Carbon Accounting for Permeable Pavement Based on the Full Life Cycle Approach and Its Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Research Scope and Boundary
2.3. Structure of Permeable Pavement
2.4. Life Cycle Carbon Inventory Analysis
2.4.1. Full Life Cycle Approach and Reference Standards
2.4.2. Production Phase
2.4.3. Transportation Phase
2.4.4. Construction Phase
2.4.5. Maintenance Phase
2.4.6. End-of-Life Phase
2.5. Energy Expert Platform
2.6. Carbon Reduction Benefits
2.6.1. Carbon Reduction Benefits of Water Recycling
2.6.2. Carbon Reduction Benefits of Mitigating the Urban Heat Island Effect
2.7. Inventory and Results Uncertainty Analysis
2.8. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Uncertainty Analysis of LCA Results
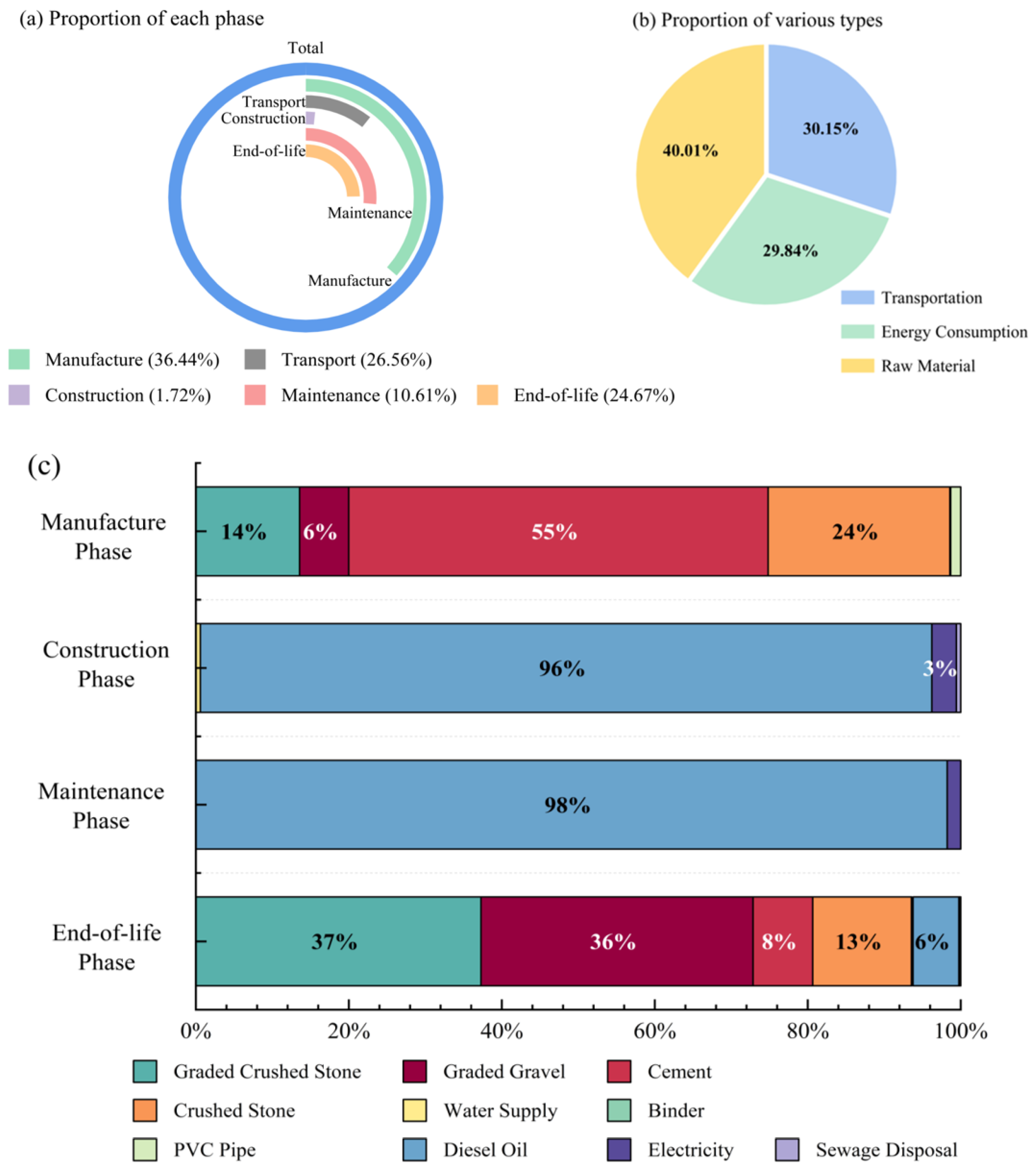
3.2. Carbon Footprint Accounting Results
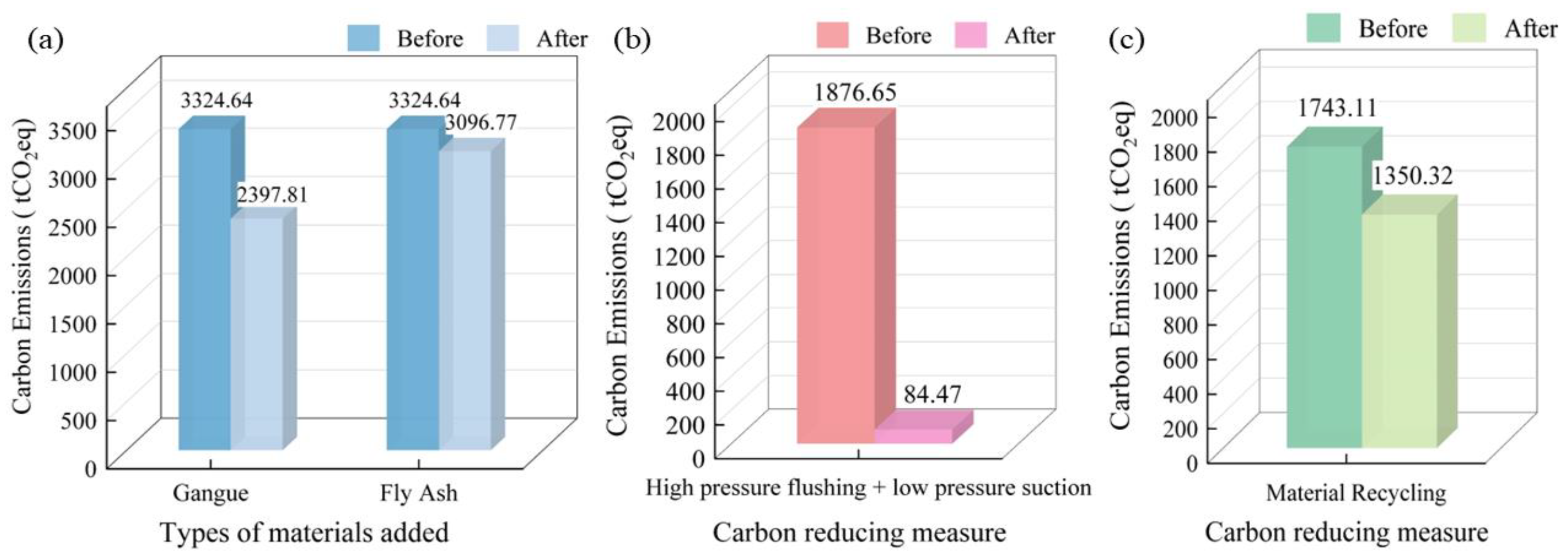
3.3. Carbon Reduction Benefits
3.4. Sensitivity and Scenario Analysis Results
3.4.1. Sensitivity Analysis Results
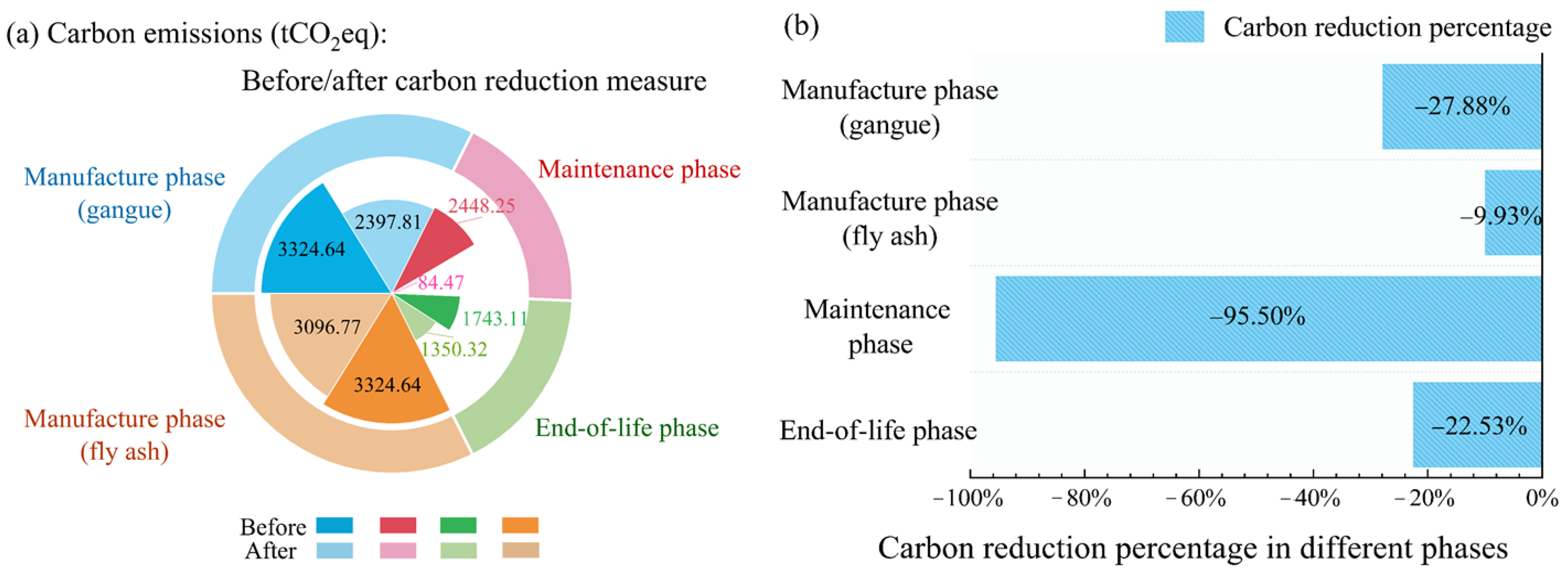
3.4.2. Carbon Reduction Measures Analysis
3.4.3. Integrated Optimization Simulation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Yi, W.; Hong, J.; Zhang, B. Has China achieved synergistic reduction of carbon emissions and air pollution? Evidence from 283 Chinese cities. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Xu, Z. Do model cities play a leading role? Evaluating the carbon abatement effects of energy saving and emission reduction demonstration cities in China. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Yoshida, Y.; Dong, L. Exploring the indirect household carbon emissions by source: Analysis on 49 Japanese cities. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 167, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizalrahman, H.; Hasyimi, V. A model for urban sector drivers of carbon emissions. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 44, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenk, C.; Arendt, R.; Bach, V.; Finkbeiner, M. Territorial-Based vs. Consumption-Based Carbon Footprint of an Urban District—A Case Study of Berlin-Wedding. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nematchoua, M.K.; Orosa, J.A.; Reiter, S. Life cycle assessment of two sustainable and old neighbourhoods affected by climate change in one city in Belgium: A review. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2019, 78, 106282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.U.; Jeon, J.; Wi, S.; Chang, S.J.; Kim, S. Effect of eco-friendly pervious concrete with amorphous metallic fiber on evaporative cooling performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifeddine, K.; Amziane, S.; Toussaint, E. Experimental investigation of physical characteristics to improve the cooling effect of permeable pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Teng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Leung, C.K.Y.; Pan, W. Reducing embodied carbon in concrete materials: A state-of-the-art review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 188, 106653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; He, P.; Yang, L.; He, X.; Lu, S.; Liu, D. Predicting future urban waterlogging-prone areas by coupling the maximum entropy and FLUS model. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 80, 103812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fini, A.; Frangi, P.; Comin, S.; Vigevani, I.; Rettori, A.A.; Brunetti, C.; Moura, B.B.; Ferrini, F. Effects of pavements on established urban trees: Growth, physiology, ecosystem services and disservices. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 226, 104501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardeh, Y.; Kinab, E.; Escadeillas, G.; Rahme, P.; Ginestet, S. Review of the optimization techniques for cool pavements solutions to mitigate Urban Heat Islands. Build. Environ. 2022, 223, 109482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Qi, F.; Cui, H. Toward carbon neutrality: A bibliometric analysis of technological innovation and global emission reductions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30, 73989–74005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, K.; Lim, J.S.; Varbanov, P.S.; Jia, X.; Ji, M.; Tao, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, B. Carbon emission pinch analysis for shipping fuel planning considering multiple period and fuel conversion rates. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttuvelu, D.V.; Wyke, S.; Vollertsen, J. Are Permeable Pavements a Sustainable Solution? A Qualitative Study of the Usage of Permeable Pavements. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf-van Dinther, R.; Leskens, A.; Veldkamp, T.; Kluck, J.; Boogaard, F. From Pilot Projects to Transformative Infrastructures, Exploring Market Receptivity for Permeable Pavement in The Netherlands. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.N.; Ghisi, E.; Thives, L.P. Permeable Pavements Life Cycle Assessment: A Literature Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghmanesh, M.; Beecham, S. A Review of Permeable Pavement Clogging Investigations and Recommended Maintenance Regimes. Water 2018, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.; Sheikh, M.N.; Hai, F.I. A critical review of the mechanisms, factors, and performance of pervious concrete to remove contaminants from stormwater runoff. Water Res. 2024, 251, 121101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yan, H.; Liao, Z.; Zhang, K.; Schmidt, A.R.; Tao, T. Laboratory analysis on the surface runoff pollution reduction performance of permeable pavements. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Chen, W.; Gao, Q.; Liu, S.; Deng, C.; Ma, Y.; Ji, G. Research on the Reduction Performance of Surface Runoff Pollution Through Permeable Pavement with Different Structures. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambito, M.; Severino, A.; Freni, G.; Neduzha, L. A Systematic Review of the Hydrological, Environmental and Durability Performance of Permeable Pavement Systems. Sustainability 2021, 13, 4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-M.; Chen, J.-W.; Lecher, T.; Chen, T.-H.; Davidson, P. Assessment of clogging of permeable pavements by measuring change in permeability. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 141352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, H. Life-cycle assessment and multi-criteria performance evaluation of pervious concrete pavement with fly ash. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 177, 105969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Jiang, J.; Gu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, F. Sustainable Urban Street Comprising Permeable Pavement and Bioretention Facilities: A Practice. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Rahman, M.M.; Beecham, S. Permeable Pavements for Flood Control in Australia: Spatial Analysis of Pavement Design Considering Rainfall and Soil Data. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Zhou, Z. Numerical Analysis on the Optimization of Evaporative Cooling Performance for Permeable Pavements. Sustainability 2022, 14, 4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeri, T.; Hassan, N.; Ghaffarianhoseini, A. Evaluation of microclimate mitigation strategies in a heterogenous street canyon in Kuala Lumpur from outdoor thermal comfort perspective using Envi-met. Urban Clim. 2023, 52, 101719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Roesler, J. Aging albedo model for asphalt pavement surfaces. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 117, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Xiao, F. Carbon emission quantification and reduction in pavement use phase: A review. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 11, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbhuiya, S.; Das, B.B. Life Cycle Assessment of Construction Materials: Methodologies, Applications and Future Directions for Sustainable Decision-Making. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Wasko, S.; Booth, B. Comparative life cycle assessment of permeable pavement and conventional pavement. Water 2024, 16, 435–460. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Abdelhady, A.; Harvey, J. Initial evaluation methodology and case studies for life cycle impact of permeability of permeable pavements. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2018, 7, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Integrated life cycle assessment of permeable pavement: Model development and case study. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2020, 85, 102381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Q.; Xia, B.; Singh, A.; Lv, Z.; Song, W. Natural gravel-recycled aggregate concrete applied in rural highway pavement: Material properties and life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 334, 130219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tota-Maharaj, K.; Paul, P. Sustainable Approaches for Stormwater Quality Improvements with Experimental Geothermal Paving Systems. Sustainability 2015, 7, 1388–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Vaddy, P.; Biligiri, K.P. Quantification of embodied energy and carbon footprint of pervious concrete pavements through a methodical lifecycle assessment framework. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 161, 104953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, N.; Akin, M.; Shi, X. Permeable concrete pavements: A review of environmental benefits and durability. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 1605–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Oeser, M. The Environmental Impact Evaluation on the Application of Permeable Pavement Based on Life Cycle Analysis. Int. J. Transp. Sci. Technol. 2019, 8, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Luo, B.; Tong, H.; Zou, Y.; Lei, Z.; Chen, S. Carbon reduction potential of a rain garden: A cradle-to-grave life cycle carbon footprint assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 434, 139806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, A.; Bamshad, O.; Golzary, A.; Buswell, R.; Osmani, M. Biases in life cycle assessment of circular concrete. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 192, 114237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santero, N.J.; Masanet, E.; Horvath, A. Life-cycle assessment of pavements Part II: Filling the research gaps. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 55, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batouli, M.; Bienvenu, M.; Mostafavi, A. Putting sustainability theory into roadway design practice: Implementation of LCA and LCCA analysis for pavement type selection in real world decision making. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2017, 52, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinari, M.; Al-Qadi, I.L.; Ozer, H.; Nielsen, E. Optimised durable pavement rolling resistance. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2023, 24 (Suppl. 1), 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trupia, L.; Parry, T.; Neves, L.C.; Lo Presti, D. Rolling resistance contribution to a road pavement life cycle carbon footprint analysis. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2017, 22, 972–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthonissen, J.; Van den Bergh, W.; Braet, J. Review and environmental impact assessment of green technologies for base courses in bituminous pavements. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2016, 60, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Zheng, H.; Lu, J.; Poon, C.S. Utilization of municipal solid waste incineration bottom ash (IBA) aggregates in high-strength pervious concrete. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 174, 105736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adresi, M.; Yamani, A.; Karimaei Tabarestani, M.; Rooholamini, H. A comprehensive review on pervious concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 407, 133308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, O.; Neithalath, N. Compressive behavior of pervious concretes and a quantification of the influence of random pore structure features. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 528, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, G.; Gulcan, A.; Cagdas, B.; Bayraktar, O.Y. The impact of recycled coarse aggregates obtained from waste concretes on lightweight pervious concrete properties. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 17369–17394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, L.; Di Mascio, P.; Fusco, C. Porous Concrete for Pedestrian Pavements. Water 2019, 11, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Sun, B.; Liu, Z.; Yin, J. Laboratory-simulated investigation on thermal behaviours of permeable concrete pavements. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18 (Suppl. 3), 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chu, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Du, Y. Alleviating urban heat island effect using high-conductivity permeable concrete pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 237, 117722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 1468; Thread—General Plan. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Choi, Y.-J.; Ahn, D.; Nguyen, T.H.; Ahn, J. Assessment of Field Compaction of Aggregate Base Materials for Permeable Pavements Based on Plate Load Tests. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muttuvelu, D.V.; Kjems, E. A Systematic Review of Permeable Pavements and Their Unbound Material Properties in Comparison to Traditional Subbase Materials. Infrastructures 2021, 6, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdeljaber, A.; Adghim, M.; Abdallah, M.; Ghanima, R.; Aljassem, F. Comparative performance and cost-integrated life cycle assessment of low impact development controls for sustainable stormwater management. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 95, 106805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14040:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Principles and Framework. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- ISO 14044:2006; Environmental Management—Life Cycle Assessment—Requirements and Guidelines. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Wang, Y.; Ni, Z.; Hu, M.