese Adsorption onto Permanganate-Modified Bamboo Biochars from Groundwater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Simulated Groundwater
2.2. Adsorbents
2.3. Characterization of Adsorbents
2.4. Adsorption Experiments
2.4.1. Study of Contact Time
2.4.2. Adsorption Kinetics
2.4.3. Adsorption Isotherms
2.5. Thermodynamics Calculations
2.6. Chemical Fractionization
3. Results and Discussion
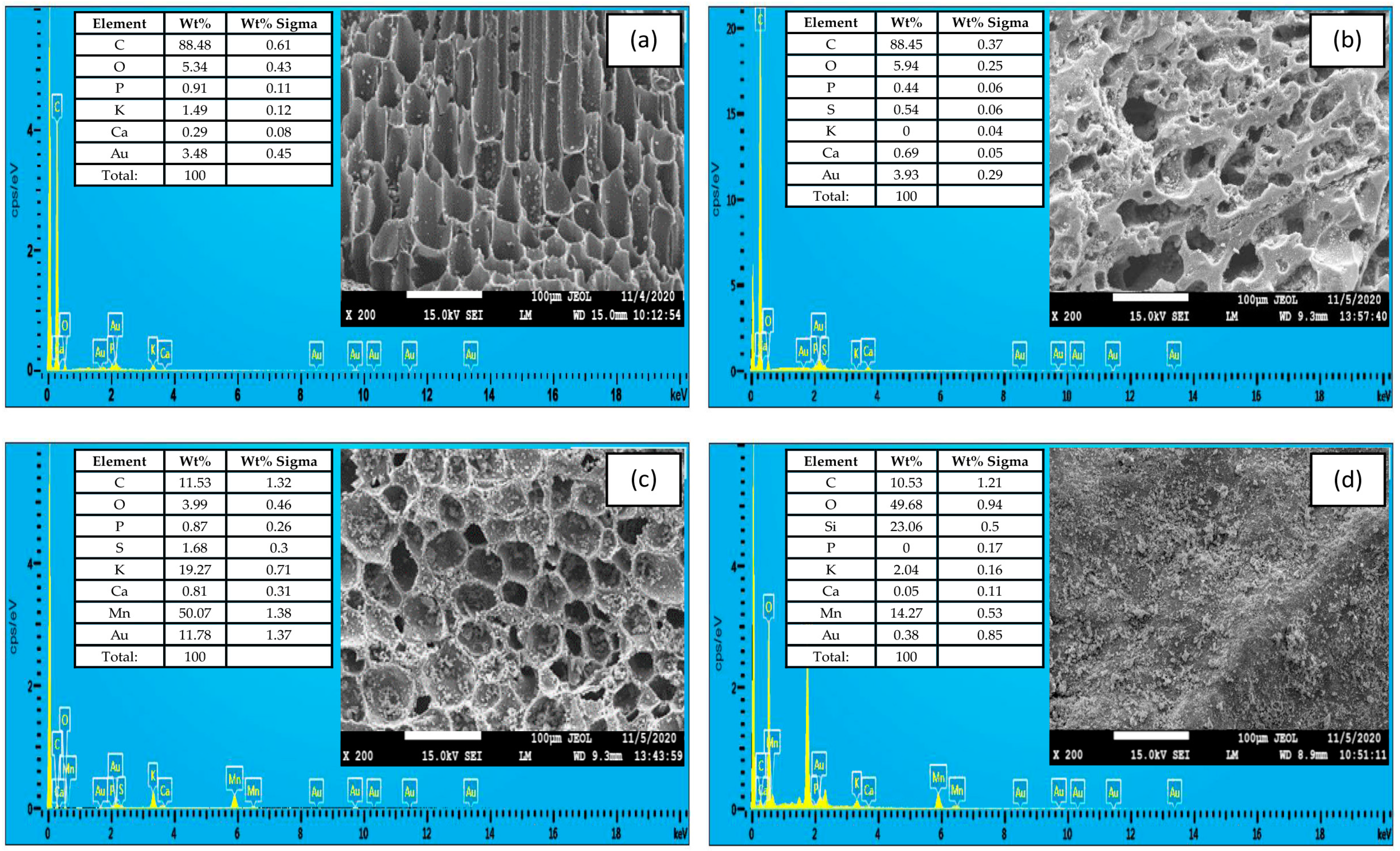
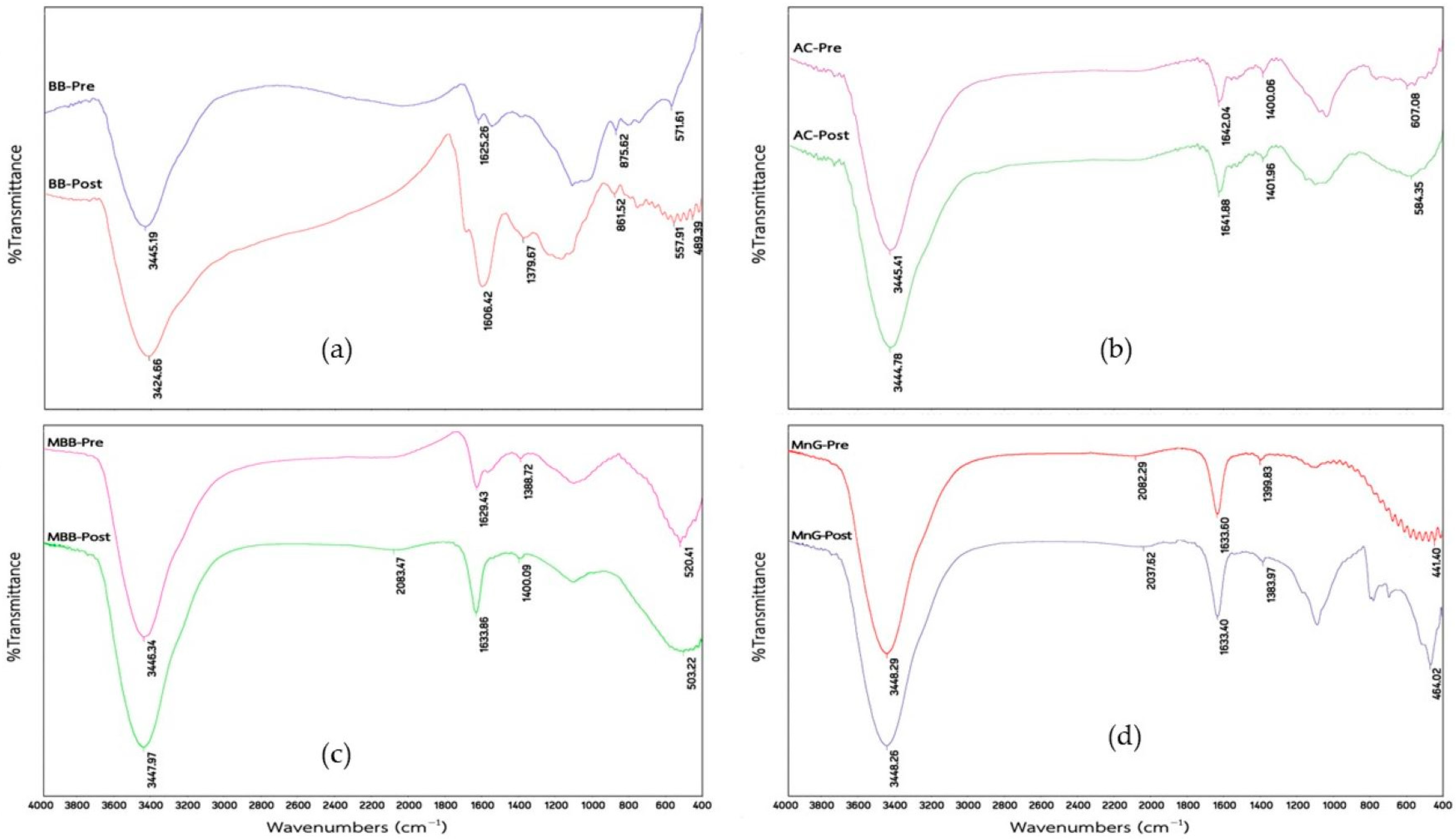
3.1. Characteristics of Biochar
3.2. Batch Experiments
3.3. Adsorption Kinetics
3.4. Adsorption Performance and Isotherm Fitting
3.5. Thermodynamic Studies
3.6. Mn Fractionization of Adsorbents
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World-Health-Organization. Drinking Water Safety Management. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240045064 (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Riojas-Rodríguez, H.; Solís-Vivanco, R.; Schilmann, A.; Montes, S.; Rodríguez, S.; Ríos, C.; Rodríguez-Agudelo, Y. Intellectual function in Mexican children living in a mining area and environmentally exposed to manganese. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 1465–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, M.F.; Sauvé, S.; Barbeau, B.; Legrand, M.; Brodeur, M.È.; Bouffard, T.; Limoges, E.; Bellinger, D.C.; Mergler, D. Intellectual impairment in school-age children exposed to manganese from drinking water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossgrove, J.; Zheng, W. Manganese toxicity upon overexposure. NMR Biomed. 2004, 17, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groundwater Analysis Division, Notification of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment, B.E.2551 (2008). Water Quality Standards Groundwater Used for Consumption. Available online: http://www.dgr.go.th/dga/th/about/350 (accessed on 11 November 2022).
- Patil, D.S.; Chavan, S.M.; Oubagaranadin, J.U.K. A review of technologies for manganese removal from wastewaters. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2006, 4, 468–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xiong, W.; Huang, T. Catalytic oxidation removal of manganese from groundwater by iron–manganese co-oxide filter films under anaerobic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yan, Z.; Du, X.; Bai, L.; Yu, H.; Ding, A.; Li, G.; Liang, H.; Aminabhavi, T.M. Removal of manganese from groundwater in the ripened sand filtration: Biological oxidation versus chemical auto-catalytic oxidation. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 382, 123033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, T.; Wen, G.; Cao, X. The simultaneous removal of ammonium and manganese from groundwater by iron-manganese co-oxide filter film: The role of chemical catalytic oxidation for ammonium removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, C.; Zhang, S. Effects of dissolved oxygen on the start-up of manganese oxides filter for catalytic oxidative removal of manganese from groundwater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 371, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahpeima, S.; Javanbakht, V.; Esmaili, J. Synthesis and characterization of activated carbon/maghemite/starch magnetic bionanocomposite and its application for permanganate removal from aqueous solution. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2018, 28, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffarel, S.R.; Rubio, J. Removal of Mn2+ from aqueous solution by manganese oxide coated zeolite. Miner. Eng. 2010, 23, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavuz, Ö.; Altunkaynak, Y.; Güzel, F. Removal of copper, nickel, cobalt and manganese from aqueous solution by kaolinite. Water Res. 2003, 37, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Bastida, C.; Martínez-Miranda, V.; Solache-Ríos, M.; Linares-Hernández, I.; Teutli-Sequeira, A.; Vázquez-Mejía, G. Drinking water characterization and removal of manganese. Removal of manganese from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Batool, S.; Ullah, H.; Hussain, Q.; Al-Wabel, M.I.; Ahmad, M.; Hussain, A.; Riaz, M.; Sik, O.Y.; Kong, J. Adsorption and thermodynamic mechanisms of manganese removal from aqueous media by biowaste-derived biochars. J. Liq. 2018, 266, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalhruaitluanga, H.; Jayaram, K.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Kumar, K.K. Lead (II) adsorption from aqueous solutions by raw and activated charcoals of Melocanna baccifera Roxburgh (bamboo)—A comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 175, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jjagwe, J.; Olupot, P.W.; Menya, E.; Kalibbala, H.M. Synthesis and application of granular activated carbon from biomass waste materials for water treatment: A review. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 292–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Niu, D.; Sang, W.; Verpoort, F. Investigating the sorption behavior of cadmium from aqueous solution by potassium permanganate-modified biochar: Quantify mechanism and evaluate the modification method. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8330–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Shi, Q.; Zeng, H.; Lu, Z.; Bi, J.; Zhang, H.; Rinklebe, J.; Lima, E.C.; Rashid, A.; Shahab, A. Efficient removal of Cd (II) from aqueous environment by potassium permanganate-modified eucalyptus biochar. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.L.; Zeng, H.H.; Lin, H.; Asfandyar, S.; Shi, Q.L.; Zhang, H. Adsorption Characteristics of Pb (Ⅱ) on Eucalyptus Biochar Modified by Potassium Permanganate. Huan Jing Ke Xue Huanjing Kexue 2021, 42, 5440–5449. [Google Scholar]
