Effects of Sustainable Rice Management on the Behavior and Bioefficacy of Bispyribac-Sodium: A Medium-Term Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Herbicide and the Analytical Procedure
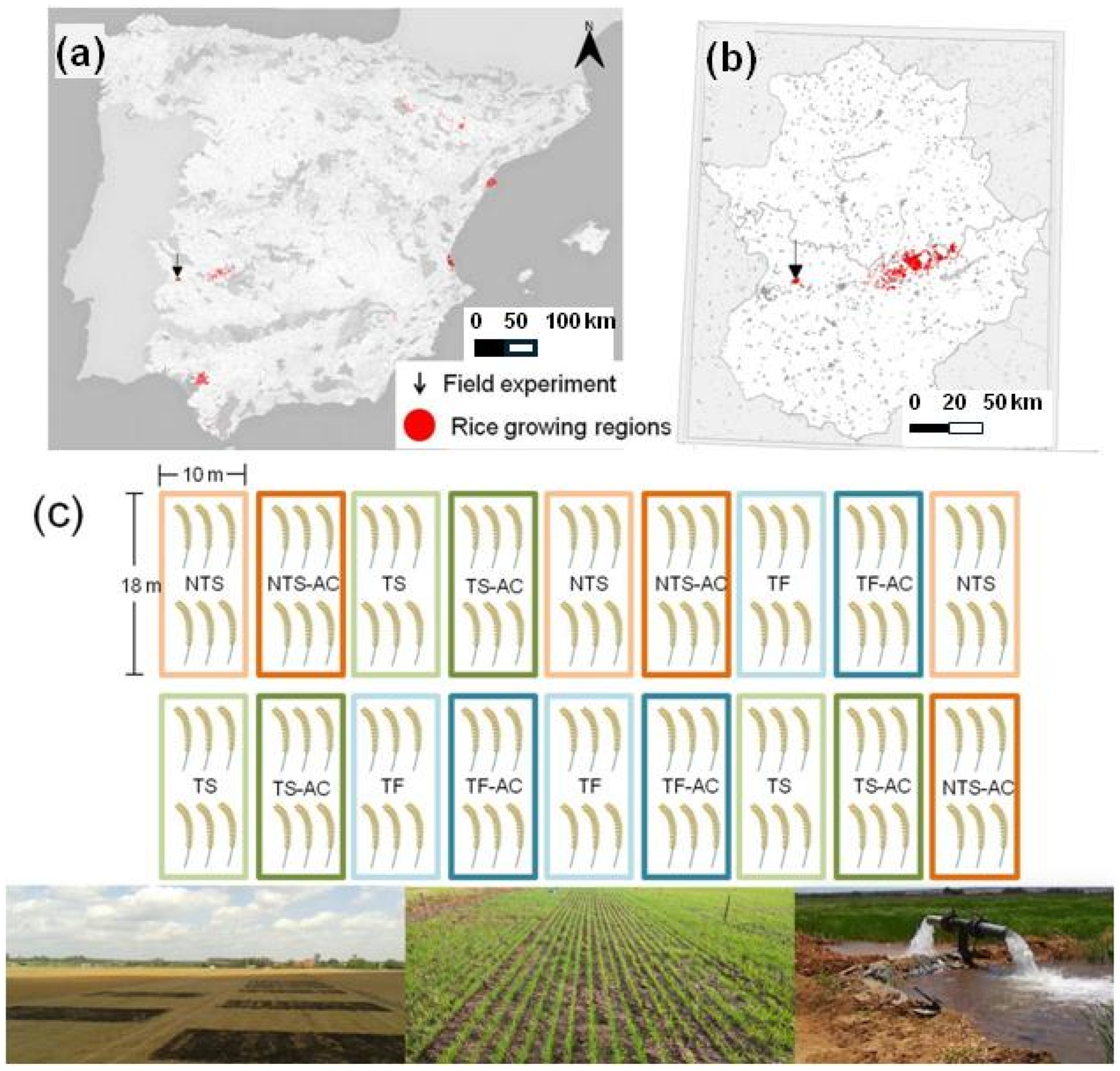
2.2. Design of the Experiments, Sampling, and Assay
2.3. Adsorption–Desorption Experiments
2.4. Dissipation Experiments
2.5. Leaching Experiments
2.6. Bioassays
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Adsorption–Desorption Experiments
