Economic and Environmental Benefit Analysis between Crumb Rubber Concrete and Ordinary Portland Cement Concrete
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. The Concept and Comparison of Similar Strength Concrete
3.1. Mix Proportions of CRC with Similar Strength
3.2. Mechanical Character of CRC with Similar Strength
3.3. Comparison with Standard Code for CRC with the Same Strength
4. Analysis of Economic Benefit
4.1. Direct Cost Calculation and Comparison of Two Types of Concrete
4.2. Further Cost Analysis
4.3. Analysis of Environmental Benefit
Calculation of CO2 Emissions
4.4. Other Environmental Benefits
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- [WBCSD] World Business Council for Sustainable Development. End-of-Life Tyres: A Framework for Effective Management Systems; World Business Council for Sustainable Development: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010; Available online: http://docs.wbcsd.org/2010/10/AFrameworkForEffectiveManagementSystems.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2018).
- [BDRC] Bosi Data Research Center. 2017–2022 China Waste Tire Market Analysis and Investment Prospects Research Report; Bosi Data Research Center: Beijing, China, 2017; Available online: http://www.bosidata.com/report/E647759GG4.html (accessed on 14 April 2024).
- Wang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Lin, K.; Wang, C. Estimation and Analysis of Energy Conservation and Emissions Reduction Effects of Warm-Mix Crumb Rubber-Modified Asphalts during Construction Period. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presti, D.L. Recycled tyre rubber modified bitumens for road asphalt mixtures: A literature review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 863–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Shan, L.; Zhang, T.; Ma, H.; Cai, Z.; Shi, H. Investigation on polymer–rubber aggregate modified porous concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martınez, J.D.; Neus, P.; Ramon, M.; Tomas, G.; Victoria, N.M.; Mastral, A. Waste tyre pyrolysis—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 23, 179–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Torgal, F.; Ding, Y.; Jalali, S. Properties and durability of concrete containing polymeric wastes (tyre rubber and polyethylene terephthalate bottles): An overview. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 30, 714–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [ETRMA] European Tyre and Rubber Manufacturers Association. End of Life Tyres: A Valuable Resource with Growing Potential; European Tyre and Rubber Manufacturers Association: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Widyatmoko, I.; Elliot, R. A Review of the Use of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Worldwide; Waste & Resources Action Programme (WRAP): Banbury, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Batayneh, M.K.; Marie, I.; Asi, I. Promoting the use of crumb rubber concrete in developing countries. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leviton, L.C.; Cook, T.D. What differentiates meta-analysis from other forms of review 1. J. Personal. 1981, 49, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsey, M.W.; Wilson, D.B. Practical Meta-Analysis; SAGE publications, Inc.: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Borenstein, M.; Hedges, L.V.; Higgins, J.P.; Rothstein, H.R. Introduction to Meta-Analysis; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Haridharan, M.K.; Murugan, R.B.; Natarajan, C.; Muthukannan, M. Influence of Waste Tyre Crumb Rubber on Compressive Strength. Static Modulus of Elasticity and Flexural Strength of Concrete. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2017; Volume 80, p. 012014. [Google Scholar]
- Isa, N.F.; Zaki, M.F.; Sofri, L.; Rahim, M.; Ghazaly, Z.; Bidin, N. The use of rubber manufacturing waste as concrete additive. Adv. Res. Appl. Mech. 2014, 4, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Bisht, K.; Ramana, P.V. Evaluation of mechanical and durability properties of crumb rubber concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Degirmenci, N. Possibility of using waste tire rubber and fly ash with Portland cement as construction materials. Waste Manag. 2009, 29, 1541–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, A. Effect of waste tyre rubber on mechanical and durability properties of concrete—A review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2018, 9, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, N.N.; Senouci, A.B. Rubber-tire particles as concrete aggregate. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 1993, 5, 478–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Ruan, S.; Zeng, L. Mechanical properties and constitutive equations of concrete containing a low volume of tire rubber particles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 70, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudaoud, Z.; Beddar, M. Effects of recycled tires rubber aggregates on the characteristics of cement concrete. Civ. Eng. 2012, 2, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjian, E.; Khorami, M.; Maghsoudi, A.A. Scrap-tyre-rubber replacement for aggregate and filler in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2009, 23, 1828–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, K.C.; Parhi, P.S.; Jena, T. Scrap-Tyre-Rubber replacement for aggregate in cement concrete: Experimental study. Int. J. Earth Sci. Eng. 2012, 5, 1692–1701. [Google Scholar]
