Abstract
Textile, printing, and dyeing industries in China are expanding annually, resulting in the discharge of significant volumes of wastewater. These effluents have complex compositions and contain diverse pollutants that pose severe hazards to aquatic systems, ecological environments, and nearby flora, fauna, and human populations. The inadequate or rudimentary treatment of these effluents can cause substantial environmental damage. Current technologies for treating textile dyeing wastewater (TDW) include physical, chemical, and biological methods, with biological treatment being noted for its low cost and environmental sustainability. In the realm of biotechnological treatment, microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and algae, exhibit significant potential. This review highlights the urgent need for effective treatment of textile dyeing wastewater (TDW), which poses severe environmental and health risks. It provides a comparative analysis of physical, chemical, and biological treatment methods, with a focus on the unique advantages of biological approaches, such as biodegradation and biosorption, for sustainable wastewater management. Key findings include recent advancements in microbial applications, challenges in scaling up, and integration into existing treatment systems. This review aims to guide future research and practical applications in achieving eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions for TDW remediation.
1. Introduction
Textile printing and dyeing is one of the most crucial industries in human society and is undergoing rapid development. Statistical data indicate that the global economic market share of the textile industry is currently valued at USD 610.91 billion and is projected to reach USD 755.38 billion by 2027 [1]. This growth, however, has led to a significant increase in the volume and complexity of discharged textile dyeing wastewater (TDW). As the world’s largest textile producer, China’s textile printing and dyeing industry accounted for 20% (1.84 billion tons) of industrial wastewater discharged in 2020, generating approximately 2.3 million tons of textile dyeing sludge containing toxic and hazardous pollutants (with a moisture content of 60%) [2,3,4,5].
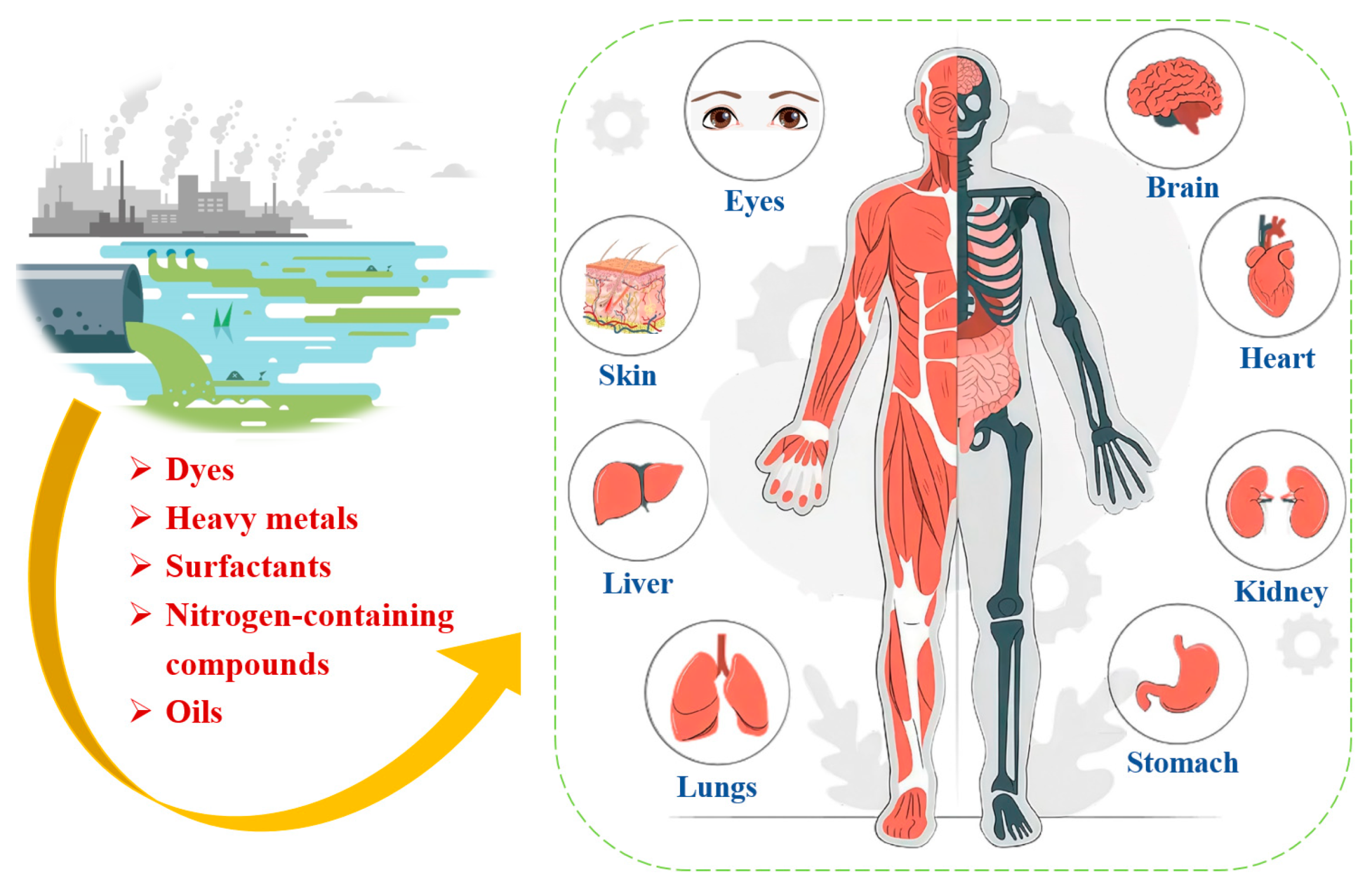
The improper discharge of such dyeing wastewater without adequate treatment poses a significant threat to the environment and water bodies. During migration, dyes can degrade or react with other elements in the environment, resulting in the formation of various dangerous and harmful compounds [6]. These toxic compounds have teratogenic and neurotoxic effects in individuals who consume contaminated agricultural and fishery products. Additionally, they exert harmful effects on organisms within ecosystems [7,8]. Even at low doses, these dyes can cause respiratory irritation, jaundice, and vomiting. Over time, organic dyes can damage the lungs, liver, kidneys, heart, and brain [9]. Furthermore, the dyes in wastewater can impede the penetration of sunlight into water bodies, thereby disrupting photosynthesis in aquatic plants [10,11]. Therefore, it is crucial to remove these toxic dyes from the increasing volumes of wastewater before they are discharged into the environment [12,13].
Traditional methods for treating textile dyeing wastewater (TDW) include physical, chemical, and biological techniques, each with distinct advantages and limitations [14]. For instance, physical methods like adsorption are effective for high dye concentrations, but face challenges in adsorbent recovery, limiting their scalability. Chemical treatments, such as Fenton oxidation and electrochemical processes, provide rapid decolorization but often produce secondary pollutants, including chemical sludge, which complicates disposal. These limitations underscore the need for environmentally sustainable alternatives like biological treatments, which leverage microbial activity to degrade or adsorb pollutants with minimal secondary waste. However, systematic reviews focusing on these biological solutions remain scarce, which this study aims to address. Wastewater pretreatment typically employs physical treatment techniques to remove solid contaminants, followed by the application of adsorbents to sequester pollutants within the aqueous phase [15]. For instance, organic clays have been shown to adsorb up to 95% of dyes [16]. For example, electro-oxidation technology has achieved removal rates of 72% for chemical oxygen demand (COD), 18% for total nitrogen (TN), and 99% for color in TDW [17]. However, certain chemical agents used in these chemical treatment methods may be unsuitable for wastewater treatment and can generate significant amounts of chemical sludge, potentially causing secondary pollution [17,18]. In comparison, biological treatments stand out for their cost-effectiveness, operational simplicity, and environmental benefits. They have been employed to remove organic compounds and color from TDW [19]. In biological treatment processes, organisms transform toxic substances into harmless or less toxic compounds through their metabolic activities [14]. It was found that the pigment and toxicity in printing and dyeing wastewater could be effectively removed by Pycnoporus laccase. Under the optimum conditions (dye concentration 50 mg/L, 1-1-hydroxybenzotriazole (HBT) as a mediator), the decolorization rate and detoxification effect reached a high level [20]. The combined microbial treatment has shown great potential in the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater. For example, the I5-ESPE microbial complex is highly biodegradable in the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater and is effective in the removal of non-stationary dyes, phenolic surfactants, and heavy metals [21]. Additionally, biomacromolecules on the surfaces of organisms, such as proteins and polysaccharides, can bind to harmful substances in the environment [22,23], facilitating the removal of pollutants.
Owing to the numerous advantages and potential applications of biological treatment methods, many researchers have focused on the biological treatment of TDW. Although some studies have been conducted on the use of biological methods for this purpose, a systematic review of these approaches is lacking. This article compiles and reviews recent research on TDW treatment technologies, providing a brief summary of physical and chemical methods, while focusing on biological treatment methods involving bacteria, fungi, and microalgae. This study aims to provide a comprehensive review of textile dyeing wastewater (TDW) treatment technologies, focusing on the environmental challenges posed by TDW and the development of sustainable solutions. While summarizing physical, chemical, and biological treatment methods, this review highlights the advantages of biological approaches, such as biodegradation and biosorption, and explores recent advancements in microbial applications. By synthesizing existing knowledge, this study seeks to identify gaps and propose directions for future research.
This review systematically analyzed studies published from 2000 to 2023 using databases such as Web of Science and Google Scholar. Search terms included “textile dyeing wastewater”, “biological treatment”, “biodegradation”, and “microbial applications”. Studies were selected based on their relevance to TDW treatment technologies and their inclusion of experimental data on dye removal efficiency, operational scalability, or sustainability. Exclusion criteria included studies lacking experimental validation or focused solely on chemical synthesis. A total of 175 peer-reviewed articles were reviewed, emphasizing advancements within the last five years to ensure timeliness and relevance.
1.1. Sources of TDW
Textile dyeing typically involves several complex steps, including sizing, desizing, scouring, bleaching, mercerizing, dyeing, printing, and finishing [24]. Among these processes, the pretreatment stage, including desizing, releases the highest amount of pollutants, accounting for nearly 50% of the total pollution load [25]. Scouring is a chemical cleaning process in the dyeing procedure, used to remove impurities from fibers, such as waxes, fatty acids, natural oils, and surfactants. Common methods include ice, bridge, tidal, and hydrodynamic scouring [26,27]. During the scouring process, byproducts such as NaOH, fats, oils, detergents, calcium, and magnesium are released [28]. The bleaching process is typically employed to eliminate unwanted dyes or colors from fibers. This process generates substances such as caustic soda, hydrogen peroxide, hypochlorite, acids, and chlorine [29]. The purpose of the mercerization process is to enhance the fiber strength, dye affinity, shrinkage resistance, and luster of yarns and fabrics. This process typically involves the use of strongly alkaline solutions [30]. During the mercerization process, in addition to increasing the wastewater pH, substances such as zinc chloride, cyclohexanol, and caustic soda are released [30,31]. The dyeing and printing stages involve treating fibers with water and dissolving various dyes and auxiliary chemicals, resulting in the discharge of dyestuff wastewater [32]. The finishing process is the final stage in textile manufacturing, transforming woven or fine-knit materials into high-quality products with specific characteristics. During finishing, the process includes the addition of crosslinking agents, functional finishing agents, softeners, acids, and salts [33]. This process contributes to water pollution [2,34]. It is estimated that the textile dyeing and printing industry requires approximately 200 L of water to produce 1 kg of textile products. This process generates significant amounts of wastewater characterized by high color, pH, suspended solids, and heavy metals, such as Cu, Cr, Zn, and As [32]. Furthermore, according to the 2022 “China Ecological and Environmental Statistics Yearbook” [35], the textile industry’s emissions of COD, ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen, and total phosphorus accounted for 16.7%, 9.2%, 13.7%, and 9.1% of the total industrial emissions, respectively. These data indicate that the textile dyeing and printing industries continue to generate substantial volumes of wastewater. The efficient and environmentally friendly treatment of these vast quantities of TDW remains a primary concern.
