Abstract
The fast fashion industry significantly impacts the environment at every stage of a product’s life cycle. The transport of products to wholesalers and stores, as one of the stages of the product life cycle, is often overlooked during the analysis of their carbon footprint. Therefore, research is needed on the impact of fast fashion on the environment through its logistics and transport, especially in relation to air emissions. This article attempts to determine how extensively fast fashion companies disclose the impact of their transport operations on their overall corporate carbon footprint, determine the proportion of total emissions attributed to transport, and evaluate the effectiveness of companies’ efforts to mitigate their transport-related environmental impact. This research used a case study method on selected brands (H&M Group, Inditex, Shein), using secondary data available in non-financial reports for 2023. As a result of the analysis of their non-financial reports on transport emissions, several key findings have been presented. Companies predominantly rely on external frameworks and standards, particularly the Global Reporting Initiative. However, the level of detail of the data presented varies. The priority for the surveyed companies is to reduce emissions from significant sources, such as production processes. The data disclosed in the reports (scope 1, 2, 3) must be clearly formulated and can be used to calculate the level of their CO2 emission reduction or increase. Companies should improve their environmental reporting by including indicators of their transport-related emissions. This approach provides a comprehensive view of their environmental impact, highlighting absolute values and efficiency metrics.
1. Introduction
The fast fashion industry, characterized by rapid production cycles and frequent collection updates, has been among the most interesting and scrutinized topics in recent years. With the emergence of ultra-fast business models, the question of limits and conducting operations while respecting planetary boundaries is raised increasingly frequently. According to “(Un)Sustainable transitions towards fast and ultra-fast fashion” [1], fast fashion is considered the second most polluting industry (after oil extraction and production). McKinsey & Company highlighted that fast fashion retailers have sped up their production processes, getting new styles to customers at a record pace and creating significant environmental and social challenges [2]. This branch of the industry significantly impacts water consumption and pollution, greenhouse gas emissions linked to fossil fuels used in production processes and transportation, the resources used, and biodiversity losses. There are also many concerns about respecting human rights in supply chains, child labor, working conditions, and health and safety. The most frequently discussed issues are in their production processes, which undoubtedly have the most significant impact on the organization’s resultant sustainable development [3,4]. However, there is a lack of studies on the environmental impact of fast fashion throughout the supply chain, particularly in logistics and transport. In this area, the most significant impact on the environment is from air emissions, which are very important from the point of view of climate change. Unfortunately, the aspect of transport and logistics is often overlooked due to its relatively small share of the overall environmental impact of fast fashion. This oversight means that the analysis of the carbon footprint resulting from the fast fashion logistics process is frequently neglected, creating a significant research gap. There is a lack of literature on this topic. Addressing this research gap is crucial, as understanding the emissions associated with transportation and logistics can provide a more accurate and holistic view of the environmental impact of the fast fashion industry. By focusing on this often-ignored area, researchers and companies can develop more effective strategies to reduce emissions and promote sustainability within the supply chain. Additionally, this focus will help and motivate companies to improve their methods for collecting data regarding transport-related emissions, which can lead to more informed actions and enhanced transparency.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Fast Fashion’s Characteristics
The fashion industry is one of the largest industrial sectors in the world. The rapid growth in the production of clothing and footwear, driven by rising wealth and consumption in developing nations, is a consequence of its conscious adoption of “fast fashion”, which has been defined as “a business model based on offering consumers frequent novelty in the form of low-priced, trend-led products” [5]. Fast fashion represents one of the world’s most important industries, driving a significant part of the global economy. It is one of the central value-creating industries of the world economy [6]. Before the COVID-19 pandemic, the fashion industry’s global revenue was estimated to be between USD 1.7 trillion and USD 2.5 trillion, according to two research reports by Euromonitor and McKinsey [7]. Moreover, the fashion industry is a significant employer worldwide, with millions of people (designers, factory workers, distribution and logistics personnel, sales associates, etc.) involved in various aspects of the industry [2]. The Ellen MacArthur Foundation states that, globally, the clothing industry employs more than 300 million people along its value chain. This sector employs millions in countries like China, Bangladesh, India, and Vietnam, where a significant share of the world’s clothing is produced [8].
Fast fashion is trendy and desirable among customers. The primary reason for this is its affordability. Companies offer trendy clothes at a low price, which allows them to access to a broader range of customers. Brands adapt quickly to the newest fashion trends, so customers do not have to wait long to be fashionable and wear the hottest trends. Wide variety and choice can be another benefit of fast fashion brands, which offer various styles so everyone can find something suitable. Their convenience should also be mentioned; brands usually combine sales in physical stores in the most visited and popular areas with their online presence via e-commerce platforms, making all shopping processes extraordinarily convenient and accessible [9]. Furthermore, clothes may not be taken care of properly and may be disposed of without much thought. This makes fast fashion an essential driver of environmental impacts [10].
2.2. Environmental Impacts of Fast Fashion
The fashion supply chain is diverse and complex, spanning four or more tiers, including design, raw material harvesting, spinning, yarn production, dyeing, weaving, cutting, stitching, and final garment construction [11]. One of the most visible side effects of fast fashion, except for its carbon footprint, is the vast amounts of waste, in the form of clothes (that could still be used), ending up in landfills [12]. The Ellen MacArthur Foundation reports that less than 1% of the material used to produce clothing is recycled into new clothing [13]. Fast fashion has a significant and detrimental impact on water quality. The industry consumes vast amounts of water for dyeing and finishing processes, which often involve toxic chemicals [14]. According to the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), 2700 liters of water is needed to produce a single cotton t-shirt. That is enough to sustain one person for 900 days [15].
The fast pace of production might cause issues with proper inventory management, resulting in a number of overproduced garments that cannot be sold. This can contribute to waste or cause problems in the developing part of the world, where massive amounts of garments, which are quite often unnecessary, are being sent. Unfortunately, many fast fashion items are designed and produced for short-term trends and are of lower quality and durability, which can lead to increasing amounts of waste. The price of the clothes also does not encourage customers to prolong the garment’s life, for instance, by repairing it. It is easier to get rid of it. In the area of waste, however, some fast fashion brands are taking tangible and visible steps toward implementing circular economy practices, for example, by renting garments, repairing unwanted garments, creating collecting programs, and creating new business models with second-hand clothes [12]. Fast fashion companies have already started incorporating circular economy principles into their business models [16,17,18,19,20]. Still, further actions need to be taken to reduce resource use and operate within planetary boundaries, including enabling textile-to-textile recycling.
In 1995, the textile industry manufactured 7.6 kg of fiber per person globally. By 2018, this amount nearly doubled to 13.8 kg per person, coinciding with the world’s population growth from 5.7 billion to 7.6 billion people. Over 60 million tonnes of clothing are purchased annually, which is projected to increase to approximately 100 million tonnes by 2030 [21]. Due to this extensive production and consumption, a significant carbon footprint is emerging.
The fashion industry is responsible for a significant amount of global CO2 emissions, exceeding those from several other sectors, such as international aviation and shipping. Textile production occurs through geographically long and complex supply chains, including the growers and processors of raw fibers, yarns, and textiles; weavers; knitters; dyers; finishers; product manufacturers; and distributors. Most textile and clothing production occurs in countries in the Global South such as India, China, and Bangladesh, which rely heavily on fossil fuels for their electricity supply, thereby increasing the carbon footprint of each clothing item produced. Additionally, the decomposition of textile waste in landfills or through incineration releases harmful chemicals and greenhouse gasses into the environment [22]. Due to its complex supply chain, the transportation of fabrics and garments from production facilities usually in developing countries [23], and energy-intensive production, the textile industry generates roughly 1.2 billion tonnes of CO2-equivalent, or nearly 10% of the world’s GHG emissions [24]. Large-scale systemic change is needed for the industry to align with the Paris Climate Change Agreement’s goals to limit global warming to 1.5 °C above pre-Industrial Revolution levels [24]. The analysis results indicate that the climate impact of clothing and footwear consumption will rise from 1.0 to 1.3 Gt carbon dioxide equivalent over the 15 years since 2015. China, India, the USA, and Brazil dominate these figures. Achieving systemic change requires collaboration among stakeholders, technological innovation, government policies, and robust infrastructure support. Decarbonization could be achieved by phasing out coal and introducing renewable energy sources [23], using bio-based feedstocks and low-emission heat sources, sustainable production and transportation processes, and an increase in the rate of recycling materials [25]. According to the McKinsey & Company home page—The McKinsey report [26], the carbon abatement goal is for industry emissions in 2030 to be 1.7 gigatons of CO2-equivalent less than they are today. The same report estimates that the fashion industry misses the 1.5 °C goal by 50% under its current trajectory. Beyond 2030, the sector will encounter an important task: the formidable task of accelerating abatement efforts. This will require defining modern business models and decoupling volumes from emissions.