- Piispanen, J.K.; Sallanko, J.T. Mn (II) removal from groundwater with manganese oxide-coated filter media. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2010, 45, 1732–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Lv, J.; Feng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xia, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, C.; Zeng, K.; Liu, Y.; et al. Simple one-pot synthesis of manganese dioxide modified bamboo-derived biochar composites for uranium (vi) removal. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 14427–14438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.P.G.C.; Campbell, P.G.; Bisson, M.J.A.C. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, D.; Gao, F.; Li, M.; Luo, X. Effects of biochar-derived sewage sludge on heavy metal adsorption and immobilization in soils. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouddane, B.; Martin, E.; Boughriet, A.; Fischer, J.C.; Wartel, M. Speciation of dissolved and particulate manganese in the Seine River estuary. Mar. Chem. 1997, 58, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obey, G.; Adelaide, M.; Ramaraj, R. Biochar derived from non-customized matamba fruit shell as an adsorbent for wastewater treatment. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2022, 7, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffarel, S.R.; Rubio, J. On the removal of Mn2+ ions by adsorption onto natural and activated Chilean zeolites. Miner. Eng. 2009, 22, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuwen, H.E.; Huimin, Y.A.N.G.; Yong, H.E. Treatment of mine water high in Fe and Mn by modified manganese sand. Min. Sci. Technol. 2010, 20, 571–575. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Elevated manganese concentrations in shallow groundwater of various aquifers in a rapidly urbanized delta, south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.H.; Szeto, Y.S.; McKay, G. Intraparticle diffusion processes during acid dye adsorption onto chitosan. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 2897–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1916, 38, 2221–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempkin, M.I.; Pyzhev, V. Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Phys. Chim. USSR 1940, 12, 327. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Padmesh, T.V.N.; Palanivelu, K.; Velan, M. Biosorption of nickel (II) ions onto Sargassum wightii: Application of two-parameter and three-parameter isotherm models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabani, M.; Amrane, A.; Bensmaili, A. Kinetic modelling of the adsorption of nitrates by ion exchange resin. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 125, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Kyzas, G.Z. Are the thermodynamic parameters correctly estimated in liquid-phase adsorption phenomena. J. Mol. Liq. 2016, 218, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.J.; Budarin, V.; Luque, R.; Clark, J.H.; Macquarrie, D.J. Tuneable porous carbonaceous materials from renewable resources. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3401–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.S.; Vijay, V.K.; Chandra, R.; Kumar, H. Production and characterization of biochar produced from slow pyrolysis of pigeon pea stalk and bamboo. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 3, 100101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Outram, J.G.; Couperthwaite, S.J.; Millar, G.J. Comparitve analysis of the physical, chemical and structural characteristics and performance of manganese greensands. J. Water Process Eng. 2016, 13, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knocke, W.R.; Hamon, J.R.; Thompson, C.P. Soluble manganese removal on oxide-coated filter media. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1988, 80, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.A.; Goodwill, J.E.; Bouchard, R.; Tobiason, J.E.; Knocke, W.R. Characterization of filter media MnOx (s) surfaces and Mn removal capability. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 2010, 102, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Liu, J.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Z.; Gong, X.; Lu, C. Manganese oxide coated river sand for Mn (II) removal from groundwater. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 90, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Q.; Chen, M.; Hu, T.; and Meng, C. Synthesis and characterization of Mn-Silicalite-1 by the hydrothermal conversion of Mn-magadiite under the neutral condition and its catalytic performance on selective oxidation of styrene. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 268, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.B.; Zhou, J.L.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chen, M. Progress in the preparation and application of modified biochar for improved contaminant removal from water and wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 214, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, H.; Yang, X.; Hu, W.; Liang, F.; Mi, B. Ash fusion characteristics of bamboo, wood and coal. Energy 2018, 161, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köse, K.; Mavlan, M.; Uzun, L.; Youngblood, J.P. Cholesterol removal via cyclodextrin-decoration on cellulose nanocrystal (CNC)-grafted poly (HEMA-GMA) nanocomposite adsorbent. Cellulose 2021, 28, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Alazba, A.A.; Amin, M.T. Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using date palm as a biosorbent: A comparative review. Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Hu, J.; Sheng, G.; Zhao, G.; Huang, Q. Effect of pH, ionic strength, foreign ions and temperature on the adsorption of Cu (II) from aqueous solution to GMZ bentonite. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2009, 349, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letterman, R.D.; Amirtharajah, A.; O’Melia, C.R. Coagulation and Flocculation. In Water Quality and Treatment, a Handbook of Community Water Supplies, American Water Works Association, 5th ed.; Letterman, R.D., Ed.; McGraw-Hill, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Available online: http://www.aeb-water.com/book/water_quality_and_treatment.pdf (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, X.; Jia, X.; Cai, M.; Bao, Y. Preparation of Si–Mn/biochar composite and discussions about characterizations, advances in application and adsorption mechanisms. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltrėnaitė-Gedienė, E.; Leonavičienė, T.; Baltrėnas, P. Comparison of Cu (II), Mn (II) and Zn (II) adsorption on biochar using diagnostic and simulation models. Chemosphere 2020, 245, 125562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunge, S.; Singh, S.; Sinha, A. Magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles from tea waste for arsenic removal. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2014, 356, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şenol, Z.M.; Şimşek, S. Insights into effective adsorption of lead ions from aqueous solutions by using chitosan-bentonite composite beads. J. Polym. Environ. 2022, 30, 3677–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Da'ana, D.A. Guidelines for the use and interpretation of adsorption isotherm models: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 393, 122383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.; Ahsan, M.; Pandey, V.; Singh, A.; Mishra, D.; Tiwari, N.; Singh, P.; Karak, T.; Khare, P. Comparative assessment for removal of anionic dye from water by different waste-derived biochar vis a vis reusability of generated sludge. Biochar 2022, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akl, M.A.; Yousef, A.M.; AbdElnasser, S. Removal of iron and manganese in water samples using activated carbon derived from local agro-residues. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 2013, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, K.A.; Rao, A.V. Adsorption of Mn (II) from aqueous solutions using pithacelobium dulce carbon. Rasayan J. Chem. 2008, 1, 840–852. [Google Scholar]
- Şenol, Z.M.; Keskin, Z.S.; Şimşek, S. Synthesis and characterization of a new hybrid polymer composite (pollene@ polyacrylamide) and its applicability in uranyl ions adsorption. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavlieva, M.P.; Geneiva, S.D.; Georgieva, V.G.; Vlaev, L.T. Thermodynamics and kinetics of the removal of manganese (II) ions from aqueous solutions by white rice husk ash. J. Molecular Liquids 2017, 211, 938–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inam, E.; Etim, U.J.; Akpabio, E.G.; Umoren, S.A. Process optimization for the application of carbon from plantain peels in dye abstraction. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2017, 11, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, T.; Herath, I.; Kumarathilaka, P.; Heu, Z.Y.; Ok, Y.S.; Vithanage, M. Efficacy of woody biomass and biochar for alleviating heavy metal bioavailability in serpentine soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, A.; Lloréns, M.; Sáez, J.; Aguilar, M.I.; Ortuño, J.F.; Meseguer, V.F. Comparative study of six different sludges by sequential speciation of heavy metals. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omri, A.; Benzina, M. Removal of manganese (II) ions from aqueous solutions by adsorption on activated carbon derived a new precursor: Ziziphus spina-christi seeds. Alex. Eng. J. 2012, 51, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.M.; Martell, A.E. Critical Stability Constants. Inorganic Complexes; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1976; Volume 4, p. 5. [Google Scholar]


