Integrating Perishables into Closed-Loop Supply Chains: A Comprehensive Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Paper Structure
2. Methodology
2.1. Source Identification
2.2. Source Selection an Evaluation
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. Bibliometric Analysis
2.3.2. Literature Review Table
3. Theoretical and Fundamental Background
3.1. Supply Chain Management
| Managing Customer Relations | Strategic Subroutines | Evaluate Corporate and Marketing Strategies | Establish Criteria for Classifying Customers | Issue Guidelines for Product/Service Agreement Differentiation Levels | Create a Metrics Structure | Create Guidelines for Distributing Process Improvement Benefits to Customers | ||
| Operational Subroutines | Segment customers | Organize the account/segment management team | Conduct internal audits of accounts | Discover opportunities within the accounts | Formulate the product/service agreement | Execute the product/service contract | Evaluate performance and produce profitability analyses | |
| Handling Customer Services | Strategic Subroutines | Formulate a customer service strategy | Create response protocols | Build infrastructure for response procedure execution | Establish a metrics system | |||
| Operational Subroutines | Identify significant events | Assess the situation and options | Execute the solution | Track and document performance | ||||
| Managing Demand | Strategic Subroutines | Select forecasting methods | Organize the flow of information | Establish synchronization protocols | Build a contingency management plan | Establish a metrics framework | ||
| Operational Subroutines | Gather data and information | Project future trends | Achieve synchronization | Enhance flexibility and minimize variability | Evaluate performance | |||
| Fulfilling Orders | Strategic Subroutines | Assess marketing strategy, SC architecture & customer service objectives | Specify order fulfillment needs | Assess logistics systems | Outline a strategy for order fulfillment | Set up a system of metrics | ||
| Operational sub-process | Process and dispatch orders | Enter order details | Execute order processing | Manage documentation processes | Select orders | Fulfill the order | Conduct post-delivery operations and assess performance | |
| Managing Manufacturing Flow | Strategic Subroutines | Evaluate strategies for manufacturing, sourcing, marketing, and logistics | Assess the need for manufacturing adaptability | Set boundaries between push and pull strategies | Determine manufacturing limitations and needs | Assess manufacturing capabilities | Construct a metrics system | |
| Operational Subroutines | Establish routing and speed through the production process | Plan for manufacturing and material management | Align capacity with demand | Evaluate performance metrics | ||||
| Managing Supplier Relations | Strategic Subroutines | Examine corporate and manufacturing strategies | Define criteria for classifying suppliers | Issue guidelines for customization levels in the product/service agreement | Construct a metrics framework | Issue guidelines for allocating process improvement benefits to suppliers | ||
| Operational Subroutines | Classify suppliers | Set up the supplier/segment management team | Conduct internal evaluations of suppliers or supplier segments | Spot opportunities with suppliers | Develop a product/service agreement and communication strategy | Implement the product/service contract | Assess performance and produce reports on supplier costs and profitability | |
| Developing and Commercializing Products | Strategic Subroutines | Assess sourcing, manufacturing, and marketing strategies | Formulate processes for idea generation and evaluation | Set criteria for membership in cross-functional product development teams | Formulate issues and constraints for product deployment | Set guidelines for new product projects | Build a metrics framework | |
| Operational Subroutines | Define new products and evaluate compatibility | Form a cross-functional team for product development | Formalize the new product development process | Develop and construct prototypes | Decide on manufacturing in-house or purchasing | Identify distribution channels | Launch products | |
| Managing Returns | Strategic Subroutines | Check compliance with environmental and legal standards | Develop guidelines for avoidance, gatekeeping, and handling | Design return networks and processing alternatives | Establish rules for credit management | Identify alternative markets | Establish a metrics structure | |
| Operational Subroutines | Accept requests for returns | Plan transportation routes | Process returned items | Choose disposition methods | Provide credit to customers or suppliers | Examine returns and evaluate performance |
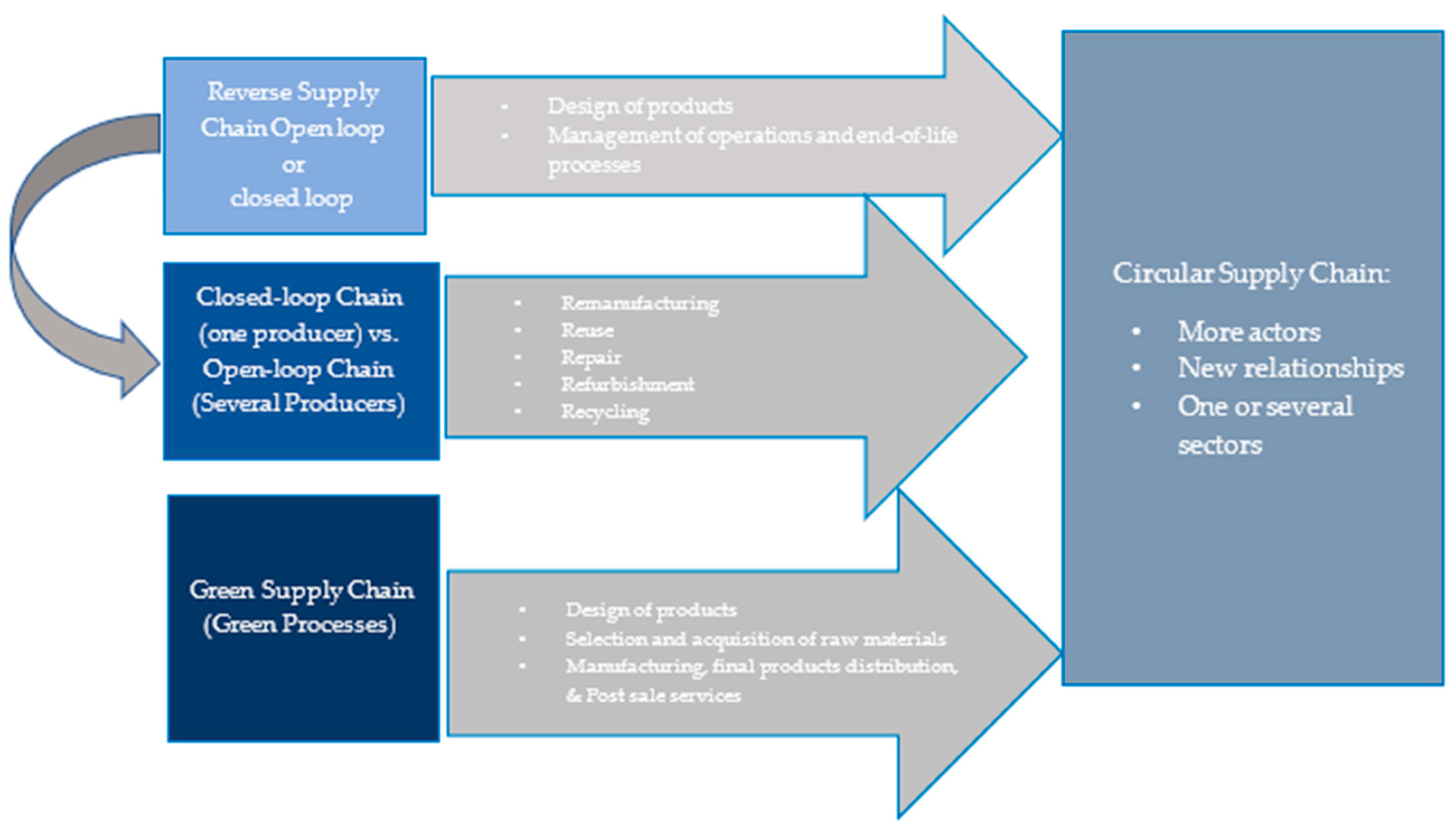
3.2. Green Supply Chains
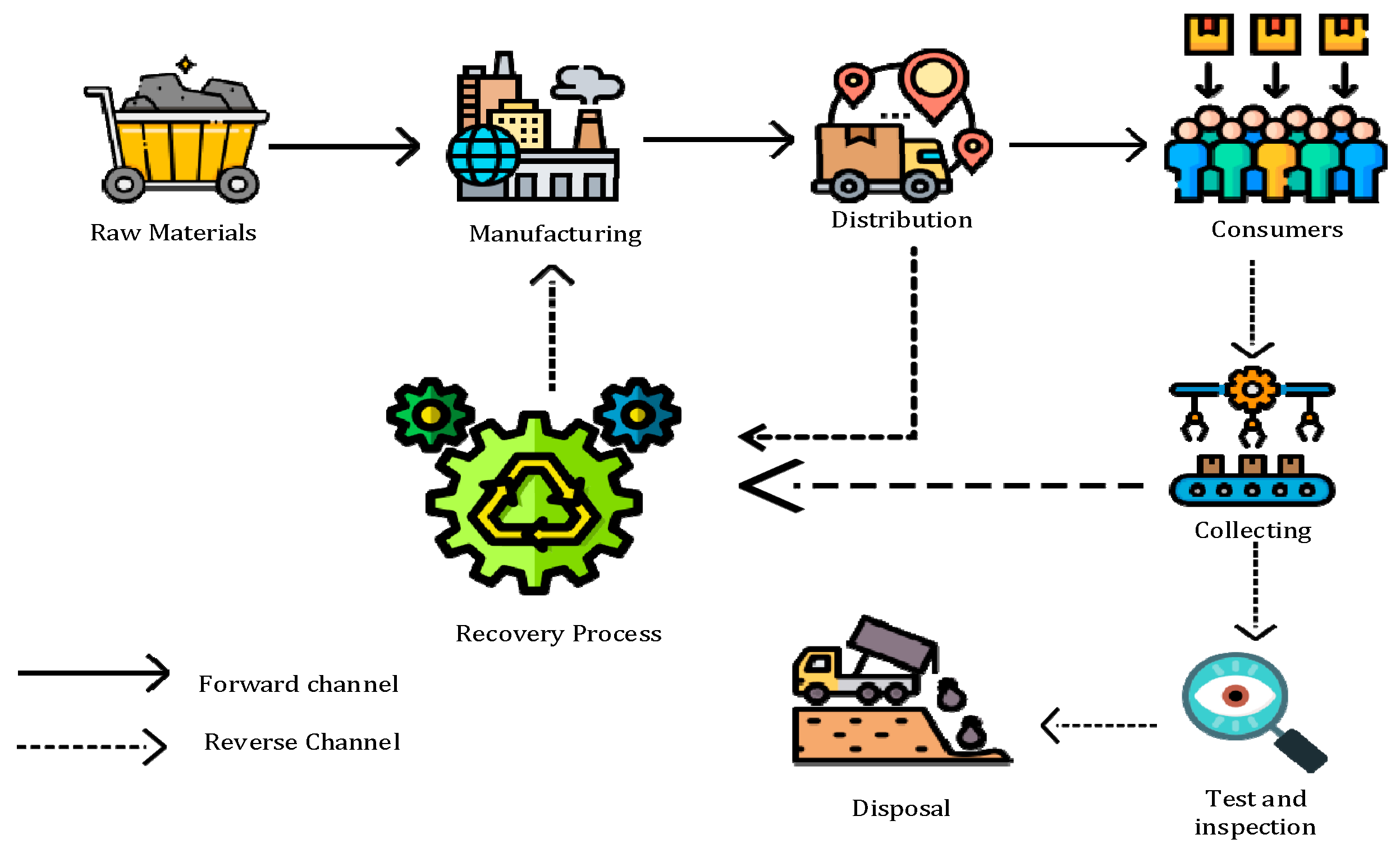
3.3. Closed-Loop Supply Chain Management
3.3.1. Advantages of an Optimal CLSC Design
3.3.2. The Reprocessing Strategies or R-Imperatives
4. Optimization and Dynamics in CLSC
4.1. Decision-Making in CLSC
4.2. Timeframes and Product Viewpoints in CLSC
4.3. Sustainability Aspects and Objective Functions in CLSC
4.4. Applications and Case Study Sectors
4.5. Modeling Approaches and Solution Techniques in the CLSC
4.6. Integration of Applications, Case Locations, Modeling Approaches, and Solution Methods
4.7. Uncertainty
5. Perishable Products
5.1. Perishability Types
5.2. Sustainability for Perishable
6. Perishables and CLSC Literature Analysis
6.1. Bibliometric Analysis
6.2. Current Research on CLSCs for Perishable Products
| No. | Author | Year | Purpose | Model Formulation | Solution Approach | Industry | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximize | Minimize | ||||||
| 1 | [181] | 2017 | Profit | Cost and environmental impact | MILP | ε-constraint | Agri-food |
| 2 | [182] | 2017 | Profit | *** | MILP | GAMS | Tire |
| 3 | [183] | 2017 | Profit | *** | MILP | GAMS | Tire |
| 4 | [184] | 2018 | *** | Cost and risk | Tri-level programming | GA | Tire |
| 5 | [185] | 2018 | SC profit | Lost sales | Regression & simulation | Maximin and Arena | Perishable |
| 6 | [186] | 2018 | Responsiveness | Costs and environmental emission effects | MILP | ɛ-constraint | Tire |
| 7 | [187] | 2018 | *** | Cost | Coordination mechanism | Finding an equilibrium | Perishable |
| 8 | [78] | 2018 | *** | Cost and environmental impact | MILP | hybrid meta-heuristic algorithms | Tire |
| 9 | [188] | 2019 | *** | Cost and environmental pollutant | MILP | Heuristic | Dairy |
| 10 | [189] | 2019 | Profit | *** | MILP | Kernel search-based heuristic and CPLEX | Perishable |
| 11 | [190] | 2019 | *** | Cost and CO2 emissions | MILP | LP-metrics | Dairy |
| 12 | [191] | 2019 | *** | Greenhouse gas emissions and cost | MINP | MCDM | Perishable |
| 13 | [192] | 2019 | *** | Economic, environmental, and social costs | MILP | LINGO 11.0 solver | Blood |
| 14 | [193] | 2020 | Profits | *** | Coordination mechanism | Finding an equilibrium | Pharmaceutical |
| 15 | [194] | 2020 | *** | cost | LP | System dynamics | Pharmaceutical |
| 16 | [195] | 2020 | Responsiveness | Cost and CO2 emissions | MILP | LP-Metrics and weighted Tchebycheff | Agri-food |
| 17 | [196] | 2020 | *** | Cost and CO2 emissions | MILP | LP-metrics | Dairy |
| 18 | [197] | 2020 | Job opportunities | Cost and energy consumption and pollution | MILP | ε-constraint | Tire |
| 19 | [24] | 2020 | *** | Cost | MILP | Pyomo and CPLEX | Perishable |
| 20 | [198] | 2020 | Time delivery of purchased products from plants to the suppliers and profits | Environmental impact | MILP | GAMS | Tire |
| 21 | [199] | 2020 | Profit | *** | Coordination mechanism and Stackelberg game | Finding an equilibrium | Dairy |
| 22 | [200] | 2020 | *** | Cost and time and carbon emissions | MINLP | ε-constraint and ACO 2 and WOA 3 and Hybrid NSGA-II and MOPSO 4 | Tire |
| 23 | [201] | 2021 | Responsiveness | Cost | MILP | ε-constraint and LP-metrics | Fish |
| 24 | [202] | 2021 | Profit | Environmental impact | MILP | Robust and heuristic | Dairy |
| 25 | [203] | 2021 | Profit and job opportunities | Environmental impact | MILP | GAMS | Tire |
| 26 | [204] | 2021 | Profit | Environmental impact | MILP | Augmented ε-constraint and meta-heuristic algorithm | Tire |
| 27 | [141] | 2021 | Profit | *** | ICCMINLP 5 | Chance-constrained programming | Perishable |
| 28 | [205] | 2021 | Demand’s coverage and reliability of facilities and responsiveness and social responsibility | Cost and CO2 emissions | MILP | ε-constraint | Tire |
