1. Introduction
In the realm of agri-food enterprises, a perplexing paradox unfolds, captivating the attention of industry observers, researchers, and economists alike. Despite the apparent extravagance of their product pricing, these businesses not only manage to steer clear of financial turmoil but also thrive, showcasing robust profit margins that exceed industry norms. This phenomenon underscores the pivotal role of digital marketing in reshaping consumer perceptions and driving demand within the agri-food sector. Central to their success is the strategic utilization of digital marketing channels to optimize profitability, despite the challenges posed by production costs. According to Järvinen & Karjaluoto [
1], an organization’s attempts to implement digital marketing metrics systems, as well as the outcomes, cannot be understood without considering the rationale for the parameters chosen, the analysis of metrics data, and the organizational circumstances surrounding the system’s use.
Digital marketing is an effective and efficient way to promote companies online, with many strategies and platforms accessible [
2]. Vollrath & Villegas [
3] suggest preventing digital marketing analytics myopia. Marketing analytics will need to be more adept at interpreting data from a greater variety of sources as the industry transitions to a more digital one. Even as technology and marketing channels change, practitioners and scholars of digital marketing analytics can still create value for businesses and consumers by using the consumer choice journey as a strategic framework [
4]. However, there is a paradox. Several businesses appear to be selling their products at high prices, and they are not bankrupting, but on the contrary, they have high profits.
The scope of this article is to explore this paradoxical phenomenon. Specifically, it aims, on the one hand, to examine specific digital marketing measurement variables and how they affect the reduction in advertising costs and, on the other hand, to propose a digital marketing strategy capable of reducing advertising costs to increase profitability, thus contributing to the efficient use of resources and sustainable development. The significance of this article lies in its potential to offer valuable insights to industry practitioners, guiding them in the development of data-driven marketing strategies that foster sustainable growth and competitive advantage in the dynamic agri-food sector. The findings of this study could contribute to the optimization of resource utilization by reducing advertising costs and increasing business profitability. By elucidating the impact of specific digital marketing measurement variables on cost reduction, this article advances the understanding and application of efficient strategies that promote sustainable development. Such insights are crucial for the survival and evolution of businesses in the rapidly changing agri-food industry, making this research highly relevant and impactful.
Relying entirely on web analytics data may result in unproductive or detrimental marketing decisions. As a result, businesses should only use web analytics data as a part of their performance evaluations. Web analytics may enhance healthcare websites by monitoring engagement, users, acquisition, content, and platforms, thereby improving usability and conversion rates [
5]. Improving web analytics systems may increase an organization’s profitability by assessing user behavior, performance results, and satisfaction of consumers [
6]. Key parameters of digital marketing, extensively researched in this work, include social and search traffic sources, the abandonment rate, the pages per visit, and the time customers spend on their websites, along with the number of returning website customers.
By harnessing the power of digital marketing metrics, agri-food enterprises can effectively reduce advertising costs, achieving profitability even in the face of high production costs. This strategic alignment with digital marketing principles empowers them to not only survive but thrive in today’s competitive landscape, forging a path to sustained success in the agri-food industry. Therefore, the following research question is raised:
RQ: “How are specific digital marketing measurement variables aligned with the reduction in advertising costs?”
The research question aims to determine what the best channel for digital marketing is in order to minimize the advertising costs and increase the profitability of agri-food businesses. Directing resources to the lowest-cost choice of digital advertising channels has as the result of, in addition to increasing profits, the saving of resources, thus contributing to sustainable development. Our research has analyzed digital marketing variables and focuses on social and search sources variables, suggesting a digital marketing strategy of directing resources to search sources rather than social sources.
The novelty of this study lies in the fact that it attempts to investigate how, through the selection of an appropriate digital marketing strategy, companies can reduce advertising costs and therefore increase their profitability, thus making efficient use of resources and contributing to sustainable development. It was revealed by our bibliographic analysis that there is a dearth of research that is comparable to this one that concurrently looks at sustainable development, business profitability, and digital marketing strategies.
This article makes a significant contribution to understanding how digital marketing strategies can optimize profitability and resource efficiency in the agri-food industry. By exploring the relationship between digital marketing variables and advertising costs, through robust analytical methods like regression analysis and fuzzy cognitive mapping, this study reveals actionable insights for agricultural enterprises. It underscores the importance of strategic digital investments, particularly in search sources, to reduce advertising costs. Moreover, the findings highlight a shift towards sustainability by minimizing resource waste, thereby setting a precedent for enhancing competitiveness and operational efficiency in the sector.
