Big Data Analytics and Organizational Performance: Mediating Roles of Green Innovation and Knowledge Management in Telecommunications
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Operational Definition of the Key Variables
1.2. Resource Based View (RBV) as Underpinning Theory
2. Literature Review and Hypothesis Development
2.1. BDA and OP
2.2. KM and GI
2.3. GI as a Mediator
2.4. KM as a Mediator
2.5. BDATCs as Moderators between BDA and GI
2.6. BDATCs as Moderators between BDA and OP
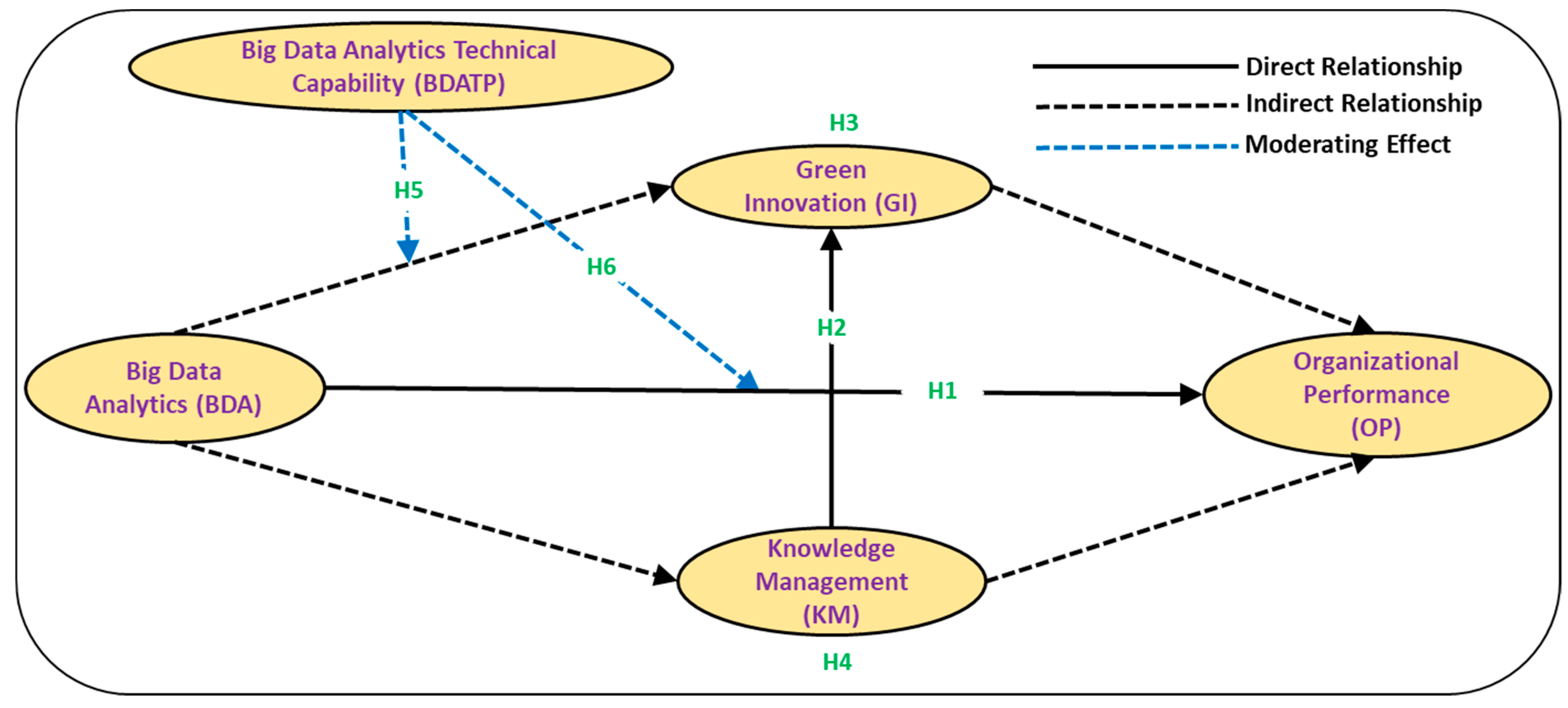
3. Proposed Research Framework
4. Methodology
5. Pre-Test and Pilot-Test
5.1. Demographic Profile of the Respondents
5.2. Common Method Bias (CMB)
6. Data Analysis
6.1. Data Analysis and Findings
6.2. Common Method Bias (CMB)
6.3. Inter-Correlations of the Study Variables
6.4. Demographic Profile of the Respondents
6.5. Evaluation of Measurement Model (Outer Model)
6.6. Assessment of Structural (Inner) Model
7. Hypotheses Testing Results
8. Discussion
9. Theoretical Implications
10. Managerial Implications
11. Limitations and Future Research Directives
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, H.; Chiang, R.H.; Storey, V.C. Business intelligence and analytics: From big data to big impact. MIS Q. 2012, 36, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, A.W. Big data analytics capabilities and green supply chain performance: Investigating the moderated mediation model for green innovation and technological intensity. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2022, 28, 1446–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khatib, A.W. Can big data analytics capabilities promote a competitive advantage? Green radical innovation, green incremental innovation and data-driven culture in a moderated mediation model. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2022, 28, 1025–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kassar, A.-N.; Singh, S.K. Green innovation and organizational performance: The influence of big data analytics. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 146, 706–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhloufi, A.; Boubker, N.; Bouri, A. Big data analytics, knowledge management and firm performance: The mediating role of business innovation capability. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 154, 651–662. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, B.; Kumar, A.; Upadhyay, P. Big data analytics capability and firm performance: The role of knowledge management capability as a mediator. Inf. Syst. Front. 2023; advance online publication. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, A.; Sağsan, M. Knowledge management and green innovation: The mediating role of big data analytics. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zameer, H.; Wang, Z. Impact of business analytics on green innovation and competitive advantage: The moderating role of environmental management accounting. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 339, 130256. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, T.; Ahmed, I.; Philbin, S.P. The impact of big data analytics on organizational performance: The role of knowledge management. J. Knowl. Manag. 2023, 27, 182–202. [Google Scholar]
