Assessment of Sighted and Visually Impaired Users to the Physical and Perceptual Dimensions of an Oasis Settlement Urban Park
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodological Approach
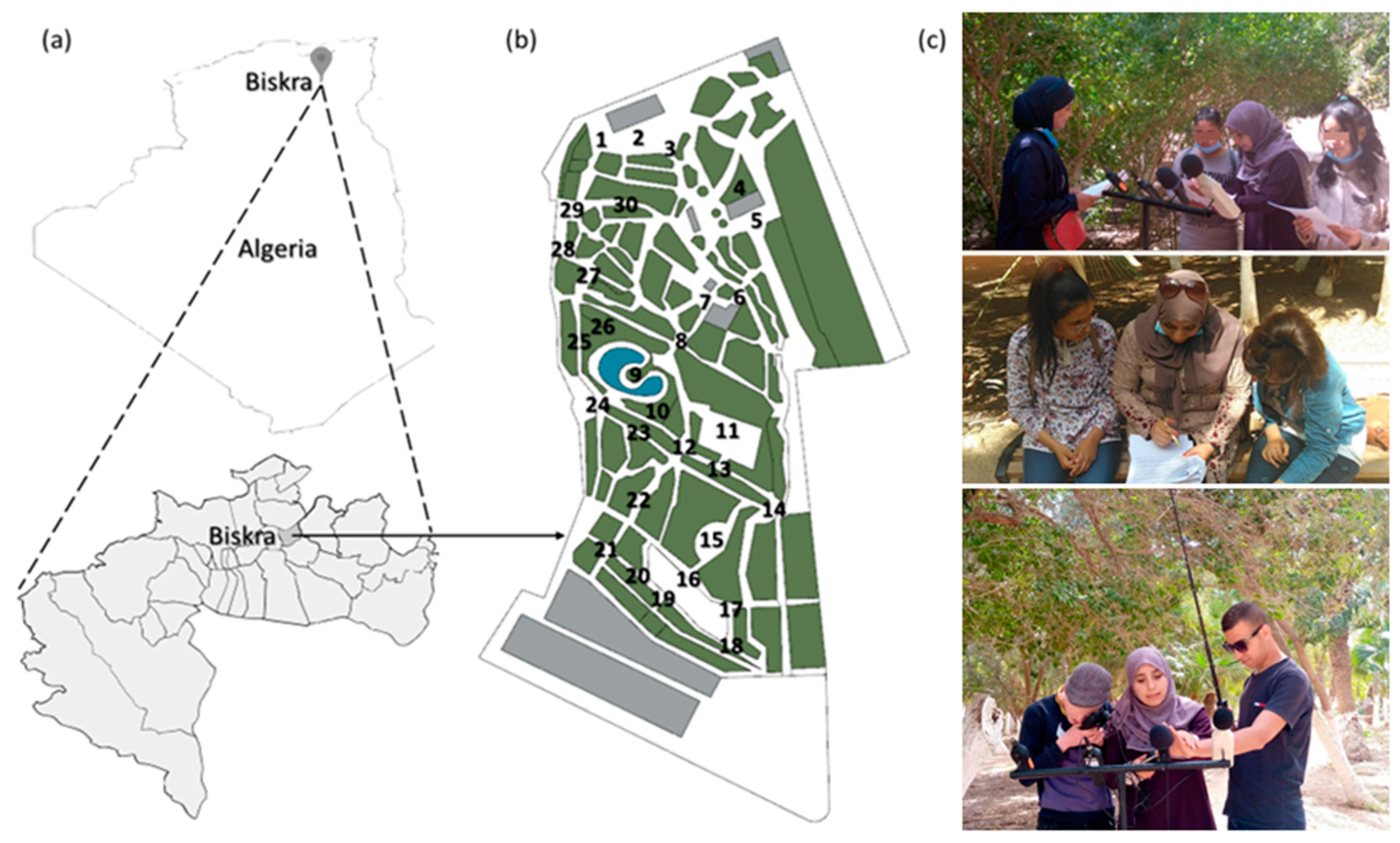
2.1. Stage 1: Physical Dimensions Measurement
2.2. Stage 2: Field Surveys (Perceptual Characterization)
2.3. Participants
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Physical Characterization of the Park
3.2. Perceptual Characterization of the Park
3.2.1. Emotional Salience of Sound
3.2.2. Evaluation of the Restorative Quality of The Park Environments
| Components | Groups | Visually Impaired People | Sighted People | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSP | MSP | PSP | MSP | |||
| Items n. | Overall Meaning of the Items | (A) | (A) | (A) | (A) | |
| Fascination | Item1 | Fascinating place | 9.29 (±2.17) | 9.11 (±1.99) | 9.65 (±0.61) | 9.60 (±1.09) |
| Item2 | Interesting place | 8.18 (±2.81) | 8.69 (±2.89) | 8.65 (±2.03) | 9.00 (±2.32) | |
| Item3 | Place hard to be bored | 7.41 (±3.22) | 8.60 (±2.81) | 8.47 (±2.16) | 8.86 (±2.39) | |
| Being-Away | Item4 | Refuge from nuisances | 8.00 (±2.39) | 7.86 (±3.75) | 8.59 (±1.46) | 7.89 (±2.99) |
| Item5 | Self-isolation | 7.18 (±3.39) | 6.86 (±4.08) | 6.53 (±3.43) | 8.60 (±1.75) | |
| Item6 | Escaping responsibility | 5.94 (±3.49) | 6.00 (±4.36) | 7.94 (±2.73) | 5.86 (±4.09) | |
| Coherence | Item7 | Good spatial arrangement | 6.65 (±2.83) | 6.14 (±3.94) | 8.35 (±1.66) | 8.71 (±2.09) |
| Item8 | Physical arrangement of the place | 5.94 (±3.96) | 6.77 (±4.17) | 8.41 (±1.87) | 8.29 (±2.74) | |
| Item9 | Tidy place | 7.59 (±1.94) | 8.20 (±3.09) | 8.53 (±1.88) | 7.80 (±2.74) | |
| Scope | Item10 | Exploration in many directions | 6.88 (±3.32) | 8.14 (±3.18) | 9.18 (±1.29) | 9.54 (±0.85) |
| Item11 | Few moving boundaries | 4.82 (±3.99) | 5.49 (±4.46) | 8.94 (±1.19) | 2.80 (±2.79) | |
3.2.3. Analysis of the Semantic Differential Scale of Multivariable Evaluation of the Park Users
4. Conclusions and Discussion
4.1. Synthesizing the Findings
4.2. Strengths and Limitations of the Study
4.3. Implication on Practice and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Select for each descriptor below. the number (1—not at all to 7—extremely) based on how much the descriptor describes the sound you presently heard |
| Pleasant |
| Unpleasant |
| Stimulating |
| Boring |
| Attractive |
| Unattractive |
| Select for each descriptor below. the number (1—not at all to 7—extremely) based on how much the descriptor describes your feeling toward the sound you presently heard |
| Calm |
| Nervous |
| Weak |
| Energetic |
| Happy |
| Sad |
Appendix B
| Please read every sentence carefully and then evaluate on a scale from 0 (Not at all) to 10 (Very much) as each statement corresponds to your experience in this place. |
| Places like that are fascinating |
| In places like this my attention is drawn to many interesting things |
| In places like this it is hard to be bored |
| Places like that are a refuge from nuisances |
| To get away from things that usually demand my attention I like to go to places like this |
| To stop thinking about the things that I must get done I like to go to places like this |
| There is a clear order in the physical arrangement of places like this. |
| In places like this it is easy to see how things are organized. |
| In places like this everything seems to have its proper place. |
| That place is large enough to allow exploration in many directions |
| In places like that there are few boundaries to limit my possibility for moving about. |
Appendix C
| Questions about nature and type of vegetation (from 0—Not at all to 10—Very much) |