Digital marketing strategies may include metrics such us website traffic, user engagement, conversion rates, customer demographics, and purchasing behavior. By analyzing these metrics, agri-food companies can gain valuable insights into consumer preferences, market trends, and the efficacy of their marketing campaigns. Ghahremani-Nahr & Nozari [
7] claim that key performance indicators are critical and delicate indicators for any firm that can successfully identify and regulate them. Measuring the effectiveness of digital marketing activities and using important indications of digital marketing performance helps boost marketing productivity while also improving the efficacy and optimization of marketing expenditure budgets. There are several measures for measuring digital marketing performance that can help improve the effectiveness of marketing initiatives. Moreover, the concept of “efficient promotions” involves the ability to allocate resources wisely and employ marketing tactics that yield the highest return on investment (ROI). It entails customizing advertising activities to resonate with target audiences, optimizing advertising expenditure, and maximizing conversion rates.
Our research underscores its originality by focusing on the intersection of digital marketing strategies in the agri-food sector, particularly highlighting the innovative use of website customer behavioral data in examining the impact of traffic sources (search and social) and other metrics on their advertising costs. Through the methodology of static FCM simulation, a unique lens is provided for exploring how optimizing digital marketing expenditures, specifically between social media and search engine resources [
8], can enhance both profitability and sustainability within agri-food businesses. This work represents a significant contribution to the literature as it highlights the importance and implication of digital marketing strategies in the agri-food sector. It focuses on cost reduction through optimizing advertisements on social media and efficiently using resources for search engine optimization. The reduction in these expenses has substantial implications not only for the profitability of businesses but also for sustainability, ensuring efficient use of limited natural resources and long-term viability of the sector. In this way, this research delves into identifying how website customer behavior can determine beneficial digital marketing strategies in the agri-food sector, and the firms’ sustainability and resource efficiency. Therefore, in
Table 1 the findings of recent and relevant studies in the field of agri-food and agricultural sectors is laid out to highlight the innovative implications of our research.
In the following paragraphs of
Section 2, a presentation of the literature regarding the peculiarities of the agri-food sector, the economic dimension of production costs in agri-food businesses, and the contribution of digital marketing and big data are provided. Overall, the literature emphasizes the importance of understanding the distinct characteristics of the agri-food sector, effectively managing production costs, and leveraging digital marketing and big data analytics to address the phenomenon, as companies in the sector can oversell their products. The development of research hypotheses then follows, as well as the research methodology. In
Section 3, the main findings, from the statistical analysis of the data and the simulation of five basic scenarios of changing the primary parameters as shown by the statistical processing of the data, are presented. In
Section 4, a discussion is held where the main findings of the statistical analysis and the results of the scenario simulation are interpreted, highlighting the proposed digital marketing strategy. Finally,
Section 5 briefly presents the conclusions of this research.
4. Discussion
The analysis reveals diverse distribution patterns across the variables (
Table 3). Skewness, indicating the asymmetry of the distribution, unveils interesting insights. Variables such as advertising costs, direct sources, referral sources, social sources, new customers, bounce rate, and returning customers exhibit positive skewness, implying a concentration of values towards the higher end. This suggests that certain agri-food firms allocate significantly higher resources to advertising activities, customer acquisition, and engagement. Conversely, pages per visit and search sources display negative skewness, suggesting a preponderance of lower values, possibly indicating areas of improvement or optimization. Furthermore, kurtosis, which characterizes the shape of the distribution, provides additional context. Leptokurtic distributions, observed in advertising costs, referral sources, new customers, and returning customers, suggest peaked distributions with heavier tails, reflecting concentrated expenditure and engagement levels. In contrast, platykurtic distributions, as seen in social sources, search sources, bounce rate, pages per visit, and time on site, indicate flatter distributions with lighter tails, illustrating greater variability in these metrics across agri-food firms. These findings underscore the importance of considering both skewness and kurtosis in understanding the distributional characteristics and potential implications for advertising strategies within the agri-food industry.
The correlation analysis of advertising costs (see
Table 3) reveals its relationship with various variables. It is known that although paid ads do not directly affect organic website search results, they indirectly impact other metrics that tend to cause a significant effect on SERP and SEO results [
69]. We observe a positive correlation with social sources, direct sources, time on site, and new customers, while it exhibits a negative correlation with referral sources, search sources, bounce rate, returning customers, and pages per visit.