1.2. Characteristics and Impacts of TDW
TDW originates from multiple industrial processes and exhibits a highly complex composition with diverse pollutant types with varying environmental impacts, as shown in Table 1. Dyeing, desizing, and scouring are the primary sources of water pollution in TDW. The characteristics of TDW include noticeable coloration, high COD, presence of suspended solids, and elevated pH levels (9–11) [36]. As shown in Figure 1, key components of TDW are dyes, heavy metals and surfactants et.al., which are very harmful to human health. The details are described as follows.

Table 1.
Characteristics of textile dyeing wastewater [18,37].
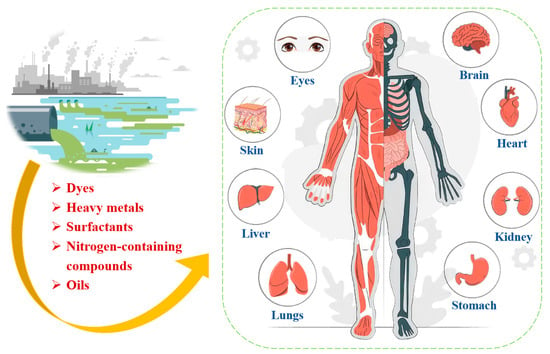
Figure 1.
Key components of textile and dyeing wastewater and their health impacts.
1.2.1. Dye
Dyes can be classified into 20–30 different groups based on their chromophore structures. Azo (monoazo, diazo, triazo, and polyazo), anthraquinone, phthalocyanine, and triarylmethane dyes constitute the majority of global commercial dyes. Azo dyes alone account for approximately 70% of the market, while anthraquinone dyes represent more than 15% [38,39,40]. Dyeing 1 kg of textiles requires approximately 150–200 L of water, and the wastewater generated from the dyeing process accounts for approximately 70–80% of the total wastewater from the textile industry [41,42]. It is estimated that 10–15% of the dyes added during dyeing end up in wastewater, leading to dye loss and significant water coloration [43,44,45].
The presence of these dyes in aquatic ecosystems is harmful to organisms and poses significant health risks to humans through the contamination of agricultural and fishery products [8,46]. Toxic dyes can cause skin allergies and respiratory irritation and, with prolonged exposure, can severely damage vital organs, including the lungs, liver, kidneys, and brain [43]. However, some dyes can cause intense coloration of water bodies, blocking sunlight and thereby hindering the photosynthetic process of aquatic plants [47]. This directly reduces dissolved oxygen levels in water, significantly affecting aquatic ecosystems.
1.2.2. Heavy Metal
In addition to dyes, TDW contains toxic heavy metals, such as cadmium, chromium, lead, and nickel [48], as well as copper, iron, manganese, and zinc [49]. The heavy metal contents in different TDWs range between 50 and 1000 mg/L [50]. Several heavy metals are toxic, even at low concentrations [51]. Notably, Cr (VI), which is commonly used as an oxidizing agent and mordant in dyeing processes, exhibits significant biotoxicity. It is carcinogenic, mutagenic, and teratogenic to animals and humans and poses severe threats to public health and environmental safety [52,53,54]. The coexistence of dyes and heavy metals in wastewater complicates pollution and remediation. High-valence cationic metals can act as oxidizing agents in the redox reactions of organic pollutants, promoting their degradation. However, these metals often form stable complexes with organic pollutants, further complicating treatment [55]. Furthermore, the toxicity of heavy metals varies with their chemical valence states, which adds complexity to their treatment [56].
1.2.3. Surfactant
Owing to their amphiphilic nature (possessing both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts), surfactants participate in a wide range of intermolecular interactions that enhance their surface activity [57]. Hence, surfactants are added to various textile dyeing and printing processes, such as desizing, scouring, and dyeing [37], and they are discharged into the wastewater generated from these processes. Surfactants are harmful molecules that require a long time to biodegrade in the environment, thereby reducing oxygen levels and harming aquatic organisms. Some surfactants, particularly those with long hydrocarbon chains or aromatic compounds, are difficult to biodegrade [57]. Surfactants can also promote eutrophication in water bodies by increasing pollutant solubility [58]. When surfactant molecules arrange themselves with their hydrophilic heads facing the water and hydrophobic tails clustered at the center, micelles are formed. These micelles can increase the solubility of pollutants, allowing hydrophobic contaminants to dissolve and remain in the solution [57]. In addition, the biotoxicity of surfactants is significant. Researchers have found that, at a surfactant concentration of 15.0 mg/L, the mortality rate of experimental fish exceeded 50%, with even lower concentrations (5.0 mg/L) causing mortality in juvenile fish [59].
1.3. Major Methods for TDW Treatment
Numerous relevant treatment methods have been developed to improve the treatment of TDW and enhance wastewater reuse rates. Broadly, these methods primarily include physical, chemical, and biological approaches. During the implementation process, wastewater is often subjected to preliminary treatment by screening, flotation, neutralization, and adjustment of water quality and quantity. Subsequently, the wastewater treatment method is selected based on cost considerations and the specific circumstances of the TDW. Biological treatment methods are widely utilized because of their low cost, good adaptability, and minimal secondary pollution.
1.3.1. Physical Treatment
As shown in Table 2, physical treatment technologies include adsorption, ion exchange, membrane filtration, coagulation/flocculation, flotation, evaporation (multiple-effect evaporation and mechanical vapor compression), and crystallization.
Adsorption processes are widely favored for their cost-effectiveness in treating high dye concentrations, lack of byproducts, and the ability to recycle and reuse materials [60]. The efficiency of adsorption is influenced by factors such as adsorption capacity, pore volume, specific surface area, particle size, and pore size distribution. Common adsorbents include silica gel, peat, fly ash, and carbon-based materials like activated carbon (AC), graphene (GR), and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) [61]. Silica gel serves as an effective alkaline dye adsorbent; however, it is prone to side reactions, such as particle or material fouling during the process, which affect its industrial reusability [62]. Peat is a natural, permeable adsorbent capable of removing various organic wastes and dyes. Experimental studies have employed it as an adsorbent for the removal of rhodamine B from wastewater; however, the removal efficiency was found to be unsatisfactory, reaching only 8.5% [63]. Solid fly ash particles, such as sugarcane bagasse fly ash, which is a byproduct of the sugar industry, can also be used for dye removal. It is deemed suitable as an adsorbent because of its lack of toxic metals and low cost. It was tested for the treatment of malachite green (MG) dye wastewater and achieved an adsorption rate of 17% [64].
The regenerability, simplicity, flexibility, heavy metal-removal capability, and high efficiency of ion exchange technology have garnered significant attention for the treatment of TDW [65,66]. For example, Marin et al. [67] achieved the removal of acid orange 10 from TDW using an anion-exchange resin. The removal of dyes through ion exchange is based on the strong interactions between the functional resin and the charge of the dye molecules [65,68]. Studies have found that anion exchange resins can remove 91.7% of disperse violet 28 at dye concentrations ranging from 10 to 500 mg/L [69].
Membrane filtration technology plays a crucial role in the treatment of TDW owing to its small pores and large solute capacity. It can filter pollutants based on their size and mass, thereby enhancing their color removal [65]. Shao et al. found that polypropylene membranes could remove approximately 95.5% of Congo red dye at an initial dye concentration of 50 mg/L [70]. Further studies have indicated that membrane filtration can remove approximately 89% of direct blue 71 [71]. However, the annual treatment cost is estimated to be approximately USD 1,099,406 [72], which is undoubtedly substantial.

Table 2.
Examples of physical treatment processes for textile dyeing wastewater.
Table 2.
Examples of physical treatment processes for textile dyeing wastewater.
| Removal Mechanism | Dye | Material | Dye Concentration | Decolorization | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorption | Congo Red | ZnO@Ze composite particles | 25–500 mg/L | 90% | [73] |
| Adsorption | Methylene Blue | Montmorillonites (Mt) with graphene oxide (GO) (Mt/GO) | 750 mg/L | 94.3% | [74] |
| Ion exchange | Methyl Violet 2B | Sulfonic acid and phosphate groups | 30 mg/L | 93% | [75] |
| Ion exchange | Acid Orange 7 | Lewatit MonoPlus MP 500 resin | 10 mg/L | 87% | [76] |
| Membrane filtration | Rhodamine B | Polyether sulfone | 5 mg/L | 98.9% | [77] |
| Membrane filtration | Congo Red | Polypropylene | 50 mg/L | 99.5% | [70] |
1.3.2. Chemical Treatments
As shown in Table 3, chemical methods primarily include advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) (such as Fenton and ozone oxidation), electrochemical methods, and photocatalysis [50].
Recently, advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) have gained widespread recognition in the development of wastewater treatment technologies. Methods such as ozone and Fenton oxidation have been effectively applied to the degradation of recalcitrant organic pollutants, including dyes [78]. As a strong oxidizing agent, ozone can be used to purify drinking water, remove toxic elements from wastewater, and facilitate the decomposition of organic waste. Additionally, ozone used in its gaseous state generates less sludge [62]. However, during the decolorization of TDW, chromophores with conjugated double bonds in dyes can decompose into potentially toxic and carcinogenic small molecules. The use of ozone oxidation can address this issue [79]. However, ozone oxidation is expensive and generates toxic and carcinogenic compounds. Environmental factors, such as temperature and pH, also influence their effectiveness [62].
Electrochemical methods are highly effective for concentrated TDW [80]. This approach operates via two mechanisms: a direct pathway at the anode and an indirect pathway at the cathode or other regions away from the anode, generating electrons via Faraday reactions [81]. In indirect mechanisms, electrons are generated in other regions of the cell via electrolysis and water decomposition [82]. This method is advantageous for dye removal because it requires fewer chemicals (or even none) during processing and does not generate sludge. However, increasing the flow rate during treatment can immediately reduce dye removal efficiency, and the electricity costs incurred are comparable to the chemical expenses [62].
In contrast, photocatalysis decomposes dye molecules into environmentally friendly water and carbon dioxide under ultraviolet (UV) or visible light. Various photocatalysts can be used for dye degradation, such as TiO2, CdS, ZrO2, ZnO, and CeO2, attracting extensive attention from researchers. The advantages of this process include low sludge production and the potential to reduce the odor of wastewater [62]. Although photocatalysis can be employed to decolorize basic, acidic, reactive, and direct dyes, its effectiveness in treating dispersed and vat dyes is limited. Photocatalytic treatment is also influenced by various factors, including the pH, UV intensity, and dye structure [83].

Table 3.
Examples of chemical treatment processes for textile dyeing wastewater.
Table 3.