2.3. Transport’s Role and Its Impact on the Environment
Although transport is not the focus when we discuss the fast fashion industry and its emissions, according to The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and its 2023 report [27] “In 2019, direct greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from the transport sector (…) accounted for 23% of global energy-related CO2 emissions, 70% of direct transport emissions came from road vehicles, while 1%, 11%, and 12% came from rail, shipping, and aviation, respectively. Emissions from shipping and aviation continue to increase.” In this report, the IPCC also expresses their concern regarding the ability of the transport sector to fulfill Paris Agreement recommendations: “Scenarios from bottom-up and top-down models indicate that without intervention, CO2 emissions from transport could grow in the range of 16% and 50% by 2050 (medium confidence)”.
Logistics results in various external impacts, such as air pollution, noise accidents, vibration, land use, and visual disturbance [28,29,30,31,32]. The emissions from freight transport are significantly influenced by the type of fuel used. Although various alternative fuels are available, diesel remains the primary fuel for goods vehicles. Diesel engines are preferred because of their efficiency and high energy density, making them suitable for the heavy loads and long distances commonly encountered in freight transport. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), diesel fuel accounts for about 76% of the energy consumption in the global road freight sector [33,34]. Statista reports that, in 2020, diesel was the dominant fuel for freight transportation, representing approximately 96% of the energy used in road freight transport [35]. These data underscore the dominance of diesel fuel in the goods transportation sector worldwide.
The primary climate impact of transportation arises from both the production and combustion of fossil fuels. This process releases significant amounts of greenhouse gasses, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), contributing to global warming and environmental degradation. Companies in the fast fashion industry frequently change their collections and aim for quick and efficient deliveries, so they choose fast and efficient transport modes. Different modes of transport contribute differently to carbon emissions. Air freight has significantly higher environmental impacts than road transport due to its high carbon emissions. According to the European Environment Agency (EEA), air freight produces up to 10 times more emissions than road transport per ton km.
Moreover, air freight-related carbon emissions are up to 44 times higher than ocean freight-related emissions due to the high energy consumption of jet fuel, which is highly refined and has a high energy content per unit weight, a high speed, and a relatively low cargo capacity [36]. In contrast, a much slower ocean vessel has a much higher cargo capacity. Although it emits a considerable amount of CO2, it carries thousands of tons of cargo, making the emissions per ton of cargo relatively low. Maritime transport is the most environmentally friendly mode of transport of the three, while air transport has the largest share in greenhouse gas production [37]. From an environmental perspective, deciding which mode of transport should be used primarily for long distances is easy; however, for companies, the lead time, costs, actions taken by competitors, and customers’ expectations are equally important. This complicates the transportation process, requiring robust mitigation plans to reduce transport-related carbon footprints. Businesses must make informed decisions about growth and profit opportunities while also considering the environmental impact of those choices.
2.4. Fast Fashion and Transport
The fast fashion industry relies heavily on a high volume of shipments to maintain its rapid inventory turnover, with frequent deliveries being essential to keeping up with market demand. A considerable quantity of goods being transported frequently is one of the consequences of this industry, and transport-related emissions contribute to the industry’s overall carbon footprint [38,39]. The typical nature of fast fashion industry supply chains is highly fragmented; while on the one had this enables them to maintain fast, cost-effective production, on the other hand this causes many challenges connected with transparency, monitoring, securing proper labor conditions, consistency, and a high disruption sensitivity level [40,41,42]. The quantitative results of Zamani et al. [43] demonstrated the potential risk of problem shifting: increased customer transportation can completely offset the benefits gained from reduced production. For transport, primarily, this increases transport-related emissions but also impacts lead times, increasing the level of complexity in synchronizing all shipping schedules and customs clearances, increasing the risk of delays and complicating the inventory process [44,45]. The results show that the carbon footprint of fast fashion consumption is 2.50 kgCO2e/one wear of jeans, 11 times higher than traditional fashion consumption. Jeans production and cross-broad transportation contributed to 91% of the carbon footprint of fast fashion consumption [46]. On top of that, the transportation process involves the extensive use of packaging materials, further increasing its environmental impact [47].
3. Aim of the Research
Considering the significant carbon footprint of the fast fashion industry described above and zooming in on transport-related emissions (a niche but increasingly important aspect of sustainable development in this industry), an attempt has been made to choose the three most important examples of companies that are part of the fast fashion industry. The selection of such a research sample (three large international companies) is a sufficient data source. Still, the authors are aware that it is also one of the limitations of this study.
In the next phase of this study, non-financial reports and publicly accessible strategies related to the transportation sector’s environmental objectives underwent quantitative and qualitative analyses. The aim was to assess how extensively these companies disclose the impact of their transport operations on their overall corporate carbon footprint. Additionally, the study aimed to determine the proportion of their total emissions attributed to transport and evaluate the effectiveness of companies’ efforts to mitigate their transport-related environmental impact (past and future). The qualitative assessment also considered the level of detail and transparency in those action plans. The research was based on data available in non-financial reports for 2023 published by the surveyed organizations.
The following research questions were asked:
RQ1:
How extensively do companies disclose the impact of their transport operations on their overall corporate carbon footprint?
RQ2:
What is the level of detail and transparency of these companies’ business plans?
RQ3:
What are the main challenges, trends, and opportunities for all stakeholders to exploit in the coming years?
This article provides recommendations for companies to enhance their reporting by including additional metrics that express their transport-related emissions efficiency.
The research findings can be utilized by representatives of these organizations to enhance action plans aimed at minimizing the negative impact of transport emissions on the environment, and they can also serve as inspiration for scientists for future academic articles expanding our discussion on the theoretical implications of the research results or conducting a more detailed analysis. This paper is organized as follows: after this Introduction, Section 2 discusses the primary characteristics of fast fashion, and Section 3 highlights transport’s role in fast fashion and its environmental impact. Finally, Section 4 reports the conclusions and implications of the study.
Conducting this research should enrich our knowledge about the fast fashion industry’s environmental protection activities, and particularly the air emissions from their transport processes.
4. Research Methodology
The following study on transport-related emissions and sustainable transformation strategies aims to present the current status of existing sustainability efforts in the area of air emissions in the fast fashion industry. Therefore, a case study method was applied to selected fast fashion brands (H&M Group, Inditex, Shein) for a specific period. By fast fashion brands, authors refer to companies that operate within the fast fashion industry, producing and selling clothing quickly and inexpensively to meet the latest fashion trends. The authors selected three companies based on several critical criteria. Firstly, affordability: all three brands offer trendy clothing to many customers at affordable prices. This affordability ensures that fashion is a luxury and available to the masses. Secondly, high volume: these companies operate on a model prioritizing high production volumes with a short product life cycle. This means that they can quickly respond to the latest fashion trends and continuously refresh their inventory, keeping customers engaged and returning for more. Thirdly, global reach: each company has a significant international presence. They have successfully expanded beyond their home markets and established a strong foothold in various regions worldwide, making their brands recognizable and accessible globally. While these similarities are notable, it is also essential to consider the differences that complicate a straightforward comparison. Established companies like H&M and Inditex have a long history and have built their reputations over decades. They have developed extensive supply chains, robust business models, and a loyal customer base. In contrast, Shein, a relatively new entrant, has taken the fast fashion model towards an ultra-fast fashion approach.
In summary, while H&M and Inditex have the advantage of experience and established infrastructure, Shein’s disruptive business model and rapid growth highlight the dynamic nature of the fashion industry. The comparison between these companies underscores the evolving landscape of fast fashion, where agility and innovation are increasingly critical to success. The research process is qualitative. It is based on data available in non-financial reports from 2023, which provide information about a company’s performance in areas other than their financial metrics. These reports typically cover their environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices.
The authors intended to revise and evaluate non-financial reports from 2023. However, it is essential to note that these three companies have different financial periods. For the H&M Group, the financial year spans from 1 November 2022 to 31 October 2023, while for Inditex, it runs from 1 February to 31 January. As sustainability reports or any other sources for Shein for 2023 were not available, the authors decided to use the most recent data included in the report for 2022. Shein’s financial year is from 1 January to 31 December.