- Elchalakani, M. High strength rubberized concrete containing silica fume for the construction of sustainable road side barriers. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 20–38. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, R.; Leng, Z.; Hsu, M.S.C.; Yu, H.; Wang, Y. Integrated sustainability assessment of asphalt rubber pavement based on life cycle analysis. In Pavement Life-Cycle Assessment; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; pp. 209–220. [Google Scholar]
- Hallmark-Haack, B.L.; Hernandez, N.B.; Williams, R.C.; Cochran, E.W. Ground Tire Rubber Modification for Improved Asphalt Storage Stability. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayasundara, M.; Mendis, P.; Crawford, R.H. A framework for the integrated cost-benefit analysis of the use of recycled aggregate concrete in structural applications. Living Learn. Res. A Better Built Environ. 2015, 12, 647–657. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasekaran, S.R.; Najafi, F.T. A Graduate Research on the Cost Effective Analysis and Environmental Impact of Using Industrial Byproducts as Supplementary Cementitious Materials in Building Construction. In Proceedings of the ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition, Columbus, OH, USA, 25–28 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mannan, M.A.; Ganapathy, C. Concrete from an agricultural waste-oil palm shell (OPS). Build. Environ. 2004, 39, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, A.S.; Al-Deen, S.; Ashraf, M. Behaviour of similar strength crumbed rubber concrete (CRC) mixes with different mix proportions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 137, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, B.S.; Gupta, R.C.; Panicker, V.J. Recycling of waste tire rubber as aggregate in concrete: Durability-related performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvakumar, S.; Venkatakrishnaiah, R. Strength properties of concrete using crumb rubber with partial replacement of fine aggregate. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2015, 4, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.K.; Hassan, A.A.A.; Abdelaleem, B.H. Flexural Behaviour of Reinforced SCC Beams Containing Recycled Crumb Rubber; Resilient Infrastructure: Landon, UK, 2016; p. 11. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, W.; Li, L.; Feng, W.; Ning, G. Mechanical and fatigue performance of rubber concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 47, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. Study on the effect of rubber particles on self-compacting and cracking resistance of concrete. Fujian Constr. Technol. 2022, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, G.; Sun, L.; Wan, Z. Study on Compressive Strength of Rubber Concrete Cube Based on Meso-level. Concrete 2022, 387, 84–87+96. [Google Scholar]
- Wakchaure, M.R.; Chavan, P.A. Waste tyre crumb rubber particle as a partial replacement to fine aggregate in concrete. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 1206–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Khaloo, A.R.; Dehestani, M.; Rahmatabadi, P. Mechanical properties of concrete containing a high volume of tire–rubber particles. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2472–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Sha, T. Experimental investigation of the mechanical and durability properties of crumb rubber concrete. Materials 2016, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; He, M.; Qiu, J.; Yuan, K. Mechanical properties and constitutive model of rubber desert sand concrete. J. Shihezi Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2023, 41, 199–206. [Google Scholar]
- International Federation for Structure Concrete. fib Model Code for Concrete Structures; International Fedaration for Structural Concrete: Lausanne, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- AS 360; Concrete Structures, Design Properties of Materials. SAI Global Limited under licience from Standards Australia Ltd.: Sydney, NSW, Australia, 2009.
- GB/T 50010-2010; Code for Design of Concrete Structure. Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- CoreLogic. Cordwell Estimator Platinum. 2021. Available online: https://www.corelogic.com.au/products/cordellplatinum (accessed on 14 April 2024).
- Mahasenan, N.; Smith, S.; Humphreys, K. The cement industry and global climate change: Current and potential future cement industry CO2 emissions. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Greenhouse Gas Control Technologies, Kyoto, Japan, 1–4 October 2002; pp. 995–1000. [Google Scholar]
- [EFCAA] European Federation of Concrete Admixture Associations. Environmental Declaration Superplasticizing Admixtures; European Federation of Concrete Admixture Associations: Ulft, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 51366-2019; Standard for Building Carbon Emissions Calculation. Ministry of Housing and Urban Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019.
- Cho, S.; Na, S. The Reduction of CO2 Emissions by Application of High-Strength Reinforcing Bars to Three Different Structural Systems in South Korea. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajaste, R.; Hurme, M. Cement industry greenhouse gas emissions–management options and abatement cost. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 4041–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, L.K.; Collins, F.G. Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions: A comparison between geopolymer and OPCC cement concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- [WORLD BANK ORG] State and Trends of Carbon Pricing. 2022. Available online: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/igo (accessed on 14 April 2024).