The positive correlation with social sources suggests that allocating more resources to social media for promotion, results in higher overall advertising costs. The positive correlation with new customers implies that acquiring new customers positively relates to overall advertising costs. Moreover, the negative relationship between the number of returning website customers and advertising costs suggests that retaining and reacquiring customers may require less investment in promotion and advertising. Conversely, attracting new customers is positively correlated with higher advertising expenditures. Therefore, agri-food firms should carefully balance their strategies to attract new customers while nurturing existing relationships to maximize the effectiveness of their advertising expenditures. The research by Michel et al. [
70] has a conclusion similar to previous findings; in an agro-industrial company, it seems that digital marketing has a moderately significant relationship with social media marketing and content marketing and a high and significant relationship with customer acquisition.
The negative correlation with search sources suggests that increasing expenditure on search advertising is linked to a decrease in total advertising costs. Enhancing search engine presence is a critical component of digital marketing for agri-food enterprises. By employing SEO strategies, like keyword optimization, businesses can boost their website’s visibility and draw organic traffic from potential customers. Improving the overall website experience is vital for retaining visitors and motivating them to explore the offerings further. This involves ensuring easy navigation, providing informative content, fast loading times, and a seamless user interface. Bhatnagar et al. [
71] highlight that poor navigation impacts website design by prolonging visits and decreasing the likelihood of a purchase. The negative correlation with bounce rate implies that lower bounce rates are associated with higher total advertising expenses. Furthermore, a rise in website abandonment rate is linked to additional decreases in advertising expenses. Effectively managing and optimizing website engagement to reduce abandonment rate can therefore lead to even greater savings in advertising costs. The negative correlation with pages per visit indicates that an increase in the average number of pages per visit is linked to a decrease in total advertising costs. This highlights the significance of delivering an engaging user experience on the website to boost user interaction and potentially reduce advertising expenditures. Afterward, an examination of the hypotheses, formulated in
Section 2.4, is carried out and the results are interpreted.
Based on the standardized coefficients and the
p-value provided for the variables social sources and search sources (see
Table 4), it appears that both variables have a significant impact on advertising costs. Therefore, the results support Hypothesis H1. Specifically, an increase in the social sources variable is associated with an increase in total advertising costs, and an increase in the search sources variable is associated with a decrease in total advertising costs. The model explains approximately 68,9% of the variability in advertising costs, social sources, and the variability in advertising costs, search sources. Note that the
p-value is statistically significant at the 0.05 level, suggesting that the relationship is likely real and not random. The Durbin–Watson statistic indicates that there is no correlation among the residual deviations, indicating no autocorrelation in the model.
There is a negative correlation between advertising costs and search sources, suggesting that allocating more resources to search engine optimization (SEO) and related strategies may result in lower overall advertising expenses. Conversely, there is a positive correlation with social sources, indicating that increasing investment in social media for promotion typically leads to higher advertising costs. This underscores the importance of balancing SEO efforts, such as keyword optimization and content enhancement, to improve organic visibility without significantly increasing advertising expenditures. Effective SEO can drive organic traffic and reduce reliance on paid advertising channels. On the other hand, enhancing social media presence often involves expenses associated with content creation, paid promotions, and community engagement efforts. Agri-food enterprises should strategically manage both SEO and social media investments to optimize their digital marketing efforts while controlling advertising costs effectively.
The standardized coefficient for bounce rate is −2.554, and the
p-value associated with this coefficient is 0.049 (see
Table 5). This indicates that there is a statistically significant relationship between advertising costs and the abandonment rate of websites. The negative standardized coefficient suggests that an increase in the abandonment rate of websites is associated with a further decrease in advertising costs. Additionally, the model explains approximately 70.8% of the variability in advertising costs. Therefore, based on the provided data, we can support Hypothesis H2, indicating that there is indeed a relationship between the advertising costs of agri-food firms and the abandonment rate of their websites.
The negative standardized coefficient and significant p-value indicate a strong relationship where higher abandonment rates on websites are associated with lower advertising costs for agri-food firms, highlighting the critical role of website engagement in marketing strategies. Higher abandonment rates typically signal that visitors do not find the website engaging or relevant. This underscores the importance for agri-food firms to focus on improving website usability, content relevance, or targeting strategies to decrease bounce rates and potentially enhance advertising effectiveness.