| 29 | [206] | 2021 | Job opportunities | Cost, environmental effects | MILP | augmented ε-constraint | Tire |
| 30 | [207] | 2021 | *** | Costs | MILP | Two hybrid meta-heuristic algorithms | Tire |
| 31 | [208] | 2021 | *** | Costs | MINLP | DE 6 | Blood |
| 32 | [209] | 2021 | Profit | *** | LP | Minmax | biofuel |
| 33 | [210] | 2022 | Job opportunities | Costs and pollution emissions | MILP | MCGP-UF 7 | Tire |
| 34 | [211] | 2022 | Profit and job opportunities | Environmental impact | MILP | Combining the LP-metrics with a heuristic | Pharmaceutical |
| 35 | [212] | 2022 | Costs and environmental impacts | Social dimension | MILP | LR 8 and CH 9 | Tire |
| 36 | [213] | 2022 | *** | Costs and environmental issues | MILP | ε-constraint | Tire |
| 37 | [214] | 2022 | CS indices | Cost | NLP | Fuzzy multi-objective optimization | Pharmaceutical and biofuel |
| 38 | [215] | 2022 | Job opportunities | Cost and CO2 emission | MILP | ε-constraint and hybrid meta-heuristic | Agri-food |
| 39 | [216] | 2022 | Profit | Delivery time and lost business days | MILP | (NSGAII)and& (MOEA) 10 | Perishable |
| 40 | [217] | 2022 | Customer satisfaction | Delivery time | MILP | ε-constraint method and NSGAII | Perishable |
| 41 | [218] | 2022 | Profit | Carbon emissions | MILP | A kernel-search heuristic based ε-constraint method | Perishable |
| 42 | [219] | 2022 | *** | Cost and CO2 emission | MILP | GAMS and genetic | Fish |
| 43 | [220] | 2022 | Profit and customer satisfaction | *** | MILP | LP-metric and goal attainment | Dairy |
| 44 | [221] | 2022 | Social impacts | Cost and CO2 emissions | MILP | Interactive fuzzy programming | Dairy |
| 45 | [222] | 2022 | Profit | *** | Coordination mechanism and Stackelberg game | Backward induction | Tire |
| 46 | [223] | 2022 | Profit and social welfare | *** | Two-stage Stackelberg game | Mathematica and MATLAB | Tire |
| 47 | [224] | 2023 | The reaction time demands | Cost and CO2 emission | MILP | Meta-heuristic and hybrid algorithms | Fish |
| 48 | [225] | 2023 | Cash flow | *** | MILP | ABD algorithm and WSM augmented ε-constraint and FMOP 11 | Dairy |
| 49 | [226] | 2023 | *** | Cost and waste | NLP | Generalized reduced gradient | Pharmaceutical |
| 50 | [227] | 2023 | Environmental and social | Cost | MILP | Augmented ε-constraint | Tire |
| 51 | [228] | 2023 | Profit and customer satisfaction | CO2 emissions | MILP | (MOGWO_SA) 12 and (MOKA_SA) 13 and (MOHHO_SA) 14 and (MOSA) 15 | Agri-food |
| 52 | [229] | 2023 | *** | Cost | MILP | Six new multi-objective evolutionary algorithms based on decomposition (MOEA/D) variants | Tire |
6.3. Detailed Evaluation of Methodology
7. Research Gaps and Future Agendas
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Bosona, T.; Gebresenbet, G. Erratum to “Food traceability as an integral part of logistics management in food and agricultural supply chain” [Food Control 33 (2013) 32–48]. Food Control 2013, 34, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, R.; Salehi-Amiri, A.; Zahedi, A.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. Designing a supply chain network for blood decomposition by utilizing social and environmental factor. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 160, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, A.; Salehi-Amiri, A.; Smith, N.R.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. Utilizing IoT to design a relief supply chain network for the SARS-COV-2 pandemic. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 104, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischmann, M.; Beullens, P.; Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J.M.; Vanwassenhove, L.N. The Impact of Product Recovery on Logistics Network Design. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2001, 10, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, R.; Qiang, Q.P.; Ke, K.; Huang, Z. Closed-loop supply chain network with interaction of forward and reverse logistics. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 27, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminipour, A.; Bahroun, Z.; Hariga, M. Cyclic manufacturing and remanufacturing in a closed-loop supply chain. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2021, 25, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahmias, S. Perishable inventory theory: A review. Oper. Res. 1982, 30, 680–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, M.M.; Chang, Y.S. Temperature management for the quality assurance of a perishable food supply chain. Food Control 2014, 40, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, S.K.; Giri, B.C. Recent trends in modeling of deteriorating inventory. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 134, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltaninejad, M.; Aghazadeh, R.; Shaghaghi, S.; Zarei, M. Using Machine Learning Techniques to Forecast Mehram Company’s Sales: A Case Study. J. Bus. Manag. Stud. 2024, 6, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, S.; Hooker, N. Private sector management of food safety: Public regulation and the role of private controls. Int. Food Agribus. Manag. Rev. 2001, 4, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simchi-Levi, D.; Kaminsky, P.; Simchi-Levi, E. Designing and Managing the Supply Chain: Concepts, Strategies, and Cases; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ellram, L.M. Supply-chain management: The industrial organisation perspective. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 1991, 21, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübner, A.H.; Kuhn, H.; Wollenburg, J. Last mile fulfilment and distribution in omni-channel grocery retailing: A strategic planning framework. Int. J. Retail. Distrib. Manag. 2016, 44, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheraghalipour, A.; Paydar, M.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. A bi-objective optimization for citrus closed-loop supply chain using Pareto-based algorithms. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 69, 33–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, A.R.M.; Genovese, A.; Brint, A.; Kumar, N. Improving reverse supply chain performance: The role of supply chain leadership and governance mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 216, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsi, A.; Diabat, A. A reverse logistics network design. J. Manuf. Syst. 2015, 37, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishvaee, M.S.; Torabi, S.A. A possibilistic programming approach for closed-loop supply chain network design under uncertainty. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2010, 161, 2668–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-C.; Xu, H.-Y.; Chen, K.-B. Operational decisions and financing strategies in a capital-constrained closed-loop supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 4690–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Wang, F.; Lai, X.; Hong, J. How Does Licensing Remanufacturing Affect the Supply Chain Considering Customer Environmental Awareness? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, M.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, Y. Managing a closed-loop supply chain with process innovation for remanufacturing. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 276, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, L.; Lu, Q.; Fan, Y. Sustainable supply chain management for perishable products in emerging markets: An integrated location-inventory-routing model. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2021, 150, 102319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejarza, F.; Baldea, M. Closed-loop real-time supply chain management for perishable products ⁎⁎We gratefully acknowledge partial financial support from the U.S. National Science Foundation through the CAREER Award 1454433 and Award CBET-1512379. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 11458–11463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejarza, F.; Baldea, M. Closed-loop optimal operational planning of supply chains with fast product quality dynamics. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 132, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolini, M.; Faccio, M.; Ferrari, E.; Gamberi, M.; Pilati, F. Fresh food sustainable distribution: Cost, delivery time and carbon footprint three-objective optimization. J. Food Eng. 2016, 174, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Soleimani, H.; Kannan, D. Reverse logistics and closed-loop supply chain: A comprehensive review to explore the future. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 240, 603–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Navarro, K.; Castro-García, L.; Assan-Barrios, K.; Vergara-Bujato, K.; Zamora-Musa, R. Reverse Logistics and Sustainability: A Bibliometric Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Yeung, J.K.W.; Lau, Y.-Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Kwong, R. A Critical Literature Review on Blockchain Technology Adoption in Supply Chains. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, D.F. Evolution of Supply Chain Management. In Competing Through Supply Chain Management: Creating Market-Winning Strategies Through Supply Chain Partnerships; Ross, D.F., Ed.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1998; pp. 72–108. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, N.; Malik, K.; Sharma, S. Transformation of Supply Chain Management to Green Supply Chain Management: Certain investigations for research and applications. Clean. Mater. 2023, 7, 100172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.M. Supply Chain Management (SCM): Theory and Evolution. Supply Chain. Manag.-Appl. Simul. 2011, 10, 24573. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, C.R.; Liane Easton, P. Sustainable supply chain management: Evolution and future directions. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2011, 41, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokhanian, S.; Sodagartojgi, A.; Tehranian, K.; Ahmadirad, Z.; Moghaddam, P.K.; Mohsenibeigzadeh, M. Exploring the impact of supply chain integration and agility on commodity supply chain performance. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2024, 22, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, S.E.; Magnan, G.M.; McCarter, M.W. Benefits, barriers, and bridges to effective supply chain management. Supply Chain. Manag. Int. J. 2008, 13, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, D.; Day, S.; Godsell, J. Supply Chain Configurations in the Circular Economy: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazancoglu, Y.; Kazancoglu, I.; Sagnak, M. A new holistic conceptual framework for green supply chain management performance assessment based on circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1282–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.H.; Yang, H.; Lee, M.; Park, S. The Impact of Institutional Pressures on Green Supply Chain Management and Firm Performance: Top Management Roles and Social Capital. Sustainability 2017, 9, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarreh, M.; Yaghoubi, S.; Bahrami, H. Pricing of Drinking Water under Dynamic Supply and Demand based on Government Role: A Game-Theoretic Approach. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 38, 2101–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Fan, Z.-P.; Wang, N. Green subsidy modes and pricing strategy in a capital-constrained supply chain. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 136, 101885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halat, K.; Hafezalkotob, A.; Sayadi, M.K. The green supply chains’ ordering and pricing competition under carbon emissions regulations of the government. Int. J. Syst. Sci. Oper. Logist. 2021, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaefarian, T.; Fander, A.; Yaghoubi, S. A dynamic game approach to demand disruptions of green supply chain with government intervention (case study: Automotive supply chain). Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 336, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, A.; De, P.K.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Lim, C.P.; Das, R. Optimal pricing policy in a three-layer dual-channel supply chain under government subsidy in green manufacturing. Math. Comput. Simul. 2022, 204, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Z. Evolutionary game of the green investment in a two-echelon supply chain under a government subsidy mechanism. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1315–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooque, M.; Zhang, A.; Thürer, M.; Qu, T.; Huisingh, D. Circular supply chain management: A definition and structured literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 882–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca, L.M.; Domingues, J.P.; Pereira, M.T.; Martins, F.F.; Zimon, D. Assessment of Circular Economy within Portuguese Organizations. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Heshmati, A.; Geng, Y.; Yu, X. A review of the circular economy in China: Moving from rhetoric to implementation. J. Clean. Prod. 2013, 42, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coenen, J.; van der Heijden, R.; van Riel, A.C.R. Making a Transition toward more Mature Closed-Loop Supply Chain Management under Deep Uncertainty and Dynamic Complexity: A Methodology. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, P.; Sassanelli, C.; Terzi, S. Towards Circular Business Models: A systematic literature review on classification frameworks and archetypes. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghakhani, S.; Pourmand, P.; Zarreh, M. A Mathematical Optimization Model for the Pharmaceutical Waste Location-Routing Problem Using Genetic Algorithm and Particle Swarm Optimization. Math. Probl. Eng. 2023, 2023, 6165495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, B.Y.; Li, K.W.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J. Pricing and warranty decisions in a two-period closed-loop supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 1688–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinezahd, M. A new multi-product closed-loop supply chain network design in dairy industry. Iran. J. Oper. Res. 2019, 10, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guide, V.D.R., Jr.; Van Wassenhove, L.N. OR FORUM—The evolution of closed-loop supply chain research. Oper. Res. 2009, 57, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, N.R.; Kumar, R. Closed loop supply chain management and reverse logistics-A literature review. Int. J. Eng. Res. Technol. 2013, 6, 455–468. [Google Scholar]
- French, M.L.; LaForge, R.L. Closed-loop supply chains in process industries: An empirical study of producer re-use issues. J. Oper. Manag. 2006, 24, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Malik, M. Organizational enablers for circular economy in the context of sustainable supply chain management. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, R.; Howard, M.; Miemczyk, J. Supply chain management and the circular economy: Towards the circular supply chain. Prod. Plan. Control 2018, 29, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, A.; Acquaye, A.A.; Figueroa, A.; Koh, S.C.L. Sustainable supply chain management and the transition towards a circular economy: Evidence and some applications. Omega 2017, 66, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, D. The circular economy, design thinking and education for sustainability. Local Econ. 2015, 30, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, S.; Kheirkhah, A. A comprehensive approach in designing a sustainable closed-loop supply chain network using cross-docking operations. Comput. Math. Organ. Theory 2018, 24, 51–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Engeland, J.; Beliën, J.; De Boeck, L.; De Jaeger, S. Literature review: Strategic network optimization models in waste reverse supply chains. Omega 2020, 91, 102012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, K.; Saito, T.; Irohara, T.; Deguchi, Y.; Hanada, K.; Abe, K.; Kishi, M.; Shimizu, T. Redesigning an existing recovery logistics network in closed loop supply chain. J. Jpn. Ind. Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 348–357. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Ziad, E.; Ju, F. A Knowledge Constrained Deep Spatio-Temporal Clustering Approach for Melt Pool Anomaly Detection in Laser Powder Bed Fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE CASE 2024, Bari, Italy, 28 August–1 September 2024. [Google Scholar]
