Bridging Built Environment Attributes and Perceived City Images: Exploring Dual Influences on Resident Satisfaction in Revitalizing Post-Industrial Neighborhoods
Abstract
1. Introduction
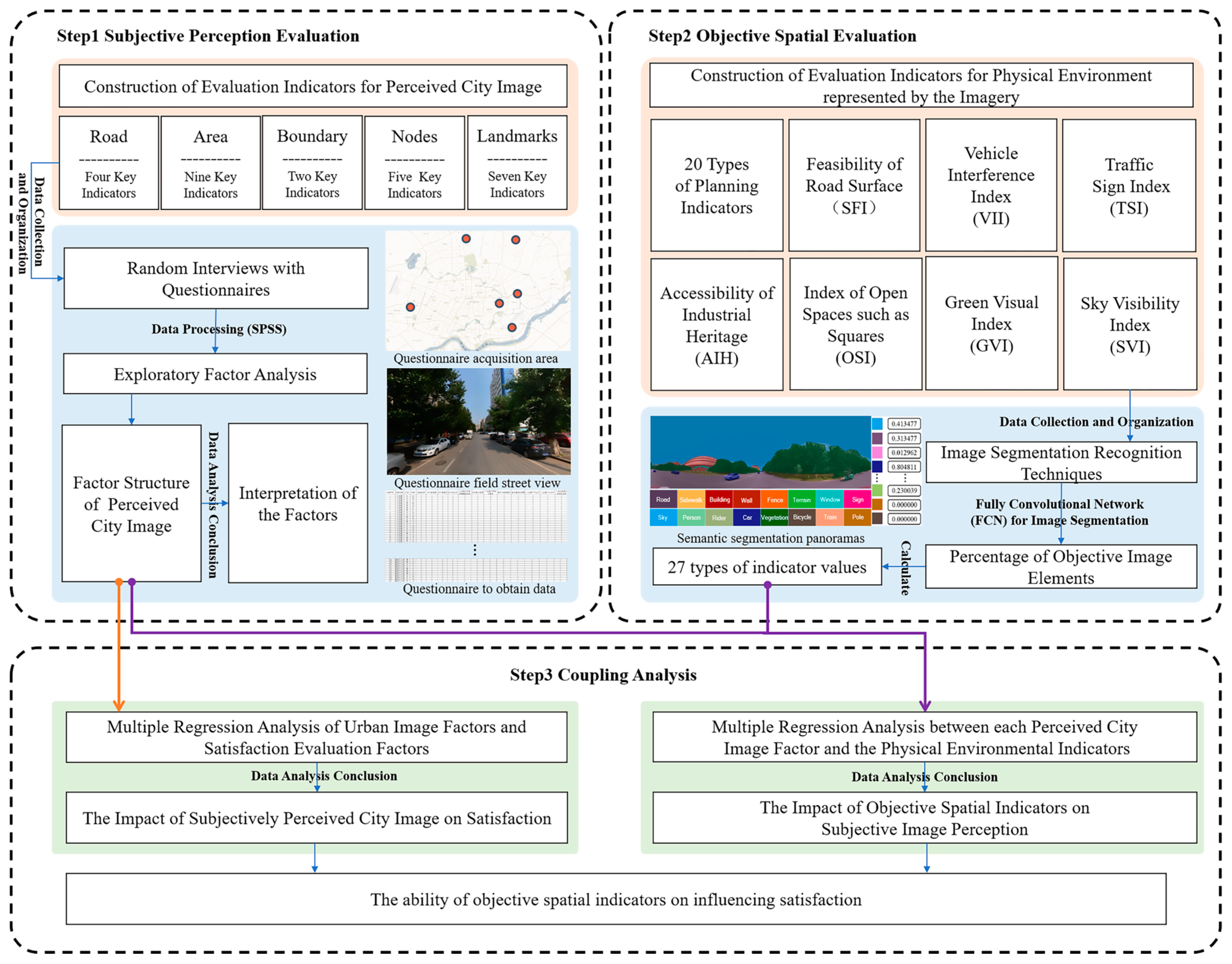
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Evaluation Indicators
2.1.1. Evaluation Indicators for Perceived Urban Image
2.1.2. Objective Evaluation Indicators Based on Visual Imagery
2.2. Research Methods
2.2.1. Exploratory Factor Analysis
2.2.2. Multiple Regression Analysis
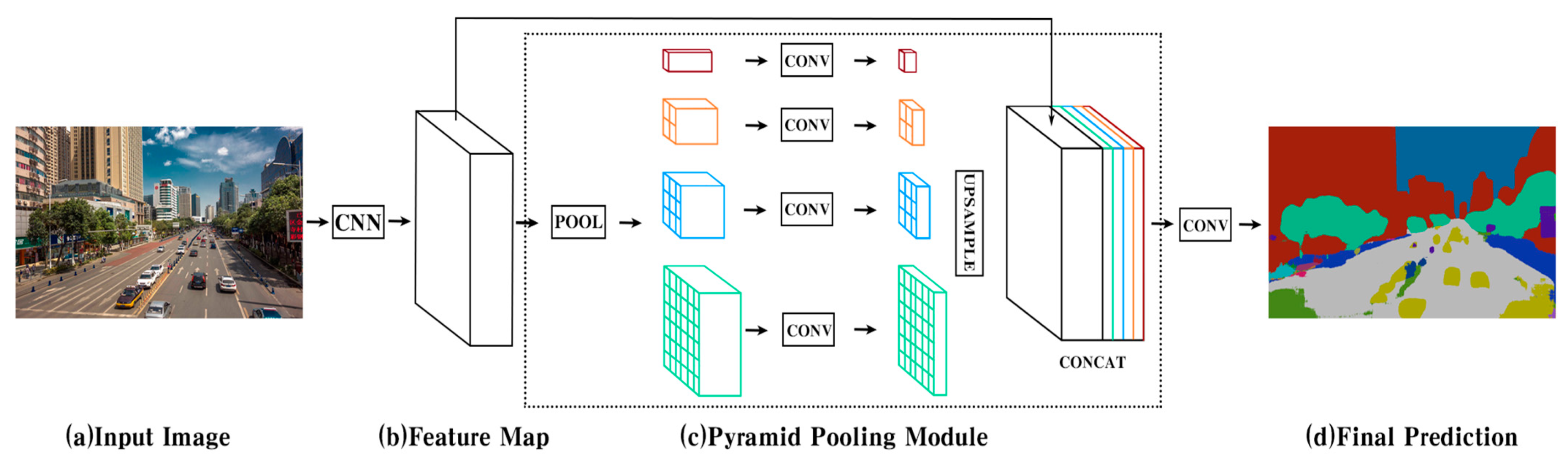
2.2.3. Semantic Segmentation of Objective Imagery Indicators
2.3. Study Area and Data
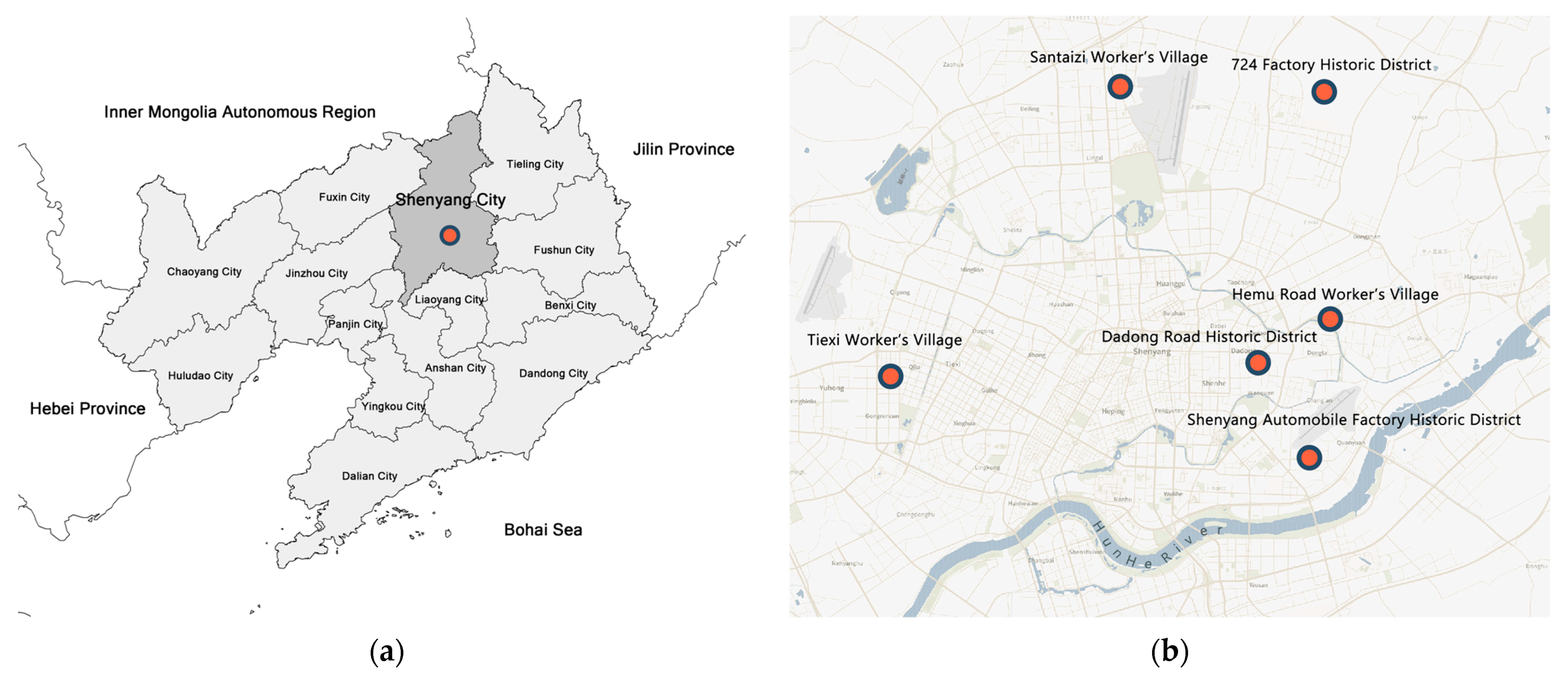
2.3.1. Study Area
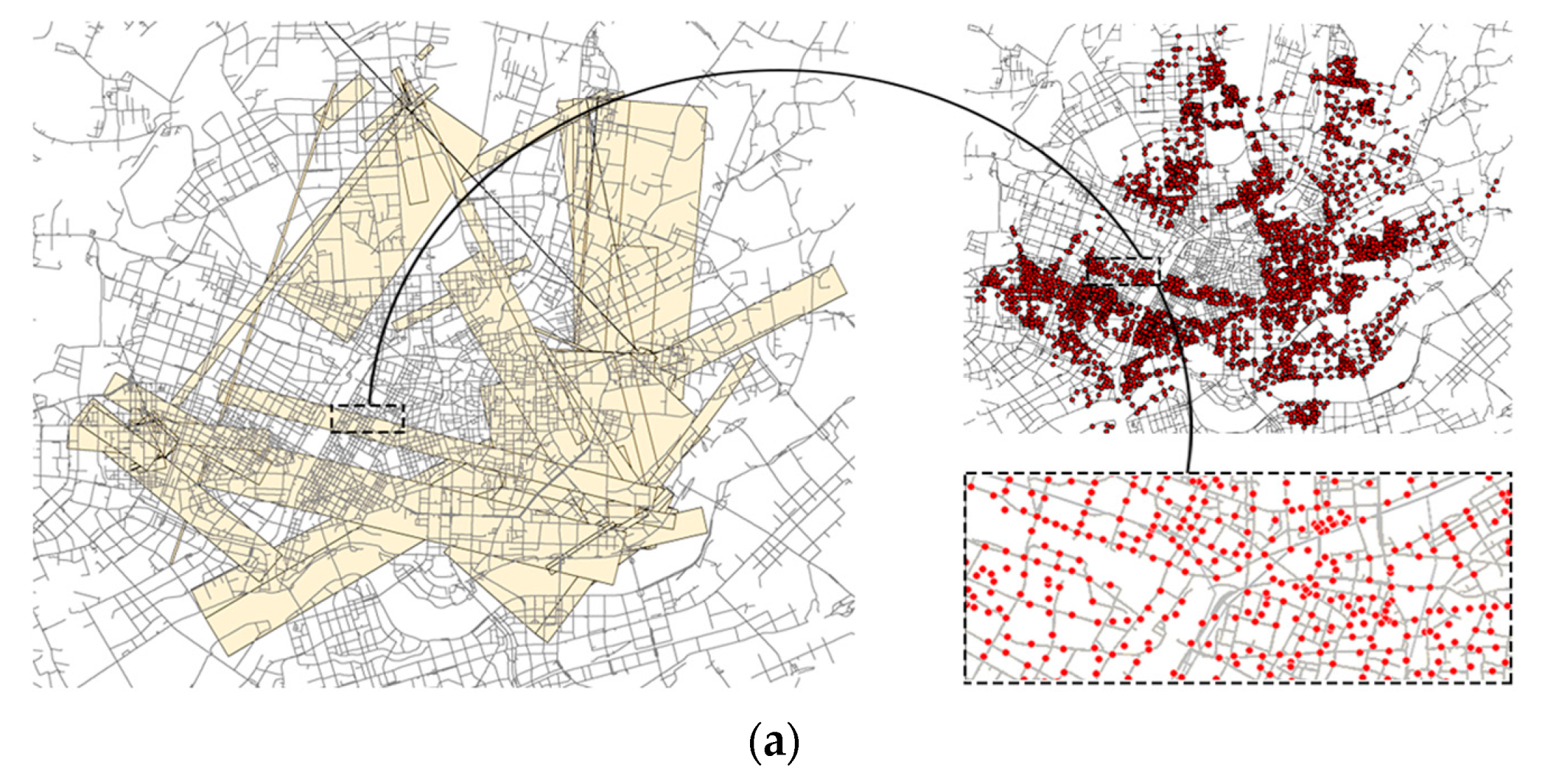
2.3.2. Research Data
3. Results
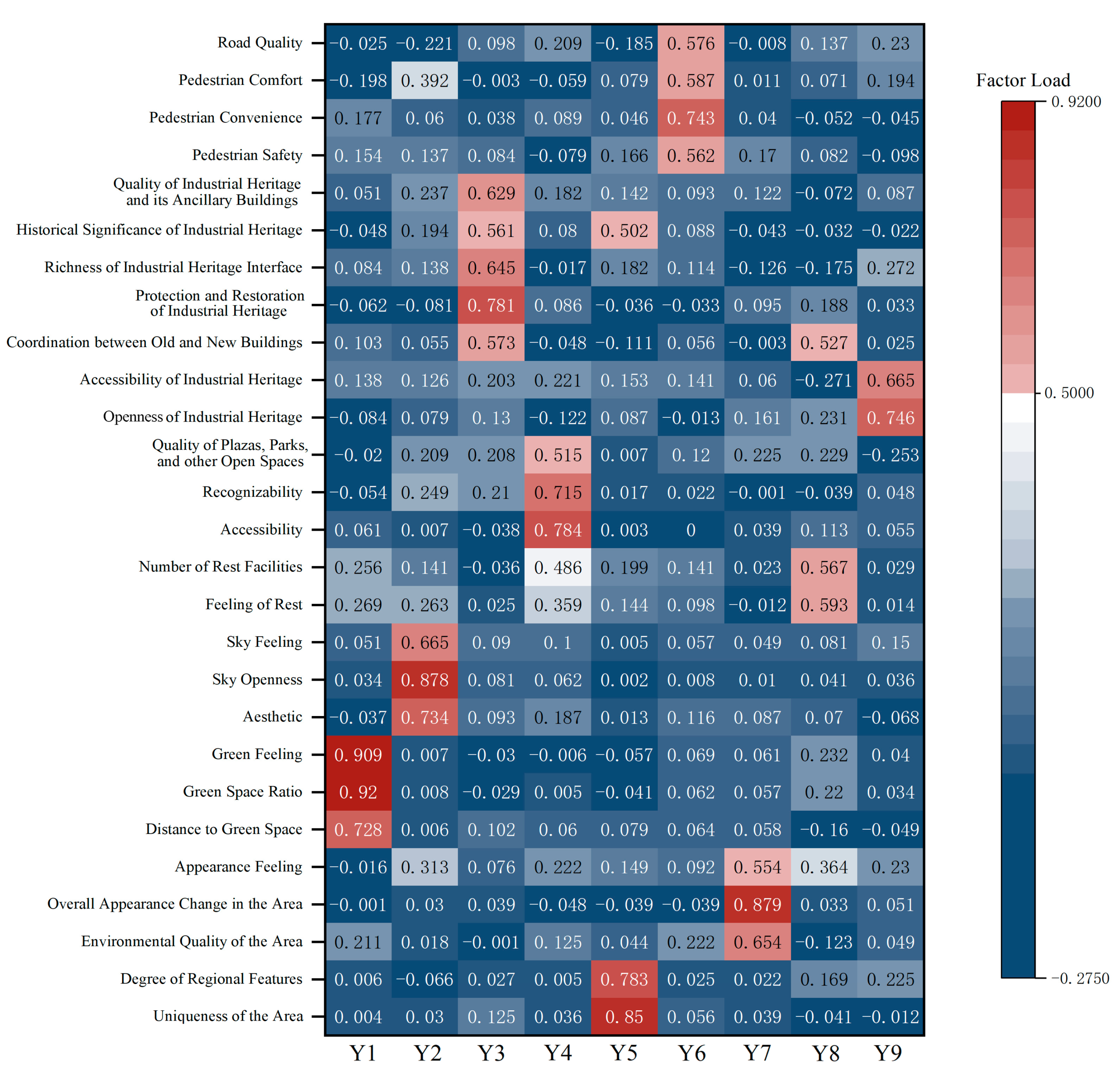
3.1. Exploratory Factor Analysis of Subjective Perception Indicators
3.2. Objective Imagery Indicators Based on Semantic Segmentation
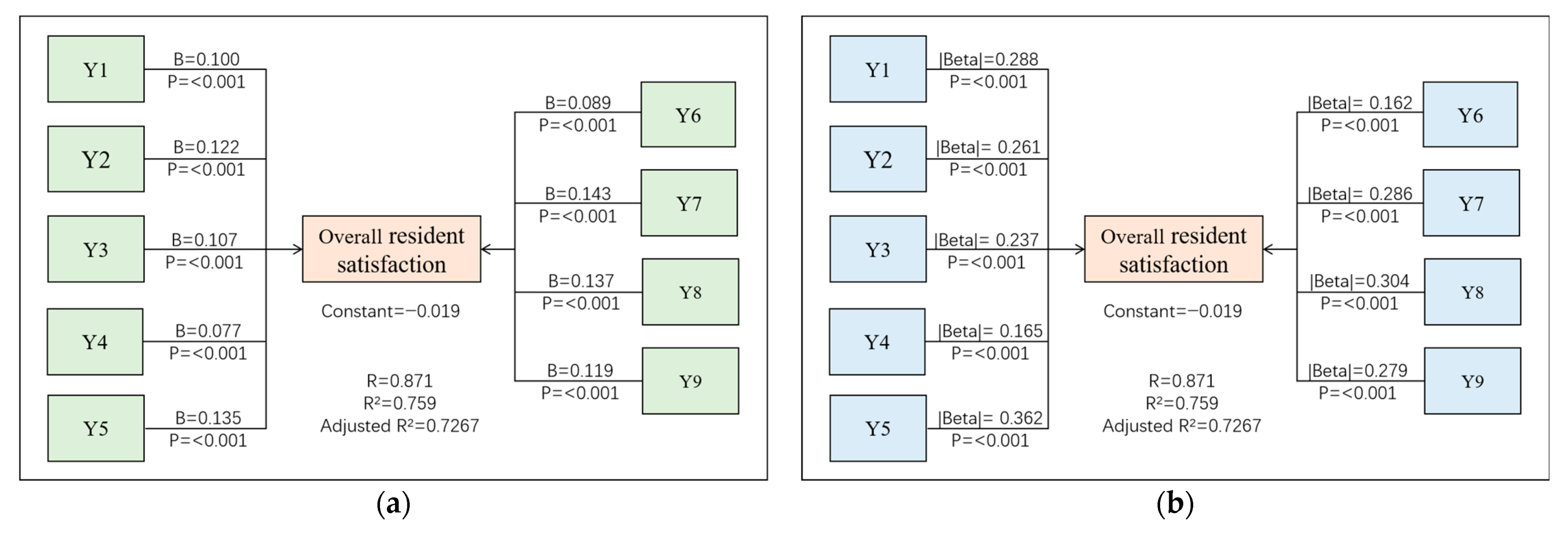
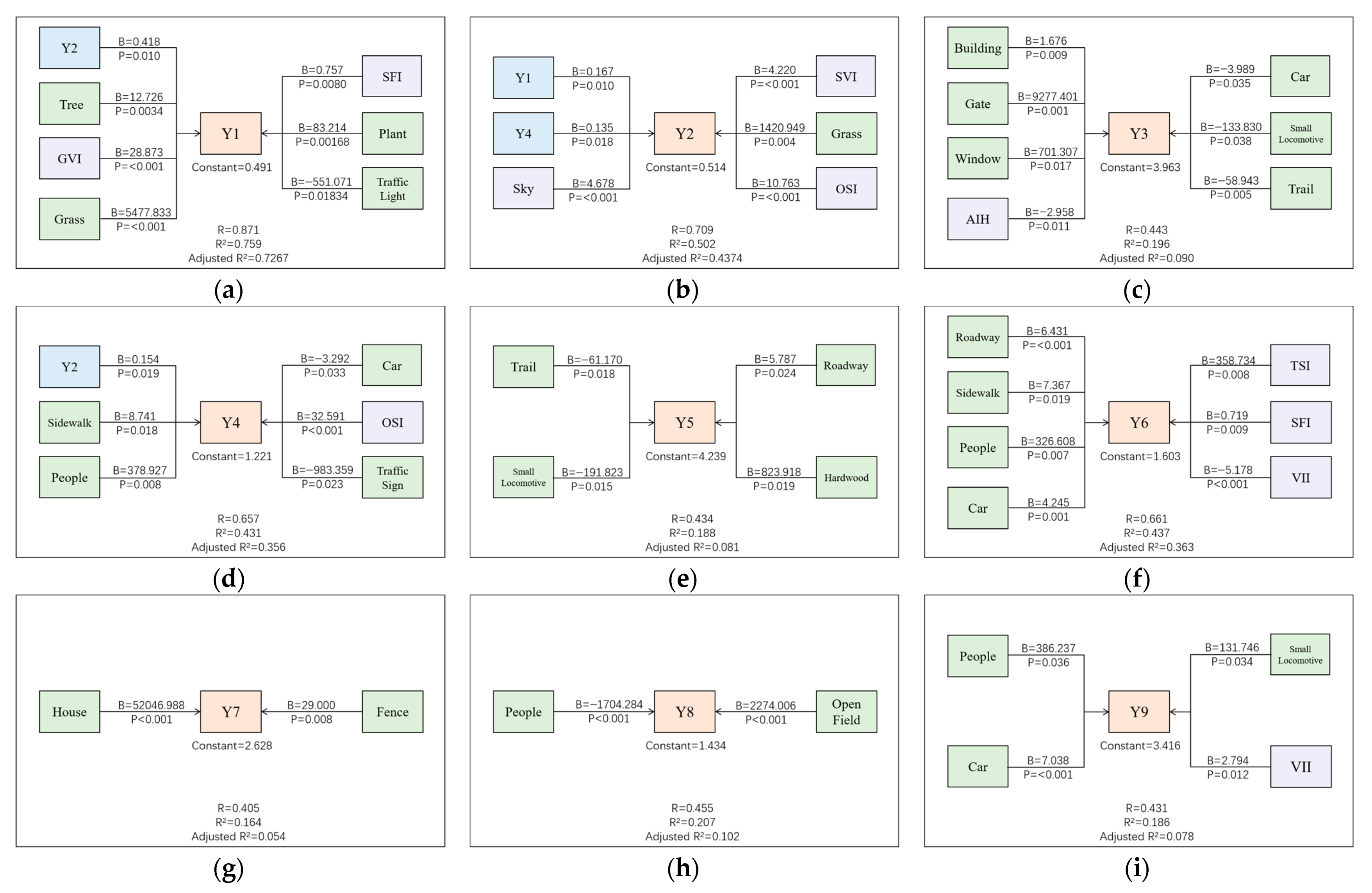
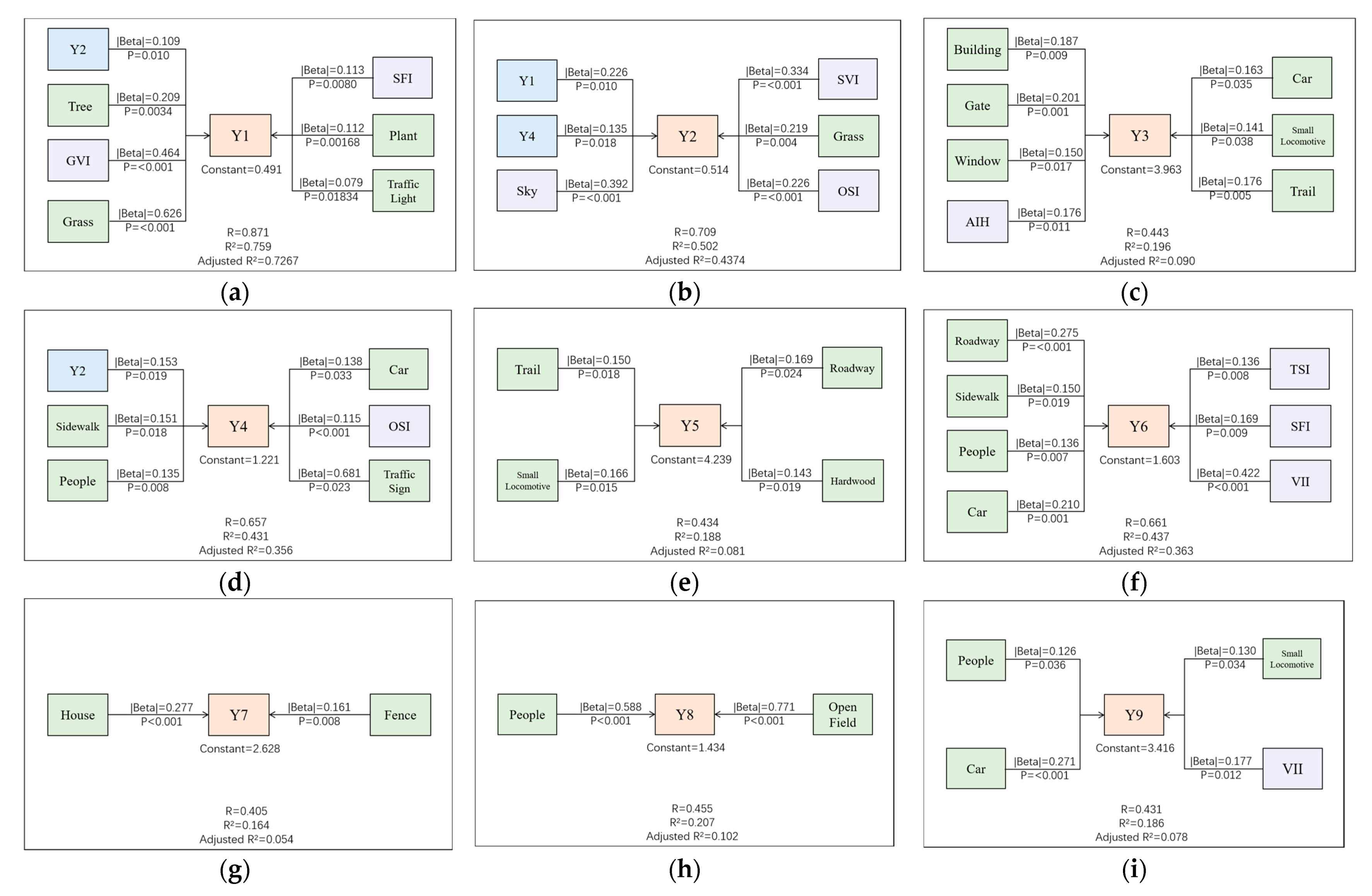
3.3. The Influence of Subjective Image Factors on Residents’ Satisfaction
3.4. Impact of Objective Spatial Indicators on Residents’ Subjective Perception Factors
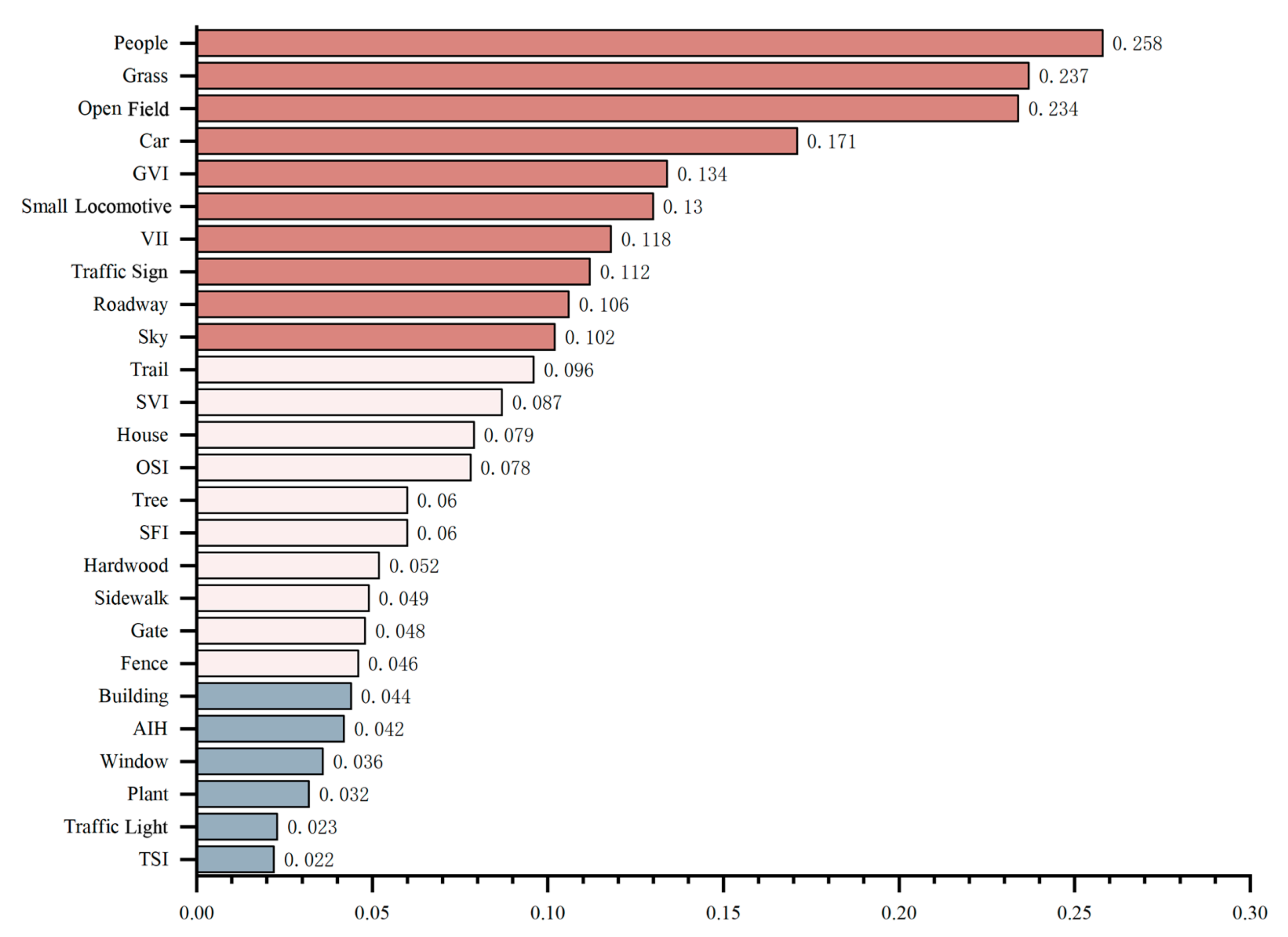
3.5. The Capacity of Objective Spatial Indicators in Influencing Residential Satisfaction
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. The Example Formula for Calculating the Score for Image Factor Y1
References
- Wan, F.A.W.Z.; Buaben, J.M. The Theory of Post-Industrial Society (Teori Masyarakat Pasca-Industri). Akademika 2021, 91, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhorst, J. Rebranding the Neoliberal City: Urban Nature as Spectacle, Medium, and Agency. Archit. Media Politics Soc. 2015, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Suocheng, D.; Zehong, L.; Bin, L.; Mei, X. Problems and Strategies of Industrial Transformation of China’s Resource-based Cities. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2007, 17, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anguelovski, I.; Connolly, J.J.T.; Masip, L.; Pearsall, H. Assessing green gentrification in historically disenfranchised neighborhoods: A longitudinal and spatial analysis of Barcelona. Urban. Geogr. 2018, 39, 458–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speer, J. The right to infrastructure: A struggle for sanitation in Fresno, California homeless encampments. Urban. Geogr. 2016, 37, 1049–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryberg-Webster, S.; Kinahan, K.L. Historic Preservation and Urban Revitalization in the Twenty-first Century. J. Plan. Lit. 2014, 29, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Shao, L.; Du, Y. Collaborating with Local Communities to Identify Improvement Priorities for Historic Urban Landscape Based on Residents’ Satisfaction: An Application of Asymmetric Impact-Performance Analysis in Dandong, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyama, Y. Spatial city image and its formative factors: A street-based neighborhood cognition analysis. Cities 2024, 149, 104898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K. The Image of the City; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Topcu, K.D.; Topcu, M. Visual Presentation of Mental Images in Urban Design Education:Cognitive Maps. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 51, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, M.; Matheau-Police, A.; Couty, C. Development of a scale of perceived environmental annoyances in urban settings. J. Environ. Psychol. 2007, 27, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, L.; Ye, Y.; Xu, W.; Law, A. Understanding tourist space at a historic site through space syntax analysis: The case of Gulangyu, China. Tour. Manag. 2016, 52, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Zheng, C.; Dong, Z.; Yao, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Zhang, J.; Song, X.; Guan, Q. Analyzing the correlation between visual space and residents’ psychology in Wuhan, China using street-view images and deep-learning technique. City Environ. Interact. 