Sustainable Management of Pollutant Transport in Defective Composite Liners of Landfills: A Semi-Analytical Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
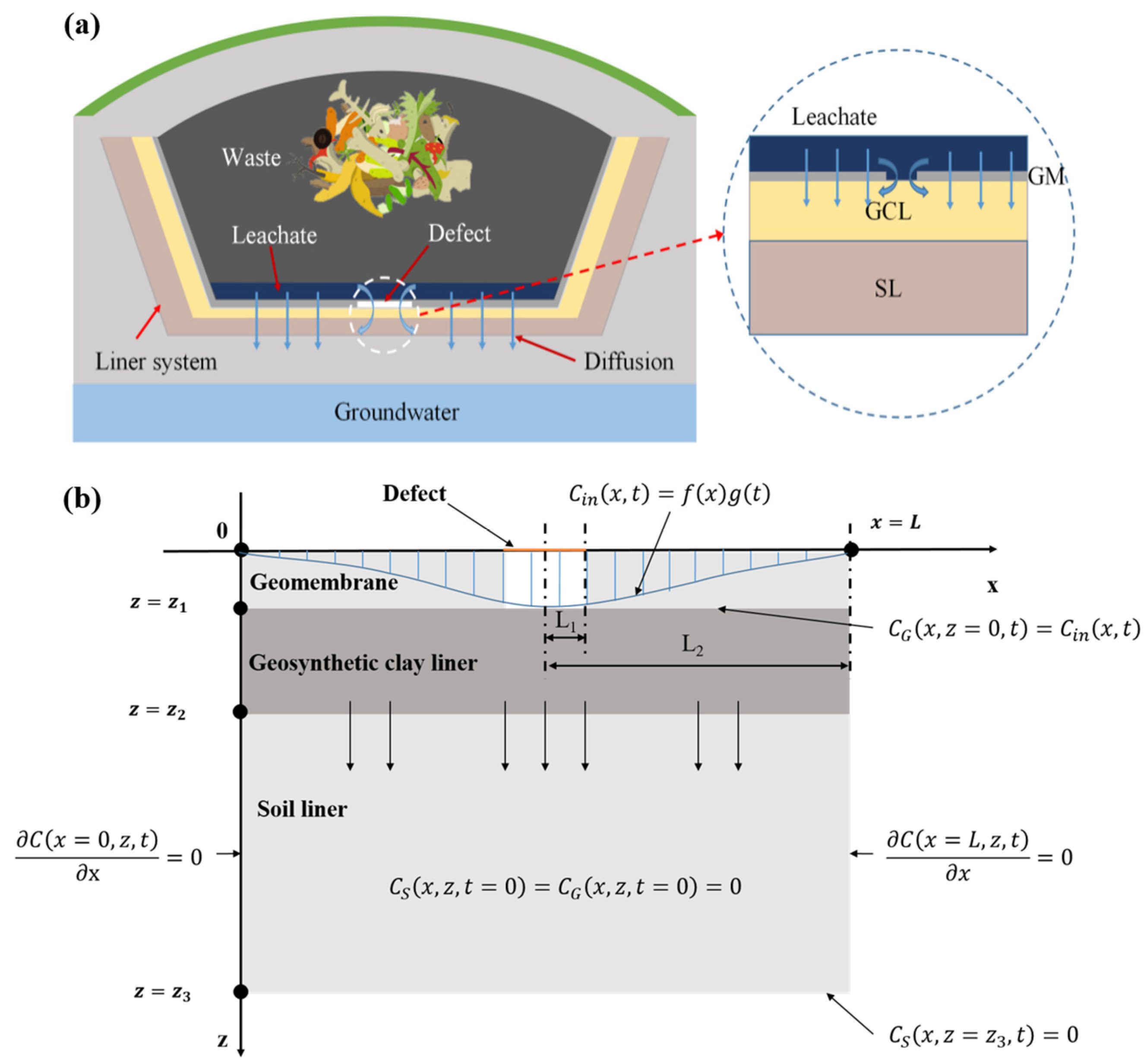
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Basic Assumptions
2.2. Governing Equations and Boundary Conditions
2.3. Analytical Solution
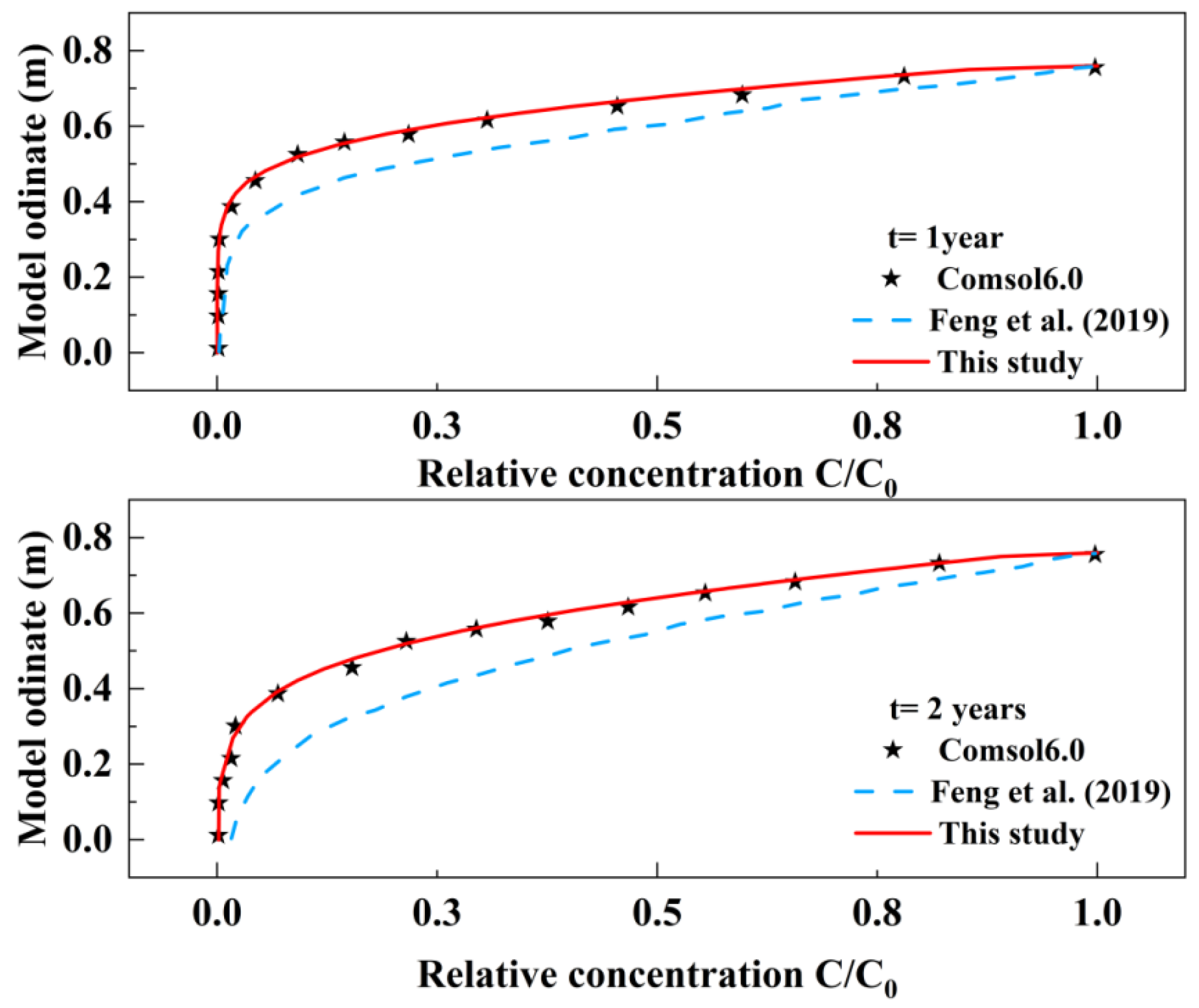
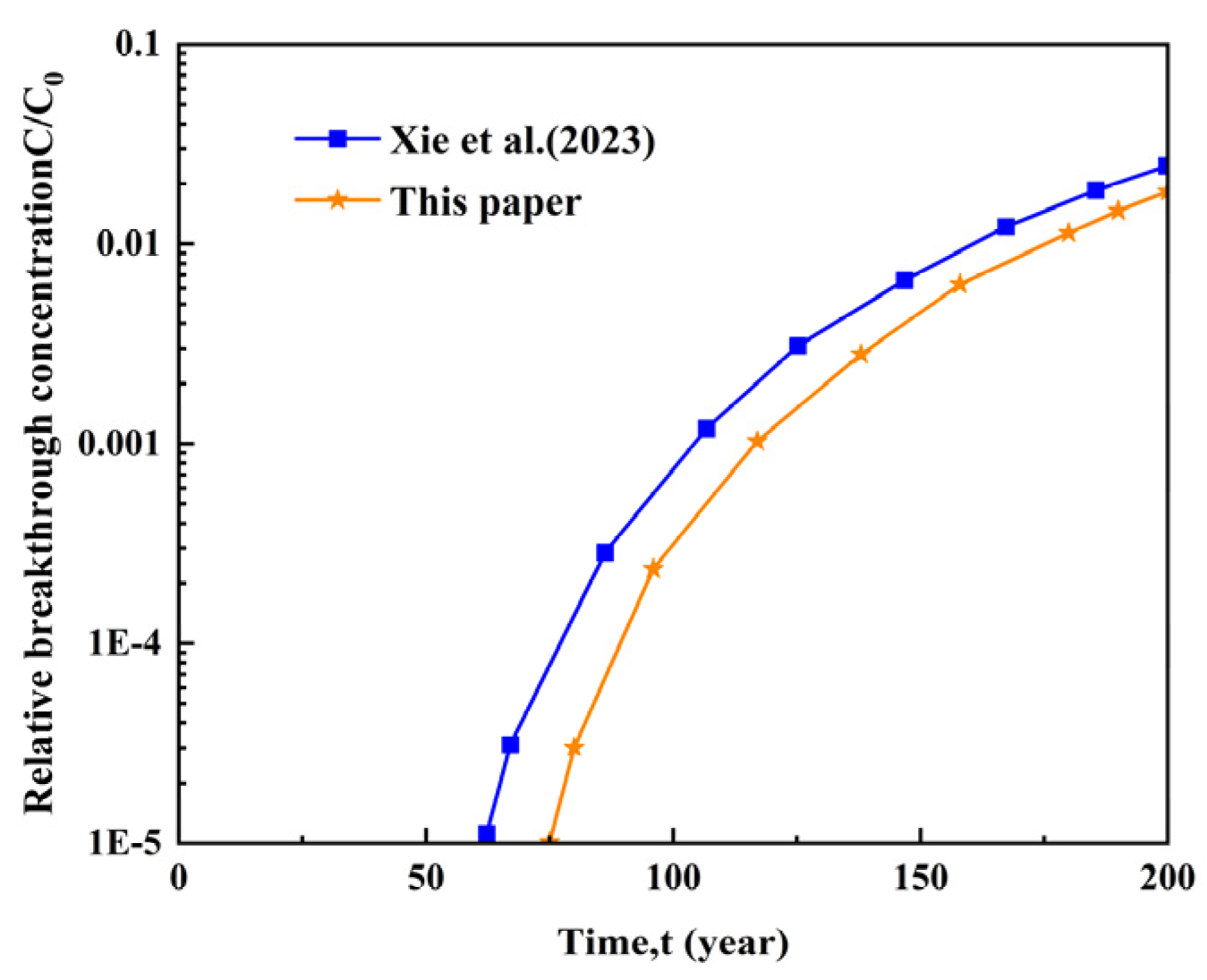
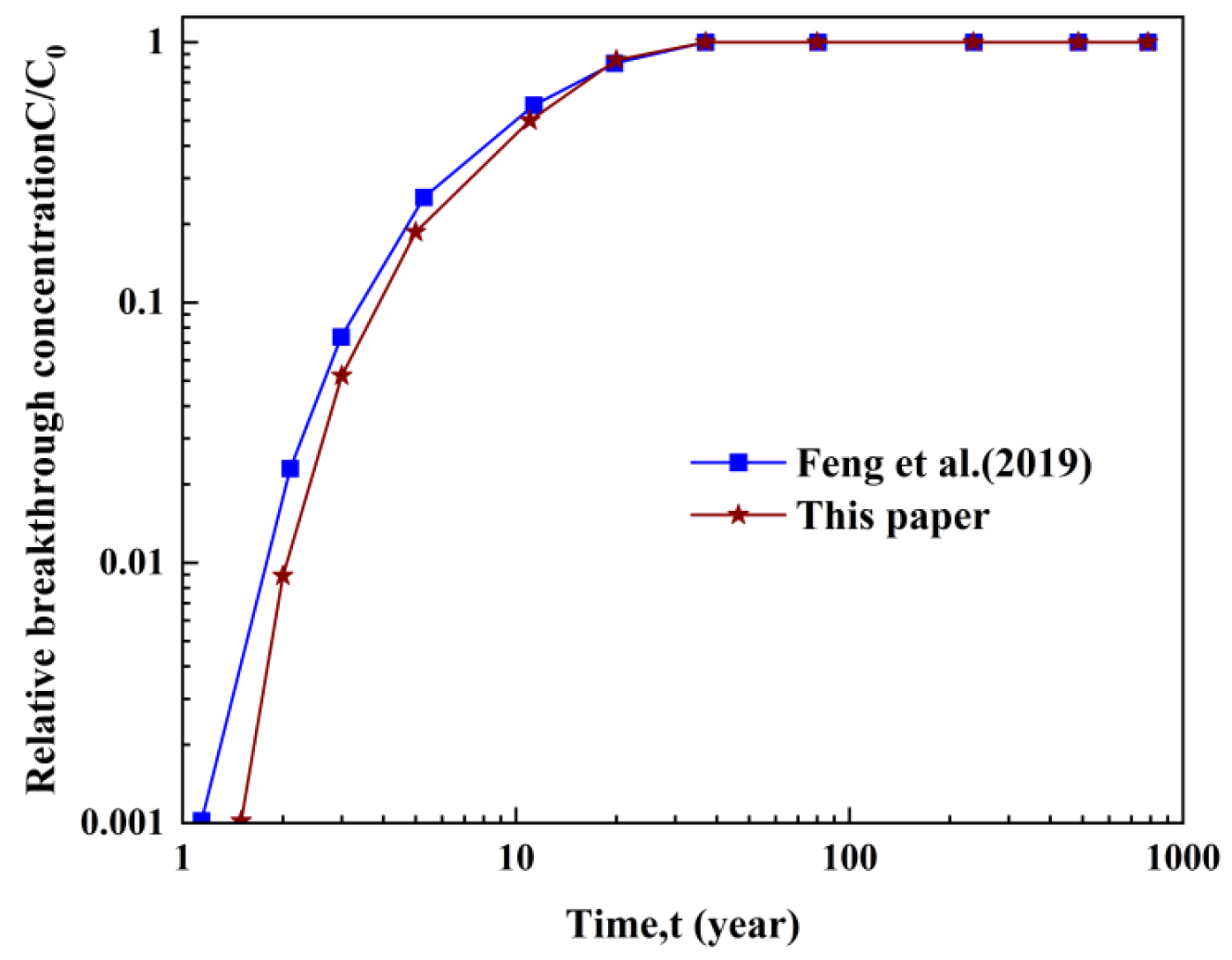
3. Model Verification
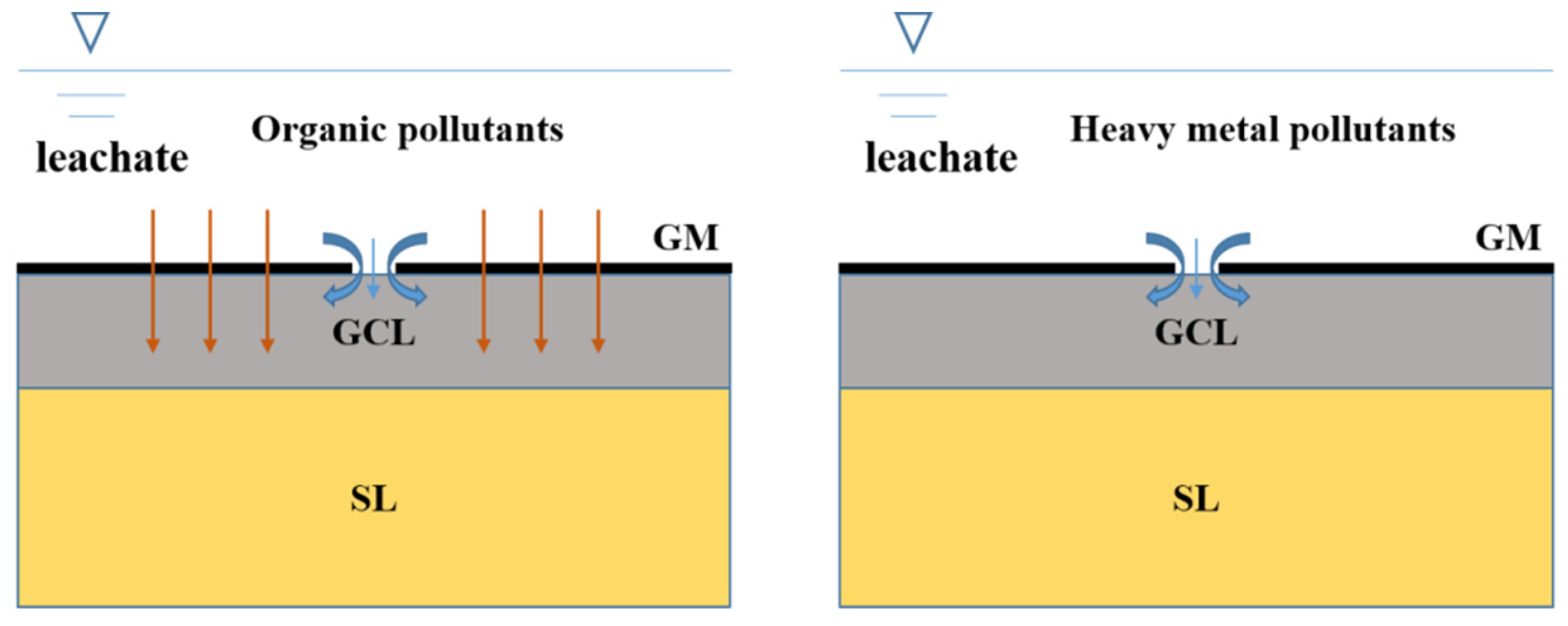
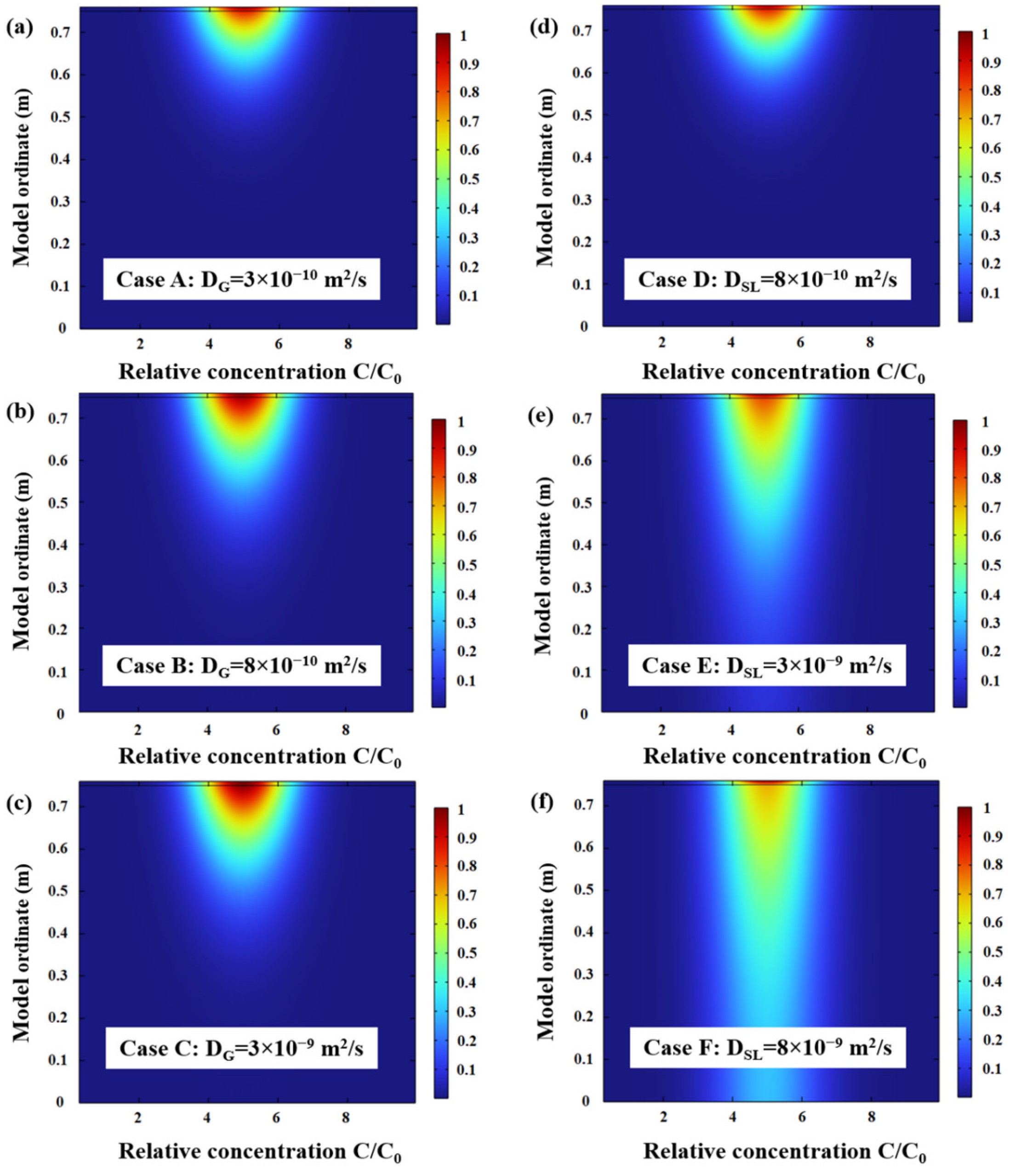
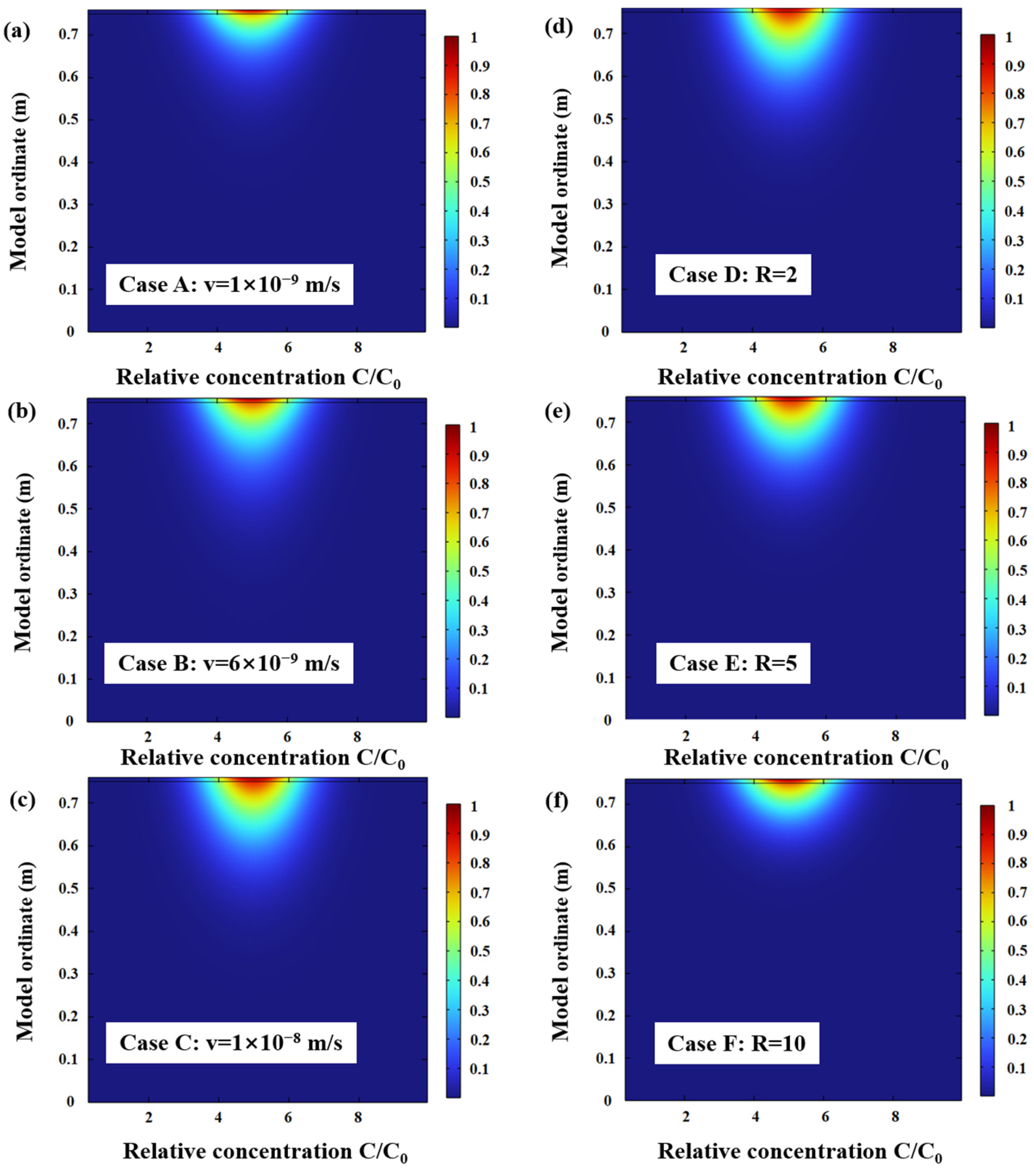
4. Uneven Distribution of Pollutant Concentrations at the Liner Leak Points
5. Pollution Prevention Performance of Composite Liner Systems
5.1. Heavy Metal Ion Zinc (Zn2+)
5.2. Organic Pollutant Toluene (TOL)
6. Results and Discussion
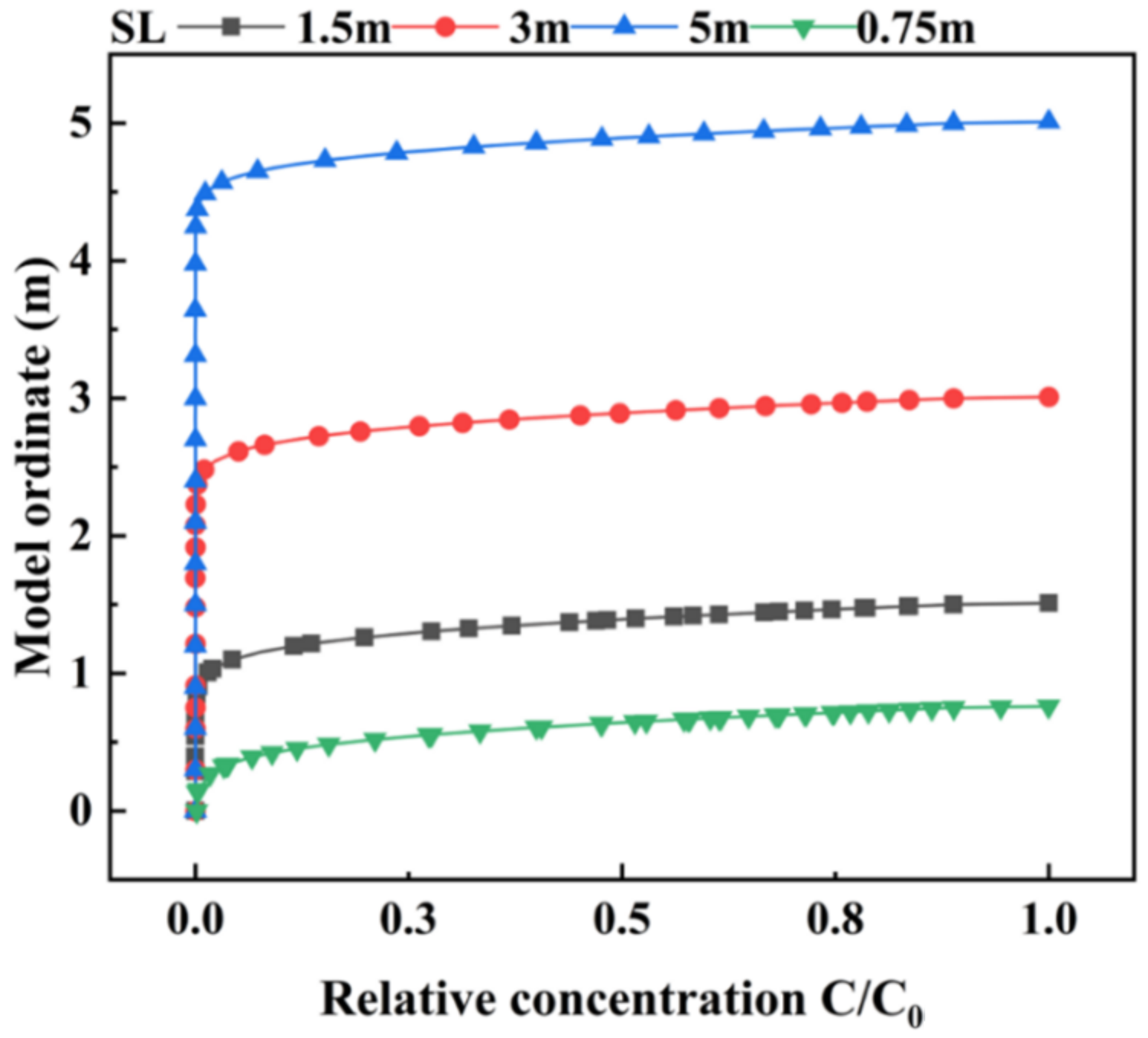
6.1. SL Thickness
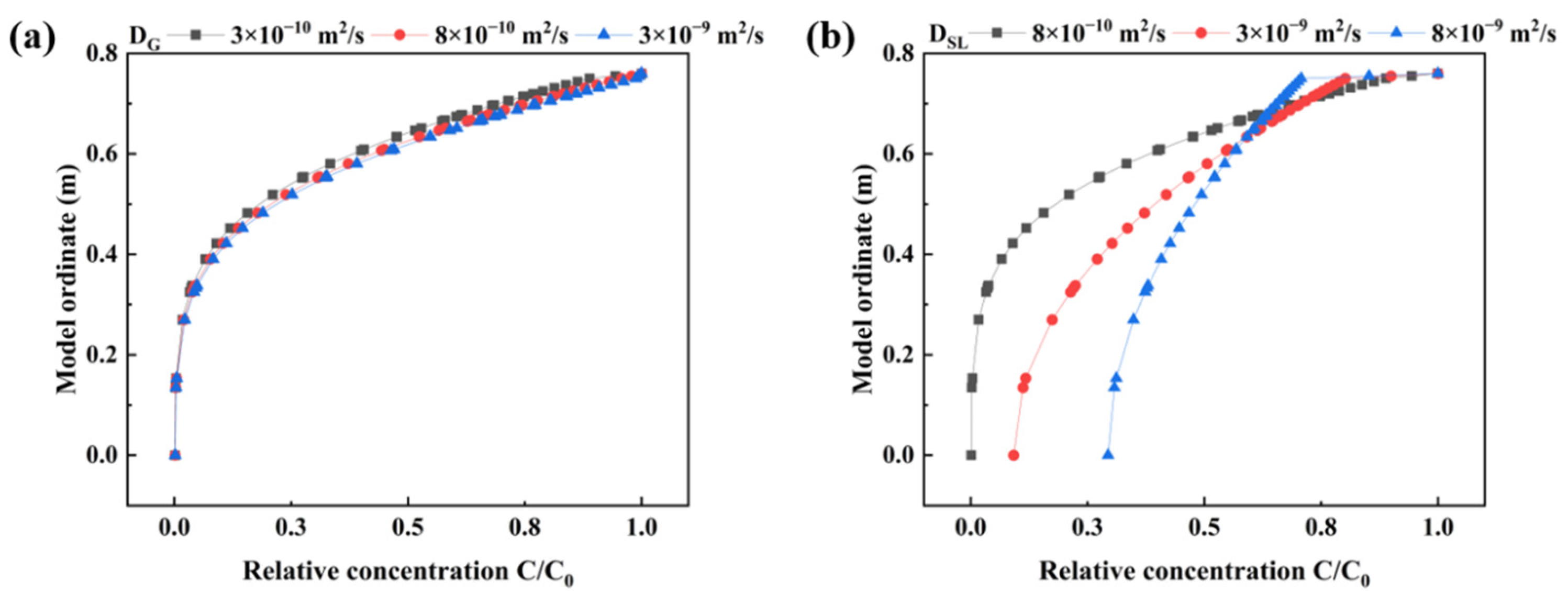
6.2. Diffusion Coefficient
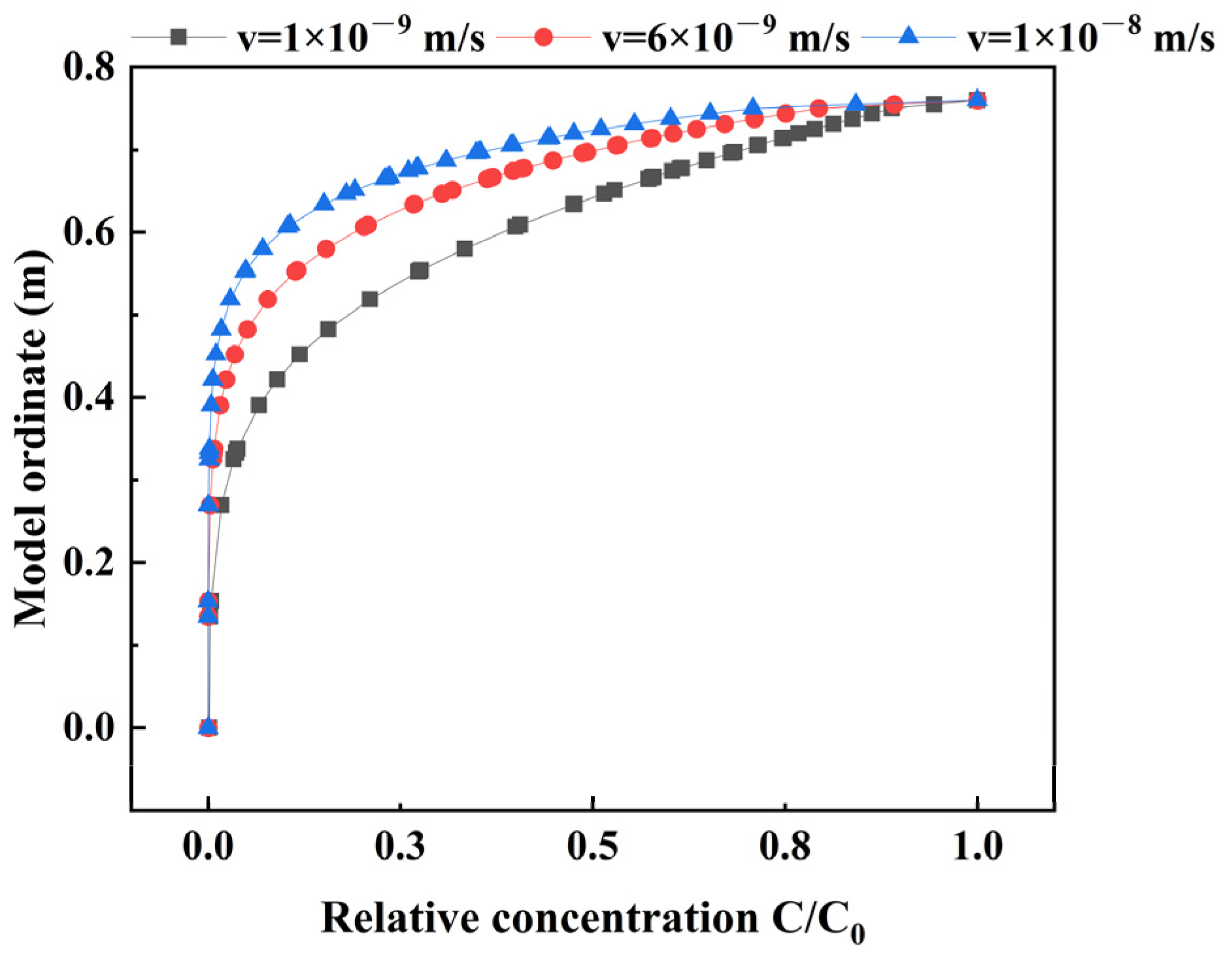
6.3. Advection Velocity
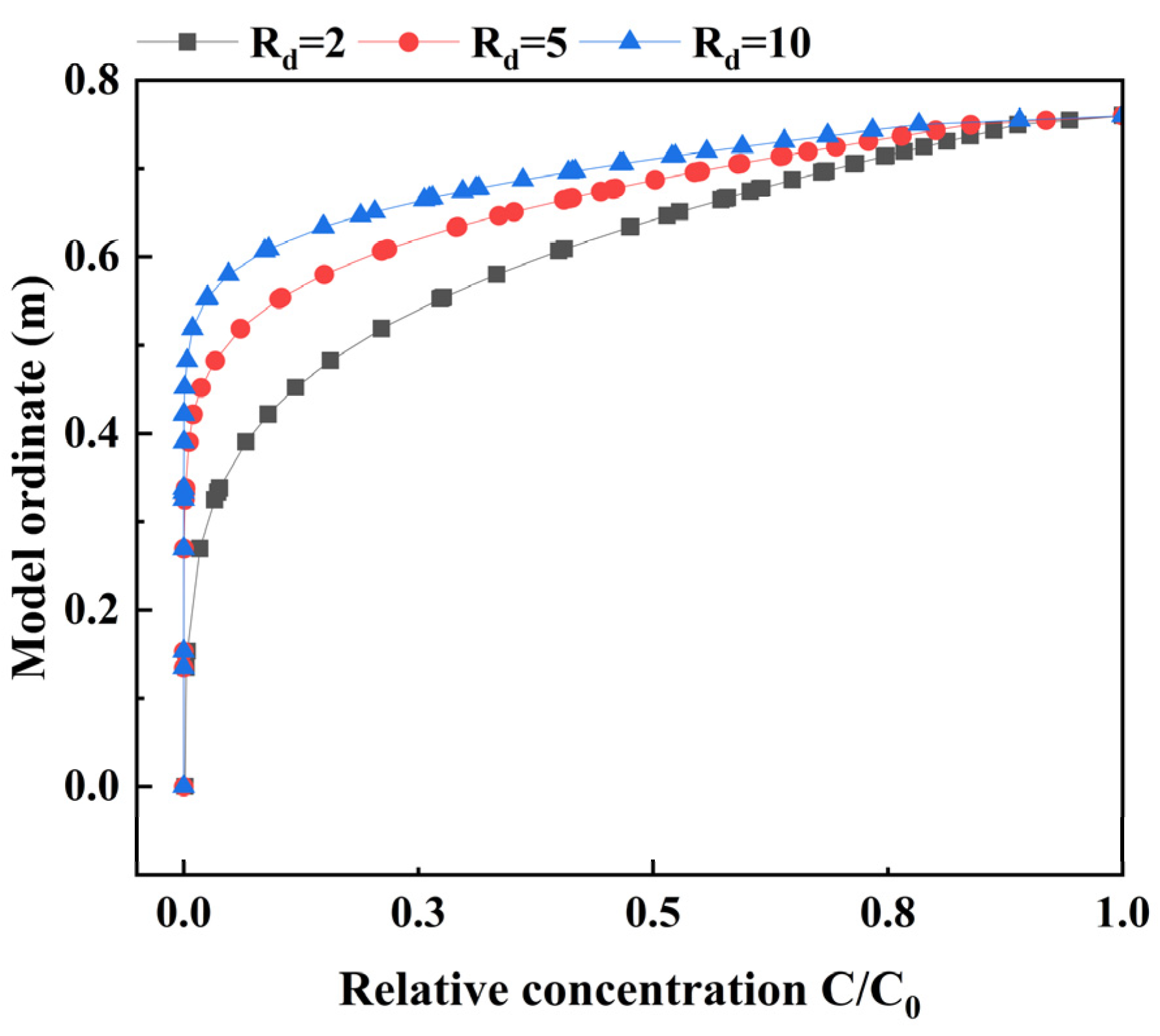
6.4. Adsorption Retardation Factor
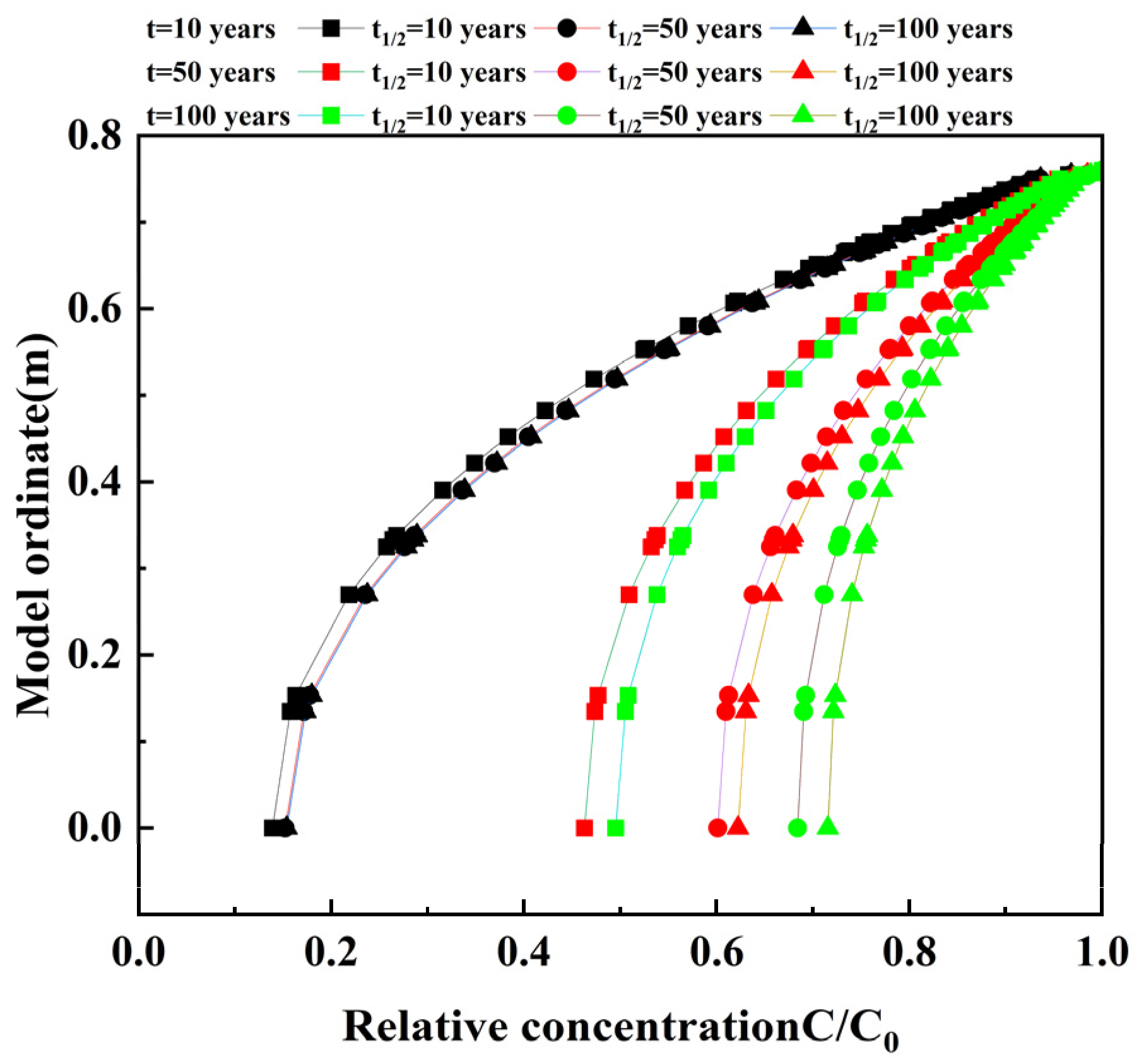
6.5. Degradation Coefficient
7. Limitations
8. Summary
- (1)
- The concentration distributions of organic pollutants and metal pollutants in the liner differ to some extent and, using the same function to describe these distributions can affect the extent of contamination. Employing two distinct concentration distribution functions enhances accuracy.
- (2)
- Compared to alternative analytical solutions and COMSOL verification results, the proposed analytical solution demonstrates a satisfactory level of accuracy, effectively describing pollutant migration processes in composite liners.
- (3)
