The Impact of Using Different Types of Compost on the Growth and Yield of Corn
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Setup
- Compost 1: sewage sludge (165 kg) + sawdust (35 kg);
- Compost 2: sewage sludge (90 kg) + sawdust (10 kg) + garden and park waste (100 kg);
- Compost 3: garden and park waste (180 kg) + sawdust (20 kg);
- Compost 4: sewage sludge (165 kg) + sawdust (35 kg) + earthworms;
- Compost 5: sewage sludge (90 kg) + sawdust (10 kg) + garden and park waste (100 kg) + earthworms;
- Compost 6: garden and park waste (180 kg) + sawdust (20 kg) + earthworms.
- A-Soil without any fertilizer;
- B-Soil + Polifoska®8 + Pulrea + INu;
- C-Soil + Compost 1: sewage sludge (165 kg) + sawdust (35 kg);
- D-Soil + Compost 2: sewage sludge (90 kg) + sawdust (10 kg) + garden and park waste (100 kg);
- E-Soil + Compost 3: garden and park waste (180 kg) + sawdust (20 kg);
- F-Soil + Compost 4: sewage sludge (165 kg) + sawdust (35 kg) + earthworms;
- G-Soil + Compost 5: sewage sludge (90 kg) + sawdust (10 kg) + garden and park waste (100 kg) + earthworms;
- H-Soil + Compost 6: garden and park waste (180 kg) + sawdust (20 kg) + earthworms.
2.2. Chemical Analysies of Compost
2.3. Seed Material
2.4. Experimental Design
2.5. Chlorophyll Fluorescence
2.6. Measurement of Gas Exchange
2.7. Soil Plant Analysis Development
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Compost Properties
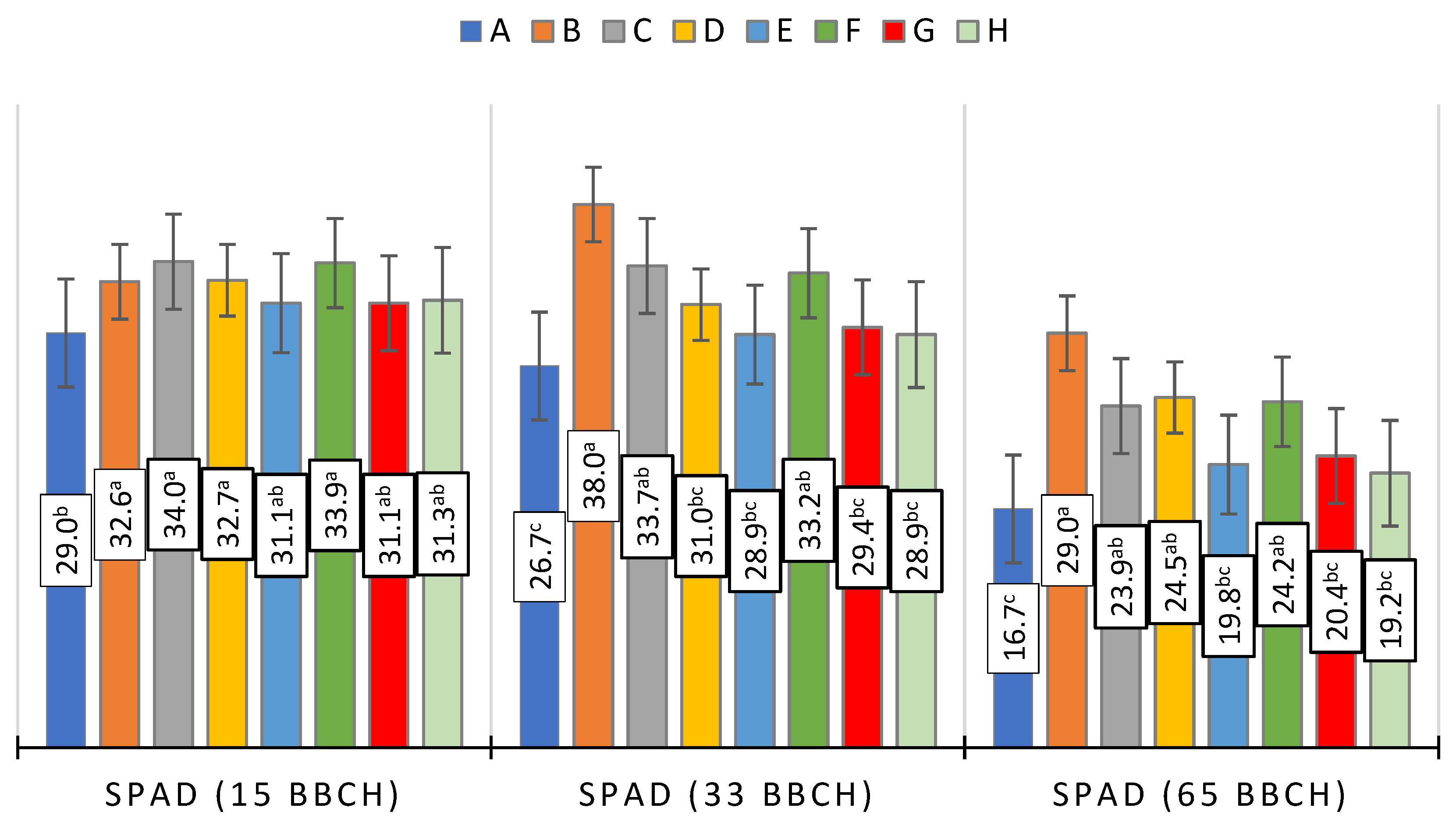
3.2. Relative Content of Chlorophyll
3.3. Chlorophyll Fluorescence
3.4. Gas Exchange
3.5. Biometric Parameters of Plants
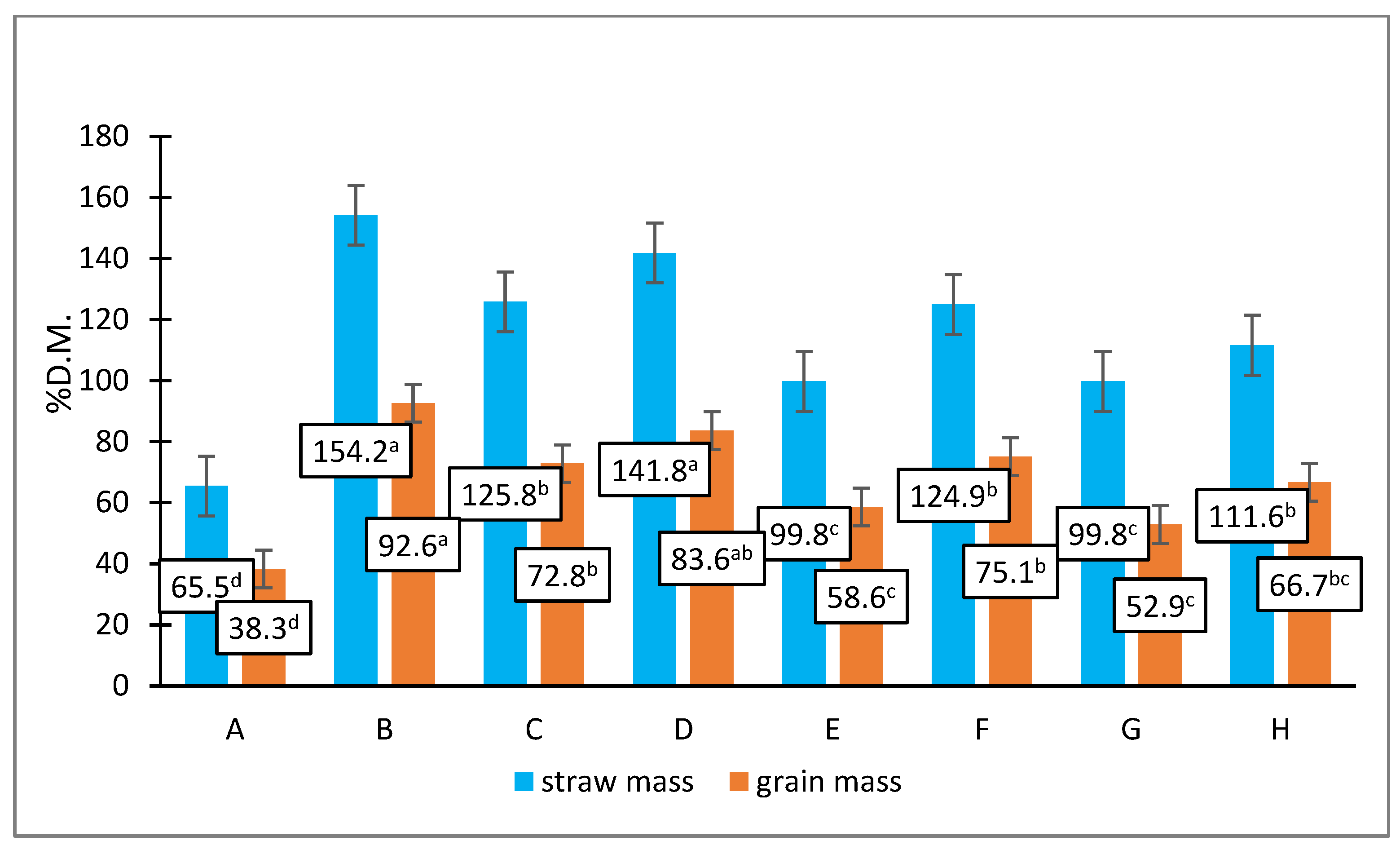
3.6. Plant Dry Weight and Grain Yield per Plant
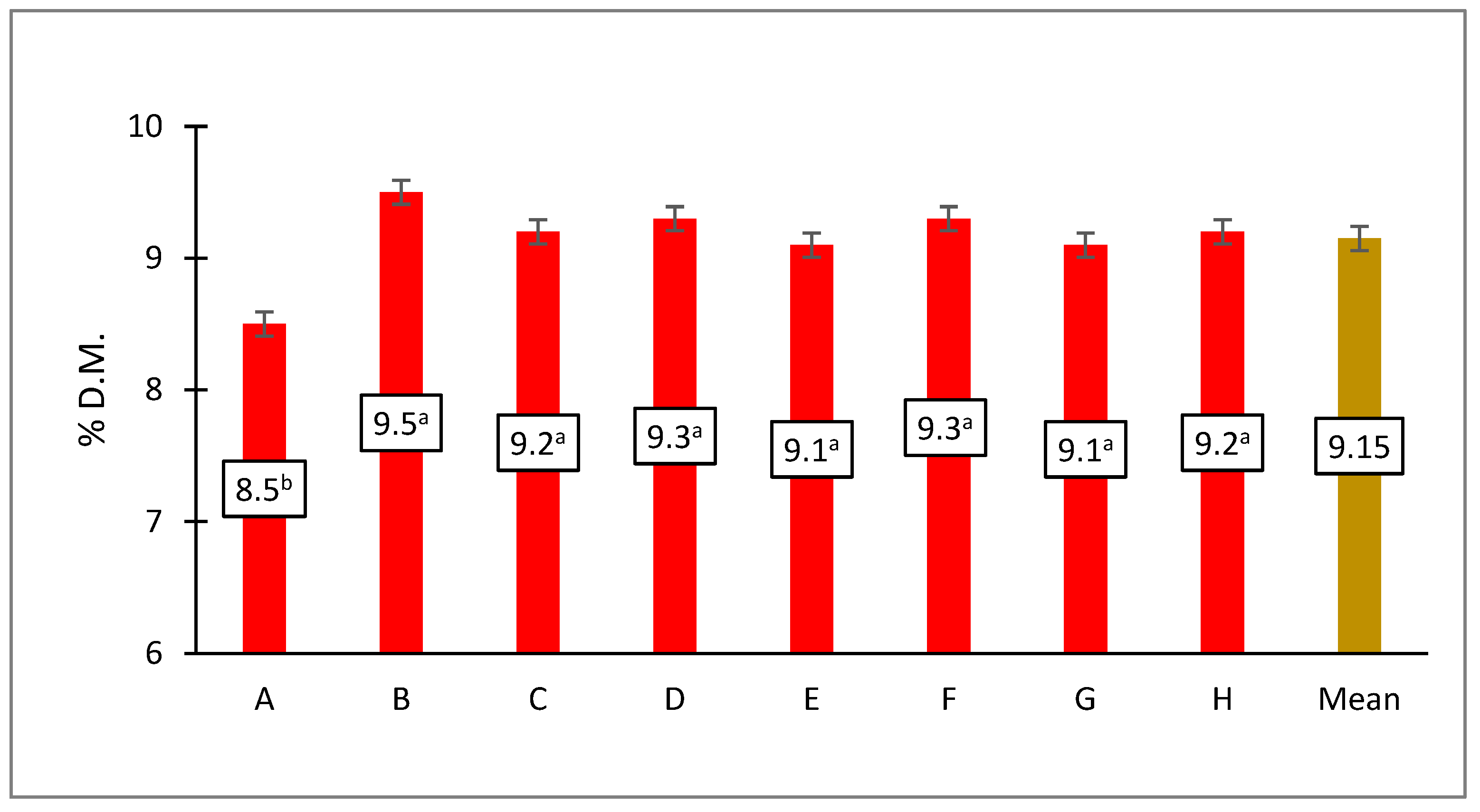
3.7. Protein Content in Grain
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sayara, T.; Basheer-Salimia, R.; Hawamde, F.; Sánchez, A. Recycling of Organic Wastes through Composting: Process Performance and Compost Application in Agriculture. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporchia, F.; Caro, D. Exploring the potential of circular solutions to replace inorganic fertilizers in the European Union. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, S.M.; Kandhro, M.A.; Bughio, Z.U.R.; Rajpar, I.; Shah, J.A.; Lund, M.M.; Bughio, H.U.R. Relative performance of various composts and NPK fertilizer on upgrowth and quality of foddermaize. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2021, 10, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strenner, M.; Chmelíková, L.; Hülsbergen, K.J. Compost fertilization in organic agriculture- A Comparison of the impact on corn plants using field spectroscopy. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oluwa, O.E.; Ade Oluwa, O.O.; Aduramigba-Modupe, V.O. Residual fertilizer value of OBD-pluscompost for maize (Zea mays) production. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2015, 6, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Gu, X.; Du, Y.; Zheng, X.; Lu, S.; Cheng, Z.; Cai, W.; Chang, T. Optimizing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilization regimes to improve maize productivity under double ridge-furrow planting with full film mulching. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.L.; Yan, Y.; Cao, J.; Christie, P.; Fan, M.S. Effects of combined application of organic amendments and fertilizers on crop yield and soil organic matter: An integrated analysis of long-term experiments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 225, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmitrowicz-Iwan, J.; Ligęza, S.; Pranagal, J.; Smal, H.; Wójcikowska-Kapusta, A. Improving acidic sandy soil properties for plant growth with dam reservoir sediments in the face of soaring fertiliser prices. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 234, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.P.; Letey, J. Organic farming challenge of timing nitrogen availability to crop nitrogen requirements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Yang, Y.D.; Zhao, J.; Nie, J.W.; Zang, H.D.; Zeng, Z.H.; Olesen, J.E. Yield benefits from replacing chemical fertilizers with manure under water deficient conditions of the winter wheat–summer maize system in the North China Plain. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 119, 126118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezahegn, A.M. Role of integrated nutrient management for sustainable maize production. Int. J. Agron. 2021, 2021, 9982884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zheng, H.F.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.Z.; Han, H.F.; Ning, T.Y. Crop-Livestock integration via maize straw recycling increased carbon sequestration and crop production in China. Agric. Syst. 2023, 210, 103722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anning, D.K.; Ghanney, P.; Qiu, H.; Abalori, T.A.; Zhang, C.; Luo, C. Stimulation of soil organic matter fractions by maize straw return and nitrogen fertilization in the Loess Plateau of Northwest China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 191, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Dai, S.; Meng, L.; He, M.; Wang, X.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, J.; Nardi, P.; Müller, C. Effects of 18 years repeated N fertilizer applications on gross N transformation rates in a subtropical rain-fed purple soil. App. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.M.; Sylvester-Bradly, R.; Philipps, L.; Hatch, D.J.; Cuttle, S.P.; Rayns, F.W.; Gosling, P. Is the productivity of organic farms restricted by the supply of available nitrogen? Soil Use Manag. 2002, 18, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Arshad, M.; Khalid, A.; Zahir, Z.A. Effectiveness of organic-/bio-fertilizer supplemented with chemical fertilizers for improving soil water retention, aggregate stability, growth and nutrient uptake of maize (Zea mays L.). J. Sustain. Agric. 2008, 31, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, U.; Afzaal, M.; Haq, I.U.; Qazi, A.; Yasar, A.; Tabinda, A.B.; Mahfooz, Y.; Naz, A.U.; Awan, H.A.; Ahmad, A. Investigating the effect of Aspergillus niger inoculated press mud (biofertilizer) on the potential of enhancing maize (Zea mays L.) yield, phosphorous use efficiency, and phosphorous agronomic efficiency. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, E.; Okoth, P.F.; Stoorvogel, J.J.; Berecha, G.; Mellisse, B.T.; Mekuriaw, A.; Gebre, S.; Selassie, Y.G.; Biratu, G.K.; Smaling, E.M. Cereal yields in Ethiopia relate to soil properties and N and P fertilizers. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosystems 2023, 126, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mącik, M.; Gryta, A.; Sas-Paszt, L.; Frąc, M. New insight into the soil bacterial and fungal microbiome after phosphorus biofertilizer application as an important driver of regenerative agriculture including biodiversity loss reversal and soil health restoration. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, K.T.; Kamara, A.Y.; Huising, J.; Adam, A.M.; Shehu, B.M.; Jibrin, J.M. Implication of blanket NPK application on nutrient balance of maize based on soil and tissue diagnosis approaches in the savannas of northern Nigeria. Environ. Res. Commun. 2023, 5, 065007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiss, L.; Demyan, M.S.; Fulford, A.; Hurisso, T.; Culman, S.W. High-throughput soil health assessment to predict corn agronomic performance. Field Crops Res. 2023, 297, 108930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Jia, J.; Liao, W.; Amsili, J.P.; Schneider, R.L.; van Es, H.M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Applicability of soil health assessment for wheat-maize cropping systems in smallholders’ farmlands. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 353, 108558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sądej, W.; Żołnowski, A.C. Comparison of the effect of various long-term fertilization systems on the content and fractional composition of humic compounds in Lessive soil. Plant Soil Environ. 2019, 65, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sądej, W.; Żołnowski, A.C.; Marczuk, O. Content of phenolic compounds in soils originating from two long-term fertilization experiments. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2016, 42, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocwa, A.; Harsanyi, E.; Széles, A.; Holb, I.J.; Szabó, S.; Rátonyi, T.; Mohammed, S. A bibliographic review of climate change and fertilization as the main drivers of maize yield: Implications for food security. Agric. Food. Secur. 2023, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mącik, M.; Gryta, A.; Sas-Paszt, L.; Frąc, M. The status of soil microbiome as affected by the application of phosphorus biofertilizer: Fertilizer enriched with beneficial bacterial strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarajuoghi, M.; Ardakani, M.R.; Nurmohammadi, G.; Kashani, A.; Rejali, F.; Mafakheri, S. Response of yield and yield components of maize (Zea mays L.) to different biofertilizers and chemical fertilizers. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2012, 12, 315–320. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, S.; Qiang, R.; Lu, E.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Q. Response of soil microbial community structure to phosphate fertilizer reduction and combinations of microbial fertilizer. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 899727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; El-Sawah, A.M.; Ali, D.F.I.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Shaghaleh, H.; Sheteiwy, M.S. The integration of bio and organic fertilizers improve plant growth, grain yield, quality and metabolism of hybrid maize (Zea mays L.). Agronomy 2020, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhou, H.; Xu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Wang, J. Fertilization highly increased the water use efficiency of spring maize in dryland of northern china: A meta-analysis. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.H.; Xu, M.G.; Gao, S.D.; Yang, X.Y.; Huang, S.M.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, B.R. Nitrogen use efficiency in a wheat–corn cropping 465 system from 15 years of manure and fertilizer applications. Field Crops Res. 2014, 157, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murmu, K.; Swain, D.K.; Ghosh, B.C. Comparative Assessment of Conventional and Organic Nutrient Management on Crop Growth and Yield and Soil Fertility in Tomato-Sweet Corn Production System. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 1617–1626. Available online: https://www.cropj.com/murmu_7_11_2013_1617_1626.pdf (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Taj, A.; Bibi, H.; Akbar, W.A.; Rahim, H.U.; Iqbal, M.; Ullah, S. Effect of poultry manure and NPK compound fertilizer on soil physicochemical parameters, NPK availability, and uptake by spring maize (Zea mays L.) in alkaline-calcareous soil. Gesunde Pflanz. 2023, 75, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Wu, S.; Meng, Q.; Feng, H.; Siddique, K.H.M. Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions by replacing inorganic fertilizer with organic fertilizer in wheat–maize rotation systems in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efosa, N.; Krause, H.M.; Hüppi, R.; Krauss, M.; Vaucher, N.; Zourek, F.; Mayer, J.; Six, J.; Bünemann, E.K. Emissions of nitrous oxide and methane after field application of liquid organic fertilizers and biochar. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 356, 108642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Tan, S.; Chen, Y.; Yan, P.; Wang, X. Effects of substituting synthetic nitrogen with organic amendments on crop yield, net greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprint: A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2023, 301, 109035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ortega, J.; Álvaro-Fuentes, J.; Cantero-Martínez, C. The use of double-cropping in combination with no-tillage and optimized nitrogen fertilization reduces soil N2O emissions under irrigation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zilio, M.; Sigurnjak, I.; Robles-Aguilar, A.A.; Michels, E.; Adani, F.; De Neve, S.; Meers, E. Dynamics of soil nitrogen and N-cycling-related genes following the application of biobased fertilizers. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 191, 105033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Guo, H.; Xu, H.; Yang, X.; Yao, Z.; Gu, J. Maize stalk incorporation increases N2O emissions that offset the benefit of SOC sequestration in a winter wheat-summer maize field: A four-year measurement in long-term fertilizer experiments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 352, 108507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xin, X.; Meng, L.; Yan, X.; Zhao, C.; Cai, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, J.; Müller, C. Long-term appropriate N management can continuously enhance gross N mineralization rates and crop yields in a maize-wheat rotation system. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 59, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadu, C.O.; Aneke, N.G.; Egbuna, S.O.; Agulanna, A.C. Comparative studies on the impact of bio-fertilizer produced from agro-wastes using thermo-tolerant actinomycetes on the growth performance of Maize (Zea-mays) and Okro (Abelmoschus esculentus). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2018, 12, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabourifard, H.; Estakhr, A.; Bagheri, M.; Hosseini, S.J.; Keshavarz, H. The quality and quantity response of maize (Zea mays L.) yield to planting date and fertilizers management. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 2, 100196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, R.K.; Behera, D.; Mohapatra, K.K.; Sethi, D.; Mandal, M.; Patra, A.K.; Ravindran, B. Juxtaposing the quality of compost and vermicompost produced from organic wastes amended with cow dung. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 114119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey Chowdhury, S.; Suhaib, K.H.; Bhunia, P.; Surampalli, R.Y. A critical review on the vermicomposting of organic wastes as a strategy in circular bioeconomy: Mechanism, performance, and future perspectives. Environ. Technol. 2023, 5, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Jha, S.; Singh, S.P.; Kumar, M.; Kumari, R.; Padbhushan, R. Organic waste recycling by vermicomposting amended with rock phosphate impacts the stability and maturity indices of vermicompost. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2023, 73, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, K.K.; Noppradit, P.; Techato, K. Potential of Eisenia fetida (Redworm) for the conversion of three varieties of organic waste. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2023, 12, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupani, P.F.; Embrandiri, A.; Garg, V.K.; Abbaspour, M.; Dewil, R.; Appels, L. Vermicomposting of green organic wastes using Eisenia fetida under field conditions: A case study of a green campus. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 2519–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hassanin, A.S.; Samak, M.R.; Ahmed, S.M.; Afifi, M.M.; El-Satar, A.; Aml, M. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals during composting and vermicomposting processes of sewage sludge. Egypt J. Chem. 2022, 65, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rékási, M.; Ragályi, P.; Sándor, D.B.; Szabó, A.; Rivier, P.A.; Farkas, C.; Szecsy, O.; Uzinger, N. Effect of composting and vermicomposting on potentially toxic element contents and bioavailability in sewage sludge digestate. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 21, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapałowska, A.; Skwiercz, A.; Tereba, A.; Puchalski, C.; Malewski, T. Next-Generation Sequencing for Evaluating the Soil Nematode Diversity and Its Role in Composting Processes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapałowska, A.; Matłok, N.; Piechowiak, T.; Szostek, M.; Puchalski, C.; Balawejder, M. Physiological and Morphological Implications of Using Composts with Different Compositions in the Production of Cucumber Seedlings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, U. Growth Stages of Mono-and Dicotyledonous Plants; BBCH Monograph; Federal Biological Research Centre for Agriculture and Forestry: Berlin, Germany; Braunschweig, Germany, 2001; p. 158. Available online: https://www.yumpu.com/en/document/view/16359822/growth-stages-of-mono-and-dicotyledonous-plants-regione- (accessed on 19 November 2023).
