Constructing and Testing AI International Legal Education Coupling-Enabling Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Constructing AI International Legal Education Coupling-Enabling Model
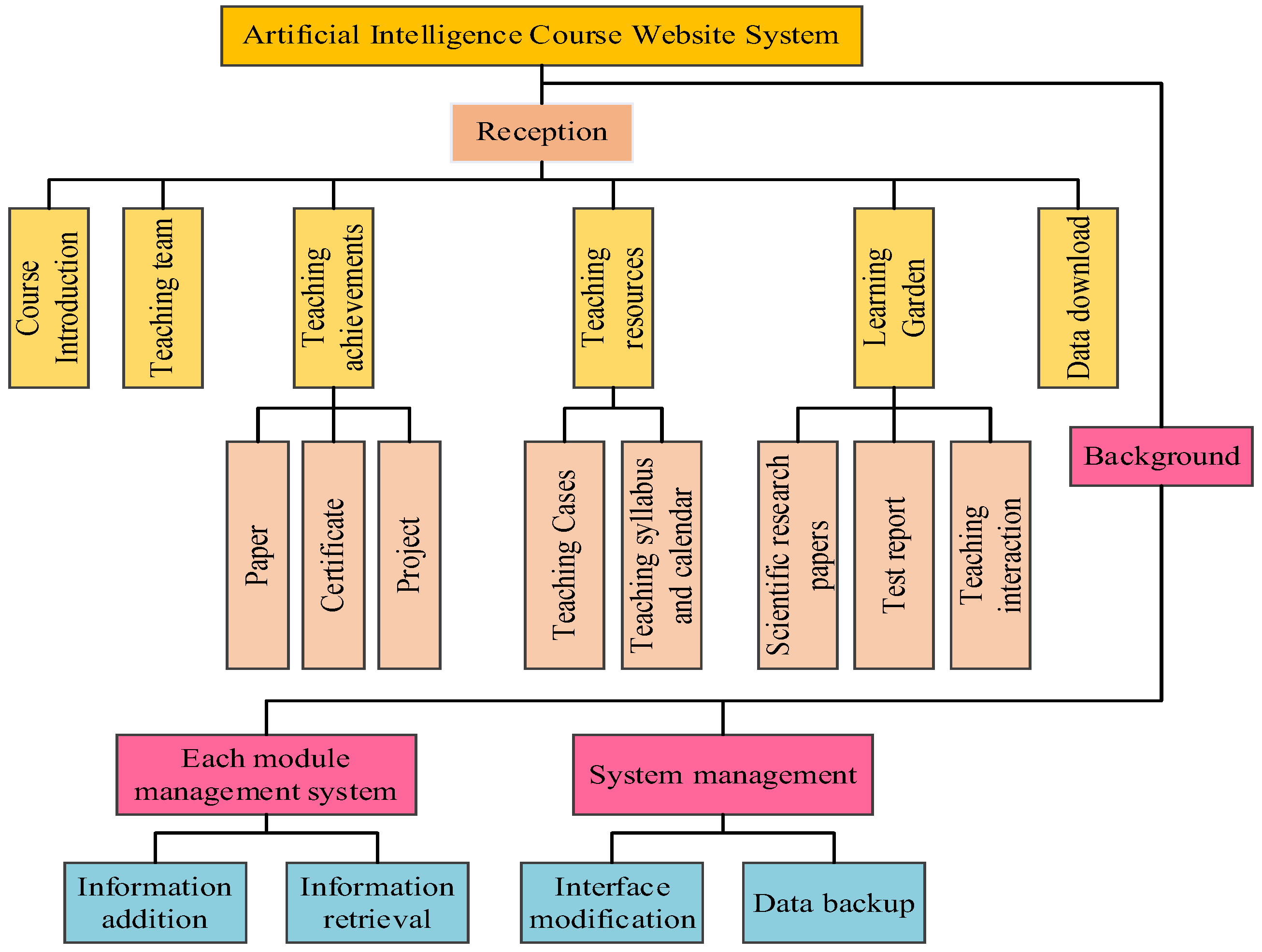
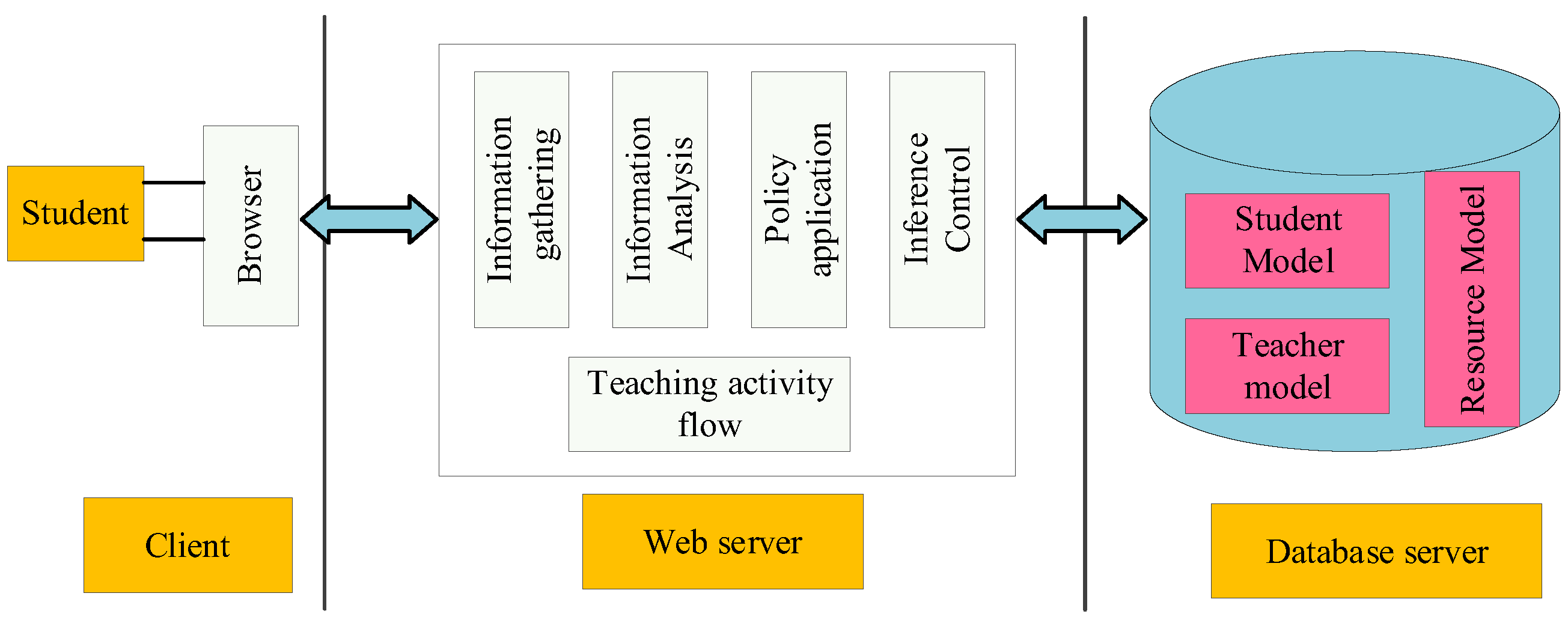
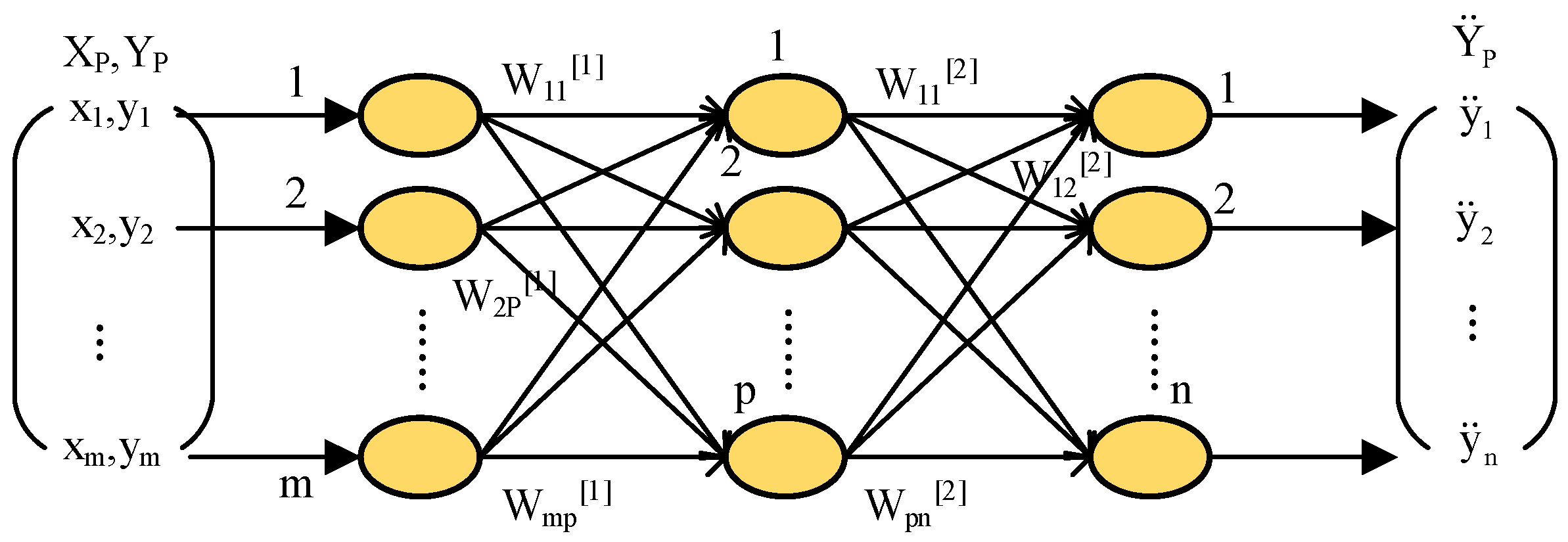
3.1. Construction of AI Teaching Model
3.2. Decision Reasoning in Intelligent Teaching
4. AI Intelligent Technology
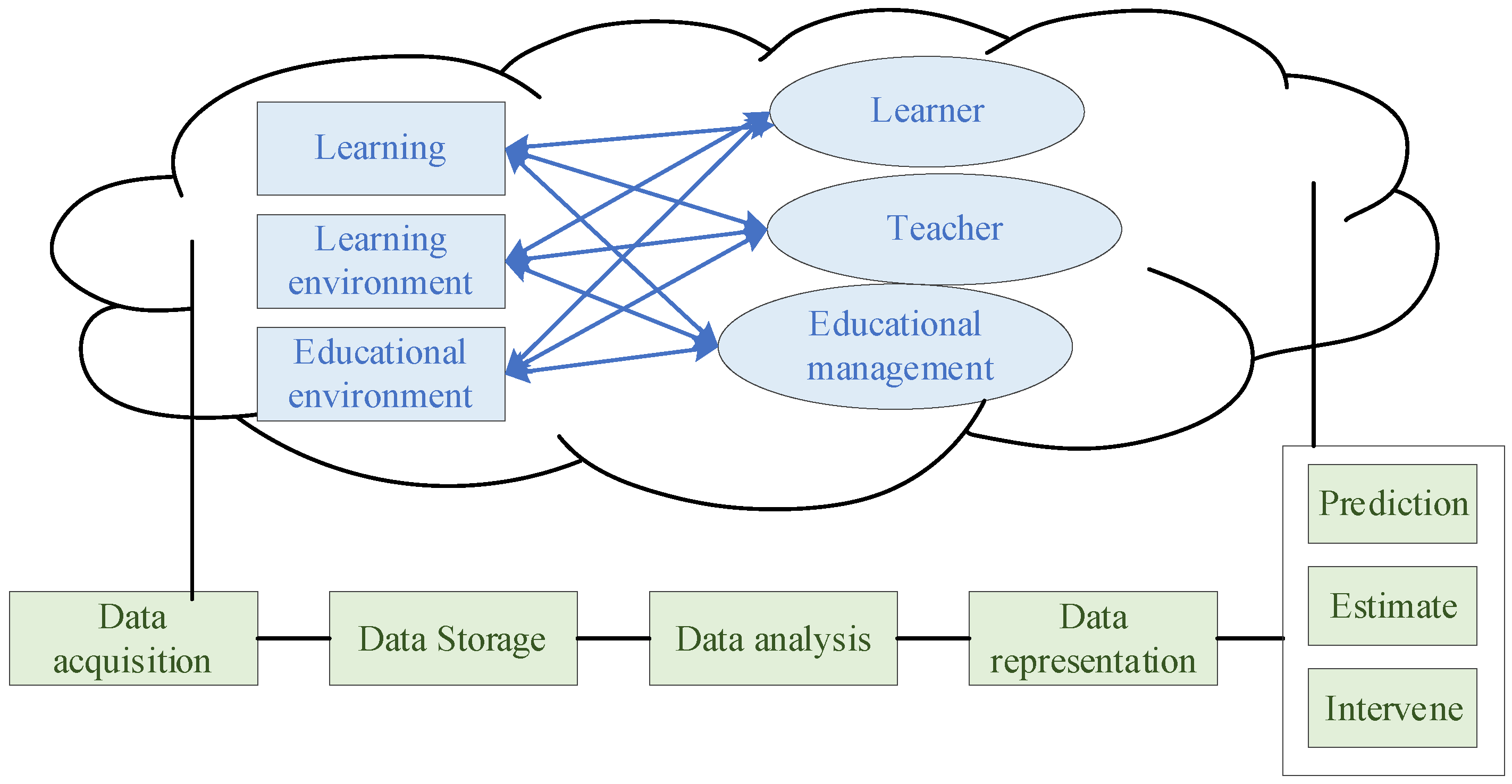
4.1. AI Data Analysis
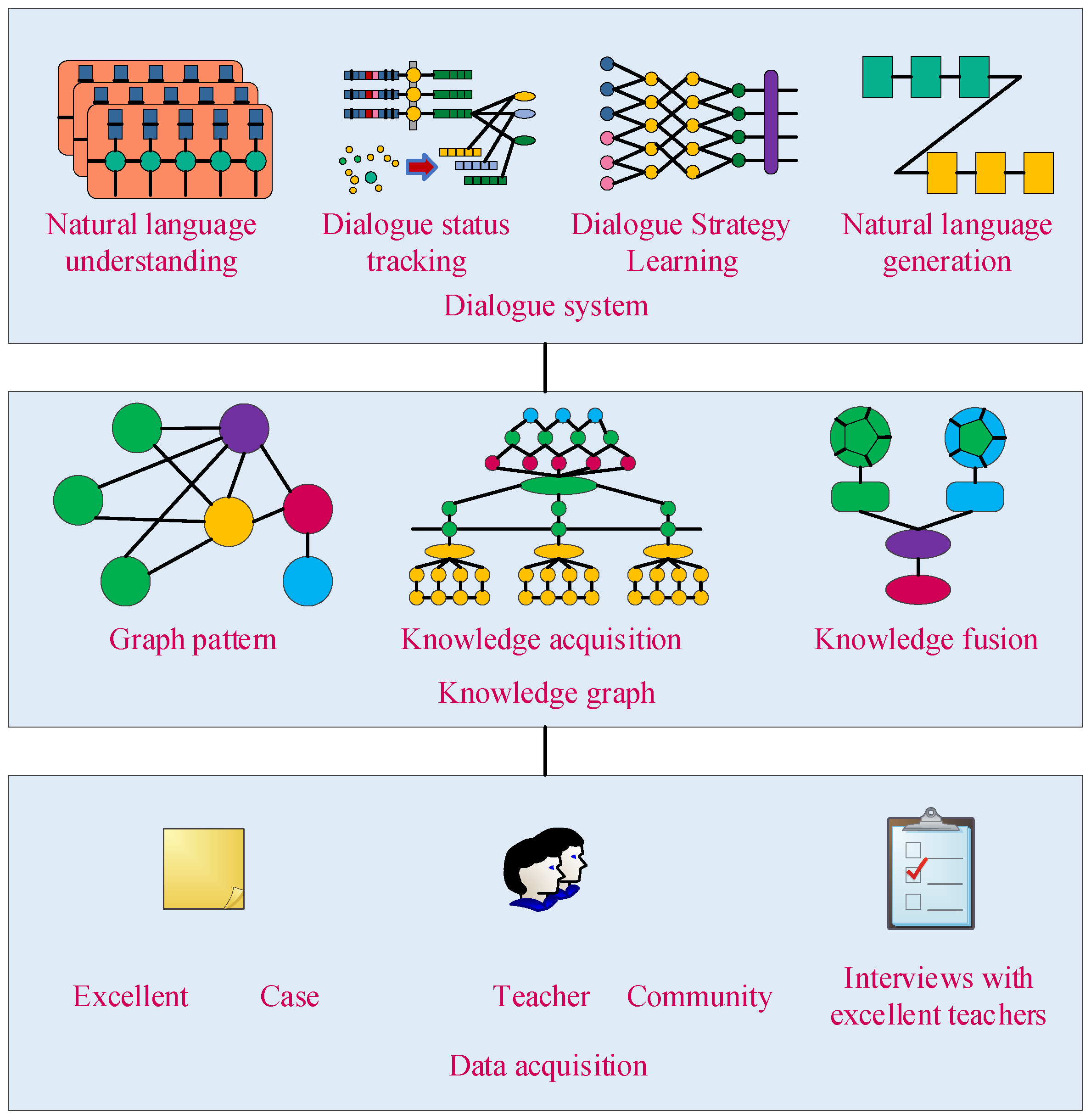
4.2. AI Knowledge Graph
4.3. AI Intelligent Diagnosis
5. Practical Analysis of the AI Model of International Legal Education
5.1. System Testing
5.2. Analysis of AI Instructional Coupling
5.2.1. Analysis of Learning Behavior
5.2.2. Completion of Assignments
5.2.3. Course Satisfaction
5.3. Long-Term Impact and Sustainability Analysis
5.3.1. Follow-Up Studies
5.3.2. Sustainability Assessment
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions
- In the teaching system test, the accuracy of the classification of the AI international law education model reaches 99.5%, and at the same time, the algorithm runs in a relatively short time, which is able to mine the learning knowledge for the user more accurately in a short period of time.
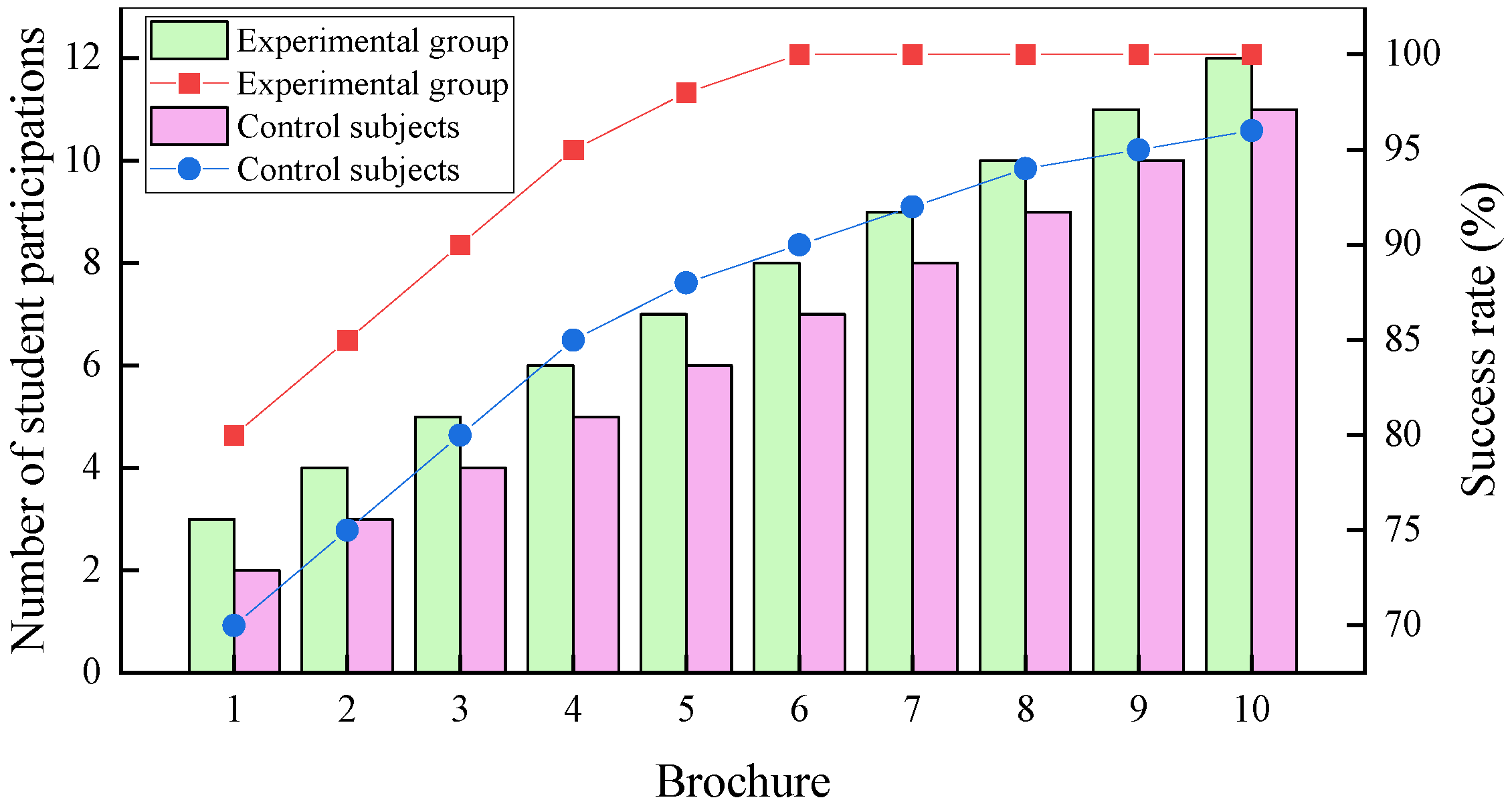