- Dahiya, N.; Singh, R.; Kaur, A. Big data analytics and competitive advantage in manufacturing firms: The role of organizational culture and technological capability. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2022, 35, 130–152. [Google Scholar]
- Mikalef, P.; Boura, M.; Lekakos, G.; Krogstie, J. Big data analytics capabilities and innovation: The mediating role of dynamic capabilities and moderating effect of the environment. Br. J. Manag. 2019, 30, 272–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Hussain, S.; Ahmad, M.A.; Rashid, A. The role of big data analytics in improving firm performance: The mediating role of knowledge management and the moderating role of environmental dynamism. J. Innov. Knowl. 2021, 6, 172–181. [Google Scholar]
- Waqas, M.; Tan, K.C. Big data analytics technical capabilities and organizational performance: The moderating role in green innovation and knowledge management. J. Bus. Res. 2023, 150, 631–642. [Google Scholar]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, A.; Mazzoleni, A. The role of big data analytics in driving green innovation and organizational performance. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 228, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahiya, R.; Le, S.; Ring, J.K.; Watson, K. Big data analytics and competitive advantage: The strategic role of firm-specific knowledge. J. Strategy Manag. 2022, 15, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Arabi, S.; Rab, R. Feasibility and challenges of 5g network deployment in least developed countries (ldc). Wirel. Sens. Netw. 2021, 13, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.H.; Chen, J.S.; Chen, P.C. Effects of green innovation on environmental and corporate performance: A stakeholder perspective. Sustainability 2015, 7, 4997–5026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitzl, C. The use of partial least squares structural equation modelling (PLS-SEM) in management accounting research: Directions for future theory development. J. Account. Lit. 2016, 37, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kock, N. Common method bias in PLS-SEM: A full collinearity assessment approach. Int. J. e-Collab. (IJEC) 2015, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Sarstedt, M.; Ringle, C.M.; Gudergan, S.P. Advanced Issues in Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. Mod. Methods Bus. Res. 1998, 295, 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Routledge: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Kiron, D.; Prentice, P.K.; Ferguson, R.B. The analytics mandate. MIT Sloan Manag. Rev. 2014, 55, 1–25. Available online: https://sloanreview.mit.edu/projects/analytics-mandate/ (accessed on 26 July 2024).