- Ortiz-Monasterio, J.I.; Sayre, K.D.; Rajaram, S.; Mcmahon, M. Genetic progress in wheat yield and nitrogen use efficiency under four nitrogen rates. Crop Sci. 1997, 37, 898–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, S.G.; Hoogenboom, G.; Nunes, M.R.; Martin-Ryals, A.D.; Sanchez, P.A. Circular agriculture increases food production and can reduce N fertilizer use of commercial farms for tropical environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 163031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, N.; Rana, D.; Joshi, N. Role of Earthworm (Eisenia fetida) in Bioconversion of Kitchen Waste in a World of Shifting Climatic Condition. In Advances in Waste Management; Siddiqui, N.A., Baxtiyarovich, A.S., Nandan, A., Mondal, P., Eds.; AIR 2021; Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Singapore, 2023; Volume 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Morais, E.G.; Silva, C.A.; Maluf, H.J.G.M.; Paiva, I.D.O.; de Paula, L.H.D. Effects of compost-based organomineral fertilizers on the kinetics of NPK release and maize growth in contrasting oxisols. Waste Biomass Valorization 2023, 14, 2299–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Dwyer, L.M.; Dutilleul, P.; Doug, W.S.; Ma, B.L.; Smith, D.L. Inter-relationships of applied nitrogen, SPAD, and yield of leafy and non-leafy maize genotypes. J. Plant Nutr. 2001, 24, 1173–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, P.; Bocianowski, J.; Nowosad, K.; Zielewicz, W.; Kobus-Cisowska, J. SPAD leaf greenness index: Green mass yield indicator of maize (Zea mays L.), genetic and agriculture practice relationship. Plants 2021, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.K.; Yeasmin, S.; Mohiuddin, K.M.; Chowdhury, M.A.H.; Saha, B.K. Peat-based organo-mineral fertilizer improves nitrogen use efficiency, soil quality, and yield of baby corn (Zea mays L.). Sustainability 2023, 15, 9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, F.; Heydari, M.; Golchin, A.; Igdelou, N.K.M. Effect of bio-fertilizers on corn (Zea mays L.) growth characteristics in Cd-spiked soils. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 2651–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, K.; Johnson, G.N. Chlorophyll fluorescence—A practical guide. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, L.; Critchley, C.; van Rensen, J.J. New fluorescence parameters for monitoring photosynthesis in plants. Photosynth. Res. 2003, 78, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wan, D.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Gaffney, P.P.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L. Anti-substitution effect of coupling crop and livestock production on fertilizer use: Evidence from Chinese smallholder farms. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 412, 137359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniswami, D.M.; Buvaneshwari, K.; Fathima, R.M.L.; Naveena, T.; Pabitha, B.; Reshma, S.; Rangila, D.; Santhiya, P.; Sharmila, D.N.; Ahamed, R.A.; et al. Comparative assessment of different biofertilizers in maize (Zea mays L.) cultivation. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 5661–5679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, M.Y.; Khade, S.K.; Patil, V.A. Effect of biofertilizers on yield and yield components of maize (Zea mays L.) varieties eco-92 and african tall. Int. J. Curr. Res. 2019, 11, 5149–5153. [Google Scholar]
- Amanolahi-Baharvand, Z.; Zahedi, H.; Sharghi, Y.; Seifolahi-Nik, S. Comparative assessment of conventional and organic nutrient management on yield and yield components of three corn cultivars. Int. J. Biosci. 2014, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajami, N. Evaluation effectiveness of chemical and biological fertilizers combination on corn (Zea mays L.) yield. J. Crop Nutr. Sci. 2016, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yessoufou, M.W.; Tovihoudji, P.G.; Sissou, Z.; Adjogboto, A.; Djenontin, A.J.; Akponikpè, P.I. Hill-placement of manure and fertilizer for improving maize nutrient-and water-use efficiencies in the northern Benin. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Yu, X.; Liang, J.; Mao, Z.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, X. A full recycling chain of food waste with straw addition mediated by black soldier fly larvae: Focus on fresh frass quality, secondary composting, and its fertilizing effect on maize. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Matos Nascimento, A.; Maciel, A.M.; Silva, J.B.G.; Mendonça, H.V.; de Paula, V.R.; Otenio, M.H. Biofertilizer application on corn (Zea mays) increases the productivity and quality of the crop without causing environmental damage. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Yao, Z.; Qiu, X.; Wang, J.; He, W. Biogas slurry topdressing as replacement of chemical fertilizers reduces leaf senescence of maize by up-regulating tolerance mechanisms. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, X.L.; Qin, S.W.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhu, A.M.; Yang, Y.L.; Zhang, X.F. Yield, phosphorus use efficiency and balance response to substituting long-term chemical fertilizer use with organic manure in a wheat-maize system. Field Crops Res. 2017, 208, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buligon, E.L.; Costa, L.A.M.; de Lucas, J., Jr.; Santos, F.T.; Goufo, P.; Costa, M.S.S.M. Fertilizer performance of a digestate from swine wastewater as synthetic nitrogen substitute in maize cultivation: Physiological growth and yield responses. Agriculture 2023, 13, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dineshkumar, R.; Subramanian, J.; Gopalsamy, J.; Jayasingam, P.; Arumugam, A.; Kannadasan, S.; Sampathkumar, P. The impact of using microalgae as biofertilizer in maize (Zea mays L.). Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M. Organic amendments alter microbiota assembly to stimulate soil metabolism for improving soil quality in wheat-maize rotation system. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 339, 117927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.C.; Zhao, N.; Huang, F.; Lv, Y.Z. Long-term effects of different organic and inorganic fertilizer treatments on soil organic carbon sequestration and crop yields on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.C.; Wang, Z.B.; Zhai, Y.C.; Zhang, L.H.; Zheng, M.J.; Yao, H.P.; Lv, L.H.; Sheng, H.P.; Zhang, J.T.; Yao, Y.R.; et al. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic fertilizer benefits grain yield, water use efficiency, and economic return of summer maize. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 217, 105287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadlalla, H.A.; Abukhlaif, H.A.; Mohamed, S.S. Effects of chemical and bio-fertilizers on yield, yield components and grain quality of maize (Zea mays L.). Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 11, 4654–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Gawad, A.M.; Morsy, A.S.M. Integrated impact of organic and inorganic fertilizers on growth, yield of maize (Zea mays L.) and soil properties under Upper Egypt conditions. J. Plant Prod. 2017, 8, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Sadras, V.O.; Wang, Z.; Du, W.; Lei, X.; Yang, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Lu, G.; et al. Yield-and protein-neutral reduction in fertilizer rate for wheat, maize and rice can reduce the release of reactive nitrogen and greenhouse gas emissions in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 064031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.W.; Ru, S.B.; Hou, Z.N.; Li, J.H. A suitable organic fertilizer substitution ratio could improve maize yield and 463 soil fertility with low pollution risk. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 988663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Uddin, S.; Ullah, O.; Shah, S.; Ali, S.U.D.T.; Ud Din, I. Yield and yield components of maize response tocompost and fertilizer-nitrogen. Food Sci. Qual. Manag. 2012, 38, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Laekemariam, F.; Gidago, G. Response of maize (Zea mays L.) to integrated fertilizer application in Wolaita, South Ethiopia. Adv. Life Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 21–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Huang, G. Effects of organic amendment incorporation on maize (Zea mays L.) growth, yield and water-fertilizer productivity under arid conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 269, 107663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Christie, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Maize yield and soil fertility with combined use of compost and inorganic fertilizers on a calcareous soil on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naderi, R.; Ghadiri, H. Urban waste compost, manure and nitrogen fertilizer effects on the initial growth of corn (Zea mays L.). Desert 2010, 15, 159–165. [Google Scholar]
- Olowoake, A.A.; Osunlola, O.S.; Ojo, J.A. Influence of compost supplemented with jatropha cake on soil fertility, growth, and yield of maize (Zea mays L.) in a degraded soil of Ilorin, Nigeria. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2018, 7, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jjagwe, J.; Chelimo, K.; Karungi, J.; Komakech, A.J.; Lederer, J. Comparative performance of organic fertilizers in maize (Zea mays L.) growth, yield, and economic results. Agronomy 2020, 10, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezahegn, A.M. Effect of Organic Fertilizers on Maize (Zea mays L.) Production and Soil Physical and Chemical Properties. World Appl. Sci. J. 2021, 39, 11–19. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter | Compost Variants | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compost 1 | Compost 2 | Compost 3 | Compost 4 | Compost 5 | Compost 6 | |
