Development of a Deep Learning-Based Flooding Region Segmentation Model for Recognizing Urban Flooding Situations
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
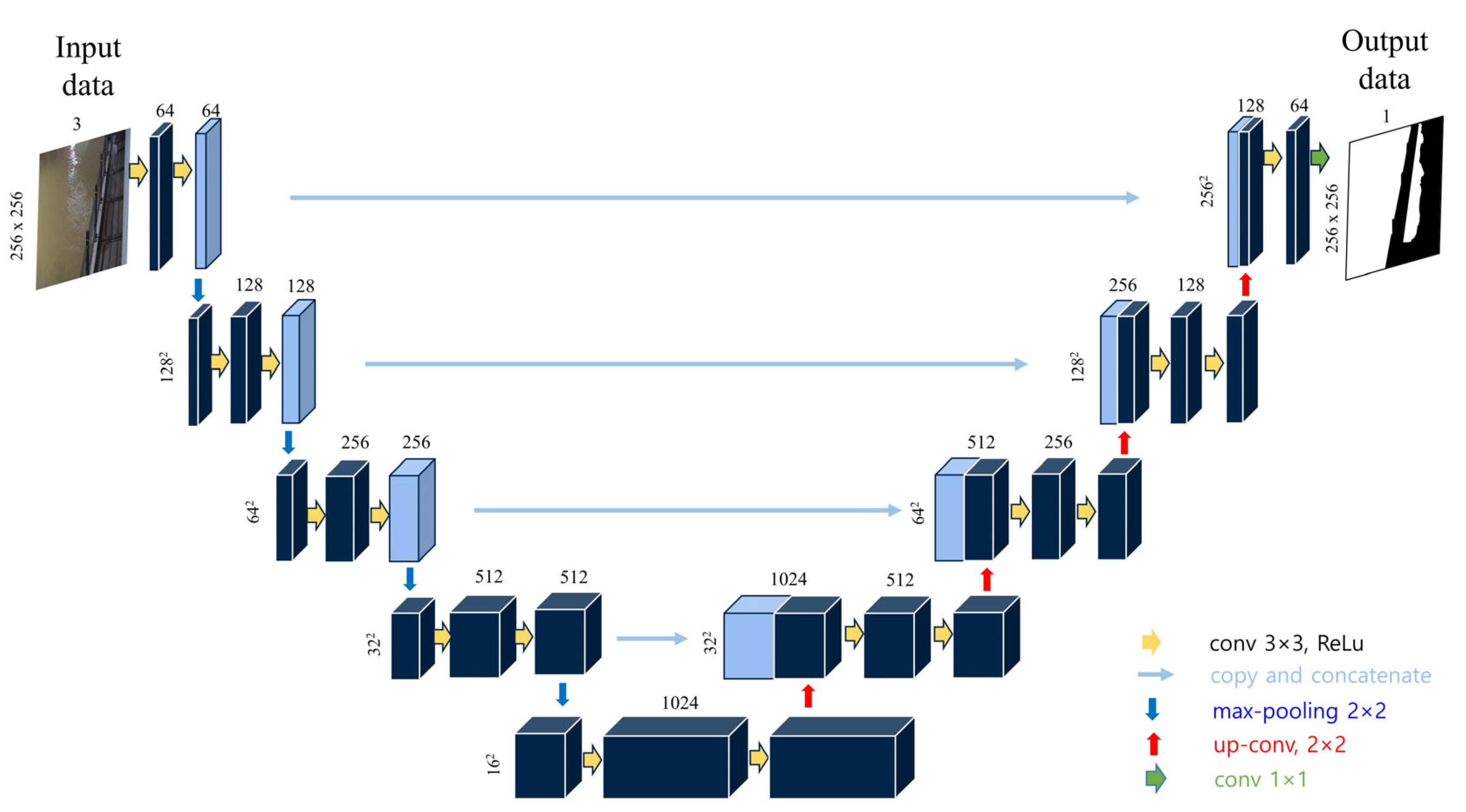