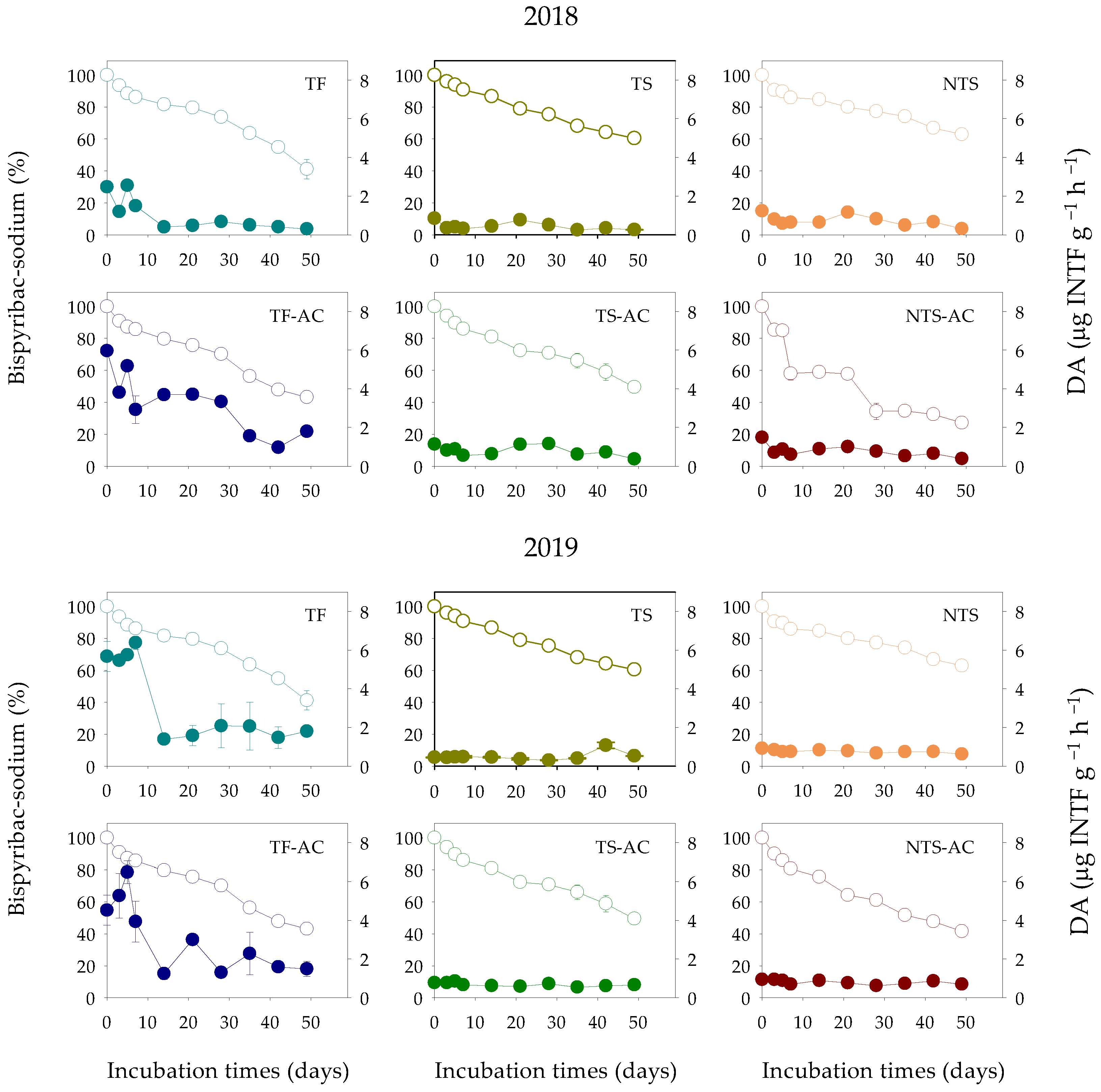
3.2. Dissipation Experiments
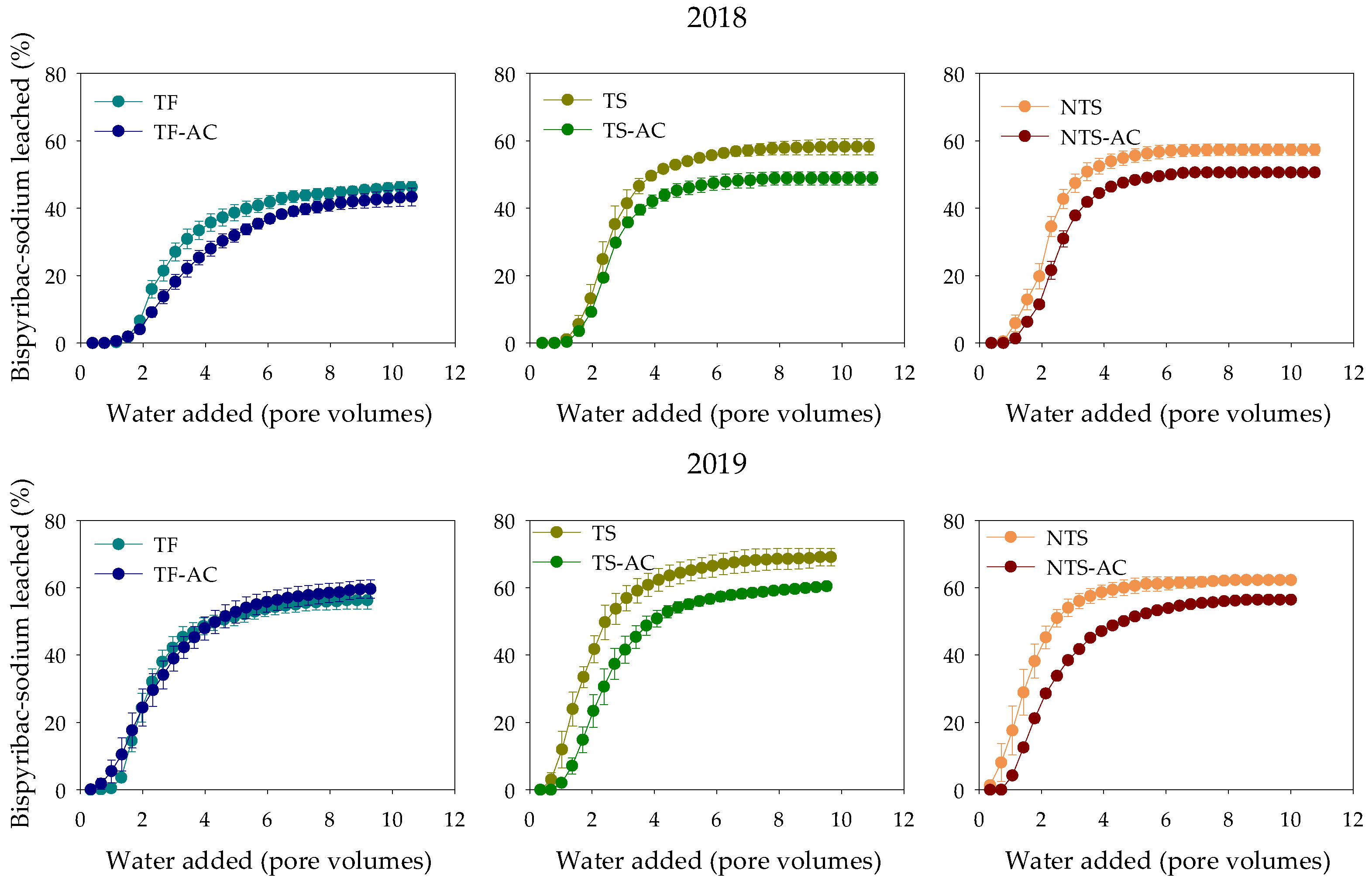
3.3. Leaching Experiments
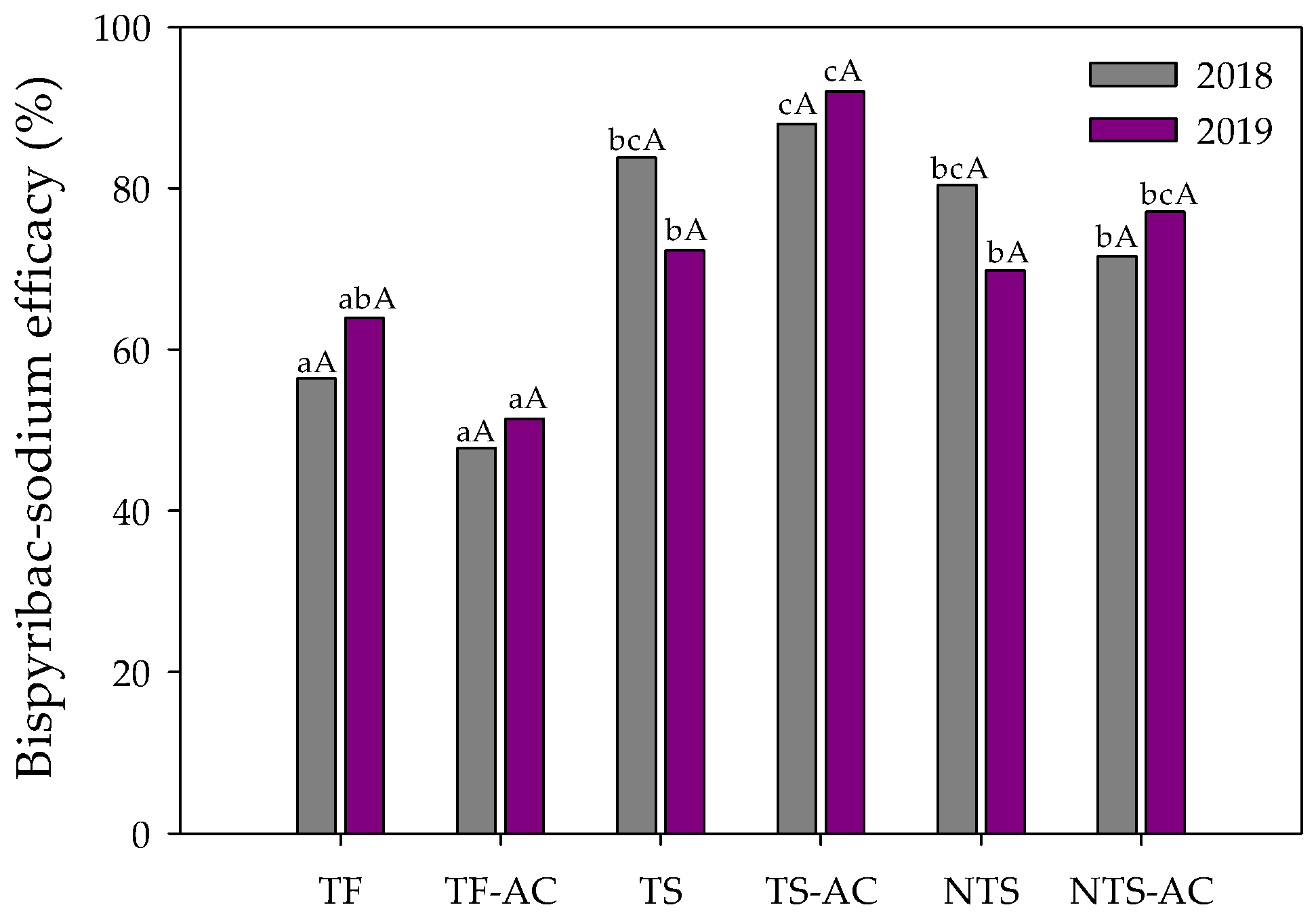
3.4. Bioassays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calha, I.; Oliveira, M.D.F.; Reis, P. Weed management challenges in rice cultivation in the context of pesticide use reduction: A survey approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, K.; Chen, Y.; Gong, H.; Feng, X.; Tang, Z.; Fu, D.; Qi, L. Benefits of mechanical weeding for weed control, rice growth characteristics and yield in paddy fields. Field Crops Res. 2023, 293, 108852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, S.; Jena, S.; Das, P.; Roul, P.K.; Maitra, S.; Shankar, T.; Sairam, M.; Swain, D.K.; Pramanick, B.; Gaber, A.; et al. Crop establishment methods and weed management practices influence the productivity and profitability of Kharif rice (Oryza sativa L.) in a hot-humid summer climatic conditions. Paddy Water Environ. 2023, 21, 447–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. European Commission. Farm to Fork Strategy. For a Fair, Healthy and Environmentally Friendly Food System. 2020. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/horizontal-topics/farm-fork-strategy_en (accessed on 15 January 2024).
