Evolutionary Multi-Objective Feature Selection Algorithms on Multiple Smart Sustainable Community Indicator Datasets
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ✓
- Introduction of multiple-objective evolutionary algorithms along with learning algorithms for the dual purpose of feature selection and predicting smart sustainable city indicators to achieve predictions with minimal subset features while maximizing accuracy.
- ✓
- The paper found minimal optimal subset features for predicting life expectancy, shopper’s online intention, energy consumption, air quality, water quality, and traffic flow in smart sustainable city.
- ✓
- The study reveals that NSGA3 consistently outperforms various other multi-objective evolutionary algorithms, including Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2 (SPEA2), Niched Pareto Genetic Algorithm (NPGA), Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm (MOGA), Pareto Envelop-Based Selection Algorithm II (PESA2), and Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithms (MOEA). This superiority is observed across multiple datasets pertaining to smart sustainable city indicators in most instances.
- ✓
- We believe that the datasets provided in this study can motivate many researchers to conduct empirical study for developing smart sustainable city from different perspectives, leading to a better understanding of the smart sustainable city.
2. Theoretical Background to Smart Sustainable Cities
2.1. Smart Sustainable City Indicators
2.2. Futuristic Smart Sustainable Cities across the World
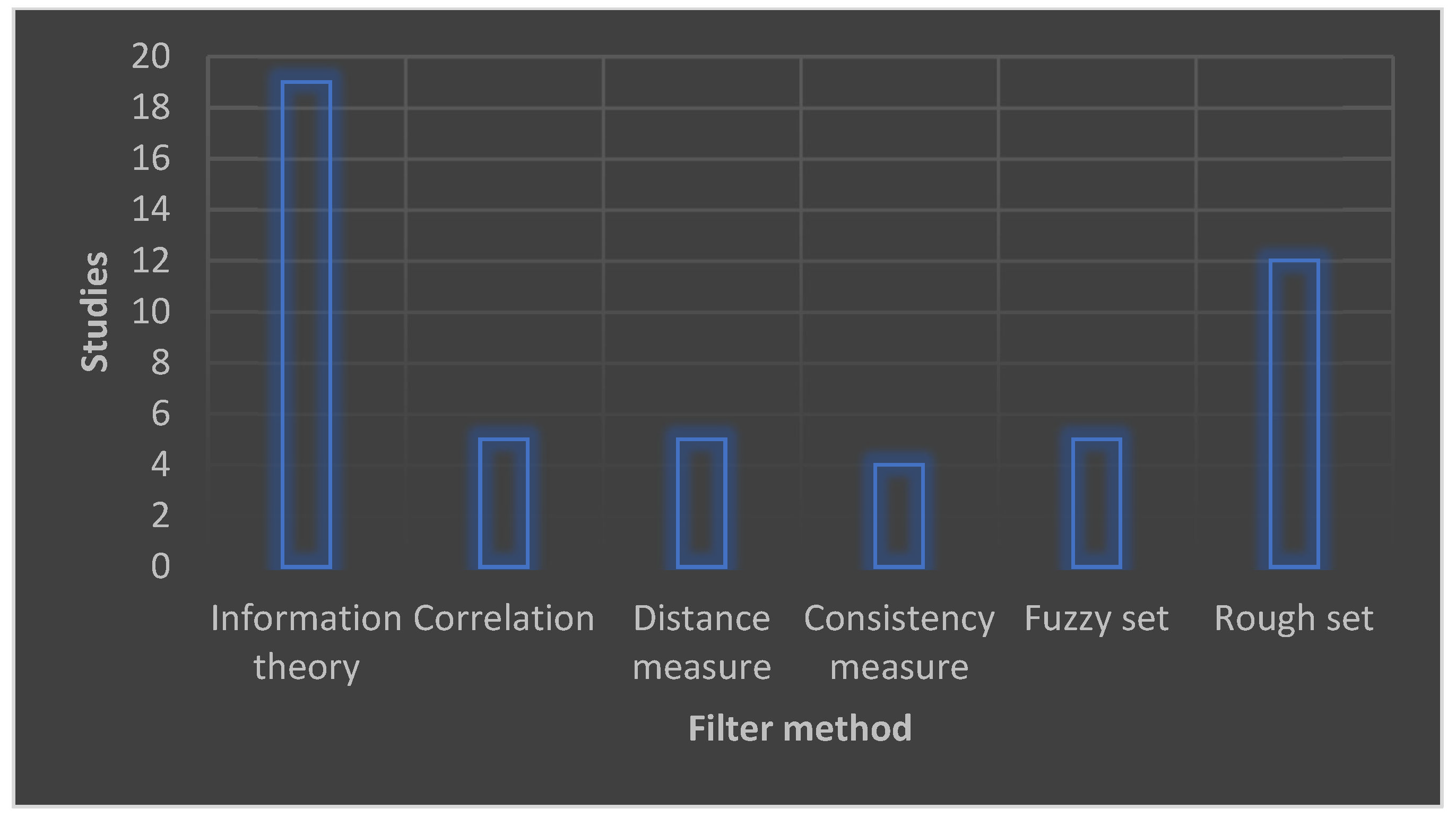
3. Related Research Works
Review of Related Works on Intelligent Frameworks in Smart Sustainable Cities
4. Feature Selection Algorithms
4.1. Non-Dominated Sorted Genetic Algorithm III
4.2. Pareto-Envelop-Based Selection Algorithm II
4.3. Multi-Objective Genetic Algorithm
4.4. Niched Pareto Genetic Algorithm
4.5. Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2
5. Formulation of the Optimization Problem
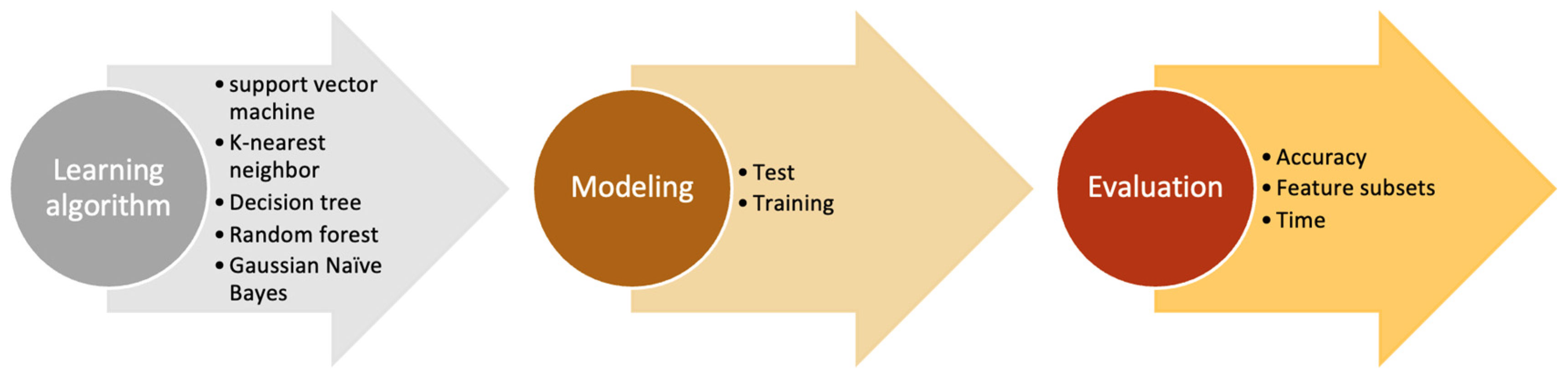
6. Methodology
6.1. Data Collection
6.2. The Proposed Framework for the Study
7. Result and Discussion
7.1. Computational Time
7.2. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Estevez, E.; Lopes, N.; Janowski, T. Smart Sustainable Cities: Reconnaissance Study. 2016. Available online: http://collections.unu.edu/eserv/UNU:5825/Smart_Sustainable_Cities_v2final.pdf (accessed on 17 June 2023).
- Law, K.H.; Lynch, J.P. Smart city: Technologies and challenges. IT Prof. 2019, 21, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pira, M. A novel taxonomy of smart sustainable city indicators. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2021, 8, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, L.; Cilfone, A.; Davoli, L.; Ferrari, G.; Adorni, P.; Di Nocera, F.; Dall’Olio, A.; Pellegrini, C.; Mordacci, M.; Bertolotti, E. IoT-enabled smart sustainable cities: Challenges and approaches. Smart Cities 2020, 3, 1039–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höjer, M.; Wangel, J. Smart sustainable cities: Definition and challenges. In ICT Innovations for Sustainability; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 333–349. [Google Scholar]