The data that were analyzed were divided into three scopes:
- Scope 1 emissions—direct emissions from sources that a company owns or controls;
- Scope 2 emissions—indirect emissions from the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling consumed by the company;
- Scope 3 emissions—all other indirect emissions in a company’s supply chain.
A case study is an empirical mode of research in which a particular phenomenon is studied in a real-life context [48]. The case study method is derived from a grounded theory that aims to construct new theories and concepts capable of explaining emerging phenomena. In qualitative research, grounded theory is gaining prominence as an approach to developing theories from data [49]. According to Rashid et al. [50], when using various data sources, a case study helps explore a phenomenon in a given subject area. Case studies can be divided according to their content and ultimate purpose (exploratory, explanatory, descriptive, or by a certain number of cases) [51]. A common trend in all types of case studies is to try and explain why a particular decision or several decisions were taken, how these decisions were implemented, and the effect of implementing these decisions [48].
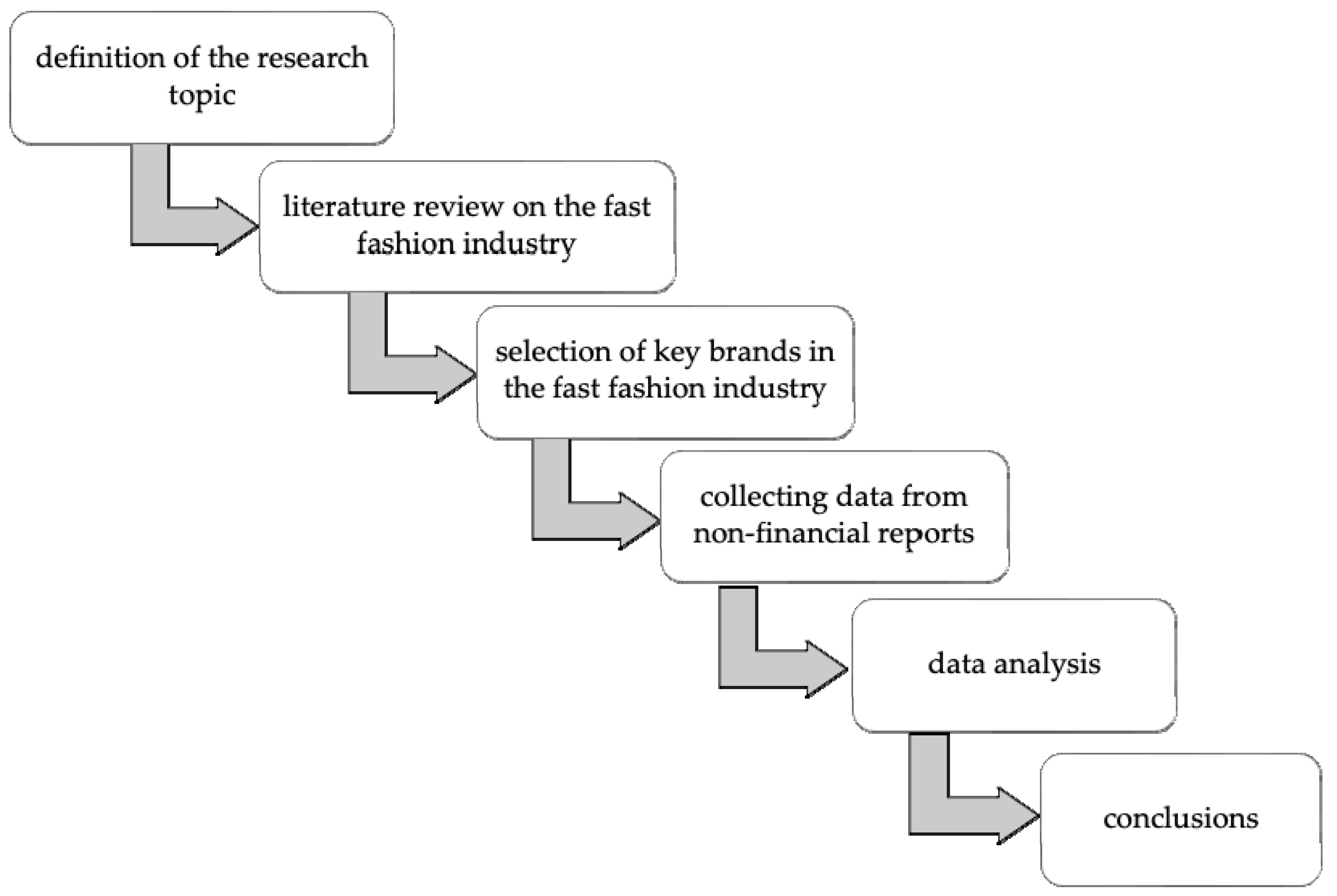
In this study, the following steps were taken: the research topic was defined, the literature on the fast fashion industry, its impact on the environment, and the impact of one of the industry’s processes—transportation—on the environment and especially on its carbon footprint was reviewed. Then, key brands in the fast fashion industry were selected, their data were collected, an analysis was carried out, and a summary and conclusions were formulated (Figure 1).
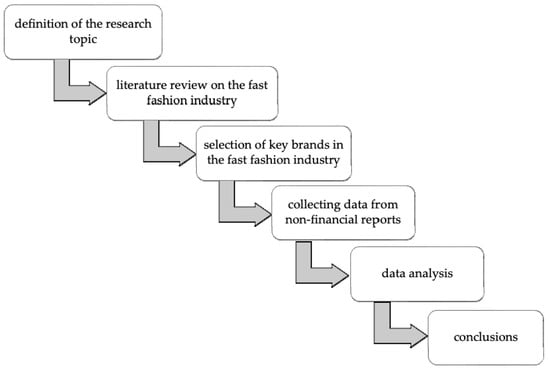
Figure 1.
Research process flowchart. Source: own work.
This study aimed to analyze the future actions that companies plan to implement to reduce transport-related emissions, as outlined in their Climate Transition Plans. This analysis focuses on the strategies and initiatives companies commit to significantly reducing their carbon footprint. By examining these plans, this study provides insights into the specific measures taken by companies, such as transitioning to low-emission vehicles, optimizing logistics and supply chains, and investing in renewable energy sources.
The study also conducted a preliminary analysis of the emission data in non-financial reports, comparing them with the CSRD requirements. The aim was to assess these companies’ readiness for the new reporting standards.
5. Analysis of Non-Financial Reports of the Selected Fast Fashion Organizations
5.1. H&M Group—Review of Their Characteristics and Non-Financial Reports
H&M Group [52] is a global fashion and design company with over 4000 stores in over 75 markets and online sales in 60. The group includes brands like H&M, COS, Monki, Cheap Monday, & Other Stories, Arket, and H&M Home.
The company aims to provide its customers with the best combination of fashion, quality, price, and sustainability. The H&M Group has a long history of actively working with sustainability. This means that they aim to grow their business by decoupling their financial growth from using finite natural resources [52]. The importance of their sustainability work is underlined in their 2030 and 2040 goals, which have been verified by the Science-Based Target Initiative (SBTi):
- 2030: Reduce their absolute scope 1, 2, and 3 CO2e emissions by 56% against their 2019 baseline;
- 2040: Have net-zero emissions.
When comparing this statement regarding targets with the information on the SBTI home page [53], we can see similarities and confirm their targets. The target’s language describes their commitment in detail and highlights their 100% renewable electricity target by 2030, up from 90,6% in 2019.
Relatively substantial progress has been achieved concerning the organization’s goals, and this is presented in Table 1. The reference year is 2019, and the data show that the company, in scopes 1, 2, and 3, recorded a reduction in emissions, by 24% in the first scope and by 22% in the second scope. According to the information in their Sustainability Disclosure, the main elements influencing the result were investments in recycled and sustainably sourced materials for garments and packaging, energy efficiency improvements, a shift to cleaner energy sources in the supply chain, and decreased stock-in-trade.

Table 1.
H&M Group’s progress in emission reduction, divided by scope of emission, in 2023.