2.1. Proposed Strategy for Flood-Prone Region Segmentation
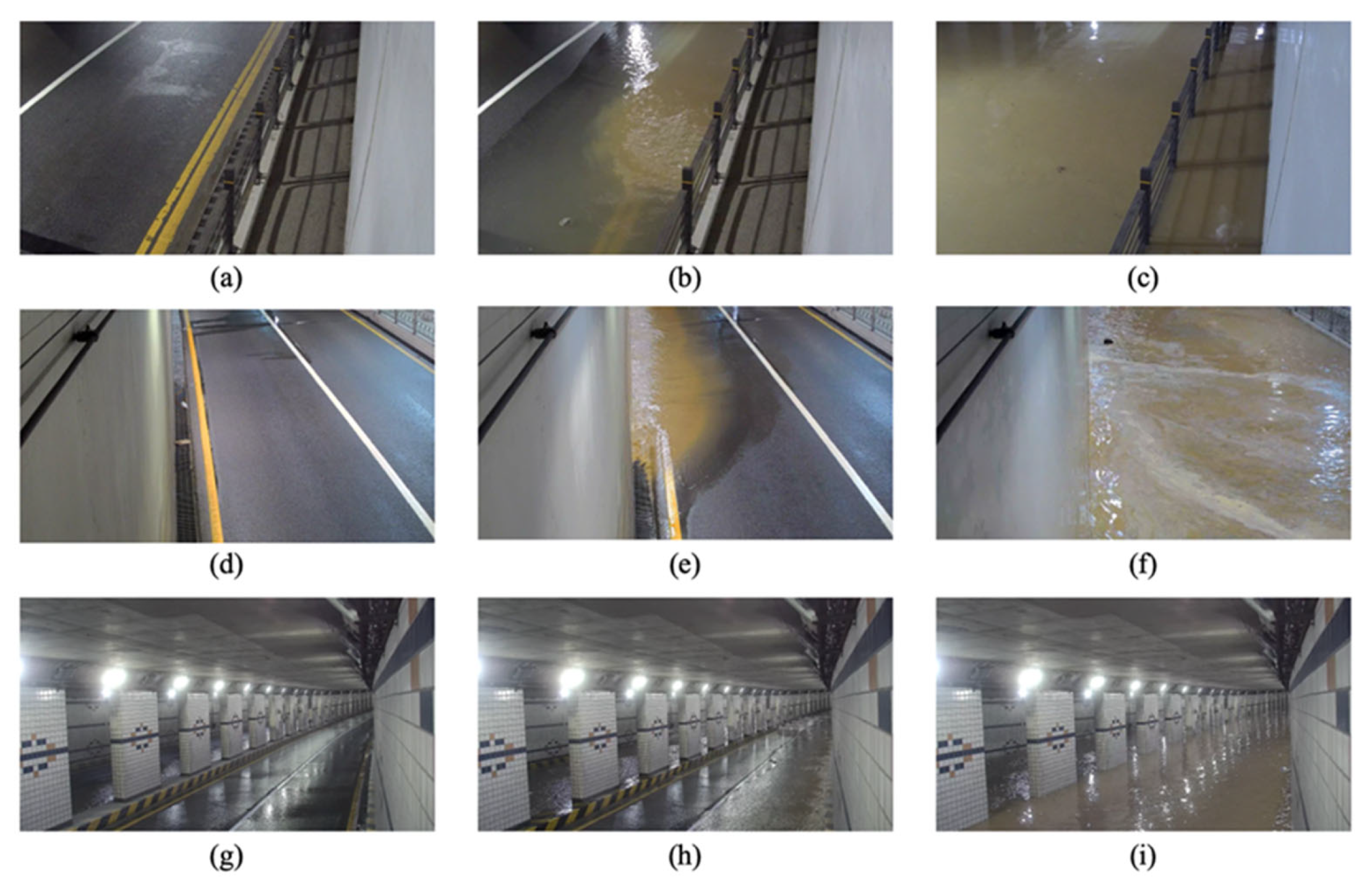
2.2. Dataset Acquisition for Neural Network Training
3. Experiments
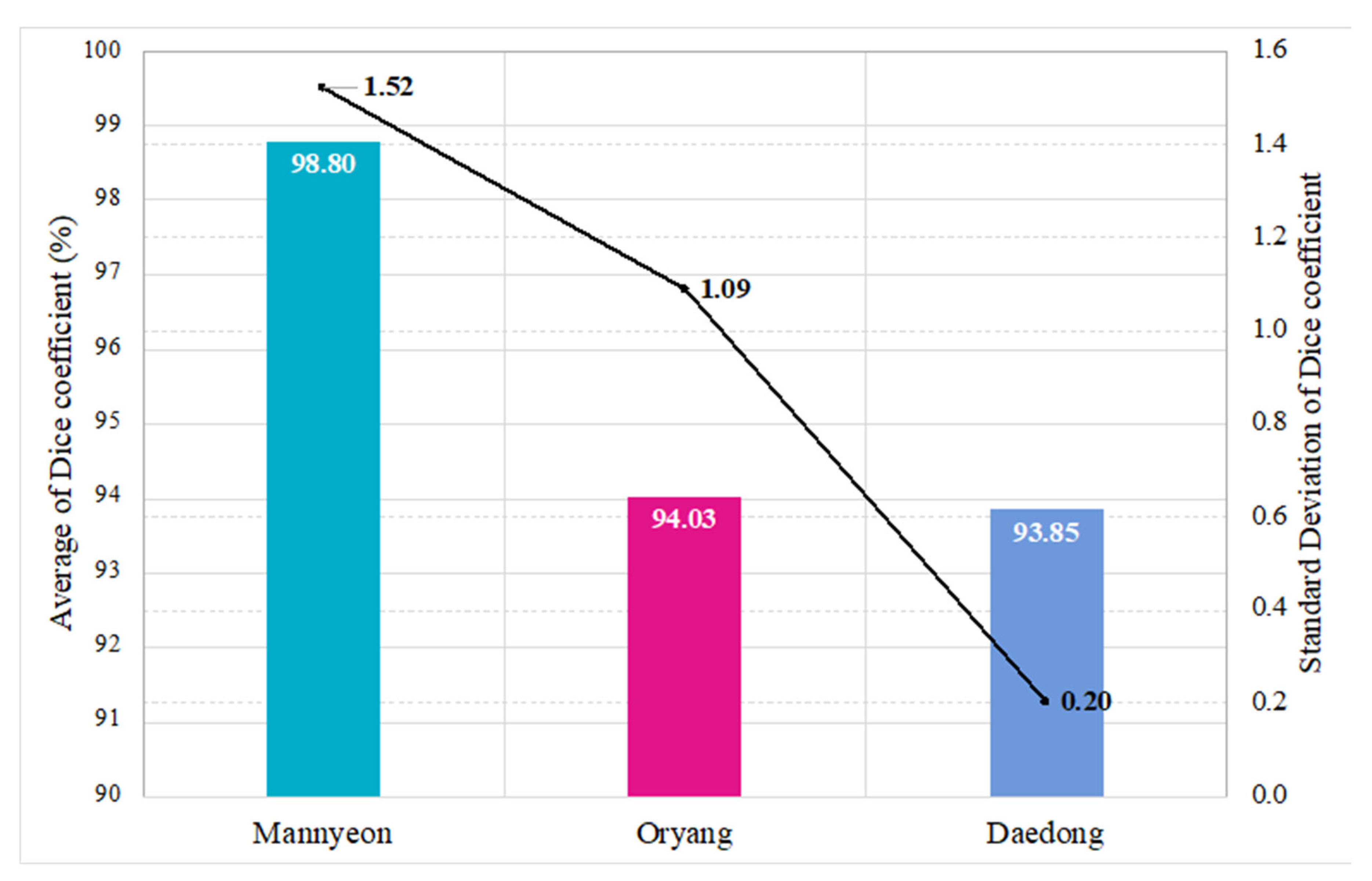
4. Results
