Health Risk Assessment of Road-Dust-Bound Heavy Metals via Ingestion Exposure from One Typical Inland City of Northern China: Incorporation of Sources and Bioaccessibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Dust Sampling
2.2. Sequential Extraction
2.3. Source Identification
2.4. Bioaccessibility via SBRC Method
2.5. Health Risk Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Pollution Characteristics of Heavy Metals
3.2. Quantitative Source Analysis Using PMF
3.3. Bioaccessibility of Heavy Metals in Road Dust
3.4. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Road Dust
3.4.1. Source-Specific Health Risks
3.4.2. Bioaccessibility-Based Health Risk
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, N.; Hou, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, S.; An, Q.; Li, P.; Li, X. Health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dust around a zinc smelting plant in China based on bioavailability and bioaccessibility. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2020, 197, 110617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qian, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, H. Chemical speciation and human health risk of trace metals in urban street dusts from a metropolitan city, Nanjing, SE China. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 456–457, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-B.; Zhao, D.; Li, J.; Li, S.-W.; Wang, N.; Juhasz, A.L.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Ma, L.Q. Using the SBRC Assay to Predict Lead Relative Bioavailability in Urban Soils: Contaminant Source and Correlation Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4989–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Yu, R.; Yan, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, G.; Huang, H. Bioaccessibility and provenance of heavy metals in the park dust in a coastal city of southeast China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 123, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-H.; Chen, L.-J.; Yu, L.; Guo, Z.-B.; Shan, C.-Q.; Lin, J.-Q.; Gu, Y.-G.; Yang, Z.-B.; Yang, Y.-X.; Shao, J.-R.; et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of human exposure to oral bioaccessibility of heavy metals via urban street dusts from different functional areas in Chengdu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Ochoa Gonzalez, R.; Harrison, R.M.; Green, D.; North, R.; Fowler, G.; Weiss, D. Isotopic signatures suggest important contributions from recycled gasoline, road dust and non-exhaust traffic sources for copper, zinc and lead in PM10 in London, United Kingdom. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-B.; Li, J.; Juhasz, A.L.; Ma, L.Q. Correlation of in Vivo Relative Bioavailability to in Vitro Bioaccessibility for Arsenic in Household Dust from China and Its Implication for Human Exposure Assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13652–13659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.-B.; Cui, X.-Y.; Li, K.; Li, J.; Juhasz, A.L.; Ma, L.Q. Assessment of in Vitro Lead Bioaccessibility in House Dust and Its Relationship to in Vivo Lead Relative Bioavailability. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 8548–8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, E.; Lin, Q.; Liu, L.; Yuan, H.; Li, Z. Occurrence, sources and health risks of toxic metal(loid)s in road dust from a mega city (Nanjing) in China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; O’Connor, D.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Liu, A.; Hou, D. Assessment of sources of heavy metals in soil and dust at children’s playgrounds in Beijing using GIS and multivariate statistical analysis. Environ. Int. 2019, 124, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wu, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Geng, X.; Zhao, M.; Sun, T.; Fan, Z. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in park soils of the largest megacity in China by using Monte Carlo simulation coupled with Positive matrix factorization model. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Liang, T.; Li, K.; Wang, L. Source and path identification of metals pollution in a mining area by PMF and rare earth element patterns in road dust. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 633, 958–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, B.; Yu, Y.; Lv, L.; Luo, X.; Yin, F. Heavy metals in road dust across China: Occurrence, sources and health risk assessment. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltani, N.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Cave, M.; Sorooshian, A.; Mahmoudi, M.R.; Ahmadi, M.R.; Golshani, R. In vitro bioaccessibility, phase partitioning, and health risk of potentially toxic elements in dust of an iron mining and industrial complex. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2021, 212, 111972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhasz, A.L.; Weber, J.; Smith, E.; Naidu, R.; Rees, M.; Rofe, A.; Kuchel, T.; Sansom, L. Assessment of Four Commonly Employed in Vitro Arsenic Bioaccessibility Assays for Predicting in Vivo Relative Arsenic Bioavailability in Contaminated Soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 9487–9494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lin, C.; Cheng, H. Metal(loid) bioaccessibility and children’s health risk assessment of soil and indoor dust from rural and urban school and residential areas. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 1291–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.-S.; Ding, J.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B.; Yu, S. Incorporating bioaccessibility into human health risk assessments of heavy metals in urban park soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 424, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Ng, J.C.; Tang, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shu, L. Assessment of human health risk due to lead in urban park soils using in vitro methods. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 128714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Bisson, M. Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal. Chem. 1979, 51, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, M.; Lee, D.; Nelson, J.; Verenitch, S.; Wilson, R. In vitro bioaccessibility round robin testing for arsenic and lead in standard reference materials and soil samples. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2024, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Environmental Protection Agency. Exposure Factors Handbook, 2011 ed.; Final Report; US Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; EPA/600/R-09/052F.