The negative standardized coefficients for both pages per visit and time on site (see
Table 6) indicate that an increase in these variables is associated with a decrease in advertising costs. The model explains approximately 63.2% of the variability in advertising costs for pages per visit and for time on site. Both
p-values are statistically significant at the 0.05 level, indicating that the relationships are likely real and not due to chance. The Durbin–Watson statistics for both variables are close to the ideal value of 2, suggesting no significant autocorrelation in the model residuals. Overall, based on these results, we can conclude that there is a significant relationship between the advertising costs of agri-food firms and both the pages per visit and time spent on site by customers on their websites, supporting Hypothesis H3. The negative standardized coefficients for both pages per visit and time on site indicate that an increase in these variables is associated with a decrease in advertising costs. This suggests that as users engage more deeply with the website (viewing more pages and spending more time), the costs associated with advertising decrease. This could be due to more effective targeting or better quality of user engagement leading to lower necessary advertising expenditure.
According to
Table 5, the negative standardized coefficient for returning customers suggests that an increase in the number of returning website customers is associated with a decrease in advertising costs. The model explains approximately 70.8% of the variability in advertising costs. The
p-value is statistically significant at the 0.05 level, indicating that the relationship is likely real and not due to chance. The Durbin–Watson statistic is close to the ideal value of two, suggesting no significant autocorrelation in the model residuals. Therefore, based on these results, we can conclude that there is indeed a significant relationship between the advertising costs of agri-food firms and the number of their returning website customers, supporting Hypothesis H4.
