Abstract
Fine and ultrafine particulate matter are consequences of air pollution in industrialized nations. The use of natural materials for filters produces fewer side effects for humans and the environment, and due to their structural characteristics, they have the potential to effectively filter out fine particles. In this study, we developed an indoor, fine-dust removal filter using Hanji, a traditional Korean paper made from natural materials derived from mulberry trees. We impregnated activated carbon (AC) into the Hanji filter and conducted air permeability and efficiency experiments to determine the improvement in indoor air quality. The Hanji filter showed a removal efficiency of 80.4% within the first minute and 99.1% efficiency by the 38th minute, maintaining an efficiency of >99% thereafter. The dust removal efficiency of the AC-embedded Hanji filter proved superior. The dust adhesion was ~20 g/m2. An AC-embedded Hanji filter has the potential to remove not only fine dust but also volatile substances. The use of natural filters is both effective and sustainable.
1. Introduction
Due to rapid industrialization and urbanization in East Asia, the region faces various environmental issues, including an increase in air pollution caused by heightened energy and vehicle usage [1,2]. Since 2013, the World Health Organization (WHO) has classified fine particles (PM10) and ultrafine particles (PM2.5), which can penetrate both respiratory and skin barriers and cause severe damage to the body, as Group 1 carcinogens [3,4]. Accordingly, there is a continuous demand for the development of technologies to reduce fine dust levels [5,6,7]. The primary sources of fine dust are air pollutants reacting in the atmosphere, emissions from burning fossil fuels such as coal and oil, and lastly, soil dust from the ground [8,9]. Exposure to such fine dust particles can lead to various respiratory diseases and they can penetrate the skin, causing various skin and eye conditions [10].
Air purifiers and filter technologies have been extensively developed and commercialized to remove such fine dust [11]. Most technologies for removing particulate matter from the air rely on trapping mechanisms [12]. Of these, dust collection technologies can be categorized into filters for larger particles and those for fine dust. For filters used to remove larger particles like solids, mesh-shaped filters made of PP (polypropylene) or PE (polyethylene) are typical, and they can be washed with water after a certain duration of use and reused for an extended period [13]. Filters for fine dust removal typically employ a low-pressure drop; electrostatic, nonwoven filters; or simple, electric filters [14].
Recently, high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters; electrostatic filters combining electrostatic precipitation with electrostatic nonwovens, catalysts, or photocatalysts; and plasma filters have been adopted for the simultaneous removal of dust and odors [15,16]. Physical filters are used to remove indoor fine dust, and the raw materials for these filters primarily consist of glass fibers (nonwovens) and polypropylene. These filters are produced using chemical adhesives, which is regrettable in terms of eco-friendliness for indoor environments [17,18].
Lately, there has been growing interest in developing sustainable materials, such as creating filters from natural materials [19,20]. When using natural materials as raw materials for filters, they are extracted from renewable resources, making them environmentally friendly. Additionally, they can decompose after use, alleviating waste disposal issues. Moreover, natural materials have fewer side effects on humans and the environment, and due to their structural characteristics, they have the potential to effectively filter out fine particles [21]. There are several considerations when making filters from natural materials, including the durability of the material, ease of the manufacturing process, performance of the filter, and issues with maintenance [18].
Hanji is a traditional paper used mainly in Korea and the surrounding East Asian region [22,23,24]. It is made from natural fibers of plants, primarily from paper mulberry, grasses, cotton, and gourds. Traditionally, people in Korea primarily applied Hanji to doors and windows as window paper. In this usage, Hanji subtly filtered the sunlight and also played a role in regulating indoor humidity [25]. Its main ingredient is cellulose, which possesses high dispersibility in water and has a large surface area, making it effective at filtering fine particles. The cellulose in Hanji has structural characteristics that include hydroxyl groups (-OH) with high hydrophilicity, easily forming hydrogen bonds. Although hydrogen bonds are weaker than chemical bonds, they form long and numerous bonds, resulting in a strong binding force. Previous studies applied cellulose filters to remove particulate and gaseous contaminants in an indoor environment [26,27,28]. In addition, activated carbon was impregnated in cellulose filters to improve their adsorption efficiency of target contaminants. Also, several studies that used Hanji as a filter to separate particles have been carried out [29]. Thus, unlike other paper materials, Hanji has no need to use separate adhesives to bind the pulp [23]. Moreover, since it is derived from nature, it is eco-friendly and biodegradable, minimizing environmental impacts after use. It does not emit harmful chemicals, making it suitable as an indoor air filter material, and its cellulose fibers are durable, making them an appropriate material for air filters [30].
In this study, we developed an indoor fine dust removal filter using Hanji, a traditional Korean paper made from natural materials, for the first time. Additionally, we developed a manufacturing method that allows the impregnation of activated carbon (AC) into the Hanji filter, aiming to produce an AC-embedded Hanji filter with superior performance. We conducted air permeability tests for the newly developed Hanji filter and the AC-embedded Hanji filter by measuring the pressure loss according to the linear velocity. Following this, we performed experiments on the efficiency of indoor fine dust removal on a semi-pilot scale to investigate the improvement in indoor air quality.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials (Hanji)
The sample was made from Chinese paper mulberry, imported and processed to remove impurities like lignin, resulting in ‘baekdak’, a purified material. This material was then pulverized with a grinder and used as a raw material by a company that manufactures Hanji in South Korea. Baekdak refers to the remaining plant fibers after soaking paper mulberry in water and shaking off the moisture; it can be considered a process of extracting plant fibers. The raw material had a moisture content of approximately 90%, and the solid (cellulose) was ~10% in the slurry state. After long-term storage of dried Hanji, it was repulverized with a mixer, diluted in water, and used by maintaining the solids at 0.2–0.5% by weight.
2.2. Production of the Hanji Filter
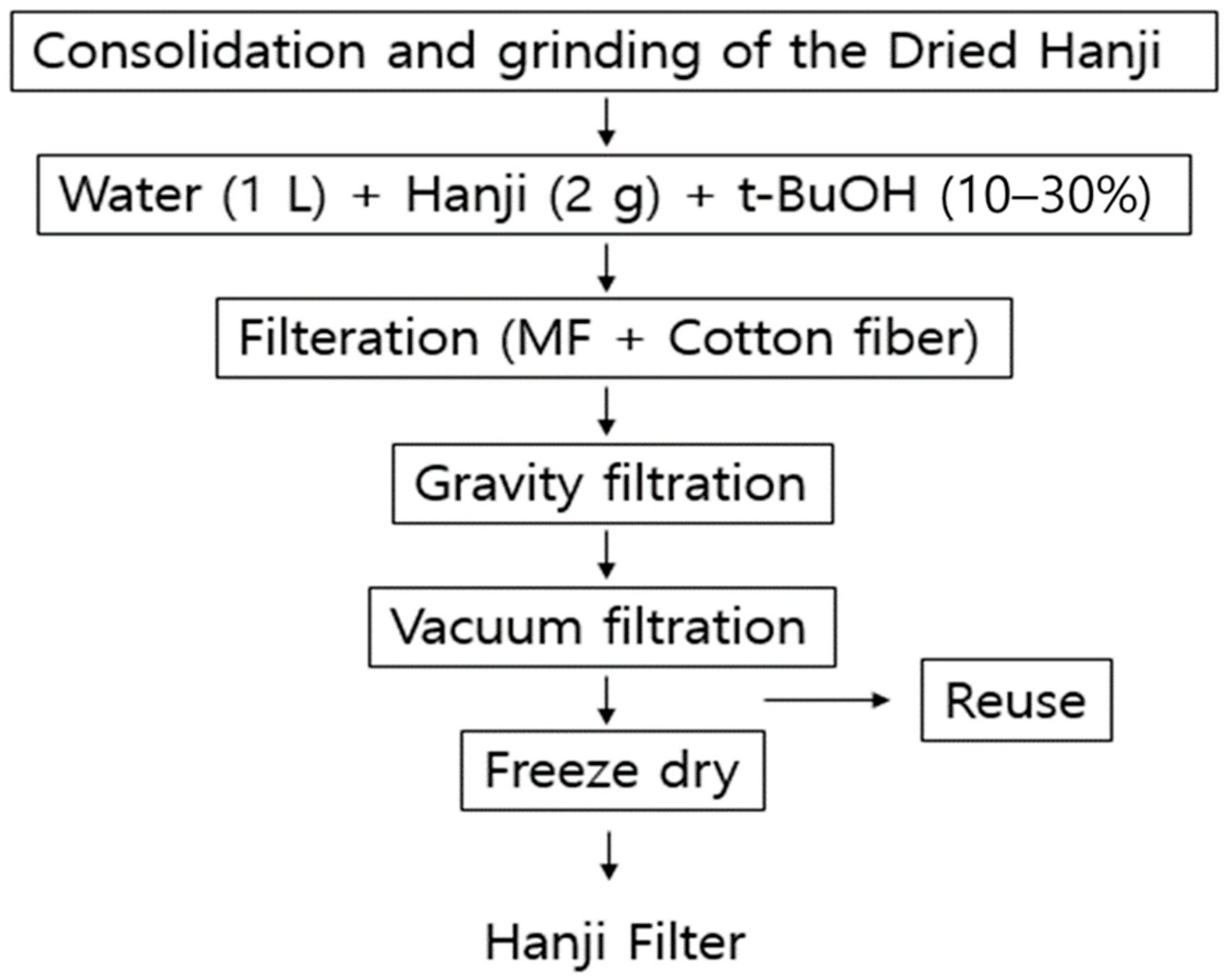
The production process of the Hanji filter is summarized in Figure 1. The dried Hanji was pressed at ~100 °C and then pulverized. An amount of 1 L of water was mixed with the pulverized Hanji, and 10–30% t-BuOH (Daejung Chemical, Siheung, Republic of Korea) was added. This mixture was stirred for ~1 h to prevent the Hanji fibers from clumping together. The mixture of Hanji fiber and t-BuOH was filtered through a filtration device. The bottom of this device was lined with a microfiltration (MF) membrane, and the top was coated with a fiber mixture of 70% cotton and 30% polyester. The membrane was used to slow down the permeation rate, whereas the fiber mixture was applied as a base layer for later transfer to a freeze dryer. The Hanji fibers, not settled by gravity, were finally vacuum-filtered to reduce their moisture content, and the filtrate was reused in a cyclical manner. The Hanji caught on the filter paper was transferred to a freeze-dryer along with the filter paper and then freeze-dried. During the freeze-drying process, the moisture and t-BuOH evaporated, leaving behind spaces that resulted in porosity. Through this process, an 18 cm x 18 cm Korean paper filter is manufactured. The following flowchart depicts the production method for the porous Hanji filter:
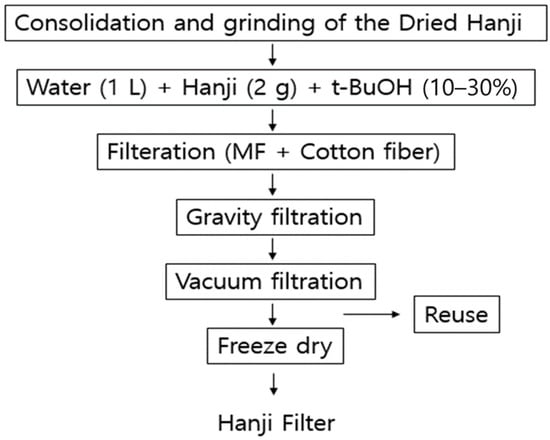
Figure 1.