- Downard, J.; Singh, A.; Bullard, R.; Jayarathne, T.; Rathnayake, C.M.; Simmons, D.L.; Wels, B.R.; Spak, S.N.; Peters, T.; Beardsley, D.; et al. Uncontrolled combustion of shredded tires in a landfill—Part 1: Characterization of gaseous and particulate emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 104, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Mix ID | W/C Ratio | Rubber Content | Cement (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | CA (kg/m3) | FA (kg/m3) | Rubber (kg/m3) | Admixture (kg/m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 14 mm | ||||||||
| 40C | 0.52 | 0 | 380 | 197.6 | 927.0 | 858.0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 40R1 | 0.5 | 5.33 | 388 | 194.0 | 465.6 | 737.2 | 663.48 | 14.73 | 0 |
| 40R2 | 0.45 | 10.63 | 388 | 174.6 | 465.6 | 737.2 | 628.56 | 29.47 | 2.52 |
| 40R3 | 0.4 | 21.11 | 388 | 155.2 | 465.6 | 737.2 | 558.72 | 58.95 | 2.45 |
| 40R4 | 0.4 | 15 | 315 | 180 | 1045 | 575 | 39 | -- | |
| 40R5 | 0.45 | 20 | 400 | 180 | 1061 | 664 | 64.2 | 3.1 | |
| 40R6 | 0.42 | 5 | 380.95 | 160 | 1169.72 | 603.39 | 93.32 | -- | |
| 40R7 | 0.4 | 5 | 500 | 200 | 686.5 | 931.7 | 17.9 | 2.37 | |
| 40R8 | 0.4 | 10 | 500 | 200 | 686.5 | 882.7 | 35.8 | 2.37 | |
| 40R9 | 0.31 | 5 | 420 | 131.5 | 1296 | 527 | 11.68 | 5 | |
| 40R10 | 0.4 | 2.5 | 388 | 155.2 | 1202.8 | 680.94 | 7.37 | 0.65 | |
| 40R11 | 0.4 | 5 | 388 | 155.2 | 1202.8 | 663.48 | 14.73 | 0.65 | |
| 40R12 | 0.4 | 7.5 | 388 | 155.2 | 1202.8 | 646.0 | 22.11 | -- | |
| 40R13 | 0.45 | 2.5 | 388 | 174.6 | 1202.8 | 680.9 | 7.37 | -- | |
| 40R14 | 0.49 | 2 | 424 | 209 | 1105 | 640 | 8.49 | 2.46 | |
| 40R15 | 0.49 | 4 | 424 | 209 | 1105 | 619 | 16.97 | 2.46 | |
| 40R16 | 0.49 | 6 | 424 | 209 | 1105 | 598 | 25.46 | 2.46 | |
| Mix ID | W/C Ratio | Rubber Content | Cement (kg/m3) | Water (kg/m3) | CA (kg/m3) | FA (kg/m3) | Rubber (kg/m3) | Admixture (kg/m3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm | 14 mm | ||||||||
| 30C | 0.5 | 0 | 380 | 190 | 927.0 | 858.0 | 0 | 1.52 | |
| 30R1 | 0.49 | 16.22 | 424 | 209 | 1105.0 | 0 | 556.0 | 42.44 | 0 |
| 30R2 | 0.50 | 13.26 | 388 | 194 | 465.6 | 737.2 | 611.10 | 36.84 | 2.5 |
| 30R3 | 0.56 | 05.40 | 300 | 167 | 1107.2 | 0 | 885.85 | 20.00 | 4.36 |
| 30R4 | 0.45 | 15 | 377.78 | 170 | 1236.44 | 565.91 | 42.94 | 0.76 | |
| 30R5 | 0.55 | 10 | 400 | 218 | 1084.3 | 515 | 37.77 | 0 | |
| 30R6 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 383.2 | 191.6 | 1067.27 | 738.03 | 3.71 | 0 | |
| 30R7 | 0.5 | 1 | 383.2 | 191.6 | 1067.27 | 734.32 | 7.417 | 0 | |
| 30R8 | 0.42 | 10 | 380.95 | 160 | 1169.72 | 627.04 | 69.67 | 0 | |
| 30R9 | 0.42 | 15 | 380.95 | 160 | 1169.72 | 592.21 | 70.49 | 0 | |
| 30R10 | 0.42 | 5 | 430 | 180 | 1197 | 563.4 | 13.4 | 0 | |
| 30R11 | 0.42 | 10 | 430 | 180 | 1197 | 533.7 | 26.8 | 0 | |