- The concentration curve of pollutants is more sensitive to changes in the diffusion coefficient of SL than to changes in the diffusion coefficient of GCL. Specifically, as the diffusion coefficient of SL increases from 8 × 10−10 m2/s to 8 × 10−9 m2/s, the concentration curves intersect. However, when the diffusion coefficient of GCL increases from 3 × 10−10 m2/s to 3 × 10−9 m2/s, the concentration distribution curve of pollutants exhibits minimal changes, indicating comparable pollution prevention capabilities in both scenarios.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gómez-García, R.; Campos, D.A.; Aguilar, C.N.; Madureira, A.R.; Pintado, M. Valorisation of food agro-industrial by-products: From the past to the present and perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 299, 113571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Kumar, S.; Das, J. Impact of leachate and landfill gas on the ecosystem and health: Research trends and the way forward towards sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, X.; Chen, W.; Schollbach, K.; Brouwers, H. Low permeability sealing materials based on sewage, digestate and incineration industrial by-products in the final landfill cover system. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Hu, P.; Lang-Yona, N.; Xu, M.; Guo, C.; Gu, J.-D. Global landfill leachate characteristics: Occurrences and abundances of environmental contaminants and the microbiome. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 461, 132446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobral, B.; Samper, J.; Montenegro, L.; Mon, A.; Guadaño, J.; Gómez, J.; Román, J.S.; Delgado, F.; Fernández, J. 2D model of groundwater flow and total dissolved HCH transport through the Gállego alluvial aquifer downstream the Sardas landfill (Huesca, Spain). J. Contam. Hydrol. 2024, 265, 104370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Zhan, L.; Lan, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Liao, G. Leachate migration investigation at an unlined landfill located in granite region using borehole groundwater TDS profiles. Eng. Geol. 2021, 292, 106259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.