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Chen, S.; Xia, B. Environmental performances and energy efficiencies of various urban green infrastructures: A life-cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Tan, K.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Experimental investigation on the influence of evaporative cooling of permeable pavements on outdoor thermal environment. Build. Environ. 2018, 140, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Skinner, C.; Ormondroyd, G.; Thevenon, M.-F. Life cycle assessment of a novel tannin-boron association for wood protection. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, A.; Akhtar, A. A novel approach for environmental impact assessment of road construction projects in India. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, M.; Kakuturu, S.; Ballock, C.; Spence, J.; Wanielista, M. Effect of Rejuvenation Methods on the Infiltration Rates of Pervious Concrete Pavements. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2010, 15, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, K.; Drake, J.; Seters, T.V.; Vander Linden, W.K. Improving Restorative Maintenance Practices for Mature Permeable Interlocking Concrete Pavements. Water 2018, 10, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H. Novel Backwashing Maintenance Method for Permeable Concrete Pavement: Two-Year Field Study. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucke, T.; White, R.; Nichols, P.; Borgwardt, S. A Simple Field Test to Evaluate the Maintenance Requirements of Permeable Interlocking Concrete Pavements. Water 2015, 7, 2542–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Zhang, J.; Xia, S.; Han, R.; Dai, Z.; She, R.; Cui, X.; Meng, B. A field performance evaluation of the periodic maintenance for pervious concrete pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 263, 121463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, L.N.; Ghisi, E.; Severis, R.M. Environmental assessment of a permeable pavement system used to harvest stormwater for non-potable water uses in a building. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 746, 141087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaverková, M.D. Landfill Impacts on the Environment—Review. Geosciences 2019, 9, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poor, C.; Kaye, J.; Struck, R.; Gonzalez, R. Permeable Pavement in the Northwestern United States: Pollution Source or Treatment Option? Sustainability 2023, 15, 12926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, H.; Sun, Z. Laboratory evaluation of PAHs removal by multi-functional green pervious concrete (MGPC) pavement. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 315, 128032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Y.; Shi, S. Life Cycle Evaluation of Permeable Pavements versus Ordinary Pavements. Urban Issues 2017, 2017, 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, B.; Lu, Q. Estimation of albedo effect in pavement life cycle assessment. J. Clean. Prod. 2014, 64, 306–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoxha, E.; Habert, G.; Lasvaux, S.; Chevalier, J.; Le Roy, R. Influence of construction material uncertainties on residential building LCA reliability. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 144, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noshadravan, A.; Wildnauer, M.; Gregory, J.; Kirchain, R. Comparative pavement life cycle assessment with parameter uncertainty. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2013, 25, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrier, G.A.; Palaniappan, S.; Habert, G. Classification of sources of uncertainty in building LCA. Energy Build. 2024, 305, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicalho, T.; Sauer, I.; Rambaud, A.; Altukhova, Y. LCA data quality: A management science perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 156, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansah, M.K.; Chen, X.; Yang, H.; Lu, L.; Li, H. Developing a tier-hybrid uncertainty analysis approach for lifecycle impact assessment of a typical high-rise residential building. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, R.; Xie, P.; Xue, G.; Ma, G. Environmental economic profiles of expressway construction via life cycle assessment. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 104, 107359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shao, X.; Ling, T.-C. Life cycle assessment of coal gangue composite cements: From sole OPC towards low-carbon quaternary binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Jiang, W.; Yang, S.; Wang, W. A sustainable low-carbon pervious concrete using modified coal gangue aggregates based on ITZ enhancement. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 377, 134310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.; Durham, S.A. A cradle to gate LCA framework for emissions and energy reduction in concrete pavement mixture design. Int. Sustain. Built Environ. 2016, 5, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, H.M.; Zaki, E.G.; Abdelsattar, D.E.; Dhmees, A.S.; Azab, M.A.; Elsaeed, S.M.; Kandil, U.F. Exosomal MicroRNAs: An Emerging Important Regulator in Acute Lung Injury. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 8804–8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, C.; Fan, Y.; Yang, J.; Ni, Z.; Hang, Z.; Liu, H. Improved Thermoelectric Properties of Graphene Reinforced Multiphase Cement Composites: Experiments and Modeling. J. Sustain. Cem. Based Mater. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Material (Layer) | Thickness (mm)/ Length (m) | Density (kg/m3) | Weight (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cement (top layer) | N/A * | 2.88 × 103 | 1.95 × 106 |
| Water (top layer) | N/A | 1.00 × 103 | 7.33 × 105 |
| CeMentitious material (top layer) | N/A | N/A | 8.20 × 103 |
| Gravel (topping) | N/A | 2.10 × 103 | 8.46 × 106 |
| Grading gravel (bedding) | 150 | 2.10 × 103 | 2.02 × 107 |
| Graded gravel (base layer) | 150 | 2.20 × 103 | 2.11 × 107 |
| PVC drainage pipe | 1.49 × 103 | 1.40 × 103 | 6.36 × 103 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Shao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Carbon Accounting for Permeable Pavement Based on the Full Life Cycle Approach and Its Application. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177293
Wang L, Shao Z, Zhang X, Wang Y. Carbon Accounting for Permeable Pavement Based on the Full Life Cycle Approach and Its Application. Sustainability. 2024; 16(17):7293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177293
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lu, Zhiyuan Shao, Xurui Zhang, and Yafei Wang. 2024. "Carbon Accounting for Permeable Pavement Based on the Full Life Cycle Approach and Its Application" Sustainability 16, no. 17: 7293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177293
APA StyleWang, L., Shao, Z., Zhang, X., & Wang, Y. (2024). Carbon Accounting for Permeable Pavement Based on the Full Life Cycle Approach and Its Application. Sustainability, 16(17), 7293. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16177293







