Survey of Antifungal in Surface- and Groundwater: A Portuguese Environmental Case Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
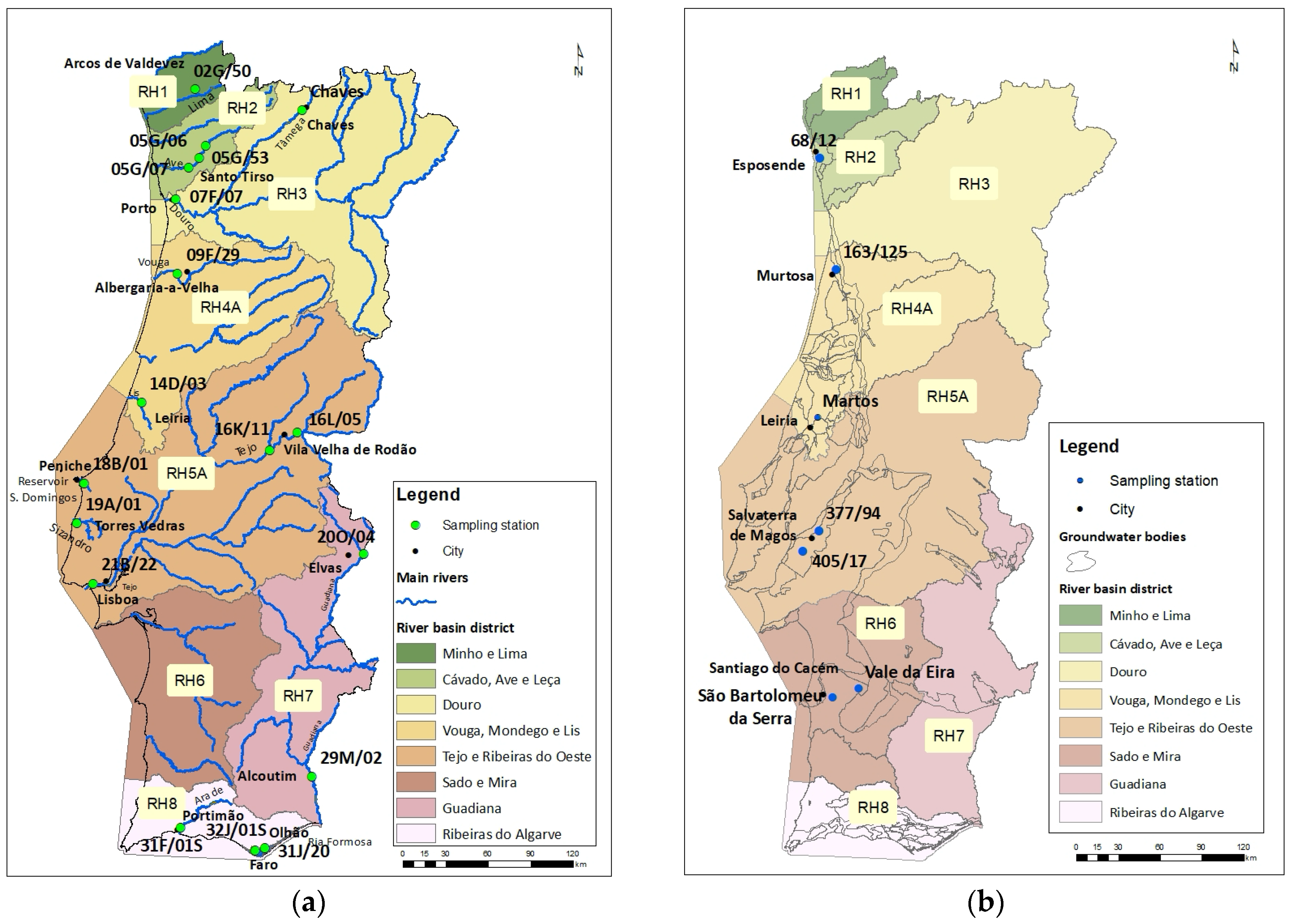
2.1. Sampling Stations and Characterisation
2.2. Passive Sampler Field Deployment
2.3. Qualitative Analysis of Antifungals in Surface-Groundwater and Data Analysis
2.4. Physicochemical Properties and Key Environmental Fate Attributes of Detected Antifungal
3. Results
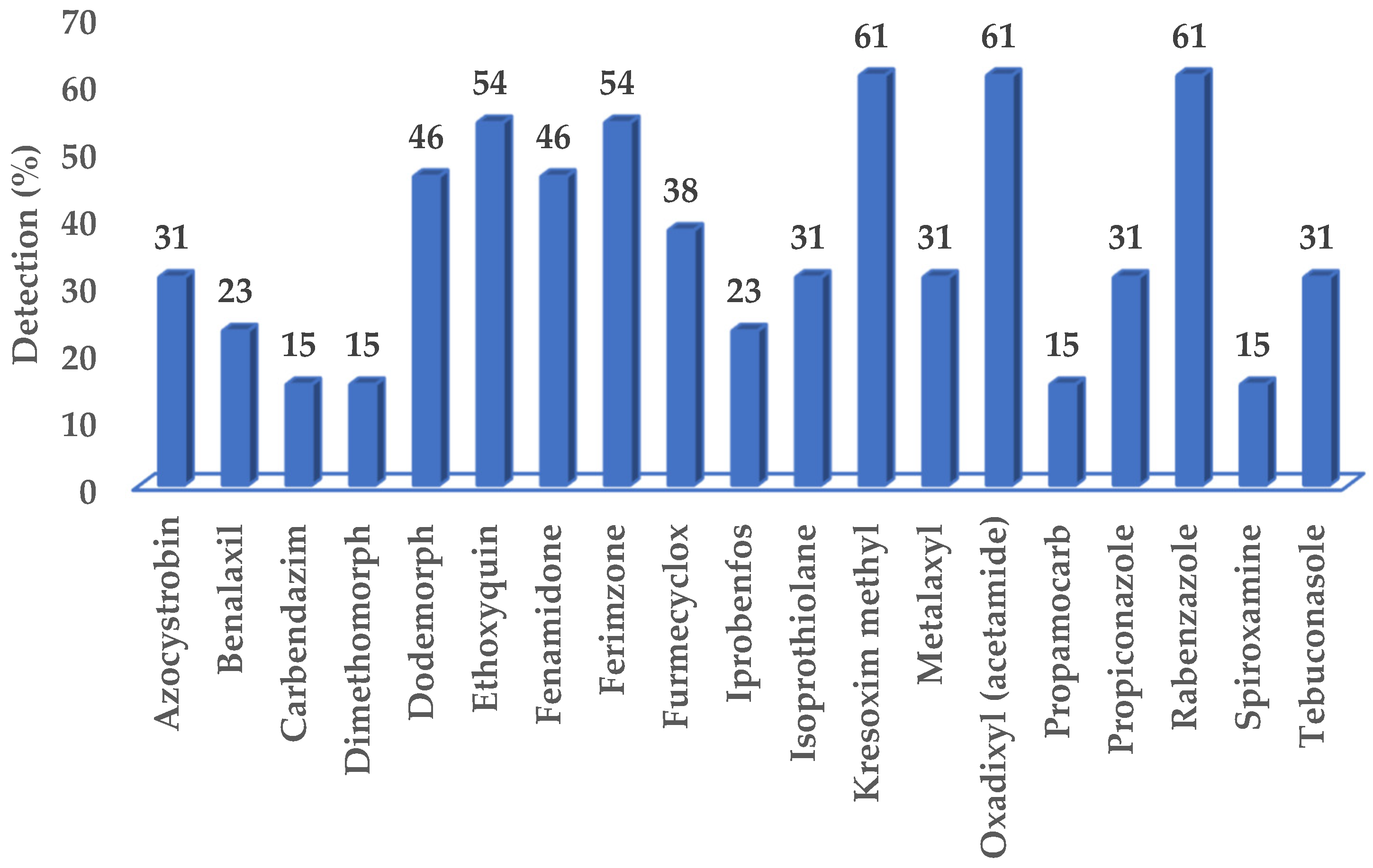
3.1. Fungicides Detected in Surface Water
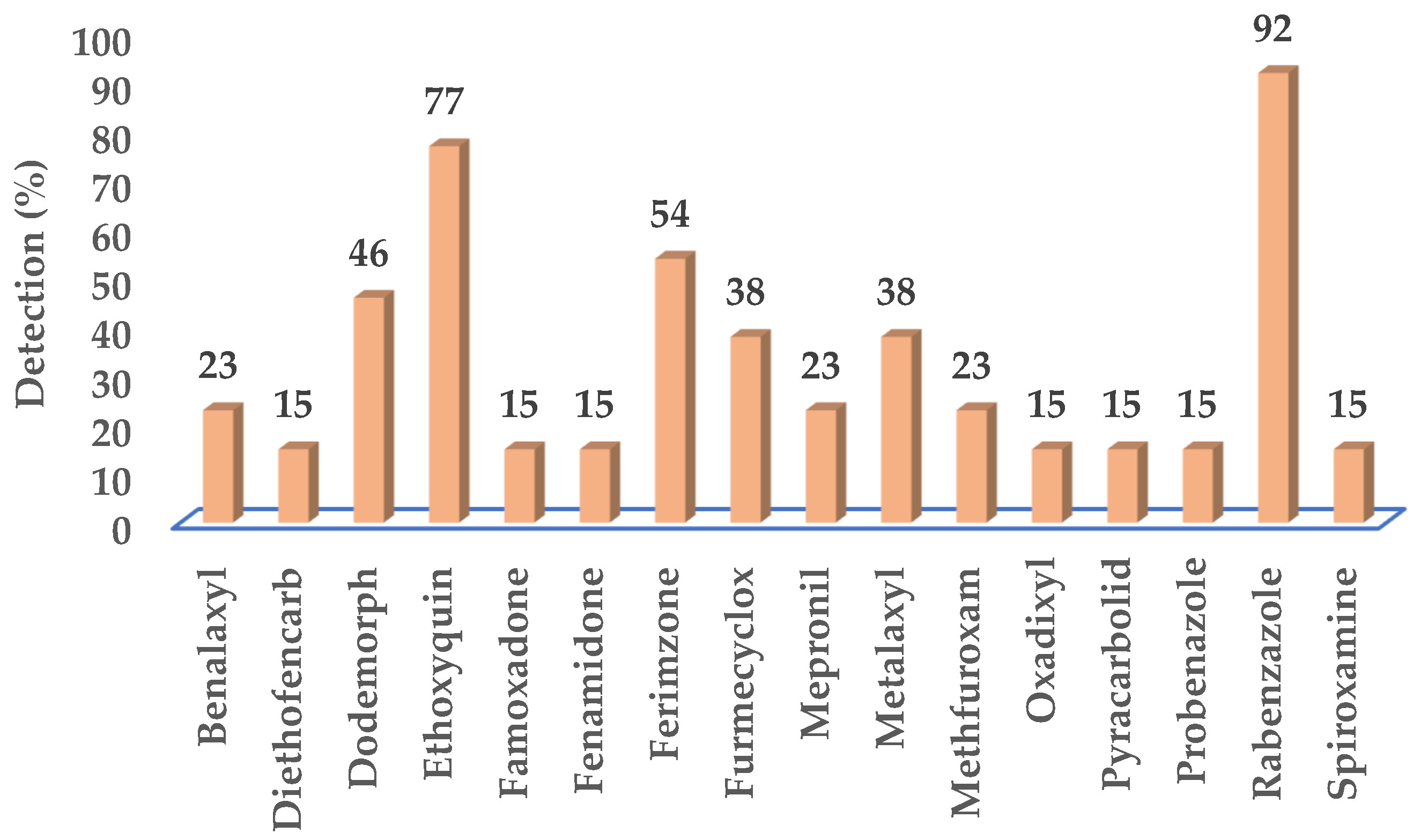
3.2. Fungicides Detected in Groundwater
3.3. Environmental Fate Parameters, Detection Frequency and Regulatory Status of All Detected Fungicides
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fisher, M.C.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Berman, J.; Bicanic, T.; Bignell, E.M.; Bowyer, P.; Bromley, M.; Brüggemann, R.; Garber, G.; Cornely, O.A.; et al. Tackling the Emerging Threat of Antifungal Resistance to Human Health. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 557–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hof, H. Critical Annotations to the Use of Azole Antifungals for Plant Protection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 2987–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infarmed, i.p. Estatística Do Medicamento e Produtos de Saúde. 2019. Available online: https://www.infarmed.pt/documents/15786/1229727/Estat%C3%ADstica+do+Medicamento+2019/b2e448a8-dc71-c2e8-a93a-f0cbef7ad6eb?version=1.0 (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Eurostat. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Agri-environmental_indicator_-_consumption_of_pesticides (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Direção-Geral de Alimentação e Veterinária. Relatório de Vendas de Produtos Fitofarmacêuticos de. 2019. Available online: https://www.dgav.pt/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/Relatorio-Vendas-2019.pdf (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Bebber, D.P. Weather Does Influence Fungal and Oomycete Crop Disease Outbreaks, but ProMED-mail Reports Don’t Prove It. New Phytol. 2022, 234, 1557–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, F.; Cazzato, S.; Walder, F.; Vogelgsang, S.; Bender, S.F.; Heijden, M.G.A. Humidity and High Temperature Are Important for Predicting Fungal Disease Outbreaks Worldwide. New Phytol. 2022, 234, 1553–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, V.S.; Rezende, C.P.; Pessoni, A.M.; De Paula, R.G.; Rangappa, K.S.; Nayaka, S.C.; Gupta, V.K.; Almeida, F. Antifungal Agents in Agriculture: Friends and Foes of Public Health. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joint Programming Initiative on Antimicrobial Resistance, JPIAMR. Strategic Research and Innovation Agenda on Antimicrobial Resistance. 2021. Available online: https://www.jpiamr.eu/app/uploads/2021/06/JPIAMR_SRIA_2021.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- World Health Organization. WHO Fungal Priority Pathogens List to Guide Research, Development and Public Health Action; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, E.M.; Warnock, D.W.; Luker, J.; Porter, S.R.; Scully, C. Emergence of Azole Drug Resistance in Candida Species from HIV-Infected Patients Receivingprolonged Fluconazole Therapy for Oral Candidosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1995, 35, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinkauf, N.; Monnet, D. Risk Assessment on the Impact of Environmental Usage of Triazoles on the Development and Spread of Resistance to Medical Triazoles in Aspergillus Species; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control: Stockholm, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Pristov, K.E.; Ghannoum, M.A. Resistance of Candida to Azoles and Echinocandins Worldwide. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, R.; Méndez, S.; Cobas, J.; Carro, N.; Neuparth, T.; Alves, N.; Santos, M.M.; Quintana, J.B.; Rodil, R. Occurrence of Persistent and Mobile Chemicals and Other Contaminants of Emerging Concern in Spanish and Portuguese Wastewater Treatment Plants, Transnational River Basins and Coastal Water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harman, C.; Allan, I.J.; Vermeirssen, E.L.M. Calibration and Use of the Polar Organic Chemical Integrative Sampler—A Critical Review. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 2724–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EC DIRECTIVE 2013/39/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council, Brussels, Belgium. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2013:226:0001:0017:EN:PDF (accessed on 2 July 2023).