| 30R12 | 0.42 | 15 | 430 | 180 | 1197 | 504.1 | 40.2 | 0 | |
| 30R13 | 0.42 | 20 | 430 | 180 | 1197 | 474.4 | 56.3 | 0 | |
| 30R14 | 0.42 | 1 | 425.7 | 178.2 | 1185.0 | 587.1 | 12 | 0 | |
| 30R15 | 0.42 | 3 | 417.1 | 174.6 | 1161.1 | 575.2 | 36 | 0 | |
| 30R16 | 0.4 | 15 | 500 | 200 | 686.5 | 833.7 | 53.8 | 2.37 | |
| 30R17 | 0.31 | 10 | 420 | 131.5 | 1296 | 500 | 22.95 | 5 | |
| 30R18 | 0.4 | 10 | 388 | 155.2 | 1202.8 | 628.56 | 29.47 | 0.65 | |
| 30R19 | 0.4 | 12.5 | 388 | 155.2 | 1202.8 | 611.1 | 36.84 | 0.65 | |
| 30R20 | 0.45 | 5 | 388 | 174.6 | 1202.8 | 663.48 | 14.73 | 0.3 | |
| 30R21 | 0.45 | 7.5 | 388 | 174.6 | 1202.8 | 646.02 | 22.11 | 0.3 | |
| 30R22 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 388 | 194 | 1202.8 | 680.94 | 7.37 | 0 | |
| 30R23 | 0.5 | 5 | 388 | 194 | 1202.8 | 663.48 | 14.73 | 0 | |
| 30R24 | 0.5 | 7.5 | 388 | 194 | 1202.8 | 646.02 | 22.11 | 0 | |
| 30R25 | 0.49 | 4 | 424 | 209 | 1105 | 619 | 16.97 | 2.46 | |
| 30R26 | 0.49 | 8 | 424 | 209 | 1105 | 577 | 33.95 | 2.46 | |
| 30R27 | 0.49 | 6 | 424 | 209 | 1105 | 598 | 25.46 | 2.46 | |
| 30R28 | 0.49 | 10 | 424 | 209 | 1105 | 556 | 42.44 | 2.46 | |
| Mix ID | Compressive Strength | Tensile Strength | Elastic Modulus | Flexural Modulus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPa | % | MPa | % | /GPa | % | MPa | % | |
| 40C | 45.8(cy) | 3 | 29.00 | 5.4 | -- | |||
| 40R1 | 39.35(cy) | −14.08 | 3.84 | 28.00 | 31.13 | 7.34 | -- | -- |
| 40R2 | 45.35(cy) | −0.98 | 4.00 | 33.33 | 30.07 | 3.69 | -- | -- |
| 40R3 | 46.05(cy) | 0.55 | 3.87 | 29.00 | 28.87 | −0.45 | -- | -- |
| 40R4 | 39.91(c) | −12.86 | 2.13 | −29.00 | 31.72 | 9.38 | 4.32 | −20.00 |
| 40R5 | 42.96(c) | −6.20 | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | |
| 40R6 | 38.66(c) | −15.59 | 3.50 | 16.67 | -- | 7.01 | 29.81 | |
| 40R7 | 43(cy) | −6.11 | 3.23 | 7.67 | -- | -- | -- | |
| 40R8 | 41.8(cy) | −8.73 | 2.94 | −2.00 | -- | -- | -- | |
| 40R9 | 38.2(c) | −16.59 | -- | -- | -- | 5.3 | −1.85 | |
| 40R10 | 41(c) | −10.48 | -- | -- | -- | 5.2 | −3.70 | |
| 40R11 | 37.5(c) | −18.12 | -- | -- | -- | 5.01 | −7.22 | |
| 40R12 | 37(c) | −19.21 | -- | -- | -- | 4.8 | −11.11 | |
| 40R13 | 38(c) | −17.03 | -- | -- | -- | 5.32 | −1.48 | |
| 40R14 | 37.92(c) | −17.21 | -- | -- | 31.66 | 9.17 | ||
| 40R15 | 35.91(c) | −21.59 | -- | -- | 31.33 | 8.03 | ||
| 40R16 | 35.8(c) | −21.83 | -- | -- | 31.3 | 7.93 | ||
| AVE () | 40.25 | −12.88 | 3.31 | 10.46 | 30.64 | 5.64 | 5.30 | −1.94 |
| STDEV () | 3.283 | 0.585 | 1.090 | 0.728 | ||||
| Coefficient of deviation () | 0.082 | 0.177 | 0.036 | 0.137 | ||||
| Mix ID | Compressive Strength | Tensile Strength | Elastic Modulus | Flexural Modulus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPa | % | MPa | % | /GPa | % | MPa | % | |