2021, 11, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yan, Y. Street tree segmentation from mobile laser scanning data using deep learning-based image instance segmentation. Urban. Urban. Gree 2024, 92, 128200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pešek, O.; Brodský, L.; Halounová, L.; Landa, M.; Bouček, T. Convolutional neural networks for urban green areas semantic segmentation on Sentinel-2 data. Remote Sens. Appl. 2024, 36, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xia, N.; Li, M. Dynamic monitoring of urban renewal based on multi-source remote sensing and POI data: A case study of Shenzhen from 2012 to 2020. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2023, 125, 103586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhao, J.; Yao, R. Remote sensing image semantic segmentation via class-guided structural interaction and boundary perception. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 252, 124019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhong, C.; Gao, Q.; Shabrina, Z.; Tu, W. Delineating urban functional zones using mobile phone data: A case study of cross-boundary integration in Shenzhen-Dongguan-Huizhou area. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 2022, 98, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Shibuya, Y.; Sekimoto, Y. Social segregation levels vary depending on activity space types: Comparison of segregation in residential, workplace, routine and non-routine activities in Tokyo metropolitan area. Cities 2024, 146, 104745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.; Ou, D.; Zheng, H. Exploring Acoustic-Visual perception and satisfaction in urban Parks: Based on behavioral analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 112022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, J.R. Key Thinkers on Space and Place, 2nd ed.; Sage: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, Q.; Cheng, H. Quantifying the spatial quality of urban streets with open street view images: A case study of the main urban area of Fuzhou. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Chau, C.K.; Lai, J.H.K. Critical factors influencing the comfort evaluation for recreational walking in urban street environments. Cities 2021, 116, 103286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Chen, H. Using google street view to reveal environmental justice: Assessing public perceived walkability in macroscale city. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2024, 244, 104995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamim, O.F.; Ukkusuri, S.V. Towards safer streets: A framework for unveiling pedestrians’ perceived road safety using street view imagery. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2024, 195, 107400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Aoki, N. Contradictions of indigenous cognition and heritage evaluation under political transformations in a working-class community in Tianjin, China. Cities 2023, 132, 104031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, F.; Dong, Y. How to achieve a balance between functional improvement and heritage conservation? A case study on the renewal of old Beijing city. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florentina-Cristina, M.; George-Laurenţiu, M.; Andreea-Loreta, C.; Constantin, D.C. Conversion of Industrial Heritage as a Vector of Cultural Regeneration. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 122, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szromek, A.R.; Herman, K.; Naramski, M. Sustainable development of industrial heritage tourism—A case study of the Industrial Monuments Route in Poland. Tour. Manag. 2021, 83, 104252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffidi, F. Average social and territorial innovation impacts of industrial heritage regeneration. Cities 2024, 148, 104907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naramski, M.; Herman, K.; Szromek, A.R. The Transformation Process of a Former Industrial Plant into an Industrial Heritage Tourist Site as Open Innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2022, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasemin Çakır, H.; Edis, E. A database approach to examine the relation between function and interventions in the adaptive reuse of industrial heritage. J. Cult. Herit. 