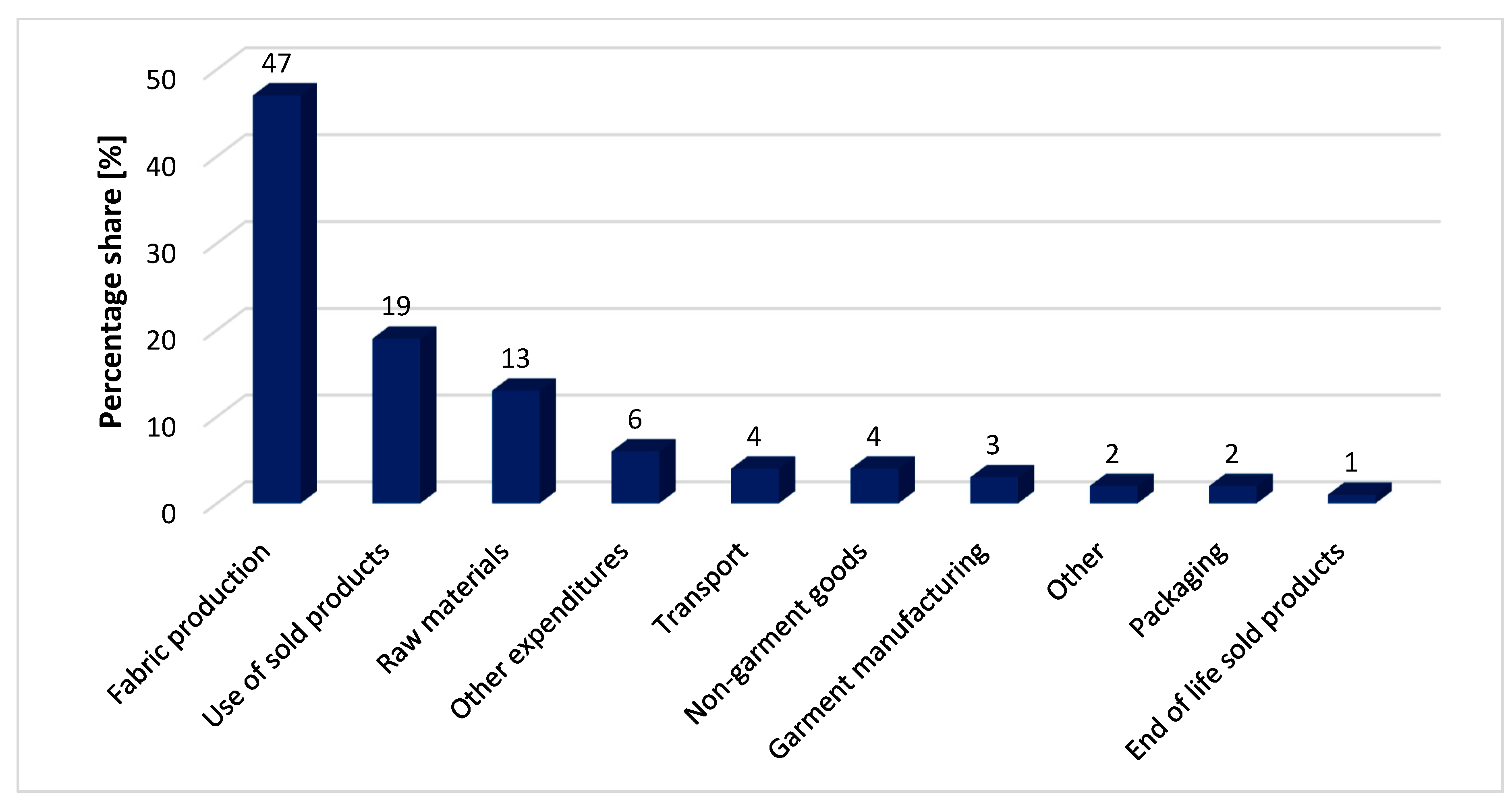
According to the information provided by their Sustainability Disclosure, a significant portion of their scope 3 emissions—approximately 63% (including the use phase of products not included in their SBTi-verified targets)—are related to production processes, such as raw materials, fabric production, and garment manufacturing. Focusing on transport emissions only, in 2023, they were 4% of all scope 3 emissions (Figure 2).
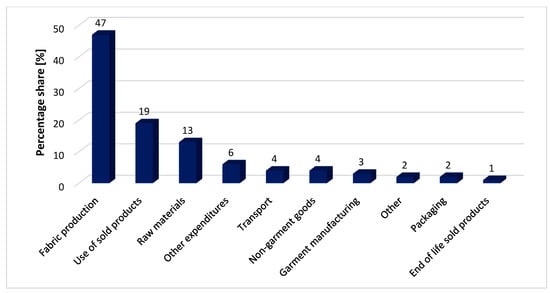
Figure 2.
Percentage share of types of scope 3 emissions from H&M Group in 2023. Source: own elaboration based on [54].
Based on the available information, the conclusion could be made that transport-related emissions have decreased yearly (Table 2), starting from the 2019 baseline. In 2023, they were −33% compared to the reference year. The main drivers of this reduction were a decrease in stock-in-trade and the maintenance of a low share of air freight, supported by transport optimization measures and a further increase in the share of alternative fuels. The company emphasizes the significance of collaborating with strategic partners to accelerate the decarbonization of its logistics. It has also highlighted that the share of preferred fuels (100% biofuel, electric, and zero-emission vehicles) accounted for 11% of the transport distance covered during 2023 [54].

Table 2.
H&M Group’s transport-related emissions, 2019–2023.
To indicate the directions and actions that will bring the company closer to its goals, the company has created the H&M Group Climate Transition Plan [55]. This plan focuses on the company’s journey towards 2030. It presents what actions they plan to take and defines its challenges and opportunities, which are divided into each part of the supply chain, including transport. According to their Transition Plan, two main actions will be taken in the transport area. The first one is connected to reducing the amount of transport by using parcel collection points instead of home delivery, improving load efficiency, consolidating shipments, and optimizing delivery schedules. The second part is connected to low-emission transport alternatives, where the expansion of electricity usage, zero emissions, and 100% biofuels is highlighted.
Interestingly, in the same document, the H&M Group transparently shares the challenges they have identified on their path toward 2030. Among them, they have listed the limited availability and infrastructure for biofuels, which is foreseen to play an essential role in the transition to electrified transport; inadequate EV infrastructure; deficient rail infrastructure; slow progress in electrifying heavier road transport; limited options in terms of affordable lower emission alternatives to air freight and ocean freight; and, since in air and sea freight they rely on average data, a limitation to the improvements they can make by their reducing speed and using more efficient vessels and fuels.
The document also includes a call to action [55]:
- To policymakers, to accelerate the development of EV infrastructure;
- To Transport Service Providers, to adopt and develop better alternatives to conventional transport methods;
- To transport buyers (including the H&M Group), to set precise requirements and provide support in financing this transition;
- To the transport industry, to develop a standard definition for sustainable biofuels.
5.2. INDITEX—Review of Its Characteristics and Non-Financial Reports
Inditex is one of the world’s largest fashion retailers, with eight brands (Zara, Pull&Bear, Massimo Dutti, Bershka, Stradivarius, Oysho, Zara Home, and Uterqüe) selling in 213 markets through their online platforms or stores [56]. Inditex expresses its commitment to sustainability by recognizing that many social, economic, and environmental challenges are now more urgent than ever. Inditex also highlights its ambition to innovate and increase efficiency to make a positive difference for people and the planet [57].
In 2023, Inditex submitted to the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) an update on their climate commitments for 2030, including their roadmap to achieving net-zero emissions in 2040. The emissions reduction goals they want to achieve are as follows [58]:
- Reduce emissions by more than 50%, including their own operations and their value chain—pare their absolute scope 1 and 2 emissions (i.e., their own emissions) by 90% and scope 3 emissions (value chain) by at least 50%, with respect to those of 2018;
- Achieve net-zero emissions, reducing at least 90% of their carbon footprint from 2018.
Some differences can be noticed when comparing those commitments with the SBTI home page. According to this resource, Inditex commits to reducing their absolute scope 1 and 2 GHG emissions from their 2018 base year by 90% by 2030. The company also commits to reducing their absolute scope 3 GHG emissions from their 2018 base year by 20% by 2030. Their 2040 target has not yet been confirmed [53]. However, the date of the targets published is indicated as being 2020, while Inditex, in its non-financial report, mentions a new submission in 2023 [58], so it might be that the data on the SBTI home page had not been updated.