Hanji filter preparation procedure using Hanji paper.
2.3. Setup for Calculation of the Operation Design Factors of the Hanji Filter
To calculate the operation design factors of the Hanji filter such as the linear value, thickness of Hanji, porosity of Hanji, content of Hanji, and amount of fine dust adhesions, the following device was designed. The Hanji filter was produced in larger sizes (30 cm × 40 cm). The resulting filter was tested for its characteristics and dust removal capacity.
The large-sized filter was then adhered onto a plastic panel where honeycomb tubes as supporters were consecutively connected. The large-scale filter (30 cm × 40 cm) was used by attaching it to commercial dust removal facilities available on the market. The device was equipped with a suction fan, and an internal pressure loss gauge and flow meter were attached. To determine the efficiency of removal, airborne particles of 5 µm or smaller were repeatedly introduced into the indoor air using exhaust gas aerosol generated from gasoline combustion in a generator.
2.4. Production of Activated Carbon-Embedded Hanji Filter
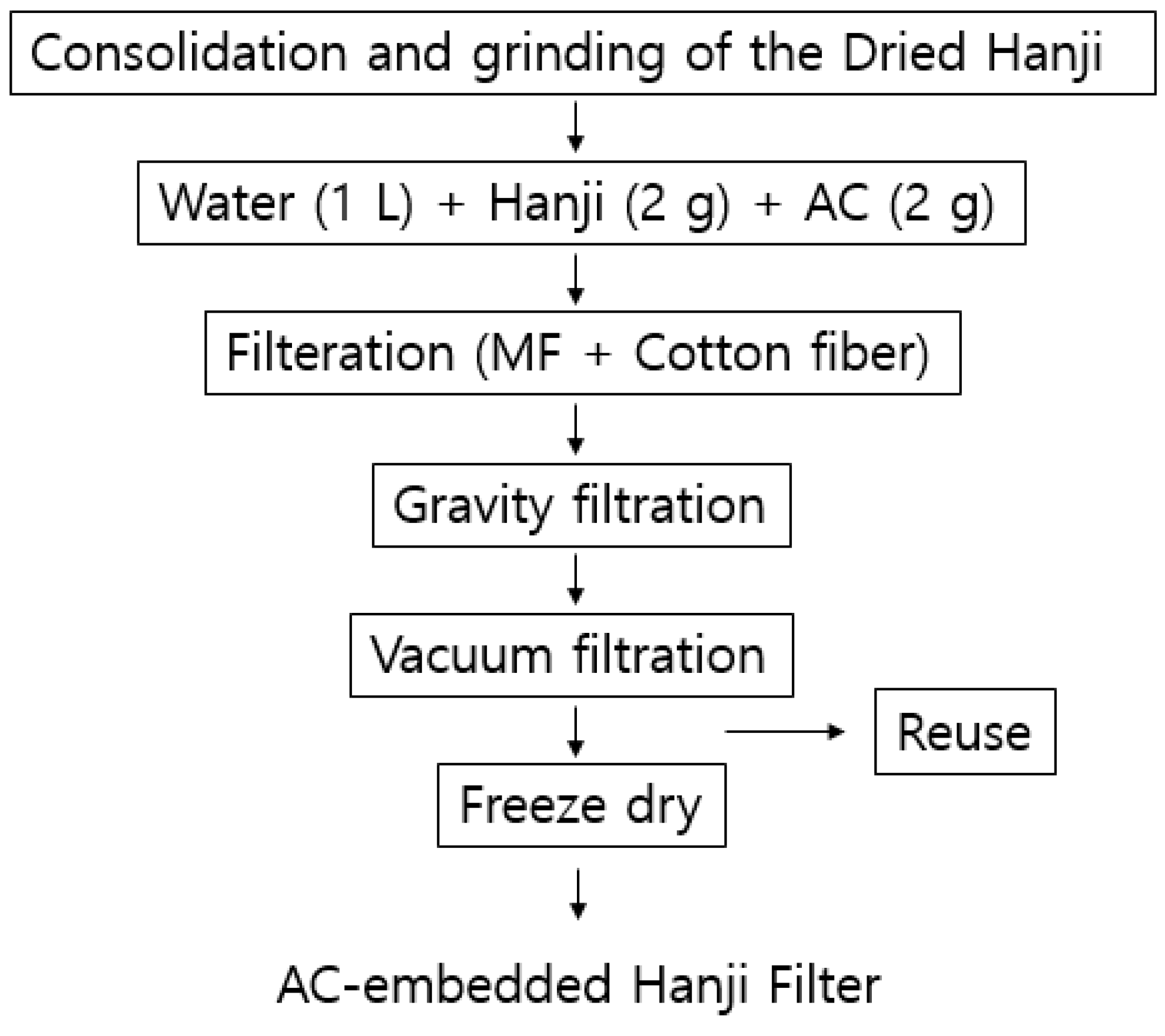
The following flowchart in Figure 2 depicts the production method for activated carbon (Samchun Chemical, Seoul, Republic of Korea)-embedded Hanji, which is similar to the method for producing Hanji fiber filters. First, the dried Hanji was compressed and then pulverized. In a 1 L beaker, ~2 g of Hanji, 2 g of powdered AC, and polyimine (Duksan Chemical, Yongin, Republic of Korea) were injected, ensuring a concentration of ~1 ppm of polyimine. This mixture was then stirred for about 2 h. For the filtration process, porous Hanji was placed on a membrane, and on top of that, the mixture of Hanji, powdered AC, and polyimine was added. During filtration, the mixture was initially filtered lightly and then filtered under high pressure. The contact time of the AC and the filter is determined by the filtering time, which was less than 1 min. The reason for using high pressure at the end is to enable the AC accumulated on the fiber surface to flow into the fiber layer, allowing for the production of a triple-layer filter with an outer cellulose fiber layer, an inner mixed layer of AC and cellulose, and a bottom layer of cellulose fiber again.
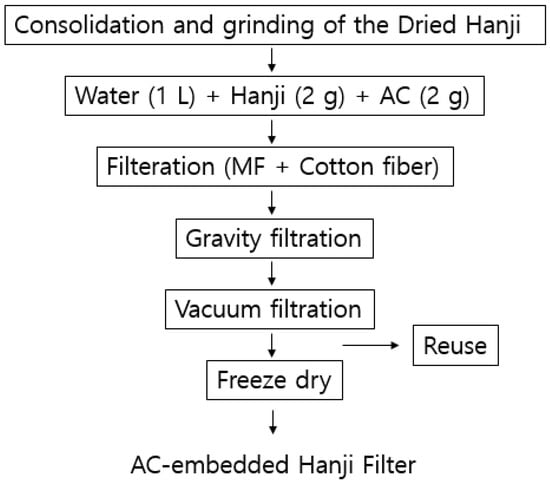
Figure 2.
Activated carbon-embedded Hanji filter preparation procedure.