2022, 58, 74–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xu, E. Investigating the spatial distribution of urban parks from the perspective of equity-efficiency: Evidence from Chengdu, China. Urban. Urban. Gree 2023, 86, 128019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, E.S.; Tan, P.Y.; Qi, J.; Waykool, R. Assessment of visual landscape quality of urban green spaces using image-based metrics derived from perceived sensory dimensions. Environ. Impact Asses 2023, 102, 107200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Tian, Q.; Cui, M.; He, M. A delicacy evaluation method for park walkability considering multidimensional quality heterogeneity. J. Transp. Geogr. 2023, 112, 103688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, W.; Dong, C. Spatial decay of recreational services of urban parks: Characteristics and influencing factors. Urban. Urban. Gree 2017, 25, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chi, J.; He, K.; Feng, S.; Wang, B. What affect the satisfaction, preferences, and visitation of pocket parks? Evidence from Shanghai. J. Outdoor Recreat. Tour. 2024, 46, 100764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Zhao, T.; Liang, X.; Hou, Y. Sensitivity of measuring the urban form and greenery using street-level imagery: A comparative study of approaches and visual perspectives. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2023, 122, 103385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yabuki, N.; Fukuda, T. Sky view factor estimation from street view images based on semantic segmentation. Urban. Clim. 2021, 40, 100999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, I.A.V.; Labib, S.M. Accessing eye-level greenness visibility from open-source street view images: A methodological development and implementation in multi-city and multi-country contexts. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 103, 105262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Nelischer, M.; Perkins, N. Quality of an urban community: A framework for understanding the relationship between quality and physical form. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 1997, 39, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertacchini, E.; Frontuto, V. Economic valuation of industrial heritage: A choice experiment on Shanghai Baosteel industrial site. J. Cult. Herit. 2024, 66, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenov, D.Y.; da Silva, L.R.R.; Ercetin, A.; Der, O.; Mikolajczyk, T.; Giasin, K. State-of-the-art review of applications of image processing techniques for tool condition monitoring on conventional machining processes. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2024, 130, 57–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, L.; Mcbride, J.; Gong, P. Can you see green? Assessing the visibility of urban forests in cities. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2009, 91, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki, D.; Lee, S. Analyzing the effects of Green View Index of neighborhood streets on walking time using Google Street View and deep learning. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2021, 205, 103920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ratti, C.; Seiferling, I. Quantifying the shade provision of street trees in urban landscape: A case study in Boston, USA, using Google Street View. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2018, 169, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, Y.; Lin, G. An integrated deep learning approach for assessing the visual qualities of built environments utilizing street view images. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intel. 2024, 130, 107805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazekas, Z.; Balázs, G.; Gerencsér, L.; Gáspár, P. Inferring the actual urban road environment from traffic sign data using a minimum description length approach. Transp. Res. Procedia 2017, 27, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Du, Y.; Li, Q. How Does the Historic Built Environment Influence Residents’ Satisfaction? Using Gradient Boosting Decision Trees to Identify Critical Factors and the Threshold Effects. Sustainability 2024, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitrakar, R.M.; Baker, D.C.; Guaralda, M. How accessible are neighbourhood open spaces? Control of public space and its management in contemporary cities. Cities 2022, 131, 103948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goretzko, D.; Pham, T.T.H.; Bühner, M. Exploratory factor analysis: Current use, methodological developments and recommendations for good practice. Curr. Psychol. 