The negative standardized coefficient and significant p-value highlight a robust relationship where a higher proportion of returning customers is associated with lower advertising costs for agri-food firms. This underscores the strategic importance of customer loyalty and retention efforts in optimizing marketing expenditures and maximizing overall profitability in the agri-food sector. Additionally, the highest R2 value (approximately 70.8%) suggests that returning customers and bounce rate are significant factors influencing advertising costs in these firms. This robust correlation emphasizes the need for strategies that enhance the user experience on the website and improve the overall efficiency of advertising efforts in the agri-food sector.
This article, after examining the relationship between digital marketing metrics and advertising costs, aims to propose a digital marketing strategy. The strategy is intended to result in a reduction in advertising costs. The two variables that were the focus of the simulation are search sources and social sources. The selected pair of variables are crucial components in formulating a comprehensive digital marketing strategy aimed at reducing advertising costs. The statistical significance of the ANOVA analysis being 0.048, indicates that there is a low probability of obtaining these results by chance alone. This suggests that the relationship between the variables (social sources and search sources) as a whole model is statistically significant. In practical terms, this means that the inclusion of these variables in the analysis has a meaningful impact on understanding and predicting outcomes related to digital marketing strategies.
Thus, five possible scenarios emerged, which are shown in
Figure 2. These scenarios were chosen strategically to highlight the potential for significant cost reductions, aligning with this study’s policy recommendation. Specifically, this study proposes that agri-food businesses should allocate their resources toward search sources rather than social sources to minimize promotional costs. This strategic direction underscores this research’s aim to optimize digital marketing investments for sustainability and profitability in the agri-food sector.
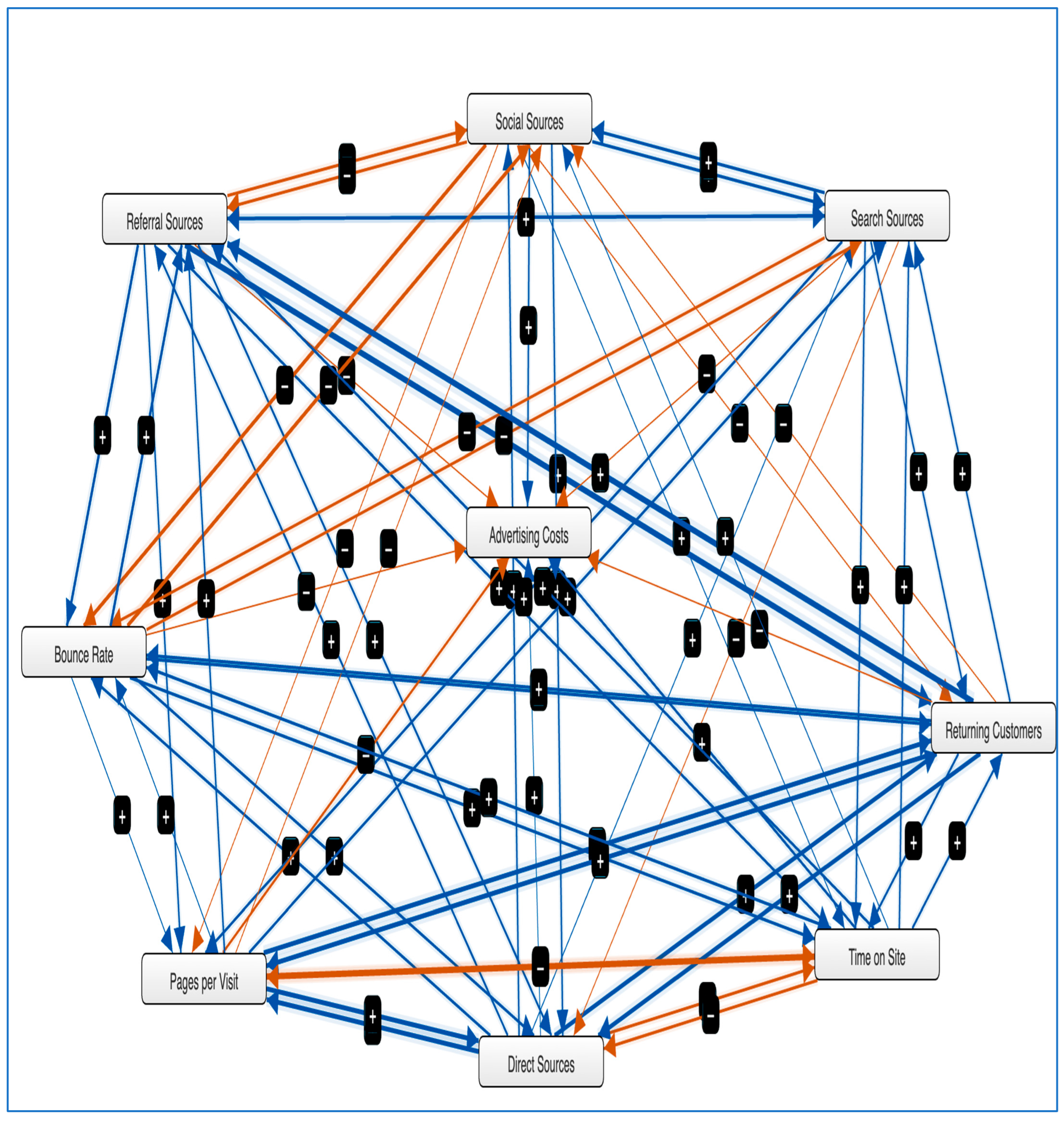
In the first scenario, which is reflected in
Figure 2a, an increase of 100% in the social sources variable is carried out, and then, there is an increase in the advertising cost variable by 6%. Then, the second scenario is carried out, which is depicted in
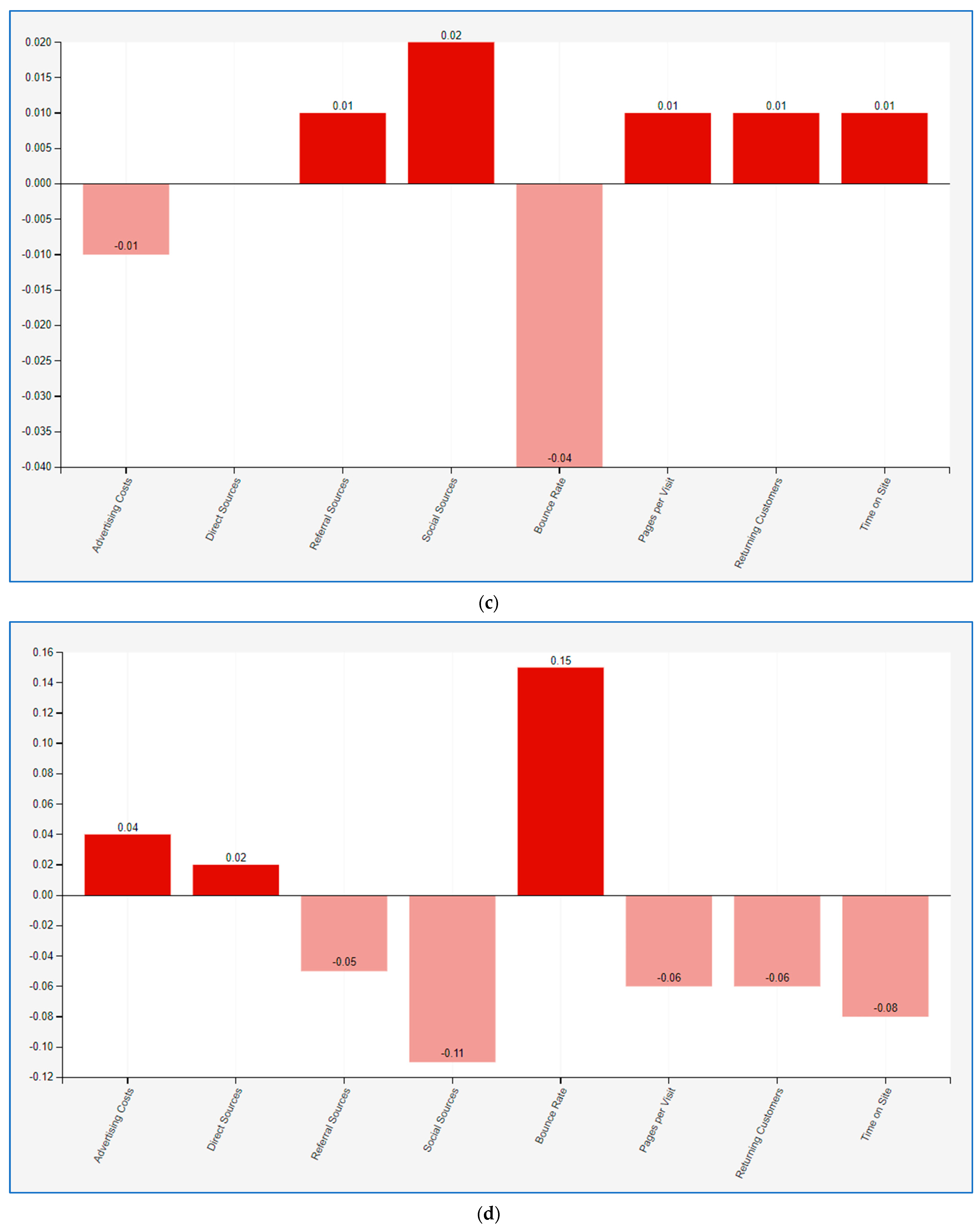
Figure 2b. In this case, a reduction in the social sources variable by 100% is carried out. This results in a reduction in the advertising cost variable by 13%. The third scenario is depicted in