Examples of chemical treatment processes for textile dyeing wastewater.
| Removal Mechanism | Dye | Treatment Conditions | Decolorization | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Advanced oxidation processes | Direct Blue 86 | Dye concentration 100 mg/L, pH 11, reaction time 35 min | 98% | [84] |
| Advanced oxidation processes | Alizarin Yellow R | Dye concentration 100 mg/L, reaction time 2 h | 94.8% | [85] |
| Electrochemical | Procion Red MX-5B | Initial dye concentration 50 mg/L, pH 7, flow rate 300 L/h, current density 10 mA/cm2 | 85% | [86] |
| Electrochemical | Reactive Red 120 | Initial dye concentration 200 mg/L, NaCl = 7914.29 mg/L, current intensity = 0.12 A, reaction time = 30 min | 99.4% | [87] |
| Photocatalysis | Methylene Blue (MB) | Dye concentration 20 mg/L, UV light intensity 4 W, liquid flow rate 2 mL/min, wavelength 254 nm | 99% | [88] |
| Photocatalysis | Congo Red (CR) | UV/NO3 photolysis using low-pressure UV (254 nm) | 81.9% | [89] |
1.3.3. Biological Treatments
Biological treatment technologies can convert biodegradable pollutants in wastewater into simple and harmless products. Compared with physical and chemical methods, biological treatment is more advantageous because of its ease of operation, minimal sludge production, reduced need for chemical reagents, energetic efficiency, environmental friendliness, and production of non-toxic byproducts [12,68]. In the treatment of TDW, biological treatment technologies can achieve dye decolorization through biomass adsorption by microorganisms and biodegradation of dyes by microbial cells, as shown in Table 4 [90]. For example, various microorganisms, such as fungi, algae, and bacteria, can transform dye molecules into less harmful forms [91,92], thereby degrading a wide range of dyes present in TDW [34]. A total of 120 strains of lactic acid bacteria were screened and found to have the ability to de-colorize textile azo dyes such as Reactive Lanasol Black B, Eriochrome Red B, and the 1, 2 metal complex I. Yellow [93]. White-rot fungi produce lignin peroxidases, manganese-dependent peroxidases, and laccases that are effective in degrading a number of azo dyes, thereby reducing toxic substances in wastewater [94]. Therefore, employing biological treatment technologies for dye-containing wastewater allows for environmentally friendly processing without significant investment or operational costs [95]. Reactor devices and reaction parameter settings associated with biological treatment methods have a significant impact on treatment efficacy. Paul Schoeber et al. [96] investigated the effects of suction time, backwash time, and aeration intensity on the treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater in a membrane bioreactor.

Table 4.
Examples of biological treatment processes for textile dyeing wastewater.
2. Biological Methods for TDW Treatment
Although physical and chemical methods used for treating TDW achieve satisfactory dye removal efficiencies, they are not environmentally friendly. Issues such as the difficulty in separating adsorbents and the potential for secondary environmental pollution are prevalent in these methods [104]. Biological treatment methods characterized by environmental friendliness, economic feasibility, genetic diversity, and flexibility have been widely applied to address TDW issues [32]. In biological treatment processes, dye degradation occurs through metabolic pathways or adsorption, utilizing both living and dead biomass, including bacteria, fungi, and algae [105].
2.1. Bacterial Biodegradation
Owing to their rapid reproduction, fast growth rate, and ubiquitous nature, bacteria have gradually become the primary focus of research for the biological treatment of TDW. Owing to their widespread use in the textile dyeing and printing industries, azo dyes [106,107,108], anthraquinone [109,110,111], and triphenylmethane (TPM) dyes [112,113] pose significant hazards to organisms and the environment when they remain in wastewater. Consequently, they have become key target compounds for bacterial degradation and decolorization. Most bacteria utilized for degrading and decolorizing dyes have been isolated from the soil surrounding textile factories [114], TDW sludge [115], and areas contaminated with dye-polluted TDW [116]. Owing to the prolonged exposure to the harsh conditions of TDW, bacteria from these sources gradually adapt to these environments, rendering them potential agents for dye degradation. Table 5 lists bacteria that have been successfully used to degrade various types of dyes.

Table 5.
Bacterial treatments for treating textile dyeing wastewater.
Research conducted by Garg et al. [124] found that certain bacteria degrade dyes through azo reductases, which reduce azo bonds to aromatic amine structures. Under these catalytic conditions, azo dyes, acting as electron acceptors, interact with nonspecific carriers in the electron transfer chain, facilitating degradation. The resulting aromatic amine metabolites can be further reduced to simpler, environmentally benign metabolic compounds under aerobic or anaerobic conditions [125]. Through liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry analysis, Ewida et al. [118] demonstrated that Bacillus megaterium KY848339.1, isolated from TDW, can completely degrade Acid Red 337 into small aliphatic compounds and CO2, achieving a degradation rate of 91% within 24 h at an initial dye concentration of 500 mg/L. Similarly, Sivasubramani et al. [126] found that the bacterial strain Bacillus megaterium PNS 15 from the same family could effectively degrade the azo dye Reactive Blue 194 under the action of azo reductase and laccase, achieving a degradation efficiency of 92.3%. Furthermore, Solís et al. [107] reported that any microbial species capable of secreting oxidases and reductases can degrade azo dyes. These findings indicate that bacteria, as biodegrading agents for dyes, can effectively degrade toxic azo dyes into non-toxic metabolites.
In contrast, owing to their stable aromatic structure, anthraquinone dyes have demonstrated resistance to bacterial biodegradation in previous studies. However, recent studies have demonstrated that some bacterial isolates secrete laccase and peroxidase enzymes that can effectively degrade anthraquinone dyes [127,128]. Farraj et al. [129] investigated Hortaea sp. from petroleum-contaminated soil and found it could degrade Solvent Green (SG) at initial concentrations as low as 10 mg/L within 24 h. Copper addition enhanced laccase activity, enabling the oxidation of phenolic compounds in anthraquinone dyes into non-toxic metabolites [44].
Adenan et al. [130] conducted experiments on the bacterial removal of triphenylmethane dyes from TDW and demonstrated that various actinomycetes isolated from soil can degrade four common TPM dyes, namely, malachite green (MG), crystal violet (CV), methyl violet (MV), and cotton blue (CB), with high efficiency. Among the isolated strains, N. alba exhibited the highest degradation efficiency for the four TPM dyes, reaching 97.0%, 95.1%, 95.8%, and 83.8%, respectively, within 14 d. Previous studies have indicated that TPM dyes are susceptible to degradation by triphenylmethane reductase, laccase, and peroxidase enzymes [131,132], which bacteria can secrete through their enzyme systems to achieve the degradation or biosorption of TPM dyes.
To enhance degradation efficiency, recent research has shifted from single bacterial strains to consortia. Previous research has demonstrated that the use of bacterial consortia can result in higher dye degradation efficiency [133]. The use of mixed culture media allows for two or more bacterial strains to coexist in the same culture medium, enabling more thorough degradation of dyes in wastewater owing to synergistic interactions among the bacteria in the consortium. Dissanayake et al. [134] employed a mixed bacterial consortium under microaerobic conditions, achieving over 95% degradation of methyl orange and Congo red within 50 h. Similarly, Das et al. [135] demonstrated that a consortium of Zobellella taiwanensis AT 1–3 and Bacillus pumilus HKG212 effectively decolorized Reactive Green 19, achieving efficiencies exceeding 97%. In comparison, the same bacteria individually achieved lower efficiencies of 86.8% and 89.5%, respectively. Mohanty and Kumar [136] identified a consortium (BP) comprising Bacillus fexus TS8, Proteus mirabilis PMS, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa NCH that completely decolorized the anthraquinone dye Indanthrene Blue RS within 9 h, significantly faster than the 19 h required by individual strains. This enhanced efficiency was attributed to the combined action of oxidases in the reaction medium.
2.2. Fungal Biodegradation
Unlike bacteria, fungi possess cell walls and mycelia composed of filamentous hyphae, enabling them to tolerate high concentrations of dyes or toxins, thus serving as more efficient biosorbents for wastewater treatment. Moreover, fungal fermentation is straightforward, with low-cost growth materials, short proliferation cycles, and high biomass yields, making it conducive to large-scale cultivation [137]. Fungi are ubiquitous in nature and have diverse species, and many living and dead fungal genera have been proven to be effective for dye decolorization. White-rot fungi are among the most efficient and extensively studied fungi for degrading synthetic dyes [138].
White-rot fungi secrete specific extracellular enzymes that degrade a variety of dyes. This process, which is akin to the degradation of lignin by lignin-peroxidase and manganese peroxidase, occurs via a radical-based chain reaction. Being a nonspecific reaction that occurs extracellularly, white-rot fungi exhibit high tolerance and broad-spectrum degradation capabilities toward TDW, enabling the removal of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, tannins, anthraquinone dyes, and azo dyes. Furthermore, this enzymatic catalytic degradation process can lead to the complete mineralization of pollutants, thus preventing the formation of toxic intermediates and secondary pollution. However, in practical engineering applications, if bacteria enter a reaction system, they compete with fungi for nutrients in the culture medium. Owing to the slower reproduction rate of fungi, bacteria tend to dominate the reaction system. This dominance inhibits the secretion of extracellular degrading enzymes, causing the entire treatment system to lose its functionality for dye degradation [139]. Table 6 lists fungi that have been successfully used to degrade various dyes.

Table 6.
Fungal treatment for textile dyeing wastewater.
Research on dye decolorization using white-rot fungi has primarily employed three methods: liquid culture, immobilization, and bioreactors. The most common approach is the liquid culture method, which involves the cultivation of fungal cells in liquid culture media containing dyes. In recent years, several studies have adopted this method and achieved significant results.
Wang et al. [144] isolated the white-rot fungus Ceriporia lacerata from decaying mulberry branches. Under static aerobic conditions in liquid culture media, this fungus demonstrated an ability to decolorize Congo Red dye. Under optimal environmental conditions (temperature: 30 °C, pH 8), the decolorization rate exceeded 90% after 48 h when 3 g of fungal mycelium was added to 20 mL of Congo Red solution with a concentration of 0.1 mg/mL. Decolorization primarily occurs through mycelial absorption and degradation by manganese peroxidase (MnP). Upadhyay and Przystaś [145] revealed that the white-rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus is capable of decolorizing solutions containing 80 mg/L of Anthraquinone Red and Disperse Red dye. After 168 h of cultivation, Pleurotus ostreatus exhibited maximum decolorization efficiencies of 94.31% and 73.13% for Anthraquinone Red and Disperse Red, respectively. Sun et al. [146] established a biodecolorization system for azo dyes (Direct Red 5 B, DR5B) using the white-rot fungus Ganoderma lucidum EN2 and alkaline lignin in a liquid culture medium. The experimental results revealed that this system achieved a decolorization efficiency of 95.16% for Direct Red 5 B within 48 h. Adsorption experiments demonstrated that alkaline lignin enhanced the biodegradation of Direct Red 5 B by Ganoderma lucidum EN2 during decolorization rather than physical adsorption by lignin or fungal mycelia. Laccase also plays a significant role in dye decolorization.
Cultivating white-rot fungi in liquid culture media for dye decolorization is not always effective, particularly at high TDW concentrations, where fungal growth may be suboptimal. Papinutti and Forchiassin [147] observed that P. chrysosporium exhibited high sensitivity to Malachite Green in liquid media, resulting in inhibited growth. Immobilizing fungal cells or enzymes mitigates these challenges by mimicking the natural growth state of white-rot fungi, which typically adhere to surfaces in their habitats [143]. Immobilized fungal systems have demonstrated several advantages over free fungal cells, including enhanced enzyme activity, increased resilience to environmental stressors (e.g., pH fluctuations and toxins), improved biomass reuse, simpler liquid–solid separation, and reduced clogging in continuous systems [148,149]. Additionally, reports have indicated that immobilized fungal cell cultures sustain enzyme secretion in a sustainable manner, surpassing the levels observed in suspended or granular forms [150,151].
