Lake Restoration Improved Ecosystem Maturity Through Regime Shifts—A Case Study of Lake Baiyangdian, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Division of Functional Groups
2.3.2. Parameter Determination
2.4. Model Uncertainty and Balancing
3. Results
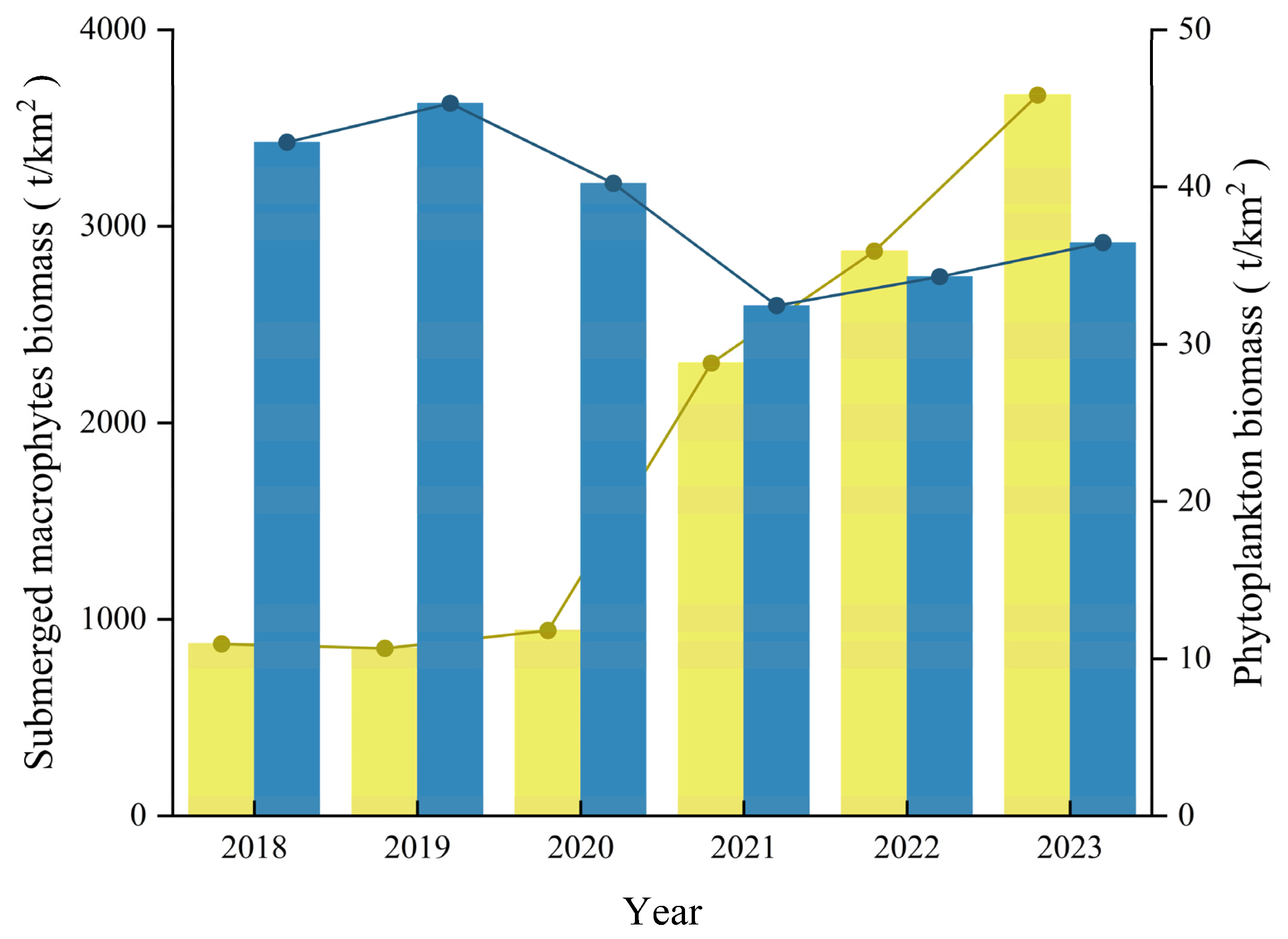
3.1. Regime Shifts of Environmental Factors and Primary Producers
3.2. Basic Parameter Analysis
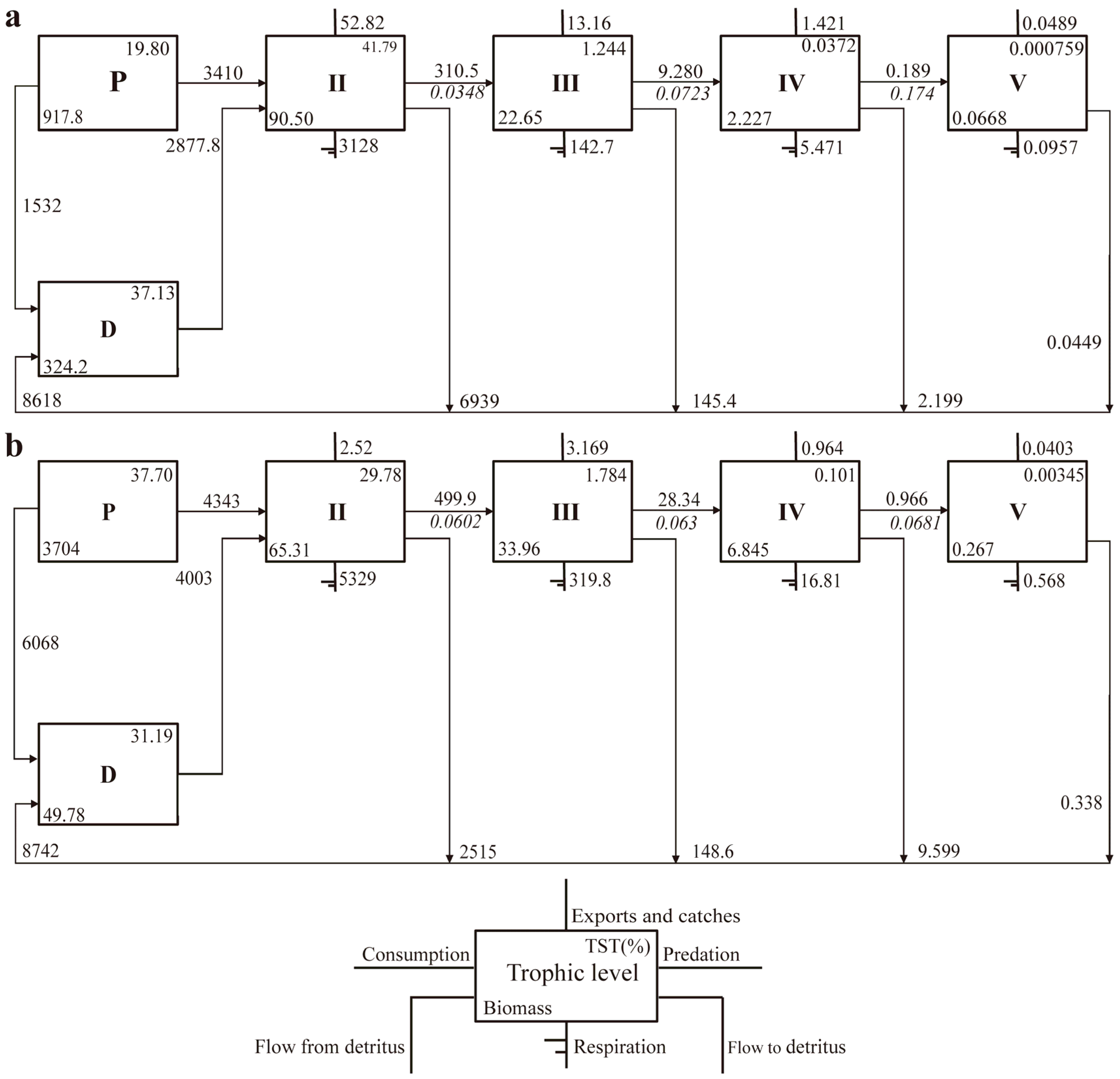
3.3. Trophic Level Energy Flows
3.4. Changes in Ecosystem Functioning
4. Discussion
4.1. Ecosystem Structure Differences
4.2. Ecosystem Evolution Trends
4.3. Potential Drivers of Ecosystemic Change
4.4. Management Recommendations for the Lake
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.; Foley, J.A.; Folke, C.; Walker, B. Catastrophic Shifts in Ecosystems. Nature 2001, 413, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.R. Catastrophic Regime Shifts in Ecosystems: Linking Theory to Observation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yin, X.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z. Simulating the Effects of Regulation Measures on Ecosystem State Changes in a Shallow Lake. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 92, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Langdon, P.G.; Chen, X.; Huang, C.; Yan, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zeng, L. Regime Shifts in Shallow Lake Ecosystems along an Urban-Rural Gradient in Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, X.; Reis, S.; Ge, S.; Gu, B. Pollution Controls in Lake Tai with the Reduction of the Watershed Nitrogen Footprint. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 332, 130132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blindow, I.; Hargeby, A.; Hilt, S. Facilitation of Clear-Water Conditions in Shallow Lakes by Macrophytes: Differences between Charophyte and Angiosperm Dominance. Hydrobiologia 2013, 737, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilt, S.; Köhler, J.; Adrian, R.; Monaghan, M.T.; Sayer, C.D. Clear, Crashing, Turbid and Back—Long-Term Changes in Macrophyte Assemblages in a Shallow Lake. Freshwater Biol. 2013, 58, 2027–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Z. The Long-Term Changes in Food Web Structure and Ecosystem Functioning of a Shallow Lake: Implications for the Lake Management. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 301, 113804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yang, Z. Modelling Phosphorus Loading to the Largest Shallow Lake in Northern China in Different Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Teklit, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Cui, X.; Duan, P. Planktonic Indicators of Trophic States for a Shallow Lake (Baiyangdian Lake, China). Limnologica 2019, 78, 125712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, H. Assessing Impacts of Flow Regulation on Trophic Interactions in a Wetland Ecosystem. J. Environ. Inform. 2013, 21, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Ye, S.; Lek, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, T.; Yuan, J.; Li, Z. The Need for Improved Fishery Management in a Shallow Macrophytic Lake in the Yangtze River Basin: Evidence from the Food Web Structure and Ecosystem Analysis. Ecol. Model. 2013, 267, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V.; Pauly, D. ECOPATH II—A Software for Balancing Steady-State Ecosystem Models and Calculating Network Characteristics. Ecol. Model. 1992, 61, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, V.; Walters, C.J. Ecopath with Ecosim: Methods, Capabilities and Limitations. Ecol. Model. 2004, 172, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofir, E.; Gal, G.; Goren, M.; Shapiro, J.; Spanier, E. Detecting Changes to the Functioning of a Lake Ecosystem Following a Regime Shift Based on Static Food-Web Models. Ecol. Model. 2016, 320, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neira, S.; Moloney, C.; Christensen, V.; Cury, P.; Shannon, L.; Arancibia, H. Analysing Changes in the Southern Humboldt Ecosystem for the Period 1970–2004 by Means of Dynamic Food Web Modelling. Ecol. Model. 2014, 274, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shen, H.Y.; Li, S.J.; Liang, Y.Z.; Lu, C.Y.; Zhang, L.L. Effects of eutrophication on the structure and function of the benthic-planktonic coupled food web in Baiyangdian Lake. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 2017–2030. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qi, Z. Evaluating the Ecological State of Chinese Lake Baiyangdian (BYD) Based on Ecological Network Analysis. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Shu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhou, J. Phytoplankton and Eutrophication Degree Assessment of Baiyangdian Lake Wetland, China. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 436965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.Y.; Wang, J.G.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Yan, J. Analysis on the changes of structure and function of Baiyangdian ecosystem in recent 10 years based on Ecopath model. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2020, 15, 169–180. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, H.; Wu, Y.; Xia, W.; Yang, L.; Chen, J.; Han, W.; Fang, J.; Xie, P. Stoichiometric Mechanisms of Regime Shifts in Freshwater Ecosystem. Water Res. 2019, 149, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, V. Ecosystem Maturity—Towards Quantification. Ecol. Model. 1995, 77, 3–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, K.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, Y.; Hu, L.; Yu, G.; Song, L. Modelling Ecosystem Structure and Trophic Interactions in a Typical Cyanobacterial Bloom-Dominated Shallow Lake Dianchi, China. Ecol. Model. 2014, 291, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwall, W.R.T.; Allison, E.H.; Turner, G.F.; Irvine, K. Lake of Flies, or Lake of Fish? A Trophic Model of Lake Malawi. Ecol. Model. 2010, 221, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morissette, L.; Hammill, M.O.; Savenkoff, C. The trophic role of marine mammals in the northern gulf of st. lawrence. Mar. Mammal Sci. 2006, 22, 74–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odum, E.P. The strategy of ecosystem development. Science 1969, 164, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noordhuis, R.; van Zuidam, B.G.; Peeters, E.T.H.M.; van Geest, G.J. Further Improvements in Water Quality of the Dutch Borderlakes: Two Types of Clear States at Different Nutrient Levels. Aquat. Ecol. 2015, 50, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.E.; Moss, B.; Eaton, J. Fish Induced Macrophyte Loss in Shallow Lakes: Top-down and Bottom-up Processes in Mesocosm Experiments. Freshw. Biol. 2002, 47, 2216–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, Z. Effects of Long-Term Environmental Flow Releases on the Restoration and Preservation of Baiyangdian Lake, a Regulated Chinese Freshwater Lake. Hydrobiologia 2014, 730, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brothers, S.M.; Hilt, S.; Meyer, S.; Köhler, J. Plant Community Structure Determines Primary Productivity in Shallow, Eutrophic Lakes. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2264–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.P.; Solomon, C.T.; Finney, B.P.; Gregory-Eaves, I. Macrophyte Biomass Predicts Food Chain Length in Shallow Lakes. Ecosphere 2015, 6, art5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, X.