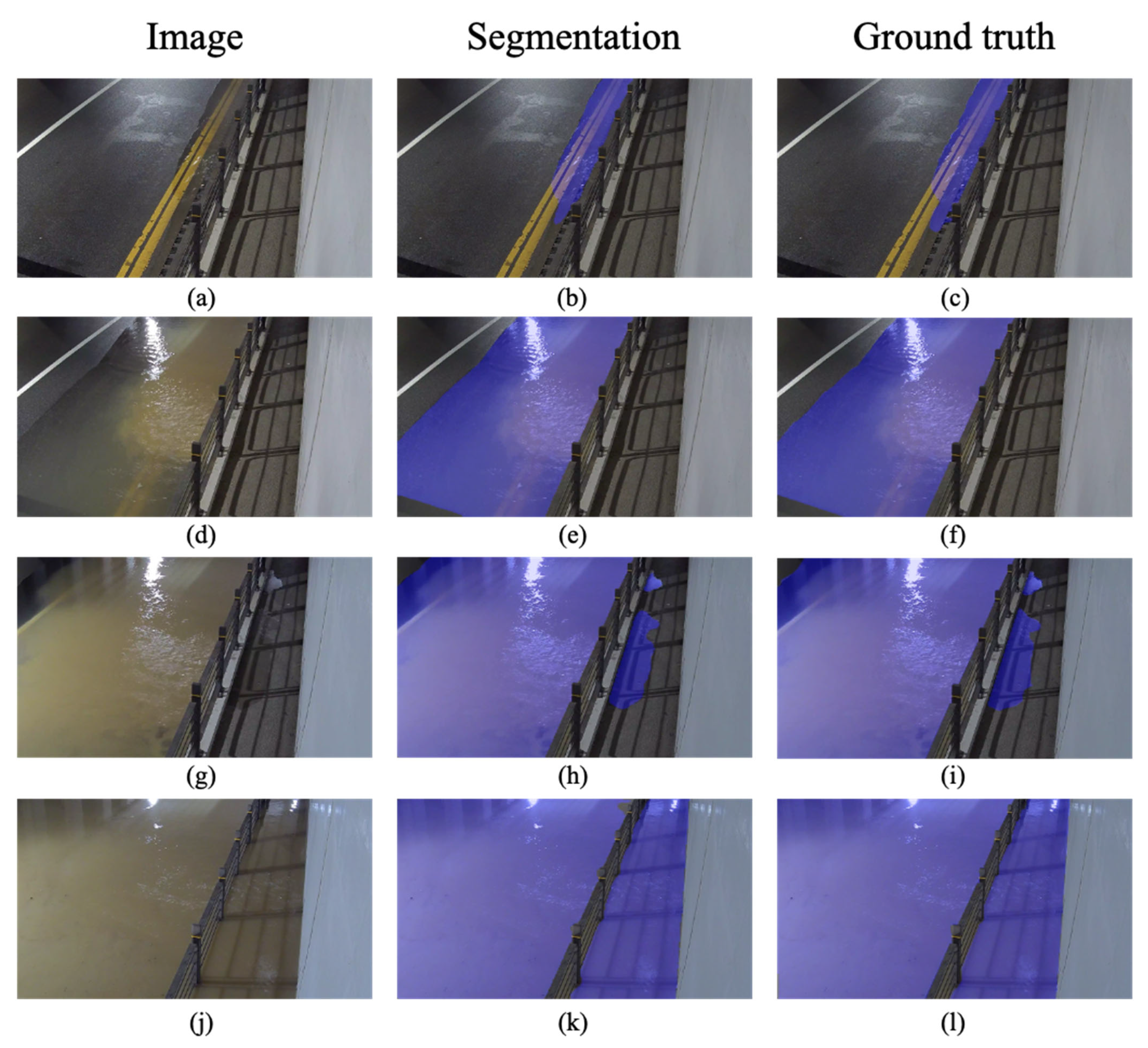
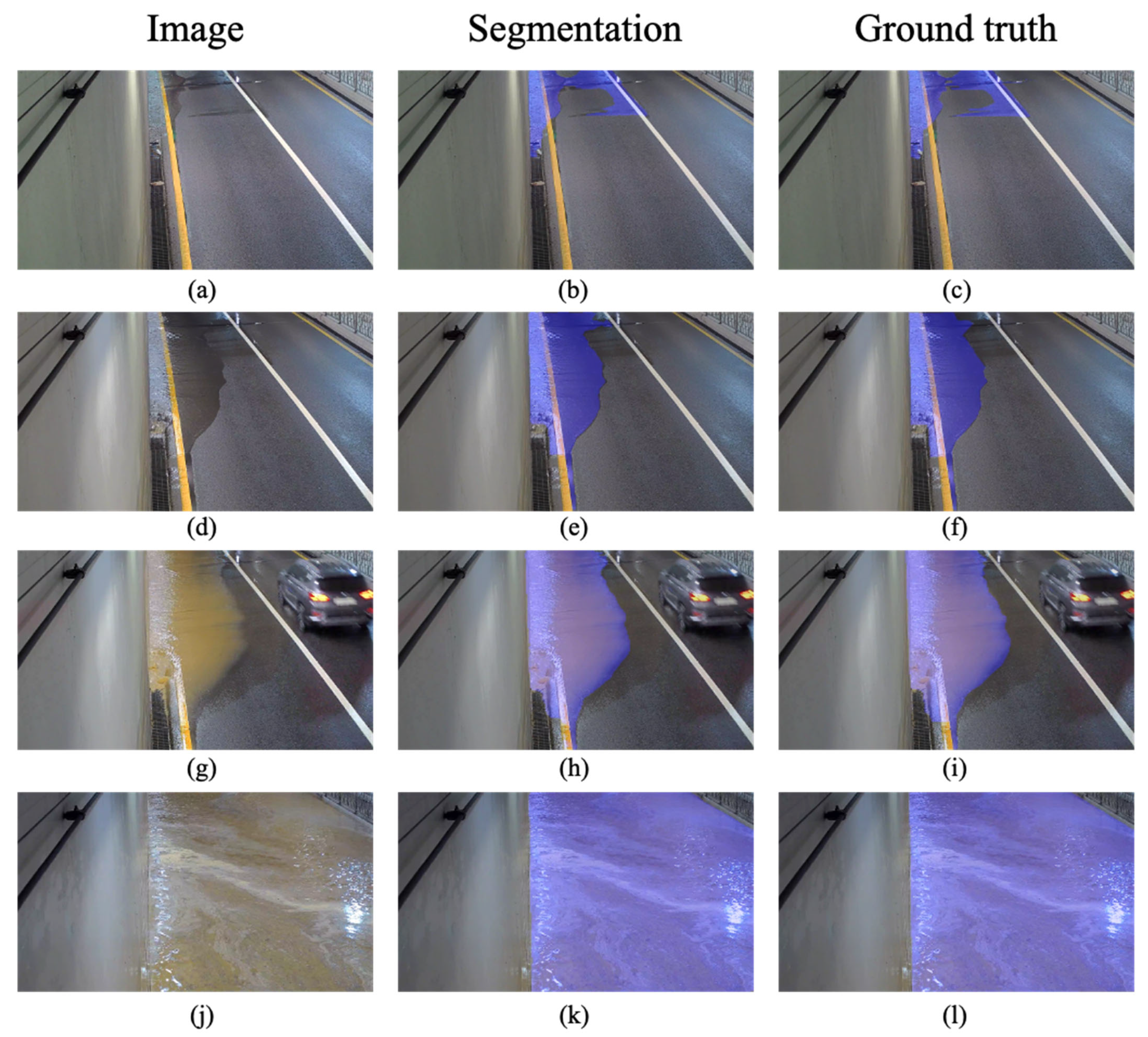
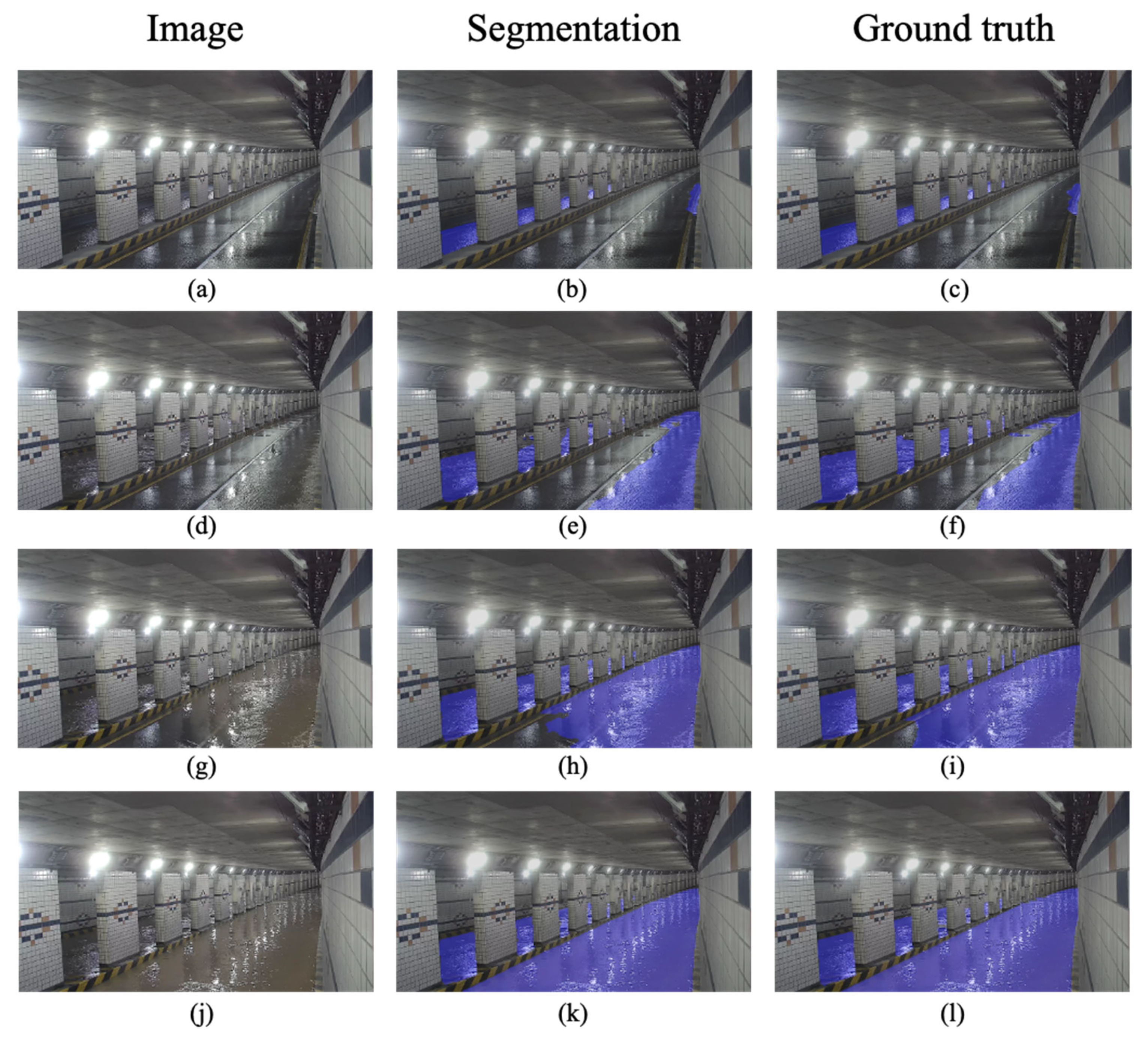
4.1. The Resultants of the Flooding Region Segmentation Model Based on U-Net
4.2. The Comparison Between Resultants of FCN and U-Net Models
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.U.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, D.S. Inundation of the Main Road along the Han River due to torrential rain. Water Future 2011, 44, 30–38. Available online: https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO201106654860778.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2024). (In Korean).