- Martins, L.D.C.; de la Torre, R.; Corlu, C.G.; Juan, A.A.; Masmoudi, M.A. Optimizing ride-sharing operations in smart sustainable cities: Challenges and the need for agile algorithms. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2021, 153, 107080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E.; Krogstie, J. Smart sustainable cities of the future: An extensive interdisciplinary literature review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2017, 31, 183–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E. Data-driven smart sustainable cities of the future: An evidence synthesis approach to a comprehensive state-of-the-art literature review. Sustain. Futures 2021, 3, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashem, I.A.T.; Usmani, R.S.A.; Almutairi, M.S.; Ibrahim, A.O.; Zakari, A.; Alotaibi, F.; Alhashmi, S.M.; Chiroma, H. Urban Computing for Sustainable Smart Cities: Recent Advances, Taxonomy, and Open Research Challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnaveni, N.; Radha, V. Feature selection algorithms for data mining classification: A survey. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 12, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Abutarboush, H.F.; Ganesh, T.; Mohamed, A.W. Metaheuristic Algorithms on Feature Selection: A Survey of One Decade of Research (2009–2019). IEEE Access 2021, 9, 26766–26791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Khalil, T.; Nasreen, S. A survey of feature selection and feature extraction techniques in machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2014 Science and Information Conference, London, UK, 27–29 August 2014; pp. 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuyan, H.K.; Chakraborty, C.; Pani, S.K.; Ravi, V. Feature and subfeature selection for classification using correlation coefficient and fuzzy model. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2021, 70, 1655–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savić, M.; Kurbalija, V.; Ivanović, M.; Bosnić, Z. A feature selection method based on feature correlation networks. In Model and Data Engineering: 7th International Conference, MEDI 2017, Barcelona, Spain, 4–6 October 2017; Proceedings 7; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 248–261. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, C.; Kulić, D.; Basir, O. An evaluation of classifier-specific filter measure performance for feature selection. Pattern Recognit. 2015, 48, 1812–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Browne, W.N.; Yao, X. A survey on evolutionary computation approaches to feature selection. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2015, 20, 606–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, R.; Nguyen, B.H.; Xue, B.; Zhang, M. A survey on evolutionary multiobjective feature selection in classification: Approaches, applications, and challenges. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2023; early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Sustainable Development Goals. 2018. Available online: https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Portney, K.E. Sustainability; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Corbett, J.; Mellouli, S. Winning the SDG battle in cities: How an integrated information ecosystem can contribute to the achievement of the 2030 sustainable development goals. Inf. Syst. J. 2017, 27, 427–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toli, A.M.; Murtagh, N. The concept of sustainability in smart city definitions. Front. Built Environ. 2020, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigitcanlar, T.; Kamruzzaman, M. Does smart city policy lead to sustainability of cities? Land Use Policy 2018, 73, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollenkamp, D.T. What Is Sustainability? How Sustainabilities Work, Benefits, and Example. 2023. Available online: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/sustainability.asp (accessed on 21 October 2023).