| pH in KCl | 5.9c | 6.3c | 7.1b | 5.8c | 7.1b | 8.1a |
| Dry matter (%) | 27.6d | 35.7c | 55.5a | 26.3d | 35.8c | 44.9b |
| N (%) | 4.02 ± 0.32a | 1.82 ± 0.14c | 1.01 ± 0.08d | 2.59 ± 0.20b | 1.86 ± 0.14c | 1.56 ± 0.12cd |
| P2O5 (g·kg−1 d.m.) | 13.00 ± 1.04a | 1.09 ± 0.01d | 2.01 ± 0.16cd | 9.42 ± 0.75b | 8.89 ± 0.71b | 3.64 ± 0.29c |
| K2O5 (g·kg−1 d.m.) | 4.93 ± 0.30bc | 6.88 ± 0.55ab | 4.63 ± 0.37c | 5.09 ± 0.40b | 7.63 ± 0.61a | 7.28 ± 0.58a |
| C:N (%) | 19.25 ± 0.91d | 23.57 ± 0.86c | 37.72 ± 0.54a | 28.06 ± 0.42b | 21.29 ± 0.38cd | 30.32 ± 0.19b |
| Mg (%) | 0.32 ± 0.03b | 0.32 ± 0.03b | 0.20 ± 0.00b | 0.34 ± 0.03b | 0.3 ± 0.03b | 0.51 ± 0.02a |
| Ca (%) | 1.7 ± 0.11bc | 1.52 ± 0.09c | 1.95 ± 0.08b | 2.13 ± 0.02ab | 1.64 ± 0.15c | 2.34 ± 0.14a |
| Pb (mg·kg−1 d.m.) | 10.0 ± 0.8a | <8.0a | <8.0a | <8.0a | <8.0a | <8.0a |
| Cr (mg·kg−1 d.m.) | <10c | <10c | 12.0 ± 0.96b | 12.0 ± 0.93b | 11.0 ± 0.90b | 23.0 ± 1.84a |
| Cu (mg·kg−1 d.m.) | 70.0 ± 5.6b | 58.0 ± 4.64c | 16.0 ± 1.28e | 84.0 ± 6.72a | 45.0 ± 3.6d | 16.0 ± 1.28e |
| Ni (mg·kg−1 d.m.) | <5.0b | <5.0b | 5.3 ± 0.42b | <5.0b | 5.1 ± 0.40b | 11.0 ± 0.88a |
| Cd (mg·kg−1 d.m.) | 0.44 ± 0.03ab | 0.42 ± 0.03ab | 0.34 ± 0.03b | 0.5 ± 0.05a | 0.38 ± 0.03b | 0.35 ± 0.03b |
| Zn (mg·kg−1 d.m.) | 253 ± 20.2b | 223 ± 17.8c | 91.0 ± 7.28d | 274 ± 21.91a | 232 ± 18.56c | 78.0 ± 6.24e |
| Hg (mg·kg−1 d.m.) | 0.132 ± 0.01b | 0.104 ± 0.01c | 0.026 ± 0.01d | 0.18 ± 0.01a | 0.066 ± 0.01d | 0.042 ± 0.01d |
| Variant | Fv/Fm (Maximal Photochemical Efficiency of PSII) | Fv/F0 (Maximum Quantum Yield of Primary Photochemistry) | PI (Performance Index) | RC/ABS (Total Numer of Active Reaction Centes for Absorbtion) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.78 ± 0.002b | 3.74 ± 0.05b | 3.11 ± 0.87d | 1.45 ± 0.25b |
| B | 0.82 ± 0.006a | 4.05 ± 0.14a | 4.37 ± 0.94b | 1.77 ± 0.26ab |
| C | 0.80 ± 0.007ab | 4.07 ± 0.17a | 4.62 ± 2.05ab | 1.71 ± 0.53ab |
| D | 0.81 ± 0.003a | 3.99 ± 0.07a | 4.22 ± 0.89b | 1.68 ± 0.24ab |
| E | 0.77 ± 0.009b | 3.70 ± 0.28b | 3.68 ± 1.18cd | 1.74 ± 0.34ab |
| F | 0.81 ± 0.009a | 4.03 ± 0.30a | 5.21 ± 1.64a | 2.01 ± 0.41a |
| G | 0.78 ± 0.007b | 3.77 ± 0.20b | 3.88 ± 1.75bc | 1.64 ± 0.49ab |
| H | 0.77 ± 0.009b | 3.76 ± 0.21b | 3.37 ± 1.42cd | 1.54 ± 0.39ab |
| Variant | Gs (Stomatal Conductance, mmlo (H2O)·m−2s−1) | E (Transpiration Rate, mmlo (H2O)·m−2s−1) | CI (Intercellular CO2 Concentration, µmol (CO2) mmol−1) | PN (Net Photosynthetic Rate, µmol (CO2)·m−2s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.11 ± 0.03a | 1.65 ± 0.25a | 188.0 ± 15.3a | 12.1 ± 2.61bc |
| B | 0.10 ± 0.09a | 1.39 ± 0.84a | 183.0 ± 45.3a | 10.8 ± 7.84c |
| C | 0.08 ± 0.02a | 1.27 ± 0.24a | 139.0 ± 39.9de | 11.5 ± 1.01bc |
| D | 0.16 ± 0.08a | 2.05 ± 0.73a | 133.5 ± 34.7e | 19.8 ± 5.88a |
| E | 0.13 ± 0.02a | 1.93 ± 0.18a | 168.5 ± 15.2ab | 15.3 ± 1.65ab |
| F | 0.10 ± 0.02a | 1.62 ± 0.16a | 163.2 ± 24.9bc | 13.1 ± 2.76bc |
| G | 0.13 ± 0.01a | 1.95 ± 0.08a | 152.0 ± 20.9cd | 16.7 ± 1.82ab |
| H | 0.13 ± 0.01a | 1.91 ± 0.09a | 147.0 ± 11.7cd | 16.4 ± 1.19ab |
| Variant | Plant Height (cm) | Length of Cob (cm) | Number of Grains in the Cob | Thousand Grain Weight (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 132.9 ± 13.91c | 11.50 ± 0.58c | 155.5 ± 56.1c | 248.1 ± 6.52e |
| B | 188.9 ± 14.58a | 17.50 ± 0.58a | 324.0 ± 51.6a | 285.2 ± 3.48a |
| C | 168.5 ± 7.12ab | 15.75 ± 1.89ab | 266.0 ± 44.1b | 273.5 ± 3.52bc |
| D | 174.5 ± 11.13ab | 15.50 ± 1.29ab | 302.3 ± 27.3ab | 276.6 ± 2.22ab |
| E | 160.1 ± 9.76b | 13.63 ± 1.25b | 221.0 ± 60.6b | 264.9 ± 5.04cd |
| F | 167.4 ± 11.41ab | 14.75 ± 1.50ab | 273.1 ± 60.7ab | 274.6 ± 2.94b |
| G | 160.2 ± 10.59b | 14.00 ± 2.16ab | 200.3 ± 29.8bc | 264.6 ± 3.39cd |
| H | 161.8 ± 10.80b | 13.25 ± 1.89b | 254.5 ± 45.8b | 261.8 ± 2.42d |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zapałowska, A.; Jarecki, W. The Impact of Using Different Types of Compost on the Growth and Yield of Corn. Sustainability 2024, 16, 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020511
Zapałowska A, Jarecki W. The Impact of Using Different Types of Compost on the Growth and Yield of Corn. Sustainability. 2024; 16(2):511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020511
Chicago/Turabian StyleZapałowska, Anita, and Wacław Jarecki. 2024. "The Impact of Using Different Types of Compost on the Growth and Yield of Corn" Sustainability 16, no. 2: 511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020511