-M.; Xing, B.; Liu, G.-D.; Liang, Y. Study on the effect of municipal solid landfills on groundwater by combining the models of variable leakage rate, leachate concentration, and contaminant solute transport. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiriga, D.; Vestgarden, L.S.; Klempe, H. Groundwater contamination from a municipal landfill: Effect of age, landfill closure, and season on groundwater chemistry. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 737, 140307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, S.; Zhu, W.; Shi, J. A new simplified method to calculate breakthrough time of municipal solid waste landfill liners. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 219, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Zhou, K.; Peng, C.; Chen, W. Characterization and treatment of landfill leachate: A review. Water Res. 2021, 203, 117525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, P.; Koliyabandara, P.A.; Cooray, A.T.; Lam, S.S.; Athapattu, B.C.; Vithanage, M. Progress and prospects in mitigation of landfill leachate pollution: Risk, pollution potential, treatment and challenges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trauger, R.; Tewes, K. Design and Installation of a State-of-the-Art Landfill Liner System in Geosynthetic Clay Liners; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 175–181. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Zhao, H.; Tian, K. Hydraulic conductivity of bentonite-polymer geosynthetic clay liners to aggressive solid waste leachates. Geotext. Geomembr. 2024, 52, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Xie, H.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tang, X. An analytical model for solute transport through a GCL-based two-layered liner considering biodegradation. Sci. Total. Environ. 