- Barrionuevo, J.M.; Berrone, P.; Ricart, J.E. Smart cities, sustainable progress. IESE Insight 2012, 14, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez Lopez, L.J.; Grijalba Castro, A.I. Sustainability and resilience in smart city planning: A review. Sustainability 2020, 13, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E. ICT for Sustainable Urban Development in the European Information Society: A Discursive Investigation of Energy Efficiency Technology; School of Culture and Society, Malmö University: Malmö, Sweden, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bibri, S.E. A foundational framework for smart sustainable city development: Theoretical, disciplinary, and discursive dimensions and their synergies. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 758–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibri, S.E. The IoT for smart sustainable cities of the future: An analytical framework for sensor-based big data applications for environmental sustainability. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 38, 230–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, C.; Pavan, V.M. Evaluating urban quality: Indicators and assessment tools for smart sustainable cities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Nagao, T.; Hannoe, S.; Nakamura, J. New key performance indicators for a smart sustainable city. Sustainability 2016, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismagiloiva, E.; Hughes, L.; Rana, N.; Dwivedi, Y. Role of smart cities in creating sustainable cities and communities: A systematic literature review. In ICT Unbounded, Social Impact of Bright ICT Adoption: IFIP WG 8.6 International Conference on Transfer and Diffusion of IT, TDIT 2019, Accra, Ghana, 21–22 June 2019, Proceedings; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 311–324. [Google Scholar]
- Jalal, M. 12 Futuristic Cities Being Built around the World, from Saudi Arabia to China. 2022. Available online: https://thenationalnews.com/arts-culture/2022/08/02/12-futuristic-cities-being-built-around-the-worldfrom-saudi-arabia-to-china (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Abdel-Basset, M.; Abdel-Fatah, L.; Sangaiah, A.K. Metaheuristic algorithms: A comprehensive review. In Computational Intelligence for Multimedia Big Data on the Cloud with Engineering Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 185–231. [Google Scholar]
- Abiodun, E.O.; Alabdulatif, A.; Abiodun, O.I.; Alawida, M.; Alabdulatif, A.; Alkhawaldeh, R.S. A systematic review of emerging feature selection optimization methods for optimal text classification: The present state and prospective opportunities. Neural Comput. Appl. 2021, 33, 15091–15118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, R.; Shen, Q. Nature inspired feature selection meta-heuristics. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2015, 44, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kaur, P. A comprehensive analysis of nature-inspired meta-heuristic techniques for feature selection problem. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2021, 28, 1103–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larabi-Marie-Sainte, S. Outlier detection based feature selection exploiting bio-inspired optimization algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, D.; Gutiérrez-Gallego, A.; Garnica, O.; Velasco, J.M.; Zekri-Nechar, K.; Zamorano-León, J.J.; Heras, N.D.L.; Hidalgo, J.I. Predicting the Risk of Overweight and Obesity in Madrid—A Binary Classification Approach with Evolutionary Feature Selection. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazer-Rau, D.; Arends, R.; Zhang, L.; Traue, H.C. Feature Selection Based on Evolutionary Algorithms for Affective Computing and Stress Recognition. Eng. Proc. 2021, 10, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhou, F. Zoo: Selecting transcriptomic and methylomic biomarkers by ensembling animal-inspired swarm intelligence feature selection algorithms. Genes 2021, 12, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leske, M.; Bottacini, F.; Afli, H.; Andrade, B.G. BiGAMi: Bi-Objective Genetic Algorithm Fitness Function for Feature Selection on Microbiome Datasets. Methods Protoc. 2022, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, S.J.; Park, J.; Economou, A.; Lee, S. Artificial intelligence-aided design: Smart design for sustainable city development. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2019, 46, 1581–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.M.; Deverajan, G.G.; Chatterjee, P.; Alnumay, W.; Ghosh, U. Effective task scheduling algorithm with deep learning for Internet of Health Things (IoHT) in sustainable smart cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 71, 102945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macke, J.; Sarate, J.A.R.; de Atayde Moschen, S. Smart sustainable cities evaluation and sense of community. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 118103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamoudi, A.K.; Abidoye, R.B.; Lam, T.Y. The Impact of Citizens’ Participation Level on Smart Sustainable Cities Outcomes: Evidence from Saudi Arabia. Buildings 2023, 13, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq, M.; Tian, Z.; Bashir, A.K.; Jolfaei, A.; Yu, X. Data mining and machine learning methods for sustainable smart cities traffic classification: A survey. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 60, 102177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aina, Y.A. Achieving smart sustainable cities with GeoICT support: The Saudi evolving smart cities. Cities 2017, 71, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Afari, P.; Owusu-Manu, D.G.; Simons, B.; Debrah, C.; Ghansah, F.A. Sustainability guidelines to attaining smart sustainable cities in developing countries: A Ghanaian context. Sustain. Futures 2021, 3, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, C.; Nesi, P.; Paoli, I.; Paolucci, M.; Zamperlin, P. A big data platform for smart and sustainable cities: Environmental monitoring case studies in Europe. In Computational Science and Its Applications—ICCSA 2020: 20th International Conference, Cagliari, Italy, 1–4 July 2020; Proceedings, Part VII 20; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 393–406. [Google Scholar]