| Parameter | Analytical Method | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | Electrometric Method | - | 6.78 |
| Chloride | Argentometric Method | mg L−1 | 140 |
| Total Hardness | EDTA Titrimetric Method | mg L−1 as CaCO3 | 420 |
| Total Dissolved Solids | Gravimetric Method | mg L−1 | 625 |
| Sulfate | Turbidimetric Method | mg L−1 | 25.28 |
| Nitrate | Colorimetric Method | mg L−1 | 2.99 |
| Ferrous | ICP-OES * | mg L−1 | 0.174 |
| Manganous | ICP-OES * | mg L−1 | 1.098 |
| Magnesium | EDTA Titrimetric Method | mg L−1 as CaCO3 | 12.91 |
| Calcium | EDTA Titrimetric Method | mg L−1 as CaCO3 | 34.75 |
| Fraction | Extractable Solvent | Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|
| Water—soluble (F1) | Deionized water | 20 |
| Exchangeable (F2) | 1M Ammonium acetate, pH 7 (Analytical grade, 98%, Q RëC™, Auckland, New Zealand) | 20 |
| Bound to Carbonate (F3) | 1M Ammonium acetate, pH 5 | 20 |
| Bound to Iron and Manganese Oxide (F4) | 0.04 M Hydroxylamine hydrochloride in 25%, acetic acid (v v−1), pH 3 (Hydroxylamine hydrochloride, analytical grade, 99%, Q RëC™, Auckland, New Zealand and acetic acid, 100%, MercK, Darmstadt, Germany) | 20 |
| Bound to Organic Matter (F5) | 30% Hydrogen peroxide (adjust pH = 2, HNO3) (Analytical grade, 30%, Q RëC™, Auckland, New Zealand | 15 |
| +3.2 M Ammonium acetate in 20% HNO3 (v v−1) (Analytical grade, 98%, Q RëC™, Auckland, New Zealand), | 5 | |
| Residual (F6) | 7 M HNO3 | 20 |
| Adsorbents | pHDI | pHpzc | Iodine No. | BET Surface Area | Pore Volume | Pore Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg g−1 | m2 g−1 | cc g−1 | Å | |||
| AC | 7.52 | 7.43 | 271.96 | 806.4 | 0.470 | 12.38 |
| BB | 8.62 | 8.10 | 67.55 | 176.2 | 0.143 | 15.21 |
| MBB | 3.70 | 7.85 | 69.13 | 104.2 | 0.079 | 15.33 |
| MnG | 3.02 | 4.72 | 6.14 | 0.147 | 0.001 | 223.10 |
| Composition | Weight (% w w−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | BB | MBB | MnG | |
| Si | 25.200 | 7.930 | 3.570 | 58.80 |
| Ca | 21.900 | 7.780 | 5.600 | 1.780 |
| Fe | 16.100 | 0.318 | - | 2.320 |
| S | 12.100 | 2.870 | 1.340 | 12.00 |
| P | 8.560 | 7.060 | 3.410 | 0.302 |
| Al | 7.270 | 0.161 | 0.081 | 4.260 |
| Cl | 2.280 | 5.620 | 1.020 | - |
| Ti | 1.960 | - | - | - |
| Zn | 1.290 | 0.327 | 0.111 | - |
| Mg | 1.090 | 2.690 | 1.750 | 0.689 |
| Cu | 0.895 | - | - | - |
| K | 0.654 | 64.50 | 24.80 | 11.20 |
| Ni | 0.541 | - | - | - |
| Cr | 0.160 | - | - | - |
| Mn | - | 0.700 | 58.30 | 8.610 |
| Adsorbents | mg g−1 | PFO | R2 | PSO | R2 | Intraparticle Diffusion | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| h−1 | mg g−1 | g mg−1h−1 | mg g−1 | mg g−1 min−1/2 | |||||
| AC | 0.088 | 0.036 | 23.02 | 0.796 | 16.741 | 0.092 | 0.999 | 0.0002 | 0.0134 |