- EC DIRECTIVE 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council, Brussels, Belgium. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32008L0105 (accessed on 2 July 2023).
- Guidance on Surface Water Chemical Monitoring under the Water Framework Directive; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2009.
- Garcia-Rodríguez, A.; Fontàs, C.; Matamoros, V.; Almeida, M.I.G.S.; Cattrall, R.W.; Kolev, S.D. Development of a Polymer Inclusion Membrane-Based Passive Sampler for Monitoring of Sulfamethoxazole in Natural Waters. Minimising the Effect of the Flow Pattern of the Aquatic System. Microchem. J. 2016, 124, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2022/1307 of 22 July 2022 Establishing a Watch List of Substances for Union-Wide Monitoring in the Field of Water Policy Pursuant to Directive 2008/105/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (Notified under Document C(2022) 5098). Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dec_impl/2022/1307/oj (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Viana, P.; Meisel, L.; Lopes, A.; de Jesus, R.; Sarmento, G.; Duarte, S.; Sepodes, B.; Fernandes, A.; dos Santos, M.M.C.; Almeida, A.; et al. Identification of Antibiotics in Surface-Groundwater. A Tool towards the Ecopharmacovigilance Approach: A Portuguese Case-Study. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.A.; Tzilivakis, J.; Warner, D.; Green, A. An International Database for Pesticide Risk Assessments and Management. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2016, 22, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Substance Information—ECHA. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/pt/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/ (accessed on 25 August 2023).
- ECHA Registration Dossier. Methyl N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-DL-Alaninate. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/pt/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/21739/5/4/1 (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- United States Environmental Protection Agency CompTox Chemicals Dashboard. Available online: https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/ (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- Suzuki, T.; Kondo, H.; Yaguchi, K.; Maki, T.; Suga, T. Estimation of Leachability and Persistence of Pesticides at Golf Courses from Point-Source Monitoring and Model to Predict Pesticide Leaching to Groundwater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information PubChem Compound Summary for CID 86298, Dimethomorph. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Dimethomorph#section=Environmental-Fate-Exposure-Summary (accessed on 16 June 2023).
- Evaluation of the New Active Cyflufenamid in the Product Cyflamid 50EW Fungicide. Public Release Summary. 2012. Available online: https://www.apvma.gov.au/sites/default/files/publication/13656-prs-cyflufenamid.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Active Substances, Safeners and Synergists. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/start/screen/active-substances (accessed on 16 September 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Conclusion on the Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Carbendazim. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Lu, Y. Residues and Dynamics of Probenazole in Rice Field Ecosystem. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 639–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Fenamidone. EFSA J. 2016, 14, 4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECHA Registration Dossier. Cis-4-[3-(p-Tert-Butylphenyl)-2-Methylpropyl]-2,6-Dimethylmorpholine. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/pt/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/33075/5/5/2 (accessed on 20 June 2023).
- AgData-Ferimzone. Available online: https://www.agropages.com/AgroData/Detail-631.htm (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- European Food Safety Authority. Conclusion on the Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Ethoxyquin. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, E.S.; Tsachidou, B.; Sułowicz, S.; Menkissoglu-Spiroudi, U.; Karpouzas, D.G. Land Spreading of Wastewaters from the Fruit-Packaging Industry and Potential Effects on Soil Microbes: Effects of the Antioxidant Ethoxyquin and Its Metabolites on Ammonia Oxidizers. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Conclusion on the Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Spiroxamine. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Picoxystrobin. EFSA J. 2016, 14, e04515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority. Conclusion on the Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Kresoxim-Methyl. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Arena, M.; Auteri, D.; Barmaz, S.; Bellisai, G.; Brancato, A.; Brocca, D.; Bura, L.; Byers, H.; Chiusolo, A.; et al. Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment of the Active Substance Trifloxystrobin. EFSA J. 2017, 15, e04989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; De Mello-Sampayo, C.; Lopes, A.; Carvalho da Silva, R.; Viana, P.; Meisel, L. Predicted Environmental Risk Assessment of Antimicrobials with Increased Consumption in Portugal during the COVID-19 Pandemic; The Groundwork for the Forthcoming Water Quality Survey. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assress, H.A.; Selvarajan, R.; Nyoni, H.; Mamba, B.B.; Msagati, T.A.M. Antifungal Azoles and Azole Resistance in the Environment: Current Status and Future Perspectives—A Review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 1011–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindberg, R.H.; Fick, J.; Tysklind, M. Screening of Antimycotics in Swedish Sewage Treatment Plants—Waters and Sludge. Water Res. 2010, 44, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruć-Fijałkowska, R.; Dragon, K.; Drożdżyński, D.; Górski, J. Seasonal Variation of Pesticides in Surface Water and Drinking Water Wells in the Annual Cycle in Western Poland, and Potential Health Risk Assessment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Ouyang, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, X.; He, M.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.; Lin, C. Occurrence, Spatiotemporal Dynamics, and Ecological Risk of Fungicides in a Reservoir-Regulated Basin. Environ. Int. 2023, 171, 107697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiryaki, O.; Temur, C. The Fate of Pesticide in the Environment. J. Biol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 4, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Chitescu, C.L.; Oosterink, E.; de Jong, J.; Stolker, A.A.M. Accurate Mass Screening of Pharmaceuticals and Fungicides in Water by U-HPLC–Exactive Orbitrap MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 403, 2997–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Ou, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Jin, J.; Tan, J. Occurrence and Ecological Potential of Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products in Groundwater and Reservoirs in the Vicinity of Municipal Landfills in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabenzazole. Available online: https://www.echemi.com/products/pid_Seven41424-rabenzazole.html (accessed on 26 September 2023).