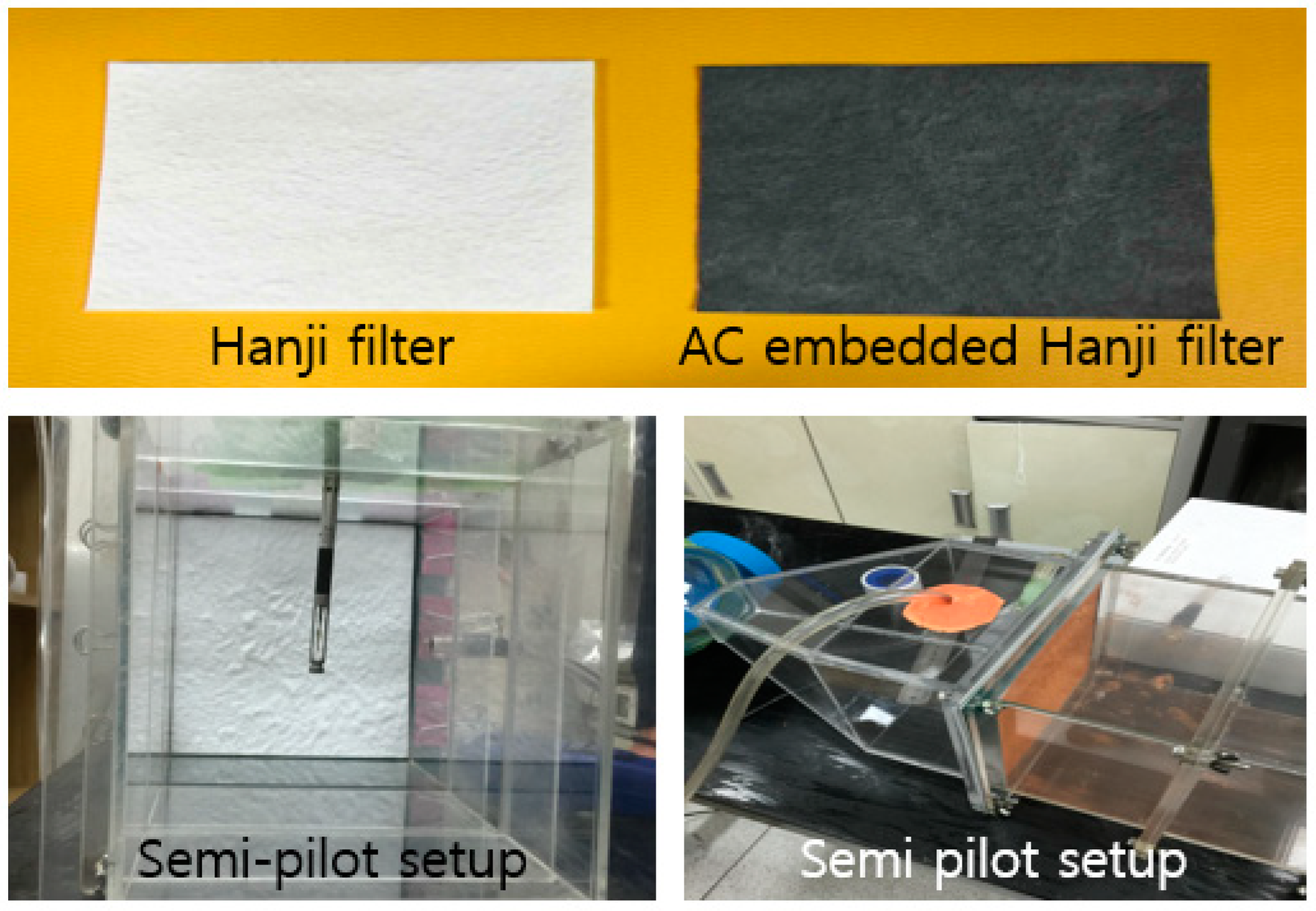
2.5. Field Application as a Semi-Pilot Experiment
For the creation of a polluted indoor environment, an experimental, semi-pilot 18 cm × 18 cm Hanji filter was used, and the experiment was conducted inside a controlled box (Figure 3). The dust removal performance test device consisted of a dust generator, headloss measurement device, dust concentration measurement device, and a suction blower. The filtration chamber was connected to a dust generator (fluidized bed dust generator, Model 3211, Kanomax Japan Inc., Osaka, Japan) and an air blower to control the dust concentration at a fixed flow rate. Dust counters were placed inside and outside the filtration chamber to monitor the number of dust particles at 1 min intervals (Dust monitor, model 3442, Kanomax, Osaka, Japan). To measure the change in filter performance according to the content of cellulose, 1.2 g content and 1.8 g content filters were prepared and compared, and to measure changes in the filter performance depending on the content of activated carbon, 0.6 g or 0.4 g of activated carbon was injected into 1.2 g cellulose filters and compared.
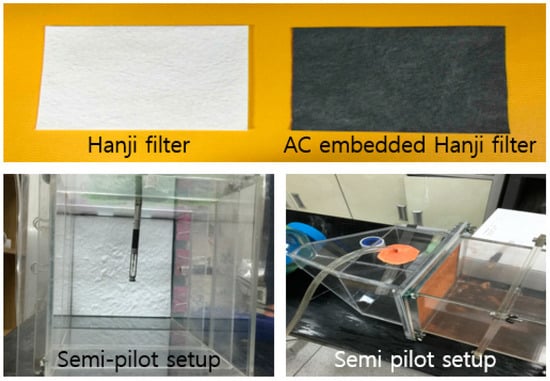
Figure 3.
Developed Hanji filter and AC-embedded Hanji filter (above); semi-pilot experimental setup for fine dust removal test (below).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Manufactured Hanji Filter
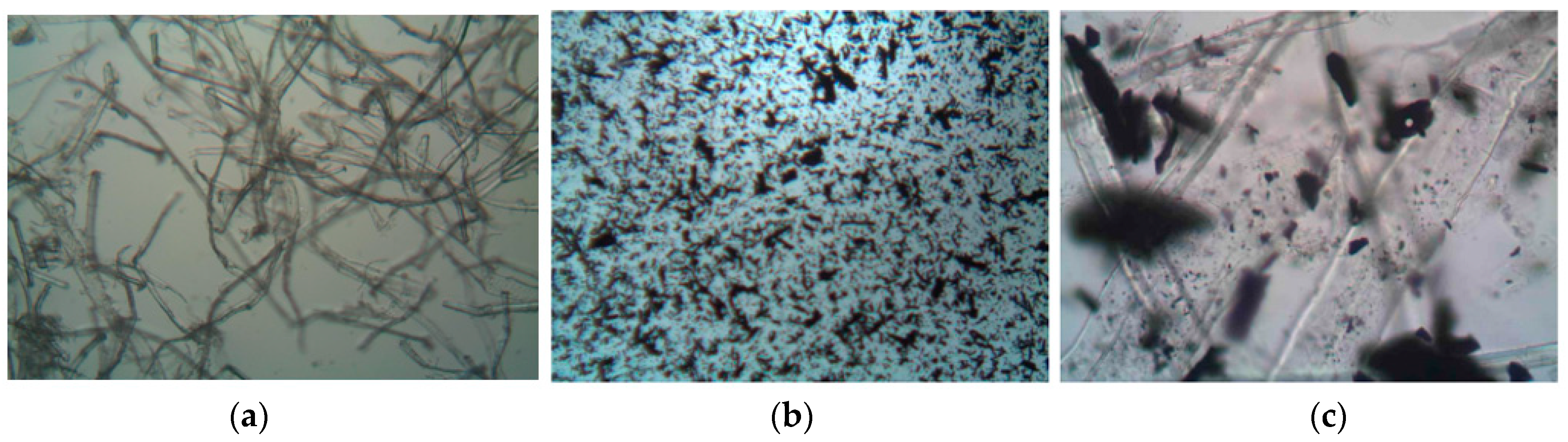
The images below display microscopic views of the Hanji filters that were produced (Figure 4). In sequence, they show the Hanji filter, the mixture of Hanji that was pulverized after infusing polyimine into the AC, and the AC-embedded Hanji filter. The final dried and compressed Hanji filter displays a fiber-like structure. The solution containing AC mixed with polyimine in Hanji is shown in Figure 4b, and the final product, the AC-embedded Hanji filter, demonstrates that the powdered AC was properly inserted into the Hanji filter fiber tubes.
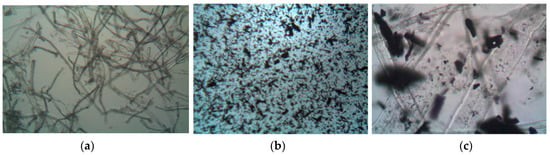
Figure 4.
Microscopic images of prepared Hanji filter samples: (a) Hanji filter, (b) Mixed solution with AC and crushed Hanji, (c) AC-embedded Hanji filter (×100).
The bulk density was measured, and as a result of the measurement, the porosity of the Hanji filter was measured to be 90–92% and the porosity of the AC-embedded Hanji filter was measured to be 90%, so there was no significant effect of the AC on its porosity.