2021, 40, 3510–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.M.; Huffcutt, A.I. A Review and Evaluation of Exploratory Factor Analysis Practices in Organizational Research. Organ. Res. Methods 2003, 6, 147–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayton, J.C.; Allen, D.G.; Scarpello, V. Factor Retention Decisions in Exploratory Factor Analysis: A Tutorial on Parallel Analysis. Organ. Res. Methods 2004, 7, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, C.; Lochan Dhar, R. Green competencies: Construct development and measurement validation. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, R.D.; Ferrando, P.J.; Trógolo, M.A.; Poó, F.M.; Tosi, J.D.; Castro, C. Exploratory factor analysis in transportation research: Current practices and recommendations. Transp. Res. Part. F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2021, 78, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, G.A.; Agustin, P.; Adiwijayanto, E.; Ohyver, M. Estimation of cost of living in a particular city using multiple regression analysis and correction of residual assumptions through appropriate methods. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2023, 216, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlKheder, S. Experimental road safety study of the actual driver reaction to the street ads using eye tracking, multiple linear regression and decision trees methods. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2024, 252, 124222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pei, T.; Chen, Y.; Song, C.; Liu, X. A Review of Urban Environmental Assessment based on Street View Images. J. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2019, 21, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.-B.; Zhang, F.; Gong, F.-Y.; Ratti, C.; Li, X. Classification and mapping of urban canyon geometry using Google Street View images and deep multitask learning. Build. Environ. 2020, 167, 106424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Ma, C.; Wu, C.; Xi, Y.; Yang, R.; Peng, N.; Zhang, C.; Ren, F. Measuring human perceptions of streetscapes to better inform urban renewal: A perspective of scene semantic parsing. Cities 2021, 110, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suel, E.; Polak, J.W.; Bennett, J.E.; Ezzati, M. Measuring social, environmental and health inequalities using deep learning and street imagery. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naranjo-Torres, J.; Mora, M.; Hernández-García, R.; Barrientos, R.J.; Fredes, C.; Valenzuela, A. A Review of Convolutional Neural Network Applied to Fruit Image Processing. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirgan, B.; Erener, A. Semantic segmentation of satellite images with different building types using deep learning methods. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2024, 34, 101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Luo, B.; Yu, L.; Chen, B.; Yang, C. BASeg: Boundary aware semantic segmentation for autonomous driving. Neural Netw. 2023, 157, 460–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Deng, X.; Shi, H.; Wang, Z.; He, H.; Xu, J.; Xiao, Y. A novel approach for assessing color harmony of historical buildings via street view image. Front. Archit. Res. 2024, 13, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Leong, W.J.; Durand, M.; Howat, I.; Wadkowski, K.; Yadav, B.; Moortgat, J. Super-resolution deep neural networks for water classification from free multispectral satellite imagery. J. Hydrol. 2023, 626, 130248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, P.; Bie, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Guan, Q. A human-machine adversarial scoring framework for urban perception assessment using street-view images. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. 2019, 33, 2363–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Shang, F.; Liu, C.; Kang, Q.; Wang, R.; Dou, C. Prioritizing Environmental Attributes to Enhance Residents’ Satisfaction in Post-Industrial Neighborhoods: An Application of Machine Learning-Augmented Asymmetric Impact-Performance Analysis. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; He, S.; Cai, Y.; Wang, M.; Su, S. Social inequalities in neighborhood visual walkability: Using street view imagery and deep learning technologies to facilitate healthy city planning. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emel Birer, P.Ç.A. Role of public space design on the perception of historical environment: A pilot study in Amasya. Front. Archit. Res. 2022, 11, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.J.; Wang, D. Environmental correlates of residential satisfaction: An exploration of mismatched neighborhood characteristics in the Twin Cities. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2016, 150, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.; Shao, G.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, P. Insights into citizens’ experiences of cultural ecosystem services in urban green spaces based on social media analytics. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2024, 244, 104999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Zheng, T. Establishing a “dynamic two-step floating catchment area method” to assess the accessibility of urban green space in Shenyang based on dynamic population data and multiple modes of transportation. Urban. For. Urban. Green. 2023, 82, 127893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Cao, X.; Wu, X.; Dong, Y. Examining pedestrian satisfaction in gated and open communities: An integration of gradient boosting decision trees and impact-asymmetry analysis. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2019, 185, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
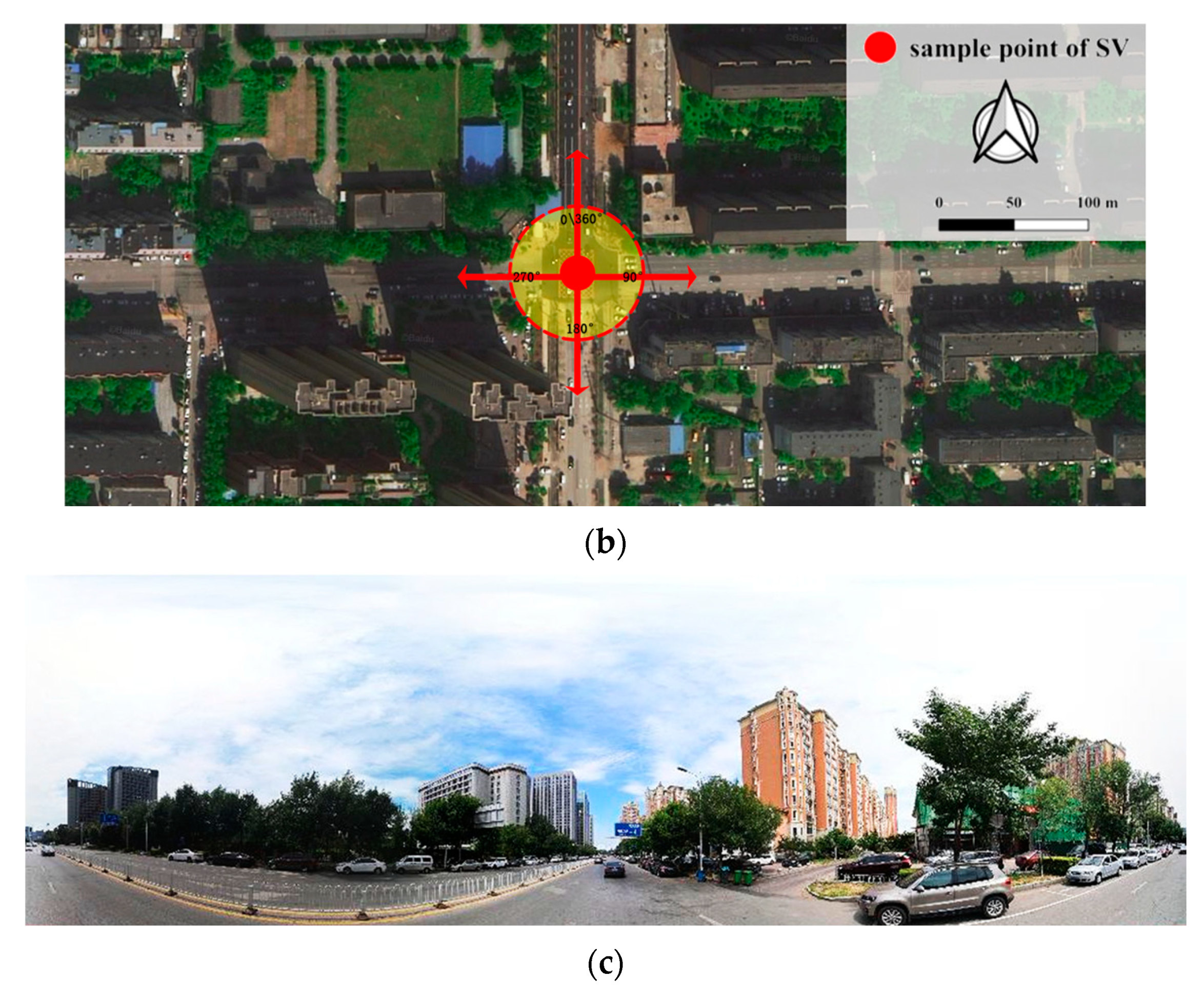
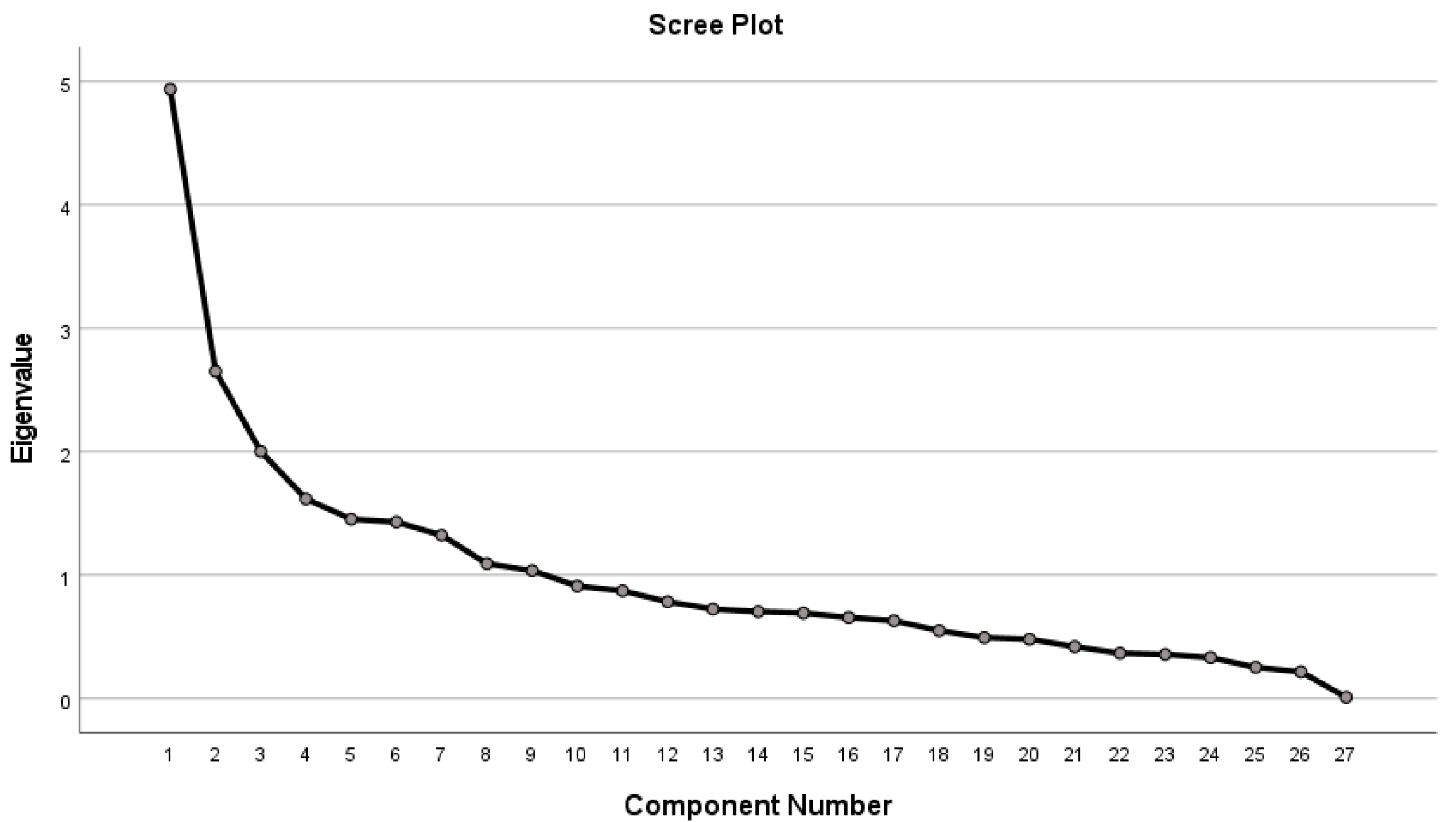

| Categories | Primary Indicators | Secondary Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Path | Road Quality [22] | Pedestrian Comfort [23] |
| Pedestrian Convenience [24] | ||
| Pedestrian Safety [25] | ||
| Landmark | Quality of Industrial Heritage and its Ancillary Buildings [26] | Historical Significance of Industrial Heritage [27] |
| Richness of Industrial Heritage Interface [28] | ||
| Protection and Restoration of Industrial Heritage [29] | ||
| Coordination between Old and New Buildings [30] | ||
| Accessibility of Industrial Heritage [31] | ||
| Openness of Industrial Heritage [32] | ||
| Node | Quality of Plazas, Parks, and other Open Spaces [33] | Recognizability [34] |
| Accessibility [35] | ||
| Number of Rest Facilities [36] | ||
| Feeling of Rest [37] | ||
| District | Appearance Feeling | Overall Appearance Change in the Area |
| Environmental Quality of the Area | ||
| Sky Feeling [38] | Sky Openness [39] | |
| Aesthetic [39] | ||
| Green Feeling [40] | Green Space Ratio [41] | |
| Distance to Green Space [41] | ||
| Edge | Degree of Regional Features | Uniqueness of the Area |
| Indicators | Formulas | Indicator Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| Street Feasibility Index | The Road Feasibility Index can be intuitively reflected in the results of street view imagery segmentation by the ratio of the pixel areas of pedestrian pathways (Wi) to vehicular roads (Ri). A higher ratio (SFIn) indicates better walkability [47]. | |
| Vehicle Interference Index | The Vehicle Interference Index is based on the premise that the presence of numerous vehicles reduces the perceived safety of the environment. The more vehicles there are, the lower the safety. This can be intuitively reflected by the ratio of the pixel areas of motor vehicles (Mi) to vehicular roads (Ri). A higher ratio (VIIn) indicates a higher vehicle interference index, making the environment feel less safe [22]. | |
| Traffic Sign Index | The Traffic Signage Index can be intuitively reflected in the results of street view imagery segmentation by the ratio of the pixel areas of traffic lights and traffic signs (Ti) to all elements (Si). A higher ratio (TSIn) indicates a greater number of required traffic signs in the traffic environment, implying increased road complexity and lower pedestrian safety [48]. | |
| Accessibility of Industrial Heritage | The Accessibility of Industrial Heritage can be intuitively reflected in the results of street view imagery segmentation by the ratio of the pixel areas of industrial heritage (Ai) to pedestrian paths (Wi). A higher ratio (AITn) indicates better accessibility to industrial heritage [49]. | |