In response to these advantages, research on immobilized white-rot fungal cells and enzymes for dye decolorization has gained traction. Among the immobilization techniques, attachment and encapsulation are the most prominent [148]. Attachment involves binding fungi to support materials such as polymers, activated carbon, or cellulose fibers. Encapsulation entails embedding fungal biomass within matrices made of materials like agar, alginate, chitosan, or cellulose [152,153].
Przystaś et al. [154] found that the selection of different solid supports during fungal immobilization significantly influences the decolorization efficiency and toxicity testing. Using attachment techniques, they immobilized white-rot fungi on materials such as polyethylene foam, polypropylene rings, ceramic tiles, and sawdust. Fungi immobilized on rings, including Polyporus picipes RWP17, Pleurotus ostreatus BWPH, and Gleophyllum odoratum DCa, showed optimal growth and achieved complete decolorization of Evans Blue and Brilliant Green dyes while eliminating phytotoxicity and reducing animal toxicity. Alam et al. [155] utilized an encapsulation approach, immobilizing Trametes hirsuta D7 on lightweight expanded clay aggregates (LECAs). The results demonstrated decolorization rates of 92% and 97% for the azo dyes Reactive Black 5 and Acid Blue 113, respectively. However, the decolorization rate for Acid Orange 7 was relatively low, at only 30%.
Solid-state fermentation (SSF) is an effective fungal immobilization method. SSF involves cultivating microorganisms on moist solid supports with minimal free liquid, often using natural substrates as energy sources or inert carriers soaked in nutrients [156]. This approach mimics the fungi’s natural environment and provides benefits over submerged fermentation, including higher ligninolytic enzyme yields, improved oxygen circulation, reduced energy requirements, and the potential for agricultural waste reuse [157,158]. Therefore, utilizing white-rot fungi immobilized via SSF to treat TDW is an environmentally friendly and efficient approach, and would enable the effective removal of dyes from wastewater while employing sustainable and eco-friendly materials for immobilizing white-rot fungi, thus furthering green and sustainable development initiatives.
Adak et al. [159] demonstrated the effectiveness of laccase extracted from Pseudolagarobasidium acaciicola LA1 for decolorizing Remazol Brilliant Blue R (90% in 4 h) and Reactive Black 5 (33% in 48 h). Similarly, Contato et al. [160] utilized laccases obtained from Pleurotus pulmonarius cultured on orange waste for the decolorization of various synthetic dyes. In their study, 11 dyes with a concentration of 0.05% were tested, with decolorization rates exceeding 80% for five dyes, whereas the remaining six dyes exhibited decolorization rates of 65% or lower. Furthermore, Bankole et al. [161] used SSF to culture a consortium of Daldinia concentrica and Xylaria polymorpha on common bean husks, achieving over 95% decolorization within 96 h. Toxicity analysis revealed a significant reduction in metabolite toxicity post-treatment, highlighting the feasibility of SSF for TDW remediation.
The use of white-rot fungi for the decolorization of TDW in bioreactors represents an advanced and efficient method. The bioreactor approach provides a stable and controlled environment for fungal growth and the expression of its decolorization capabilities. Bioreactors provide a controlled environment to optimize fungal activity and integrate multiple technologies for enhanced results. Recently, Diorio et al. [162] conducted several studies proposing low-cost, environmentally friendly, and innovative bioreactor systems. The system operates in two stages: in the first stage, Trametes versicolor is immobilized in spherical high-density plastic polyethylene containers filled with wheat bran as the growth substrate, where dye decolorization occurred at 28 °C; in the second stage, the extracellular extract of T. versicolor was employed for dye decolorization at 50 °C. Upon the completion of both stages, the decolorization efficiency for Malachite Green dye reached 97%. This system separated the fungal growth stage (under sterile conditions) from the decolorization stage (under non-sterile conditions). Utilizing immobilized fungi in structured bioreactor systems thus streamlines the treatment process and enhances dye removal performance.
2.3. Algal Biodegradation
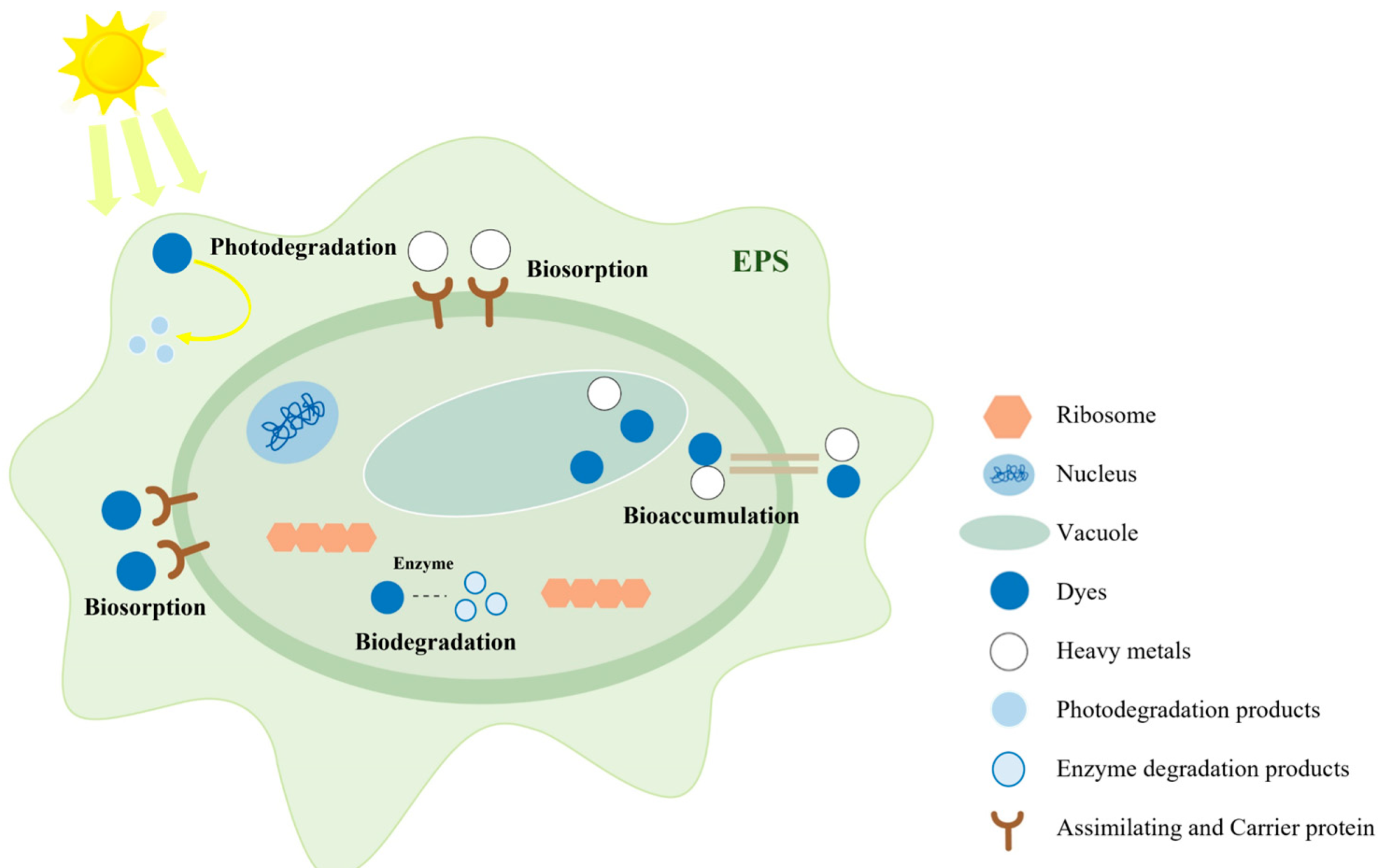
The use of algae to treat TDW has gained increasing attention. Algae are widely distributed in nature, abundant, and highly utilizable. As shown in Figure 2, the general process of algae treatment of TDW includes biosorption, biodegradation, photodegradation, and bioaccumulation. They possess a larger surface area compared with other organisms, with a strong binding capacity, exhibiting significant potential for the biosorption and electrostatic attraction of pollutants in wastewater [163]. Algae, as primary producers, possess cell walls containing various functional groups, such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, amino, and phosphate. These functional groups play crucial roles in the removal of pollutants from water [164]. Furthermore, compared with traditional treatment methods, algae-based treatment approaches are often easier to operate under standard atmospheric conditions, adaptable to various photobioreactors, and sustainable [165]. Table 7 presents some algal species capable of effectively degrading various types of dyes.
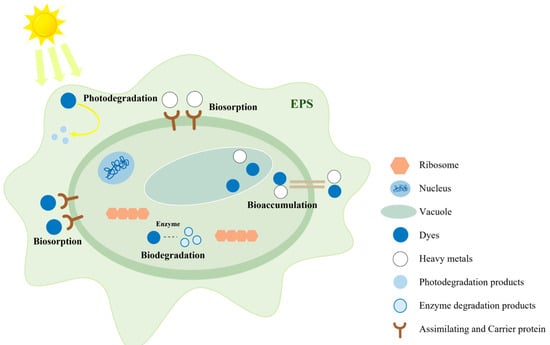
Figure 2.
The general process of algae treatment of printing and dyeing wastewater.

Table 7.
Algal treatment for textile dyeing wastewater.
Algae can degrade dyes of various colors, primarily through biosorption. Biosorption is a fundamental mechanism by which algae remove different types of dyes. This process involves forming complexes between dyes and functional groups on algal surfaces, such as amino, phosphate, carboxyl, and hydroxyl groups. Other biosorption mechanisms include ion exchange with cationic molecules and van der Waals interactions that enhance dye absorption [171]. Biological flocculation is a component of algal bio-adsorption. As dyes undergo transformation via metabolism-assisted processes, dye molecules aggregate on the surface of extracellular biopolymers produced by algae [172]. These exogenous long-chain biopolymers, which comprise surface functional groups, exhibit excellent flocculation properties and continually adsorb and precipitate dye molecules from aqueous solutions.
Biological transformation or degradation represents another form of algae-mediated adsorption. Various species of Chlorella and Scenedesmus can degrade azo dyes, producing aromatic amines that are subsequently transformed into singular organic molecules, such as carbon dioxide [172]. Factors influencing the algae-mediated remediation process include the pH and dye structure. As pH affects dye solubility, it is one of the most critical factors influencing biological adsorption. Additionally, it affects the ionization states of various organic functional groups (such as amines, carboxyls, and hydroxyls) present on the adsorbent’s surface and the chemical properties of the dye solution [173]. As the optimal pH decreases, each biologically assisted process or reaction slows.