- Pan, H.; Lu, X.; Lei, K. A comprehensive analysis of heavy metals in urban road dust of Xi’an, China: Contamination, source apportionment and spatial distribution. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, T.; Mao, H.; Talbot, R.; Nie, X.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, C.; et al. Characteristics and potential sources of atmospheric particulate mercury in Jinan, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 1424–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, E.; Yan, M.; Zheng, S.; Fan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, J. Contamination and source apportionment of metals in urban road dust (Jinan, China) integrating the enrichment factor, receptor models (FA-NNC and PMF), local Moran’s index, Pb isotopes and source-oriented health risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Zheng, N.; Tang, L.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Hua, X. Pollution characteristics, sources, and health risk assessment of human exposure to Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb pollution in urban street dust across China between 2009 and 2018. Environ. Int. 2019, 128, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, T.; Cui, J. Geochemical Contamination, Speciation, and Bioaccessibility of Trace Metals in Road Dust of a Megacity (Guangzhou) in Southern China: Implications for Human Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 15942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Yang, L. A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem. J. 2010, 94, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wang, W.; Chan, C.Y.; Cheung, K.C.; Man, Y.B.; Wang, X.; Wong, M.H. Contamination and risk assessment (based on bioaccessibility via ingestion and inhalation) of metal(loid)s in outdoor and indoor particles from urban centers of Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Gao, B.; Wang, P.; Zhou, H.; Lu, J. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of heavy metals in street dusts from different functional areas in Beijing, China. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2015, 112, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.U.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Abbas, Q.; Ullah, H.; Munir, M.A.M.; Fu, B. Pollution characteristics and human health risks of potentially (eco)toxic elements (PTEs) in road dust from metropolitan area of Hefei, China. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Yu, B.; Zuo, L.; Wang, L.; Lei, K.; Fan, P.; Liang, T.; Rennert, T.; Rinklebe, J. Source-specific risk judgement and environmental impact of potentially toxic elements in fine road dust from an integrated industrial city, North China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, M.; Darijani, T.; Alipour, V. Heavy metal pollution of road dust in a city and its highly polluted suburb; quantitative source apportionment and source-specific ecological and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2021, 273, 129656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Adamo, I.; Ferella, F.; Rosa, P. Wasted liquid crystal displays as a source of value for e-waste treatment centers: A techno-economic analysis. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2019, 19, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Huang, J.; Huang, D.; Yang, J.; Song, Y.; Zeng, G. Heavy metals in road dust from Xiandao District, Changsha City, China: Characteristics, health risk assessment, and integrated source identification. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 13100–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, A.; Bautista, F.; Gutiérrez-Ruiz, M.; Ceniceros-Gómez, A.E.; Cejudo, R.; Goguitchaichvili, A. Heavy metal pollution of street dust in the largest city of Mexico, sources and health risk assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lu, X. Contamination characteristics and source apportionment of potentially toxic elements in the topsoil of Huyi District, Xi’an City, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayrault, S.; Catinon, M.; Boudouma, O.; Bordier, L.; Agnello, G.; Reynaud, S.; Tissut, M. Street Dust: Source and Sink of Heavy Metals To Urban Environment. In Proceedings of the E3S Web of Conferences, Rome, Italy, 23–27 September 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gope, M.; Masto, R.E.; George, J.; Hoque, R.R.; Balachandran, S. Bioavailability and health risk of some potentially toxic elements (Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn) in street dust of Asansol, India. Ecotox. Environ. Safe 2017, 138, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Li, M.-Y.; Chen, X.-Q.; Wang, J.-Y.; Li, L.-Z.; Tu, C.; Luo, Y.-M.; Li, H.-B.; Ma, L.Q. As, Cd, and Pb relative bioavailability in contaminated soils: Coupling mouse bioassay with UBM assay. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Luo, J.