Optimizing Glyphosate Removal from Water Using a Peracetic Acid-Assisted Advanced Oxidation Process: A Response Surface Methodology Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Determination of Glyphosate Concentration
2.3. Determination of Oxidant Concentration
2.4. Experimental Setup
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Kinetic Study
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Results
3.2. Optimization of Process Parameters by Response Surface Methodology
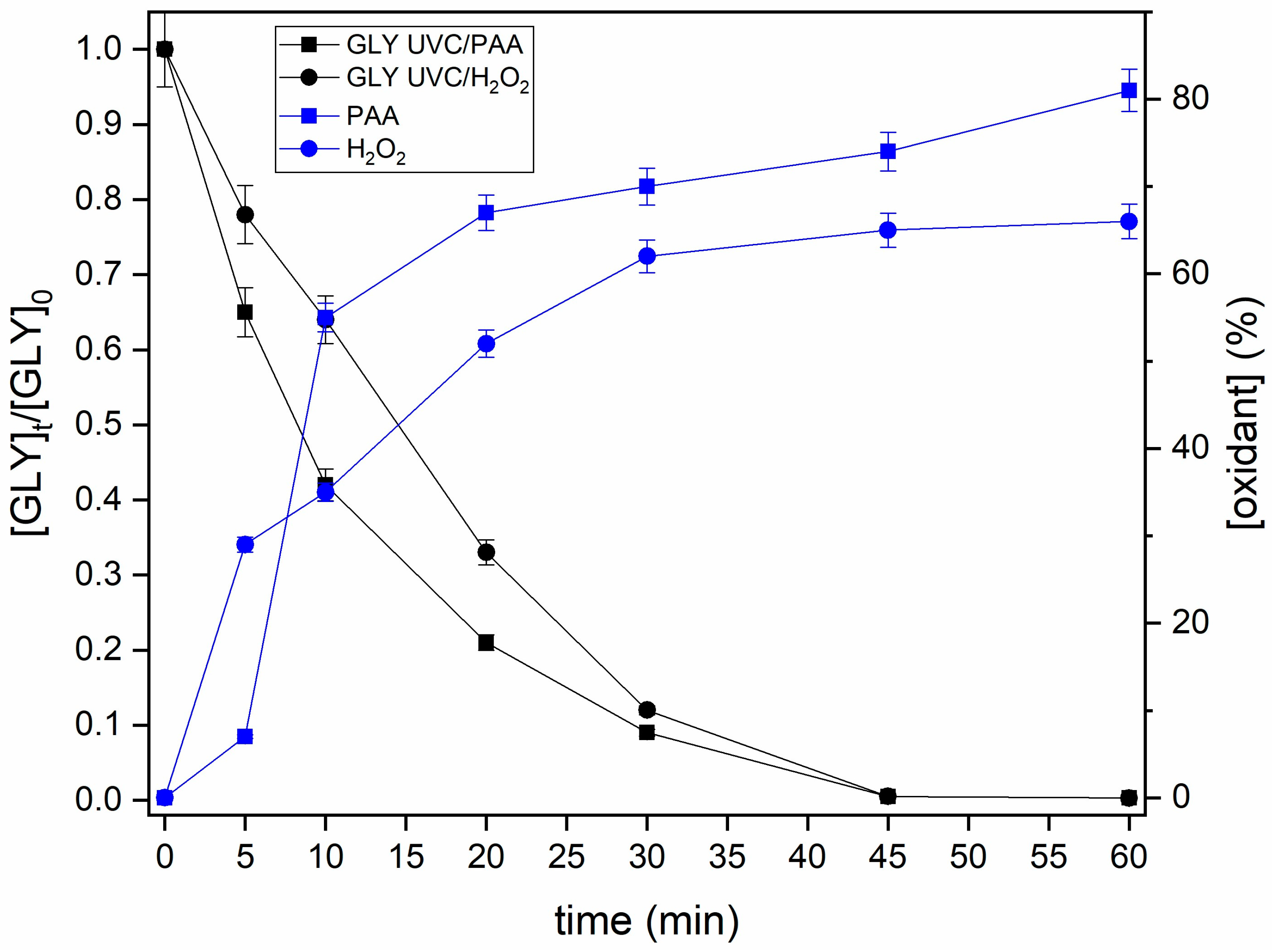
3.3. Kinetic Study
- (i)
- PAA/GLY = 3/1 and 45 min of treatment time
- (ii)
- H2O2/GLY = 3/1 and 45 min of treatment time
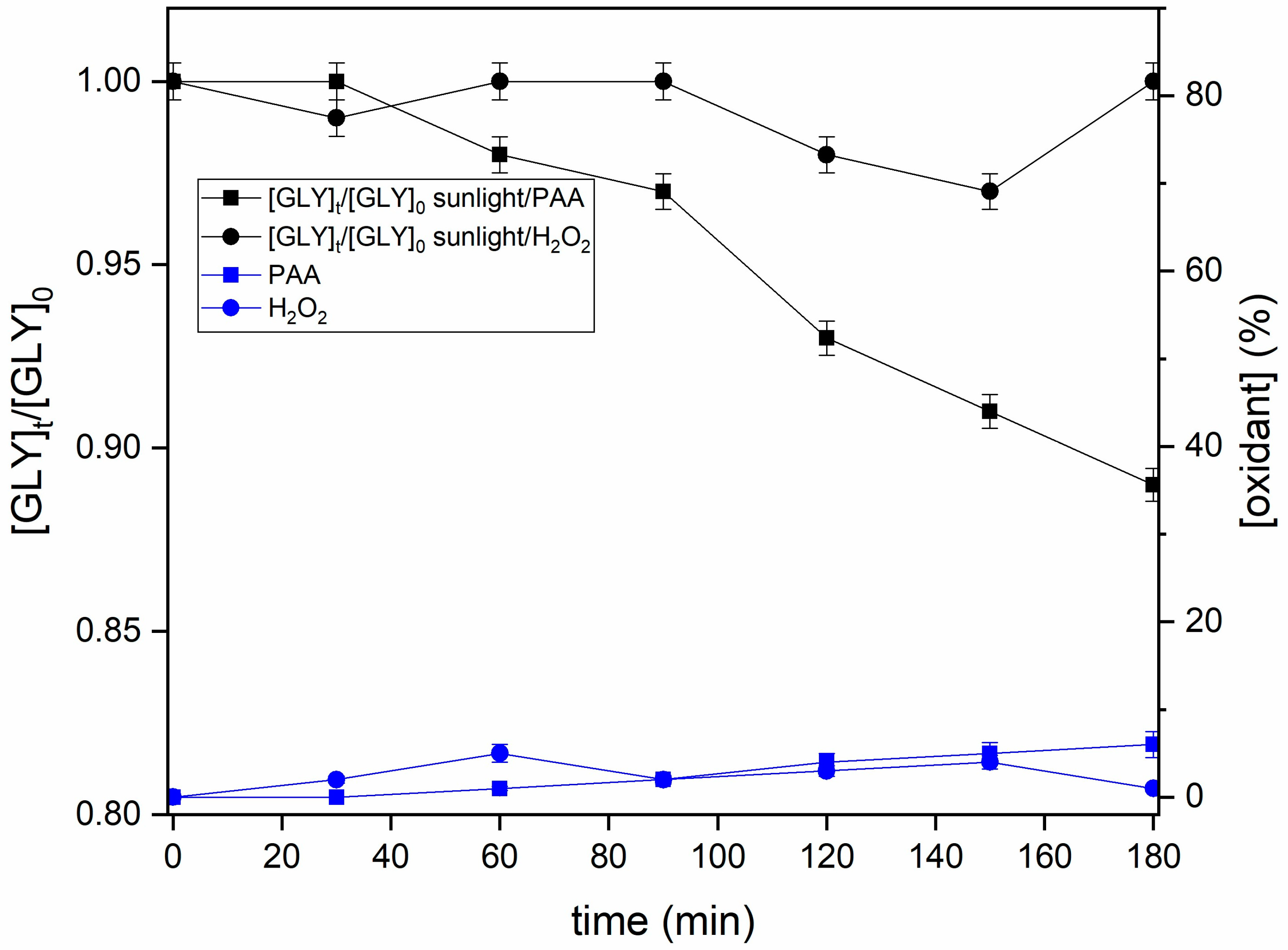
3.4. Sunlight-Activated Processes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Espinoza-Montero, P.J.; Vega-Verduga, C.; Alulema-Pullupaxi, P.; Fernández, L.; Paz, J.L. Technologies Employed in the Treatment of Water Contaminated with Glyphosate: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostini, L.P.; Dettogni, R.S.; dos Reis, R.S.; Stur, E.; dos Santos, E.V.W.; Ventorim, D.P.; Garcia, F.M.; Cardoso, R.C.; Graceli, J.B.; Louro, I.D. Effects of Glyphosate Exposure on Human Health: Insights from Epidemiological and In Vitro Studies. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, S.; Jing, Y.; Nowak, K.M. Fate of Glyphosate and Its Degradation Products AMPA, Glycine and Sarcosine in an Agricultural Soil: Implications for Environmental Risk Assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamar-Ayala, C.A.; Carrera-Cevallos, J.V.; Vasquez-Medrano, R.; Espinoza-Montero, P.J. Fate, Eco-Toxicological Characteristics, and Treatment Processes Applied to Water Polluted with Glyphosate: A Critical Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1476–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiol, M.; Giannì, B.; Prete, M. Herbicides in River Water across the Northeastern Italy: Occurrence and Spatial Patterns of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Glufosinate Ammonium. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 24368–24378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapporto Nazionale Pesticidi Nelle Acque. Dati 2017–2018. Available online: https://www.isprambiente.gov.it/it/pubblicazioni/rapporti/rapporto-nazionale-pesticidi-nelle-acque-dati-2017-2018 (accessed on 22 January 2021).
- Torretta, V.; Katsoyiannis, I.A.; Viotti, P.; Rada, E.C. Critical Review of the Effects of Glyphosate Exposure to the Environment and Humans through the Food Supply Chain. Sustainability 2018, 10, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Soric, A.; Boutin, O. Treatment Technologies and Degradation Pathways of Glyphosate: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 742, 140559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assalin, M.R.; De Moraes, S.G.; Queiroz, S.C.N.; Ferracini, V.L.; Duran, N. Studies on Degradation of Glyphosate by Several Oxidative Chemical Processes: Ozonation, Photolysis and Heterogeneous Photocatalysis. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2009, 45, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zavareh, S.; Farrokhzad, Z.; Darvishi, F. Modification of Zeolite 4A for Use as an Adsorbent for Glyphosate and as an Antibacterial Agent for Water. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 155, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Adelodun, A.A. Recent Advances on the Adsorption of Herbicides and Pesticides from Polluted Waters: Performance Evaluation via Physical Attributes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 93, 117–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorilli, S.; Rivoira, L.; Calì, G.; Appendini, M.; Bruzzoniti, M.C.; Coïsson, M.; Onida, B. Iron Oxide inside SBA-15 Modified with Amino Groups as Reusable Adsorbent for Highly Efficient Removal of Glyphosate from Water. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 411, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivoira, L.; Appendini, M.; Fiorilli, S.; Onida, B.; Del Bubba, M.; Bruzzoniti, M.C. Functionalized Iron Oxide/SBA-15 Sorbent: Investigation of Adsorption Performance towards Glyphosate Herbicide. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21682–21691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, H.; Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, S. Recent Advances in Glyphosate Biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5033–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferhi, S.; Vieillard, J.; Garau, C.; Poultier, O.; Demey, L.; Beaulieu, R.; Penalva, P.; Gobert, V.; Portet-Koltalo, F. Pilot-Scale Direct UV-C Photodegradation of Pesticides in Groundwater and Recycled Wastewater for Agricultural Use. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Ma, D.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, C.; Cao, C.; Zhao, P.; Huang, Q. Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Herbicide Glyphosate in Water by Magnetically Separable and Recyclable BiOBr/Fe3O4 Nanocomposites under Visible Light Irradiation. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 368, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Verma, N. Evaluation of Degradation and Mineralization of Glyphosate Pollutant in Wastewater Using Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation over Fe-Dispersed Carbon Nanofibrous Beads. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannaki, D.; Medana, C.; Binetti, R.; Calza, P.; Roslev, P. Effect of UV-A, UV-B and UV-C Irradiation of Glyphosate on Photolysis and Mitigation of Aquatic Toxicity. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, F.; Lin, Y.; Deng, N.; Bazhin, N.; Glebov, E. Photodegradation of Glyphosate in the Ferrioxalate System. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 148, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, H.; He, W.; Wang, A.; Liu, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Huang, C.P. An Activated Carbon Fiber Cathode for the Degradation of Glyphosate in Aqueous Solutions by the Electro-Fenton Mode: Optimal Operational Conditions and the Deposition of Iron on Cathode on Electrode Reusability. Water Res. 2016, 105, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Clusellas, A.; Angelis, L.D.; Beltramo, M.; Bava, M.; Frankenberg, J.D.; Vigliarolo, J.; Giovanni, N.D.; Stripeikis, J.D.; Rengifo-Herrera, J.A.; Cortalezzi, M.M.F. de Glyphosate and AMPA Removal from Water by Solar Induced Processes Using Low Fe(III) or Fe(II) Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2019, 5, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.E.C.; Tadayozzi, Y.S.; Putti, F.F.; Santos, F.A.; Forti, J.C. Degradation of Commercial Glyphosate-Based Herbicide via Advanced Oxidative Processes in Aqueous Media and Phytotoxicity Evaluation Using Maize Seeds. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 840, 156656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junges, C.M.; Vidal, E.E.; Attademo, A.M.; Mariani, M.L.; Cardell, L.; Negro, A.C.; Cassano, A.; Peltzer, P.M.; Lajmanovich, R.C.; Zalazar, C.S. Effectiveness Evaluation of Glyphosate Oxidation Employing the H2O2/UVC Process: Toxicity Assays with Vibrio Fischeri and Rhinella Arenarum Tadpoles. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2013, 48, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal, E.; Negro, A.; Cassano, A.; Zalazar, C. Simplified Reaction Kinetics, Models and Experiments for Glyphosate Degradation in Water by the UV/H2O2 Process. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2015, 14, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manassero, A.; Passalia, C.; Negro, A.C.; Cassano, A.E.; Zalazar, C.S. Glyphosate Degradation in Water Employing the H2O2/UVC Process. Water Res. 2010, 44, 3875–3882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, A.; Coll, A.; Lescano, M.; Zalazar, C. Advanced Oxidation of Commercial Herbicides Mixture: Experimental Design and Phytotoxicity Evaluation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 21393–21402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faggiano, A.; Ricciardi, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Cucciniello, R.; Motta, O.; Rizzo, L.; Proto, A. Combination of Foam Fractionation and Photo-Fenton like Processes for Greywater Treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 293, 121114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, A.; Motta, O.; Carotenuto, M.; Ricciardi, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Proto, A. Optimizing Levofloxacin Decontamination in Aquatic Environment: Iron-Modified Biochar in Heterogeneous Fenton Processes with Peroxide and Persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. Adv. 2024, 18, 100602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklos, D.B.; Remy, C.; Jekel, M.; Linden, K.G.; Drewes, J.E.; Hübner, U. Evaluation of Advanced Oxidation Processes for Water and Wastewater Treatment—A Critical Review. Water Res. 2018, 139, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faggiano, A.; De Carluccio, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Ricciardi, M.; Cucciniello, R.; Proto, A.; Rizzo, L. Photo-Fenton like Process as Polishing Step of Biologically Co-Treated Olive Mill Wastewater for Phenols Removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 305, 122525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironti, C.; Dell’Annunziata, F.; Giugliano, R.; Folliero, V.; Galdiero, M.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Proto, A.; Franci, G. Comparative Analysis of Peracetic Acid (PAA) and Permaleic Acid (PMA) in Disinfection Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 797, 149206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, X.; Eloranta, J.; Huang, C.-H.; Santoro, D.; Sun, W.; Lu, Z.; Li, C. Peracetic Acid-Based Advanced Oxidation Processes for Decontamination and Disinfection of Water: A Review. Water Res. 2021, 188, 116479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formisano, F.; Fiorentino, A.; Rizzo, L.; Carotenuto, M.; Pucci, L.; Giugni, M.; Lofrano, G. Inactivation of Escherichia Coli and Enterococci in Urban Wastewater by Sunlight/PAA and Sunlight/H2O2 Processes. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2016, 104, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, T.; Heyninck, T.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Comparison of Organic Peracids in Wastewater Treatment: Disinfection, Oxidation and Corrosion. Water Res. 2015, 85, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Huang, C.-H. Reactivity of Peracetic Acid with Organic Compounds: A Critical Review. ACS EST Water 2021, 1, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Liu, W.; Cao, H.; Zhao, H.; Huang, C.-H. Oxidation of Amino Acids by Peracetic Acid: Reaction Kinetics, Pathways and Theoretical Calculations. Water Res. X 2018, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Du, P.; Dobson, J.T.; Huang, C.-H. Advanced Oxidation Process with Peracetic Acid and Fe(II) for Contaminant Degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13312–13322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, L.; Lofrano, G.; Gago, C.; Bredneva, T.; Iannece, P.; Pazos, M.; Krasnogorskaya, N.; Carotenuto, M. Antibiotic Contaminated Water Treated by Photo Driven Advanced Oxidation Processes: Ultraviolet/H2O2 vs Ultraviolet/Peracetic Acid. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 205, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhou, X.; Du, P.; Zhang, T.; Cai, M.; Sun, P.; Huang, C.