- López-Piñeiro, A.; Martín-Franco, C.; Terrón-Sánchez, J.; Vicente, L.A.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Albarrán, Á.; Nunes, J.M.R.; Peña, D. Environmental fate and efficiency of bispyribac-sodium in rice soils under conventional and alternative production systems affected by fresh and aged biochar amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes-Díaz, A.; Alonso-Prados, E.; Alonso-Prados, J.L.; Sandín-España, P. Assessing the effect of organic amendments on the degradation of profoxydim in paddy soils: Kinetic modeling and identification of degradation products. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, B.; Parihar, C.M.; Jat, M.L.; Patra, K.; Nayak, H.S.; Reddy, K.S.; Sarkar, A.; Anand, A.; Naguib, W.; Gupta, N.; et al. Combining sub-surface fertigation with conservation agriculture in intensively irrigated rice under rice-wheat system can be an option for sustainably improving water and nitrogen use-efficiency. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbat, G.; Cufí, S.; Duran-Ros, M.; Pinsach, J.; Puig-Bargués, J.; Pujol, J.; de Cartagena, F.R. Modeling approaches for determining dripline depth and irrigation frequency of subsurface drip irrigated rice on different soil textures. Water 2020, 12, 1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straffelini, E.; Tarolli, P. Climate change-induced aridity is affecting agriculture in Northeast Italy. Agric. Syst. 2023, 208, 103647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Agriculture and Rural Development. Agri-Food Data Portal. Rice Production. 2024. Available online: https://agridata.ec.europa.eu/extensions/DashboardRice/RiceProduction.html (accessed on 30 April 2024).
- Kima, A.S.; Kima, E.; Bacyé, B.; Ouédraogo, P.A.W.; Traore, O.; Traore, S.; Nandkangré, H.; Chung, W.G.; Wang, Y.M. Evaluating supplementary water methodology with saturated soil irrigation for yield and water productivity improvement in semi-arid rainfed rice system, Burkina Faso. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.A.B.; Parfitt, J.M.B.; Timm, L.C.; Faria, L.C.; Concenço, G.; Stumpf, L.; Nörenberg, B.G. Sprinkler irrigation in lowland rice: Crop yield and its components as a function of water availability in different phenological phases. Field Crops Res. 2020, 248, 107714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vories, E.; Stevens, W.G.; Rhine, M.; Straatmann, Z. Investigating irrigation scheduling for rice using variable rate irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 179, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, A.; Murtas, A.; Ballone, F. Swater use and crop coefficients in sprinkler irrigated rice. Ital. J. Agron. 2009, 4, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, C.M.; Meena, B.R.; Nayak, H.S.; Patra, K.; Sena, D.R.; Singh, R.; Jat, S.L.; Sharma, D.K.; Mahala, D.M.; Patra, S.; et al. Co-implementation of precision nutrient management in long-term conservation agriculture-based systems: A step towards sustainable energy-water-food nexus. Energy 2022, 254, 124243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.N.A.; Uddin, M.K.; Sulaiman, M.F.; Amin, A.M.; Hossain, M.; Aziz, A.A.; Mosharrof, M. Impact of organic amendment with alternate wetting and drying irrigation on rice yield, water use efficiency and physicochemical properties of soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, K.G.; Thakur, A.K.; Ambast, S.K. Current rice farming, water resources and micro-irrigation. Curr. Sci. 2019, 116, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, S.; Fernández, D.; Peña, D.; Albarrán, Á.; López-Piñeiro, A. Behaviour of bispyribac-sodium in aerobic and anaerobic rice-growing conditions with and without olive-mill waste amendment. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavipour, T.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Doaei, S.; Noorhosseini, S.A.; Damalas, C.A. Azolla (Azolla filiculoides) compost improves grain yield of rice (Oryza sativa L.) under different irrigation regimes. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 209, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourencetti, J.; Bonini, C.D.S.B.; Andreotti, M.; Alves, M.C.; Bonini Neto, A.; Santos, M.A.; Barretto, V.C.D.M.; de Figueredo, R.W.R. Evolution of Soil Chemical Fertility in an Area under Recovery for 30 Years with Anthropic Intervention. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alburquerque, J.A.; Gonzálvez, J.; García, D.; Cegarra, J. Agrochemical characterisation of “alperujo”, a solid by-product of the two-phase centrifugation method for olive oil extraction. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 91, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejón, P.; Alaejos, J.; García-Álbala, J.; Fernández, M.; Madejón, E. Three-year study of fast-growing trees in degraded soils amended with composts: Effects on soil fertility and productivity. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 169, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sosa, L.L.; Sánchez-Piñero, M.; Girón, I.; Corell, M.; Madejón, E. Addition of compost changed responses of soil-tree system in olive groves in relation to the irrigation strategy. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 284, 108328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, F.; Scherner, A.; Massey, J.H.; Zanella, R.; Avila, L.A. Dissipation of Clomazone, Imazapyr, and Imazapic herbicides in paddy water under two rice flood management regimes. Weed Technol. 2017, 31, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okmen, G.; Donmez, G.; Donmez, S. Influence of nitrate, phosphate and herbicide stresses on nitrogenase activity and growth of cyanobacteria isolated from paddy fields. J. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2007, 1, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, N.; Kaur, P.; Jain, D.; Bhullar, M.S. In-vitro evaluation of rice straw biochars’ effect on bispyribac-sodium dissipation and microbial activity in soil. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2020, 191, 110204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chirukuri, R.; Atmakuru, R. Sorption characteristics and persistence of herbicide bispyribac sodium in different global soils. Chemosphere 2015, 138, 932–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, D.C.; Noldin, J.A.; Deschamps, F.C.; Resgalla, C., Jr. Ecological risk analysis of pesticides used on irrigated rice crops in southern Brazil. Chemosphere 2016, 162, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nag, S.K.; Kookana, R.; Smith, L.; Krull, E.; Macdonald, L.M.; Gill, G. Poor efficacy of herbicides in biochar-amended soils as affected by their chemistry and mode of action. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gámiz, B.; Velarde, P.; Spokas, K.A.; Hermosín, M.C.; Cox, L. Biochar soil additions affect herbicide fate: Importance of application timing and feedstock species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Sharma, N.; Kaur, K. Influence of pyrolysis temperature on rice straw biochar properties and corresponding effects on dynamic changes in bispyribac-sodium adsorption and leaching behavior in soil. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 463–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Piñeiro, A.; Sánchez-Llerena, J.; Peña, D.; Albarrán, Á.; Ramírez, M. Transition from flooding to sprinkler irrigation in Mediterranean rice growing ecosystems: Effect on behaviour of bispyribac sodium. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 223, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámiz, B.; Velarde, P.; Spokas, K.A.; Celis, R.; Cox, L. Changes in sorption and bioavailability of herbicides in soil amended with fresh and aged biochar. Geoderma 2019, 337, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Han, T.; Ren, T.; Sanderman, J.; Rui, Y.; Wang, B.; Smith, P.; Xu, M.; Li, Y. Declines in soil carbon storage under no tillage can be alleviated in the long run. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amami, R.; Ibrahimi, K.; Sher, F.; Milham, P.J.; Khriji, D.; Annabi, H.A.; Abrougui, K.; Chehaibi, S. Effects of conservation and standard tillage on soil physico-chemical properties and overall quality in a semi-arid agrosystem. Soil Res. 2022, 60, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldán, A.; Salinas-García, J.R.; Alguacil, M.M.; Caravaca, F. Changes in soil enzyme activity, fertility, aggregation and C sequestration mediated by conservation tillage practices and water regime in a maize field. Appl Soil Ecol 2005, 30, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya, T.; Cornelis, W.M.; Nyssen, J.; Govaerts, B.; Getnet, F.; Bauer, H.; Amare, K.; Raes, D.; Haile, M.; Deckers, J. Medium-term effects of conservation agriculture based cropping systems for sustainable soil and water management and crop productivity in the Ethiopian highlands. Field Crops Res. 2012, 132, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.S.; Zheng, M.; Ahmad, S.; Cao, C.G. Effects of short-term tillage and fertilization on grain yields and soil properties of rice production systems in central China. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 577–584. [Google Scholar]
- López-Fando, C.; Pardo, M.T. Changes in soil chemical characteristics with different tillage practices in a semi-arid environment. Soil Till. Res. 2009, 104, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liben, F.M.; Tadesse, B.; Tola, Y.T.; Wortmann, C.S.; Kim, H.K.; Mupangwa, W. Conservation agriculture effects on crop productivity and soil properties in Ethiopia. Agron. J. 2018, 110, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BPDB. Biopesticides Properties Database. University of Hertfordshire. 2024. Available online: http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/bpdb/ (accessed on 7 February 2024).
- FAO. Guidelines for Soil Description; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2006; Available online: https://www.fao.org/3/a0541e/a0541e.pdf (accessed on 22 April 2024).