As the organization emphasized in its non-financial reports, its total GHG emissions have remained stable compared to 2018. Scope 1 emissions were reduced by 40% compared to the base year, and scope 2 emissions had an even higher reduction by implementing renewable energy-based solutions for electricity by using, for example, PPAs (Power Purchase Agreements) and EACs (Energy Attribute Certificates). In the area with the largest share of emissions—scope 3—there has not been much change since 2018. However, a slightly negative trend can be observed. Although there was a decrease in their carbon footprint in 2022, emissions increased again by 5% in 2023 compared to the previous year. Additionally, this was a minor change of 0.17% compared to the baseline (Table 3).

Table 3.
Inditex’s progress in emission reduction, divided by scope of emission, in 2023.
The organization did not explain its situation when presenting these figures. However, it highlighted that the gradual implementation of its Climate Transition Plan will allow it to make progress in reducing emissions associated with the rest of its scope 3 categories. On the one hand, the available data indicate that the company is actively and effectively reducing its direct emissions (scope 1) and indirect emissions (scope 2). However, more effort and tangible actions are needed to address the indirect emissions within scope 3 (supply chain).
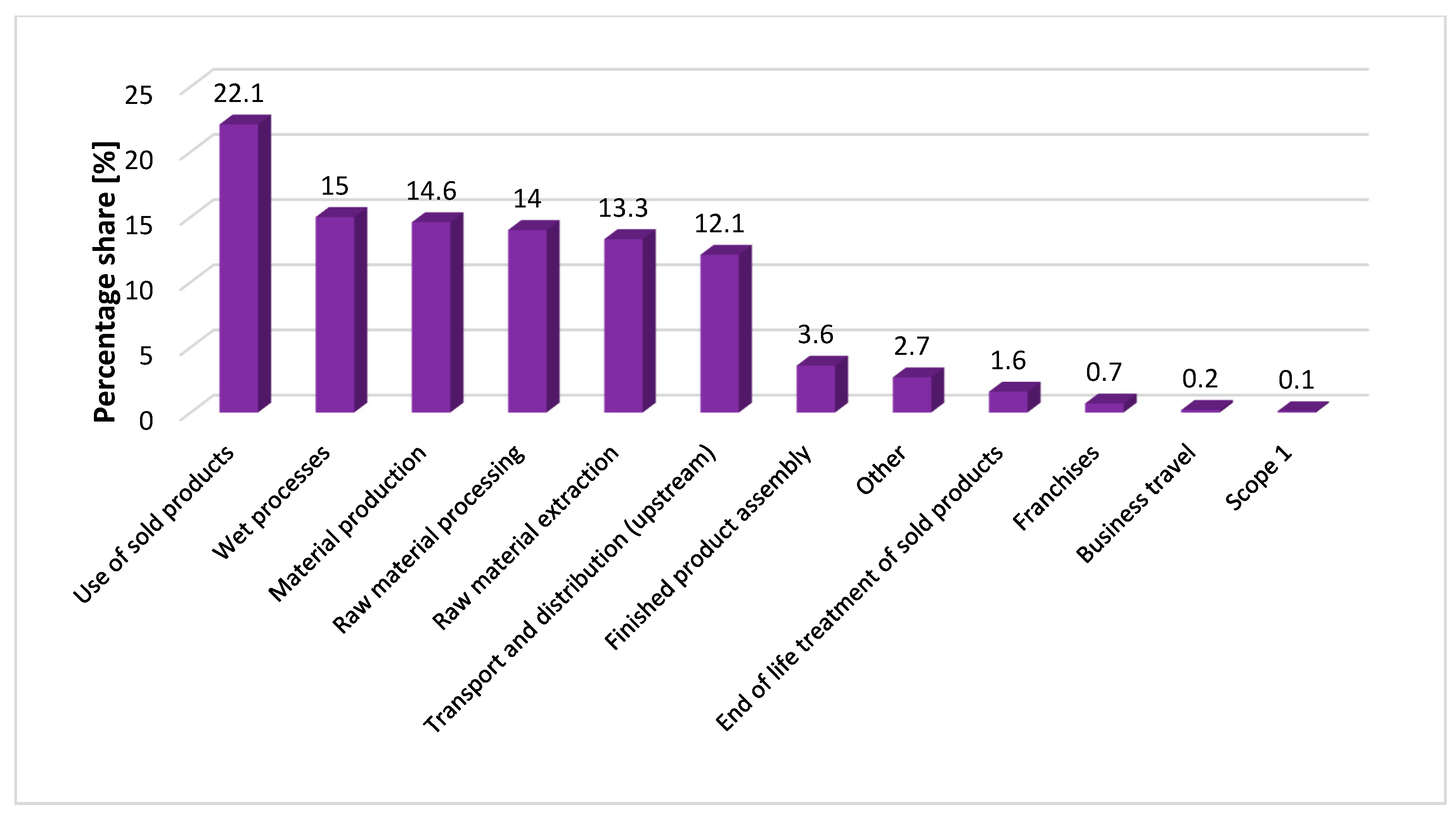
Figure 3 provides information about the split between scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions. According to the available information in their non-financial report, a significant portion of their scope 3 emissions—almost 60% (including the use phase of products, which is not included in the target shared with the SBTI)—are related to production processes, such as material production, wet processes, raw material extraction, and raw material processing. When we focus on transport emissions only, then in 2023, these were 12% of all scope 3 emissions.
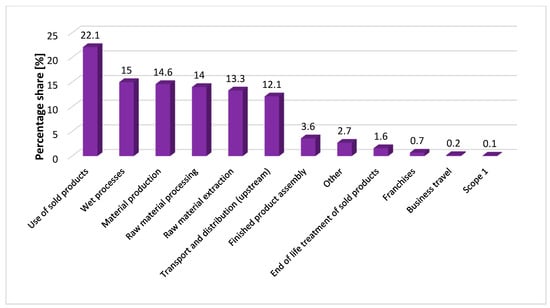
Figure 3.
Percentage share of scope 1, 2, and 3 greenhouse gas emissions from Inditex in 2023. Source: own elaboration based on [58].
While analyzing the data, discrepancies were identified between the emissions data reported in the company’s non-financial report for 2023 [58] and its Climate Transition Plan [59], specifically regarding the total emissions value in the base year used (2018). According to the report (Table 4), the total emissions were stated as being 17,059,810 tCO2e, whereas the second document indicates a value of 16,827,000 tCO2e. It is important to note that the purpose of this research is not to determine which number is correct. However, given this difference and the absence of specific data on their transport carbon footprint, the calculations below are based on the available information:

Table 4.
Inditex’s transport-related emissions in 2018 and 2023.
- Transport-related emissions for 2023 have been calculated based on the numbers available in the non-financial report, since the share of emissions for 2023 is provided there.
- Transport-related emissions for 2018 have been calculated based on numbers available in the Climate Transition Plan, since the share of emissions for 2018 is provided there.
The transport emissions figures encompass upstream transport emissions only. It has been highlighted that the company is working to provide more comprehensive data in the future. Upstream transportation emissions refer to the greenhouse gas emissions produced when a company moves goods it has purchased. This includes moving products from suppliers to the company’s location, often through third-party transport services [60]. These emissions can arise from various transportation and distribution activities throughout the value chain, such as air transport, rail transport, road transport, marine transport, and the storage of purchased products in warehouses and distribution centers [61]. The GHG Protocol defines downstream transportation emissions as the greenhouse gas emissions arising from the distribution and delivery of products after the point of sale. These emissions occur when goods move from a company’s facilities to its customers or end-users [61]. In 2023, Inditex’s transport-related emissions increased significantly, by 24% compared to their baseline. Unfortunately, the specific reasons for this increase are unclear in the relevant documents. However, when examining the evolution of net sales, there is a substantial rise between the baseline and 2023. While this increase could be linked to higher sales volume and transport needs, it remains speculative. Their 2023 financial report highlights strong sales in both their online and retail channels.
On top of that, their Climate Transition Plan highlights the importance of the optimization measures for transport-related carbon footprint reduction implemented in recent years, such as designing new protocols to make precise use of space, standardizing packaging to maximize the number of items sent in each shipment, redesigning routes to minimize return trips with empty trucks [59]. Despite implementing those measures, transport-related emissions increased. Unfortunately, data regarding the emissions share of different transport modes (air, road, rail, ocean) is missing, making further analysis of the possible causes impossible.
Inditex is committed to driving its transformation toward being a more sustainable business and making progress in the fight against climate change. This is one reason behind the creation of its Climate Transition Plan, which outlines the various actions necessary to achieve the climate goals it has committed to.