| The Park is home to a variety of plants |
| The land is rich in vegetation |
| The grass is suitable for relaxing |
| You can easily get in touch with nature |
| Questions on thermal environment (from 0—Not at all to 10—Very much) |
| The Park has areas shaded by plants |
| I come to the park to stay cool |
| The Park is sunny |
| Questions on acoustic comfort (from 0—Not at all to 10—Very much) |
| In the park you can hear the sounds of nature |
| In the park you can hear a nice background music |
| Inside the park. musicians or singers perform |
| In some places you can hear the flow of water |
| The Park is a quiet place |
| In the park. the noise of vehicular traffic is absent |
| In the park you can hear the children playing |
| There are some parts of the park that are a bit noisy |
| Objective questions (from 0—Not at all to 10—Very much) |
| The paths in the park feature beautiful textures |
| Water is used as an ornamental element |
| The flooring is comfortable and you can walk comfortably |
| There are enough places to sit |
| The seats are comfortable |
| In the park you can feel the scents of nature |
| There are no particular smells in the park |
| In the park you can smell bad smells caused by the presence of waste |
| In the park there are bad smells caused by vehicular traffic |
| Subjective questions (from 0—Not at all to 10—Very much) |
| Inside the park I relax and stop to reflect |
| In the park I can interact with other people |
| In the park I do physical activity |
| In the park I dedicate myself to artistic activities |
| In the park I like to spend time with my family and with my loved ones |
| I use the park for jogging or walking outdoors |
| In the park I feel at peace and I am very well |
| When I’m in the park I have a feeling of pleasure (I feel happy!) |
| In this park I feel at ease and I feel connected to it |
| I am attracted to this place. I will come again |
| I feel safe in the park |
References
- Coté, M. La Ville et le Désert: Le bas-Sahara Algérien; Karthala Éditions: Paris, France, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Cheng, W.; Qi, J. Coordinated evaluation and development model of oasis urbanization from the perspective of new urbanization: A case study in Shandan County of Hexi Corridor, China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzir, T.A.K.; Berkouk, D.; Zemmouri, N. Evaluation and analysis of the Algerian oases soundscape: Case of El Kantara and Sidi Okba. Acoust. Aust. 2020, 48, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haridi, N.M.A.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Ayad, H.M.; El Sayad, Z.T. Comparative Analysis of the Desert and Green Vernacular Architecture in the Oases of Egypt. In Cultural Sustainable Tourism: A Selection of Research Papers from IEREK Conference on Cultural Sustainable Tourism (CST); Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 2017, pp. 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, C.F.B. Green space configuration and its impact on human behavior and URBAN environments. Urban Clim. 2021, 35, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Herzele, A.; Wiedemann, T. A monitoring tool for the provision of accessible and attractive urban green spaces. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 63, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.C.; Maheswaran, R. The health benefits of urban green spaces: A review of the evidence. J. Public Health 2011, 33, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, J.Y.; Hong, J.Y. Classification of urban park soundscapes through perceptions of the acoustical environments. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 141, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesura, A. The role of urban parks for the sustainable city. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 68, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkouk, D.; Bouzir, T.A.K.; Boucherit, S.; Khelil, S.; Mahaya, C.; Matallah, M.E.; Mazouz, S. Exploring the Multisensory Interaction between Luminous, Thermal and Auditory Environments through the Spatial Promenade Experience: A Case Study of a University Campus in an Oasis Settlement. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Luo, T.; Behm, H. Landscape effects on soundscape experience in city parks. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 454, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Kang, J.; Behm, H.; Luo, T. Effects of landscape on soundscape perception: Soundwalks in city parks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 123, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grahn, P.; Stigsdotter, U.K. The relation between perceived sensory dimensions of urban green space and stress restoration. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2010, 94, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothencz, G.; Blaschke, T. Urban parks: Visitors’ perceptions versus spatial indicators. Land Use Policy 2017, 64, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucherit, S.; Berkouk, D.; Bouzir, K.; Masullo, M.; Maffei, L. A Review of Inclusive Design and Multisensory Interactions Studies and Applications in Public Spaces. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2022; p. 012017. [Google Scholar]
- Calleri, C.; Astolfi, A.; Armando, A.; Shtrepi, L. On the ability to correlate perceived sound to urban space geometries. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2016, 27, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitidara, N.P.A.; Sarwono, J.; Suprijanto, S.; Soelami, F.X. The multisensory interaction between auditory, visual, and thermal to the overall comfort in public open space: A study in a tropical climate. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 78, 103622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffei, L.; Boucherit, S.; Berkouk, D.; Masullo, M. Physical and Perceptual Dimensions of Open Urban Spaces in Biskra, Algeria; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Washington, DC, USA, 2021; pp. 3160–3166. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Cruz, S.; Morales-Hernandez, L.A.; Perez-Soto, G.I.; Benitez-Rangel, J.P.; Camarillo-Gomez, K.A. An Outdoor Navigation Assistance System for Visually Impaired People in Public Transportation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 130767–130777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, K.W.M. Accessible park environments and facilities for the visually impaired. Facilities 2013, 31, 590–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediastika, C.E.; Sudarsono, A.S.; Kristanto, L. Using the Sonic Perception to Improve Public Spaces and Develop a Place Identity. Cities’ Vocabularies: The Influences and Formations. In Advances in Science. Technology and Innovation; Mohareb, N., Versaci, A., Mahgoub, Y., Maruthaveeran, S., Alberti, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediastika, C.E.; Sudarsono, A.S.; Kristanto, L. The sound perceptions of urban pavements by sighted and visually impaired people—A case study in Surabaya, Indonesia. J. Urban. Int. Res. Placemaking Urban Sustain. 2022, 15, 106–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botteldooren, D.; Van Renterghem, T.; Guastavino, C.; Can, A.; Fiebig, A.; Wunderli, J.