- Robinson, R.F.A.; Mills, G.A.; Gravell, A.; Schumacher, M.; Fones, G.R. Occurrence of Organic Pollutants in the River Itchen and River Test—Two Chalk Streams in Southern England, UK. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 17965–17983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Pastor, P.; Triacchini, G. The 2018 European Union Report on Pesticide Residues in Food; European Food Safety Authority (EFSA): Parma, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, F.; Chena, X.; Liua, X.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Shan, W.; Zheng, Y. Simultaneous Determination of Five Pyrazole Fungicides in Cereals, Vegetables and Fruits Using Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1262, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 38441, Rabenzazole. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Rabenzazole (accessed on 2 September 2023).
- Pluym, N.; Burkhardt, T.; Rögner, N.; Scherer, G.; Weber, T.; Scherer, M.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Monitoring the Exposure to Ethoxyquin between 2000 and 2021 in Urine Samples from the German Environmental Specimen Bank. Environ. Int. 2023, 172, 107781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Additives, Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP); Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Bastos, M.D.L.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Fašmon Durjava, M.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; López Puente, S.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of a Feed Additive Consisting of Ethoxyquin (6-ethoxy-1,2-dihydro-2,2,4-trimethylquinoline) for All Animal Species (FEFANA Asbl). EFSA J. 2022, 20, e07166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Journal of the European Union. Commission Decision of 8 December 2008 Concerning the Non-Inclusion of Certain Active Substances in Annex I to Council Directive 91/414/EEC and the Withdrawal of Authorisations for Plant Protection Products Containing These Substances. 2008. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eudn/2008/941/contents (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Official Journal of the European Union Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2022/1375 of 5 August 2022 Concerning the Denial of Authorisation of Ethoxyquin as a Feed Additive Belonging to the Functional Group of Antioxidants and Repealing Implementing Regulation (EU) 2017/962. 2022. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg_impl/2022/1375/oj (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Chau, H.T.C.; Kadokami, K.; Duong, H.T.; Kong, L.; Nguyen, T.T.; Nguyen, T.Q.; Ito, Y. Occurrence of 1153 Organic Micropollutants in the Aquatic Environment of Vietnam. Adv. Environ. Chem. Pollut. 2015, 25, 7147–7156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fungicides for Wood Protection—World Viewpoint and Evaluation/Testing in Slovakia. In Fungicides; Carisse, O. (Ed.) InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2010; pp. 95–122. ISBN 978-953-307-266-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chaplain, V.; Mamy, L.; Vieuble-Gonod, L.; Mougin, C.; Benoit, P.; Barriuso, E.; Nelieu, S. Fate of Pesticides in Soils: Toward an Integrated Approach of Influential Factors. In Pesticides in the Modern World—Risks and Benefits; Stoytcheva, M., Ed.; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2011; ISBN 978-953-307-458-0. [Google Scholar]
- European Union. Commission Regulation (EU) 2015/400-of 25 February 2015-Amending Annexes II, III and V to Regulation (EC) No 396/2005 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards Maximum Residue Levels; Official Journal of the European Union: Brussels, Belgium, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, J.; Le Coustumer, P.; Peyraube, N.; Granger, D.; Thiennot, R.; Ley, L. Occurrence of Fungicide Oxadixyl in the Surface Water of an Urban Lake. Environ. Anal. Ecol. Stud. 2019, 6, 638–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabale, R.P.; Shabeer TP, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Utture, S.C.; Banerjee, K.; Oulkar, D.P.; Adsule, P.G.; Deshmukh, M.B. Adsorption–Desorption and Leaching Behavior of Kresoxim-Methyl in Different Soils of India: Kinetics and Thermodynamic Studies. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo, S.; Romo, S.; Soria, J.; Picó, Y. Pesticide Contamination in Water and Sediment of the Aquatic Systems of the Natural Park of the Albufera of Valencia (Spain) during the Rice Cultivation Period. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohaupt, V.; Völker, J.; Altenburger, R.; Birk, S.; Kirst, I.; Kühnel, D.; Küster, E.; Semerádová, S.; Šubelj, G.; Whalley, C. Pesticides in European Rivers, Lakes and Groundwaters—Data Assessment; European Topic Centre on Inland, Coastal and Marine Waters: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2020; p. 86. [Google Scholar]