To make progress in transport-related emissions reduction, they are working on three priority lines of action, which they apply to their transport network wherever possible [59]:
- Optimize loads to increase efficiency and occupancy levels.
- Analyze global flows to reduce the distance garments travel and promote multimodality.
- Incorporate new fleets to transition to equipment with less environmental impact and alternative fuels and propulsion methods.
They emphasize the importance of collaboration and provide specific examples that contribute to achieving their emissions reduction goals. The organization has committed to using alternative fuels for at least 90% of their sea shipments by 2025.
5.3. Shein—Review of Its Characteristics and Non-Financial Reports
Shein, a fast-fashion retailer from China, is a relatively new company that emerged in 2012. Despite its recent establishment, it competes with fashion giants like Zara and H&M. Its mission is to make the beauty of fashion accessible to all, reimagining fashion by leveraging a small-batch on-demand production model. This model allows for more choices at more affordable prices [62].
While the group has not specifically released a non-financial report, its Sustainability and Social Impact Report is available on its home page. This document was published in 2021 and 2022. Unfortunately, a similar report for 2023 has not been made publicly available.
They are committed to decarbonizing their supply chain, sourcing responsible materials, and protecting biodiversity and animal welfare through collective action. They have also outlined two emission-related goals [63]:
- Reduce their greenhouse gas emissions (scopes 1, 2, and 3) by 25% by 2030;
- Become carbon-neutral in their scope 2 emissions by 2030.
Based on the available data, the reference year for the above targets is 2021.
The company has said that science-based targets have been set to support the decarbonization of its supply chain. However, more information needs to be provided about submitting this target to the SBTI, which has been confirmed on the SBTI home page [53,63]. Table 5 was generated using data from that report, based on our calculation of the available data.

Table 5.
Shein’s progress in emission reduction, divided by scope of emissions.
In 2022, its emissions increased by 52%, while its production volume increased by 57%, according to the company’s statement. The change in absolute emissions from 6.04 to 9.17 million tonnes of CO2 e is being explained as resulting from the strong growth of the business. They admit that they were at the beginning of their mitigation journey and began implementing decarbonization programs at the end of the 2022 fiscal year.
The report should include a detailed breakdown of their emission shares. However, based on the data provided in the report, the authors made calculations—by summing the tons of CO2e for each scope and determining the proportion of each scope in their overall emissions—and found that it is as follows: scope 1—0.04%; scope 2—0.21%; scope 3—99.75%.
More than 99% of emissions are from scope 3, meaning less than 1% came from Shein’s corporate operations.
There is very little information about the transport part of their emissions, but again, based on the available data, this can be calculated—see Table 6.

Table 6.
Transport-related emissions from Shein in 2021–2022.
These transport emissions-related figures encompass both upstream and downstream transport emissions.
The significant 55% increase from 2022 compared to 2021 aligns with the explanation of the overall emission rise being attributed to business growth. It also highlights that the company needs to take additional preventive measures to tackle its transport-related emissions. No specific Climate Transition Plan was found during the research.
6. Results and Discussion
Several salient conclusions emerge after analyzing the data and content within non-financial reports about these companies’ transport-related emissions.
As a prevailing practice, companies underscore their reliance on external frameworks and standards, notably the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)— the TCFD framework is not included in their non-financial reports. However, the authors intended to highlight the common frameworks the companies use, as this is part of their non-financial report. Furthermore, there is a concerted effort to align reporting practices with the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), which mandates adherence to the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). This distinction is particularly evident in the H&M Group’s report. Their detailed disclosures already encompass several elements mandated by the ESRS, such as their scope 3 emissions (kilotonnes) and % change from the previous year, split by category; the absolute value of their scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions reduction; and the percentage of their scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions reduction (in terms of emissions from the base year). While the Inditex report meets some requirements, specific analyses should be included. For instance, it provides absolute greenhouse gas emissions values divided into scopes and gives the shares of emissions per category. However, it does not present emissions values for specific categories (in tCO2e) or the percentage change in scope 3 GHG emissions. Fortunately, since the data is available, implementing these improvements should be straightforward. It is essential to remember that the CSRD aims to enhance transparency and enable stakeholders to assess companies’ impact on people, the environment, and the financial risk related to sustainability issues.
The data extracted from the non-financial reports published by the surveyed organizations are difficult to compare. Table 7 provides a comprehensive summary of the data extracted from the available non-financial reports. The subsequent conclusion highlights that more than directly comparing these companies and their results is needed, as this may lead to misleading interpretations.

Table 7.
Summary of data extracted from non-financial reports.
Therefore, focusing on each company’s progress in managing their transport-related emissions is essential. This approach allows for a more accurate assessment of their efforts and achievements in reducing their environmental impact. By focusing on specific advancements within the framework of transport-related emissions, we can better understand how each company contributes to their sustainability goals. This perspective acknowledges each company’s unique challenges and strategies and promotes a more nuanced environmental performance evaluation. The upcoming unified frameworks for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting will enhance our ability to compare companies’ results more effectively. By introducing standardization and transparency, these frameworks require detailed disclosures on various ESG factors, making it easier to assess and compare companies’ performance in areas such as carbon emissions, labor practices, and governance structures. Another critical aspect is accountability. Companies will be held accountable for their ESG practices, allowing stakeholders to compare how companies address similar challenges. Overall, these frameworks will promote greater transparency and accountability in the corporate world, facilitating more accurate comparisons of companies’ sustainability and ethical practices. However, unified frameworks only address some issues, despite their relatively detailed requirements. The companies in this research have disclosed information on transport-related emissions with varying levels of specificity. Analyzing the H&M Group reports was straightforward, and we obtained absolute figures for their scope 3 GHG emissions, emission shares per category (including transport), and the historical evolution of their transport-related carbon footprint. To gain insights into transport-related emissions from other companies, one must perform one’s own calculations and search for data across various documents, such as their Climate Transition Plan.
During our research, an additional conclusion emerged. Comparing absolute transport-related emissions across individual companies is pointless due to varying business sizes and different methods of calculating emissions within scope 3 of their GHG emissions. The H&M Group tries to rely on primary data, while Inditex employs ton–kilometer estimates. The H&M Group’s approach to road transport involves information from transport partners regarding fuel type and quantity multiplied by the appropriate emission factor. In contrast, Inditex considers tons transported and kilometers traveled for each mode of transport, using relevant emission factors. Both methodologies align with frameworks such as that of the GLEC (Global Logistics Emission Council). Considering our earlier feedback, comparing progress within a single company remains valid, although this approach has limitations.
Factors beyond companies’ optimization efforts, such as macroeconomic conditions, can influence their absolute transport-related emissions. Additional efficiency indicators that reflect a company’s activities are recommended to address this. One such measure could be CO2e emissions per transported kilometer. This would highlight the company’s efforts in terms of transport optimization and the adoption of alternative fuels. By including efficiency metrics, companies can offer a more comprehensive view of their environmental impact, and particularly in terms of how effectively they manage and reduce emissions from transportation activities, highlighting both absolute values and efficiency metrics. By adopting this approach, companies can enhance transparency and provide stakeholders with a clearer understanding of their commitment to sustainability and efforts to mitigate climate change. However, achieving this would require companies to prioritize the use of primary data for their calculations. While this may pose a significant challenge, technological advancements and ongoing efforts to enhance reporting transparency make it a feasible goal.
All three companies have committed to prioritizing enhancing their data collection and calculation processes. Their goal is to comply with upcoming regulations and ensure transparent reporting. By focusing on these improvements, they aim to meet industry standards and provide accurate insights into their environmental impact.
Among the three researched companies, two (Inditex and the H&M Group) have outlined their intended actions to mitigate the carbon footprint of their transport operations within their Climate Transition Plans. These actions are broadly categorized into three key areas:
- Transport Optimization Measures—maximizing vehicle capacity, reducing empty runs, and optimizing transportation routes;
- Low-Emission Transport Modes—utilizing low-emission means of transport, including rail and ocean freight;
- Low- or Zero-Emission Fuels—implementing the electrification of transport and exploring biofuels.
