Evaluating the Yields of the Rainfed Potato Crop under Climate Change Scenarios Using the AquaCrop Model in the Peruvian Altiplano
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Details
2.3. Climate Data
2.4. Field Data Collection and AquaCrop Model Input Data
2.5. AquaCrop Model Calibration and Validation
2.6. Development of Climate Change Scenarios
3. Results
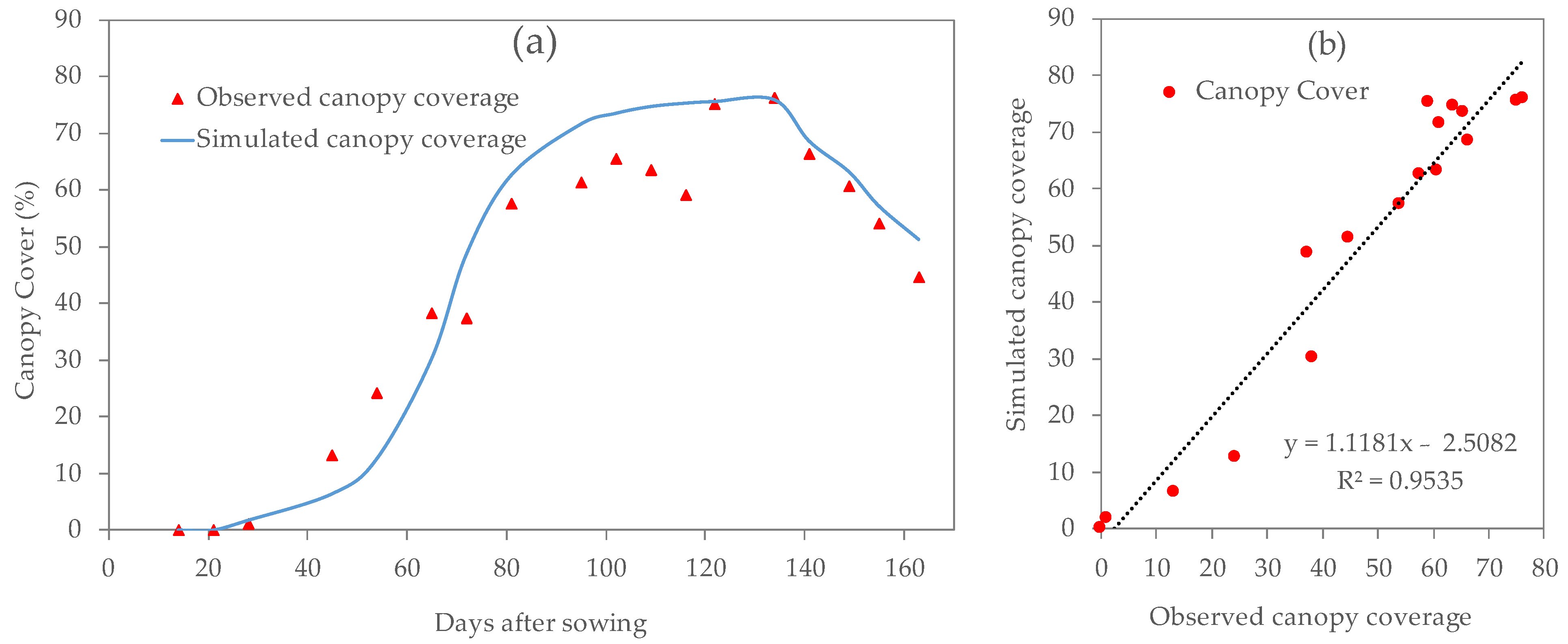
3.1. Calibration and Validation of the AquaCrop Model
3.2. Precipitation Changes
3.3. Analysis of the Change in Maximum and Minimum Temperature
3.4. Crop Yields under Climate Change Scenarios
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, J.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Ling, Y.; De Wulf, A.; De Maeyer, P. The Conflicts of Agricultural Water Supply and Demand under Climate Change in a Typical Arid Land Watershed of Central Asia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Nhung, T.; Le Vo, P.; Van Nghi, V.; Quoc Bang, H. Salt Intrusion Adaptation Measures for Sustainable Agricultural Development under Climate Change Effects: A Case of Ca Mau Peninsula, Vietnam. Clim. Risk Manag. 2019, 23, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eum, H.-I.; Fajard, B.; Tang, T.; Gupta, A. Potential Changes in Climate Indices in Alberta under Projected Global Warming of 1.5–5 °C. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 47, 101390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drebenstedt, I.; Marhan, S.; Poll, C.; Kandeler, E.; Högy, P. Annual Cumulative Ambient Precipitation Determines the Effects of Climate Change on Biomass and Yield of Three Important Field Crops. Field Crop. Res. 2023, 290, 108766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uleberg, E.; Hanssen-Bauer, I.; van Oort, B.; Dalmannsdottir, S. Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture in Northern Norway and Potential Strategies for Adaptation. Clim. Chang. 2014, 122, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, F.; Lyne, V.; Liu, T. Vegetation-Induced Asymmetric Diurnal Land Surface Temperatures Changes across Global Climate Zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewthong, N.; Ditthakit, P. Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture Water Demand in Lower Pak Phanang River Basin, Southern Part of Thailand. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 192, 03043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bially, M.E.; Saudy, H.S.; El-Metwally, I.M.; Shahin, M.G. Sunflower Response to Application of L-Ascorbate Under Thermal Stress Associated with Different Sowing Dates. Gesunde Pflanz. 2022, 74, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kattel, R.R.; Subedi, A.P. Climate Change and Agriculture Sector Frontier in Maize Cultivation among Chepang Communities of Nepal: Reviewed of Empirical Evidence. J. Maize Res. Dev. 2017, 3, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, L.M.; Samaniego, J.; Alatorre, J.E.; Ferrer, J.; Reyes, O. Cambio Climático, Agricultura y Pobreza: Una Aproximación Empírica; CEPAL: Santiago, Chile, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kuzucu, M.; Dökmen, F.; Günes, A. Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture Production Under Rain-Fed Condition. Int. J. Electron. Mech. Mechatron. Eng. 2016, 6, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Cheng, M.; Liao, Z.; Guo, J.; Zhang, F.; Fan, J.; Feng, H.; Yang, Q.; Wu, L.; Wang, X. Performance Evaluation of AquaCrop and DSSAT-SUBSTOR-Potato Models in Simulating Potato Growth, Yield and Water Productivity under Various Drip Fertigation Regimes. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 276, 108076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, W.; Barutçular, C.; Farooq, M.U.; Ahmad, H.; Jan, M.F.; Ahmad, Z.; Nawaz, H.; Li, M. Climate Change in Relation to Agriculture: A Review. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2022, 20, e03R01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eulenstein, F.; Willms, M.; Schindler, U.; Müller, L.; Mirschel, W.; Dalchow, C.; Augustin, J.; Wiggering, H. What Are the Efects of Climate Change on Agriculture in North East Central Europe? AgEcon Search 2006, 1, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Sayğı, H. Adverse Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture: An Evaluation of Fruit and Honey Bee Farming. Asian J. Agric. Rural Dev. 2020, 10, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochieng, J.; Kirimi, L.; Mathenge, M. Effects of Climate Variability and Change on Agricultural Production: The Case of Small Scale Farmers in Kenya. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2016, 77, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, Y. Sustainable Agriculture in the Face of Climate Change: Exploring Farmers’ Risk Perception, Low-Carbon Technology Adoption, and Productivity in the Guanzhong Plain of China. Water 2023, 15, 2228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simarmata, T.; Khais Proyoga, M.; Herdiyantoro, D.; Setiawati, M.R.; Adinata, K.; Stöber, S. Climate Resilient Sustainable Agriculture for Restoring the Soil Health and Increasing Rice Productivity as Adaptation Strategy to Climate Change in Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 748, 012039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhao, H. Sustainable Agriculture and Climate Change. In Innovations in Sustainable Agriculture; Farooq, M., Pisante, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 441–468. ISBN 978-3-030-23168-2. [Google Scholar]
- Semeraro, T.; Scarano, A.; Leggieri, A.; Calisi, A.; De Caroli, M. Impact of Climate Change on Agroecosystems and Potential Adaptation Strategies. Land 2023, 12, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurgel, A.C.; Reilly, J.; Blanc, E. Challenges in Simulating Economic Effects of Climate Change on Global Agricultural Markets. Clim. Chang. 2021, 166, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mibulo, T.; Kiggundu, N. Evaluation of FAO AquaCrop Model for Simulating Rainfed Maize Growth and Yields in Uganda. Agronomy 2018, 8, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wale, A.; Dessie, M.; Kendie, H. Evaluating the Performance of AquaCrop Model for Potato Production Under Deficit Irrigation. Air Soil Water Res. 2022, 15, 117862212211082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belizario, G. Epistemología Ambiental Aplicada al Cambio Climático y su Impacto en la Agricultura; ILAE, Primera, Ltd., Eds.; Instituto Latinoamericano de Altos Estudios: Bogotá, Colombia, 2021; ISBN 9789585367524. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, F.; Qin, P.; Zhang, J.; Lin, E.; Boken, V. Uncertainties in Assessing the Effect of Climate Change on Agriculture Using Model Simulation and Uncertainty Processing Methods. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2011, 56, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garreaud, R.; Vuille, M.; Clement, A.C. The Climate of the Altiplano: Observed Current Conditions and Mechanisms of Past Changes. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2003, 194, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillco Zolá, R.; Bengtsson, L.; Berndtsson, R.; Martí-Cardona, B.; Satgé, F.; Timouk, F.; Bonnet, M.-P.; Mollericon, L.; Gamarra, C.; Pasapera, J. Modeling Lake Titicaca Daily and Monthly Evaporation. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 23, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Maldonado, F.E.; Castaño-Marín, A.M.; Góez-Vinasco, G.A.; Marin, F.R. Gross Primary Production of Rainfed and Irrigated Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) in the Colombian Andean Region Using Eddy Covariance Technique. Water 2021, 13, 3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekanmbi, T.; Wang, X.; Basheer, S.; Nawaz, R.A.; Pang, T.; Hu, Y.; Liu, S. Assessing Future Climate Change Impacts on Potato Yields—A Case Study for Prince Edward Island, Canada. Foods 2023, 12, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G. Using the FAO-56 Dual Crop Coefficient Method over an Irrigated Region as Part of an Evapotranspiration Intercomparison Study. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droogers, P.; Allen, R.G. Estimating Reference Evapotranspiration Under Inaccurate Data Conditions. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2002, 16, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laqui, W.; Zubieta, R.; Rau, P.; Mejía, A.; Lavado, W.; Ingol, E. Can Artificial Neural Networks Estimate Potential Evapotranspiration in Peruvian Highlands? Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 5, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Allen, R.G. History and Evaluation of Hargreaves Evapotranspiration Equation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesh, B.; Reddy, K.S.; Polisgowdar, B.S.; Maruthi, V.; Satishkumar, U.; Ayyanagoudar, M.S.; Rao, S.; Veeresh, H. Assessment of Climate Change Impact on Maize (Zea mays L.) through Aquacrop Model in Semi-Arid Alfisol of Southern Telangana. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, F.; Camargo, D.; Ortega, J.F.; Córcoles, J.I.; Domínguez, A. Evaluation of Aquacrop Model for a Potato Crop under Different Irrigation Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 164, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. Some Comments on the Evaluation of Model Performance. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1982, 63, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. ASABE 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, P.D.; Porter, J.R.; Wilson, D.R. A Test of the Computer Simulation Model ARCWHEAT1 on Wheat Crops Grown in New Zealand. Field Crop. Res. 1991, 27, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vuuren, D.P.; Edmonds, J.; Kainuma, M.; Riahi, K.; Thomson, A.; Hibbard, K.; Hurtt, G.C.; Kram, T.; Krey, V.; Lamarque, J.-F.; et al. The Representative Concentration Pathways: An Overview. Clim. Chang. 2011, 109, 5–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.C.; Lyra, A.; Mourão, C.; Dereczynski, C.; Pilotto, I.; Gomes, J.; Bustamante, J.; Tavares, P.; Silva, A.; Rodrigues, D.; et al. Evaluation of the Eta Simulations Nested in Three Global Climate Models. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2014, 3, 438–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.C.; Lyra, A.; Mourão, C.; Dereczynski, C.; Pilotto, I.; Gomes, J.; Bustamante, J.; Tavares, P.; Silva, A.; Rodrigues, D.; et al. Assessment of Climate Change over South America under RCP 4.5 and 8.5 Downscaling Scenarios. Am. J. Clim. Chang. 