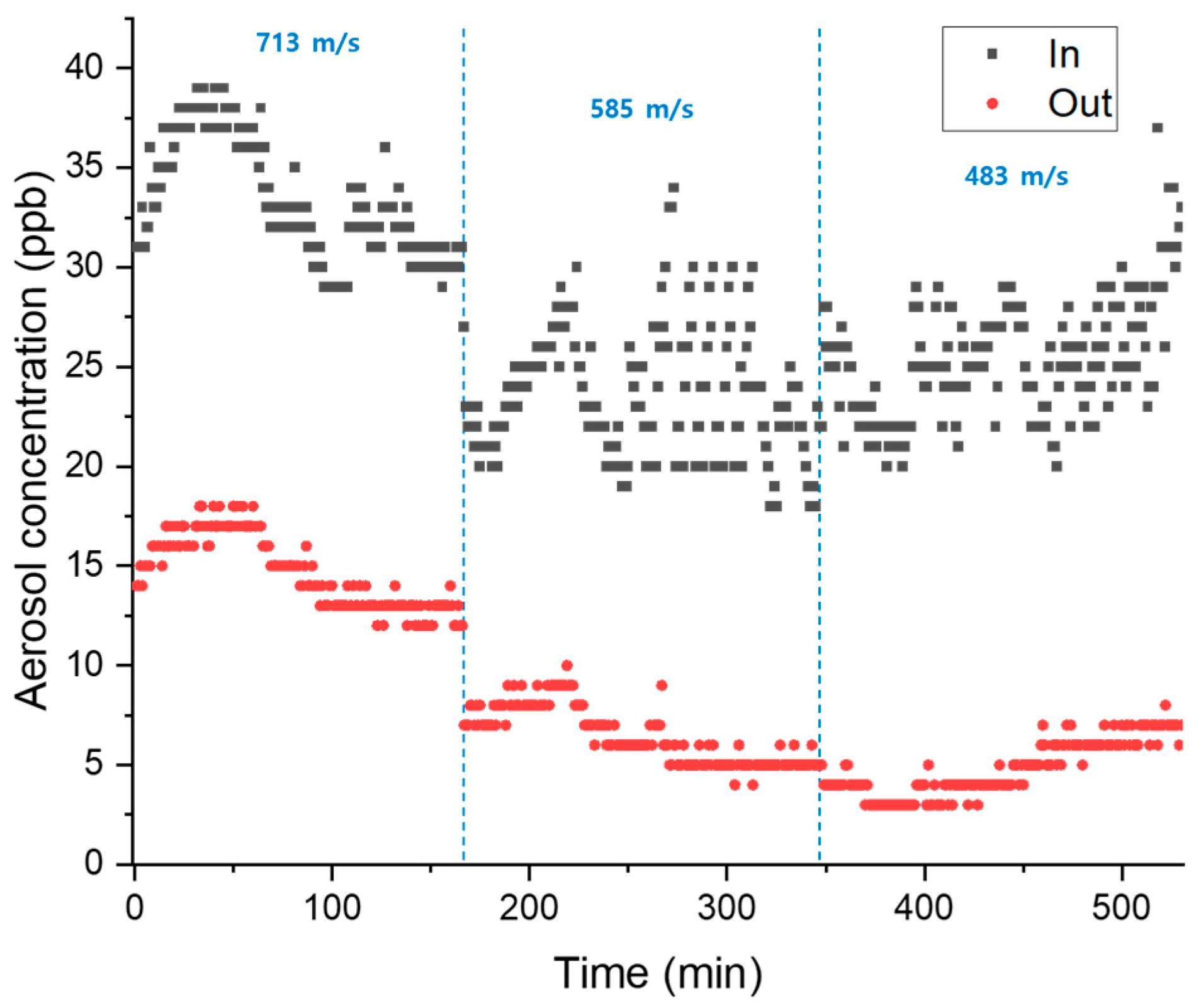
An experiment to remove an aerosol was conducted using a large-scale dust removal device to determine the optimal linear velocity. After installing the manufactured Hanji in a commercial dust removal facility, the concentration of the aerosol before and after removal by the Hanji filter was measured at various linear velocities (713, 585, and 483 cm/s), as shown in Figure 5. The concentration distribution of the incoming aerosol was 20–40 ug/m3, and the outflow concentration was 10–20 ug/m3 at 713 cm/sec linear velocity. For linear velocities of 483 cm/s and 585 cm/s, it was less than 10 ug/m3. The removal efficiency of the filter at the three different velocities was 63.3% at 713 m/s, 72.76% at 585 m/s, and 81.06% at 483 m/s, showing that it appears to increase as the linear speed decreases. Typically, in South Korea, the concentration of dust particles smaller than 10 µm in the atmosphere is ~50 µg/m3. Alerts or warnings for fine dust are issued when the concentration exceeds 100 µg/m3 [31].
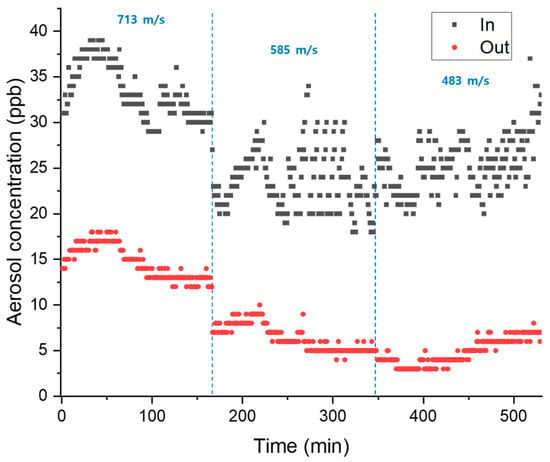
Figure 5.
Aerosol concentration before and after Hanji-filtering according to changes in linear velocity (at 713, 585, and 483 m/s).
Based on the experimental results, it was possible to remove ultrafine dust at concentrations lower than standard atmospheric levels. However, when operating at high speeds, due to the internal suction pressure within the filter, it is necessary to increase the filter’s surface area to reduce the speed inside the filter. Based on these findings, when commercializing and using the filter, it is deemed preferable to manufacture the filters in a roll form to increase the contact area rather than using flat filters [32].
Table 1 reports the physical characteristics and operating conditions of the Hanji fiber filter produced in this study, based on the preliminary aerosol test results according to the linear velocity. The final thickness of the produced Hanji was ~0.8 mm, the porosity was ~90%, and the Hanji content per unit area was 7.4 mg/cm2. For a Hanji filter with these characteristics, the optimal dust removal linear velocity was 7 cm/sec; with a consistent head loss of ~25 mm H2O, the maximum dust removal per unit area was 3.6 g/cm2.

Table 1.
Operation design factors of the Hanji filter.
3.2. Pressure Loss Changes According to the Linear Velocity of the AC-Embedded Hanji Filter
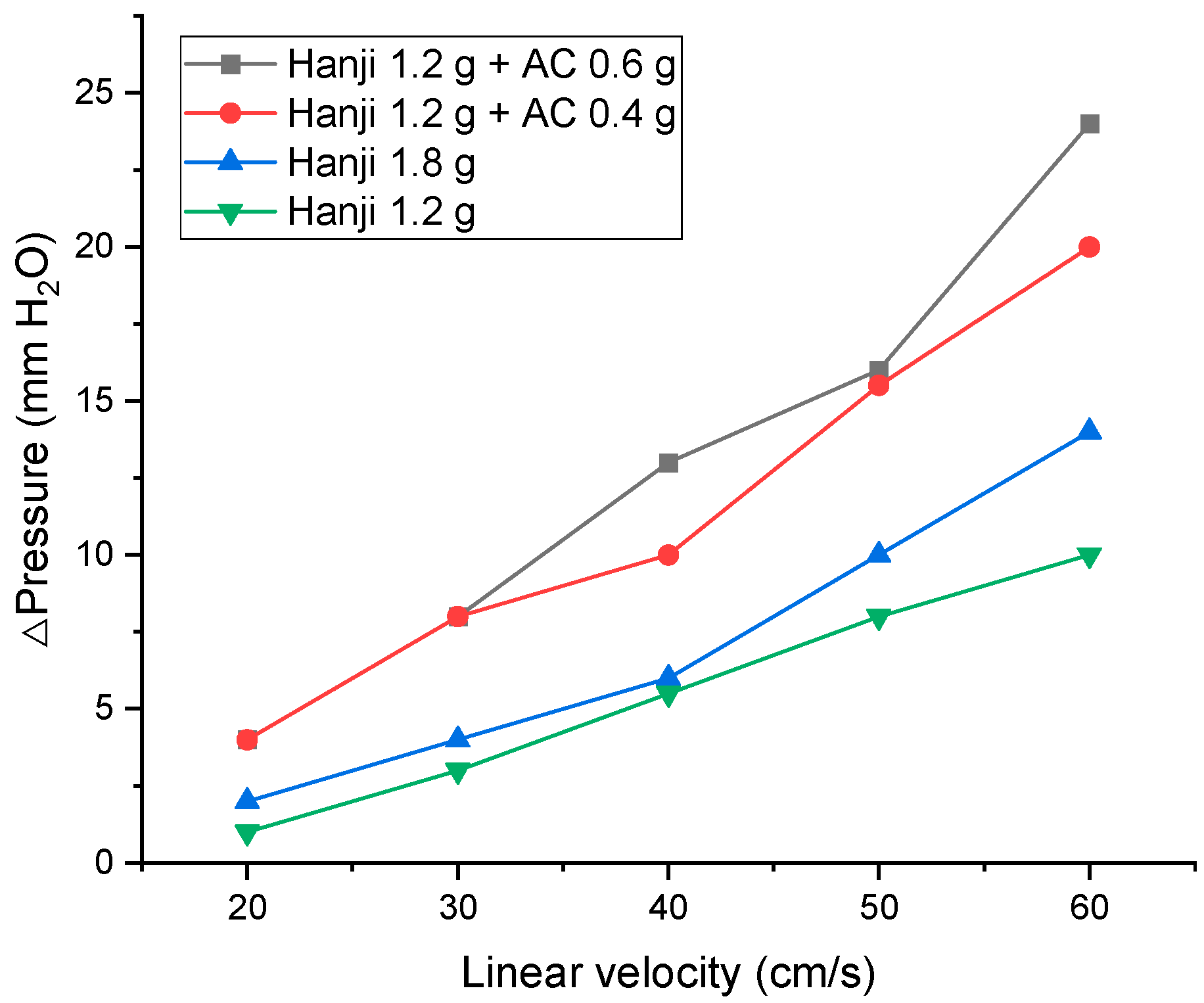
To evaluate the dust-filtering characteristics of the Hanji filter and the AC-embedded Hanji filter, we first examined the head loss (pressure loss) according to the linear velocity and the different types of Hanji filter. Figure 6 presents the measurements of the pressure loss changes by linear velocity due to the cellulose content and AC content in the Hanji filter and the AC-embedded Hanji filter with a size of 18 cm × 18 cm (324 cm2). Comparing the Hanji manufactured with a cellulose content of 1.2 g (3.1 mg/cm2) to that with 1.8 g (5.6 mg/cm2), the pressure loss increased with the increase in the cellulose content. This is because, as the cellulose content in the Hanji increases, a thicker filter is produced [33]. The reason for the increase in pressure loss as the filter thickness increases has been proven by many researchers [34,35,36]. According to Davies’ filtration theory, widely used in gas filtration media, the pressure loss and filtration efficiency of the filter media heavily depend on the media’s structure, the properties of the constituent fibers, and the usage environment [37]. Specifically, the pressure loss increases in direct proportion to the thickness of the filter media. Furthermore, AC embedded at the same cellulose content (1.2 g) further increased the pressure loss. However, no further increase in pressure loss was observed as the content of AC increased. This is attributed to the overall porosity of the filter decreasing due to AC impregnation, leading to a greater pressure loss [38]. In the case of the AC-embedded Hanji, even when operated at 60 cm/s, the maximum pressure loss was 20 mm H2O. This is considerably lower than conventional air filters (100 mm H2O), indicating that the developed AC-embedded Hanji filter exhibits high air permeability.