2014, 466, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Sun, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, L. Semi-analytical solution for two-dimensional contaminant transport through composite liner with strip defects. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 440, 137404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainab, B.; Wireko, C.; Li, D.; Tian, K.; Abichou, T. Hydraulic conductivity of bentonite-polymer geosynthetic clay liners to coal combustion product leachates. Geotext. Geomembr. 2021, 49, 1129–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touze-Foltz, N.; Xie, H.; Stoltz, G. Performance issues of barrier systems for landfills: A review. Geotext. Geomembr. 2021, 49, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Hamdan, S. Performance of GCLs after long-term wet–dry cycles under a defect in GMB in a landfill. Geosynth. Int. 2023, 30, 225–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Reinert, J.; Li, Y.; Awad, R. The need to consider the service life of all components of a modern MSW landfill liner system. Waste Manag. 2023, 161, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.-C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Nai, C.-X.; Dong, L.; Liu, J.-C.; Huang, Q.-F. Evolution of geomembrane degradation and defects in a landfill: Impacts on long-term leachate leakage and groundwater quality. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Thomas, H.R.; Chen, Y.; Sedighi, M.; Zhan, T.L.; Tang, X. Diffusion of organic contaminants in triple-layer composite liners: An analytical modeling approach. Acta Geotech. 2013, 10, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Liu, J.; Ma, J.; Yu, X. Study on transport and transformation of contaminant through layered soil with large deformation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 12764–12779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, H.