- Wang, Y.; Kung, L.; Wang WY, C.; Cegielski, C.G. Developing a big data-enabled transformation model in healthcare: A practice-based view. Inf. Manag. 2018, 55, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, R.; Gunasekaran, A.; Childe, S.J.; Wamba, S.F.; Papadopoulos, T. The impact of big data on world-class sustainable manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 105, 3565–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; George, J.F. Toward the development of a big data analytics capability. Inf. Manag. 2016, 53, 1049–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S. The drivers of green brand equity: Green brand image, green satisfaction, and green trust. J. Bus. Ethics 2020, 93, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Khan, S.A.R.; Kumar, A. The impact of big data analytics on green innovation and firm performance in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 247, 119832. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M.; Walsh, G.; Lerner, D.; Fitza, M.A.; Li, Q. Green innovation, managerial concern and firm performance: An empirical study. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2018, 27, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côrte-Real, N.; Oliveira, T.; Ruivo, P. Assessing business value of Big Data Analytics in European firms. J. Bus. Res. 2017, 70, 379–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciampi, F.; Demi, S.; Magrini, A.; Marzi, G.; Papa, A. Exploring the impact of big data analytics capabilities on business model innovation: The mediating role of entrepreneurial orientation. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 123, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, S.; Wamba, S.F.; Gunasekaran, A.; Dubey, R.; Childe, S.J. How to improve firm performance using big data analytics capability and business strategy alignment? Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2016, 182, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Kung, L.; Byrd, T.A. Big data analytics: Understanding its capabilities and potential benefits for healthcare organizations. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2020, 126, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Constructs | BDA | GI | KM | OP | BDATC | Mean | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDA | 1 | 3.677 | 0.581 | ||||
| GI | 0.441 ** | 1 | 3.539 | 0.548 | |||
| KM | 0.495 ** | 0.435 ** | 1 | 3.580 | 0.615 | ||
| OP | 0.781 ** | 0.537 ** | 0.663 ** | 1 | 3.550 | 0.629 | |
| BDATC | 0.520 ** | 0.414 ** | 0.778 ** | 0.632 ** | 1 | 3.570 | 0.648 |
| Constructs | Items | F.L | CA | CR | AVE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDA | BDA 1 | 0.780 | 0.895 | 0.897 | 0.658 |
| BDA 2 | 0.875 | ||||
| BDA 3 | 0.838 | ||||
| BDA 4 | 0.849 | ||||
| BDA 5 | 0.782 | ||||
| BDA 6 | 0.731 | ||||
| BDATC | BDATC 1 | 0.660 | 0.916 | 0.93 | 0.71 |
| BDATC 2 | 0.890 | ||||
| BDATC 3 | 0.868 | ||||
| BDATC 4 | 0.894 | ||||
| BDATC 5 | 0.891 | ||||
| BDATC 6 | 0.829 | ||||
| GI | GI 1 | 0.076 | 0.913 | 0.916 | 0.698 |
| GI 2 | 0.866 | ||||
| GI 3 | 0.824 | ||||
| GI 4 | 0.832 | ||||
| GI 5 | 0.854 | ||||
| GI 6 | 0.867 | ||||
| KM | KM 1 | 0.764 | 0.903 | 0.906 | 0.674 |
| KM 2 | 0.855 | ||||
| KM 3 | 0.854 | ||||
| KM 4 | 0.846 | ||||
| KM 5 | 0.805 | ||||
| KM 6 | 0.836 | ||||
| OP | OP 1 | 0.821 | 0.93 | 0.931 | 0.741 |
| OP 2 | 0.881 | ||||
| OP 3 | 0.867 | ||||
| OP 4 | 0.905 | ||||
| OP 5 | 0.837 | ||||
| OP 6 | 0.851 |