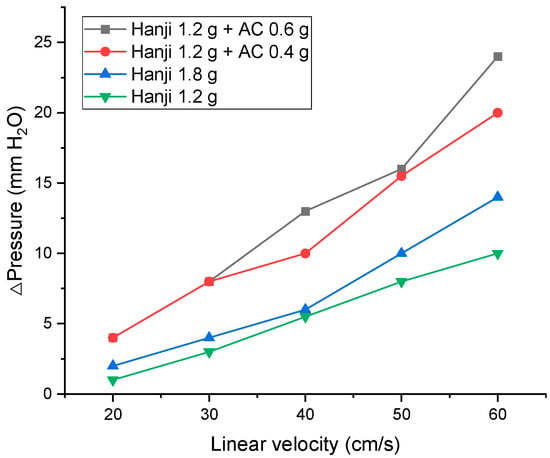
Figure 6.
Changes in pressure according to the linear velocity and type of Hanji filter.
3.3. Hanji Filter for Fine Dust Removal
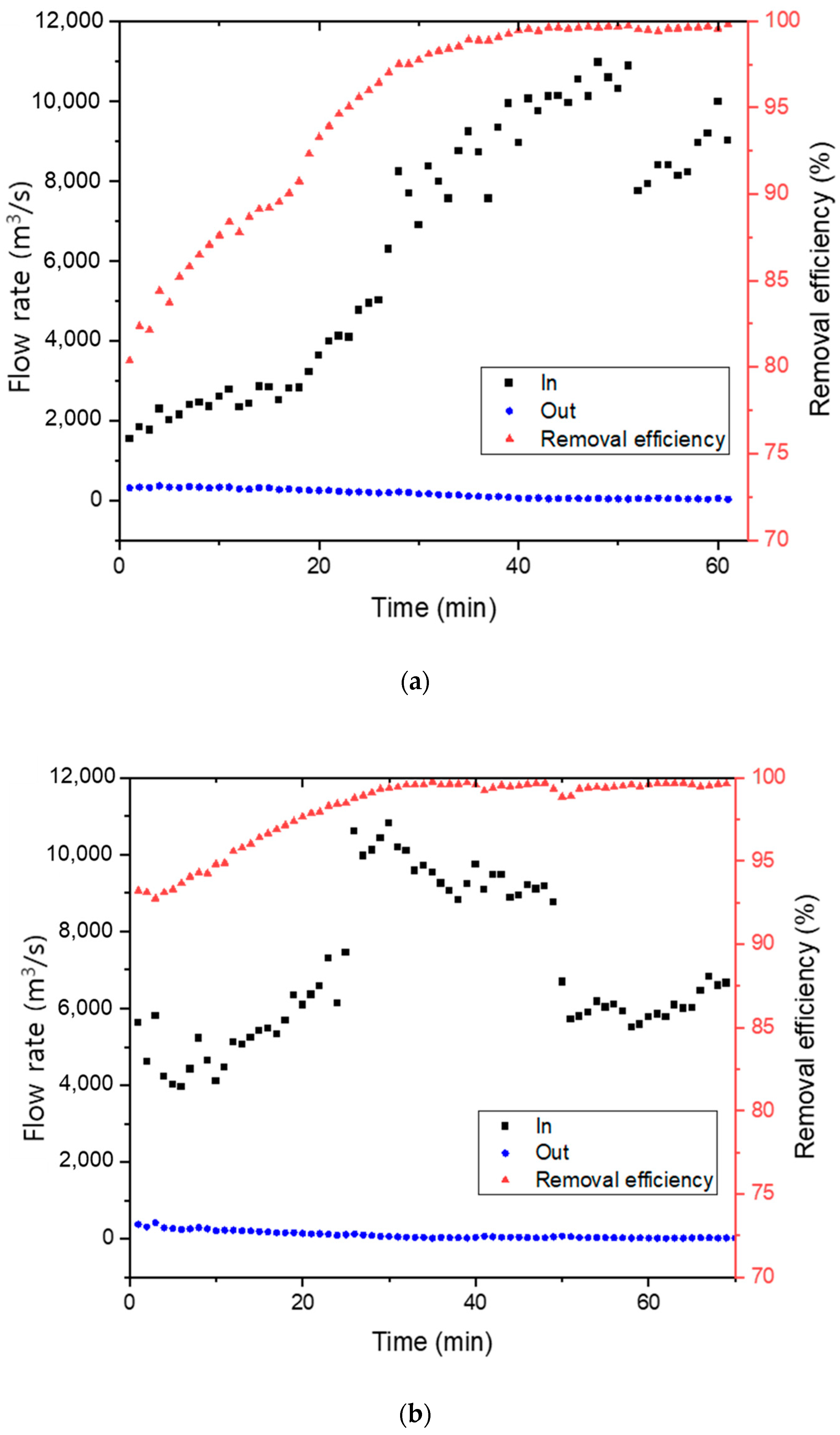
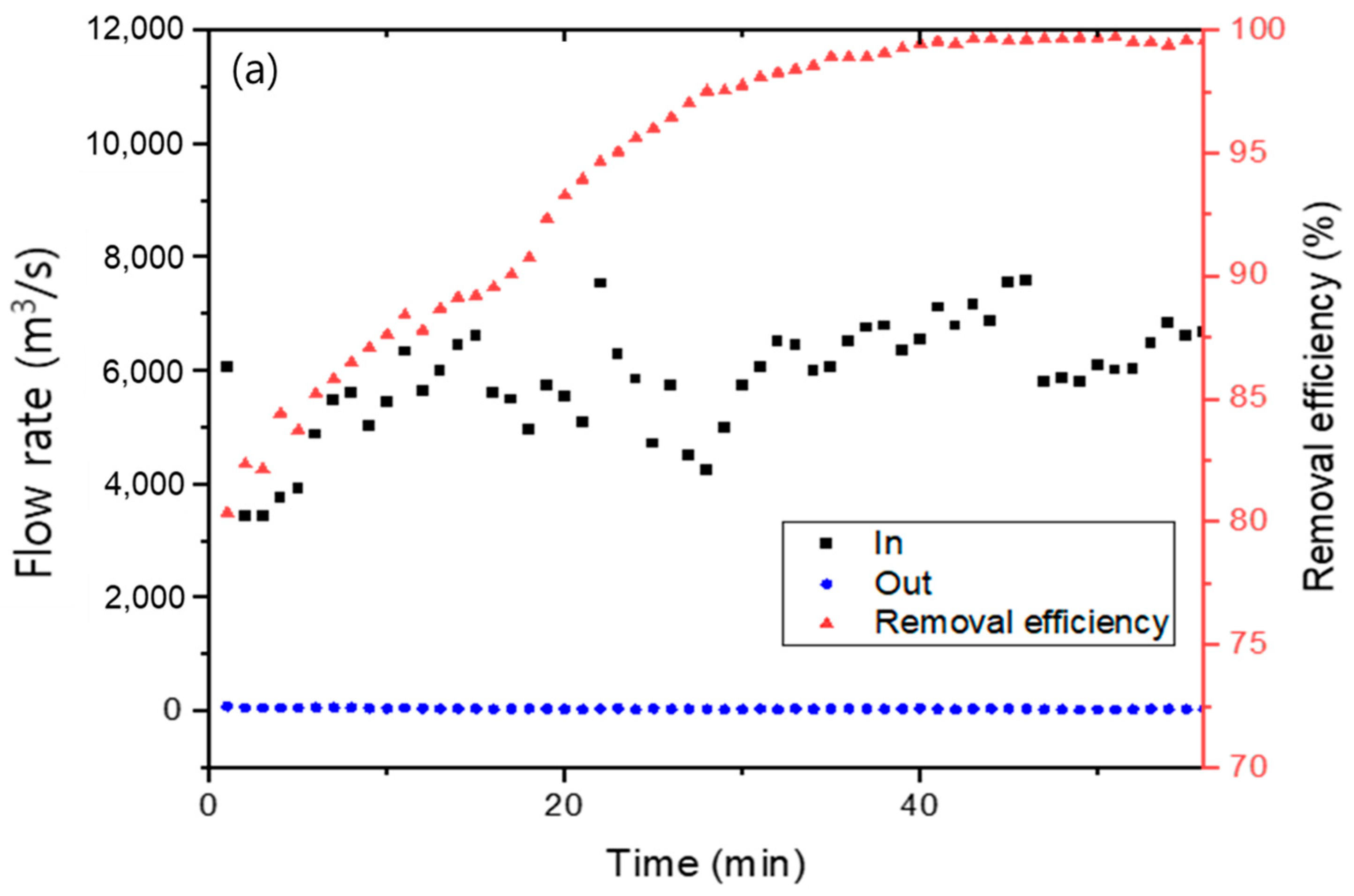
Figure 7 presents the dust removal efficiency of the manufactured Hanji filter. The dust removal efficiency was measured by artificially introducing standard dust particles of 1 to 5 µm in size, and experiments were also simultaneously conducted on the ambient indoor air dust. The cellulose content of the Hanji filter used for this purpose was compared for cases where it was manufactured with 1.2 g and 1.8 g. For the 1.2 g case, the dust removal efficiency was 80.4% in the first minute, which increased to 99.1% by the 38th minute. The removal rate increased to 99.8% by the 62nd minute. In the case of 1.2 g, some dust initially passed through, resulting in a slightly lower removal efficiency. However, over time, the filtered dust inside the filter served as a kind of filtering layer, thus improving the removal efficiency.