| Open Space Index | The Open Space Index can be intuitively reflected in the results of street view imagery segmentation by the ratio of the pixel areas of open spaces (Oi) to all elements (Si). A higher ratio (OSIn) indicates a higher proportion of open activity spaces like squares [50]. | |
| Green Visual Index | The Green Visual Index in street view imagery segmentation results can be intuitively reflected by the ratio of green vegetation (Gi) to all elements (Si) pixel districts. A higher ratio (GVIn) indicates higher comfort [44,45]. | |
| Sky Visibility Index | The Sky Visibility Index can be intuitively reflected in the results of street view image segmentation by the ratio of the pixel areas of the sky (Vi) to all elements (Si). A higher ratio (SVIn) indicates higher spatial visibility and greater comfort [39,46]. |
| Variable | Value | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | Female | 46.58% |
| Male | 53.42% | |
| Age Groups | Under 18 | 6.84% |
| 18–40 | 19.21% | |
| 40–60 | 25.74% | |
| 60–80 | 42.35% | |
| Over 80 | 5.86% | |
| Ethnic Groupe | Han | 92.83% |
| Manchu | 5.54% | |
| Mongolian | 1.63% | |
| Political Identity | Young Pioneer | 2.28% |
| League Member | 3.58% | |
| Party Member | 14.01% | |
| Reserve Party Member | 0.65% | |
| The Masses | 79.15% | |
| Else | 0.33% | |
| Education | Junior high or below | 49.19% |
| High school | 20.52% | |
| Vocational school | 12.38% | |
| Bachelor | 14.98% | |
| Postgraduate or above | 2.93% | |
| Income | Below CNY 50,000 | 39.09% |
| CNY 50,000–100,000 | 30.29% | |
| CNY 100,000–150,000 | 23.45% | |
| CNY 150,000–200,000 | 4.89% | |
| Over CNY 200,000 | 2.28% | |
| Work Experience 1 | Oneself | 37.46% |
| Family Member | 15.63% | |
| None | 46.91% | |
| Residency Duration | Below 5 years | 43.17% |
| 5–10 years | 15.31% | |
| 10–15 years | 14.32% | |
| 15–20 years | 10.91% | |
| Over 20 years | 16.29% |
| Attributes | Mean | Very Low | Low | Neutral | High | Very High |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Road Quality | 4.14 | 1.99% | 12.96% | 52.82% | 1.33% | 30.90% |
| Pedestrian Comfort | 3.55 | 0.00% | 7.64% | 36.54% | 49.17% | 6.65% |
| Pedestrian Convenience | 4.06 | 0.00% | 2.65% | 10.30% | 65.79% | 21.26% |
| Pedestrian Safety | 3.85 | 0.04% | 0.62% | 29.57% | 53.49% | 16.28% |
| Quality of Industrial Heritage and its Ancillary Buildings | 3.31 | 0.00% | 12.96% | 44.85% | 40.53% | 1.66% |
| Historical Significance of Industrial Heritage | 3.36 | 0.00% | 11.63% | 43.19% | 42.86% | 2.32% |
| Richness of Industrial Heritage Interface | 3.59 | 0.00% | 16.28% | 27.24% | 37.54% | 18.94% |
| Protection and Restoration of Industrial Heritage | 3.33 | 0.00% | 23.59% | 25.91% | 44.19% | 6.31% |
| Coordination between Old and New Buildings | 3.31 | 0.00% | 14.62% | 40.86% | 43.19% | 1.33% |
| Accessibility of Industrial Heritage | 3.94 | 0.66% | 5.32% | 19.27% | 49.17% | 25.58% |
| Openness of Industrial Heritage | 4.23 | 0.00% | 4.32% | 22.26% | 19.93% | 53.49% |
| Quality of Plazas, Parks, and other Open Spaces | 3.57 | 0.00% | 10.30% | 30.90% | 50.83% | 7.97% |
| Recognizability | 3.91 | 0.30% | 2.59% | 23.72% | 53.12% | 20.27% |
| Accessibility | 3.64 | 0.35% | 12.62% | 20.60% | 54.80% | 11.63% |
| Number of Rest Facilities | 3.67 | 0.66% | 12.96% | 17.94% | 55.48% | 12.96% |
| Feeling of Rest | 3.57 | 0.66% | 10.63% | 26.91% | 54.49% | 7.31% |
| Sky Feeling | 3.60 | 0.66% | 11.96% | 21.93% | 57.81% | 7.64% |
| Sky Openness | 3.65 | 0.66% | 9.30% | 22.26% | 59.47% | 8.31% |
| Aesthetic | 3.62 | 1.33% | 10.63% | 21.93% | 56.48% | 9.63% |
| Green Feeling | 3.25 | 6.31% | 24.25% | 19.27% | 38.54% | 11.63% |
| Green Space Ratio | 3.27 | 6.31% | 23.92% | 17.94% | 40.53% | 11.30% |
| Distance to Green Space | 3.06 | 8.30% | 19.27% | 38.87% | 25.25% | 8.31% |
| Appearance Feeling | 3.86 | 0.00% | 2.66% | 22.92% | 60.47% | 13.95% |
| Overall Appearance Change in the Area | 3.56 | 0.00% | 7.30% | 40.21% | 41.53% | 10.96% |
| Environmental Quality of the Area | 3.84 | 0.00% | 5.32% | 16.61% | 67.11% | 10.96% |
| Degree of Regional Features | 3.72 | 5.98% | 7.31% | 21.26% | 39.53% | 25.91% |
| Uniqueness of the Area | 3.94 | 3.65% | 6.31% | 16.61% | 39.21% | 34.22% |
| Resident satisfaction | 2.89 | 0.00% | 14.62% | 82.72% | 1.99% | 0.66% |
| Kaiser–Meyer–Olkin Measure of Sampling Adequacy. | 0.712 | |
| Bartlett’s Test of Sphericity | Approx. Chi-Square | 3199.841 |
| df | 351 | |
| Sig. | 0.000 | |