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zheng, J. Analytical solutions for organic contaminant diffusion in triple-layer composite liner system considering the effect of degradation. Acta Geotech. 2019, 15, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.-J.; Peng, M.-Q.; Chen, Z.-L.; Chen, H.-X. Transient analytical solution for one-dimensional transport of organic contaminants through GM/GCL/SL composite liner. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 650, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.H.; Feng, S.J.; Zhu, Z.W. Analytical model for reactive contaminant back-diffusion from low-permeability aquitards with internal source zones. J. Hydrol. 2025, 646, 132306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-H.; Luo, B.; Zhou, H.-T.; Chen, Y.-H. Generalized solutions for advection–dispersion transport equations subject to time- and space-dependent internal and boundary sources. Comput. Geotech. 2024, 178, 106944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominijanni, A.; Manassero, M. Steady-state analysis of pollutant transport to assess landfill liner performance. Environ. Geotech. 2021, 8, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouholahnejad, E.; Sadrnejad, S.A. Numerical Simulation of Leachate Transport Into the Groundwater at Landfill Sites. In Proceedings of the 18th World IMACS Congress and MODSIM09 International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Cairns, Australia, 13–17 July 2009; pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Chen, Y.; Lou, Z. An analytical solution to contaminant transport through composite liners with geomembrane defects. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2010, 53, 1424–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Feng, S. An analytical model for volatile organic compound transport through a composite liner consisting of a geomembrane, a GCL, and a soil liner. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 22, 2824–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Li, T.; Peng, M.