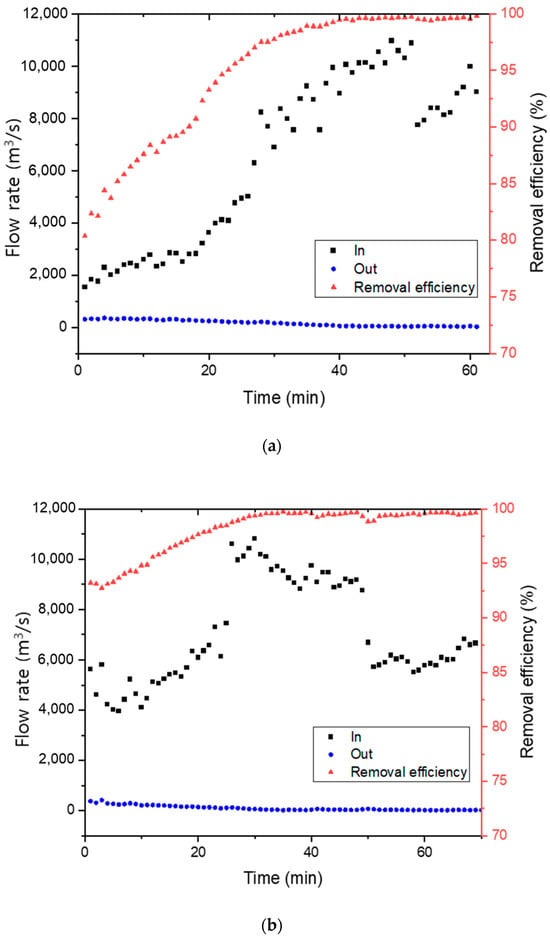
Figure 7.
Fine dust removal efficiency of Hanji filters: (a) 1.2 g of Hanji filter content (3.1 mg/cm2), (b) 1.8 g of Hanji filter content (5.6 mg/cm2).
Based on the air filter capture theory, the primary removal mechanism for fine dust can be attributed to the electrostatic attraction between fibers and dust or the adhesive force between dust particles [39,40]. It appears that as the amount of dust trapped in the filter increased, the adhesive force for incoming dust also rose, leading to a gradual increase in the removal rate [41]. The Hanji filter with a denser arrangement, manufactured with a cellulose content of 1.8 g, demonstrated a high removal efficiency from the start. It was 93.2% in the first minute, 99.1% by the 28th minute, and subsequently maintained a removal efficiency of over 99%.
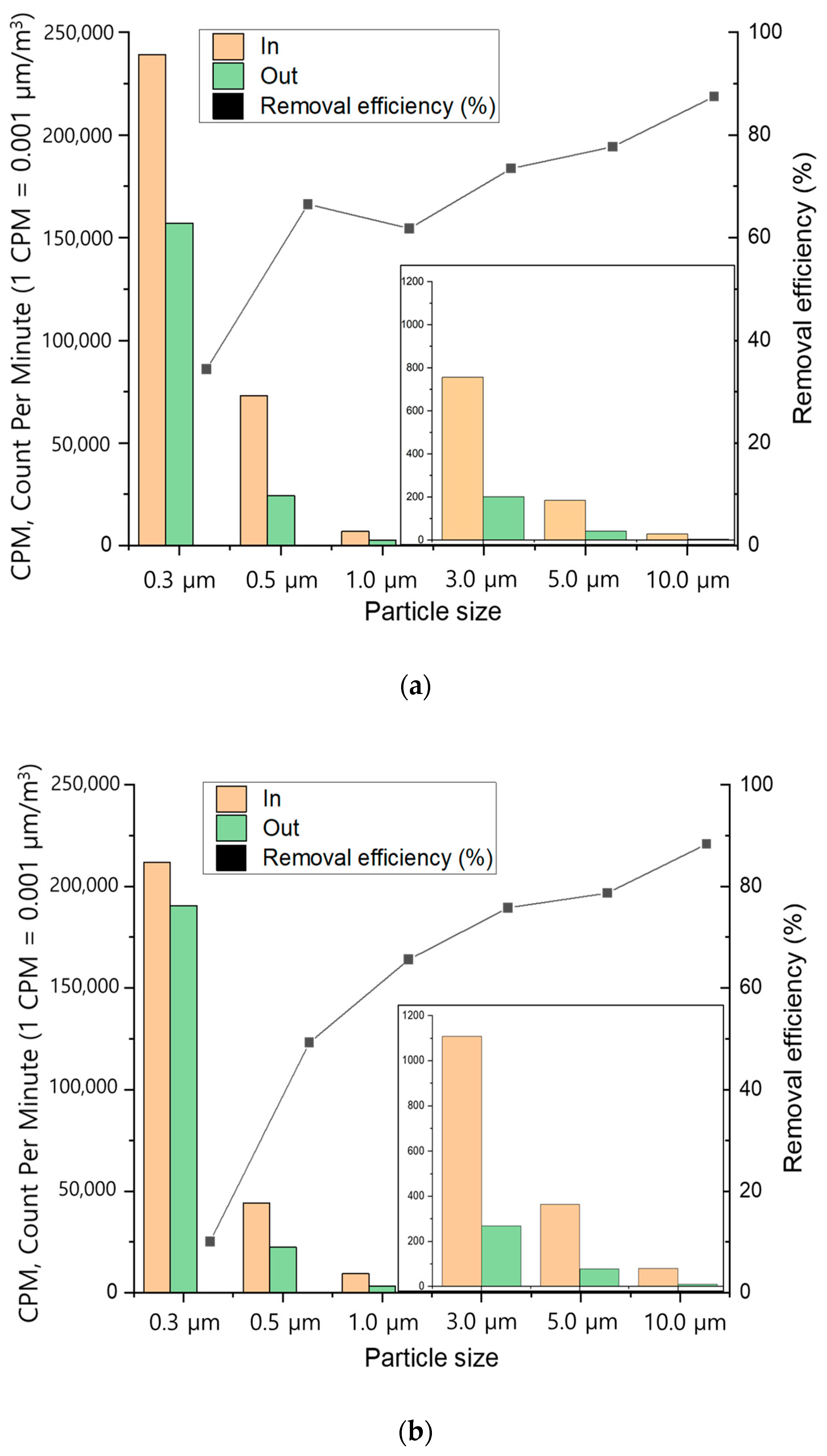
The following Figure 8 presents the dust size-specific removal efficiency when treating very low dust concentration indoor air using the Hanji filter. The removal efficiency of dust sizes below PM10 for dry Hanji filters of 1.2 g and 1.8 g indicates that while dust of 0.3 µm can be effectively removed to some extent, sizes above 0.5 µm are more effectively removed. The figure depicts the dust accumulated on the Hanji filter before and after dust removal. Even when dust accumulated on the surface of the Hanji filter, continuous processing was possible without any change in head loss. Moreover, this confirmed that no dust was passing through the backside or after the filtering process.