- Parlina, A.; Ramli, K.; Murfi, H. Exposing emerging trends in smart sustainable city research using deep autoencoders-based fuzzy c-means. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huovila, A.; Bosch, P.; Airaksinen, M. Comparative analysis of standardized indicators for Smart sustainable cities: What indicators and standards to use and when? Cities 2019, 89, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paes, V.D.C.; Pessoa, C.H.M.; Pagliusi, R.P.; Barbosa, C.E.; Argôlo, M.; de Lima, Y.O.; Salazar, H.; Lyra, A.; de Souza, J.M. Analyzing the Challenges for Future Smart and Sustainable Cities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haarstad, H. Constructing the sustainable city: Examining the role of sustainability in the ‘smart city’ discourse. J. Environ. Policy Plan. 2017, 19, 423–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslem, S. A novel parsimonious spherical fuzzy analytic hierarchy process for sustainable urban transport solutions. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2024, 128, 107447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, A.A.; Veisi, O.; Fakhr, B.V.; Du, D. Predicting solar radiation in the urban area: A data-driven analysis for sustainable city planning using artificial neural networking. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 105042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, N.U.; Ahmed, I.; Adnan, M.; Ali, M.; Naeem, F. Experts and intelligent systems for smart homes’ Transformation to Sustainable Smart Cities: A comprehensive review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 238, 122380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, C.; Chakraborti, A.; Majumder, S. Recent Advancements in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Sustainable Energy Management. In Sustainable Energy Solutions with Artificial Intelligence, Blockchain Technology, and Internet of Things; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2024; pp. 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, K. Multi-Objective Optimization Using Evolutionary Algorithms; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ishibuchi, H.; Imada, R.; Setoguchi, Y.; Nojima, Y. Performance comparison of NSGA-II and NSGA-III on various many-objective test problems. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computation (CEC), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 24–29 July 2016; pp. 3045–3052. [Google Scholar]
- Corne, D.W.; Jerram, N.R.; Knowles, J.D.; Oates, M.J. PESA-II: Region-based selection in evolutionary multiobjective optimization. In Proceedings of the 3rd Annual Conference on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7–11 July 2001; pp. 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- Goodarzian, F.; Ghasemi, P.; Gonzalez, E.D.S.; Tirkolaee, E.B. A sustainable-circular citrus closed-loop supply chain configuration: Pareto-based algorithms. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 328, 116892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Ishibuchi, H. MOGA: Multi-objective genetic algorithms. IEEE Int. Conf. Evol. Comput. 1995, 1, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, W.C.; Chuang, M.C. Using multi-objective genetic algorithm for partner selection in green supply chain problems. Expert Syst. Appl. 2011, 38, 4244–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolpakar, N.A.; Lodhi, S.S.; Pathak, S.; Sharma, M.A. Application of multi-objective genetic algorithm (MOGA) optimization in machining processes. In Optimization of Manufacturing Processes; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 185–199. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Xu, B.; Lu, G.; Du, C.; Huang, N. Multi-objective optimization of PEM fuel cell by coupled significant variables recognition, surrogate models and a multi-objective genetic algorithm. Energy Convers. Manag. 2021, 236, 114063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, J.; Nafpliotis, N.; Goldberg, D.E. A niched Pareto genetic algorithm for multiobjective optimization. In Proceedings of the First IEEE Conference on Evolutionary Computation. IEEE World Congress on Computational Intelligence, Orlando, FL, USA, 27–29 June 1994; pp. 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Baraldi, P.; Pedroni, N.; Zio, E. Application of a niched Pareto genetic algorithm for selecting features for nuclear transients classification. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2009, 24, 118–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zio, E.; Baraldi, P.; Pedroni, N. Feature selection for transients classification by a niched Pareto genetic algorithm. In Applied Artificial Intelligence; Taylor and Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2006; pp. 938–945. [Google Scholar]
- Zitzler, E.; Laumanns, M.; Thiele, L. SPEA2: Improving the strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm. TIK Rep. 2001, 103, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, B.; Cervante, L.; Shang, L.; Browne, W.N.; Zhang, M. Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms for filter based feature selection in classification. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Tools 2013, 22, 1350024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Das, S.; Ghatak, S.; Das, A.K. Strength pareto evolutionary algorithm based gene subset selection. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Big Data Analytics and Computational Intelligence (ICBDAC), Chirala, India, 23–25 March 2017; pp. 79–85. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, R.; Das, S.K.; Mohanty, M. Shear Wave Velocity-Based Liquefaction Susceptibility of Soil Using Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) with Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm (SPEA 2). In Earthquake Geotechnics: Select Proceedings of 7th ICRAGEE 2021; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 33–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Singh, D.; Singh Uppal, R. Parallel strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm-II based image encryption. IET Image Process. 2020, 14, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrdad, S.; Dadsetani, R.; Amiriyoon, A.; Leon, A.S.; Reza Safaei, M.; Goodarzi, M. Exergo-economic optimization of organic rankine cycle for saving of thermal energy in a sample power plant by using of strength pareto evolutionary algorithm II. Processes 2020, 8, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Chen, S.; Jiang, S.; Xiong, N. Improved strength Pareto evolutionary algorithm based on reference direction and coordinated selection strategy. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 36, 4693–4722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Zhang, M.; Browne, W.N. Particle swarm optimization for feature selection in classification: A multi-objective approach. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2012, 43, 1656–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vito, S.; Massera, E.; Piga, M.; Martinotto, L.; Di Francia, G. On field calibration of an electronic nose for benzene estimation in an urban pollution monitoring scenario. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 129, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Fang, X. An Improved Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2 with Adaptive Crossover Operator for Bi-Objective Distributed Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Delivery. Mathematics 2023, 11, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Liu, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, T. An Improved Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm 2 with application to the optimization of distributed generations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2012, 64, 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongur, V.; Ülker, E. B-spline curve knot estimation by using niched pareto genetic algorithm (npga). In Intelligent and Evolutionary Systems: The 19th Asia Pacific Symposium, IES 2015, Bangkok, Thailand, 22–25 November 2015, Proceedings; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Li, X.; Yang, X. Dimensional synthesis for multi-linkage robots based on a niched Pareto genetic algorithm. Algorithms 2020, 13, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi Brojeni, P.; Abazari, S.; Madani, M. Pesa ii algorithm-based optimal coordination of directional overcurrent relays in microgrid. Comput. Intell. Electr. Eng. 2022, 13, 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, H.; Yadav, S.P. Using reference point-based NSGA-II to system reliability. Constraints 2017, 1, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Pasha, J.; Moses, R.; Sobanjo, J.; Ozguven, E.E.; Dulebenets, M.A. Development of exact and heuristic optimization methods for safety improvement projects at level crossings under conflicting objectives. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2022, 220, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulebenets, M.A. An Adaptive Polyploid Memetic Algorithm for scheduling trucks at a cross-docking terminal. Inf. Sci. 2021, 565, 390–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulebenets, M.A. A Diffused Memetic Optimizer for reactive berth allocation and scheduling at marine container terminals in response to disruptions. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2023, 80, 101334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, E.; Pillay, N. A study of ant-based pheromone spaces for generation constructive hyper-heuristics. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2022, 72, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Region | Country | Name | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | Malaysia | BiodiverCity | The city is planned to be a car-free environment with autonomous public transportation systems |
| Asia | Japan | Woven city | Fully automated, powered by artificial intelligence technologies |
| North America | USA | Telosa | Commuting within the city to access services will take a maximum of 15 min and no fossil-fuel-powered vehicle will be allowed in the city |
| Asia | Saudi Arabia | NEOM—The Line | There will be no cars and carbon emissions will be zero; 20 min will be enough to go to anywhere in the city |
| Asia | Maldives | Floating city | Designed to float on water and be resistant to climate changes |
| Asia | China | Chengdu future city | The city will mainly utilize autonomous vehicles |
| Africa | Senegal | Akon City | The economy of the city will be based on blockchain and cryptocurrency |
| Sustainability Theme | Indicator Dataset | Description | Features | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Health | Life expectancy | The datasets contained 19 features with real values of life expectancy determinant factors | Adult Mortality (c1), infant deaths (c2), alcohol (c3), percentage expenditure (c4), hepatitis B (c5), measles (c6), BMI, under-five deaths (c7), polio (c8), total expenditure (c9), diphtheria (c10), HIV/AIDS (c11), GDP, population, thinness 1–19 years (c13), thinness 5–9 years (c14), income composition of resources (c15), schooling, life expectancy (c16) | Kaggle (publicly available) |
| Atmosphere | Air quality | The datasets contained 9358 instances of responses for hourly averages from sensors embedded in an air quality device. It has 15 features. | CO (GT) (a1), PT08.S1 (CO) (a2), NMHC (GT) (a3), C6H6 (GT) (a4), PT08.S2 (NMHC) (a5), NOx (GT) (a6), PT08.S3 (NOx) (a7), NO2 (GT) (a8), PT08.S4 (NO2) (a9), PT08.S5 (O3) (a10), T, RH, AH | [77] (publicly available) |
| Consumption and production patterns | Energy consumption | The data were collected from smart steel industry located in South Korea. The data contained 11 features with 35,040 instances. | Usage_kWh (E1), Lagging_Current_Reactive.Power_kVarh (E2), Leading_Current_Reactive_Power_kVarh (E3), CO2 (tCO2) (E4), Lagging_Current_Power_Factor (E5), Leading_Current_Power_Factor (E6), NSM, Day_of_week (E7), Load_Type (E8) | UCL repository (publicly available) |
| Online services | Online shoppers’ intentions | The data contained 12,330 instances of sessions in which 10,422 were negative classes while 1908 were positive. The number of features in the dataset is 18. | Administrative, Administrative_Duration (D1), Informational (D17), D17_Duration (D2), ProductRelated (D4), ProductRelated_Duration (D5), BounceRates (D6), ExitRates (D7), PageValues (D8), SpecialDay (D9), Month, OperatingSystems (D10), Browser, Region (D15), TrafficType (D11), Weekend (D12), Revenue, Customer_Retention (D13) | UCL repository (publicly available) |
| Consumption and production patterns | Traffic flow | The datasets contained 48,204 instances of records with 9 features. The interstate data were collected on hourly bases. Includes weather and holiday features. | Temp, 3_1h, 8_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume | UCL Repository (publicly available) |
| Fresh water | Water quality | The data contained 20 features with 400,000 instances taken from a water base. | ResultMeanValue (b20), PopulationDensity (B1), TerraMarineProtected_2016_2018 (B2), TouristMean_1990_2020 (B3), VenueCount (B19), netMigration_2011_2018 (B4), droughts_floods_temperature (B5), literacyRate_2010_2018 (B6), combustibleRenewables_2009_2014 (B7), gdp (B8), composition_food_organic_waste_percent (B9), composition_glass_percent (B10), composition_metal_percent (B11), composition_other_percent (B12), composition_paper_cardboard_percent (B13), composition_plastic_percent (B14), composition_rubber_leather_percent (B15), composition_wood_percent (B16), composition_yard_garden_green_waste_percent (B17), waste_treatment_recycling_percent (B18) | Kaggle (publicly available) |