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, S. Geochemical fractionation, bioavailability, and potential risk of heavy metals in sediments of the largest influent river into Chaohu Lake, China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 290, 118018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padoan, E.; Romè, C.; Ajmone-Marsan, F. Bioaccessibility and size distribution of metals in road dust and roadside soils along a peri-urban transect. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 601–602, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Huan, Y.; Wang, R.; Liang, T. Concentrations, spatial distribution, sources and environmental health risks of potentially toxic elements in urban road dust across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Xue, J.; Zhu, Z. Comparison of heavy metal bioaccessibility between street dust and beach sediment: Particle size effect and environmental magnetism response. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 777, 146081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
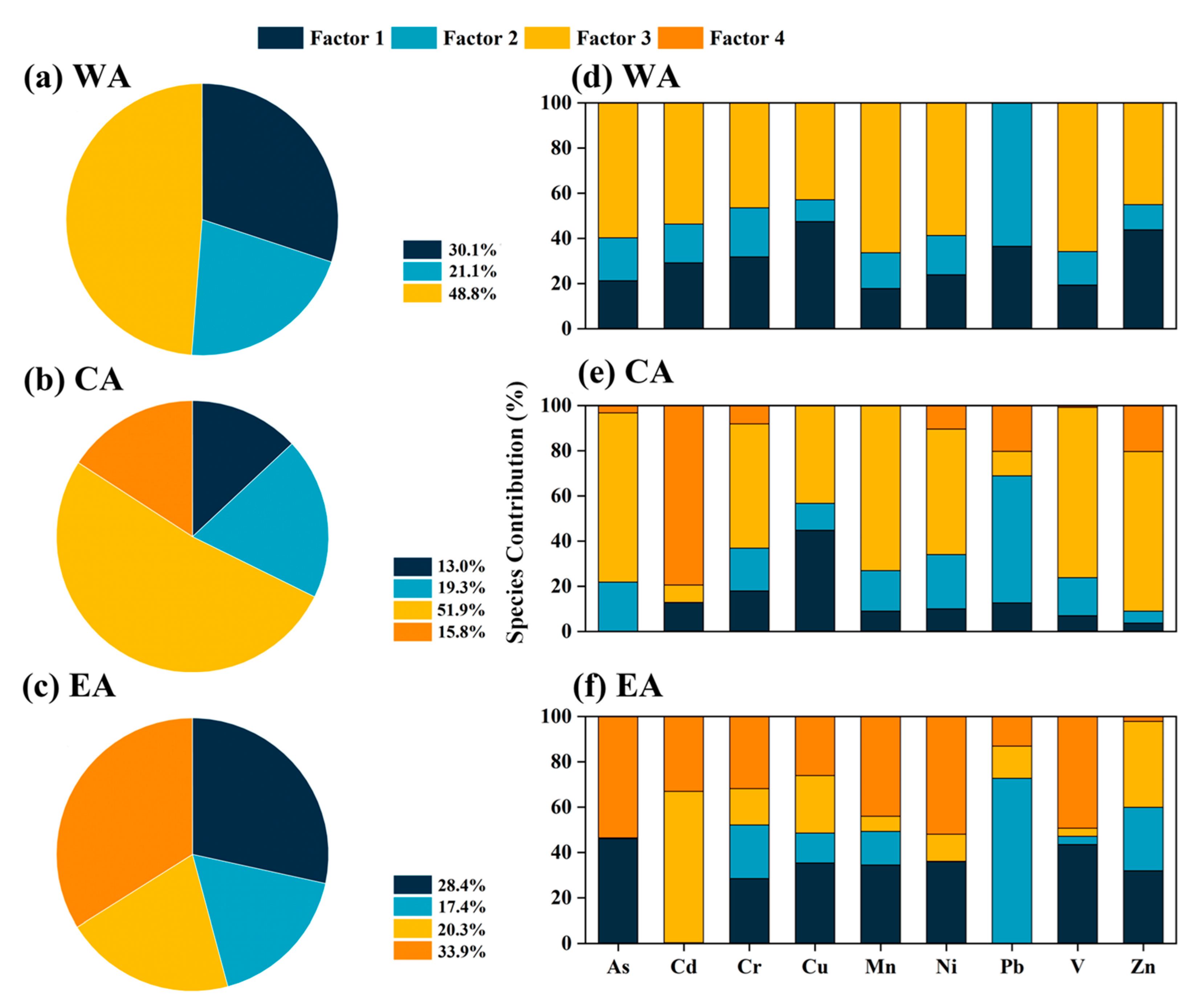


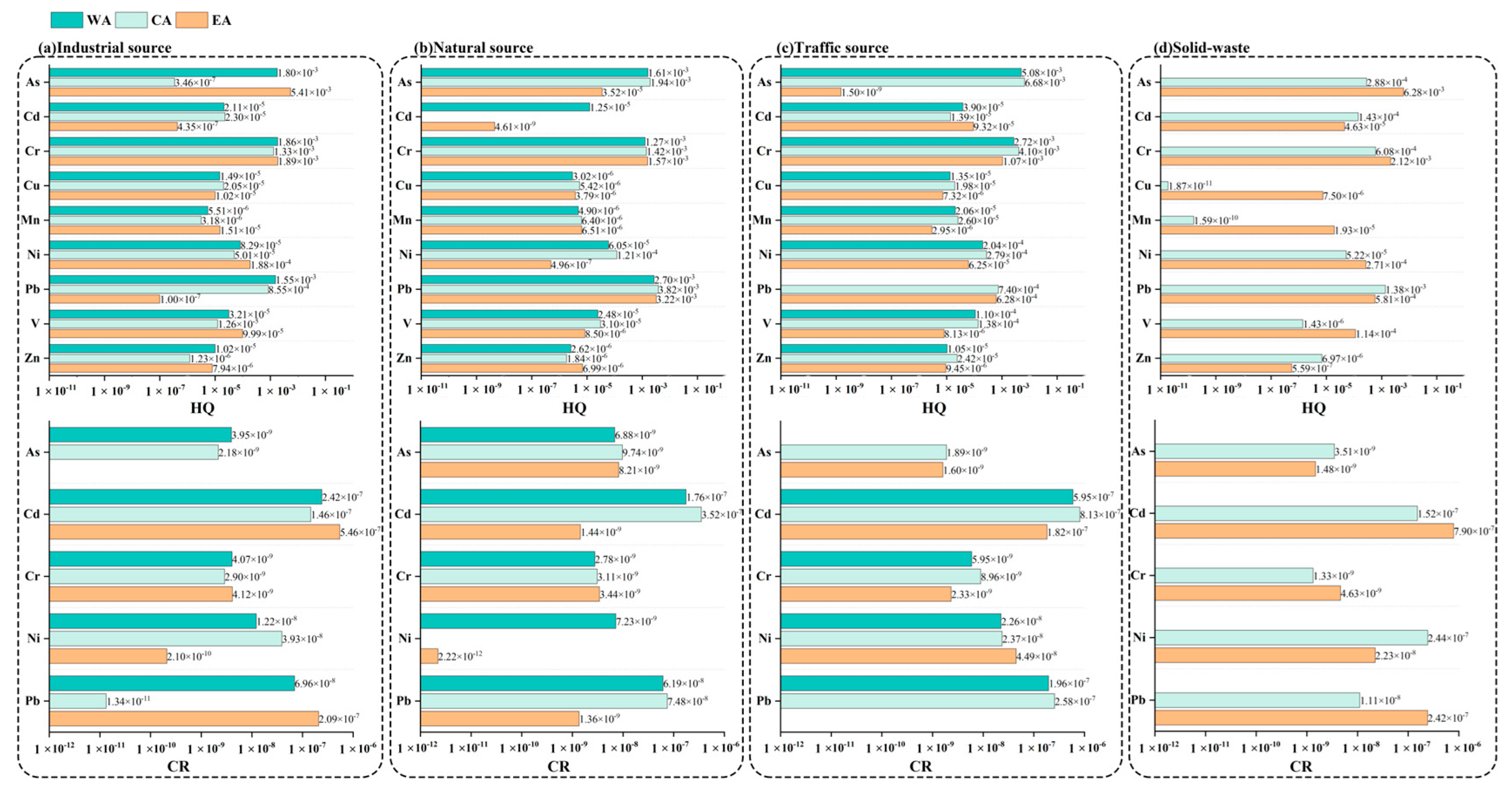

| Sample ID | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Mn | Ni | Pb | V | Zn |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WA | |||||||||
| Max | 12.1 | 0.44 | 69.8 | 73.3 | 767 | 28.1 | 88.6 | 54.3 | 433 |
| Min | 4.90 | 0.15 | 40.6 | 19.8 | 311 | 14.0 | 25.0 | 27.3 | 125 |
| Mean | 7.66 | 0.24 | 52.9 | 44.1 | 500 | 20.9 | 44.7 | 41.0 | 245 |
| SD | 2.40 | 0.10 | 11.2 | 16.9 | 161 | 5.13 | 20.2 | 11.8 | 122 |
| CV(%) | 31.3 | 40.8 | 21.2 | 38.2 | 32.2 | 24.5 | 45.2 | 28.8 | 49.7 |
| CA | |||||||||
| Max | 11.8 | 9.22 | 183 | 284 | 746 | 75.6 | 268 | 52.5 | 592 |
| Min | 5.94 | 0.09 | 38.1 | 18.9 | 451 | 17.0 | 13.7 | 40.6 | 165 |
| Mean | 8.04 | 1.77 | 67.3 | 64.2 | 574 | 30.2 | 71.5 | 45.1 | 361 |
| SD | 1.71 | 3.12 | 36.8 | 65.8 | 82.9 | 15.2 | 72.7 | 3.26 | 158 |
| CV(%) | 21.3 | 176 | 54.6 | 102 | 14.4 | 50.3 | 102 | 7.24 | 43.9 |
| EA | |||||||||
| Max | 17.8 | 1.18 | 91.4 | 68.3 | 1049 | 51.5 | 112 | 90.5 | 750 |
| Min | 7.86 | 0.14 | 41.1 | 27.2 | 541 | 19.5 | 23.7 | 43.8 | 107 |
| Mean | 10.6 | 0.39 | 60.0 | 40.4 | 708 | 31.4 | 46.7 | 56.6 | 263 |
| SD | 3.20 | 0.33 | 17.6 | 12.2 | 152 | 11.0 | 28.1 | 14.0 | 202 |
| CV(%) | 30.3 | 86.1 | 29.4 | 30.0 | 21.5 | 35.1 | 60.3 | 24.8 | 76.7 |
| BV | 10.3 | 0.14 | 67.8 | 24 | 573 | 30.1 | 24 | 80.1 | 67.5 |