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Semi-analytical solution for the two-dimensional transport of organic contaminant through geomembrane with strip defects to the underlying soil liner. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Géoméch. 2022, 47, 392–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shi, J.; He, J. Rule of diffusion of organic pollutants through GCL + AL liners considering biodegradation. J. Hohai Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2015, 43, 16–21. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, A. The Accurate Numerical Inversion of Laplace Transforms. IMA J. Appl. Math. 1979, 23, 97–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.-H.; Feng, S.-J.; Zheng, Q.-T.; Peng, C.-H. A two-dimensional analytical model for organic contaminants transport in a transition layer-cutoff wall-aquifer system. Comput. Geotech. 2020, 128, 103816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foose, G.J.; Benson, C.H.; Edil, T.B. Comparison of Solute Transport in Three Composite Liners. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2002, 128, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Cai, P.; Yan, H.; Zhu, X.; Thomas, H.R.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y. Analytical model for contaminants transport in triple composite liners with depth-dependent adsorption process. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.R.; Babu, G.S. Effects of Compaction and Initial Degree of Saturation on Contaminant Transport Through Barrier. In Proceedings of the PanAm Unsaturated Soils, Dallas, TX, USA, 12–15 November 2017; pp. 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, K.; Thomas, J. A comparison of the convective and diffusive flux of organic contaminants through landfill liner systems. Waste Manag. Res. J. A Sustain. Circ. Econ. 1998, 16, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Daalia, A.; Narang, K.; Garg, S.; Agarwal, P.; Mudgal, A. Cost Effectiveness of flexible pavement on stabilised expansive soils. Int. J. Geomate. 