The actions described in their Climate Transition Plans reflect their commitment to sustainable transport practices, albeit at a high and generalized level. However, assessing whether these actions will enable these companies to achieve their targets remains challenging. Notably, the companies presented have yet to establish specific goals for their transport-related emissions. Instead, they have set targets for reducing their scope 3 greenhouse gas emissions, which encompass their transport footprints. The absence of specific transport-related targets may explain the limited data included in their sustainability reporting. However, there are reasons behind this approach. Firstly, transport emissions constitute a relatively small share of emissions—ranging from 4% of the H&M Group’s total emissions to 12% of Inditex’s emissions. Understandably, companies prioritize reducing emissions from significant contributors like production processes. Yet, as production becomes progressively decarbonized, transport’s share could grow, especially given the fast-paced demand for same-day and next-day deliveries. Thus, transport-related emissions may play an increasingly crucial role in the future. Similarly, companies that enhance transparency and specificity in this area may find themselves in a winning position. Not only do they address emissions and progress toward targets, but they also build trust among current and future customers.
All companies have underscored the significance of industry-wide collaboration. Given the formidable challenges associated with fast fashion, a collective approach is essential. In transport, collaboration could involve strengthening relationships with transport business partners. By sharing the risk of implementing sustainable solutions, companies can accelerate the development of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure and enhance biofuels’ availability. Notably, the H&M Group acknowledges that their success in reducing transport emissions hinges on the progress achieved by their service providers.
For many customers, fashion is much more than just clothing. It is a way of expressing their personality, identity, and creativity and being themselves.
As consumer awareness and regulatory demands increase, fast fashion brands might face pressure to embrace more sustainable transportation choices and reduce shipment frequencies. Based on the reviewed non-financial reports, some companies proactively utilize electric or hybrid delivery vehicles and sustainable packaging to minimize their environmental footprint. When making purchasing decisions, customers should consider sustainability. They play a central role in influencing fashion companies. By expressing their demands, customers encourage companies to meet their expectations.
The global fashion industry encounters several challenges related to sustainability and social responsibility. Notably, the fast fashion model contributes significantly to carbon emissions and gives rise to various social and environmental issues. Nevertheless, it is difficult to imagine living in a world without textiles. The textile industry is also a significant sector in the global economy, employing hundreds of millions of people worldwide. These benefits notwithstanding, the way companies design, produce, and distribute clothes has drawbacks that are becoming increasingly clear.
Despite progress in incorporating circular economy practices, the textile system still operates almost linearly: large amounts of non-renewable resources are extracted to produce clothes that are often used for only a short time, after which they are mostly sent to landfills or incinerated.
As one of the most prevalent challenges in this industry, companies acknowledge the need to enhance their internal data collection, analysis, and reporting processes to align with upcoming standards. Simultaneously, they recognize the opportunity in this activity to improve their transparency. Organizations strive to meet regulatory requirements and leverage transparency as a strategic advantage.
An additional challenge lies in effectively implementing the actions outlined in companies’ Climate Transition Plans to measure progress and achieve committed targets. Simultaneously, there is an opportunity for further development, particularly in alternative fuel’s availability and optimizing low-emission transport modes. However, pursuing these opportunities may require additional investments.
7. Conclusions and Recommendations
Although concerted efforts are being made to align reporting practices with the CSRD, which requires compliance with the ESRS, the surveyed organizations publish the data that are convenient for them. Implementing mandatory and unified standards will assist stakeholders in navigating and making informed decisions. This requires greater involvement on their part. This is all the more so because, according to the CSRD, information on, among other things, the environmental impact of organizations should be transparent and allow stakeholders to assess the impact of these organizations on people, the environment, and financial risks related to sustainability issues. It is challenging to compare the environmental impact of these organizations, despite them representing the same industry. The upcoming unified framework for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting will increase the possibility of a more effective comparison of these companies’ results. However, this will depend on many factors and, above all, on the extent and the level of reference chosen by these organizations. Therefore, it is recommended that each organization should focus on minimizing their negative environmental impacts, including reducing their transport emissions. Focusing on specific progress in transport-related emissions makes it possible to understand better how each company contributes to achieving the SDGs.
An additional recommendation is to introduce additional performance indicators that reflect the company’s activities and more clearly present the environmental impact resulting from the transport of products. One such indicator could be CO2e emissions per transported kilometer.
In addition, organizations should set specific targets for transport-related emissions, which could help to achieve results in this area. Organizations will also find it easier to include relevant data in their sustainability reports.
The fast fashion industry, in particular, should focus on customer satisfaction, and customers should consider sustainability when making purchasing decisions. Customers play a crucial role in influencing fashion companies. It is recommended that fast fashion companies consider their environmental impact related to transportation, as this area may play an increasingly important role in the future. Companies that increase their transparency and detail in this area may find themselves in a winning position. Not only are they addressing emissions and making progress toward their goals, but they are also building trust with current and future customers.
Given the scope of fast fashion activities worldwide, it is worth paying attention to the requirements of EU directives and ensuring the implementation of sustainable development goals, particularly those related to reducing air emissions worldwide. Therefore, the environmental impact resulting from fast fashion transport activities may constitute a basis for future research and influence policy implications not only in the European Union but worldwide.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.-F., A.P. and J.K.B.; methodology, A.M.-F. and A.P.; software, A.M.-F. and A.P.; validation, A.M.-F., A.P. and J.K.B.; formal analysis, A.M.-F. and A.P.; investigation, A.M.-F. and A.P.; resources, A.M.-F. and A.P.; data curation, A.P.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.-F. and A.P.; writing—review and editing, A.M.-F., A.P. and J.K.B.; visualization, A.M.-F., A.P. and J.K.B.; supervision, A.M.-F., A.P. and J.K.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available in a publicly accessible repository. The original data presented in the study are openly available in references [54,55,56,58,59].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dzhengiz, T.; Haukkala, T.; Sahimaa, O. (Un)Sustainable Transitions towards Fast and Ultra-Fast Fashion. Fash. Text. 2023, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKinsey & Company Home Page. What Is Fast Fashion? Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/featured-insights/mckinsey-explainers/what-is-fast-fashion# (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Choi, T.M.; Cheng, T.C.E. Sustainable Fashion Supply Chain Management: From Sourcing to Retailing; Springer Series in Supply Chain Management (SSSCM) Series; Tang, E.S., Ed.; University of California Press: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 1, ISBN 978-3-319-12702-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bick, R.; Halsey, E.; Ekenga, C.C. The global environmental injustice of fast fashion. Environ. Health 2018, 17, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niinimäki, K. (Ed.) Sustainable Fashion in a Circular Economy; Aalto University: Espoo, Finland, 2018; ISBN 978-952-60-0089-3/978-952-60-0090-9. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/301138773.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- McKinsey & Company Home Page. The State of Fashion. 2017. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/state-of-fashion# (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Fashion United Home Page. Global Fashion Industry Statistics. Available online: https://fashionunited.com/global-fashion-industry-statistics (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Global Textile Source Home Page. Top 10 Clothing Manufacturing Countries in the World. 2023. Available online: https://globaltextilesource.com/news/top-10-clothing-manufacturing-countries-in-the-world (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Profolus Home Page. Fast Fashion: Advantages and Disadvantages. 2023. Available online: https://www.profolus.com/topics/fast-fashion-advantages-disadvantages (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Roos, S.; Zamani, B.; Sandin, G.; Peters, G.M.; Svanstrom, M. Will clothing be sustainable? Clarifying sustainable fashion. In Textiles and Clothing Sustainability: Implications in Textiles and Fashion; Muthu, S.S., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S. Environmental and Social Impact of Fashion: Towards an Eco-friendly, Ethical Fashion. Int. J. Interdiscip. Multidiscip. Stud. 2015, 2, 22–35. [Google Scholar]