- MahmoumGonbadi, A.; Genovese, A.; Sgalambro, A. Closed-loop supply chain design for the transition towards a circular economy: A systematic literature review of methods, applications and current gaps. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 323, 129101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudbari, E.S.; Ghomi, S.M.T.F.; Eicker, U. Designing a multi-objective closed-loop supply chain: A two-stage stochastic programming, method applied to the garment industry in Montréal, Canada. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 6131–6162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, L.; Liang, X.; Yao, J.; Luo, P. Price Optimization of Closed-loop Supply Chain With Uncertain Demand Under Multi-channel Cross Influence. SAGE Open 2023, 13, 21582440231218065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Das, D.; Schultmann, F.; Fröhling, M. Design and planning of a closed-loop supply chain with three way recovery and buy-back offer. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 604–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golroudbary, S.R.; Zahraee, S.M. System dynamics model for optimizing the recycling and collection of waste material in a closed-loop supply chain. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2015, 53, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Kimiagari, A.M.; Karimi, B.; Hejazi, T.H. Closed-loop supply chain network design under a fuzzy environment. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2014, 59, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadsisakht, A.; Ryan, S.M. Closed-loop supply chain network design with multiple transportation modes under stochastic demand and uncertain carbon tax. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 195, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Berenguer, G.; Pan, X. Location, inventory and testing decisions in closed-loop supply chains: A multimedia company. IISE Trans. 2019, 51, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadambala, D.K.; Subramanian, N.; Tiwari, M.K.; Abdulrahman, M.; Liu, C. Closed loop supply chain networks: Designs for energy and time value efficiency. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi, A.; Asl-Najafi, J.; Yaghoubi, S. A dynamic bi-objective closed-loop supply chain network design considering supplier selection and remanufacturer subcontractors. Uncertain Supply Chain. Manag. 2018, 6, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wu, D.; Shi, L. Distribution-free stochastic closed-loop supply chain design problem with financial management. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabaki, M.S.; Khamseh, A.A.; Mohammadi, M. A priority-based firefly algorithm for network design of a closed-loop supply chain with price-sensitive demand. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 135, 814–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrokh, M.; Azar, A.; Jandaghi, G.; Ahmadi, E. A novel robust fuzzy stochastic programming for closed loop supply chain network design under hybrid uncertainty. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 2018, 341, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardan, E.; Govindan, K.; Mina, H.; Gholami-Zanjani, S.M. An accelerated benders decomposition algorithm for a bi-objective green closed loop supply chain network design problem. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeballos, L.J.; Méndez, C.A.; Barbosa-Povoa, A.P. Design and planning of closed-loop supply chains: A risk-averse multistage stochastic approach. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6236–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebjamnia, N.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. Sustainable tire closed-loop supply chain network design: Hybrid metaheuristic algorithms for large-scale networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 196, 273–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alumur, S.A.; Nickel, S.; Saldanha-Da-Gama, F.; Verter, V. Multi-period reverse logistics network design. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2012, 220, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Singh, R.K.; Murtaza, Q. A literature review and perspectives in reverse logistics. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2015, 97, 76–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, A.; Hosseini Dolatabadi, S.H.; Heidari, M.; Khorrami, B.M.; Luo, Y. Hydrogen: An Integral Player in the Future of Sustainable Transportation. A survey of Fuel Cell Vehicle Technologies, Adoption Patterns, and Challenges. Preprints 2023, 2023100415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özceylan, E.; Demirel, N.; Çetinkaya, C.; Demirel, E. A closed-loop supply chain network design for automotive industry in Turkey. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2017, 113, 727–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, S.; Barbosa-Póvoa, A.P.; Escudero, L.F.; Gomes, M.I.; Pizarro, C. On risk management of a two-stage stochastic mixed 0–1 model for the closed-loop supply chain design problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 274, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroter, M.; Spengler, T. Designing control management systems for parts recovery and spare parts management in the final phase within closed-loop supply chains. Int. J. Integr. Supply Manag. 2004, 1, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Kumar, S.; Soni, G.; Jain, V.; Rathore, A.P.S. Closed-loop supply chain network design and modelling under risks and demand uncertainty: An integrated robust optimization approach. Ann. Oper. Res. 2020, 290, 837–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgarbossa, F.; Russo, I. A proactive model in sustainable food supply chain: Insight from a case study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 596–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, K.; Jha, P.; Garg, K. Product recovery optimization in closed-loop supply chain to improve sustainability in manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2016, 54, 1463–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani-Ahranjani, A.; Bozorgi-Amiri, A.; Seifbarghy, M.; Najafi, E. Sustainability in paper industry closed-loop supply chain (case study: East Azerbaijan province, Iran). J. Ind. Syst. Eng. 2017, 10, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani, H. A new sustainable closed-loop supply chain model for mining industry considering fixed-charged transportation: A case study in a travertine quarry. Resour. Policy 2021, 74, 101230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, A.; Zegordi, S.H.; Nikbakhsh, E. Robust closed-loop global supply chain network design under uncertainty: The case of the medical device industry. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2015, 53, 1596–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouralikhani, H.; Naderi, B.; Arshadi Khamseh, A. Supply Chain Network Design Under Uncertainty: A Case Study Research in Fast Moving Consumer Goods. J. Adv. Math. Model. 2021, 11, 124–168. [Google Scholar]
- Saedinia, R.; Vahdani, B.; Etebari, F.; Nadjafi, B.A. Robust gasoline closed loop supply chain design with redistricting, service sharing and intra-district service transfer. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2019, 123, 121–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akçalı, E.; Çetinkaya, S. Quantitative models for inventory and production planning in closed-loop supply chains. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2011, 49, 2373–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strategic Planning of Circular Supply Chains with Multiple Downgraded Market Levels: A Methodological Proposal (Doctoral Dissertation, University of Sheffield). Available online: https://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/34173/1/MahmoumGonbadi%20Azar%2C190268093%20-%20Azar%20MahmoumGonbadi.pdf (accessed on 14 April 2024).
- Rothlauf, F. Design of Modern Heuristics: Principles and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; Volume 8. [Google Scholar]