2016, 10, 1595–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, V.S.; Dikarev, D.V.; Kochetkov, I.V.; Ivanov, V.V.; Anisimova, L.N.; Tomson, A.V.; Korneev, Y.N.; Frigidov, R.A.; Sanzharov, A.I. The study of the combined effect of soil properties on the rate of diffusion of 60Co. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4385–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, M.; Venkatraman, S.; Bheda, M.; Patil, M. Numerical Studies on the Performance of Geosynthetic Reinforced Soil Walls Filled with Marginal Soil. Indian Geotech. J. 2023, 53, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, K.H.; Zhou, T.; Leong, K.C. Experimental Study of Passive Heat Transfer Enhancement in a Drag-Reducing Flow. Heat Transf. Eng. 2007, 28, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameijeiras-Mariño, Y.; Opfergelt, S.; Schoonejans, J.; Vanacker, V.; Sonnet, P.; de Jong, J.; Delmelle, P. Impact of low denudation rates on soil chemical weathering intensity: A multiproxy approach. Chem. Geol. 2017, 456, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysikopoulos, C.V.; Kitanidis, P.K.; Roberts, P.V. Analysis of one-dimensional solute transport through porous media with spatially variable retardation factor. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Yeh, H.-D. A simple analytical solution for organic contaminant diffusion through a geomembrane to unsaturated soil liner: Considering the sorption effect and Robin-type boundary. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.-J.; Peng, M.-Q.; Chen, H.-X.; Chen, Z.-L. Fully transient analytical solution for degradable organic contaminant transport through GMB/GCL/AL composite liners. Geotext. Geomembr. 2019, 47, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.-H.; Feng, S.-J.; Chen, H.-X.; Ding, X.