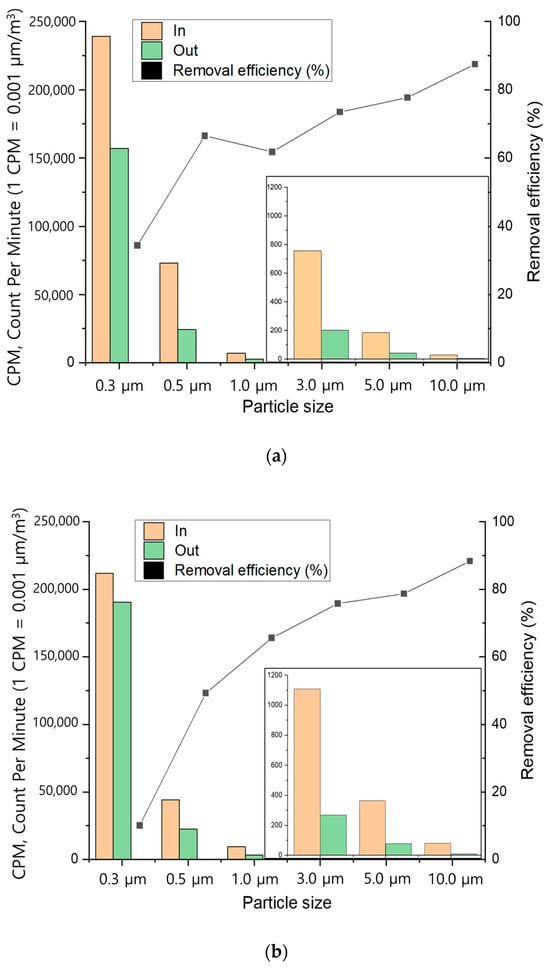
Figure 8.
Fine dust removal test results of Hanji filters according to dust size by (a) 1.2 g of Hanji filter content (3.1 mg/cm2), (b) 1.8 g of Hanji filter content (5.6 mg/cm2).
3.4. Fine Dust Filtration Efficiency of the AC-Embedded Hanji Filter
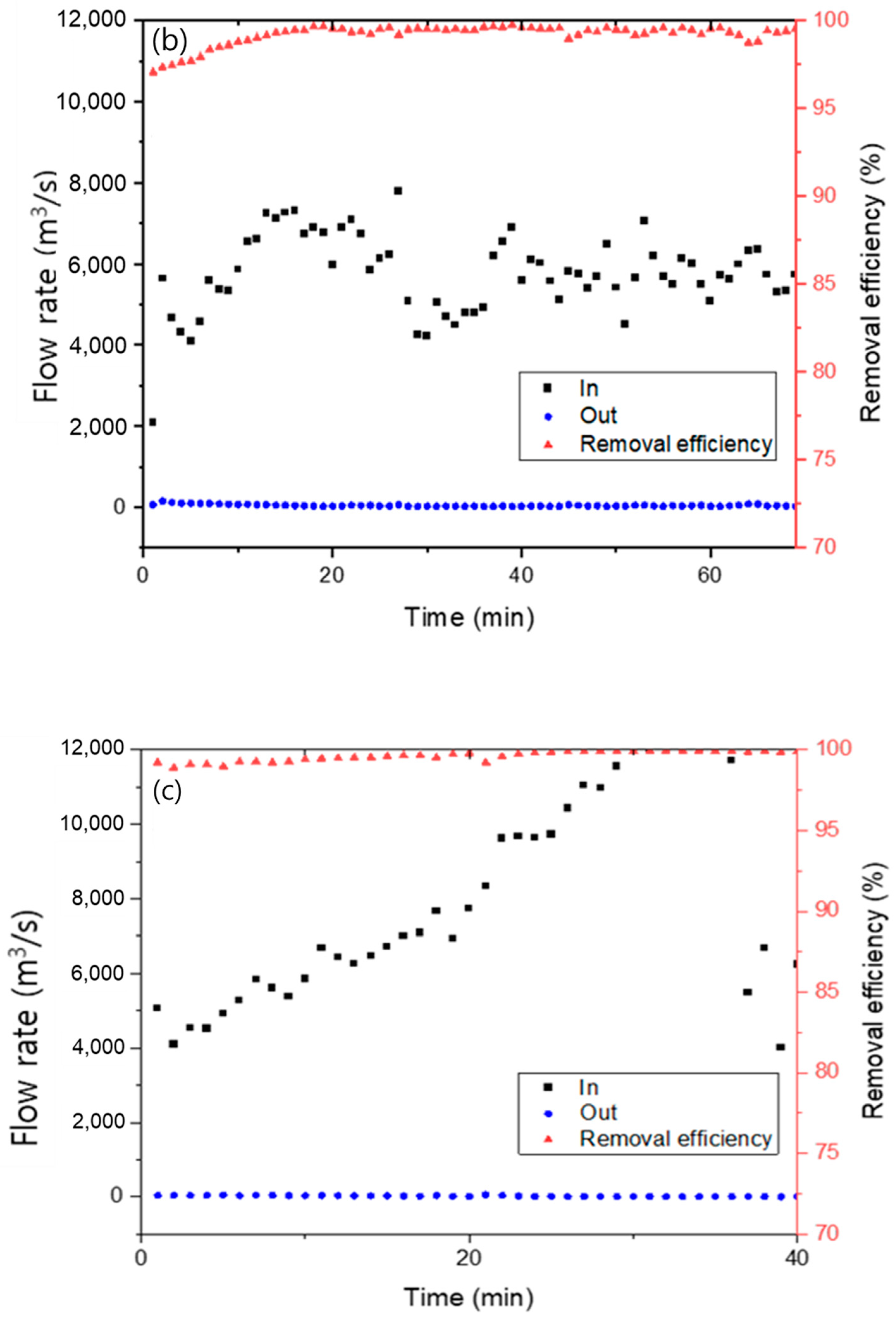
Figure 9 presents the dust removal efficiency of the Hanji filter embedded with AC. Dust removal efficiency was measured using standard dust of sizes 1–5 µm and ambient atmospheric dust. The Hanji filter, manufactured with 1.2 g of Hanji content, was compared by varying the content of the embedded AC. For a Hanji content of 1.2 g, and when powdered AC was added at 0.4 g, 0.6 g, and 0.8 g, the removal efficiency of 0.8 g of AC was consistently above 98% from the start, while the removal efficiency of 0.4 g and 0.6 g of AC was low at first, but it increased over time. Furthermore, as the content of powdered AC increased, the efficiency was consistently above 99%. AC is well-known to act as a filter capable of removing dust [42,43]. Not only does powdered AC greatly enhance dust removal efficiency, it can also function as a filter when combined with Hanji [44].
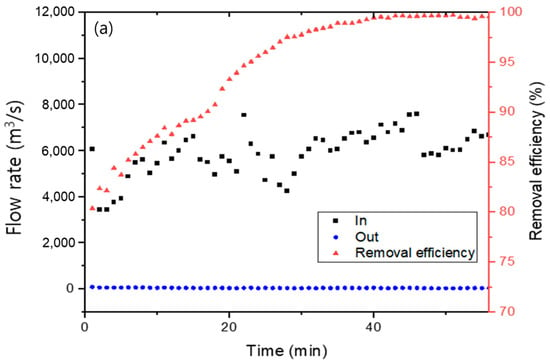
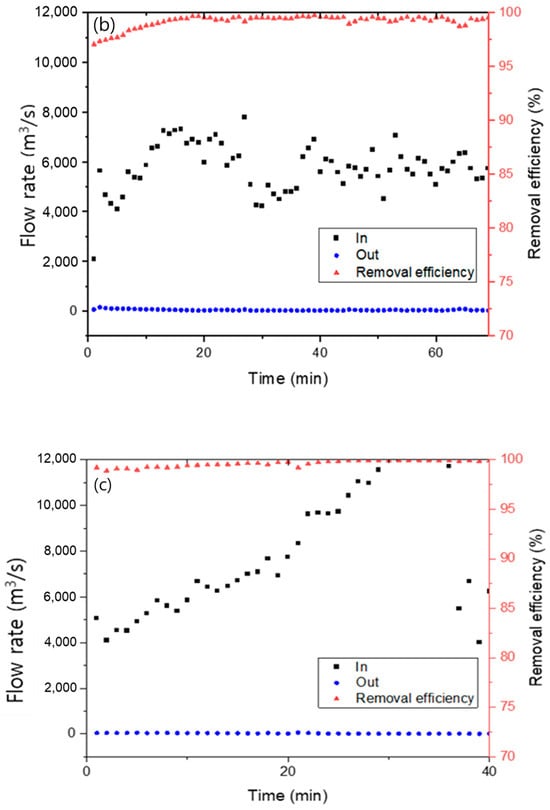
Figure 9.
Fine dust removal efficiency of 1.2 g Hanji filter embedded with (a) 0.4 g of AC, (b) 0.6 g of AC, (c) 0.8 g of AC.
Here, the attachable dust amount per unit area of the Hanji filter was calculated based on the accumulated amount of attached dust. The weight of the filter before and after dust adhesion was measured for four different filters, and the average attached amount per filter unit area was calculated (Table 2). The dust adhesion on the filter increased as the content of Hanji and AC increased. The average dust adhesion per unit area for the four filters was estimated to be ~20 g/m2. Since the fine dust reduction efficiency did not change even after activated carbon impregnation, it was determined that the activated carbon was stably attached.

Table 2.
Fine dust adhesion per unit area of prepared filter samples.