Figure 2c and concerns the increase in the search source variable to 100%. A slight reduction in advertising costs by 1% is observed. Afterward, in the fourth scenario depicted in
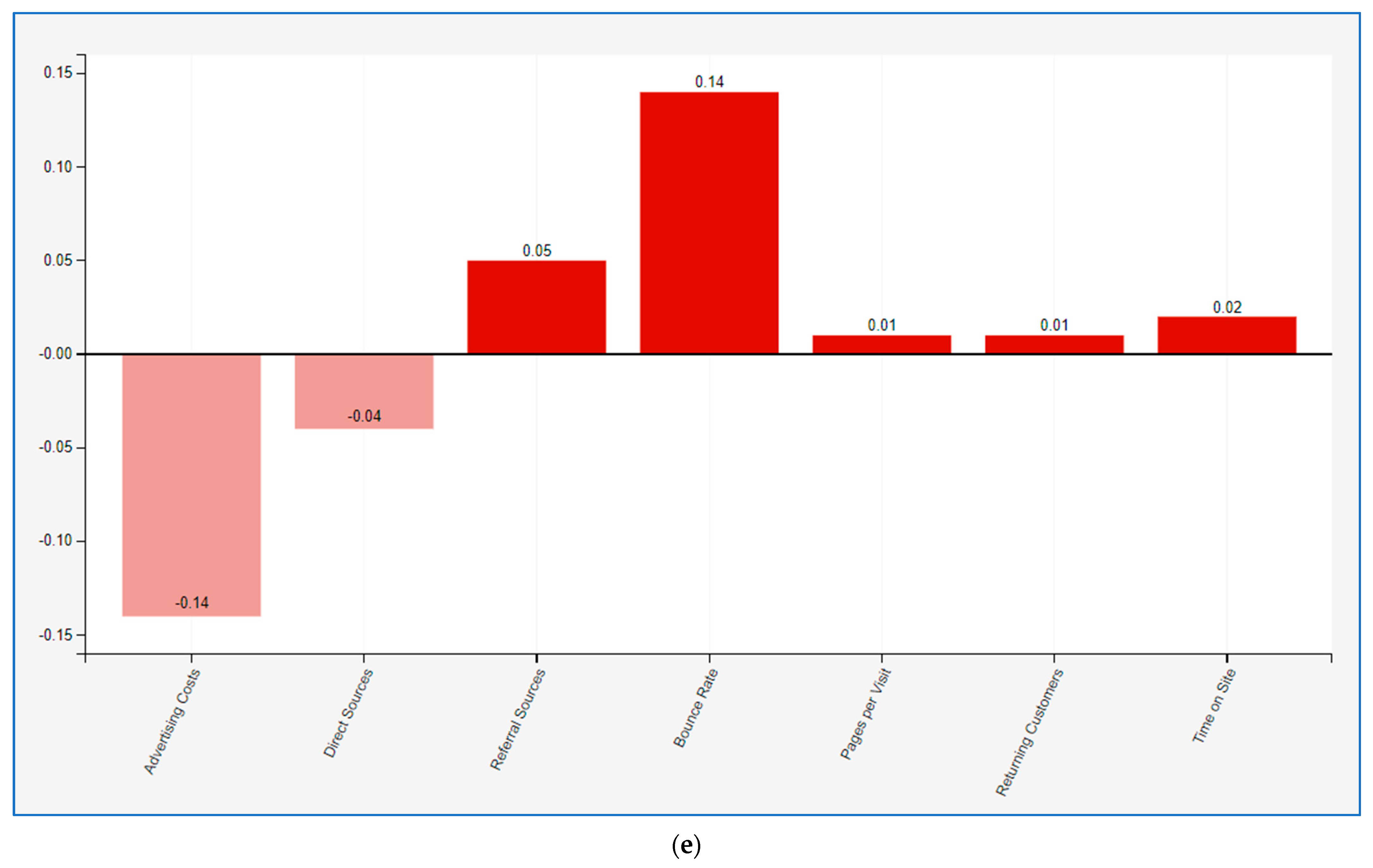
Figure 2d, a reduction in the search sources variable is attempted by 100%, which results in an increase in the advertising cost variable by four percent. Ultimately, the fifth scenario is executed, entailing a simultaneous modification of both variables. Consequently, an endeavor is undertaken to augment the search sources variable by 100% and diminish the social sources variable by 100%. It is observed that the concurrent modification of the two upper variables results in a noteworthy decrease of 14% in the advertising cost variable, as depicted in
Figure 2e.
The scenarios are designed to demonstrate a marketing strategy that achieves a reduction in advertising costs. After each variable has been examined separately, they are then compared simultaneously. The simulation shows that the fifth scenario offers the best digital marketing strategy for the reduction in advertising costs. The distribution of resources into social media marketing frequently results in cost escalation, as illustrated by the initial simulation scenario. This outcome arises from multiple factors. Firstly, heightened competition within social media platforms drives up advertising expenditures, as businesses compete for visibility and engagement. Secondly, the dynamic nature of social media necessitates ongoing monitoring, analysis, and adjustment of marketing strategies, demanding additional human and financial resources. Platforms such as Facebook prioritize establishing personal connections with users to cultivate customer loyalty [
72], intensifying the need for enhanced resource allocation to maintain these relationships. While social media enhances web traffic, it does not necessarily lead to significant increases in product orders and sales revenue [
47]. Additionally, targeting specific audience segments on social media platforms often demands investment in advanced tools and technologies, which further drives up costs. Therefore, careful resource allocation is essential in social media marketing to mitigate the risk of excessive spending and ensure efficient use of resources across different marketing channels. This caution is warranted because managerial actions may not always yield the desired effects. For instance, in the fourth scenario analyzed, reducing investment in search sources ultimately resulted in higher advertising costs.