- Choe, S.J.; Gang, S.G.; Han, S.J.; Lee, D.R. A Study on Inundation Damage in Urban Areas due to Torrential Rain: Focusing on Gangnam, Seoul. Water Future 2011, 44, 25–29. Available online: https://www.dbpia.co.kr/journal/articleDetail?nodeId=NODE10135294 (accessed on 10 April 2024). (In Korean).
- Moon, H.J.; Kang, H.S.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, J.K. Development and Application of Urban Inundation Sensor. Water Future 2020, 53, 55–59. Available online: https://www.kwra.or.kr/media/17/publication/2020/09/17/Vol.53_No.8_p.55.pdf (accessed on 10 April 2024). (In Korean).
- Heo, H.K.; An, E.S.; Song, Y.M. Identifying Characteristics of Flood-Risk Buildings Through Data Linkage—Focusing on the Gangnam Station Area in Seoul. Auri Brief, No. 265. Korea Research Institute for Human Settlements: 2023. Available online: https://www.auri.re.kr/publication/view.es?mid=a10313000000&publication_type=brief&publication_id=1979 (accessed on 10 April 2024). (In Korean).
- KBS News. (2023, July 20). Heavy Rains in Korea Cause Extensive Damage and Prompt Disaster Declarations. KBS News. Available online: https://news.kbs.co.kr/news/pc/view/view.do?ncd=7727405 (accessed on 10 April 2024). (In Korean).
- Kim, H. (2023, July 25). Five Scenes Prove the Osong Flood Disaster Was a Man-Made Tragedy. The Hankyoreh 21. Available online: https://h21.hani.co.kr/arti/society/society_general/54157.html (accessed on 10 April 2024). (In Korean).
- Jang, J.K.; Park, M.K.; Lee, N.E.; Lee, J.M.; Yang, D.M. Real-time prediction of urban inundation based on SWMM 1D-1D model. J. Korea Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2020, 2020, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.I.; Han, K.Y.; Lee, J.Y. Prediction of urban flood extent by LSTM model and logistic regression. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. Res. (KSCE) 2020, 40, 273–283. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.-S. Adaptive Blending Method of Radar-Based and Numerical Weather Prediction QPFs for Urban Flood Forecasting. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.S.; Cho, J.W.; Lee, H.S.; Hwang, J.G.; Moon, H.J. Development of an ANN-Based Urban Flood Alert Criteria Prediction Model and the Impact of Training Data Augmentation. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2021, 21, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Li, X.; Tsai, B.; Chen, Q.; Jafari, N. V-Flood Net: A video segmentation system for urban flood detection and quantification. Environ. Model. Softw. 2023, 160, 105586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, N.H.; Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Le, C.-Y.; Betzer, L.P.; Liang, Y. Real-time water level monitoring using live cameras and computer vision techniques. Comput. Geosci. 2021, 147, 104642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.E., Jr.; Nonato, L.G.; Ueyama, J. A river flooding detection system based on deep learning and computer vision. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 40231–40251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, W.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; An, B.; Li, R. A Near-Real-Time Flood Detection Method Based on Deep Learning and SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, B.; Arbabkhah, H. Enhanced Flood Detection Through Precise Water Segmentation Using Advanced Deep Learning Models. J. Civ. Eng. Res. 2024, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, O.; Apan, A.; Paudyal, D.R.; Perera, K. Convolutional Neural Network-Based Deep Learning Approach for Automatic Flood Mapping Using NovaSAR-1 and Sentinel-1 Data. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2023, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemni, E.; Bullock, J.; Belabbes, S.; Bromley, L. Fully Convolutional Neural Network for Rapid Flood Segmentation in Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vongkusolkit, J.; Peng, B.; Wu, M.; Huang, Q.; Andresen, C.G. Near Real-Time Flood Mapping with Weakly Supervised Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potnis, A.V.; Shinde, R.C.; Durbha, S.S.; Kurte, K.R. Multi-Class Segmentation of Urban Floods from Multispectral Imagery Using Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2019—2019 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Yokohama, Japan, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. ICLR 2015. 