- Peña, D.; Albarrán, Á.; López-Piñeiro, A.; Rato-Nunes, J.M.; Sánchez-Llerena, J.; Becerra, D. Impact of oiled and de-oiled olive mill waste amendments on the sorption, leaching, and persistence of S-metolachlor in a calcareous clay soil. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2013, 48, 767–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trevors, J.T. Dehydrogenase activity in soil: A comparison between the INT and TTC assay. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1984, 16, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, S.B. Adsorption and leaching behaviour of bispyribac-sodium in soils. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2015, 94, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Devi, S.; Kaur, P.; Sondhia, S. Behaviour of bispyribac sodium in soil and its impact on biochemical constituents of rice. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 4791–4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, J.M.; Hale, T. Increasing and decreasing pH to enhance the biological activity of nicosulfuron. Weed Technol. 2005, 19, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, M.R.; El-Aswad, A.F.; Aly, M.I.; Badawy, M.E.I. Sorption characteristics and thermodynamic parameters of bispyribac-sodium and metribuzin on alluvial soil with difference in particle size and pH value. Curr. Chem. Lett. 2023, 12, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alister, C.A.; Araya, M.A.; Kogan, M. Adsorption and desorption variability of four herbicides used in paddy rice production. J. Environ. Sci. Health B 2010, 46, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalsi, N.K.; Kaur, P. Dissipation of bispyribac sodium in aridisols: Impact of soil type, moisture and temperature. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2019, 170, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimche, G.B.; Machado, S.L.O.; Oliveira, M.A.; Zanella, R.; Dressler, V.L.; Flores, E.M.M.; Gonçalves, F.F.; Donato, F.F.; Nunes, M.A.G. Imazethapyr and imazapic, bispyribac-sodium and penoxsulam: Zooplankton and dissipation in subtropical rice paddy water. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 514, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Jaramillo, M.; Cox, L.; Hermosín, M.C.; Cerli, C.; Kalbitz, K. Influence of green waste compost on azimsulfuron dissipation and soil functions under oxic and anoxic conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpio, M.J.; Marín-Benito, J.M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.J.; Rodríguez-Cruz, M.S. Accelerated dissipation of two herbicides after repeated application in field experiments with organically-amended soil. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, P.; Kaur, H.; Kaur Kalsi, N.; Bhullar, M.S. Evaluation of leaching potential of penoxsulam and bispyribac sodium in Punjab soils under laboratory conditions. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 7376–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, M.R.; El-Aswad, A.F.; Badawy, M.E.I.; Aly, M.I. Impact of organic amendments addition to sandy clay loam soil and sandy loam soil on leaching process of chlorantraniliprole insecticide and bispyribac-sodium herbicide. Curr. Chem. Lett. 2024, 13, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Rao, L.; Hu, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, B.; Tang, L. Effects of different factors on the adsorption–desorption behavior of Glyamifop and its migration characteristics in agricultural soils across China. Microchem. J. 2021, 170, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Sheng, G.; Huang, M. Bioavailability of diuron in soil containing wheat-straw-derived char. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 354, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavari, S.; Kamyab, H.; Binti Abd Manan, T.S.; Chelliapan, S.; Asadpour, R.; Yavari, S.; Saparim, N.B.; Baloo, L.; Sidik, A.B.C.; Kirpichnikova, I. Bio-efficacy of imidazolinones in weed control in a tropical paddy soil amended with optimized agrowaste-derived biochars. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, D.; Albarrán, Á.; Gómez, S.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Rato-Nunes, J.M.; López-Piñeiro, A. Effects of olive mill wastes with different degrees of maturity on behaviour of S-metolachlor in three soils. Geoderma 2019, 348, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| TOC (g kg−1) | WSOC (mg kg−1) | HA (g kg−1) | FA (g kg−1) | pH | EC (dS m−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | ||||||