-H.; Yang, C.-B. An analytical model for one-dimensional diffusion of degradable contaminant through a composite geomembrane cut-off wall. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 242, 103845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Pollutants | GM | GCL | SL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thickness, L (m) | - | 0.0015 | 0.01 | 0.75 |
| Porosity, n | - | - | 0.7 | 0.3 |
| Dry density, ρd (g/cm3) | - | - | 0.79 | 1.62 |
| Hydraulic conductivity, k (m/s) | - | - | 0.5 × 10−10 | 1 × 10−7 |
| Effective diffusion coefficient, D (m2 /s) | - | 3 × 10−13 | 3 × 10−10 | 8 × 10−10 |
| Zn2+ | 6 × 10−15 | 7.15 × 10−10 | 8.9 × 10−10 | |
| TOL | 3 × 10−13 | 3 × 10−10 | 8 × 10−10 | |
| Distribution coefficient, Kd (mL/g) | - | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Partition coefficient, Kg | - | 100 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, S.; Sun, B.; Su, X. Sustainable Management of Pollutant Transport in Defective Composite Liners of Landfills: A Semi-Analytical Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 10954. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162410954
Zhao S, Sun B, Su X. Sustainable Management of Pollutant Transport in Defective Composite Liners of Landfills: A Semi-Analytical Model. Sustainability. 2024; 16(24):10954. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162410954
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Shan, Botao Sun, and Xinjia Su. 2024. "Sustainable Management of Pollutant Transport in Defective Composite Liners of Landfills: A Semi-Analytical Model" Sustainability 16, no. 24: 10954. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162410954
APA StyleZhao, S., Sun, B., & Su, X. (2024). Sustainable Management of Pollutant Transport in Defective Composite Liners of Landfills: A Semi-Analytical Model. Sustainability, 16(24), 10954. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162410954