- Smalling, K.L.; Kuivila, K.M.; Orlando, J.L.; Phillips, B.M.; Anderson, B.S.; Siegler, K.; Hunt, J.W.; Hamilton, M. Environmental Fate of Fungicides and Other Current-Use Pesticides in a Central California Estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 73, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlakidis, P.; Gounari, I.; Georgiou, A.; Adamidis, G.; Vryzas, Z.; Gikas, G.D. Removal of Two Triazole Fungicides from Agricultural Wastewater in Pilot-Scale Horizontal Subsurface Flow Constructed Wetlands. Agronomy 2023, 13, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konschak, M.; Zubrod, J.P.; Baudy, P.; Fink, P.; Kenngott, K.G.J.; Englert, D.; Röder, N.; Ogbeide, C.; Schulz, R.; Bundschuh, M. Chronic Effects of the Strobilurin Fungicide Azoxystrobin in the Leaf Shredder Gammarus Fossarum (Crustacea; Amphipoda) via Two Effect Pathways. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.; Sanchez, C.L.; Brammer-Robbins, E.; Pena-Delgado, C.; Kroyter, N.; El Ahmadie, N.; Watkins, J.M.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Bowden, J.A.; Souders, C.L.; et al. Neurotoxicity Assessment of QoI Strobilurin Fungicides Azoxystrobin and Trifloxystrobin in Human SH-SY5Y Neuroblastoma Cells: Insights from Lipidomics and Mitochondrial Bioenergetics. NeuroToxicology 2022, 91, 290–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Souders, C.L.; Wang, S.; Ganter, J.; He, J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Cheng, H.; Martyniuk, C.J. Behavioral and Developmental Toxicity Assessment of the Strobilurin Fungicide Fenamidone in Zebrafish Embryos/Larvae (Danio Rerio). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 228, 112966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, B.L.; Simon, J.M.; McCoy, E.S.; Salazar, G.; Fragola, G.; Zylka, M.J. Identification of Chemicals That Mimic Transcriptional Changes Associated with Autism, Brain Aging and Neurodegeneration. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, B.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Peng, Y.; Yang, J.; Liao, X.; Liu, F.; Guo, J.; Hu, C.; Lu, H. The Immunotoxicity and Neurobehavioral Toxicity of Zebrafish Induced by Famoxadone-Cymoxanil. Chemosphere 2020, 247, 125870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency. Chemicals Evaluated for Carcinogenic Potential by the Office of Pesticide Programs. 2022. Available online: http://npic.orst.edu/chemicals_evaluated.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Fungicides Acting on Mitosis and Cell Division. In Modern Crop Protection Compounds; Krämer, W.; Schirmer, U. (Eds.) Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 581–603. ISBN 978-3-527-31496-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lacey, E. Mode of Action of Benzimidazoles. Parasitol. Today 1990, 6, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, J.M.; Rehnberg, G.L.; Cooper, R.L.; Gray, L.E.; Hein, J.F.; McElroy, W.K. Effects of the Benomyl Metabolite, Carbendazim, on the Hypothalamic-Pituitary Reproductive Axis in the Male Rat. Toxicology 1989, 57, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-Y. Androgen Receptor Plays a Vital Role in Benomyl- or Carbendazim-Induced Reproductive and Developmental Toxicity and Endocrine-Disrupting Activity in Rats. In Endocrine Disruptors; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78984-151-0. [Google Scholar]
- Nakai, M.; Hess, R.A.; Moore, B.J.; Guttroff, R.F.; Strader, L.F.; Linder, R.E. Acute and Long-term Effects of a Single Dose of the Fungicide Carbendazim (Methyl 2-Benzimidazole Carbamate) on the Male Reproductive System in the Rat. J. Androl. 1992, 13, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. Reregistration Eligibility Decision (RED) Thiabendazole. 2002. Available online: https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/reg_actions/reregistration/red_PC-060101_1-May-02.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