2017. Available online: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980 (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Zhou, Q.; Teng, S.; Situ, Z.; Liao, X.; Feng, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Z. A deep-learning-technique-based data-driven model for accurate and rapid flood predictions in temporal and spatial dimensions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 1791–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseiny, H. A deep learning model for predicting river flood depth and extent. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 145, 105186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Chen, W.; Panahi, M.; Falah, F.; Rahmati, O.; Uuemaa, E.; Kalantari, Z.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; Rezaie, F.; Tiefenbacher, J.P.; et al. Urban flood modeling using deep-learning approaches in Seoul, South Korea. J. Hydrol. 2021, 601, 126684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Yu, T.; Chu, S. Advancing Rapid Urban Flood Prediction: A Spatiotemporal Deep Learning Approach with Uneven Rainfall and Attention Mechanism. J. Hydroinformatics 2024, 26, 1409–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, B.; Huang, G.; Chen, W. Research progress and prospects of urban flooding simulation: From traditional numerical models to deep learning approaches. Environ. Model. Softw. 2025, 183, 106213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.; Li, X.; Bai, G.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, L.; Du, Y.; Ma, Y.; Fu, D.; Zhang, X. A deep learning technique based flood propagation experiment. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Luo, C.; Fu, G. Assessing Surface Water Flood Risks in Urban Areas Using Machine Learning. Water 2021, 13, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wu, W.; Nathan, R.; Wang, Q.J. A rapid flood inundation modelling framework using deep learning with spatial reduction and reconstruction. Environ. Model. Softw. 2021, 143, 105112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Woo, H.A.; Kim, M.Y.; Noh, S.J. Applying deep learning based super-resolution technique for high-resolution urban flood analysis. J. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2023, 56, 641–653. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Bentivoglio, R.; Isufi, E.; Jonkman, S.N.; Taormina, A.R. Deep Learning Methods for Flood Mapping: A Review of Existing Applications and Future Research Directions. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 4345–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanim, A.H.; McRae, C.B.; Tavakol-Davani, H.; Goharian, E. Flood Detection in Urban Areas Using Satellite Imagery and Machine Learning. Water 2022, 14, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henonin, J.; Russo, B.; Mark, O.; Gourbesville, P. Real-time urban flood forecasting and modelling—A state of the art. J. Hydroinformatics 2013, 15, 717–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Situ, Z.; Feng, W.; Liu, H.; Liao, X.; Zhang, J.; Ge, X.; Chen, G. Deep learning, geometric characterization and hydrodynamic modeling for assessing sewer defect impacts on urban flooding: A case study in Guangzhou, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouma, Y.O.; Tateishi, R. Urban Flood Vulnerability and Risk Mapping Using Integrated Multi-Parametric AHP and GIS: Methodological Overview and Case Study Assessment. Water 2014, 6, 1515–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshkonesh, A.; Nazari, R.; Nikoo, M.R.; Karimi, M. Enhancing flood risk assessment in urban areas by integrating hydrodynamic models and machine learning techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Felton, T.; Mostafavi, A. Interpretable machine learning for predicting urban flash flood hotspots using intertwined land and built-environment features. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2024, 110, 102096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseiny, H.; Nazari, F.; Smith, V.; Nataraj, C. A Framework for Modeling Flood Depth Using a Hybrid of Hydraulics and Machine Learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaffaroni, M.; Rossi, C. Water Segmentation with Deep Learning Models for Flood Detection and Monitoring. Water Segmentation with Deep Learning Models for Floods. In Proceedings of the 17th ISCRAM Conference, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 24–27 May 2020; Available online: https://iris.unito.it/handle/2318/1832212 (accessed on 18 July 2024).