| 30C | 32.5(c) | -- | 3 | -- | 28.3 | 5.38 | -- | |
| 30R1 | 33.67(cy) | 3.60 | 3.01 | 0.33 | 25.37 | −10.35 | -- | -- |
| 30R2 | 31.93(cy) | −1.75 | 2.98 | −0.67 | 29.33 | 3.64 | -- | -- |
| 30R3 | 34.6(cy) | 6.46 | 3.26 | 8.67 | 29.30 | 3.53 | -- | -- |
| 30R4 | 33.71(y) | 2.47 | -- | 25.31 | −10.56 | -- | -- | |
| 30R5 | 32(cy) | −1.54 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 3.0 | −44.24 |
| 30R6 | 32.5(c) | 0.00 | 3.05 | 1.67 | -- | -- | 3.6 | −33.09 |
| 30R7 | 33(c) | 1.54 | 3.07 | 2.33 | -- | -- | 3.57 | 8.36 |
| 30R8 | 33.47(c) | 2.98 | 2.96 | −1.33 | -- | -- | 5.83 | 0.74 |
| 30R9 | 29.63(c) | −8.83 | 2.59 | −13.67 | -- | 5.42 | −5.20 | |
| 30R10 | 34.52(c) | 6.22 | 2.33 | −22.33 | 29.6 | 4.59 | -- | -- |
| 30R11 | 34.19(c) | 5.20 | 2.32 | −22.67 | 27.88 | −1.48 | -- | -- |
| 30R12 | 33.82(c) | 4.06 | 2.31 | −23.00 | 26.71 | −5.62 | -- | -- |
| 30R13 | 33.41(c) | 2.80 | 2.29 | −23.67 | 24.73 | −12.61 | -- | -- |
| 30R14 | 31.6(c) | −2.77 | 2.15 | −28.33 | 29.22 | 3.25 | -- | -- |
| 30R15 | 29.99(c) | −7.72 | 2.14 | −28.67 | 21.88 | −22.69 | -- | -- |
| 30R16 | 35.3(cy) | 8.62 | 2.67 | −11.00 | -- | -- | -- | |
| 30R17 | 32.6(cy) | 0.31 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 5.1 | −5.20 |
| 30R18 | 33.5(c) | 3.08 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 4.56 | −15.24 |
| 30R19 | 30(c) | −7.69 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 4.48 | −16.73 |
| 30R20 | 33(c) | 1.54 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 5.06 | −5.95 |
| 30R21 | 30.5(c) | −6.15 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 4.94 | −8.18 |
| 30R22 | 33.7(c) | 3.69 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 5.08 | −5.58 |
| 30R23 | 30.7(c) | −5.54 | -- | -- | -- | -- | 4.96 | −7.81 |
| 30R24 | 29.3(c) | −9.85 | -- | -- | -- | 4.7 | −12.64 | |
| 30R25 | 33.47(c) | 2.98 | -- | -- | 29.8 | 5.30 | -- | -- |
| 30R26 | 33.31(c) | 2.49 | -- | -- | 30 | 6.01 | -- | -- |
| 30R27 | 32.66(c) | 0.49 | -- | -- | 28.33 | 0.11 | -- | -- |
| 30R28 | 30.98(c) | −4.68 | -- | -- | 28 | −1.06 | -- | -- |
| AVE () | 32.54 | 0.12 | 2.64 | −12.00 | 27.53 | −2.71 | 4.64 | −13.75 |
| STDEV () | 1.567 | 0.368 | 2.256 | 0.768 | ||||
| Coefficient of deviation () | 0.048 | 0.139 | 0.082 | 0.166 | ||||
| Mix ID | Tensile Strength | Elastic Modulus | Mix ID | Tensile Strength | Elastic Modulus | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AS3600 | fib2010 | AS3600 | CHA | AS3600 | fib2010 | AS3600 | CHA | ||
| 30R1 | 1.029 | 0.962 | 0.93 | 0.85 | 40R1 | 1.215 | 1.106 | 0.94 | 0.96 |
| 30R2 | 1.046 | 0.987 | 1.08 | 0.98 | 40R2 | 1.179 | 1.048 | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| 30R3 | 1.100 | 1.023 | 1.08 | 0.98 | 40R3 | 1.132 | 1.004 | 0.87 | 0.89 |
| 30R12 | 0.788 | 0.736 | 0.98 | 0.89 | 40R4 | 0.669 | 0.608 | 0.96 | 0.98 |