Various researchers have made significant progress in the field of TDW treatment using microalgae. Cardoso et al. [174] compared the efficacy of Spirulina platensis (SP) and commercial activated carbon (AC) as adsorbents for removing Reactive Red 120 dye from wastewater. Their experimental results indicated that the maximum adsorption of Reactive Red 120 dye occurred at pH 2 and room temperature (298 K), with adsorption capacities of 482.2 and 267.2 mg/g for SP and AC adsorbents, respectively. Thermodynamic studies suggested that the adsorption processes for both adsorbents were spontaneous, exothermic, and favorable. The removal efficiencies of the SP and AC adsorbents for simulated industrial TDW ranged from 94.4% to 99.0% and 93.6% to 97.7%, respectively. On the other hand, Arteaga et al. [175] investigated the decolorization efficiency of Chlorella vulgaris toward Aniline Blue dye. The experimental results demonstrated that C. vulgaris achieved complete removal of Aniline Blue dye at initial concentrations of 25, 50, 75, and 100 mg/L. Analysis of variance indicated that the dye removal efficiency depended on the initial concentration and removal time; the optimal treatment was observed after 11 days, when the initial concentration of Aniline Blue dye was 75 mg/L.
In addition to microalgae, many macroalgae exhibit strong resilience and cleansing effects on contaminated water bodies. Macroalgae, as the name suggests, are multicellular algae with large physical forms, with some reaching lengths exceeding 1 m. The bioremediation functions of macroalgae primarily involve the absorption, degradation, and transfer of pollutants, thereby reducing nutrient concentrations in water bodies, improving water quality, and minimizing or ultimately eliminating pollution.
In recent years, green algal blooms have become increasingly pronounced. Among the strategies for the prevention and mitigation of green algal blooms, resource utilization of macroalgae (such as Enteromorpha prolifera and Ulva pertusa) has attracted increasing attention from researchers. Li et al. [176] utilized naturally air-dried and pulverized E. prolifera, a green alga, as a biosorbent for treating wastewater containing Acid Red B (ARB) dye. Under the conditions of a contact time of 60 min, pH ranging from 4 to 9, temperature between 303 and 313 K, agitation rate of 150 rpm, and biosorbent dosage of 0.25 g/L, the decolorization efficiency of the biosorbent toward wastewater containing 100 mg/L ARB dye reached 90.86%. The Langmuir equation calculated the maximum equilibrium adsorption capacity to be within the range of 1111.11 to 3333.33 mg/g. Özer et al. [177] prepared biosorbents from naturally air-dried Spirogyra rhizopus algae by heat-treating them at 105 °C, followed by pulverization. These biosorbents were used to treat wastewater containing the Acid Blue 290 (AB 290) and Acid Blue 324 (AB 324) dyes. The optimal initial pH and temperature for the biosorption of AB 290 and AB 324 were determined to be 2.0 at 30 °C and 3.0 at 25 °C, respectively. The optimum biosorption conditions were identified as follows: initial dye concentration of 100 mg/L, biosorbent dosage of 0.5 g/L, pH 2.0, and temperature of 30 °C for AB 290 dye adsorption, and pH 3.0 and temperature of 25 °C for AB 324 dye adsorption. The maximum monolayer adsorption capacities of this biosorbent for AB 290 and AB 324 dyes were 1356.6 and 367.0 mg/g, respectively.
Brown algae and other large algal species have also been utilized for dye decolorization. Brown algae are globally abundant, including more large algal species than green algae, making them easier to collect. Moreover, the adsorption capacity of brown algae is often much higher than those of other biological materials, and sometimes surpasses those of activated carbon and natural zeolites [178]. Vijayaraghavan and Yun [179] employed seaweed (Laminaria sp.) to adsorb wastewater containing Reactive Black 5 (RB5) dye. Dried seaweed powder treated with HCl was used to treat RB5 solution at an initial concentration of 200 mg/L. Under a temperature of 25 °C and pH of 1, the adsorption capacity reached 53.8 mg/g, higher than that of untreated seaweed powder (39.4 mg/g). Simultaneously, the feasibility of the continuous removal of RB5 dye from water by Laminaria sp. was investigated in an up-flow packed-bed column (diameter, 1 cm; height, 12 cm). When the bed height, flow rate, and initial RB5 concentration were 10 cm, 1 mL/min, and 50 mg/L, respectively, Laminaria sp. exhibited adsorption capacities and removal efficiency for RB5 of 41.9 mg/g and 72.7%. Tan et al. [180] utilized dried A. filiculoides powder to treat industrial TDW containing Basic Orange (BO) dye. Their study revealed that the saturated adsorption capacity of dried A. filiculoides powder for BO was maximized at temperatures below 30 °C, reaching 833 mg/g. The investigation of the adsorption mechanism indicated that the process involved multiple mechanisms, including ion exchange adsorption, physical adsorption through intraparticle diffusion, and chemical adsorption on particle surfaces. Results from treating actual industrial wastewater showed that, after treatment with 5 g/L of dried A. filiculoides powder, the CODCr of the wastewater decreased from 459.2 to 259.02 mg/L, with a removal efficiency of 43.6%. Furthermore, when 100 mg/L of BO dye was added to the wastewater, the decolorization rate reached 79.3%.
3. Research and Development Needs
The methods for treating TDW include physical, chemical, and biological approaches. However, physical and chemical methods have certain limitations, such as high energy consumption, poor renewability, and the potential for secondary pollution. Biological methods have achieved significant advancements in the treatment of TDW; however, certain aspects require further exploration. The choice of biological material significantly affects the efficiency of pollutant removal from TDW. Given the complex composition and high pollutant concentrations of such wastewater, the selection of biological materials with strong pollution resistance and rapid reproduction is essential for thriving in harsh environments. Additionally, the use of biological materials capable of producing high-value byproducts can lead to economic benefits.
Among various biological methods, the use of algae for treating TDW has demonstrated tremendous potential. Algae can effectively mitigate chemical toxicity, reduce health risks, and minimize resource demand, making them suitable for addressing industry-specific challenges. Cultivating algae in TDW offers favorable conditions for biomass production, lowers treatment costs, and enables the generation of high-value-added products. Additionally, algae possess exceptional carbon sequestration capabilities, which support energy-efficient production of biofuels, biogas, organic fertilizers, and animal feed. Integrating algae into conventional treatment systems can further reduce costs and environmental impacts while enhancing industrial sustainability. However, optimizing algal bioremediation requires advancements in reactor design, algae selection, cultivation strategies, and harvesting techniques. Innovations in bioreactor configurations, system optimization, and harvesting methods will be pivotal in advancing algal bioremediation technologies. These developments can drive the widespread adoption of sustainable wastewater treatment in the textile dyeing and printing industry, contributing to enhanced environmental sustainability and economic circularity.
In addition to traditional biological treatment techniques, highly efficient bacterial isolation techniques can be used to screen specialized bacteria capable of efficiently treating TDW. Genetic and cellular engineering techniques can be employed to modify microorganisms to better meet the needs of the treatment of TDW. Fermentation engineering can simultaneously remove pollutants and produce high-value recyclable metabolites. Enzyme engineering can produce highly specific and efficient catalytic degradation enzymes that can effectively remove specific pollutants from TDW. Biological flocculation technology can produce microbial flocculants, thereby reducing the cost of flocculants and enabling sustainable production. Microbial immobilization techniques can enhance the activity of microorganisms in TDW and reduce microbial loss during treatment.
Despite their potential, biological treatments face challenges in real-world applications. Scaling up microbial systems is hindered by factors such as environmental variability, high operational costs, and limited dye-specific degradation pathways. Additionally, the integration of biological methods with existing chemical or physical systems could mitigate individual limitations, but requires further exploration. Future research should prioritize the development of cost-effective immobilization techniques and hybrid reactor designs to enhance scalability and performance.
Future research should focus on leveraging advancements in genetic engineering to develop microbial strains with enhanced dye-degrading capabilities. Hybrid systems combining bioremediation with physical processes, such as photocatalysis or membrane filtration, could further improve efficiency and reduce operational costs. Interdisciplinary collaboration between microbiology, materials science, and chemical engineering will be critical in optimizing reactor designs and exploring novel applications, such as bio-based resource recovery from treated wastewater.
4. Conclusions
TDW contains complex and diverse pollutants, making direct discharge a significant source of water pollution. Comprehensive treatments using physical, chemical, and biological methods are essential. Biological treatment methods, particularly those involving microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and microalgae, are more environmentally friendly and sustainable than physical and chemical techniques. These microorganisms have shown significant potential for the treatment and reuse of TDW. Research on their applications will enhance the maturity and environmental sustainability of these technologies.