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Learning Algorithm | Selected Features (Accuracy) | Accuracy on All Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSGA3 | SVM | A6, A7, A8 and A10, T (92.75%) | 90.15% |
| KNN | A3, A6, A7, A8 and A10 (92.34%) | 89.40% | |
| GNB | A1, A2, A3, A4, A6, A7, A8 and RH (92.34%) | 88.94% | |
| RFC | A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9 and A10 (93.37%) | 90.40% | |
| ANN | A6, A7 and A8 (94.22%) | 91.22% | |
| MOEA | SVM | A6, A7, A8 and A10, T (93.51%) | 90.54% |
| KNN | A3, A6, A7, A8 and A10 (93.32%) | 90.34% | |
| GNB | A1, A2, A3, A4, A6, A7, A8 and RH (93.41%) | 90.44% | |
| RFC | A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, and A10 (93.41%) | 90.53% | |
| ANN | A6, A7 and A8 (93.51%) | 90.53% | |
| SPEA2 | SVM | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10, T, RH, AH (87.37%) | 87.37% |
| KNN | A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (87.37%) | 87.18% | |
| GNB | A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (87.37%) | 87.27% | |
| RFC | A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (87.66%) | 87.36% | |
| ANN | A1, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (87.45%) | 87.36% | |
| NPGA | SVM | A4, A5, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (84.04%) | 83.44% |
| KNN | A4, A5, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (85.22%) | 83.26% | |
| GNB | A4, A5, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (84.00%) | 83.35% | |
| RFC | A4, A5, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (86.75%) | 83.43% | |
| ANN | A5, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (84.02%) | 83.43% | |
| MOGA | SVM | A4, A5, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (82.65%) | 89.86% |
| KNN | A4, A5, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (88.86%) | 89.66% | |
| GNB | A4, A5, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (88.65%) | 89.76% | |
| RFC | A4, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (89.65%) | 89.85% | |
| ANN | A5, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (85.85%) | 89.85% | |
| PESA2 | SVM | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10, T, RH, AH (87.37%) | 85.84% |
| KNN | A4, A5, A3, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (86.00%) | 85.65% | |
| GNB | A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10, T, RH, AH (86.25%) | 85.75% | |
| RFC | A5, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A9, A10 (85.83%) | 85.83% | |
| ANN | A4, A5, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10 (85.83%) | 85.83% |
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Learning Algorithm | Selected Features (Accuracy) | Accuracy on All Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSGA3 | SVM | b20, b1, b2, b3, b4, b6, b9, b12, b13, b14, b16, b17, b18 (92.66) | 90.33% |
| KNN | b20, b1, b2, b3, b4, b6, b9, b12, b13, b14, b17, b18 (94.32) | 87.65% | |
| GNB | b20, b1, b2, b9, b12, b13, b14, b17, b18 (89.77) | 93.65% | |
| RFC | b20, b1, b9, b12, b13, b14, b17, b18 (94.32) | 90.65% | |
| ANN | b20, b9, b12, b13, b14, b17, b18 (95.62) | 95.01% | |
| MOEA | SVM | b20, b1, b2, b3, b4, b6, b9, b12, b13, b14, b16, b17, b18 (92.48) | 88.98% |
| KNN | b20, b1, b6, b9, b12, b14, b17, b18 (88.89) | 86.47% | |
| GNB | b20, b1, b2, b9, b12, b13, b14, b17, b18 (93.33) | 92.67% | |
| RFC | b20, b1, b9, b12, b13, b14, b17, b18, gdp (90.73) | 89.61% | |
| ANN | b20, b9, b12, b13, b14, b18 (94.90) | 94.30% | |
| SPEA2 | SVM | b20, b1, b2, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (81.72%) | 85.87% |
| KNN | b20, b1, b2, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (81.72%) | 83.44% | |
| GNB | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (81.72%) | 89.43% | |
| RFC | b20, b1, b2, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (81.72%) | 86.47% | |
| ANN | b20, b1, b2, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (81.72%) | 91.00% | |
| NPGA | SVM | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (77.49%) | 82.00% |
| KNN | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (77.49%) | 79.69% | |
| GNB | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (77.49%) | 85.40% | |
| RFC | b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (77.49%) | 82.58% | |
| ANN | b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (77.49%) | 86.90% | |
| MOGA | SVM | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (84.33%) | 88.31% |
| KNN | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (84.33%) | 85.82% | |
| GNB | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (84.33%) | 91.97% | |
| RFC | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (84.33%) | 88.94% | |
| ANN | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (84.33%) | 93.59% | |
| PESA-II | SVM | b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (83.62%) | 84.36% |
| KNN | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (83.62%) | 81.98% | |
| GNB | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b17 (83.62%) | 87.86% | |
| RFC | b20, b1, b2, b3, b19, b4, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16 (83.62%) | 84.96% | |
| ANN | b20, b1, b2, b5, b6, b7, gdp, b9, b10, b11, b12, b13, b14, b15, b16, b17 (83.62%) | 89.41% |
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Learning Algorithm | Selected Features (Accuracy) | Accuracy on All Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSGA3 | SVM | C1, C2, C3, C5, Meailes, BMI, C8, C10 (90.52) | 89.59% |
| KNN | C1, C2, C5, Meailes, BMI, C7, C8, C10, C13 (87.19) | 87.19% | |
| GNB | C2, C3, C5, Meailes, BMI, C8, C10, C14 (89.66) | 87.25% | |
| RFC | C1, C2, C3, C5, Meailes, BMI, C7, C8, C10, C14 (88.33) | 86.45% | |
| ANN | C1, C2, C3, C5, Meailes, BMI, C8, C10, C13, C14 (92.75) | 89.75% | |
| MOEA | SVM | C1, C2, C3, C5, Meailes, BMI, C8, C10 (89.66) | 88.74% |
| KNN | C1, C2, C3, C5, Meailes, C7, C8, C10, C13 (86.34) | 86.34% | |
| GNB | C1, C2, C3, C5, Meailes, BMI, C7, C8, C10, C13, C14 (88.79) | 86.40% | |
| RFC | C1, C2, C3, C5, C6, C7, C8, C10, C13 (87.56) | 85.70% | |
| ANN | C1, C2, C3, C5, Meailes, BMI, C7, C8, C10 (91.92) | 88.95% | |
| SPEA2 | SVM | C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, C16 (85.63) | 85.63% |
| KNN | C2, C3 C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, C16 (85.63) | 83.32% | |