| 30R13 | 0.786 | 0.736 | 0.91 | 0.82 | 40R14 | 0.96 | 0.97 | ||
| 30R14 | 0.759 | 0.717 | 1.08 | 0.97 | 40R15 | 0.95 | 0.96 | ||
| Average | 0.918 | 0.860 | 1.010 | 0.915 | Average | 1.049 | 0.942 | 0.932 | 0.948 |
| STDEV | 0.142 | 0.132 | 0.073 | 0.065 | STDEV | 0.221 | 0.196 | 0.032 | 0.030 |
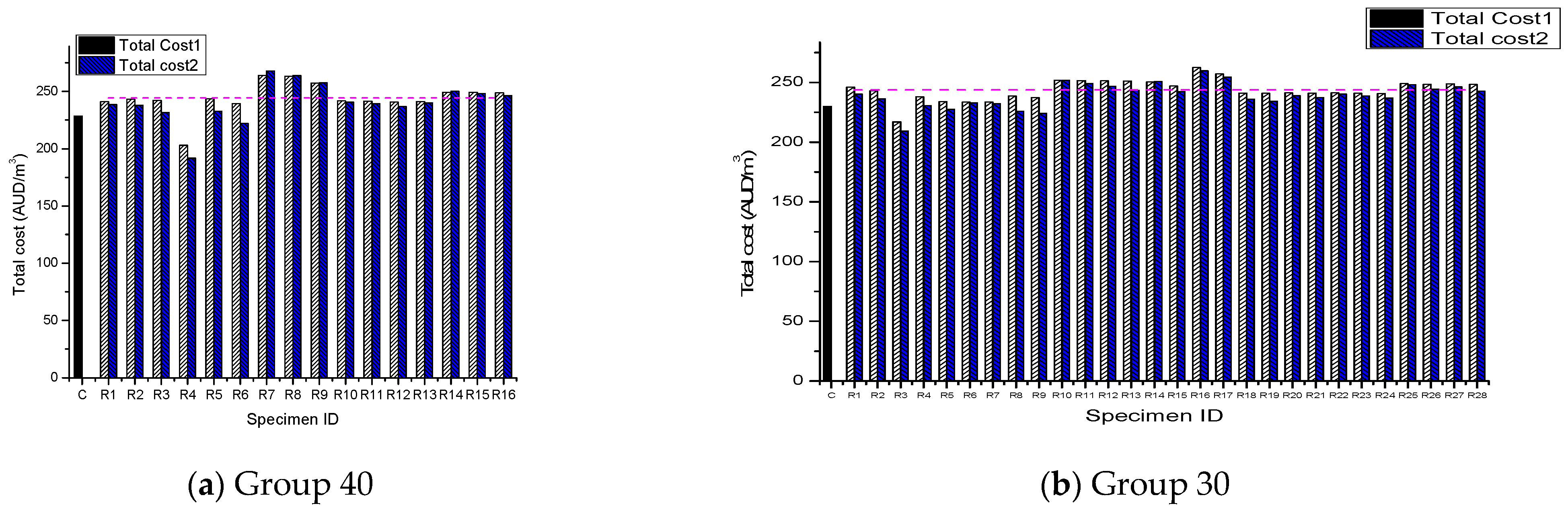
| Specimen ID | Component/Total % | Total Cost AUD/m3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | CA | FA | Rubber | Total | Comparison % | |
| 40C | 60.4 | 24.35 | 15.03 | 0 | 228.39 | |
| 40R1 | 58.43 | 29.94 | 11.01 | 0.42 | 241.06 | 5.55 |
| 40R2 | 57.93 | 29.68 | 10.34 | 0.82 | 243.13 | 6.45 |
| 40R3 | 58.15 | 29.79 | 9.23 | 1.65 | 242.22 | 6.06 |
| 40R4 | 56.28 | 30.86 | 11.32 | 1.31 | 203.17 | −11.04 |
| 40R5 | 59.67 | 26.16 | 10.91 | 1.79 | 243.35 | 6.55 |
| 40R6 | 57.77 | 29.32 | 10.08 | 2.65 | 239.37 | 4.81 |
| 40R7 | 68.73 | 15.60 | 14.11 | 0.46 | 264.07 | 15.62 |
| 40R8 | 68.93 | 15.64 | 13.41 | 0.92 | 263.32 | 15.30 |
| 40R9 | 59.22 | 30.21 | 8.19 | 0.31 | 257.44 | 12.72 |
| 40R10 | 58.25 | 29.85 | 11.26 | 0.21 | 241.80 | 5.87 |
| 40R11 | 58.29 | 29.87 | 10.98 | 0.41 | 241.61 | 5.79 |
| 40R12 | 58.5 | 29.98 | 10.73 | 0.62 | 240.76 | 5.42 |
| 40R13 | 58.39 | 29.92 | 11.29 | 0.21 | 241.20 | 5.61 |
| 40R14 | 61.71 | 26.58 | 10.26 | 0.23 | 249.39 | 9.20 |
| 40R15 | 61.78 | 26.61 | 9.94 | 0.46 | 249.13 | 9.08 |
| 40R16 | 61.85 | 26.64 | 9.61 | 0.7 | 248.87 | 8.97 |
| AVE | 244.37 | 6.99 | ||||
| Specimen ID | Component/Total % | The Total Cost AUD/m3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | CA | FA | Rubber | Total | Comparison % | |
| 30C | 60.00 | 24.19 | 14.93 | 0.00 | 229.89 | |
| 30R1 | 62.60 | 26.96 | 9.05 | 1.17 | 245.88 | 6.96 |
| 30R2 | 57.97 | 29.70 | 10.06 | 1.03 | 242.97 | 5.69 |
| 30R3 | 50.20 | 30.63 | 16.34 | 0.63 | 216.92 | −5.64 |
| 30R4 | 57.60 | 31.16 | 9.51 | 1.23 | 238.08 | 3.56 |
| 30R5 | 62.05 | 27.80 | 8.80 | 1.10 | 233.99 | 1.78 |
| 30R6 | 59.60 | 27.44 | 12.65 | 0.11 | 233.41 | 1.53 |
| 30R7 | 59.57 | 27.42 | 12.58 | 0.22 | 233.51 | 1.58 |
| 30R8 | 57.93 | 29.40 | 10.51 | 1.98 | 238.70 | 3.83 |
| 30R9 | 58.26 | 29.57 | 9.98 | 2.02 | 237.37 | 3.25 |
| 30R10 | 61.98 | 28.52 | 8.95 | 0.36 | 251.83 | 9.54 |
| 30R11 | 62.05 | 28.55 | 8.49 | 0.72 | 251.55 | 9.42 |
| 30R12 | 62.12 | 28.58 | 8.02 | 1.09 | 251.28 | 9.30 |
| 30R13 | 62.14 | 28.59 | 7.55 | 1.52 | 251.18 | 9.26 |
| 30R14 | 61.71 | 28.40 | 9.38 | 0.33 | 250.39 | 8.92 |
| 30R15 | 61.30 | 28.21 | 9.32 | 0.99 | 246.98 | 7.44 |
| 30R16 | 69.12 | 15.69 | 12.70 | 1.39 | 262.59 | 14.22 |
| 30R17 | 59.29 | 30.24 | 7.78 | 0.61 | 257.12 | 11.85 |
| 30R18 | 58.39 | 29.92 | 10.42 | 0.83 | 241.21 | 4.92 |
| 30R19 | 58.44 | 29.94 | 10.14 | 1.04 | 241.01 | 4.84 |