Author Contributions
Investigation, Y.L. and J.C.; writing—original draft, Y.L. and J.C.; data curation, D.D.; formal analysis, D.D. and Z.Z. (Ziyang Zhang); conceptualization, C.L. and Z.Z. (Ziwen Zhao); supervision, C.L. and W.C.; writing—review and editing, W.C. and Z.Z. (Ziwen Zhao); funding acquisition, Z.Z. (Ziwen Zhao). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Special Basic Research Fund for Central Public Research Institutes of China (No. PM-zx703-202305-271), Science and Technology Projects in Guangzhou (2023A04J1028), and Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (2023A1515111143).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Jiménez-Delgado, G.; Quintero-Ariza, I.; Romero-Gómez, J.; Montero-Bula, C.; Rojas-Castro, E.; Santos, G.; Sá, J.C.; Londoño-Lara, L.; Hernández-Palma, H.; Campis-Freyle, L. Implementation of Lean Six Sigma to Improve the Quality and Productivity in Textile Sector: A Case Study; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 395–412. [Google Scholar]
- Kant, R. Textile dyeing industry an environmental hazard. Nat. Sci. 2011, 4, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ning, X.-a.; Chen, G.; Lin, M.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Concentrations and speciation of heavy metals in sludge from nine textile dyeing plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 98, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Mooney, H.; Hull, V.; Davis, S.J.; Gaskell, J.; Hertel, T.; Lubchenco, J.; Seto, K.C.; Gleick, P.; Kremen, C. Systems integration for global sustainability. Science 2015, 347, 1258832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Ai, F.; Jin, L.; Zhu, N.; Meng, X.-Z. Identification of industrial sewage sludge based on heavy metal profiles: A case study of printing and dyeing industry. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 12377–12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Khan, T.A.; Islam, M.A.; Tabrez, U. A review on the treatment of dyes in printing and dyeing wastewater by plant biomass carbon. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 354, 127168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarab, N.; Hsini, A.; Essekri, A.; Laabd, M.; Lakhmiri, R.; Albourine, A. Removal of an emerging pharmaceutical pollutant (metronidazole) using PPY-PANi copolymer: Kinetics, equilibrium and DFT identification of adsorption mechanism. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 11, 100416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Rangabhashiyam, S.; Dulta, K.; Umeh, C.T.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Aniagor, C.O.; Eshiemogie, S.O.; Iwuchukwu, F.U.; Igwegbe, C.A. Recent advances in hydrochar application for the adsorptive removal of wastewater pollutants. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 184, 419–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qahtani, S.D.; Snari, R.M.; Alamrani, N.A.; Aljuhani, E.; Bayazeed, A.; Aldawsari, A.M.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Synthesis and adsorption properties of fibrous-like aerogel from acylhydrazone polyviologen: Efficient removal of reactive dyes from wastewater. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 1822–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, A.; Foroutan, R.; Esmaeili, H.; Peighambardoust, S.J.; Hemmati, S.; Ramavandi, B. Montmorillonite clay/starch/CoFe2O4 nanocomposite as a superior functional material for uptake of cationic dye molecules from water and wastewater. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 284, 126088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O.; Ighalo, J.O.; Emenike, E.C.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Adeniyi, A.G. Do adsorbent pore size and specific surface area affect the kinetics of methyl orange aqueous phase adsorption? J. Chem. Lett. 2021, 2, 188–198. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, J.; Bakhsh, E.M.; Hussain, N.; Bilal, M.; Akhtar, K.; Fagieh, T.M.; Danish, E.Y.; Asiri, A.M.; Su, X.; Khan, S.B. A new biosource for synthesis of activated carbon and its potential use for removal of methylene blue and eriochrome black T from aqueous solutions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 179, 114676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwuozor, K.O.; Ighalo, J.O.; Ogunfowora, L.A.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Igwegbe, C.A. An empirical literature analysis of adsorbent performance for methylene blue uptake from aqueous media. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Qiang, X.; Gu, W.; Ma, Z.; Wang, G. An overview of biological mechanisms and strategies for treating wastewater from printing and dyeing processes. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Song, M.; Zeng, B.; Shen, L.; Zhao, L.; Lin, H. Novel cetyltrimethylammonium bromide modified mixed adsorbent for efficient treatment of dyeing and printing wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2023, 176, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshmiri-Naqab, R.; Taghavijeloudar, M. Could organoclay be used as a promising natural adsorbent for efficient and cost-effective dye wastewater treatment? J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, T.; Mei, Y.; Pan, B. Treatment of reverse-osmosis concentrate of printing and dyeing wastewater by electro-oxidation process with controlled oxidation-reduction potential (ORP). Chemosphere 2018, 201, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solayman, H.; Hossen, M.A.; Abd Aziz, A.; Yahya, N.Y.; Leong, K.H.; Sim, L.C.; Monir, M.U.; Zoh, K.-D. Performance evaluation of dye wastewater treatment technologies: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, B.; Chen, J. Reuse of printing and dyeing wastewater in processess assessed by pilot-scale test using combined biological process and sub-filter technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2009, 17, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Chen, Y.; Guan, J.; Ding, Y.; He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shukurov, N.; Romanholo Ferreira, L.F.; Liu, J.; Zhu, M. Biodecolorization and Ecotoxicity Abatement of Disperse Dye-Production Wastewater Treatment with Pycnoporus Laccase. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, V.H.T.; Kim, J.; Chang, S.; Bang, D. Investigating Bio-Inspired Degradation of Toxic Dyes Using Potential Multi-Enzyme Producing Extremophiles. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa, A.L.D.; Carissimi, E.; Dotto, G.L.; Sander, H.; Feris, L.A. Biosorption of rhodamine B dye from dyeing stones effluents using the green microalgae Chlorella pyrenoidosa. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Shenashen, M.; Hasan, M.N.; Znad, H.; Salman, M.S.; Awual, M.R. Natural biodegradable polymeric bioadsorbents for efficient cationic dye encapsulation from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 323, 114587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen, D.; Scholz, M. Textile dye wastewater characteristics and constituents of synthetic effluents: A critical review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 1193–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varadarajan, G.; Venkatachalam, P. Sustainable textile dyeing processes. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016, 14, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhav, S.; Ahamad, A.; Singh, P.; Mishra, P.K. A review of textile industry: Wet processing, environmental impacts, and effluent treatment methods. Environ. Qual. Manag. 2018, 27, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatha, S.A.S.; Asgher, M.; Iqbal, H.M. Enzyme-based solutions for textile processing and dye contaminant biodegradation—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 14005–14018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarayu, K.; Sandhya, S. Aerobic biodegradation pathway for Remazol Orange by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 160, 1241–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindhal, T.; Rakholiya, P.; Varjani, S.; Pandey, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Ng, H.Y.; Taherzadeh, M.J. A critical review on advances in the practices and perspectives for the treatment of dye industry wastewater. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Adeyanju, C.A.; Ogunniyi, S.; Adeniyi, A.G.; Abdulkareem, S.A. An empirical review of the recent advances in treatment of natural fibers for reinforced plastic composites. Compos. Interfaces 2021, 28, 925–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, A.; Ananthashankar, R.; Alhattab, M.; Ramakrishnan, V.V. Production, characterization and treatment of textile effluents: A critical review. J. Chem. Eng. Process Technol. 2014, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ewuzie, U.; Saliu, O.D.; Dulta, K.; Ogunniyi, S.; Bajeh, A.O.; Iwuozor, K.O.; Ighalo, J.O. A review on treatment technologies for printing and dyeing wastewater (PDW). J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 50, 103273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, B.M.; Ibrahim, N.A. Recent developments in sustainable finishing of cellulosic textiles employing biotechnology. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 284, 124701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holkar, C.R.; Jadhav, A.J.; Pinjari, D.V.; Mahamuni, N.M.; Pandit, A.B. A critical review on textile wastewater treatments: Possible approaches. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. China Ecological and Environmental Statistics Yearbook. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/sthjtjnb/202312/W020231229339540004481.pdf (accessed on 8 December 2024).
- Manu, B.; Chaudhari, S. Anaerobic decolorisation of simulated textile wastewater containing azo dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, X.; Jiao, F.; Liu, W. Review on dyeing wastewater treatment technology. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 54, 1219–1229. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.; Pan, T.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Zheng, H. Reactive black 5 dyeing wastewater treatment by electrolysis-Ce (IV) electrochemical oxidation technology: Influencing factors, synergy and enhancement mechanisms. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, S.; Khalid, A.; Arshad, M.; Mahmood, T.; Crowley, D.E. Detoxification of azo dyes by bacterial oxidoreductase enzymes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routoula, E.; Patwardhan, S.V. Degradation of anthraquinone dyes from effluents: A review focusing on enzymatic dye degradation with industrial potential. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Shaid, A.; Bashar, M.; Khan, M.A. Scope of reusing and recycling the textile wastewater after treatment with gamma radiation. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3063–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yukseler, H.; Uzal, N.; Sahinkaya, E.; Kitis, M.; Dilek, F.B.; Yetis, U. Analysis of the best available techniques for wastewaters from a denim manufacturing textile mill. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 203, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge, A.M.; Athira, K.; Alves, M.B.; Gardas, R.L.; Pereira, J.F. Textile dyes effluents: A current scenario and the use of aqueous biphasic systems for the recovery of dyes. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyo, S.; Makhanya, B.P.; Zwane, P.E. Use of bacterial isolates in the treatment of textile dye wastewater: A review. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyavahare, G.; Jadhav, P.; Jadhav, J.; Patil, R.; Aware, C.; Patil, D.; Gophane, A.; Yang, Y.-H.; Gurav, R. Strategies for crystal violet dye sorption on biochar derived from mango leaves and evaluation of residual dye toxicity. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, F.R.; Soares, A.M.; de Oliveira, D.P.; Gravato, C. Toxicity of dyes to zebrafish at the biochemical level: Cellular energy allocation and neurotoxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 235, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Carr, C.M. A critical review on recent advancements of the removal of reactive dyes from dyehouse effluent by ion-exchange adsorbents. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuyie, M. Heavy metals concentration in effluents of textile industry, Tikur Wuha River and milk of cows watering on this water source, Hawassa, Southern Ethiopia. J. Nat. Sci. Res. 2014, 4, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- El-Kassas, H.Y.; Mohamed, L.A. Bioremediation of the textile waste effluent by Chlorella vulgaris. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2014, 40, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Chang, H.; Liang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Ren, L.; Liang, H. Research progress and trends on state-of-the-art membrane technologies in textile wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 333, 125853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental chemistry and ecotoxicology of hazardous heavy metals: Environmental persistence, toxicity, and bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebeir, M.; Liu, H. Kinetics and mechanisms of Cr (VI) formation via the oxidation of Cr (III) solid phases by chlorine in drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Z.-H.; Qian, W.; Zhang, Z.-W.; Jin, J.-C.; Chen, Z.-L.; Guo, P.-R.; Dong, F.-X.; Yan, L.; Kong, L.-J.; Chu, W. Removals of Cr (VI) and Cd (II) by a novel nanoscale zero valent iron/peroxydisulfate process and its Fenton-like oxidation of pesticide atrazine: Coexisting effect, products and mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 397, 125382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Dai, X.; Huang, Z.; Wang, T.; Cui, L.; Ye, J.; Wu, P. Simultaneous and efficient photocatalytic reduction of Cr (VI) and oxidation of trace sulfamethoxazole under LED light by rGO@ Cu2O/BiVO4 pn heterojunction composite. Chemosphere 2019, 221, 824–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Tian, Q.; Hou, L.; Rao, R.; Yao, C.; Zhu, H. The self-boosting ultrafast removal of Cr (VI) and organic dye in textile wastewater through sulfite-induced redox processes. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 355, 124182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunnick, K.M.; Morris, A.M.; Badding, M.A.; Barger, M.; Stefaniak, A.B.; Sabolsky, E.M.; Leonard, S.S. Evaluation of the effect of valence state on cerium oxide nanoparticle toxicity following intratracheal instillation in rats. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 992–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jena, G.; Dutta, K.; Daverey, A. Surfactants in water and wastewater (greywater): Environmental toxicity and treatment options. Chemosphere 2023, 341, 140082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoletti, A.; Federici, S.; Borgese, L.; Bergese, P.; Ferroni, M.; Depero, L.E.; Bontempi, E. Embodied energy as key parameter for sustainable materials selection: The case of reusing coal fly ash for removing anionic surfactants. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 141, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effendi, I.; Nedi, S.; Pakpahan, R. Detergent Disposal into Our Environmentand Its Impact on Marine Microbes. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2017, 97, 012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bal, G.; Thakur, A. Distinct approaches of removal of dyes from wastewater: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 50, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapdan, I.K.; Kargi, F. Simultaneous biodegradation and adsorption of textile dyestuff in an activated sludge unit. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 973–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabir, M.; Yasin, M.; Hussain, M.; Shafiq, I.; Akhter, P.; Nizami, A.-S.; Jeon, B.-H.; Park, Y.-K. A review on recent advances in the treatment of dye-polluted wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 112, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, H.I.; Lim, L.B.; Priyantha, N. Sorption characteristics of peat from Brunei Darussalam for the removal of rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution: Adsorption isotherms, thermodynamics, kinetics and regeneration studies. Desalination Water Treat. 2015, 55, 664–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mall, I.D.; Srivastava, V.C.; Agarwal, N.K.; Mishra, I.M. Adsorptive removal of malachite green dye from aqueous solution by bagasse fly ash and activated carbon-kinetic study and equilibrium isotherm analyses. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 264, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tohamy, R.; Ali, S.S.; Li, F.; Okasha, K.M.; Mahmoud, Y.A.-G.; Elsamahy, T.; Jiao, H.; Fu, Y.; Sun, J. A critical review on the treatment of dye-containing wastewater: Ecotoxicological and health concerns of textile dyes and possible remediation approaches for environmental safety. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 231, 113160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsami, S.; Mohamadizaniani, M.; Sarrafzadeh, M.-H.; Rene, E.R.; Firoozbahr, M. Recent advances in the treatment of dye-containing wastewater from textile industries: Overview and perspectives. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 143, 138–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, N.M.; Pascu, L.F.; Demba, A.; Nita-Lazar, M.; Badea, I.A.; Aboul-Enein, H. Removal of the Acid Orange 10 by ion exchange and microbiological methods. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 6357–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, R.; Purchase, D.; Saratale, G.D.; Saratale, R.G.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Chandra, R.; Bharagava, R.N. Ecotoxicological and health concerns of persistent coloring pollutants of textile industry wastewater and treatment approaches for environmental safety. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayramoglu, G.; Kunduzcu, G.; Arica, M.Y. Preparation and characterization of strong cation exchange terpolymer resin as effective adsorbent for removal of disperse dyes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2020, 60, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Qi, Y.; Liang, S.; Qin, S.; Yu, J. Polypropylene composite hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes with an acrylic hydrogel surface by in situ ultrasonic wave-assisted polymerization for dye removal. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fradj, A.B.; Boubakri, A.; Hafiane, A.; Hamouda, S.B. Removal of azoic dyes from aqueous solutions by chitosan enhanced ultrafiltration. Results Chem. 2020, 2, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağtaş, M.; Yılmaz, Ö.; Dilaver, M.; Alp, K.; Koyuncu, I. Hot water recovery and reuse in textile sector with pilot scale ceramic ultrafiltration/nanofiltration membrane system. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 256, 120359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, S.; Shaw, R.; Tiwari, S.; Tiwari, S.K. Adsorption dynamics of Congo red dye removal using ZnO functionalized high silica zeolitic particles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 487, 907–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yu, W.; He, S.; Yu, S.; Chen, Y.; Lu, L.; Shu, Z.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H. Rapid adsorption of cationic dye-methylene blue on the modified montmorillonite/graphene oxide composites. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-S.; Liu, C.-H.; Chu, K.H.; Suen, S.-Y. Removal of cationic dye methyl violet 2B from water by cation exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 309, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzkiewicz, M. Anion exchange resins as effective sorbents for acidic dye removal from aqueous solutions and wastewaters. Solvent Extr. Ion Exch. 2012, 30, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Fang, S.; Chen, W. A PEG-tannic acid decorated microfiltration membrane for the fast removal of Rhodamine B from water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 207, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkadokula, N.Y.; Kola, A.K.; Naz, I.; Saroj, D. A review on advanced physico-chemical and biological textile dye wastewater treatment techniques. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2020, 19, 543–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles-Cuevas, S.; Oller, I.; Agüera, A.; Llorca, M.; Pérez, J.S.; Malato, S. Combination of nanofiltration and ozonation for the remediation of real municipal wastewater effluents: Acute and chronic toxicity assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 323, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, K.P.; Argyriou, R.; Economou, C.N.; Charalampous, N.; Dailianis, S.; Tatoulis, T.I.; Tekerlekopoulou, A.G.; Vayenas, D.V. Treatment of printing ink wastewater using electrocoagulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 237, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, M.; Al-Sarawy, A.; El-Dein, W.S. Electrochemical degradation of some organic dyes by electrochemical oxidation on a Pb/PbO2 electrode. Desalination Water Treat. 2011, 26, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahmadi, M.F.; Bensalah, N.; Gadri, A. Treatment of aqueous wastes contaminated with Congo Red dye by electrochemical oxidation and ozonation processes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1163–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slokar, Y.M.; Le Marechal, A.M. Methods of decoloration of textile wastewaters. Dye. Pigment. 1998, 37, 335–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaan, M.A.; El Nemr, A.; Madkour, F.F. Testing the advanced oxidation processes on the degradation of Direct Blue 86 dye in wastewater. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 43, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Guo, Y.-Q.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Liang, B.; Kong, F.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Wang, A.-J. Azo dye removal in a membrane-free up-flow biocatalyzed electrolysis reactor coupled with an aerobic bio-contact oxidation reactor. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 239, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotillas, S.; Llanos, J.; Cañizares, P.; Clematis, D.; Cerisola, G.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Panizza, M. Removal of Procion Red MX-5B dye from wastewater by conductive-diamond electrochemical oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 263, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafpoor, A.A.; Davoudi, M.; Rahmanpour Salmani, E. Decolorization of synthetic textile wastewater using electrochemical cell divided by cellulosic separator. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2017, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, J.; Hasal, P. Photocatalytic degradation of textile dyes in a TiO2/UV system. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2013, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Luo, C.; Tan, F.; Cheng, X.; Ma, Q.; Wu, D.; Li, P.; Zhang, F.; Ma, J. Degradation of Congo red by UV photolysis of nitrate: Kinetics and degradation mechanism. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 262, 118276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popli, S.; Patel, U.D. Destruction of azo dyes by anaerobic–aerobic sequential biological treatment: A review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.F.S.; Albuquerque, C.D.C.; Salgueiro, A.A.; Sarubbo, L.A. Color removal from industrial dyeing and laundry effluent by microbial consortium and coagulant agents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 118, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, G.; Meehan, C.; Conneely, A.; Kirby, N.; Robinson, T.; Nigam, P.; Banat, I.; Marchant, R.; Smyth, W. Microbial decolourisation and degradation of textile dyes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 56, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbanna, K.; Hassan, G.; Khider, M.; Mandour, R. Safe Biodegradation of Textile Azo Dyes by Newly Isolated Lactic Acid Bacteria and Detection of Plasmids Associated with Degradation. J. Bioremediation Biodegrad. 2010, 1, 112. [Google Scholar]
- Vikas, K.; Preeti, P.; Sudip Kumar, S.; Sangeeta, R. Harnessing the potential of white rot fungi and ligninolytic enzymes for efficient textile dye degradation: A comprehensive review. Water Environ. Res. 2024, 96, e10959. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, A.; Mohd-Setapar, S.H.; Chuong, C.S.; Khatoon, A.; Wani, W.A.; Kumar, R.; Rafatullah, M. Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: Novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 30801–30818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeberl, P.; Brik, M.; Bertoni, M.; Braun, R.; Fuchs, W. Optimization of operational parameters for a submerged membrane bioreactor treating dyehouse wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Al Biruni, M.T.; Azad, S.; Ahmed, T. Adsorptive removal of dye from textile wastewater employing Moringa oleifera leaves biochar as a natural biosorbent. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 11075–11091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.R.; King, P.; Wolde, Z.; Mulu, M. Application of optimization response surface for the biosorption of crystal violet dye from textile wastewater onto Clerodendrum fragrans leaves. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 17133–17148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, N.; Sinchai, P.S.; Tansom, U. Banana peel as bioremediation agent in textile dyes decolorization for wastewater management. Biochem. Syst. Ecol. 2023, 106, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramzan, U.; Shakoori, F.R.; Zahid, M.T.; Majeed, W.; Zahra, I.; Abbas, S.Z.; Hedfi, A.; Hassan, S.; Shakoori, A.R.; Mutery, A.A. Biodegradation and decolorization of textile azo dyes by Paramecium caudatum isolated from industrial wastewater. Water 2022, 14, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Vazquez, I.; Robledo-Rizo, J.G.; Muñoz-Páez, K.M.; Pérez-Rangel, M.; de la Luz Ruiz-Aguilar, G.M. Simultaneous hydrogen production and decolorization of denim textile wastewater: Kinetics of decolorizing of indigo dye by bacterial and fungal strains. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2020, 51, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekanayake, E.; Manage, P. Decolourisation and detoxification of CI Direct Blue 201 textile dye by two fungal strains of genus Aspergillus. J. Natl. Sci. Found. Sri Lanka 2020, 106, 104582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fawwaz, A.T.; Abdullah, M. Decolorization of methylene blue and malachite green by immobilized Desmodesmus sp. isolated from North Jordan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2016, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhou, Q.; Xu, H.; Chen, H.; Xue, G. Advances from conventional to biochar enhanced biotreatment of dyeing wastewater: A critical review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavithra, K.G.; Jaikumar, V. Removal of colorants from wastewater: A review on sources and treatment strategies. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 75, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafqat, M.; Khalid, A.; Mahmood, T.; Siddique, M.T.; Han, J.I.; Habteselassie, M.Y. Evaluation of bacteria isolated from textile wastewater and rhizosphere to simultaneously degrade azo dyes and promote plant growth. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 2760–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solis-Oba, M.M.; Solís, A.; Pérez, H.I.; Manjarrez, N.; Flores, M. Microbial decolouration of azo dyes. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1723–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, M.; Sanganyado, E.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, W.; Song, H. Azo dye degrading bacteria tolerant to extreme conditions inhabit nearshore ecosystems: Optimization and degradation pathways. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerboneschi, M.; Corsi, M.; Bianchini, R.; Bonanni, M.; Tegli, S. Decolorization of acid and basic dyes: Understanding the metabolic degradation and cell-induced adsorption/precipitation by Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8235–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Xu, X.; Wen, Z.; Kang, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, Y.; Huang, D. Decolorization pathways of anthraquinone dye Disperse Blue 2BLN by Aspergillus sp. XJ-2 CGMCC12963. Bioengineered 2017, 8, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velayutham, K.; Madhava, A.K.; Pushparaj, M.; Thanarasu, A.; Devaraj, T.; Periyasamy, K.; Subramanian, S. Biodegradation of Remazol Brilliant Blue R using isolated bacterial culture (Staphylococcus sp. K2204). Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 2900–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayed, L.; Chaieb, K.; Cheref, A.; Bakhrouf, A. Biodegradation and decolorization of triphenylmethane dyes by Staphylococcus epidermidis. Desalination 2010, 260, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheriaa, J.; Khaireddine, M.; Rouabhia, M.; Bakhrouf, A. Removal of triphenylmethane dyes by bacterial consortium. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 512454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.; Malik, A. Toxicity evaluation of textile effluents and role of native soil bacterium in biodegradation of a textile dye. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 4446–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meerbergen, K.; Willems, K.A.; Dewil, R.; Van Impe, J.; Appels, L.; Lievens, B. Isolation and screening of bacterial isolates from wastewater treatment plants to decolorize azo dyes. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018, 125, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Bouraie, M.; El Din, W.S. Biodegradation of Reactive Black 5 by Aeromonas hydrophila strain isolated from dye-contaminated textile wastewater. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2016, 26, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Kumar, A. Optimization and kinetic studies on decolorization of Vat Green XBN by a newly isolated bacterial strain Proteus mirabilis PMS. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewida, A.Y.; El-Sesy, M.E.; Abou Zeid, A. Complete degradation of azo dye acid red 337 by Bacillus megaterium KY848339. 