4. Conclusions
Hanji is a traditional Korean paper made from the natural cellulose found in the bark of paper mulberry. This study developed a dust-removal filter using Hanji, a natural material. Taking advantage of the fact that cellulose, the main component of Hanji, does not dissolve in water, we aimed to create a filter with excellent air permeability and appropriately sized pores. In this study, we sought to dissolve as much cellulose as possible to produce a homogeneous filter material via chemical and biological pretreatment methods. Since the pore characteristics of the filter surface and interior were determined during the freeze-drying process through the rapid cooling and sublimation of the solvent, we switched from the conventional drying method with water to drying with an alcoholic solvent to produce a filter with pores suitable for the intended purpose. To modify the Hanji filter, we manufactured an AC-embedded Hanji filter by spraying powdered AC onto the Hanji filter and compressing it. We conducted experiments to improve indoor air quality using both the Hanji filter and the AC-embedded Hanji filter:
- (1)
- When producing the Hanji filter, the appropriate Hanji content per unit area to ensure porosity and minimal head loss was 51 g/m2. For the AC-embedded Hanji filter, the appropriate Hanji content per unit area was 31 g/m2, and the AC content was 31 g/m2.
- (2)
- The Hanji filter showed a removal efficiency of 80.4% within the first minute, 99.1% efficiency by the 38th minute, and maintained an efficiency of over 99% thereafter. The AC-embedded Hanji filter showed a removal rate of 93.2% within the first minute and 99.1% by the 28th minute. While the Hanji filter performed well, the dust removal efficiency of the AC-embedded Hanji filter proved to be superior.
- (3)
- The dust adhesion amount per unit area for both the Hanji filter and the AC-embedded Hanji filter varied depending on the Hanji and AC content, but on average, it was calculated to be ~20 g/m2.
The AC-embedded Hanji filter has the potential to remove not only fine dust but also volatile substances. Future research will require comparative studies to investigate the removal of volatile organic compounds and compare them with commercially available air purifier filters. The use of natural filters is both effective and sustainable.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.S.K.; Validation, S.B.; Formal analysis, Y.Y.; Investigation, J.B., S.K. and K.S.K.; Resources, J.B.; Data curation, S.K.; Writing—original draft, J.B., S.K., Y.Y. and S.B.; Writing—review & editing, S.B.; Funding acquisition, J.B. and S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the “Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology” (KICT), Rep. of Korea, grant numbers #20230095-001 and #20230160-001.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Ji, M.; Higuchi, K. Variability of East Asia dust events and their long-term trend. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3156–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, S.; Jacob, D.J.; Pendergrass, D.C.; Colombi, N.K.; Shah, V.; Yang, L.H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Kim, H.; Sun, Y. Coarse particulate matter air quality in East Asia: Implications for fine particulate nitrate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 4271–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Luo, X.-S.; Huang, W.; Pang, Y.; Yang, J.; Tang, M.; Mehmood, T.; Zhao, Z. Toxicity assessment and heavy metal components of inhalable particulate matters (PM2. 5 & PM10) during a dust storm invading the city. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 162, 859–866. [Google Scholar]
- do Nascimento, C.M.; de Oliveira, S.A.; Santana, O.A.; Carvalho, H. Changes in air pollution due to COVID-19 lockdowns in 2020: Limited effect on NO2, PM2. 5, and PM10 annual means compared to the new WHO Air Quality Guidelines. J. Glob. Health 2022, 12, 05043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Calheiros, C.S.; Villanueva, F.; Alonso-Cuevilla, N.P.; Gabriel, M.F.; Silva, G.V. Indoor air quality: A review of cleaning technologies. Environments 2022, 9, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebiyi, F.M. Air quality and management in petroleum refining industry: A review. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2022, 4, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, D.S.; Martins, L.D.; Aguiar, M.L. Air pollution control for indoor environments using nanofiber filters: A brief review and post-pandemic perspectives. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2022, 11, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, S.; Chowdhury, S.; Crowley, J.N.; Tadic, I.; Drewnick, F.; Borrmann, S.; Eger, P.; Fachinger, F.; Fischer, H.; Predybaylo, E. Severe atmospheric pollution in the Middle East is attributable to anthropogenic sources. Commun. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Ginoux, P.; Malm, W. Intercontinental transport of pollution and dust aerosols: Implications for regional air quality. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 5501–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Kim, J.-E. Fine, ultrafine, and yellow dust: Emerging health problems in Korea. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Wang, J.; Zhao, B. Health benefits and cost of using air purifiers to reduce exposure to ambient fine particulate pollution in China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheek, E.; Guercio, V.; Shrubsole, C.; Dimitroulopoulou, S. Portable air purification: Review of impacts on indoor air quality and health. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisk, W.J.; Faulkner, D. Performance and cost of particle air filtration technologies. Indoor Air 2001, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, F. Air filtration in the free molecular flow regime: A review of high-efficiency particulate air filters based on carbon nanotubes. Small 2014, 10, 4543–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Kang, G.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, G. High–Performance Multifunctional Electrospun Fibrous Air Filter for Personal Protection: A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 122175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yin, X.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Electrospun nanofibers for high-performance air filtration. Compos. Commun. 2019, 15, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Lu, T.; Cui, J.; Samal, S.K.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Bio-based electrospun nanofiber as building blocks for a novel eco-friendly air filtration membrane: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, H.; Cao, Q. Degradable nanofiber for eco-friendly air filtration: Progress and perspectives. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 306, 122642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, W.-H.; Pan, S. Hierarchically structured all-biomass air filters with high filtration efficiency and low air pressure drop based on pickering emulsion. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 14266–14274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, M.; Riva, L.; Caruso, M.; Punta, C. Cellulose for the production of air-filtering systems: A critical review. Materials 2022, 15, 976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfim, D.P.; Cruz, F.G.; Bretas, R.E.; Guerra, V.G.; Aguiar, M.L. A sustainable recycling alternative: Electrospun PET-membranes for air nanofiltration. Polymers 2021, 13, 1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.-I.; Chung, Y.J.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, J.-W. Effect of radiation on disinfection and mechanical properties of Korean traditional paper, Hanji. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.-L.; Ra, J.-B. Orientation properties of Korean traditional paper-Hanji. J. Korea Tech. Assoc. Pulp Pap. Ind. 2013, 45, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.-R.; Kim, H.-W.; Lim, H.-A. A Study on the Design of Traditional Food Package Under the Use of Hanji (I)-Design of Korean dried confectionary package. J. Korea Tech. Assoc. Pulp Pap. Ind. 2007, 39, 68–77. [Google Scholar]
- Min-Jeong, S.; Hoon, S. An Experimental Study on the Effect of Hanji Windows on Indoor Air Temperature and Humidity Control. J. Korean Hous. Assoc. 2006, 17, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, E.-S.; Kang, C.-W.; Kang, H.-Y.; Jang, S.-S. Sound absorption property of traditional Korean natural wallpaper (Hanji). J. Korean Wood Sci. Technol. 2018, 46, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yoon, Y.H.; Kim, K.S. Performance of activated carbon-impregnated cellulose filters for indoor VOCs and dust control. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- d’Halluin, M.; Rull-Barrull, J.; Bretel, G.; Labrugère, C.; Le Grognec, E.; Felpin, F.X. Chemically modified cellulose filter paper for heavy metal remediation in water. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.N.; Saito, T.; Fujisawa, S.; Fukuzumi, H.; Isogai, A. Ultrastrong and high gas-barrier nanocellulose/clay-layered composites. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 1927–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, H.J.; Ju, Y.C.; Park, S.C.; Lim, H.A.; Lee, H.H.; Choi, J.W.; Song, H.H.; Lee, Y.S. Studies on Physical Properties and Potential as Coffee Filter Application for Hanji According to Different Contents of Paper Mulberry Fibers. Korea Soc. Packag. Sci. Technol. 2020, 26, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, M.J.; Kim, Y.P. Trends of the PM10 concentrations and high PM10 concentration cases in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 35, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.-B.; Park, D.-S.; Cho, Y.-M.; Kim, J.-B.; NanGoong, S.; Han, T.-W.; Cho, K.-H.; Kim, T.-S. Development of air cleaning roll-filter for improving IAQ in subway. J. Korean Soc. Railw. 2011, 14, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Poon, W.S.; Liu, B.Y. Dust Loading Behavior of Engine and General Purpose Air Cleaning Filters; 0148-7191; SAE Technical Paper: Warrendale, PA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jokisch, S.; Neuenfeldt, M.; Scheibel, T. Silk-based fine dust filters for air filtration. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2017, 1, 1700079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulejko, P.; Krištof, O.; Dohnal, M. An Assessment on Average Pressure Drop and Dust-Holding Capacity of Hollow-Fiber Membranes in Air Filtration. Membranes 2021, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, Y.; Chen, D.-R.; Pui, D.Y. Effects of particle polydispersity and shape factor during dust cake loading on air filters. Powder Technol. 1998, 98, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C. The retention of particles in filters. J. Aerosol Sci. 1974, 5, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, A.; Merati, A.A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Bagherzadeh, R. Effects of porosity gradient of multilayered electrospun nanofibre mats on air filtration efficiency. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englesberg, J. Filtration—Theory and Practice. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1964, 56, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Gu, Z.; Cai, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. Filtration of dust in an electrostatically enhanced granular bed filter for high temperature gas cleanup. Powder Technol. 2020, 368, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, O.; Park, M. Electrostatic enhancement of fine dust filtration in a granular bed filter. Environ. Eng. Res. 2001, 6, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Roegiers, J.; Denys, S. Development of a novel type activated carbon fiber filter for indoor air purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; De, S.; Saha, P. Removal of VOCs and improvement of indoor air quality using activated carbon air filter. In Advances in Structural Technologies: Select Proceedings of CoAST 2019; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Wei, F.; Yang, X. Carbon nanotubes/activated carbon fiber based air filter media for simultaneous removal of particulate matter and ozone. Build. Environ. 2017, 125, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).