| 30R20 | 58.37 | 29.91 | 11.00 | 0.42 | 241.31 | 4.97 |
| 30R21 | 58.41 | 29.93 | 10.72 | 0.62 | 241.11 | 4.88 |
| 30R22 | 58.38 | 29.91 | 11.29 | 0.21 | 241.26 | 4.94 |
| 30R23 | 58.43 | 29.94 | 11.01 | 0.42 | 241.06 | 4.86 |
| 30R24 | 58.48 | 29.96 | 10.73 | 0.62 | 240.86 | 4.77 |
| 30R25 | 61.78 | 26.61 | 9.94 | 0.46 | 249.13 | 8.37 |
| 30R26 | 61.91 | 26.67 | 9.28 | 0.93 | 248.60 | 8.14 |
| 30R27 | 61.85 | 26.64 | 9.61 | 0.70 | 248.87 | 8.25 |
| 30R27 | 61.98 | 26.70 | 8.96 | 1.16 | 248.34 | 8.03 |
| AVE | 243.80 | 6.05 | ||||
| Component or Processing | Cement | FA | CA | Admixture | Crumb Rubber | Combustion Rubber Tires |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | 0.9 | 0.041 | 0.014 | 2 | 0.124 | −2.89 |
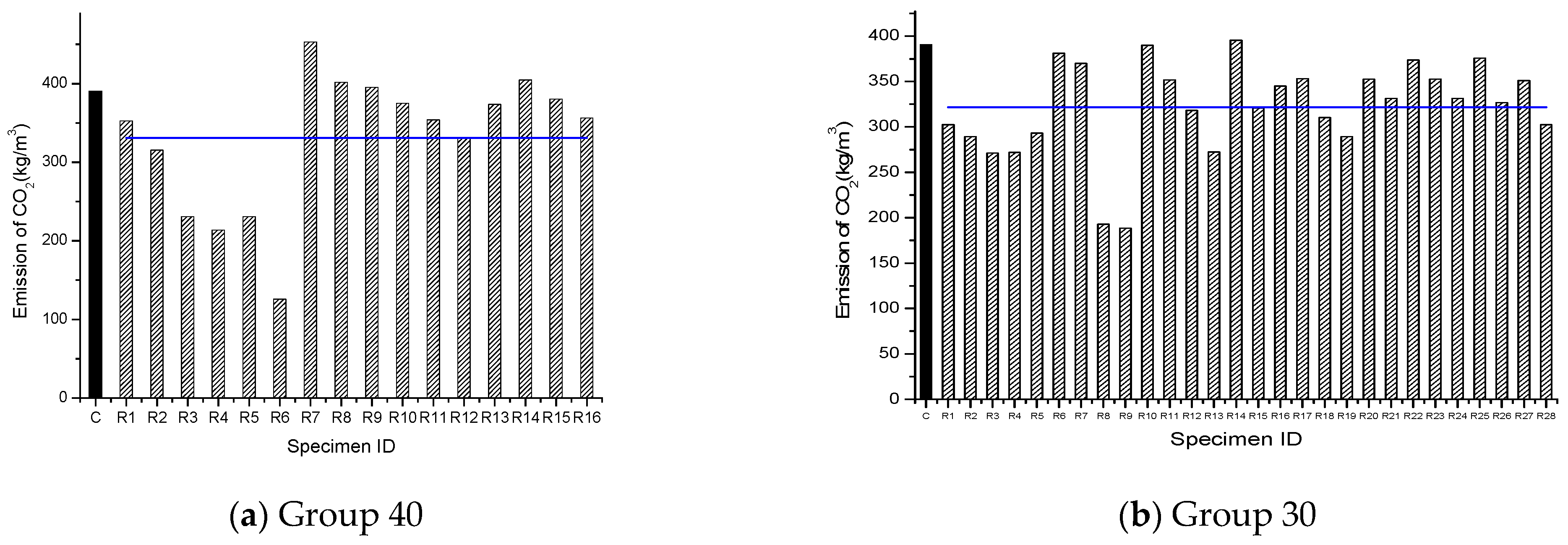
| Specimen ID | CO2 Emission Quantity of Mixtures kg/m3 | Total CO2 Emissions kg/m3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | CA | FA | Rubber | Total | Comparison % | |
| 40C | 342.00 | 12.98 | 35.18 | 0.00 | 390.16 | |
| 40R1 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 27.20 | −40.74 | 352.50 | −9.62 |
| 40R2 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 25.77 | −81.51 | 315.34 | −19.79 |
| 40R3 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 22.91 | −163.06 | 230.79 | −40.82 |
| 40R4 | 283.5 | 14.63 | 23.58 | −107.87 | 213.83 | −45.17 |
| 40R5 | 360.00 | 14.85 | 27.22 | −177.58 | 230.70 | −40.85 |
| 40R6 | 342.86 | 16.38 | 24.74 | −258.12 | 125.85 | −67.73 |
| 40R7 | 450.00 | 9.61 | 38.20 | −49.51 | 453.04 | 16.16 |
| 40R8 | 450.00 | 9.61 | 36.19 | −99.02 | 401.52 | 2.95 |
| 40R9 | 378.00 | 18.14 | 21.61 | −32.31 | 395.44 | 1.40 |
| 40R10 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 27.92 | −20.39 | 374.87 | −3.88 |
| 40R11 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 27.20 | −40.74 | 353.80 | −9.28 |
| 40R12 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 26.49 | −61.16 | 331.37 | −15.03 |
| 40R13 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 27.92 | −20.39 | 373.57 | −4.21 |
| 40R14 | 381.60 | 15.47 | 26.24 | −23.48 | 404.75 | 3.78 |
| 40R15 | 381.60 | 15.47 | 25.38 | −46.94 | 380.43 | −2.45 |
| 40R16 | 381.60 | 15.47 | 24.52 | −70.42 | 356.09 | −8.70 |
| AVE | 331 | −15.16 | ||||
| Specimen ID | CO2 Emission Quantity of Mixtures kg/m3 | Total CO2 Emissions kg/m3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | CA | FA | Rubber | Total | Comparison % | |
| 30C | 342.00 | 12.98 | 35.18 | 0.00 | 390.16 | |
| 30R1 | 381.60 | 15.47 | 22.80 | −117.39 | 302.48 | −22.44 |
| 30R2 | 349.20 | 16.83 | 25.06 | −101.90 | 289.19 | −25.85 |
| 30R3 | 270.00 | 15.50 | 36.32 | −55.32 | 271.24 | −30.45 |
| 30R4 | 340.00 | 17.31 | 23.2 | −118.77 | 271.74 | −30.32 |
| 30R5 | 360.00 | 15.18 | 21.12 | −104.47 | 293.12 | −24.84 |