2014, 3, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, A.; Tavares, P.; Chou, S.C.; Sueiro, G.; Dereczynski, C.; Sondermann, M.; Silva, A.; Marengo, J.; Giarolla, A. Climate Change Projections over Three Metropolitan Regions in Southeast Brazil Using the Non-Hydrostatic Eta Regional Climate Model at 5-Km Resolution. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2018, 132, 663–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teutschbein, C.; Seibert, J. Bias Correction of Regional Climate Model Simulations for Hydrological Climate-Change Impact Studies: Review and Evaluation of Different Methods. J. Hydrol. 2012, 456–457, 12–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willkofer, F.; Schmid, F.-J.; Komischke, H.; Korck, J.; Braun, M.; Ludwig, R. The Impact of Bias Correcting Regional Climate Model Results on Hydrological Indicators for Bavarian Catchments. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2018, 19, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, K.; Liu, Y.; Guo, R.; Chen, L. Assessing the Vulnerability and Risk of Maize to Drought in China Based on the AquaCrop Model. Agric. Syst. 2021, 189, 103040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DRA. Serie Histórica de Producción Agrícola. 2018. Available online: https://www.agropuno.gob.pe/estadistica-agraria-informatica/agricola/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Sanabria, J.; Lhomme, J.P. Climate Change and Potato Cropping in the Peruvian Altiplano. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grados, D.; García, S.; Schrevens, E. Assessing the Potato Yield Gap in the Peruvian Central Andes. Agric. Syst. 2020, 181, 102817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, D.; Steduto, P.; Hsiao, T.C.; Fereres, E. AquaCrop—The FAO Crop Model to Simulate Yield Response to Water: II. Main Algorithms and Software Description. Agron. J. 2009, 101, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, P.L.; Sanjuanelo, C.D.; Ñústez, L.C.E.; Moreno-Fonseca, L.P. Growth and Phenology of Three Andean Potato Varieties (Solanum tuberosum L.) under Water Stress. Agron. Colomb. 2016, 34, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, C. Ampliando la frontera agrícola de la papa (Solanum tubrosum L.) Para disminuir los efectos del cambio climático. Univ. Soc. Rev. Científica Univ. Cienfuegos 2018, 10, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Tonconi, J. Producción Agrícola Alimentaria y Cambio Climático: Un Análisis Económico en el Departamento de Puno, Perú Food Production Agriculture and Climate Change: An Economic Analysis in the Department of Puno, Peru. Idesia 2015, 33, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrazas, O.A. Estrategias Ecológicas para el Manejo del Tizón Tardío de la Papa. Phytophthora Infestans. 2017, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sanabria, J.; Marengo, J.; Valverde, M. Escenarios de Cambio Climático Con Modelos Regionales Sobre El Altiplano Peruano (Departamento de Puno). Rev. Peru. Geo-Atmosférica RPGA 2009, 149, 134–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lujano, E.; Hidalgo, L.; Tapia, B.; Lujano, A. Cambios Proyectados de Los Recursos Hídricos Bajo Escenarios de Emisiones RCP4.5 y 8.5 de Modelos Climáticos Globales Del CMIP5 En El Altiplano Peruano. Rev. Investig. Altoandinas J. High Andean Res. 2016, 18, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Miao, C.; Fan, X.; Gou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, H. Quantifying the Uncertainty Sources of Future Climate Projections and Narrowing Uncertainties with Bias Correction Techniques. Earths Future 2022, 10, e2022EF002963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iles, C.E.; Vautard, R.; Strachan, J.; Joussaume, S.; Eggen, B.R.; Hewitt, C.D. The Benefits of Increasing Resolution in Global and Regional Climate Simulations for European Climate Extremes. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 5583–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrin, G. El Cambio Climático En América Latina: Su Influencia en el Sector Agrícola y en la Producción del Cultivo de Papa. 2008. Available online: http://www.papaslatinas.org/home/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Magrin.pdf (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Galera, K.; Gonzáñez, K. Efectos Del Cambio Climático Sobre La Producción de Papa En El Municipio de Villapinzón (Cundinamarca-Colombia) a Partir Del Enfoque Ricardiano. Rev. Investig. Agrar. Ambient. 2014, 5, 231–242. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R.; Jerez, E. Efecto De las Temperaturas en el Rendimiento de la Papa. Cultiv. Trop. 2017, 38, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Martín, R.; Jeréz, E. Evaluación del Rendimiento en Papa de las Temperaturas. Inca 2015, 36, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Alavi, G.; Diels, J.; Willems, P.; Magali, G. Simulacion de La Produccion de Quinua En el Altiplano Boliviano Con el Modelo de AQUACROP Con Escenarios Futuros Generados Por LARS-WG y QPM. Investig. E Innov. Agropecu. Recur. Nat. 2015, 2, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- Egerer, S.; Puente, A.F.; Peichl, M.; Rakovec, O.; Samaniego, L.; Schneider, U.A. Limited Potential of Irrigation to Prevent Potato Yield Losses in Germany under Climate Change. Agric. Syst. 2023, 207, 103633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroz, R.; Ramírez, D.A.; Kroschel, J.; Andrade-Piedra, J.; Barreda, C.; Condori, B.; Mares, V.; Monneveux, P.; Perez, W. Impact of Climate Change on the Potato Crop and Biodiversity in Its Center of Origin. Open Agric. 2018, 3, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Jiménez, J.; Andersson, B.; Wiik, L.; Zhan, J. Modelling Potato Yield Losses Caused by Phytophthora Infestans: Aspects of Disease Growth Rate, Infection Time and Temperature under Climate Change. Field Crop. Res. 2023, 299, 108977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, D.; Fonseca, A.; Stolarski, O.; Freitas, T.R.; Guimarães, N.; Santos, J.A.; Fraga, H. Climate Change Impacts on the Côa Basin (Portugal) and Potential Impacts on Agricultural Irrigation. Water 2023, 15, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradel, W.; Gatto, M.; Hareau, G.; Pandey, S.K.; Bhardway, V. Adoption of Potato Varieties and Their Role for Climate Change Adaptation in India. Clim. Risk Manag. 2019, 23, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, E.; Manners, R.; Adewopo, J.; Thiele, G.; Friedmann, M.; Thornton, P. Strategizing Research and Development Investments in Climate Change Adaptation for Root, Tuber and Banana Crops in the African Great Lakes Region: A Spatial Prioritisation and Targeting Framework. Agric. Syst. 2022, 202, 103464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, G.; Mijatović, D.; Rojas, W.; Flores, J.; Pinto, M.; Mamani, G.; Condori, E.; Hilaquita, D.; Gruberg, H.; Padulosi, S. Climate Change and Crop Diversity: Farmers’ Perceptions and Adaptation on the Bolivian Altiplano. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2018, 20, 703–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El–Bially, M.E.; Saudy, H.S.; Hashem, F.A.; El–Gabry, Y.A.; Shahin, M.G. Salicylic Acid as a Tolerance Inducer of Drought Stress on Sunflower Grown in Sandy Soil. Gesunde Pflanz. 2022, 74, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andati, P.; Majiwa, E.; Ngigi, M.; Mbeche, R.; Ateka, J. Effect of Climate Smart Agriculture Technologies on Crop Yields: Evidence from Potato Production in Kenya. Clim. Risk Manag. 2023, 41, 100539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Characteristic | Values |
|---|---|
| Total area | 150.0 m2 |
| Number of plots | 6 |
| Plot area | 25.0 m2 |
| Number of rows per plot | 6 |
| Furrow length | 10.0 m |
| Row spacing | 0.42 m |
| Plant spacing | 0.40 m |
| Number of plants per row | 25 |
| Soil texture | sandy loam |
| Field capacity | 27.6% |
| Permanent wilting point | 14.2% |
| Bulk density | 1.6 g cm−3 |
| Saturation percentage | 42–49% |
| Hydraulic conductivity | 400 mm day−1 |
| Soil depth | 0–60 cm |
| pH | 5.8 |
| Organic matter | 3.15% |
| Total nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium | 0.15%, 8.6 ppm, 119 ppm |
| Stage | r | NRMSE | NEC | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 0.98 | 17.8 | 0.86 | 0.96 |
| Validation | 1.00 | 26.9 | 0.72 | 0.95 |
| Stage | r | NRMSE | NEC | d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 0.98 | 6.4 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| Validation | 0.96 | 9.6 | 0.96 | 0.98 |
| Stage | Performance (t ha−1) | Difference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Observed | Simulated | Absolute | Percentual | |
| Calibration | 11.73 | 11.78 | −0.06 | −0.44 |
| Validation | 11.12 | 10.57 | 0.53 | 0.87 |
| Routes | Scenarios | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CANESM2 | HADGEM2-ES | MIROC 5 | |
| RCP 4.5 | −1.90% | −2.93% | −5.40% |
| RCP 8.5 | 2.30% | 0.92% | 0.49% |
| Fuente | Average Annual Performance (t year−1) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | |
| Simulated | 10.21 | 10.39 | 10.49 | 10.57 | 10.66 | 10.77 | 10.91 | 11.00 | 11.12 | 11.23 | 11.33 | 12.91 | 12.49 |
| DRA | 9.58 | 9.69 | 9.08 | 7.13 | 8.56 | 9.38 | 10.11 | 9.53 | 10.34 | 9.66 | 11.57 | 10.60 | 11.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puma-Cahua, J.; Belizario, G.; Laqui, W.; Alfaro, R.; Huaquisto, E.; Calizaya, E. Evaluating the Yields of the Rainfed Potato Crop under Climate Change Scenarios Using the AquaCrop Model in the Peruvian Altiplano. Sustainability 2024, 16, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010071
Puma-Cahua J, Belizario G, Laqui W, Alfaro R, Huaquisto E, Calizaya E. Evaluating the Yields of the Rainfed Potato Crop under Climate Change Scenarios Using the AquaCrop Model in the Peruvian Altiplano. Sustainability. 2024; 16(1):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010071
Chicago/Turabian StylePuma-Cahua, Jesus, Germán Belizario, Wilber Laqui, Roberto Alfaro, Edilberto Huaquisto, and Elmer Calizaya. 2024. "Evaluating the Yields of the Rainfed Potato Crop under Climate Change Scenarios Using the AquaCrop Model in the Peruvian Altiplano" Sustainability 16, no. 1: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010071
APA StylePuma-Cahua, J., Belizario, G., Laqui, W., Alfaro, R., Huaquisto, E., & Calizaya, E. (2024). Evaluating the Yields of the Rainfed Potato Crop under Climate Change Scenarios Using the AquaCrop Model in the Peruvian Altiplano. Sustainability, 16(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16010071