-J.; Cheng, S. Phytoplankton Community Structure and Water Quality Assessment in an Ecological Restoration Area of Baiyangdian Lake, China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.K.; Chen, H.Y.; Li, N.; Li, P.Y.; Di, S.A.; Ma, B.L. Study on water pollution prevention and control of sewage outlets in key areas around Baiyangdian Lake. In Proceedings of the 23rd Academic Annual Meeting of the Environmental Science Society of Five Provinces and Cities in North China, 2023; pp. 127–132. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Barrio Froján, C.R.S.; Cooper, K.M.; Bremner, J.; Defew, E.C.; Wan Hussin, W.M.R.; Paterson, D.M. Assessing the Recovery of Functional Diversity after Sustained Sediment Screening at an Aggregate Dredging Site in the North Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf S. 2011, 92, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, G.P.; Philip, B.; Kate, L.; Mathers, J.P.; Paul, J.W.; Dapeng, Y. The effects of water injection dredging on low-salinity estuarine ecosystems: Implications for fish and macroinvertebrate communities. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 122, 107224. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.L.; Li, F. Effects of sediment dredging on freshwater system: A comprehensive review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. 2023, 30, 119612–119626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.C.; Berlow, E.L.; Coleman, D.C.; Ruiter, P.C.; Dong, Q.; Hastings, A.; Johnson, N.C.; McCann, K.S.; Melville, K.; Morin, P.J.; et al. Detritus, Trophic Dynamics and Biodiversity. Ecol. Lett. 2004, 7, 584–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, D.; Christensen, V.; Guénette, S.; Pitcher, T.J.; Sumaila, U.R.; Walters, C.J.; Watson, R.; Zeller, D. Towards Sustainability in World Fisheries. Nature 2002, 418, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; He, Q.-S.; Yang, B.; He, W.; Xu, F.-L.; Annette, B.G.J.; Kuiper, J.J.; van Gerven, L.P.A.; Qin, N.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Hydrological Regulation Drives Regime Shifts: Evidence from Paleolimnology and Ecosystem Modeling of a Large Shallow Chinese Lake. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 737–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xian, Y.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Wei, W.; Xi, H.; Zheng, B. Wetland Ecosystem Status and Restoration Using the Ecopath with Ecosim (EWE) Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.H.; Xu, D.P.; Ren, L.; Xu, R. Ecological capacity assessment of silver carp and bighead carp in Taihu Lake based on Ecopath model. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 28, 785–795. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, E.S.; Li, Y.K.; Zang, R.W.; Wang, H. Preliminary analysis on the structure and function of Chaohu Lake ecosystem based on Ecopath model. J. Fish. Sci. China 2021, 38, 417–425. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Liu, J.R.; Wang, L.; Wu, Z.X.; Yu, Z.M.; Liu, M.L. Structure and function analysis of Qiandao Lake ecosystem based on Ecopath model. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 2021, 45, 308–317. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Feng, D.X.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.K.; Yu, N.; Chen, L.Q. Ecosystem structure and energy flow characteristics of Dianshan Lake based on nutrient channel model. J. Fish. Sci. China. 2011, 18, 867–876. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.F.; Gao, X.W.; Chen, J.C. Study on nutritional structure and energy flow of Wuli Lake ecosystem based on Ecopath model. J. Fish. Sci. China 2012, 19, 417–481. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Xie, S.; Lek, S.; Li, Z. Food web structure and ecosystem properties of the largest impounded lake along the eastern route of China’s South-to-North Water Diversion Project. Ecol. Inform. 2018, 43, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


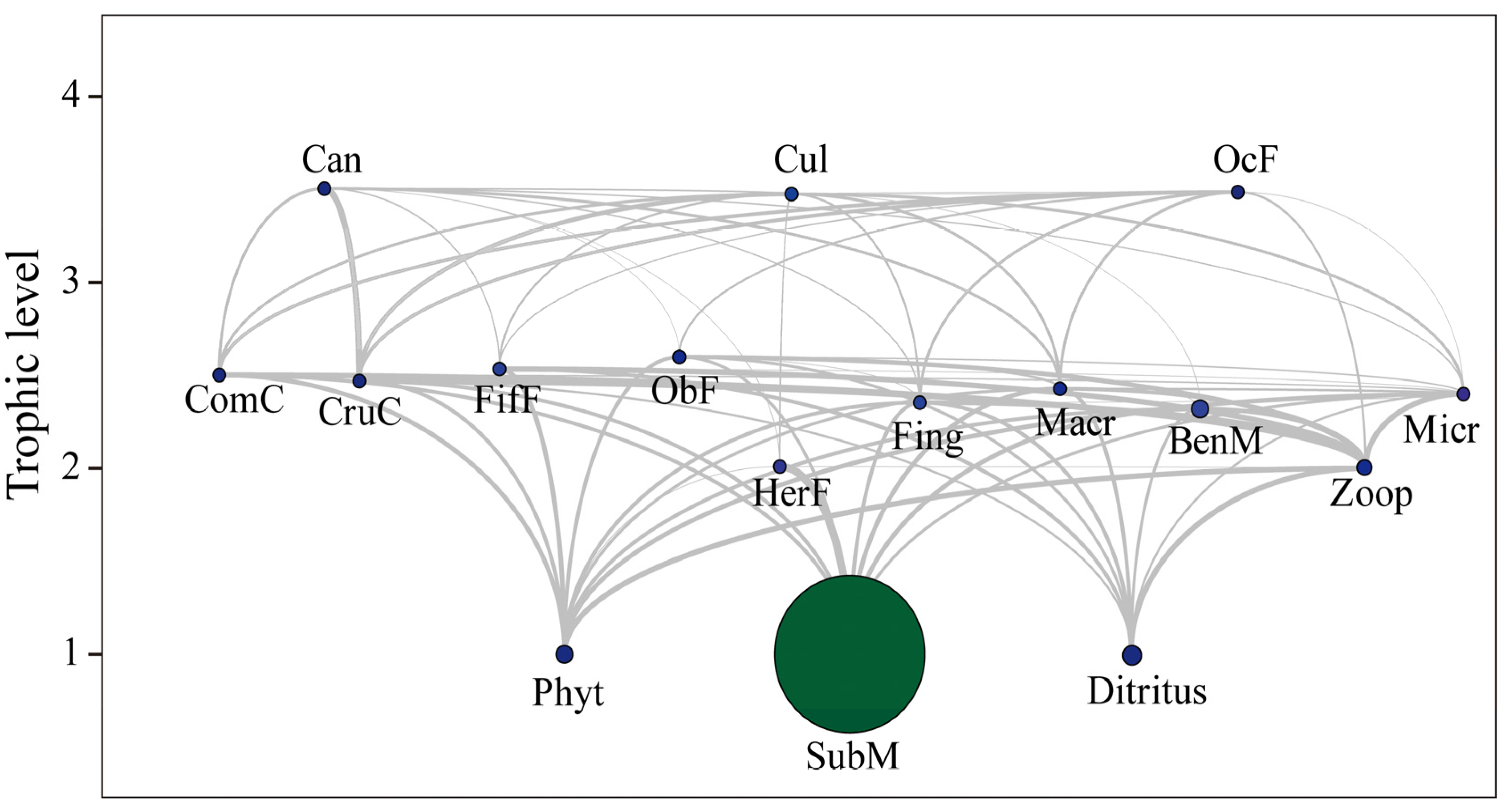
| Group | Abbreviation | Trophic Level | Biomass (t/km²) | P/B | Q/B | EE | P/Q |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Snakehead | Sna | 3.49 | 3.07 | 0.86 | 3.86 | 0.280 | 0.223 |
| 2. Large culters | LarC | 3.47 | 6.78 | 0.67 | 3.20 | 0.435 | 0.211 |
| 3. Common carp | ComC | 2.50 | 5.05 | 1.98 | 10.69 | 0.972 | 0.185 |
| 4. Crucian carp | CruC | 2.45 | 14.81 | 1.72 | 9.10 | 0.847 | 0.189 |
| 5. Other carnivorous fish | OcF | 3.48 | 5.95 | 0.92 | 3.80 | 0.354 | 0.242 |
| 6. Filter-feeding fish | FifF | 2.53 | 2.50 | 1.67 | 8.00 | 0.952 | 0.209 |
| 7. Other benthivorous fish | ObF | 2.60 | 0.925 | 2.4 | 8.29 | 0.931 | 0.290 |
| 8. Herbivorous fishes | HerF | 2.01 | 0.82 | 1.47 | 8.23 | 0.818 | 0.179 |
| 9. Fingerling | Fing | 2.35 | 3.55 | 3.26 | 11.00 | 0.849 | 0.296 |
| 10. Macrocrustaceans | Macr | 2.43 | 4.11 | 5.2 | 24.23 | 0.578 | 0.215 |
| 11. Benthic mollusks | BenM | 2.32 | 34.32 | 3.36 | 27.20 | 0.004 | 0.124 |
| 12. Microzoobenthos | Micr | 2.4 | 0.881 | 20.12 | 68.30 | 0.793 | 0.295 |
| 13. Zooplankton | Zoop | 2 | 23.62 | 51.51 | 316.2 | 0.379 | 0.163 |
| 14. Phytoplankton | Phyt | 1 | 36.65 | 159 | 0.681 | ||
| 15. Submerged macrophytes | SubM | 1 | 3667 | 1.25 | 0.082 | ||
| 16. Detritus | Ditritus | 1 | 49.78 | 0.458 |
| Group Name | 2018 | 2023 |
|---|---|---|
| Carnivorous fish | 5.87 | 15.8 |
| Filter-feeding fish | 0.02 | 2.50 |