- Gueye, S. The Trends and Trailblazers Creating a Circular Economy for Fashion. 2021. Available online: https://www.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/articles/the-trends-and-trailblazers-creating-a-circular-economy-for-fashion (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Ellen MacArthur Foundation Home Page. A New Textiles Economy: Redesigning Fashion’s Future. 2017. Available online: https://archive.ellenmacarthurfoundation.org/assets/downloads/A-New-Textiles-Economy.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Bailey, K.; Basu, A.; Sharma, S. The Environmental Impacts of Fast Fashion on Water Quality: A Systematic Review. Water 2022, 14, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF) Home Page. Handle with Care—Understanding the Hidden Environmental Costs of Cotton. Available online: https://www.worldwildlife.org/magazine/issues/spring-2014/articles/handle-with-care (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- Ki, C.W.; Park, S.; Ha-Brookshire, J.E. Toward a Circular Economy: Understanding Consumers’ Moral Stance on Corporations’ and Individuals’ Responsibilities in Creating a Circular Fashion Economy. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021, 30, 1121–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niinimäki, K.; Peters GRissanen TGwilt APerry, P.; Dahlbo, H. Paying the environmental price for fast fashion. Nat. Rev. EarthEnviron. 2020, 1, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostermann, C.M.; Steinbruch, F.K.; Callegaro-de-Menezes, D.; Nascimento, L.D.S. Drivers to implement the circular economy in born-sustainable business models: A case study in the fashion industry. Rev. Gestão 2021, 28, 223–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchi, A. The circular fashion—The implementation of the circular economy by the fashion industry. Curr. Trends Fash. Technol. Text. Eng. 2020, 6, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmeguid, A.; Afy-Sararah, M.; Salonitis, K. Investigating the challenges of applying the principles of the circular economy in the fashion industry: A systematic review. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 32, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelheit, E. How fast fashion can cut its staggering environmental impact. Nature 2022, 609, 653–654. [Google Scholar]
- Juanga-Labayen, J.P.; Labayen, I.V.; Yuan, Q. A review of textile recycling practices and challenges. Textiles 2022, 2, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Memon, H.A.; Wang, Y.; Marriam, I.; Tebyetekerwa, M. Circular Economy and sustainability of the clothing and textile Industry. Mat. Circ. Econ. 2021, 3, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNFCCC Home Page. UN Helps Fashion Industry Shift to Low Carbon. United Nations: United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. 2018. Available online: https://unfccc.int/news/un-helps-fashion-industry-shift-to-low-carbon (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- McKinsey & Company Home Page. Fashion on Climate—How the Fashion Industry Can Urgently Act to Reduce Its Greenhouse Gas Emissions. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/retail/our-insights/fashion-on-climate (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- McKinsey & Company Home Page. The McKinsey Report. 2020. Available online: https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2020/11/sustainable-fashion-reduce-greenhouse-gas-emissions (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- IPCC. Sixth Assessment Report Working Group III Home Page. Mitigation of Climate Change Chapter 10: Transport. Available online: https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg3/chapter/chapter-10 (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- McKinnon, A.; Browne, M.; Piecyk, M.; Whiteing, A. Green Logistics, Improving the Environmental Sustainability of Logistics, 3rd ed.; Kogan Page: London, UK, 2015; ISBN 1-5231-0374-4/0-7494-7186-7. [Google Scholar]
- Centobelli, P.; Cerchine, R.; Esposito, E. Evaluating environmental sustainability strategies in freight transport and logistics industry. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020, 29, 1563–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Xu, R. Assessing the role of environmental regulations in improving energy efficiency and reducing CO2 emissions: Evidence from the logistics industry. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 96, 106831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangiaracina, R.; Perego, A.; Perotti, S.; Tumino, A. Assessing the environmental impact of logistics in online and offline B2C purchasing processes in the apparel industry. Int. J. Logist. Syst. Manag. 2015, 23, 98–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storto, C.; Evangelista, P. Infrastructure efficiency, logistics quality and environmental impact of land logistics systems in the EU: A DEA-based dynamic mapping. Res. Transp. Bus. Manag. 2023, 46, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEA Home Page. Report 2021 Transport Topics. Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/transport (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- IEA Home Page. Report 2020 Energy Technology Perspectives. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/energy-technology-perspectives-2020 (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Statista Home Page. Energy Consumption in Global Road Freight Transport. Available online: https://www.statista.com/topics/7476/transportation-emissions-worldwide (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- European Environment Agency Home Page. Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Transport in Europe. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/analysis/indicators/greenhouse-gas-emissions-from-transport (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Bilgili, L. Operational Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Air, Rail, Road, and Sea Transport Modes in Life Cycle Perspective. In Transportation Energy and Dynamics; Sharma, S.K., Upadhyay, R.K., Kumar, V., Valera, H., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Meng, X.; Tian, J.; Xing, C.; Wang, C.; Wood, J.A. review of transportation carbon emissions research using bibliometric analyses. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2023, 10, 878–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, A.L.C.; Thome, A.M.T. Carbon Emissions in Transportation: A Synthesis Framework. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, D.; Altuntas, C. Sustainable supply chain management in the fast fashion industry: An analysis of corporate reports. Eur. Manag. J. 2014, 32, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, L.; Nadvi, K. Hiding in Plain Sight: Transparency and Ethics in Fashion Industry Global Value Chains. In International Business and SDG 8; Sinkovics, N., Sinkovics, R.R., Boussebaa, M., Fletcher, M., Eds.; The Academy of International Business, Palgrave Macmillan: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.S.W.; Seifert, M.; Cherrier, H. Anti-consumption and Governance in the Global Fashion Industry: Transparency is Key. In Governing Corporate Social Responsibility in the Apparel Industy after Rana Plaza; Hira, A., Benson-Rea, M., Eds.; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, B.; Sandin, G.; Peters, G.M. Life cycle assessment of clothing libraries: Can collaborative consumption reduce the environmental impact of fast fashion? J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 162, 1368–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.A. Literature Review, Container Shipping Supply Chain: Planning Problems and Research Opportunities. Logistic 2021, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovancová, J.; Popovičová, M.; Huttmanová, E. Decoupling transport-related greenhouse gas emissions and economic growth in the European Union countries. J. Sustain. Dev. Energy Water Environ. Syst. 2023, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, M.; Guan, D.; Yang, Z. The carbon footprint of fast fashion consumption and mitigation strategies—A case study of jeans. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, R.F.; Chi, T. A study of companies’ business responses to fashion e-commerce’s environmental impact. Int. J. Fash.Des. Technol. Educ. 2017, 11, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, R.M.; Souza, I.; Pereira, E.; Belém, A.C.; Pinto, C.M.; Lazzaris, J.; Fonseca, P. Characterizing project management of lean initiatives in industrial companies—Crossing perspectives based on case studies. Eng. Manag. Prod. Serv. 2023, 15, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, M.; Rosa, A.; Martins, A.; Jayantilal, S. Grounded Theory—An Illustrative in the Portuguese Footwear Industry. Adm. Sci. 2023, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A.; Warraich, M.A.; Sabir, S.S.; Waseem, A. Case Study Method: A Step-by-Step Guide for Business Researchers. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2019, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, C.; Tsikriktsis, N.; Frohlich, M. Case research in operations management. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2002, 22, 195–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H&M Group Home Page. Available online: https://hmgroup.com (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Science Based Targets Initiative Home Page. Target Dashboard. Available online: https://sciencebasedtargets.org/target-dashboard (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- H&M Group Sustainability Disclosure. 2023. Available online: https://hmgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/HM-Group-Sustainability-Disclosure-2023.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- H&M Group Climate Transition Plan. Available online: https://hmgroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Climate-Transition-Plan.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Inditex Annual Report. 2023. Available online: https://www.inditex.com/itxcomweb/api/media/9673b05d-e761-4558-8e1a-8c4f38344628/Inditex_Group_Annual_Report_2023.pdf?t=1710506486195 (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- InditexHome Page. Available online: www.inditex.com (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Inditex, Statement on Non-Finance Information. 2023. Available online: https://www.inditex.com/itxcomweb/api/media/cc6b203a-de08-4ff9-8989-e0ca52e03472/Statement_of_Non_Financial_Information_2023.pdf?t=1710759711321 (accessed on 29 July 2024).
- Inditex, Climate Transition Plan. Available online: https://www.inditex.com/itxcomweb/api/media/450e8c9d-3266-4ffe-abb0-62fe206a188c/Inditex+Climate+Transition+Plan.pdf?t=1710345903031 (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Carbon Analytics Home Page. Scope 3—Category 4: Upstream Transportation and Distribution—Carbon Analytics. Available online: https://www.carbonanalytics.com/blog/scope-3-category-4-upstream-transportation-and-distribution (accessed on 3 August 2024).
- GreenHouse Gas Protocol Home Page. Chapter 4.pdf. Available online: https://ghgprotocol.org (accessed on 3 August 2024).
- Shein GroupHome Page. Available online: https://www.sheingroup.com/our-impact (accessed on 30 July 2024).
- Shein Group Home Page. ESG Reports. Sustainability and Social Impact Report. 2022. Available online: https://www.sheingroup.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/2022_SHEIN_SustainabilitySocialImpactReport-1.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).