| GNB | C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C16 (85.63) | 83.38% | |
| RFC | C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, C16 (85.63) | 82.70% | |
| ANN | C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, C16 (85.63) | 85.84% | |
| NPGA | SVM | C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, C16 (78.65%) | 81.78% |
| KNN | C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, C16 (78.65%) | 79.57% | |
| GNB | C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, (78.65%) | 79.62% | |
| RFC | C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, C16 (78.65%) | 78.98% | |
| ANN | C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6, BMI, C7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, C13, C14, C15, Schooling, C16 (78.65%) | 81.97% | |
| MOGA | SVM | c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (87.65) | 88.07% |
| KNN | C1, c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (87.65) | 85.69% | |
| GNB | C1, c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (87.65) | 85.75% | |
| RFC | C1, c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (87.65) | 85.06% | |
| ANN | C1, c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (87.65) | 88.28% | |
| PESA2 | SVM | C1, c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (81.22%) | 84.14% |
| KNN | C1, c2, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (81.22%) | 81.86% | |
| GNB | C1, c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (81.22%) | 81.92% | |
| RFC | c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, Schooling, C16 (81.22%) | 81.25% | |
| ANN | C1, c2, C3, c4, C5, C6, BMI, c7, C8, C9, C10, C11, GDP, Population, c13, c14, C15, C16 (81.22%) | 84.33% |
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Learning Algorithm | Selected Features (Accuracy) | Accuracy on All Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSGA3 | SVM | temp, 3_1h, 8_1h, weather_main, traffic_volume (96.88) | 94.66% |
| KNN | temp, 8_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (93.45) | 95.89% | |
| GNB | temp, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (94.22) | 93.75% | |
| RFC | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (95.45) | 94.65% | |
| ANN | temp, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (98.14) | 96.56% | |
| MOEA | SVM | temp, 3_1h, 8_1h, weather_main, traffic_volume (95.96) | 93.76% |
| KNN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (92.66) | 95.07% | |
| GNB | temp, 8_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (93.39) | 92.93% | |
| RFC | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (94.71) | 93.91% | |
| ANN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (97.28) | 95.71% | |
| SPEA2 | SVM | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (89.28%) | 90.48% |
| KNN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (89.28%) | 91.74% | |
| GNB | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (89.28%) | 89.68% | |
| RFC | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (89.28%) | 90.62% | |
| ANN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (89.28%) | 92.36% | |
| NPGA | SVM | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (85.75%) | 86.41% |
| KNN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (85.75%) | 87.61% | |
| GNB | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (85.75%) | 85.64% | |
| RFC | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (85.75%) | 86.55% | |
| ANN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (85.75%) | 88.20% | |
| MOGA | SVM | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (90.55%) | 93.06% |
| KNN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (90.55%) | 94.36% | |
| GNB | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (92.23%) | 92.23% | |
| RFC | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (90.55%) | 93.21% | |
| ANN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (90.55%) | 94.99% | |
| PESA2 | SVM | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (87.65%) | 88.90% |
| KNN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (87.65%) | 90.14% | |
| GNB | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (87.65%) | 88.11% | |
| RFC | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (89.25%) | 89.04% | |
| ANN | temp, 3_1h, 1_all, weather_main, traffic_volume (87.25%) | 90.74% |
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Learning Algorithm | Selected Features (Accuracy) | Accuracy on All Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSGA3 | SVM | Administrative, D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, Revenue, D13 (94.96) | 92.02% |
| KNN | D1, D2, D4, D5, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11 (92.66) | 92.19% | |
| GNB | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11 (94.34) | 90.65% | |
| RFC | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11 (93.65) | 93.03% | |
| ANN | D1, D17, D2, D4, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11 (92.15) | 92.03% | |
| MOEA | SVM | Administrative, D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, Revenue, D13 (92.41) | 87.88% |
| KNN | D1, D2, D4, D5, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11 (90.09) | 88.04% | |
| GNB | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11 (88.49) | 86.57% | |
| RFC | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11 (89.54) | 88.83% | |
| ANN | D1, D17, D2, D4, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11 (88.00) | 87.89% | |
| SPEA2 | SVM | Administrative, D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue, (80.45%) | 84.80% |
| KNN | Administrative, D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue, (80.45%) | 84.96% | |
| GNB | Administrative, D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, (80.45%) | 83.54% | |
| RFC | Administrative, D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, (80.45%) | 85.72% | |
| ANN | Administrative, D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, Browser, D15, D11, (80.45%) | 84.81% | |
| NPGA | SVM | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue, D13 (80.45%) | 80.99% |
| KNN | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue, (80.45%) | 81.14% | |
| GNB | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue, D13 (80.45%) | 79.78% | |
| RFC | Administrative, D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue (80.45%) | 81.86% | |
| ANN | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue (80.45%) | 81.00% | |
| MOGA | SVM | D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, (82.45%) | 87.22% |