-M.; Kang, J.; Aletta, F. Abstracts of the Second Urban Sound Symposium. Proceedings 2021, 72, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediastika, C.E.; Sudarsono, A.S.; Kristanto, L.; Tanuwidjaja, G.; Sunaryo, R.G.; Damayanti, R. Appraising the sonic environment of urban parks using the soundscape dimension of visually impaired people. Int. J. Urban Sci. 2020, 24, 216–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Xu, X.; Lao, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; García, E.H.; He, L.; Zhu, J. Evaluating the impact of urban green space and landscape design parameters on thermal comfort in hot summer by numerical simulation. Build. Environ. 2017, 123, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, P.; Karimi, E.; Monazzam, M.R.; Abbaspour, M.; Taghavi, L. Analytical comparison of traffic noise indices—A case study in District 14 of Tehran City. J. Low Freq. Noise Vib. Act. Control. 2016, 35, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalawapudi, K.; Singh, T.; Vijay, R.; Goyal, N.; Kumar, R. Effects of COVID-19 pandemic on festival celebrations and noise pollution levels. Noise Mapp. 2021, 8, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guha, A.K.; Chowdhury, A.K.; Debsarkar, A.; Chakrabarty, S. Assessment of Noise Pollution of Kolkata Metro Railway System and Its Impact on Urban Receptors-A Case Study. IJRAT 2020, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunashal, R.B.; Patil, Y.B. Assessment of noise pollution indices in the city of Kolhapur, India. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 37, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniadis, D.; Katsoulas, N.; Papanastasiou, D.Κ. Thermal Environment of Urban Schoolyards: Current and Future Design with Respect to Children’s Thermal Comfort. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, M. Semantic differential analysis of the soundscape in urban open public spaces. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, W.J.; Bruce, N.S.; Murphy, J.E. Soundscape reproduction and synthesis. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2014, 100, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, S.R. The production of a Perceived Restorativeness Soundscape Scale. Appl. Acoust. 2013, 74, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, S.R.; Guastavino, C. Exploring the validity of the Perceived Restorativeness Soundscape Scale: A psycholinguistic approach. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Qiu, L.; Gao, T. Associations between perceived occurrences of different sounds and perceived restorativeness in urban parks. In INTER-NOISE and NOISE-CON Congress and Conference Proceedings; Institute of Noise Control Engineering: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 3449–3456. [Google Scholar]
- Pasini, M.; Berto, R.; Brondino, M.; Hall, R.; Ortner, C. How to measure the restorative quality of environments: The PRS-11. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 159, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masullo, M.; Maffei, L.; Iachini, T.; Rapuano, M.; Cioffi, F.; Ruggiero, G.; Ruotolo, F. A questionnaire investigating the emotional salience of sounds. Appl. Acoust. 2021, 182, 108281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrín, F.; Hernández-Fernaud, E.; Hess, S.; Hernández, B. Discrimination of Urban Spaces with Different Level of Restorativeness Based on the Original and on a Shorter Version of Hartig et al.’s Perceived Restorativeness Scale. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analysis and Evaluation of Road Traffic Noise in Al-Dammam: A Business City of the Eastern Province of KSA. Available online: https://scialert.net/abstract/?doi=jest.2010.47.55 (accessed on 26 February 2023).