| Component | Initial Eigenvalues | Extraction Sums of Squared Loadings | Rotation Sums of Squared Loadings | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | Total | % of Variance | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 4.938 | 18.290 | 18.290 | 4.938 | 18.290 | 18.290 | 2.544 | 9.422 | 9.422 |
| 2 | 2.652 | 9.821 | 28.110 | 2.652 | 9.821 | 28.110 | 2.421 | 8.968 | 18.390 |
| 3 | 2.002 | 7.416 | 35.526 | 2.002 | 7.416 | 35.526 | 2.290 | 8.481 | 26.872 |
| 4 | 1.617 | 5.990 | 41.516 | 1.617 | 5.990 | 41.516 | 2.051 | 7.596 | 34.467 |
| 5 | 1.453 | 5.383 | 46.899 | 1.453 | 5.383 | 46.899 | 1.853 | 6.863 | 41.331 |
| 6 | 1.431 | 5.299 | 52.198 | 1.431 | 5.299 | 52.198 | 1.734 | 6.422 | 47.752 |
| 7 | 1.323 | 4.900 | 57.098 | 1.323 | 4.900 | 57.098 | 1.685 | 6.241 | 53.993 |
| 8 | 1.093 | 4.047 | 61.145 | 1.093 | 4.047 | 61.145 | 1.570 | 5.816 | 59.809 |
| 9 | 1.037 | 3.840 | 64.986 | 1.037 | 3.840 | 64.986 | 1.398 | 5.177 | 64.986 |
| Attributes | Component | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | Y2 | Y3 | Y4 | Y5 | Y6 | Y7 | Y8 | Y9 | |
| Road Quality | −0.079 | −0.212 | 0.020 | 0.111 | −0.172 | 0.386 | −0.069 | 0.076 | 0.169 |
| Pedestrian Comfort | −0.128 | 0.143 | −0.091 | −0.125 | −0.007 | 0.365 | −0.065 | 0.056 | 0.089 |
| Pedestrian Convenience | 0.024 | −0.041 | −0.018 | 0.005 | −0.009 | 0.480 | −0.030 | −0.100 | −0.102 |
| Pedestrian Safety | 0.010 | 0.013 | 0.008 | −0.140 | 0.076 | 0.348 | 0.070 | 0.030 | −0.173 |
| Quality of Industrial Heritage and its Ancillary Buildings | 0.029 | 0.035 | 0.282 | 0.045 | −0.010 | −0.018 | 0.047 | −0.143 | −0.039 |
| Historical Significance of Industrial Heritage | −0.015 | 0.027 | 0.226 | −0.021 | 0.236 | 0.001 | −0.043 | −0.064 | −0.146 |
| Richness of Industrial Heritage Interface | 0.069 | 0.020 | 0.286 | −0.034 | 0.003 | 0.016 | −0.117 | −0.174 | 0.126 |
| Protection and Restoration of Industrial Heritage | −0.049 | −0.132 | 0.417 | −0.019 | −0.111 | −0.059 | 0.056 | 0.118 | −0.067 |
| Coordination between Old and New Buildings | −0.018 | −0.045 | 0.299 | −0.172 | −0.138 | −0.002 | −0.043 | 0.394 | −0.047 |
| Accessibility of Industrial Heritage | 0.089 | 0.000 | −0.009 | 0.168 | −0.014 | −0.002 | −0.041 | −0.299 | 0.498 |
| Public Accessibility of Industrial Heritage | −0.059 | −0.008 | −0.037 | −0.119 | −0.037 | −0.081 | 0.028 | 0.196 | 0.566 |
| Quality of Plazas, Parks, and other Open Spaces | −0.062 | −0.003 | 0.081 | 0.218 | −0.020 | 0.027 | 0.117 | 0.056 | −0.255 |
| Recognizability | −0.025 | 0.021 | 0.040 | 0.417 | −0.047 | −0.056 | −0.050 | −0.179 | 0.028 |
| Accessibility | −0.004 | −0.103 | −0.081 | 0.477 | −0.023 | −0.057 | −0.027 | −0.064 | 0.075 |
| Number of Rest Facilities | 0.021 | −0.037 | −0.109 | 0.169 | 0.097 | 0.016 | −0.073 | 0.318 | 0.008 |
| Feeling of Rest | 0.034 | 0.045 | −0.069 | 0.070 | 0.060 | −0.015 | −0.094 | 0.353 | −0.008 |
| Sky Feeling | 0.024 | 0.313 | −0.034 | −0.043 | −0.051 | −0.048 | −0.035 | −0.012 | 0.084 |
| Sky Openness | 0.033 | 0.443 | −0.036 | −0.085 | −0.044 | −0.085 | −0.054 | −0.046 | −0.010 |
| Aesthetic | −0.021 | 0.336 | −0.021 | −0.007 | −0.030 | 0.001 | 0.004 | −0.033 | −0.105 |
| Green Feeling | 0.361 | 0.008 | −0.016 | −0.067 | −0.043 | −0.031 | −0.021 | 0.064 | 0.040 |
| Green Space Ratio | 0.367 | 0.008 | −0.017 | −0.058 | −0.032 | −0.037 | −0.023 | 0.052 | 0.035 |
| Distance to Green Space | 0.331 | 0.009 | 0.058 | 0.035 | 0.035 | −0.022 | 0.013 | −0.240 | −0.061 |
| Appearance Feeling | −0.078 | 0.052 | −0.058 | 0.002 | 0.038 | −0.045 | 0.291 | 0.193 | 0.100 |
| Overall Appearance Change in the Area | −0.037 | −0.031 | 0.022 | −0.080 | −0.032 | −0.089 | 0.581 | −0.019 | −0.043 |
| Environmental Quality of the Area | 0.061 | −0.052 | −0.024 | 0.052 | 0.007 | 0.079 | 0.407 | −0.191 | −0.036 |
| Degree of Regional Features | −0.024 | −0.086 | −0.102 | −0.038 | 0.455 | −0.034 | −0.016 | 0.134 | 0.099 |
| Uniqueness of the Area | −0.001 | −0.031 | −0.032 | −0.011 | 0.505 | −0.009 | 0.021 | −0.049 | −0.120 |
| Category | Type | Mean | Median | SD | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Twenty directly obtained indicators | Building | 0.1034 | 0.0973 | 0.0416 | 0.0268 | 0.2706 |
| Sky | 0.2829 | 0.2798 | 0.0398 | 0.0728 | 0.3762 | |
| Tree | 0.1126 | 0.1105 | 0.0506 | 0.0136 | 0.3723 | |
| Roadway | 0.1445 | 0.1412 | 0.0280 | 0.0473 | 0.2327 | |