| Omnivorous fish | 21.85 | 20.79 |
| Herbivorous fish | 3.77 | 0.82 |
| Fingerling | 6.00 | 3.55 |
| Mollusk | 35.95 | 34.32 |
| Other meiobenthos | 26.05 | 4.99 |
| Zooplankton | 15.93 | 23.62 |
| Phytoplankton | 42.85 | 36.65 |
| Submerged macrophytes | 874.93 | 3667.20 |
| Detritus | 324.50 | 49.78 |
| Parameter | In the Year 2018 | In the Year 2023 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| II | III | IV | II | III | IV | |
| Producer % | 4.128 | 9.153 | 20.51 | 5.955 | 6.337 | 6.790 |
| Detritus % | 3.171 | 6.353 | 15.87 | 6.091 | 6.265 | 6.828 |
| All flows % | 3.483 | 7.226 | 17.35 | 6.020 | 6.302 | 6.809 |
| Proportion of total flow originating from detritus | 0.66 | 0.46 | ||||
| From primary producers | 9.185% | 6.351% | ||||
| From detritus | 6.837% | 6.387% | ||||
| Total transfer efficiencies | 7.587% | 6.369% | ||||
| Parameter | 2018 | 2023 | Harvest Simulated Output in 2023 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total system throughput (t/km2) | 24,958 | 28,034 | 22,689 |
| Total primary production/total respiration | 1.51 | 1.84 | 1.37 |
| Total biomass/total throughput (/a) | 0.041 | 0.136 | 0.074 |
| Connectance index | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.33 |
| System omnivory index | 0.097 | 0.168 | 0.168 |
| Finn’s cycling index (FCI) | 36.40 | 8.39 | 12.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Jin, L.; Si, Y.; Mu, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Y. Lake Restoration Improved Ecosystem Maturity Through Regime Shifts—A Case Study of Lake Baiyangdian, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 9372. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16219372
Li H, Jin L, Si Y, Mu J, Liu Z, Liu C, Zhang Y. Lake Restoration Improved Ecosystem Maturity Through Regime Shifts—A Case Study of Lake Baiyangdian, China. Sustainability. 2024; 16(21):9372. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16219372
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hongxiang, Lei Jin, Yujie Si, Jiandong Mu, Zhaoning Liu, Cunqi Liu, and Yajuan Zhang. 2024. "Lake Restoration Improved Ecosystem Maturity Through Regime Shifts—A Case Study of Lake Baiyangdian, China" Sustainability 16, no. 21: 9372. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16219372
APA StyleLi, H., Jin, L., Si, Y., Mu, J., Liu, Z., Liu, C., & Zhang, Y. (2024). Lake Restoration Improved Ecosystem Maturity Through Regime Shifts—A Case Study of Lake Baiyangdian, China. Sustainability, 16(21), 9372. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16219372