- Basnyat, B.; Roy, N.; Gangopadhyay, A. Flood Detection using Semantic Segmentation and Multimodal Data Fusion. In Proceedings of the 6th IEEE International Workshop on Pervasive Context-Aware Smart Cities and Intelligent Transport System, Kassel, Germany, 22–26 March 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2015/papers/Long_Fully_Convolutional_Networks_2015_CVPR_paper.pdf (accessed on 19 July 2024).
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Angelov, P.; Soares, E.; Longepe, N.; Mathieu, P.P. An Interpretable Deep Semantic Segmentation Method for Earth Observation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 11th International Conference on Intelligent Systems (IS), Warsaw, Poland, 12–14 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.F.; Chang, M.J.; Lin, G.F. A novel AI-based model for real-time flooding image recognition using superresolution generative adversarial network. J. Hydrol. 2024, 638, 131475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S, V.; Krishnamurthi, I.; M, N.H. Flood Detection and Segmentation Using Deep Learning Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Smart Systems for Electrical, Electronics, Communication and Computer Engineering (ICSSEECC), Coimbatore, India, 28–29 June 2024; pp. 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, Q.K.; Song, S.K. Water Level Forecasting based on Deep Learning: A Use Case of Trinity River-Texas-The United States. J. KIISE 2017, 44, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.J.; Jeon, B.H. Development of Flood Nomograph for Inundation Forecasting in Urban Districts. J. Korean Soc. Hazard Mitig. 2013, 13, 37–42. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munawar, H.S.; Hammad, A.W.A.; Waller, S.T. A review on flood management technologies related to image processing and machine learning. Autom. Constr. 2021, 132, 103916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, B.; Wang, F. Extraction and Classification of Flood-Affected Areas Based on MRF and Deep Learning. Water 2023, 15, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Study | Task | Model |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time water level monitoring using live cameras and computer vision techniques (2021) [12] | The prediction of water levels from images with the segmentation model | FCN |
| A Near-Real-Time Flood Detection Method Based on Deep Learning and SAR Images (2023) [14] | Flooding detection with SAR images and a deep learning model | U-Net |
| Enhanced Flood Detection Through Precise Water Segmentation Using Advanced Deep Learning Models (2024) [15] | Flooding region segmentation | SegNet, U-Net, FCN-32s |
| A deep-learning-technique-based data-driven model for accurate and rapid flood predictions in temporal and spatial dimensions (2023) [21] | Flooding prediction on simulated flood maps | LSTM |
| A rapid flood inundation modelling framework using deep learning with spatial reduction and reconstruction (2021) [28] | A rapid flood inundation modeling framework | LSTM |
| Water Segmentation with Deep Learning Models for Flood Detection and Monitoring (2024) [38] | Pixel-wise flooding region segmentation | SegNet, U-Net, FCN-32s, PSPNet |
| Flood Detection using Semantic Segmentation and Multimodal Data Fusion (2021) [39] | Real-time flooding detection with semantic segmentation | U-Net |
| Underpass | Quantity | The Size of Image |
|---|---|---|
| Mannyeon | 124 | 1080 × 1920 |
| Oryang | 244 | 1080 × 1920 |
| Daedong | 173 | 1080 × 1920 |
| Underpass | Training Set | Test Set |
|---|---|---|
| Mannyeon | 110 | 14 |
| Oryang | 214 | 30 |
| Daedong | 172 | 7 |
| Underpass | FCN-16s | FCN-8s | U-Net |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mannyeon | 41.33% | 38.64% | 98.80% |
| Oryang | 32.02% | 31.64% | 94.03% |
| Daedong | 41.33% | Not trained | 93.85% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoo, J.; Lee, J.; Jeung, S.; Jung, S.; Kim, M. Development of a Deep Learning-Based Flooding Region Segmentation Model for Recognizing Urban Flooding Situations. Sustainability 2024, 16, 11041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162411041
Yoo J, Lee J, Jeung S, Jung S, Kim M. Development of a Deep Learning-Based Flooding Region Segmentation Model for Recognizing Urban Flooding Situations. Sustainability. 2024; 16(24):11041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162411041
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoo, Jaeeun, Jungmin Lee, Sejin Jeung, Seungkwon Jung, and Myeongin Kim. 2024. "Development of a Deep Learning-Based Flooding Region Segmentation Model for Recognizing Urban Flooding Situations" Sustainability 16, no. 24: 11041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162411041
APA StyleYoo, J., Lee, J., Jeung, S., Jung, S., & Kim, M. (2024). Development of a Deep Learning-Based Flooding Region Segmentation Model for Recognizing Urban Flooding Situations. Sustainability, 16(24), 11041. https://doi.org/10.3390/su162411041