1 isolated from textile wastewater. Water Sci. 2019, 33, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unnikrishnan, S.; Khan, M.H.; Ramalingam, K. Dye-tolerant marine Acinetobacter baumannii-mediated biodegradation of reactive red. Water Sci. Eng. 2018, 11, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Joshiba, G.J. Sustainable approach to decolourize methyl orange dye from aqueous solution using novel bacterial strain and its metabolites characterization. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2021, 23, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad Hanapi, N.H.; Sayid Abdullah, S.H.Y.; Khairuddin, Z.; Mahmod, N.H.; Monajemi, H.; Ismail, A.; Lananan, F.; Suhaili, Z.; Endut, A.; Juahir, H. COD removal and colour degradation of textile dye effluents by locally isolated microbes. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2022, 102, 7835–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, M.Z.; Hussain, M.E.; Hakim, A.; Islam, K.; Uddin, M.N.; Azad, A.K. Biodegradation of reactive textile dye Novacron Super Black G by free cells of newly isolated Alcaligenes faecalis AZ26 and Bacillus spp obtained from textile effluents. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barathi, S.; Aruljothi, K.; Karthik, C.; Padikasan, I.A.; Ashokkumar, V. Biofilm mediated decolorization and degradation of reactive red 170 dye by the bacterial consortium isolated from the dyeing industry wastewater sediments. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, N.; Garg, A.; Mukherji, S. Eco-friendly decolorization and degradation of reactive yellow 145 textile dye by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Thiosphaera pantotropha. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Banerjee, A.; Halder, U.; Biswas, R.; Bandopadhyay, R. Degradation of synthetic azo dyes of textile industry: A sustainable approach using microbial enzymes. Water Conserv. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasubramani, K.; Ganesh, P.; Sivagurunathan, P.; Kolanjinathan, K.; Raman, H. Biodegradation potential of an estuarine bacterium Bacillus megaterium PNS 15 against an azo dye, reactive Blue 194. J. Appl. Biol. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Falade, A.; Mabinya, L.; Okoh, A.; Nwodo, U. Peroxidases Produced by New Ligninolytic Bacillus strains Isolated from Marsh and Grassland Decolourized Anthraquinone and Azo Dyes. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2019, 28, 3163–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legerská, B.; Chmelová, D.; Ondrejovič, M. Degradation of synthetic dyes by laccases–a mini-review. Nova Biotechnol. Chim. 2016, 15, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Farraj, D.A.; Elshikh, M.S.; Al Khulaifi, M.M.; Hadibarata, T.; Yuniarto, A.; Syafiuddin, A. Biotransformation and Detoxification of Antraquione Dye Green 3 using halophilic Hortaea sp. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2019, 140, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenan, N.H.; Lim, Y.Y.; Ting, A.S.Y. Discovering decolorization potential of triphenylmethane dyes by actinobacteria from soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.-S.; Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, J.-H.; Kang, D.-W.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, Y.-C. Triphenylmethane reductase from Citrobacter sp. strain KCTC 18061P: Purification, characterization, gene cloning, and overexpression of a functional protein in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 7955–7960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshetti, G.; Parshetti, S.; Telke, A.; Kalyani, D.; Doong, R.; Govindwar, S.P. Biodegradation of crystal violet by Agrobacterium radiobacter. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruppathi, K.; Rangasamy, K.; Ramasamy, M.; Muthu, D. Evaluation of textile dye degrading potential of ligninolytic bacterial consortia. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, M.; Liyanage, N.; Herath, C.; Rathnayake, S.; Fernando, E.Y. Mineralization of persistent azo dye pollutants by a microaerophilic tropical lake sediment mixed bacterial consortium. Environ. Adv. 2021, 3, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Mishra, S. Removal of textile dye reactive green-19 using bacterial consortium: Process optimization using response surface methodology and kinetics study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 612–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.S.; Kumar, A. Biodegradation of Indanthrene Blue RS dye in immobilized continuous upflow packed bed bioreactor using corncob biochar. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Pal, D.B.; Mohammad, A.; Alhazmi, A.; Haque, S.; Yoon, T.; Srivastava, N.; Gupta, V.K. Biological remediation technologies for dyes and heavy metals in wastewater treatment: New insight. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, I.S.; Udayanga, D.; Jayasanka, D.; Hewawasam, C. Textile dye decolorization by white rot fungi–A review. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 25, 101687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinfling, A.; Martínez, M.J.; Martinez, A.; Bergbauer, M.; Szewzyk, U. Transformation of industrial dyes by manganese peroxidases from Bjerkandera adusta and Pleurotus eryngii in a manganese-independent reaction. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1998, 64, 2788–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, G.; Kunduhoglu, B. Biological decolorization of some reactive textile dyes by eight fungal isolates obtained from soil and textile industry wastewater. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2014, 23, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar]
- Durruty, I.; Fasce, D.; González, J.F.; Wolski, E.A. A kinetic study of textile dyeing wastewater degradation by Penicillium chrysogenum. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gül, Ü.D. Treatment of dyeing wastewater including reactive dyes (Reactive Red RB, Reactive Black B, Remazol Blue) and Methylene Blue by fungal biomass. Water SA 2013, 39, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thampraphaphon, B.; Phosri, C.; Pisutpaisal, N.; Thamvithayakorn, P.; Chotelersak, K.; Sarp, S.; Suwannasai, N. High potential decolourisation of textile dyes from wastewater by manganese peroxidase production of newly immobilised Trametes hirsuta PW17-41 and FTIR analysis. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Chu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, X. Decolorization and degradation of Congo red by a newly isolated white rot fungus, Ceriporia lacerata, from decayed mulberry branches. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2017, 117, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, R.; Przystaś, W. Decolorization of Two Dyes Using White Rot Fungus (BWPH) Strain and Evaluation of Zootoxicity of Post Process Samples. Archit. Civ. Eng. Environ. 2022, 15, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, P.; Ullah, M. Efficient azo dye biodecolorization system using lignin-co-cultured white-rot fungus. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papinutti, V.L.; Forchiassin, F. Modification of malachite green by Fomes sclerodermeus and reduction of oxicity to Phanerochaete chrysosporium. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 231, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, S.R. Dye removal by immobilised fungi. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arica, M.Y.; Sharif, F.A.; Alaeddinoǧlu, N.; Hasirci, N.; Hasirci, V. Covalent immobilization of Aspergillus niger on pHEMA membrane: Application to continuous flow reactors. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1993, 58, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Shoda, M. Batch decolorization of molasses by suspended and immobilized fungus of Geotrichum candidum Dec 1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 1999, 88, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtui, G.; Sawada, T.; Kuwahara, M.; Nakamura, Y. Lignin-degrading Enzyme Production by Bjerkandera Adusta Immobilized on Polyurethane Foam. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 1999, 88, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Couto, S.R.; Sanromán, M.A.; Hofer, D.; Gübitz, G. Stainless steel sponge: A novel carrier for the immobilisation of the white-rot fungus Trametes hirsuta for decolourization of textile dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papinutti, L.; Martínez, M.J. Production and characterization of laccase and manganese peroxidase from the ligninolytic fungus Fomes sclerodermeus. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. Int. Res. Process Environ. Clean Technol. 2006, 81, 1064–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przystaś, W.; Zabłocka-Godlewska, E.; Grabińska-Sota, E. Efficiency of decolorization of different dyes using fungal biomass immobilized on different solid supports. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2018, 49, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, R.; Mahmood, R.A.; Islam, S.; Ardiati, F.C.; Solihat, N.N.; Alam, M.B.; Lee, S.H.; Yanto, D.H.Y.; Kim, S. Understanding the biodegradation pathways of azo dyes by immobilized white-rot fungus, Trametes hirsuta D7, using UPLC-PDA-FTICR MS supported by in silico simulations and toxicity assessment. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, A. Solid-state fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 13, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, S.R.; Sanromán, M.A. Coconut flesh: A novel raw material for laccase production by Trametes hirsuta under solid-state conditions.: Application to Lissamine Green B decolourization. J. Food Eng. 2005, 71, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, S.O.; Urek, R.O. Production of ligninolytic enzymes by solid state fermentation using Pleurotus ostreatus. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 15, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adak, A.; Tiwari, R.; Singh, S.; Sharma, S.; Nain, L. Laccase production by a novel white-rot fungus Pseudolagarobasidium acaciicola LA 1 through solid-state fermentation of Parthenium biomass and its application in dyes decolorization. Waste Biomass Valorization 2016, 7, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contato, A.G.; Inácio, F.D.; Brugnari, T.; de Araújo, C.A.V.; Maciel, G.M.; Haminiuk, C.W.I.; Peralta, R.M.; de Souza, C.G.M. Solid-state fermentation with orange waste: Optimization of Laccase production from Pleurotus pulmonarius CCB-20 and decolorization of synthetic dyes. Acta Scientiarum. Biol. Sci. 2020, 42, e52699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankole, P.O.; Adekunle, A.A.; Govindwar, S.P. Biodegradation of a monochlorotriazine dye, cibacron brilliant red 3B-A in solid state fermentation by wood-rot fungal consortium, Daldinia concentrica and Xylaria polymorpha: Co-biomass decolorization of cibacron brilliant red 3B-A dye. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diorio, L.A.; Fréchou, D.S.; Levin, L.N. Removal of dyes by immobilization of Trametes versicolor in a solid-state micro-fermentation system. Rev. Argent. De Microbiol. 2021, 53, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, A.; Carballo, J.; Pérez, M.J.; Domínguez, J.M. Biological treatment of model dyes and textile wastewaters. Chemosphere 2017, 181, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighalo, J.O.; Dulta, K.; Kurniawan, S.B.; Omoarukhe, F.O.; Ewuzie, U.; Eshiemogie, S.O.; Ojo, A.U.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Progress in microalgae application for CO2 sequestration. Clean. Chem. Eng. 2022, 3, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenpour, S.F.; Hennige, S.; Willoughby, N.; Adeloye, A.; Gutierrez, T. Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazal, T.; Rehman, M.S.U.; Javed, F.; Akhtar, M.; Mushtaq, A.; Hafeez, A.; Din, A.A.; Iqbal, J.; Rashid, N.; Rehman, F. Integrating bioremediation of textile wastewater with biodiesel production using microalgae (Chlorella vulgaris). Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarbajova, V.; Kolackova, M.; Chaloupsky, P.; Dobesova, M.; Capal, P.; Pilat, Z.; Samek, O.; Zemanek, P.; Svec, P.; Sterbova, D.S. Physiological and transcriptome profiling of Chlorella sorokiniana: A study on azo dye wastewater decolorization. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 460, 132450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.N.; Watharkar, A.D.; Rane, N.R.; Jeon, B.-H.; Govindwar, S.P. Decolorization and detoxification of dye mixture and textile effluent by lichen Dermatocarpon vellereceum in fixed bed upflow bioreactor with subsequent oxidative stress study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruthanayagam, A.; Mani, P.; Kaliappan, K.; Chinnappan, S. In vitro and in silico studies on the removal of methyl orange from aqueous solution using Oedogonium subplagiostomum AP1. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahini, R.; Esmaeili, H.; Foroutan, R. Adsorption of methyl violet from aqueous solution using brown algae Padina sanctae-crucis. Turk. J. Biochem. 2018, 43, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, E. Biosorption: A review of the latest advances. Processes 2020, 8, 1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, P.; Dey, A. Phycoremediation–An emerging technique for dye abatement: An overview. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 147, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotto, G.; Lima, E.; Pinto, L. Biosorption of food dyes onto Spirulina platensis nanoparticles: Equilibrium isotherm and thermodynamic analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 103, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, N.F.; Lima, E.C.; Royer, B.; Bach, M.V.; Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.; Calvete, T. Comparison of Spirulina platensis microalgae and commercial activated carbon as adsorbents for the removal of Reactive Red 120 dye from aqueous effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arteaga, L.C.; Zavaleta, M.P.; Eustaquio, W.M.; Bobadilla, J.M. Removal of aniline blue dye using live microalgae Chlorella vulgaris. J. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 2, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Meng, F.; Zhou, Y. Adsorption Behavior of Acid Bordeaux B from Aqueous Solution onto Waste Biomass of Enteromorpha prolifera. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2014, 23, 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- Özer, A.; Akkaya, G.; Turabik, M. Biosorption of acid blue 290 (AB 290) and acid blue 324 (AB 324) dyes on Spirogyra rhizopus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 135, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, H.; Sultan, M.; Jahanzeb, Q. Removal of basic dye methylene blue by using bioabsorbents Ulva lactuca and Sargassum. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 2649–2655. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Yun, Y.-S. Biosorption of CI Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solution using acid-treated biomass of brown seaweed Laminaria sp. Dye. Pigment. 2008, 76, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-y.; Li, G.; Lu, X.-Q.; Chen, Z.-l. Biosorption of Basic Orange using dried A. filiculoides. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1333–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).