| BB | 0.076 | 0.063 | 9.743 | 0.949 | 2.725 | 0.080 | 0.991 | 0.0001 | 0.0062 |
| MBB | 4.700 | 0.019 | 0.198 | 0.918 | 0.015 | 6.954 | 0.956 | 0.0059 | 0.1165 |
| MnG | 2.120 | 0.006 | 0.017 | 0.129 | 11.085 | 3.579 | 0.986 | 0.0114 | 0.3019 |
| Adsorbents | Langmuir Isotherm | RL | Freundlich Isotherm | R2 | Temkin Isotherm | R2 | D-R Isotherm | R2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | |||||||||||||
| mg g−1 | L mg−1 | (mg g−1) (mg L−1)1/n | kJ mol−1 | L g−1 | kJ mol−1 | mol2 kJ−2 | |||||||
| AC | 0.620 | 0.812 | 0.959 | 0.135 | 0.174 | 1.912 | 0.740 | 0.114 | 0.8471 | 0.829 | 3.774 | 0.0351 | 0.945 |
| BB | 0.803 | 0.308 | 0.990 | 0.292 | 0.160 | 1.313 | 0.945 | 0.128 | 0.8651 | 0.998 | 3.026 | 0.0546 | 0.998 |
| MBB | 21.277 | 0.378 | 0.966 | 0.252 | 5.384 | 1.346 | 0.956 | 12.946 | 0.0147 | 0.835 | 1.671 | 0.1790 | 0.797 |
| MnG | 24.450 | 0.229 | 0.990 | 0.357 | 4.305 | 1.288 | 0.980 | 8.503 | 0.0178 | 0.964 | 1.697 | 0.1737 | 0.887 |
| Adsorbents | Initial pH | Type of Water | Initial Mn Concentration mg L−1 | mg g−1 | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Farmyard manure-derived biochar | 6 | Mn solution | 2 | 6.652 | [15] |
| Activated carbon modified by nitric acid | 5–6 | Mn solution | 5 | 10.00 | [55] |
| Activated carbon modified by persulfate | 5–6 | Mn solution | 5 | 6.660 | [55] |
| Pithecellobium dulce carbon | 7.2 | Mn solution | 5 | 0.415 | [56] |
| BB | 6.78 | Groundwater | 5 | 0.803 | This study |
| MBB | 6.78 | Groundwater | 5 | 21.27 | This study |
| Adsorbents | Temperature (K) | Thermodynamics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔG° | ΔH° | ΔS° | ||
| kJ mol−1 | kJ mol−1 | J mol−1K−1 | ||
| BB | 298 | −33.89 | 52.88 | 290.41 |
| 303 | −34.65 | |||
| 308 | −36.81 | |||
| AC | 298 | −33.57 | 309.40 | 1148.41 |
| 303 | −37.09 | |||
| 308 | −45.10 | |||
| MBB | 298 | −35.62 | −14.93 | 68.55 |
| 303 | −35.16 | |||
| 308 | −36.32 | |||
| MnG | 298 | −37.21 | 103.63 | 466.44 |
| 303 | −33.90 | |||
| 308 | −42.00 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilamas, A.; Vinitnantharat, S.; Pinisakul, A. Manganese Adsorption onto Permanganate-Modified Bamboo Biochars from Groundwater. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6831. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086831
Wilamas A, Vinitnantharat S, Pinisakul A. Manganese Adsorption onto Permanganate-Modified Bamboo Biochars from Groundwater. Sustainability. 2023; 15(8):6831. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086831
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilamas, Arachaporn, Soydoa Vinitnantharat, and Anawat Pinisakul. 2023. "Manganese Adsorption onto Permanganate-Modified Bamboo Biochars from Groundwater" Sustainability 15, no. 8: 6831. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086831
APA StyleWilamas, A., Vinitnantharat, S., & Pinisakul, A. (2023). Manganese Adsorption onto Permanganate-Modified Bamboo Biochars from Groundwater. Sustainability, 15(8), 6831. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15086831