- Klibi, W.; Martel, A.; Guitouni, A. The design of robust value-creating supply chain networks: A critical review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 203, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tal, A.; Nemirovski, A. Robust optimization—Methodology and applications. Math. Program. 2002, 92, 453–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simangunsong, E.; Hendry, L.; Stevenson, M. Supply-chain uncertainty: A review and theoretical foundation for future research. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2012, 50, 4493–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Dong, M. Dynamic network design for reverse logistics operations under uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2009, 45, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pishvaee, M.S.; Rabbani, M.; Torabi, S.A. A robust optimization approach to closed-loop supply chain network design under uncertainty. Appl. Math. Model. 2011, 35, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-F.; Hsu, H.-W. A possibilistic approach to the modeling and resolution of uncertain closed-loop logistics. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Mak. 2012, 11, 177–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabripoor, A.; Amirsahami, A.; Ghousi, R. Credibility based chance constrained programming for parallel machine scheduling under linear deterioration and learning effects with considering setup times dependent on past sequences. J. Proj. Manag. 2023, 8, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskorouchi, A.; Mohammadi, E.; Sadjadi, S.J. Robust Portfolio Optimization based on Evidence Theory. Sci. Iran. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavimanshadi, M.; Anaraki, M.G.; Mowlai, M.; Ahmadirad, Z. A Multistage Stochastic Optimization Model for Resilient Pharmaceutical Supply Chain in COVID-19 Pandemic Based on Patient Group Priority. In Proceedings of the 2024 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium (SIEDS), Charlottesville, VA, USA, 3 May 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Soyster, A.L. Convex programming with set-inclusive constraints and applications to inexact linear programming. Oper. Res. 1973, 21, 1154–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaoui, L.E.; Lebret, H. Robust Solutions to Least-Squares Problems with Uncertain Data. SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 1997, 18, 1035–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Tal, A.; Nemirovski, A. Robust solutions of Linear Programming problems contaminated with uncertain data. Math. Program. 2000, 88, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsimas, D.; Sim, M. The Price of Robustness. Oper. Res. 2004, 52, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazami, A.; Saidi-Mehrabad, M.; Seyed-Hosseini, S. A Bi-objective Robust Optimization Model for an Integrated Production-distribution Problem of Perishable Goods with Demand Improvement Strategies: A Case Study. Int. J. Eng. 2021, 34, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.Y.; Blau, G.; Pekny, J.F.; Reklaitis, G.V.; Eversdyk, D. A simulation based optimization approach to supply chain management under demand uncertainty. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2004, 28, 2087–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Othman, W.B.; Lababidi, H.M.; Alatiqi, I.M.; Al-Shayji, K. Supply chain optimization of petroleum organization under uncertainty in market demands and prices. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2008, 189, 822–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biçe, K.; Batun, S. Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network Design under Demand, Return and Quality Uncertainty. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2020, 155, 107081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeballos, L.J.; Gomes, M.I.; Barbosa-Povoa, A.P.; Novais, A.Q. Addressing the uncertain quality and quantity of returns in closed-loop supply chains. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2012, 47, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, L.G. Supply chain optimisation for the process industries: Advances and opportunities. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2009, 33, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangal, D.; Gupta, T.K. Management of demand uncertainty in supply chain cost planning. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2015, 22, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.Y.; Blau, G.; Pekny, J.F.; Reklaitis, G.V.; Eversdyk, D. Integrated safety stock management for multi-stage supply chains under production capacity constraints. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2008, 32, 2570–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakšič, M.; Fransoo, J.; Tan, T.; de Kok, A.; Rusjan, B. Inventory Management with Advance Capacity Information. Nav. Res. Logist. (NRL) 2011, 58, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.I.; Zeballos, L.J.; Barbosa-Povoa, A.P.; Novais, A.Q. Optimization of Closed-Loop Supply Chains under Uncertain Quality of Returns. In Computer Aided Chemical Engineering; Pistikopoulos, E.N., Georgiadis, M.C., Kokossis, A.C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-Y.; Yan, N.-N.; Qiu, R.-Z. Dynamic models of closed-loop supply chain and robust H∞ control strategies. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2009, 47, 2279–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandaly, D.; Satir, A.; Shanker, L. Impact of lead time variability in supply chain risk management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 180, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilko, J.; Ritala, P.; Edelmann, J. On uncertainty in supply chain risk management. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2014, 25, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Managing the uncertainty problems of municipal solid waste disposal. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 240, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childerhouse, P.; Towill, D.R. Reducing uncertainty in European supply chains. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2004, 15, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vachon, S.; Hajmohammad, S. Supply chain uncertainty and environmental management. Asian J. Sustain. Soc. Responsib. 2016, 1, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahnam, M.; Yadollahpour, M.R.; Famil-Dardashti, V.; Hejazi, S.R. Supply chain modeling in uncertain environment with bi-objective approach. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2009, 56, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Nie, J.; Tsai, S.-B. Dynamic Collection Strategy and Coordination of a Remanufacturing Closed-Loop Supply Chain under Uncertainty. Sustainability 2017, 9, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, T. Pricing and Collection Rate Decisions and Reverse Channel Choice in a Socially Responsible Supply Chain With Green Consumers. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 67, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabat, A.; Al-Salem, M. An integrated supply chain problem with environmental considerations. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2015, 164, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Kafa, N.; Klibi, W. Carbon emission-compliance green location-inventory problem with demand and carbon price uncertainties. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2020, 142, 102038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, H.; Dutta, P.; Krishnamoorthy, M.; Suryawanshi, P. Facility Location and Distribution Planning in a Disrupted Supply Chain. In Operations Research and Optimization: FOTA 2016, Kolkata, India, 24–26 November 2018; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 269–284. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, C.; Adulyasak, Y.; Rousseau, L.-M. Robust facility location under demand uncertainty and facility disruptions. Omega 2021, 103, 102429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kull, T.J.; Oke, A.; Dooley, K.J. Supplier Selection Behavior Under Uncertainty: Contextual and Cognitive Effects on Risk Perception and Choice. Decis. Sci. 2014, 45, 467–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saputro, T.E.; Figueira, G.; Almada-Lobo, B. Integrating supplier selection with inventory management under supply disruptions. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 3304–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahay, N.; Ierapetritou, M. Flexibility assessment and risk management in supply chains. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 4166–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreedevi, R.; Saranga, H. Uncertainty and supply chain risk: The moderating role of supply chain flexibility in risk mitigation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 193, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, M.T.; Nickel, S.; Saldanha-Da-Gama, F. Facility location and supply chain management—A review. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2009, 196, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zabinsky, Z.B. Incorporating uncertainty into a supplier selection problem. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 134, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouadni, S.; Rebai, A. Inventory management with supplier selection problem: Supply uncertainty. In Proceedings of the 2013 5th International Conference on Modeling, Simulation and Applied Optimization (ICMSAO), Hammamet, Tunisia, 28–30 April 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanzadeh Amin, S.; Zhang, G. A three-stage model for closed-loop supply chain configuration under uncertainty. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2013, 51, 1405–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghan, E.; Nikabadi, M.S.; Amiri, M.; Jabbarzadeh, A. Hybrid robust, stochastic and possibilistic programming for closed-loop supply chain network design. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2018, 123, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, Y. Designing Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network for High-Salvage Perishable Products Under Uncertain Environment. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 102236–102250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, P.; Meyr, H.; Almeder, C.; Almada-Lobo, B. Managing perishability in production-distribution planning: A discussion and review. Flex. Serv. Manuf. J. 2013, 25, 389–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodheim, E.; Derman, C.; Prastacos, G. On the Evaluation of a Class of Inventory Policies for Perishable Products Such as Blood. Manag. Sci. 1975, 21, 1320–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, Y.; Mangla, S.; Patil, P. Analyzing Challenges to Transportation for Successful Sustainable Food Supply Chain Management Implementation in Indian Dairy Industry; Springer: Singapore, 2018; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Osvald, A.; Stirn, L.Z. A vehicle routing algorithm for the distribution of fresh vegetables and similar perishable food. J. Food Eng. 2008, 85, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaesmen, I.Z.; Scheller-Wolf, A.; Deniz, B. Managing Perishable and Aging Inventories: Review and Future Research Directions. In Planning Production and Inventories in the Extended Enterprise: A State of the Art Handbook; Kempf, K.G., Keskinocak, P., Uzsoy, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 1, pp. 393–436. [Google Scholar]
- Rijpkema, W.A.; Rossi, R.; GAJ van der Vorst, J. Effective sourcing strategies for perishable product supply chains. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2014, 44, 494–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Teng, J.-T. Pricing and lot-sizing decisions for perishable goods when demand depends on selling price, reference price, product freshness, and displayed stocks. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 270, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirci, M.; Isaksson, O.; Seifert, R. Managing Perishability in the Fruit and Vegetable Supply Chains. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, J.; Scudder, G. Supply chain strategies for perishable products: The case of fresh produce. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2009, 18, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirabelli, G.; Solina, V. Optimization Strategies for the Integrated Management of Perishable Supply Chains: A Literature Review. J. Ind. Eng. Manag. 2022, 15, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadavi, N. Dynamic Price Dispersion of Seasonal Goods in Bertrand–Edgeworth Competition. Appl. Econ. Financ. 2024, 11, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, Z.N.L.; Larsen, S.B.; Nielsen, A.P.; Groth, A.; Gregersen, N.G.; Ghosh, A. Combining or separating forward and reverse logistics. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2018, 29, 216–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkaabneh, F.; Diabat, A.; Gao, H.O. Benders decomposition for the inventory vehicle routing problem with perishable products and environmental costs. Comput. Oper. Res. 2020, 113, 104751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biuki, M.; Kazemi, A.; Alinezhad, A. An integrated location-routing-inventory model for sustainable design of a perishable products supply chain network. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 260, 120842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, L.C.; Laporte, G. Optimal joint replenishment, delivery and inventory management policies for perishable products. Comput. Oper. Res. 2014, 47, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palak, G.; Ekşioğlu, S.D.; Geunes, J. Heuristic algorithms for inventory replenishment with perishable products and multiple transportation modes. IISE Trans. 2018, 50, 345–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, O. Managing perishable inventory. In Wiley encyclopedia of operations research and management science; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thierry, M.; Salomon, M.; Van Nunen, J.; Van Wassenhove, L. Strategic Issues in Product Recovery Management. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1995, 37, 114–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AriaNezhad, M.G.; Makuie, A.; Khayatmoghadam, S. Developing and solving two-echelon inventory system for perishable items in a supply chain: Case study (Mashhad Behrouz Company). J. Ind. Eng. Int. 2013, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorim, P.; Günther, H.-O.; Almada-Lobo, B. Multi-objective integrated production and distribution planning of perishable products. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012, 138, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedhosseini, S.M.; Ghoreyshi, S.M. Integration of production and distribution decisions of perishable products considering feasible delivery routes. Int. J. Appl. Manag. Sci. 2014, 6, 267–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyedhosseini, S.; Ghoreyshi, S. An integrated production and distribution planning model for perishable products. Int. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 23, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aazami, A.; Saidi-Mehrabad, M. A production and distribution planning of perishable products with a fixed lifetime under vertical competition in the seller-buyer systems: A real-world application. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 223–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Baboli, A.; Rekik, Y. Multi-objective inventory routing problem: A stochastic model to consider profit, service level and green criteria. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 2017, 101, 59–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chu, F.; Côté, J.-F.; Coelho, L.C.; Chu, C. The multi-plant perishable food production routing with packaging consideration. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 221, 107472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, V.; Muratore, G. Effects of packaging on shelf life of fresh celery. J. Food Eng. 2009, 90, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chu, F.; Chen, K. Coordinated Production Inventory Routing Planning for Perishable Food. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2017, 50, 4246–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.; Zhihui, T.; Baozhen, Y. Optimization of two-stage location–routing–inventory problem with time-windows in food distribution network. Ann. Oper. Res. 2019, 273, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahumada, O.; Villalobos, J.R. Operational model for planning the harvest and distribution of perishable agricultural products. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2011, 133, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Seifi, A. Considering lost sale in inventory routing problems for perishable goods. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 87, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accorsi, R.; Gallo, A.; Manzini, R. A climate driven decision-support model for the distribution of perishable products. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 917–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onggo, B.S.; Panadero, J.; Corlu, C.G.; Juan, A.A. Agri-Food Supply Chains with Stochastic Demands: A Multi-Period Inventory Routing Problem with Perishable Products. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2019, 97, 101970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manouchehri, F.; Nookabadi, A.S.; Kadivar, M. Production routing in perishable and quality degradable supply chains. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Miller, F.A.; Brandão, T.R.S.; Silva, C.L.M. On the Use of the Gompertz Model to Predict Microbial Thermal Inactivation Under Isothermal and Non-Isothermal Conditions. Food Eng. Rev. 2011, 3, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Zhao, L.; Gong, X.; Faiz, N. The perishable products case to achieve sustainable food quality and safety goals implementing on-field sustainable supply chain model. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2023, 87, 101562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Krikke, H. Managing a Sustainable and Resilient Perishable Food Supply Chain (PFSC) after an Outbreak. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouzdani, J.; Govindan, K. On the sustainable perishable food supply chain network design: A dairy products case to achieve sustainable development goals. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mangla, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Karamperidis, S. Challenges in perishable food supply chains for sustainability management: A developing economy perspective. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 29, 1809–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, N.R.; Rather, R.A.; Farooq, A.; Padder, S.A.; Baba, T.R.; Sharma, S.; Mubarak, N.M.; Khan, A.H.; Singh, P.; Ara, S. New insights in food security and environmental sustainability through waste food management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 31, 17835–17857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banasik, A.; Kanellopoulos, A.; Claassen, G.; Bloemhof-Ruwaard, J.M.; van der Vorst, J.G. Closing loops in agricultural supply chains using multi-objective optimization: A case study of an industrial mushroom supply chain. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2017, 183, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.H.; Zhang, G.; Akhtar, P. Effects of uncertainty on a tire closed-loop supply chain network. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 73, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedram, A.; Bin Yusoff, N.; Udoncy, O.E.; Mahat, A.B.; Pedram, P.; Babalola, A. Integrated forward and reverse supply chain: A tire case study. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Mirjalili, S. Hybrid optimizers to solve a tri-level programming model for a tire closed-loop supply chain network design problem. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 70, 701–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasani, A.; Eskandarpour, M.; Fattahi, M. A simulation-based optimisation approach for multi-objective inventory control of perishable products in closed-loop supply chains under uncertainty. Int. J. Adv. Oper. Manag. 2018, 10, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.B. A stochastic multi-objective location-allocation-routing problem for tire supply chain considering sustainability aspects and quantity discounts. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 704–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jin, L.; Liao, S. Order policy for emergency medicine with return uncertainty in a closed-loop supply chain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yavari, M.; Geraeli, M. Heuristic method for robust optimization model for green closed-loop supply chain network design of perishable goods. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 226, 282–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chu, F.; Che, A.; Yu, Y.; Feng, X. Novel model and kernel search heuristic for multi-period closed-loop food supply chain planning with returnable transport items. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 57, 7439–7456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, M.; Zaker, H. An integrated two-layer network model for designing a resilient green-closed loop supply chain of perishable products under disruption. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darestani, S.A.; Hemmati, M. Robust optimization of a bi-objective closed-loop supply chain network for perishable goods considering queue system. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 136, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidhi, M.; Pillai, V.M. Product disposal penalty: Analysing carbon sensitive sustainable supply chains. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2019, 128, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Motlagh, S.-M.; Nami, N.; Farshadfar, Z. Collection disruption management and channel coordination in a socially concerned closed-loop supply chain: A game theory approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 276, 124173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean manufacturing in pharmaceutical closed-loop supply chain. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2020, 26, 14–38. [CrossRef]
- Jabarzadeh, Y.; Yamchi, H.R.; Kumar, V.; Ghaffarinasab, N. A multi-objective mixed-integer linear model for sustainable fruit closed-loop supply chain network. Manag. Environ. Qual. Int. J. 2020, 31, 1351–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yavari, M.; Zaker, H. Designing a resilient-green closed loop supply chain network for perishable products by considering disruption in both supply chain and power networks. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2020, 134, 106680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare Mehrjerdi, Y.; Shafiee, M. Multiple-sourcing in sustainable closed-loop supply chain network design: Tire industry case study. Int. J. Supply Oper. Manag. 2020, 7, 202–221. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolazimi, O.; Esfandarani, M.S.; Salehi, M.; Shishebori, D. Robust design of a multi-objective closed-loop supply chain by integrating on-time delivery, cost, and environmental aspects, case study of a Tire Factory. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Motlagh, S.-M.; Ebrahimi, S.; Zirakpourdehkordi, R. Coordination of dual-function acquisition price and corporate social responsibility in a sustainable closed-loop supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 251, 119629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Pruncu, C.I.; Khan, R.; Naeem, K.; Ghaffar, A.; Ashraf, P.; Room, S. A Trade-off Analysis of Economic and Environmental Aspects of a Disruption Based Closed-Loop Supply Chain Network. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasihi, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Najafi, S.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M. Developing a bi-objective mathematical model to design the fish closed-loop supply chain. Int. J. Eng. 2021, 34, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Jahani, H.; Abareshi, A.; Goh, M. Sustainable closed-loop supply chain for dairy industry with robust and heuristic optimization. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 157, 107324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, M.; Gupta, S.M. Designing a sustainable green closed-loop supply chain under uncertainty and various capacity levels. Logistics 2021, 5, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemzadeh, Z.; Sadeghieh, A.; Shishebori, D. A stochastic multi-objective closed-loop global supply chain concerning waste management: A case study of the tire industry. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 5794–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazli-Khalaf, M.; Naderi, B.; Mohammadi, M.; Pishvaee, M.S. The design of a resilient and sustainable maximal covering closed-loop supply chain network under hybrid uncertainties: A case study in tire industry. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 9949–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjerdi, Y.Z.; Shafiee, M. A resilient and sustainable closed-loop supply chain using multiple sourcing and information sharing strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 289, 125141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathollahi-Fard, A.M.; Dulebenets, M.A.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Safaeian, M.; Mirzahosseinian, H. Two hybrid meta-heuristic algorithms for a dual-channel closed-loop supply chain network design problem in the tire industry under uncertainty. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, A.; Mokhtari, H.; Niaki, S.T.A. Designing a closed-loop blood supply chain network considering transportation flow and quality aspects. Sustain. Oper. Comput. 2021, 2, 170–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garai, A.; Chowdhury, S.; Sarkar, B.; Roy, T.K. Cost-effective subsidy policy for growers and biofuels-plants in closed-loop supply chain of herbs and herbal medicines: An interactive bi-objective optimization in T-environment. Appl. Soft Comput. 2021, 100, 106949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momenitabar, M.; Ebrahimi, Z.D.; Arani, M.; Mattson, J.; Ghasemi, P. Designing a sustainable closed-loop supply chain network considering lateral resupply and backup suppliers using fuzzy inference system. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazvar, Z.; Zokaee, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Salari, S.A.-S.; Nayeri, S. Designing a sustainable closed-loop pharmaceutical supply chain in a competitive market considering demand uncertainty, manufacturer’s brand and waste management. Ann. Oper. Res. 2021, 315, 2057–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vali-Siar, M.M.; Roghanian, E. Sustainable, resilient and responsive mixed supply chain network design under hybrid uncertainty with considering COVID-19 pandemic disruption. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 30, 278–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirian, J.; Khalili, H.A.; Mehrabian, A. Designing an optimization model for green closed-loop supply chain network of heavy tire by considering economic pricing under uncertainty. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 53107–53120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garai, A.; Sarkar, B. Economically independent reverse logistics of customer-centric closed-loop supply chain for herbal medicines and biofuel. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 129977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydanlou, P.; Jolai, F.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Fathollahi-Fard, A.M. A multi-objective optimization framework for a sustainable closed-loop supply chain network in the olive industry: Hybrid meta-heuristic algorithms. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 203, 117566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Kaveh, F.; Peivandizadeh, A. Resilient Supply Chain Planning for the Perishable Products under Different Uncertainty. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1606331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdrodbari, M.A.; Harsej, F.; Sadeghpour, M.; Aghdam, M.M. A robust multi-objective model for managing the distribution of perishable products within a green closed-loop supply chain. J. Ind. Manag. Optim. 2022, 18, 3155–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Che, A.; Chu, F. Improved model and efficient method for bi-objective closed-loop food supply chain problem with returnable transport items. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2022, 60, 1051–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnomo, M.R.A.; Wangsa, I.D.; Rizky, N.; Jauhari, W.A.; Zahria, I. A multi-echelon fish closed-loop supply chain network problem with carbon emission and traceability. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 210, 118416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alinezhad, M.; Mahdavi, I.; Hematian, M.; Tirkolaee, E.B. A fuzzy multi-objective optimization model for sustainable closed-loop supply chain network design in food industries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2022, 24, 8779–8806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behzadianfar, M.; Eydi, A.; Shahrokhi, M. A sustainable closed loop supply chain design problem in intuitionistic fuzzy environment for dairy products. Soft Comput. 2022, 26, 1417–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R. Recycling Performance of the Tire Remanufacturing with Production Capacity Constraints considering Carbon Tax and Technology Subsidy. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 2022, 2484775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, F.; Fan, Y.; Guan, G.; Zheng, J. Government Subsidy Decision-Making for Waste Tire Recycling under the Coexistence of the Retailer and the Internet Recycling Platform. Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2022, 2022, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasihi, M.; Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, R.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Najafi, S.E. Designing a sustainable fish closed-loop supply chain network under uncertainty. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 90050–90087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goli, A.; Tirkolaee, E.B. Designing a portfolio-based closed-loop supply chain network for dairy products with a financial approach: Accelerated Benders decomposition algorithm. Comput. Oper. Res. 2023, 155, 106244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhandi, V.; Chen, P.-S. Closed-loop supply chain inventory model in the pharmaceutical industry toward a circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Amin, S.H.; Fang, L. A multi-objective approach for designing a tire closed-loop supply chain network considering producer responsibility. Appl. Math. Model. 2023, 115, 616–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholian-Jouybari, F.; Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, M.; Bavar, A.; Bavar, A.; Mosallanezhad, B. A design of a circular closed-loop agri-food supply chain network—A case study of the soybean industry. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2023, 36, 100530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavi, R.K.; Shekarabi, S.A.H.; Mavi, N.K.; Arisian, S.; Moghdani, R. Multi-objective optimisation of sustainable closed-loop supply chain networks in the tire industry. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge-Zhang, S.; Cai, T.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Mu, P.; Cui, J. Investigation and Suggestions regarding Residents’ Understanding of Waste Classification in Chinese Prefecture-Level Cities—A Case Study of Maanshan City, Anhui Province, China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 11124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


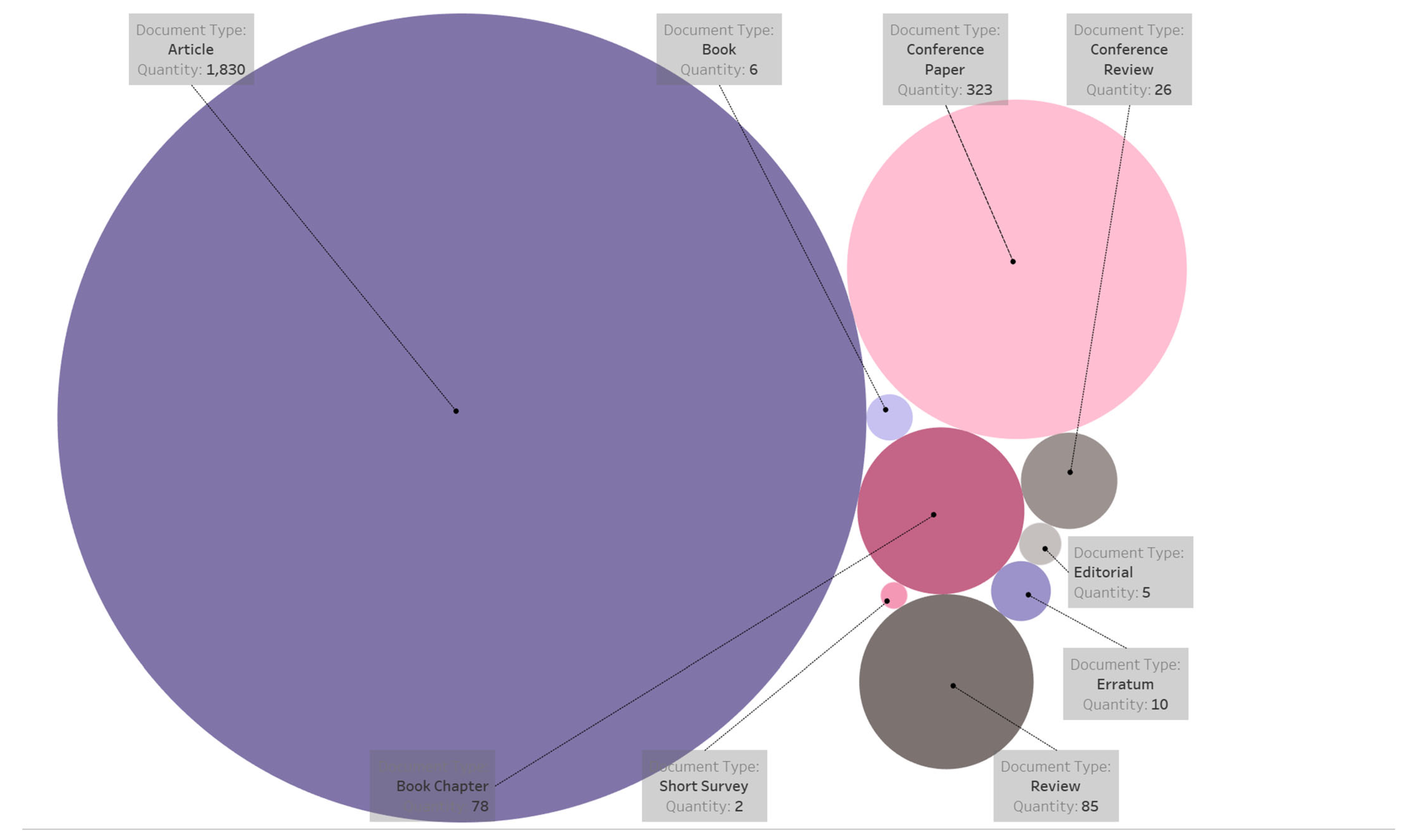

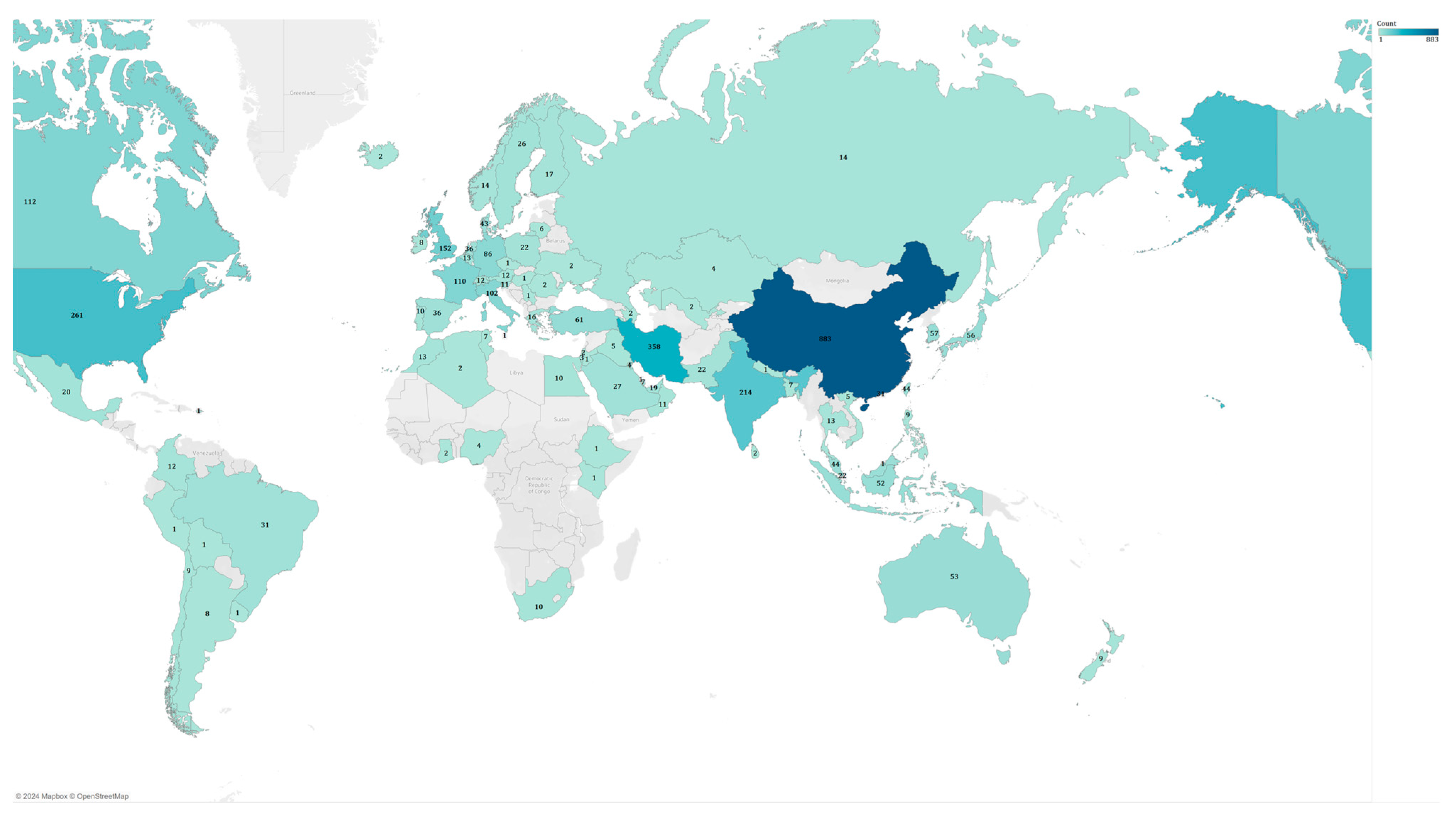
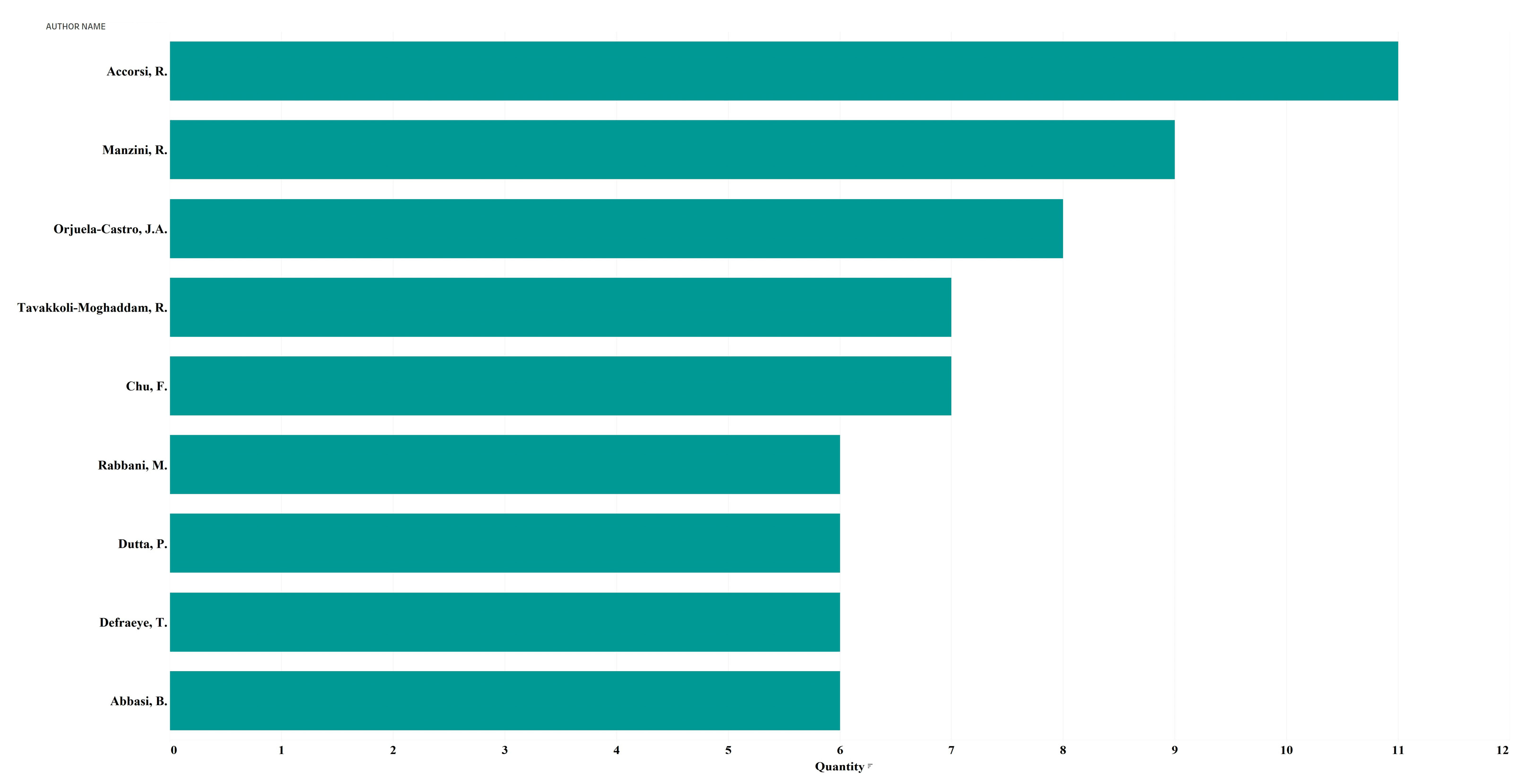

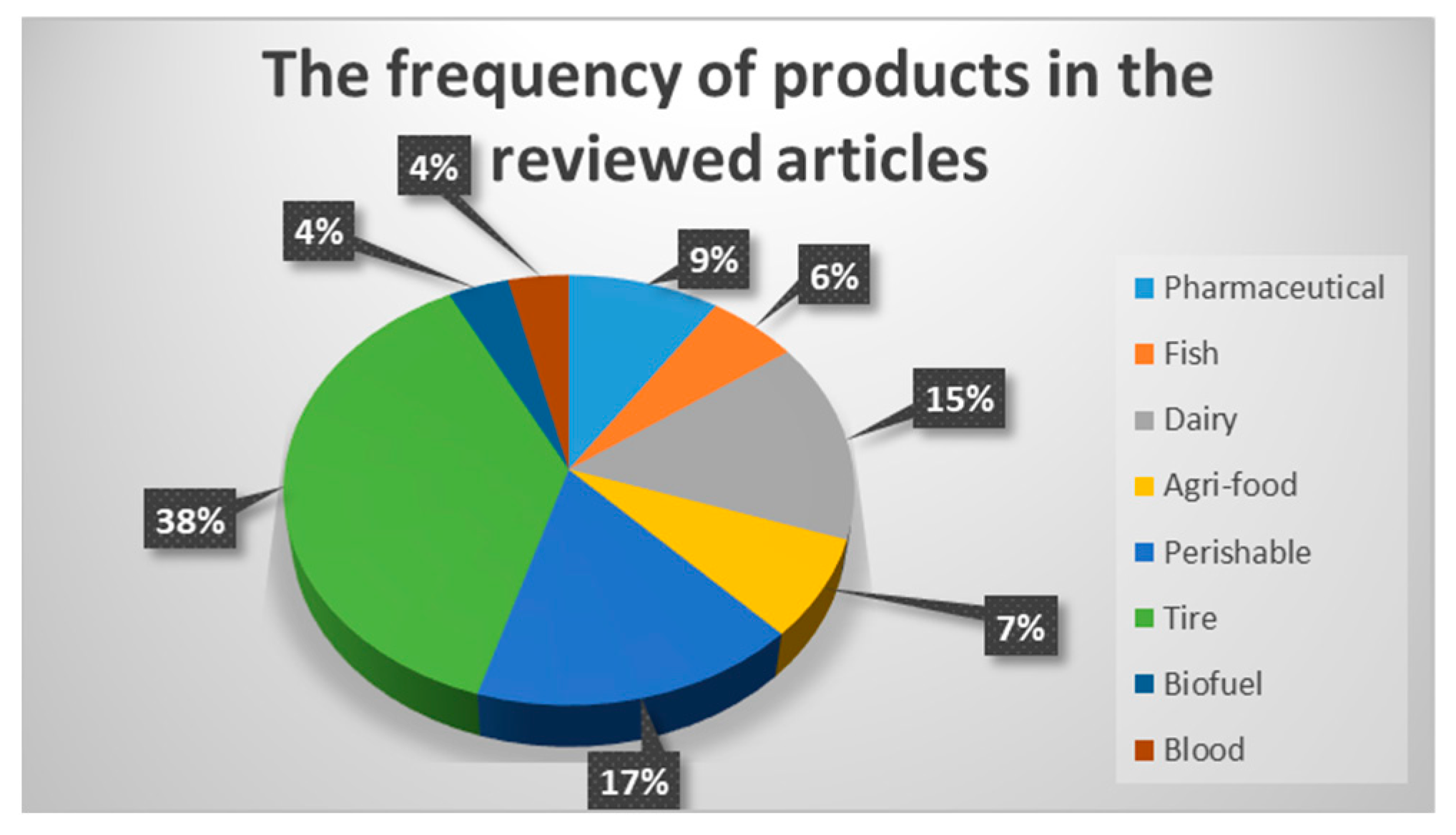
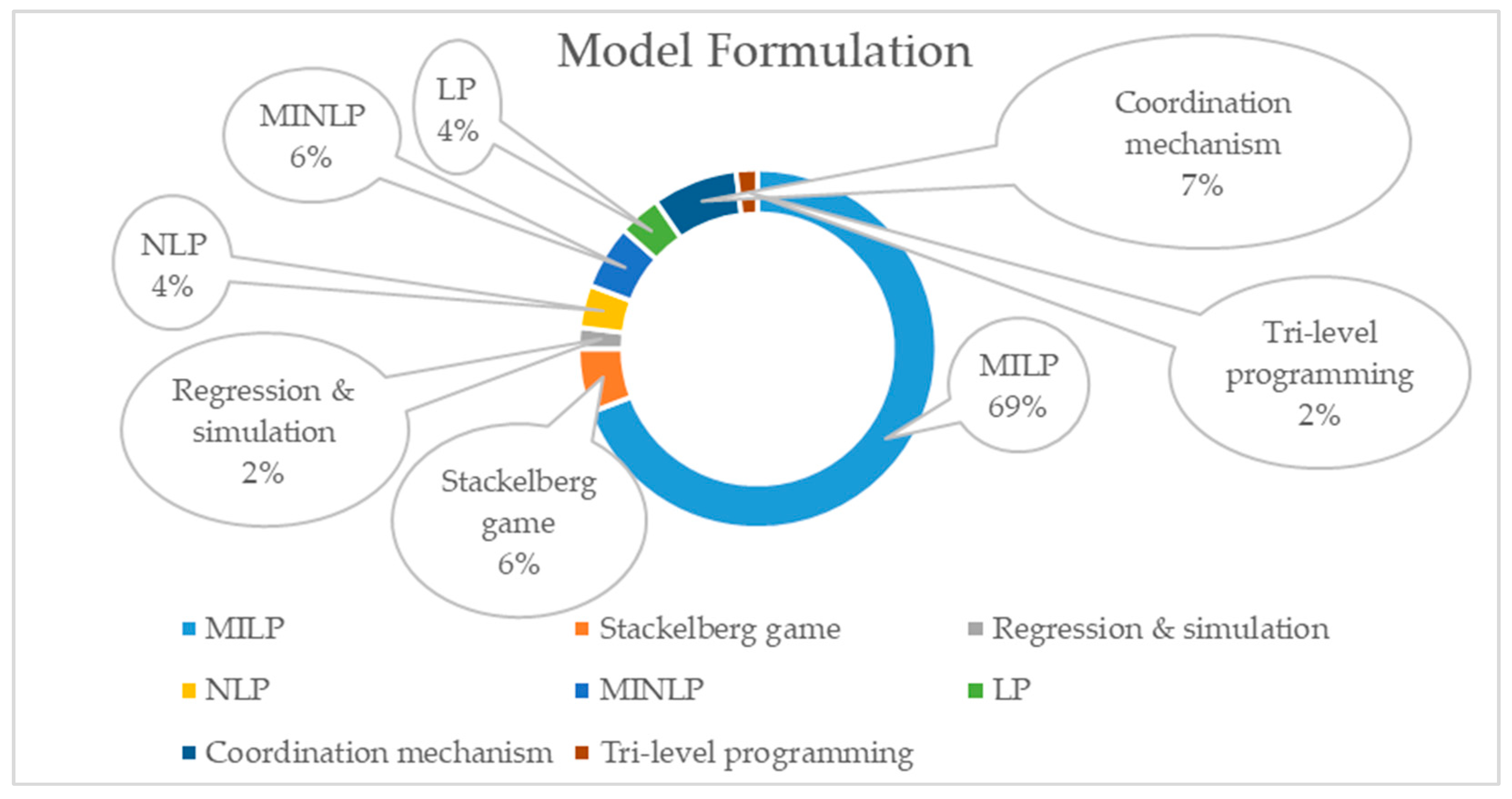
| Search | Keyword | Found Articles |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | “Closed-loop supply chain” AND Perishable | 17 |
| 2 | “Closed-loop supply chain” AND agri-food | 3 |
| 3 | “Closed-loop supply chain” AND dairy | 7 |
| 4 | “Closed-loop supply chain” AND fish | 3 |
| 5 | “Closed-loop supply chain” AND pharmaceutical | 8 |
| 6 | “Closed-loop supply chain” AND tire | 23 |
| 7 | “Closed-loop supply chain” AND biofuel | 2 |
| 8 | “Closed-loop supply chain” AND blood | 3 |
| Total articles found: | 65 | |
| Environmental Indicators | Economic Indicators | Social Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Emissions (environmental CO2) | Cost-based consideration | Fixed and variable job opportunities |
| Environmental impacts | Profit-based consideration | Customer satisfaction |
| Waste generation | Time | Worker injuries |
| Energy consumption | Risk measures | Social responsibility |
| Carbon policies | Net present value (NPV) | Missed working days |
| Defective rate | Quality-based indicator | Training hours, community service hours |
| Greenness score | Flexibility | |
| Life cycle analysis | ||
| Disposal rate |
| No. | Modeling Approaches | No. | Solution Methodologies |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mixed Integer Linear Programming | 1 | Exact |
| 2 | Mixed Integer Non-Linear Programming | 2 | Metaheuristics |
| 3 | Mixed Integer Programming | 3 | Fuzzy optimization |
| 4 | Stochastic Programming | 4 | Robust optimization |
| 5 | Fuzzy Mixed Integer Linear Programming | 5 | Simulation |
| 6 | Linear programming | 6 | Heuristics |
| 7 | Fuzzy linear programming | 7 | Possibilistic approaches |
| 8 | Nonlinear programming | 8 | MCDM 1 |
| 9 | Robust mixed integer linear programming | 9 | Stochastic optimization |
| 10 | 10 | Stochastic Robust optimization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarreh, M.; Khandan, M.; Goli, A.; Aazami, A.; Kummer, S. Integrating Perishables into Closed-Loop Supply Chains: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156705
Zarreh M, Khandan M, Goli A, Aazami A, Kummer S. Integrating Perishables into Closed-Loop Supply Chains: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability. 2024; 16(15):6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156705
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarreh, Mobin, Mohammad Khandan, Alireza Goli, Adel Aazami, and Sebastian Kummer. 2024. "Integrating Perishables into Closed-Loop Supply Chains: A Comprehensive Review" Sustainability 16, no. 15: 6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156705
APA StyleZarreh, M., Khandan, M., Goli, A., Aazami, A., & Kummer, S. (2024). Integrating Perishables into Closed-Loop Supply Chains: A Comprehensive Review. Sustainability, 16(15), 6705. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16156705