- Rennit, P.; Maikov, K. Perceived restoration scale method turned into (used as the) evaluation tool for parks and open green spaces, using Tartu city parks as an example. City Territ. Arch. 2015, 2, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohly, H.; White, M.P.; Wheeler, B.W.; Bethel, A.; Ukoumunne, O.C.; Nikolaou, V.; Garside, R. Attention Restoration Theory: A systematic review of the attention restoration potential of exposure to natural environments. J. Toxicol. Environ. Heal. Part B 2016, 19, 305–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röder, B.; Rösler, F. Memory for environmental sounds in sighted, congenitally blind and late blind adults: Evidence for cross-modal compensation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2003, 50, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, L.E.; Evans, G.W. The Effects of Noise on Pre-School Children’s Pre-Reading Skills. J. Environ. Psychol. 2000, 20, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mediastika, C.E.; Sudarsono, A.S.; Kristanto, L.; Tanuwidjaja, G.; Sunaryo, G.; Damayanti, R. Recalling the sonic perception of visually impaired people of Surabaya’s urban parks. In Proceedings of the MATEC Web of Conferences, Banjarmasin, Indonesia, 11–12 October 2018; p. 02007. [Google Scholar]
- Mediastika, C.E.; Sudarsono, A.S.; Kristanto, L. Indonesian shopping malls: A soundscape appraisal by sighted and visually impaired people. Archit. Eng. Des. Manag. 2020, 18, 184–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carles, J.L.; Barrio, I.L.; De Lucio, J.V. Sound influence on landscape values. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1999, 43, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viollon, S.; Lavandier, C.; Drake, C. Influence of visual setting on sound ratings in an urban environment. Appl. Acoust. 2002, 63, 493–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.Y.; Jeon, J.Y. The effects of audio–visual factors on perceptions of environmental noise barrier performance. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2014, 125, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šakaja, L. The non-visual image of the city: How blind and visually impaired white cane users conceptualize urban space. Soc. Cult. Geogr. 2018, 21, 862–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Descriptive Statistics | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicators | Thermal Environment | Acoustic Environment | |||
| SVF | MRT [°C] | PET [°C] | Leq [dB(A)] | NC [dB(A)] | |
| Measurement Points Number | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Mean | 0.21 | 47.02 | 31.48 | 51.52 | 3.44 |
| Std. Deviation | 0.15 | 4.031 | 3.50 | 2.91 | 2.30 |
| Minimum | 0.040 | 40.80 | 25.50 | 46.54 | 0.21 |
| Maximum | 0.56 | 55.00 | 37.60 | 57.51 | 8.03 |
| ANOVA—FASC | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cases | Sum of Squares | df | Mean Square | F | p | η² | η²p | ω² |
| Age | 53.877 | 1 | 53.877 | 21.568 | <0.001 | 0.171 | 0.177 | 0.162 |
| Health condition | 9.819 | 1 | 9.819 | 3.931 | 0.050 | 0.031 | 0.038 | 0.023 |
| Age ✻ Health condition | 2.031 | 1 | 2.031 | 0.813 | 0.369 | 0.006 | 0.008 | 0.000 |
| Residuals | 249.800 | 100 | 2.498 | |||||
| Components | Code | Variables | Average (SIG and VIP) | SD | Mean Ranks (SIG) | Mean Ranks (VIP) | Sig. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nature and type of vegetation | NV1 | Plant variety | 9.39 | 1.28 | 72.37 | 66.03 | 0.251 |
| NV3 | Vegetation riches | 9.24 | 1.48 | 72.37 | 66.04 | 0.276 | |
| NV4 | Relaxation in the grass | 6.86 | 3.56 | 71.28 | 67.86 | 0.616 | |