| TF | 10.8aB | 293abB | 0.858aA | 0.831bA | 5.52aA | 1.93bA |
| TF-AC | 20.9cA | 716cA | 1.48bA | 0.971cA | 5.92bA | 1.52aA |
| TS | 10.2aA | 257abA | 0.911aA | 0.891bA | 6.27cA | 1.87bA |
| TS-AC | 16.6bA | 721cB | 1.41bA | 1.25eA | 6.89eB | 2.08cA |
| NTS | 11.1aA | 211aA | 0.869aA | 0.559aA | 6.73dB | 1.45aA |
| NTS-AC | 16.8bA | 392bA | 1.53bA | 1.05dA | 6.94eB | 1.79bA |
| 2019 | ||||||
| TF | 10.1aA | 240aA | 0.833abA | 0.939bA | 5.64aB | 2.74bB |
| TF-AC | 21.4eA | 562cA | 1.44cA | 0.996bA | 6.11bB | 2.65bB |
| TS | 11.6bB | 356bB | 0.736aA | 1.00bA | 6.29cA | 2.12aA |
| TS-AC | 18.6dB | 402bA | 1.30cA | 1.18cA | 6.62eA | 3.93cB |
| NTS | 12.3cA | 333bB | 0.958bA | 0.775aB | 6.46dA | 5.97dB |
| NTS-AC | 21.6eB | 357bA | 1.96dA | 1.04bA | 6.61eA | 3.73cB |
| M | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| Y | *** | ** | NS | * | *** | *** |
| M × Y | ** | *** | * | NS | *** | *** |
| nf | Kd | R2 | H | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | ||||
| TF | 0.929abcA | 0.973dB | 0.991 | 386aA |
| TF-AC | 0.979cA | 1.067eB | 0.988 | 481abA |
| TS | 0.909abcA | 0.486bA | 0.984 | 996bB |
| TS-AC | 0.944bcA | 0.537cA | 0.989 | 1894cB |
| NTS | 0.848aA | 0.387aA | 0.982 | 316aA |
| NTS-AC | 0.879abB | 0.512bcA | 0.989 | 641abA |
| 2019 | ||||
| TF | 0.889bcA | 0.776dA | 0.994 | 462abA |
| TF-AC | 0.924cA | 0.905eA | 0.997 | 496abA |
| TS | 0.892bcA | 0.489aA | 0.998 | 416abA |
| TS-AC | 0.863abA | 0.664bB | 0.997 | 872cA |
| NTS | 0.865bA | 0.482aB | 0.996 | 330aA |
| NTS-AC | 0.821aA | 0.717cB | 0.996 | 625bA |
| M | * | *** | *** | |
| Y | * | * | * | |
| M × Y | NS | *** | ** |
| t1/2 (days) | R2 | DA (µg INTF g−1 h−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | |||
| TF | 32.3bA | 0.955 | 9.77cA |
| TF-AC | 27.5aA | 0.902 | 31.78dA |
| TS | 59.5dA | 0.934 | 5.21aA |
| TS-AC | 38.7cA | 0.979 | 8.58bB |
| NTS | 60.6dA | 0.809 | 8.27bB |
| NTS-AC | 40.4cA | 0.949 | 8.74bA |
| 2019 | |||
| TF | 46.6aB | 0.914 | 33.65cB |
| TF-AC | 43.2aB | 0.955 | 31.13cA |
| TS | 67.7cB | 0.992 | 4.96aA |
| TS-AC | 55.7bB | 0.955 | 6.81abA |
| NTS | 86.4dB | 0.954 | 7.63bA |
| NTS-AC | 41.3aA | 0.986 | 8.03bA |
| M | *** | *** | |
| Y | *** | *** | |
| M × Y | *** | *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López-Piñeiro, A.; Vicente, L.; Fernández-Rodríguez, D.; Albarrán, Á.; Nunes, J.M.R.; Peña, D. Effects of Sustainable Rice Management on the Behavior and Bioefficacy of Bispyribac-Sodium: A Medium-Term Study. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104157
López-Piñeiro A, Vicente L, Fernández-Rodríguez D, Albarrán Á, Nunes JMR, Peña D. Effects of Sustainable Rice Management on the Behavior and Bioefficacy of Bispyribac-Sodium: A Medium-Term Study. Sustainability. 2024; 16(10):4157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104157
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez-Piñeiro, Antonio, Luis Vicente, Damián Fernández-Rodríguez, Ángel Albarrán, José Manuel Rato Nunes, and David Peña. 2024. "Effects of Sustainable Rice Management on the Behavior and Bioefficacy of Bispyribac-Sodium: A Medium-Term Study" Sustainability 16, no. 10: 4157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104157
APA StyleLópez-Piñeiro, A., Vicente, L., Fernández-Rodríguez, D., Albarrán, Á., Nunes, J. M. R., & Peña, D. (2024). Effects of Sustainable Rice Management on the Behavior and Bioefficacy of Bispyribac-Sodium: A Medium-Term Study. Sustainability, 16(10), 4157. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16104157