Before utilizing social media for business purposes, it is crucial to develop strategies tailored to the product and target audience. According to Kilgour et al. [
73], effective social media marketing requires aligning messages with target audiences and achieving robust customer engagement. This principle holds particular relevance in the agri-food sector, where the target audience may not be highly active on social media platforms. Given the demographic characteristics of agri-food consumers and the diverse nature of agri-food products, conveying specialized knowledge and tailored messaging through social media can be challenging. Therefore, allocating resources to social media marketing for agri-food products without careful consideration of the target audience’s online behavior and preferences may lead to inefficient resource allocation and suboptimal results. The simulation indicates that the most effective strategy for reducing advertising costs involves reducing social sources of advertising while increasing investment in search engine marketing. This is the business operation proposal that our research suggests.
This perspective contrasts with that of Inegbedion et al. [
74], who argue that leveraging social media platforms like Instagram and WhatsApp significantly reduces costs and enhances marketing efficiency, thereby increasing turnover in agricultural products in South-South Nigeria. As our research revealed, the use of social media should not be preferred as a means of digital marketing; however, it is an excellent tool for communication. Madonna et al. [
75] highlight that platforms such as Facebook, WhatsApp, and Instagram can facilitate community participation in agriculture by promoting social interaction, discussions, and consultation, ultimately enhancing product promotion and marketing through e-commerce to achieve sustainable development goals. Thus, while social media offers valuable opportunities for engagement and community building in agriculture, its role in direct digital marketing strategies should be carefully evaluated based on specific industry dynamics and audience preferences.