- Corrales Vargas, A.; Peñaloza Castañeda, J.; Rietz Liljedahl, E.; Mora, A.M.; Menezes-Filho, J.A.; Smith, D.R.; Mergler, D.; Reich, B.; Giffin, A.; Hoppin, J.A.; et al. Exposure to Common-Use Pesticides, Manganese, Lead, and Thyroid Function among Pregnant Women from the Infants’ Environmental Health (ISA) Study, Costa Rica. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 151288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, E.; Nørhede, P.; Boberg, J.; Krag Isling, L.; Kroghsbo, S.; Hadrup, N.; Bredsdorff, L.; Mortensen, A.; Christian Larsen, J. Identification of Cumulative Assessment Groups of Pesticides. EFSA Support. Publ. 2012, 9, 269E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); Ippolito, A.; Kardassi, D.; Lythgo, C.; Tiramani, M. Peer Review of the Pesticide Risk Assessment for the Active Substance Spiroxamine in Light of Confirmatory Data Submitted. EFSA J. 2021, 19, e06385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, S.; Walls, C.; Rate, D. Spiroxamines: Human Health Risk Assessment for Spiroxamine on Imported Artichoke, Asparagus and Fruiting Vegetables (Crop Group 8); Office of Chemical afety and Pollution Prevention: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vandeputte, P.; Ferrari, S.; Coste, A.T. Antifungal Resistance and New Strategies to Control Fungal Infections. Int. J. Microbiol. 2011, 2012, 713687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepesheva, G.I.; Waterman, M.R. Sterol 14α-Demethylase Cytochrome P450 (CYP51), a P450 in All Biological Kingdoms. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 2007, 1770, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkboel, C.H.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Elgaard, C.; Olesen, M.-L.K.; Kretschmann, A.C.; Styrishave, B. The Classic Azole Antifungal Drugs Are Highly Potent Endocrine Disruptors in vitro Inhibiting Steroidogenic CYP Enzymes at Concentrations Lower than Therapeutic Cmax. Toxicology 2019, 425, 152247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beijer, K.; Jönsson, M.; Shaik, S.; Behrens, D.; Brunström, B.; Brandt, I. Azoles Additively Inhibit Cytochrome P450 1 (EROD) and 19 (Aromatase) in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss). Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 198, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankley, G.T.; Cavallin, J.E.; Durhan, E.J.; Jensen, K.M.; Kahl, M.D.; Makynen, E.A.; Thomas, L.M.; Wehmas, L.C.; Villeneuve, D.L. A Time-Course Analysis of Effects of the Steroidogenesis Inhibitor Ketoconazole on Components of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal Axis of Fathead Minnows. Aquat. Toxicol. 2012, 114–115, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riat, A.; Plojoux, J.; Gindro, K.; Schrenzel, J.; Sanglard, D. Azole Resistance of Environmental and Clinical Aspergillus Fumigatus Isolates from Switzerland. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Moreno, C.; Lavergne, R.-A.; Hagen, F.; Morio, F.; Meis, J.F.; Le Pape, P. Fungicide-Driven Alterations in Azole-Resistant Aspergillus Fumigatus Are Related to Vegetable Crops in Colombia, South America. Mycologia 2019, 111, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compendium of Pesticide Common Names-Fungicides. Available online: http://www.bcpcpesticidecompendium.org/class_fungicides.html (accessed on 1 September 2023).
- FRAC Code List ©*2022: Fungal Control Agents Sorted by Cross-Resistance Pattern and Mode of Action (Including Coding for FRAC Groups on Product Labels). 2022. Available online: https://www.mssoy.org/uploads/files/frac-code-list-2022_1.pdf (accessed on 28 December 2023).
| Active Substance | Water Solub. (20 °C) 1 | Log Kow 1 | Log Koc 1 | DT50 Soil (Days) 1 | DT50 Water/Water-Sediment (Days) 1 | GUS Leaching Index 1 | Detection (Freq. %) | Status during the Survey Period in EU 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benalaxyl | Low | 3.54 | 3.70 | 36.0–66.8 | 38.0/168.2 | 2.29 | S (23), G (23) | Approved |
| Metalaxyl | High | 1.65 3 | 2.20 | 14.1 | 106.0/56.0 | 2.06 | S (31), G (31) | Approved |
| Pyracarbolid | High | 2.22 | 2.18 | NA | NA | NA | G (15) | Not Approv. |
| Methfuroxam | Low | 3.16 | 2.26 4 | NA | NA | NA | G (23) | Not Approv. |
| Mepronil | Low | 3.66 | 2.98 | 46.0–50.5 5 | 276.0/NA | 1.72 | G (23) | Not Approv. |