-H. Oxidation of β-Lactam Antibiotics by Peracetic Acid: Reaction Kinetics, Product and Pathway Evaluation. Water Res. 2017, 123, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollman, J.; Dominic, J.A.; Achari, G. Degradation of Pharmaceutical Mixtures in Aqueous Solutions Using UV/Peracetic Acid Process: Kinetics, Degradation Pathways and Comparison with UV/H2O2. Chemosphere 2020, 248, 125911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallini, G.S.; de Campos, S.X.; de Souza, J.B.; Vidal, C.M.D.S. Comparison of Methodologies for Determination of Residual Peracetic Acid in Wastewater Disinfection. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2013, 93, 906–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faggiano, A.; Ricciardi, M.; Motta, O.; Fiorentino, A.; Proto, A. Greywater Treatment for Reuse: Effect of Combined Foam Fractionation and Persulfate-Iron Based Fenton Process in the Bacterial Removal and Degradation of Organic Matter and Surfactants. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variables | Code | Range and Levels | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | L [1] | L [2] | L [3] | L [4] | L [5] | |
| Coded value | −α | −1 | 0 | +1 | +α | |
| mol OX: mol GLY | X1 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Time (min.) | X2 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 60 |
| Oxidant type | X3 | - | PAA | - | H2O2 | - |
| Parameter | Kinetic Order | k (min−1) | t1/2 (min) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UVC/PAA | First | 0.099 | 7 | 0.98 |
| UVC/H2O2 | First | 0.096 | 7 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faggiano, A.; Fiorentino, A.; Ricciardi, M.; Proto, A.; Motta, O. Optimizing Glyphosate Removal from Water Using a Peracetic Acid-Assisted Advanced Oxidation Process: A Response Surface Methodology Approach. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135741
Faggiano A, Fiorentino A, Ricciardi M, Proto A, Motta O. Optimizing Glyphosate Removal from Water Using a Peracetic Acid-Assisted Advanced Oxidation Process: A Response Surface Methodology Approach. Sustainability. 2024; 16(13):5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135741
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaggiano, Antonio, Antonino Fiorentino, Maria Ricciardi, Antonio Proto, and Oriana Motta. 2024. "Optimizing Glyphosate Removal from Water Using a Peracetic Acid-Assisted Advanced Oxidation Process: A Response Surface Methodology Approach" Sustainability 16, no. 13: 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135741
APA StyleFaggiano, A., Fiorentino, A., Ricciardi, M., Proto, A., & Motta, O. (2024). Optimizing Glyphosate Removal from Water Using a Peracetic Acid-Assisted Advanced Oxidation Process: A Response Surface Methodology Approach. Sustainability, 16(13), 5741. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16135741