| NV5 | Touch with nature | 9.17 | 1.45 | 72.09 | 66.50 | 0.362 | |
| Thermal environment | ThC1 | Shading of plants | 9.53 | 0.99 | 71.09 | 68.18 | 0.599 |
| ThC2 | Cool state | 8.72 | 2.47 | 73.07 | 64.86 | 0.176 | |
| ThC3 | Sunning | 6.4 | 3.62 | 70.32 | 69.46 | 0.900 | |
| Acoustic comfort | AC1 | Natural sounds | 9 | 2.10 | 80.78 | 51.96 | 0.000 |
| AC2 | Music in the background | 6.63 | 3.89 | 83.26 | 47.82 | 0.000 | |
| AC3 | Singers’ Song | 3.96 | 3.70 | 73.51 | 64.13 | 0.178 | |
| AC4 | Water flow sounds | 8.9 | 1.86 | 70.86 | 68.56 | 0.713 | |
| AC5 | Quietness | 9.04 | 1.85 | 67.23 | 74.63 | 0.209 | |
| AC6 | Absence of traffic noise | 6.26 | 4.02 | 65.01 | 78.35 | 0.051 | |
| AC7 | Noise of children playing | 7.72 | 3.45 | 76.81 | 58.61 | 0.005 | |
| AC8 | Noisy | 6.88 | 3.47 | 73.84 | 63.58 | 0.131 | |
| Objective questions related to space | OQ1 | Beautiful textures | 8.6 | 2.36 | 69.82 | 70.31 | 0.94 |
| OQ3 | Ornamental water | 9.25 | 1.78 | 68.86 | 71.90 | 0.582 | |
| OQ5 | Walking Comfortable Floors | 8.62 | 2.36 | 62.76 | 82.12 | 0.002 | |
| OQ6 | Seating areas | 7.26 | 2.62 | 76.86 | 58.52 | 0.008 | |
| OQ9 | Comfortable seating | 6.76 | 2.95 | 78.86 | 55.18 | 0.001 | |
| OQ10 | Scents from nature | 9.14 | 1.92 | 68.56 | 72.40 | 0.499 | |
| OQ11 | Absence of particular smells | 5.64 | 3.99 | 63.18 | 81.41 | 0.009 | |
| OQ12 | Bad smells from waste products | 1.95 | 3.08 | 72.43 | 65.94 | 0.330 | |
| OQ13 | Bad smells from traffic | 1.61 | 2.76 | 71.52 | 67.46 | 0.524 | |
| Subjective questions related to behavior | SQ1 | Relaxation and reflection | 8.2 | 2.85 | 66.21 | 76.34 | 0.116 |
| SQ2 | Interaction with people | 8.91 | 2.18 | 68.34 | 72.77 | 0.444 | |
| SQ3 | Physical activity | 7.29 | 3.50 | 64.79 | 78.71 | 0.041 | |
| SQ4 | Artistic activity | 4.13 | 3.91 | 67.23 | 74.63 | 0.282 | |
| SQ5 | Spending time with family and friends | 8.55 | 2.52 | 74.62 | 62.27 | 0.049 | |
| SQ6 | Jogging and walking | 8.12 | 2.94 | 69.36 | 71.07 | 0.791 | |
| SQ7 | Feeling of peace | 9.14 | 1.69 | 70.10 | 69.83 | 0.961 | |
| SQ8 | Feeling of pleasure | 9.49 | 1.26 | 68.87 | 71.88 | 0.548 | |
| SQ9 | Feeling of ease and connection to the park | 8.99 | 1.65 | 70.06 | 69.90 | 0.98 | |
| SQ10 | The attraction | 9.28 | 1.53 | 67.57 | 74.06 | 0.257 | |
| SQ11 | Feeling of security | 9.5 | 1.28 | 69.35 | 71.09 | 0.732 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boucherit, S.; Maffei, L.; Masullo, M.; Berkouk, D.; Bouzir, T.A.K. Assessment of Sighted and Visually Impaired Users to the Physical and Perceptual Dimensions of an Oasis Settlement Urban Park. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15087014
Boucherit S, Maffei L, Masullo M, Berkouk D, Bouzir TAK. Assessment of Sighted and Visually Impaired Users to the Physical and Perceptual Dimensions of an Oasis Settlement Urban Park. Sustainability. 2023; 15(8):7014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15087014
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoucherit, Samiha, Luigi Maffei, Massimiliano Masullo, Djihed Berkouk, and Tallal Abdel Karim Bouzir. 2023. "Assessment of Sighted and Visually Impaired Users to the Physical and Perceptual Dimensions of an Oasis Settlement Urban Park" Sustainability 15, no. 8: 7014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15087014
APA StyleBoucherit, S., Maffei, L., Masullo, M., Berkouk, D., & Bouzir, T. A. K. (2023). Assessment of Sighted and Visually Impaired Users to the Physical and Perceptual Dimensions of an Oasis Settlement Urban Park. Sustainability, 15(8), 7014. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15087014