| Window | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0004 | 0.0000 | 0.0055 | |
| Grass | 0.0023 | 0.0012 | 0.0037 | 0.0000 | 0.0299 | |
| Sidewalk | 0.0466 | 0.0443 | 0.0178 | 0.0098 | 0.1043 | |
| People | 0.0008 | 0.0007 | 0.0009 | 0.0000 | 0.0117 | |
| Door | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0002 | 0.0000 | 0.0021 | |
| Plant | 0.0021 | 0.0016 | 0.0022 | 0.0000 | 0.0105 | |
| Car | 0.1087 | 0.1086 | 0.0270 | 0.0215 | 0.2029 | |
| House | 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.0010 | 0.0000 | 0.0083 | |
| Open Field | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0003 | 0.0000 | 0.0025 | |
| Fence | 0.0032 | 0.0028 | 0.0024 | 0.0000 | 0.0187 | |
| Runway | 0.0014 | 0.0006 | 0.0024 | 0.0000 | 0.0268 | |
| Hardwood | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0002 | 0.0000 | 0.0012 | |
| Truck | 0.0007 | 0.0005 | 0.0008 | 0.0000 | 0.0066 | |
| Traffic signs | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0014 | |
| Small Locomotive | 0.0009 | 0.0007 | 0.0009 | 0.0000 | 0.0055 | |
| Traffic Lights | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0001 | 0.0000 | 0.0009 | |
| Seven indicators obtained through calculation. | SFI | 0.3482 | 0.3183 | 0.1859 | 0.0498 | 1.7228 |
| VII | 0.1159 | 0.1166 | 0.0272 | 0.0297 | 0.2129 | |
| TSI | 0.0002 | 0.0001 | 0.0002 | 0.0000 | 0.0014 | |
| AIH | 0.1120 | 0.1069 | 0.0496 | 0.0268 | 0.4935 | |
| OSI | 0.0481 | 0.0455 | 0.0180 | 0.0098 | 0.1162 | |
| GVI | 0.1171 | 0.1150 | 0.0521 | 0.0148 | 0.3723 | |
| SVI | 0.2829 | 0.2798 | 0.0398 | 0.0728 | 0.3762 |
| Perceptual Factor | Objective Index | Objective Index|Beta| | Overall Satisfaction|Beta| | Objective Index Satisfaction Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y1 | Tree | 0.209 | 0.288 | 0.060 |
| GVI | 0.464 | 0.134 | ||
| Grass | 0.626 | 0.180 | ||
| SFI | 0.113 | 0.033 | ||
| Plant | 0.112 | 0.032 | ||
| Traffic Light | 0.079 | 0.023 | ||
| Y2 | Sky | 0.392 | 0.261 | 0.102 |
| SVI | 0.334 | 0.087 | ||
| Grass | 0.219 | 0.057 | ||
| OSI | 0.226 | 0.059 | ||
| Y3 | Building | 0.187 | 0.237 | 0.044 |
| Gate | 0.201 | 0.048 | ||
| Window | 0.150 | 0.036 | ||
| AIH | 0.176 | 0.042 | ||
| Car | 0.163 | 0.039 | ||
| Small Locomotive | 0.141 | 0.033 | ||
| Trail | 0.176 | 0.042 | ||
| Y4 | Sidewalk | 0.151 | 0.165 | 0.025 |
| People | 0.135 | 0.022 | ||
| Car | 0.138 | 0.023 | ||
| OSI | 0.115 | 0.019 | ||
| Traffic Sign | 0.681 | 0.112 | ||
| Y5 | Trail | 0.150 | 0.362 | 0.054 |
| Small Locomotive | 0.166 | 0.060 | ||
| Roadway | 0.169 | 0.061 | ||
| Hardwood | 0.143 | 0.052 | ||
| Y6 | Roadway | 0.275 | 0.162 | 0.045 |
| Sidewalk | 0.150 | 0.024 | ||
| People | 0.136 | 0.022 | ||
| Car | 0.210 | 0.034 | ||
| TSI | 0.136 | 0.022 | ||
| SFI | 0.169 | 0.027 | ||
| VII | 0.422 | 0.068 | ||
| Y7 | House | 0.277 | 0.286 | 0.079 |
| Fence | 0.161 | 0.046 | ||
| Y8 | People | 0.588 | 0.304 | 0.179 |
| Open Field | 0.771 | 0.234 | ||
| Y9 | People | 0.126 | 0.279 | 0.035 |
| Car | 0.271 | 0.076 | ||
| Small Locomotive | 0.130 | 0.036 | ||
| VII | 0.177 | 0.049 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, X.; Li, K.; Liu, C.; Shang, F. Bridging Built Environment Attributes and Perceived City Images: Exploring Dual Influences on Resident Satisfaction in Revitalizing Post-Industrial Neighborhoods. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7272. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177272
Ji X, Li K, Liu C, Shang F. Bridging Built Environment Attributes and Perceived City Images: Exploring Dual Influences on Resident Satisfaction in Revitalizing Post-Industrial Neighborhoods. Sustainability. 2024; 16(17):7272. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177272
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Xian, Kai Li, Chang Liu, and Furui Shang. 2024. "Bridging Built Environment Attributes and Perceived City Images: Exploring Dual Influences on Resident Satisfaction in Revitalizing Post-Industrial Neighborhoods" Sustainability 16, no. 17: 7272. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177272
APA StyleJi, X., Li, K., Liu, C., & Shang, F. (2024). Bridging Built Environment Attributes and Perceived City Images: Exploring Dual Influences on Resident Satisfaction in Revitalizing Post-Industrial Neighborhoods. Sustainability, 16(17), 7272. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177272