| Dimethomorph | Low | 2.68 | 3.80 6 | 8.6–44.0 | 10.0/38.0 | 2.26 | S (15) | Approved |
| Furmecyclox | Moderate | 4.38 | 2.80 4 | NA | NA | NA | S (38), G (38) | Not Approv. |
| Oxycarboxin ** | High | 0.77 | 1.98 4 | 42.3 | 9.8/1000.0 | NA | G (10) | Not Approv. |
| Cyflufenamid ** | Low | 4.70 | 3.02 7 | 25.3 | 4.3/77.2 | 1.12 | G (10) | Approved |
| Cycloheximide ** | High | 0.55 | 1.70 | NA | NA | NA | G (10) | Not Approv. |
| Imazalil * | Moderate | 2.56 | NA | 6.4 | 7.8/117.0 | 0.26 | S (10) | Approved |
| Flusilazole ** | Low | 3.90 | 3.20 | 94.0 | 1.0/365.0 | 1.54 | G (10) | Not Approv. |
| Propiconazole | Moderate | 3.72 | 3.00 | 35.2 | 6.0/561.0 | 1.58 | S (31) | Approved 8 |
| Tebuconazole ** | Low | 3.70 | 2.85 4 | 47.1 | 42.6/365.0 | 1.86 | S (31), G (10) | Approved |
| Tetraconazole * | Moderate | 3.56 | NA | 430.0 | 2.0/340.0 | 2.47 | S (10) | Approved |
| Tricyclazole * | High | 1.40 | 2.20 | 130.0 | 93.0/453.0 | 3.89 | S (10) | Not Approv. |
| Benomyl * | Low | 1.40 | 3.30 | 67.0 | NA | −0.07 | S (10) | Not Approv. |
| Carbendazim ** | Low | 1.48 | 2.35 9 | 22.0–40.0 | 7.9/33.7 | 2.21 | S (15), G (10) | Approved 10 |
| Rabenzazole | Moderate to High | 2.62 | 3.31 4 | NA | NA | NA | S (61), G (92) | Not Approv. |
| Thiabendazole * | Low | 2.39 | 3.60 4 | 724.0 | 1.6/4.0 | 1.94 | S (10) | Approved |
| Probenazole | Moderate | 1.40 | 2.45 4 | 1.7 11 | NA | NA | G (15) | Not Approv. |
| Propamocarb | High | 0.84 | 2.86 | 14.0–30.0 | NA | NA | S (15) | Approved |
| Diethofencarb | Low | 2.89 | 2.42 4 | 5.4 | 9.8/24.9 | 1.09 | G (15) | Not Approv. |
| Isoprothiolane | Moderate | 3.30 | 3.13 | NA | NA | NA | S (31) | Not Approv. |
| Fenamidone | Low | 2.80 | 2.59 12 | 8.1–15.4 | 24.0/97.0 | 1.28 | S (46), G (15) | Approved 13 |
| Dodemorph | Moderate | 4.60 | 3.22 4 | 41.0 | 1.3/23.0 | −0.65 | S (46), G (46) | Approved |
| Fenpropimorph * | Low | 4.50 | 3.64 14 | 25.5 | 2.65/38.0 | 0.50 | S (10) | Not Approv. |
| Iprobenfos ** | High | 3.37 | 3.70 | 15.0 | NA | 0.35 | S (23), G (10) | Not Approv. |
| Famoxadone | Low | 4.65 | 3.58 | 1.6–20.0 | 0.1/0.7 | 1.09 | G (15) | Approved |
| Oxadixyl | High | 0.65 | 1.56 | 75.0 | 25.0/21.0 | 4.58 | S (61), G (15) | Not Approv. |
| Fludioxonil * | Low | 4.12 | 5.20 | 16.0 | 2.0/575.0 | −1.35 | S (10) | Approved |
| Ferimzone | Moderate | 2.98 | 2.57 4 | 3.0–14.0 15 | NA | NA | S (54), G (54) | Not Approv. |
| Pyroquilon * | High | 1.57 | 2.58 4 | 70.0 | NA | NA | S (10) | Not Approv. |
| Ethoxyquin | Moderate | 3.39 | 3.51 | 2.2 16 | NA | 6.70 17 | S (54), G (77) | Not Approv. |
| Spiroxamine | Moderate | 2.89 | 2.82–3.81 18 | 52.4 | 0.8/66.2 | −0.28 | S (15), G (15) | Approved |
| Azoxystrobin ** | Low | 2.50 | 2.77 | 180.7–248.0 | 6.1/205.0 | 3.10 | S (31), G (10) | Approved |
| Picoxystrobin ** | Low | 3.69 4 | 2.88–3.08 19 | 19.3 | 7.5/56.0 | 1.35 | G (10) | Approved 20 |
| Kresoxim-Methyl ** | Low | 3.40 | 2.34–2.57 21 | 1.0–3.0 21 | 0.85/1.30 | 0 | S (61), G (10) | Approved |
| Trifloxystrobin ** | Low | 4.50 | 3.36 22 | 1.7 | 1.1/2.40 | 0.15 | G (10) | Approved |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Mello-Sampayo, C.; Viana, P.; Lopes, A.; Carvalho da Silva, R.; de Jesus, R.; Sarmento, G.; Almeida, A.; Meisel, L. Survey of Antifungal in Surface- and Groundwater: A Portuguese Environmental Case Study. Sustainability 2024, 16, 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020594
De Mello-Sampayo C, Viana P, Lopes A, Carvalho da Silva R, de Jesus R, Sarmento G, Almeida A, Meisel L. Survey of Antifungal in Surface- and Groundwater: A Portuguese Environmental Case Study. Sustainability. 2024; 16(2):594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020594
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Mello-Sampayo, Cristina, Paula Viana, Ana Lopes, Rita Carvalho da Silva, Rosário de Jesus, Georgina Sarmento, Anabela Almeida, and Leonor Meisel. 2024. "Survey of Antifungal in Surface- and Groundwater: A Portuguese Environmental Case Study" Sustainability 16, no. 2: 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020594
APA StyleDe Mello-Sampayo, C., Viana, P., Lopes, A., Carvalho da Silva, R., de Jesus, R., Sarmento, G., Almeida, A., & Meisel, L. (2024). Survey of Antifungal in Surface- and Groundwater: A Portuguese Environmental Case Study. Sustainability, 16(2), 594. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16020594