The agriculture and agri-food sectors are increasingly emphasizing sustainability and transparency in supply chains, driven by rapid industrialization, growing global food demand, and heightened concerns about food quality and safety. According to Mangla et al. [
76], research identifies ten factors that influence sustainable development in the agri-food sector. Two of these factors, which are also pertinent to this study, include understanding customer behavior and effectively managing costs. These factors underscore the importance for companies and the food sector as a whole to comprehend customer behavior thoroughly. This understanding enables the strategic allocation of financial resources towards initiatives that reduce operational costs and ultimately minimize inefficient resource utilization, thereby promoting sustainable development.
As concluded by Hidayati et al. [
23], value-chain governance that integrates sustainability drivers provides a holistic approach to balancing social and environmental impacts with profit maximization. This approach opens up higher-value markets for smallholders in developing nations within the agri-food sector. Businesses in this sector can derive substantial benefits from implementing digital marketing strategies that cater to the distinct behaviors of digital consumers. These strategies enable them to reduce operational costs, optimize resource utilization, and customize their offerings, thereby facilitating the sale of products at higher prices.
5. Conclusions
The scope of this article is to explore the paradoxical phenomenon, wherein agri-food businesses sell their products at high prices and show profitability despite production costs. Specifically, it aims to examine how specific digital marketing measurement variables relate to advertising costs. Also, our research tries to propose a digital marketing strategy, capable of reducing advertising costs, thereby increasing profitability and contributing to efficient resource utilization and sustainable development. This research used the linear regression method to extract statistically significant results as well as the correlation between digital marketing metrics and advertising costs. After studying the digital marketing metrics, this research focuses on the variable search sources and social sources to submit a digital marketing strategy proposal. Afterwards, a simulation is carried out using the FCM model, and five possible scenarios are analyzed. The conclusions of our research are as follows:
Advertising costs of agribusinesses are positively and statistically significantly related to social traffic sources.
Advertising costs of agribusinesses are negatively and statistically significantly related to search traffic sources, bounce rate, the number of returning website customers, pages per visit, and time on site customers spend on their websites.
Optimal Resource Allocation: Agri-food businesses can achieve cost efficiencies by prioritizing investments in search sources over social sources in their digital marketing strategies.
Impact on Sustainability: Effective digital marketing strategies not only enhance profitability but also contribute to sustainable practices by reducing advertising costs and resource wastage.
Strategic Recommendation: This study suggests that agribusinesses should focus on targeted digital marketing efforts tailored to search engine optimization (SEO) rather than social media platforms.
As the global population increases, it is crucial to develop strategies that enhance food production, minimize resource consumption, and reduce environmental impact, addressing the significant issue of food loss and waste throughout the value chains [
77]. Since 1987, when the definition of sustainable development was given by the Brundtland Report as the development that satisfies current needs without jeopardizing the capacity of future generations to fulfill their own needs [
78], the central question remains the same: what can governments, businesses, and consumers do to promote sustainable development? As technology evolves and new methods of production and marketing appear, such as digital marketing, this must be the basic question that is asked. The intertwining effects of climate change and human activities on ecosystems, biodiversity, and the availability of natural resources pose significant obstacles to achieving sustainable agriculture [
79]. These factors are outside the sphere of influence of agri-food companies; at least, agri-food companies should try to direct the resources that are for digital marketing to effective uses, as shown by our research: the use of search sources rather than social media, so that they will not waste resources and thus contribute to sustainable development. Businesses can achieve profitability, despite high costs and prices, by allocating resources to the appropriate digital advertising channels in an efficient manner.
This study’s limitations include the focus on the five largest agri-food companies based on 2023 market capitalization, potentially limiting the generalizability of findings to smaller firms or different geographic regions. The observation period of 180 days from 1 July 2023 to 31 January 2024 might not capture long-term trends or seasonal variations adequately. Furthermore, reliance on the Semrush [
50] decision support system (DSS) for web analytics data collection introduces potential biases or inaccuracies, impacting the reliability of this study’s conclusions. Future research could benefit from expanding the sample to include medium-sized and small enterprises, exploring diverse geographic areas, and conducting longitudinal studies to better understand the sustained effects of digital marketing strategies on profitability in the agri-food sector.