| 30R6 | 344.88 | 14.94 | 30.26 | −10.26 | 381.12 | −2.28 |
| 30R7 | 344.88 | 14.94 | 30.11 | −20.52 | 370.01 | −5.12 |
| 30R8 | 342.86 | 16.38 | 20.91 | −192.71 | 192.83 | −50.56 |
| 30R9 | 342.86 | 16.38 | 17.09 | −194.98 | 188.54 | −51.66 |
| 30R10 | 387.00 | 16.76 | 23.10 | −37.06 | 389.79 | −0.05 |
| 30R11 | 387.00 | 16.76 | 21.88 | −74.13 | 351.51 | −9.87 |
| 30R12 | 387.00 | 16.76 | 20.67 | −111.19 | 318.15 | −18.42 |
| 30R13 | 387.00 | 16.76 | 19.45 | −155.73 | 272.40 | −30.15 |
| 30R14 | 383.13 | 16.59 | 24.07 | −33.19 | 395.52 | 1.42 |
| 30R15 | 375.39 | 16.26 | 23.58 | −99.58 | 320.57 | −17.80 |
| 30R16 | 450.00 | 9.61 | 34.18 | −148.81 | 344.98 | −11.54 |
| 30R17 | 378.00 | 18.14 | 20.50 | −63.48 | 353.16 | −9.45 |
| 30R18 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 25.77 | −81.51 | 310.30 | −20.44 |
| 30R19 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 25.06 | −101.90 | 289.19 | −25.85 |
| 30R20 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 27.20 | −40.74 | 352.50 | −9.62 |
| 30R21 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 26.49 | −61.16 | 331.37 | −15.03 |
| 30R22 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 27.92 | −20.39 | 373.57 | −4.21 |
| 30R23 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 27.20 | −40.74 | 352.50 | −9.62 |
| 30R24 | 349.20 | 16.84 | 26.49 | −61.16 | 331.37 | −15.03 |
| 30R25 | 381.60 | 15.47 | 25.38 | −46.94 | 375.51 | −3.72 |
| 30R26 | 381.60 | 15.47 | 23.66 | −93.91 | 326.82 | −16.20 |
| 30R27 | 381.60 | 15.47 | 24.52 | −70.42 | 351.17 | −9.96 |
| 30R28 | 381.60 | 15.47 | 22.80 | −117.39 | 302.48 | −22.44 |
| AVE | 321.54 | −17.55 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, G.; Al-Deen, S.; Guan, X.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, C. Economic and Environmental Benefit Analysis between Crumb Rubber Concrete and Ordinary Portland Cement Concrete. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114758
Xiong G, Al-Deen S, Guan X, Qin Q, Zhang C. Economic and Environmental Benefit Analysis between Crumb Rubber Concrete and Ordinary Portland Cement Concrete. Sustainability. 2024; 16(11):4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114758
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Guanghong, Safat Al-Deen, Xiao Guan, Qing Qin, and Chenghua Zhang. 2024. "Economic and Environmental Benefit Analysis between Crumb Rubber Concrete and Ordinary Portland Cement Concrete" Sustainability 16, no. 11: 4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114758
APA StyleXiong, G., Al-Deen, S., Guan, X., Qin, Q., & Zhang, C. (2024). Economic and Environmental Benefit Analysis between Crumb Rubber Concrete and Ordinary Portland Cement Concrete. Sustainability, 16(11), 4758. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16114758