| KNN | D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, (82.45%) | 87.38% | |
| GNB | D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, (82.45%) | 85.92% | |
| RFC | D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, (82.45%) | 88.16% | |
| ANN | D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, (82.45%) | 87.23% | |
| PESA2 | SVM | D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue, D13 (80.45%) | 83.32% |
| KNN | D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue, D13 (80.45%) | 83.47% | |
| GNB | D1, D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, (80.45%) | 82.08% | |
| RFC | D1, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue, D13 (80.45%) | 84.22% | |
| ANN | D17, D2, D4, D5, D6, D7, D8, D9, Month, D10, Browser, D15, D11, D12, Revenue (80.45%) | 83.33% |
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Learning Algorithm | Selected Features (Accuracy) | Accuracy on All Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| NSGA3 | SVM | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (97.68) | 95.33% |
| KNN | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (97.65) | 96.75% | |
| GNB | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, E7, E8 (97.22) | 94.66% | |
| RFC | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, E7, E8 (96.75) | 97.03% | |
| ANN | E1, E2, E3, E5, NSM, E6, E7, E8 (98.17) | 97.59% | |
| MOEA | SVM | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (96.21) | 96.21% |
| KNN | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.87) | 90.87% | |
| GNB | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, E7, E8 (94.86) | 93.00% | |
| RFC | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, E7, E8 (95.81) | 95.62% | |
| ANN | E1, E2, E3, E5, NSM, E6, E7, E8 (92.47) | 90.56% | |
| SPEA2 | SVM | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.44%) | 92.84% |
| KNN | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.44%) | 87.69% | |
| GNB | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.44%) | 89.75% | |
| RFC | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.44%) | 92.27% | |
| ANN | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.44%) | 87.39% | |
| NPGA | SVM | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (80.64%) | 88.66% |
| KNN | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (80.64%) | 83.74% | |
| GNB | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (80.64%) | 85.71% | |
| RFC | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (80.64%) | 88.12% | |
| ANN | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (80.64%) | 83.46% | |
| MOGA | SVM | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (89.84%) | 95.49% |
| KNN | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (89.84%) | 90.19% | |
| GNB | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (89.84%) | 92.30% | |
| RFC | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (89.84%) | 94.90% | |
| ANN | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (89.84%) | 89.88% | |
| PESA2 | SVM | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.44%) | 91.22% |
| KNN | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (90.44%) | 86.15% | |
| GNB | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.44%) | 88.17% | |
| RFC | E1, E2, E3, E4, E5, E6, NSM, E7, E8 (90.44%) | 90.66% | |
| ANN | E1, E2, E3, E5, E6, NSM, E8 (90.44%) | 85.86% |
| Evolutionary Algorithm | Learning Algorithm | Air Quality | Life Expectancy | Traffic Volume | Online Shoppers’ Intention | Energy Consumption | Water Quality | Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSGA3 | SVM | 0.987 | 0.789 | 0.234 | 1.256 | 0.567 | 0.768 | 1.341 |
| KNN | 0.923 | 0.795 | 0.234 | 1.266 | 0.597 | 0.775 | 1.347 | |
| GNB | 0.919 | 0.801 | 0.234 | 1.275 | 0.567 | 0.783 | 1.352 | |
| RFC | 1.087 | 0.807 | 0.235 | 1.285 | 0.569 | 0.790 | 1.386 | |
| ANN | 1.011 | 0.813 | 0.268 | 1.295 | 0.567 | 0.798 | 1.390 | |
| MOEA | SVM | 0.895 | 0.689 | 0.269 | 1.262 | 0.678 | 0.876 | 1.527 |
| KNN | 0.996 | 0.999 | 0.269 | 1.273 | 0.678 | 0.883 | 1.595 | |
| GNB | 0.932 | 1.449 | 0.270 | 1.284 | 0.698 | 0.890 | 1.662 | |
| RFC | 0.928 | 2.101 | 0.270 | 1.295 | 0.688 | 0.897 | 1.762 | |
| ANN | 1.097 | 3.046 | 0.271 | 1.306 | 0.689 | 0.904 | 1.931 | |
| SPEA2 | SVM | 1.897 | 0.989 | 0.456 | 3.345 | 0.789 | 0.967 | 2.633 |
| KNN | 1.911 | 0.996 | 0.459 | 3.370 | 0.795 | 0.974 | 2.653 | |
| GNB | 1.926 | 1.004 | 0.463 | 3.395 | 0.801 | 0.982 | 2.672 | |
| RFC | 1.940 | 1.011 | 0.466 | 3.421 | 0.807 | 0.989 | 2.693 | |
| ANN | 1.955 | 1.019 | 0.470 | 3.446 | 0.813 | 0.996 | 2.713 | |
| NPGA | SVM | 2.014 | 2.234 | 0.512 | 3.985 | 0.920 | 0.999 | 2.793 |
| KNN | 2.027 | 2.251 | 0.516 | 4.015 | 0.927 | 1.006 | 2.814 | |
| GNB | 2.040 | 2.268 | 0.520 | 4.045 | 0.934 | 1.014 | 2.835 | |
| RFC | 2.054 | 2.285 | 0.524 | 4.075 | 0.941 | 1.022 | 2.856 | |
| ANN | 2.067 | 2.302 | 0.528 | 4.106 | 0.948 | 1.029 | 2.877 | |
| MOGA | SVM | 2.001 | 2.452 | 0.624 | 3.894 | 0.884 | 0.994 | 2.728 |
| KNN | 2.000 | 2.470 | 0.629 | 3.923 | 0.891 | 1.001 | 2.746 | |
| GNB | 1.999 | 2.489 | 0.633 | 3.953 | 0.897 | 1.009 | 2.764 | |
| RFC | 1.997 | 2.508 | 0.638 | 3.982 | 0.904 | 1.017 | 2.783 | |
| ANN | 1.996 | 2.526 | 0.643 | 4.012 | 0.911 | 1.024 | 2.801 | |
| PESA-II | SVM | 1.981 | 2.189 | 0.782 | 4.123 | 0.906 | 1.024 | 2.864 |
| KNN | 1.983 | 2.205 | 0.788 | 4.154 | 0.913 | 1.032 | 2.884 | |
| GNB | 1.985 | 2.222 | 0.794 | 4.185 | 0.920 | 1.039 | 2.904 | |
| RFC | 1.987 | 2.239 | 0.800 | 4.216 | 0.927 | 1.047 | 2.924 | |
| ANN | 1.989 | 2.255 | 0.806 | 4.248 | 0.933 | 1.055 | 2.944 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almutairi, M.S. Evolutionary Multi-Objective Feature Selection Algorithms on Multiple Smart Sustainable Community Indicator Datasets. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041511
Almutairi MS. Evolutionary Multi-Objective Feature Selection Algorithms on Multiple Smart Sustainable Community Indicator Datasets. Sustainability. 2024; 16(4):1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041511
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmutairi, Mubarak Saad. 2024. "Evolutionary Multi-Objective Feature Selection Algorithms on Multiple Smart Sustainable Community Indicator Datasets" Sustainability 16, no. 4: 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041511
APA StyleAlmutairi, M. S. (2024). Evolutionary Multi-Objective Feature Selection Algorithms on Multiple Smart Sustainable Community Indicator Datasets. Sustainability, 16(4), 1511. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041511