| City | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Mn | Ni | Pb | V | Zn | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WA, Jinan, Shandong | 7.66 | 0.24 | 52.9 | 44.1 | 500 | 20.9 | 44.7 | 41.0 | 245 | This study |
| CA, Jinan, Shandong | 8.04 | 1.77 | 67.3 | 64.2 | 574 | 30.2 | 71.5 | 45.1 | 361 | This study |
| EA, Jinan, Shandong | 10.6 | 0.39 | 60.0 | 40.4 | 708 | 31.4 | 46.7 | 56.6 | 263 | This study |
| Xiamen, Fujian | 12.0 | 1.33 | 143 | 259 | - | 52.0 | 202 | 43.6 | 911 | [4] |
| Beijing | - | 0.72 | 84.7 | 69.9 | - | 25.2 | 105 | - | 222 | [29] |
| Chengdu, Sichuan | - | 1.68 | 84.8 | 98.9 | - | 24.5 | 81.3 | - | 296 | [5] |
| Guangzhou, Guangdong | 21.3 | 0.73 | 150 | 117 | - | 35.4 | 150 | 39.3 | 475 | [26] |
| Hefei, Anhui | 2.00 | - | 139 | 41.6 | 241 | 28.6 | - | 31.4 | 130 | [30] |
| Xi’an, Shanxi | - | - | 145 | 54.7 | 511 | 30.8 | 125 | 69.6 | 269 | [22] |
| NanJing, Jiangsu | 13.9 | 0.72 | - | 133 | - | - | 102 | - | 281 | [9] |
| Shanghai | 8.30 | 0.30 | 115 | 40.4 | - | 37.4 | 45.0 | 86.4 | 145 | [11] |
| Shijiazhuang, Hebei | 27.2 | 65.0 | 60.9 | 539 | 24.9 | 61.5 | - | 438 | [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, S.; Han, L.; Wu, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Li, J. Health Risk Assessment of Road-Dust-Bound Heavy Metals via Ingestion Exposure from One Typical Inland City of Northern China: Incorporation of Sources and Bioaccessibility. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156550
Chen S, Han L, Wu Y, Liu X, Liu C, Liu Y, Li H, Li J. Health Risk Assessment of Road-Dust-Bound Heavy Metals via Ingestion Exposure from One Typical Inland City of Northern China: Incorporation of Sources and Bioaccessibility. Sustainability. 2024; 16(15):6550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156550
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Shuo, Lei Han, Yushuang Wu, Xiaojuan Liu, Chenglang Liu, Yuzhen Liu, Hongbo Li, and Jie Li. 2024. "Health Risk Assessment of Road-Dust-Bound Heavy Metals via Ingestion Exposure from One Typical Inland City of Northern China: Incorporation of Sources and Bioaccessibility" Sustainability 16, no. 15: 6550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156550
APA StyleChen, S., Han, L., Wu, Y., Liu, X., Liu, C., Liu, Y., Li, H., & Li, J. (2024). Health Risk Assessment of Road-Dust-Bound Heavy Metals via Ingestion Exposure from One Typical Inland City of Northern China: Incorporation of Sources and Bioaccessibility. Sustainability, 16(15), 6550. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156550