| HTNT | Fornell Larker | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Constructs | BDA | BDATC | GI | KM | OP | Constructs | BDA | BDATC | GI | KM | OP |
| BDA | BDA | 0.811 | |||||||||
| BDATC | 0.574 | BDATC | 0.526 | 0.843 | |||||||
| GI | 0.516 | 0.479 | GI | 0.472 | 0.442 | 0.835 | |||||
| KM | 0.546 | 0.856 | 0.507 | KM | 0.499 | 0.78 | 0.465 | 0.821 | |||
| OP | 0.825 | 0.667 | 0.623 | 0.703 | OP | 0.759 | 0.622 | 0.574 | 0.703 | 0.861 | |
| Targeted Companies | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Grameenphone Ltd. | Largest company with GSM and 5 G technology in Bangladesh |
| Robi Axiata Limited | Second-largest mobile company, providing 4.5 G across all 64 districts |
| Banglalink Digital Communications Limited | Third-largest mobile network company |
| Teletalk Bangladesh Ltd. | Government mobile operator company for public |
| Bangladesh Telecommunications Company Limited (BTCL) | Provides landline telecommunications services across urban areas |
| R-Square | Endogenous Variables | R Square | R Square Adjusted | 0.26: Substantial, 0.13: Moderate, 0.02: Weak [25] | |
| GI | 0.297 | 0.291 | |||
| KM | 0.249 | 0.248 | |||
| OP | 0.707 | 0.704 | |||
| Effect Size (F-Square) | Exogenous Variables | GI | KM | OP | 0.35: Substantial, 0.15: Medium effect, 0.02 Weak effect [25] |
| BDA | 0.064 | 0.332 | 0.53 | ||
| GI | 0.082 | ||||
| KM | 0.029 | 0.092 | |||
| Collinearity (Inner VIF) | Exogenous Variables | DC | DIL | SAE | VIF ≤ 5.0 [21] |
| BDA | 1.949 | 1 | 2.073 | ||
| GI | 1.422 | ||||
| KM | 2.738 | 2.817 | |||
| Hypotheses | OS/Beta | SD | 95% C.I Blas Corrected | T | P | Decision | Mediation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LL | UL | |||||||
| H1: BDA -> OP | 0.567 | 0.062 | 0.449 | 0.681 | 9.124 | 0 | Supported | |
| H2: KM -> GI | 0.236 | 0.115 | 0.022 | 0.445 | 2.053 | 0.041 | Supported | |
| H3: BDA -> GI -> OP | 0.055 | 0.031 | 0.01 | 0.125 | 1.998 | 0.046 | Supported | Partial |
| H4: BDA -> KM -> GI | 0.118 | 0.056 | 0.003 | 0.222 | 2.094 | 0.037 | Supported | Partial |
| H5: BDATC × BDA -> GI | −0.006 | 0.052 | −0.104 | 0.098 | 0.112 | 0.911 | Not Supported | |
| H6: BDATC × BDA -> OP | 0.06 | 0.029 | 0.002 | 0.118 | 2.064 | 0.04 | Supported | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aljehani, S.B.; Abdo, K.W.; Nurul Alam, M.; Aloufi, E.M. Big Data Analytics and Organizational Performance: Mediating Roles of Green Innovation and Knowledge Management in Telecommunications. Sustainability 2024, 16, 7887. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16187887
Aljehani SB, Abdo KW, Nurul Alam M, Aloufi EM. Big Data Analytics and Organizational Performance: Mediating Roles of Green Innovation and Knowledge Management in Telecommunications. Sustainability. 2024; 16(18):7887. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16187887
Chicago/Turabian StyleAljehani, Sultan Bader, Khalid Waleed Abdo, Mohammad Nurul Alam, and Esam Mohammed Aloufi. 2024. "Big Data Analytics and Organizational Performance: Mediating Roles of Green Innovation and Knowledge Management in Telecommunications" Sustainability 16, no. 18: 7887. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16187887
APA StyleAljehani, S. B., Abdo, K. W., Nurul Alam, M., & Aloufi, E. M. (2024). Big Data Analytics and Organizational Performance: Mediating Roles of Green Innovation and Knowledge Management in Telecommunications. Sustainability, 16(18), 7887. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16187887