- In the coupling analysis, the average number of visits in the experimental class is 128, and the final score of the student who has watched the video for the longest time is also 13 points more than that of the control class, and there is a situation in which the submission rate of three assignments is 100%. The coupling of legal education and AI to empower development can help teachers to reduce mechanical repetitive labor.
- In the long-term impact and sustainability analysis, the career development of students in the experimental group showed a clear advantage in terms of the employment rate, which rapidly increased from 75% to 100%, and they achieved a 95% success rate in the fourth year. The positive impact of the sustainability of the AI-coupled empowerment model in actual law practice is highlighted.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, W. Artificial Intelligence education for young children: Why, what, and how in curriculum design and implementation. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, W.; Tuomi, I. State of the art and practice in AI in education. Eur. J. Educ. 2022, 57, 542–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Hou, Y. Artificial Intelligence Empowers the Integrated Development of Legal Education: Challenges and Responses. Futur. Hum. Image 2021, 16, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artolovni, A.; Tomičić, A.; Mosler, E.L. Ethical, legal, and social considerations of AI-based medical decision-support tools: A scoping review. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2022, 161, 104738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, G.-J.; Chien, S.-Y. Definition, roles, and potential research issues of the metaverse in education: An artificial intelligence perspective. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Xiao, C.; Tu, C.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.; Sun, M. How Does NLP Benefit Legal System: A Summary of Legal Artificial Intelligence. arXiv Prepr. 2020, arXiv:2004.12158. [Google Scholar]
- Gerke, S.; Minssen, T.; Cohen, G. Ethical and legal challenges of artificial intelligence-driven healthcare. In Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, F.; Jiao, P. Artificial intelligence in education: The three paradigms. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2021, 2, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas-Ch, W.; Arias-Navarrete, A.; Palacios-Pacheco, X. Proposal of an Architecture for the Integration of a Chatbot with Artificial Intelligence in a Smart Campus for the Improvement of Learning. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A. Employing Adaptive Learning and Intelligent Tutoring Robots for Virtual Classrooms and Smart Campuses: Reforming Education in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. In Advanced Computing and Intelligent Technologies: Proceedings of ICACIT 2022; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2022; Volume 914, p. 395. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, C.K.Y. A comprehensive AI policy education framework for university teaching and learning. Int. J. Educ. Technol. High. Educ. 2023, 20, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, J.; Howard, A. Emerging challenges in AI and the need for AI ethics education. AI Ethics 2020, 1, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, C.; Selwyn, N. Deep learning goes to school: Toward a relational understanding of AI in education. Learn. Media Technol. 2019, 45, 251–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, W.; Porayska-Pomsta, K.; Holstein, K.; Sutherland, E.; Baker, T.; Shum, S.B.; Santos, O.C.; Rodrigo, M.T.; Cukurova, M.; Bittencourt, I.I.; et al. Ethics of AI in Education: Towards a Community-Wide Framework. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2021, 32, 504–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemorin, S.; Vlachidis, A.; Ayerakwa, H.M.; Andriotis, P. AI hyped? A horizon scan of discourse on artificial intelligence in education (AIED) and development. Learn. Media Technol. 2023, 48, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knox, J. Artificial intelligence and education in China. Learn. Media Technol. 2020, 45, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, H.; Bernacki, M.; Greene, J.A. Psychological foundations of emerging technologies for teaching and learning in higher education. Curr. Opin. Psychol. 2020, 36, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himeur, Y.; Elnour, M.; Fadli, F.; Meskin, N.; Petri, I.; Rezgui, Y.; Bensaali, F.; Amira, A. AI-big data analytics for building automation and management systems: A survey, actual challenges and future perspectives. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 4929–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzanares, M.C.S.; Hernanz, R.J.P.; Yáñez, M.J.Z.; López, G.A.; Sánchez, R.M.; Rodríguez, A.C.; Martín, C.; Arribas, S.R. Eye-tracking technology and data-mining techniques used for a behavioral analysis of adults engaged in learning processes. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 172, e62103. [Google Scholar]
- Jakobi, T.; Stevens, G.; Seufert, A.M.; Becker, M. Webtracking under the new data protection law: Design potentials at the intersection of jurisprudence and HCI. In Proceedings of the Mensch und Computer, Hamburg, Germany, 8–11 September 2019; pp. 309–319. [Google Scholar]
- Corte, L.D. On proportionality in the data protection jurisprudence of the CJEU. Int. Data Priv. Law 2022, 12, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuncuoglu, A. Designing one year curriculum to teach artificial intelligence for middle school. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM Conference on Innovation and Technology in Computer Science Education, Vilnius, Lithuania, 21 June 2020; pp. 96–102. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, K.; Yang, Z.; Yu, C.-H.; Buehler, M.J. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in design of mechanical materials. Mater. Horizons 2021, 8, 1153–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vital, T.P.; Sangeeta, K.; Kumar, K.K. Student Classification Based on Cognitive Abilities and Predicting Learning Performances Using Machine Learning Models. Int. J. Comput. Digit. Syst. 2021, 10, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J. The theory of bifurcated educational system and its implications for school improvement. Int. J. Leadersh. Educ. 2020, 26, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullaeva, B.S.; Sobirova, M.A.; Abduganiev, O.T.; Abdullaev, D.N. The specifics of modern legal education and upbringing of schoolchildrenin the countries of the post-soviet world. J. Adv. Res. Dyn. Control Syst. 2020, 12, 2706–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Shalini, S. A Study on the Effectiveness of Problem-based Learning in Legal Education in India. Asian J. Leg. Educ. 2021, 8, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F. Application of artificial intelligence in modern art teaching. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn. 2020, 15, 238–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novalinda, R.; Dakhi, O.; Fajra, M.; Azman, A.; Masril, M.; Ambiyar, A.; Verawadina, U. Learning Model Team Assisted Individualization Assisted Module to Improve Social Interaction and Student Learning Achievement. Univers. J. Educ. Res. 2020, 8, 7974–7980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, F.; Zheng, L.; Jiao, P. Artificial intelligence in online higher education: A systematic review of empirical research from 2011 to 2020. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2022, 27, 7893–7925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Artificial intelligence in educational leadership: A symbiotic role of human-artificial intelligence decision-making. J. Educ. Adm. 2021, 59, 256–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Set | K-Means Instructional Model | Teaching System of Vector Machine | AI Education Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data set 1 | 69.5% | 82.6% | 99.5% |
| Data set 2 | 62.4% | 78.4% | 98.8% |
| Data set 3 | 60.2% | 74.2% | 97.9% |
| Data set 4 | 54.7% | 68.2% | 96.4% |
| Classes | Class Size | Data Recording | Total Number of Times | Average Times |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental class | 150 | Number of logins | 7859 | 252 |
| Number of visits | 6008 | 128 | ||
| Number of comments | 5078 | 108 | ||
| Number of views | 7950 | 224 | ||
| Number of likes | 6948 | 145 | ||
| Control class | 150 | Number of logins | 6489 | 105 |
| Number of visits | 5190 | 95 | ||
| Number of comments | 4467 | 79 | ||
| Number of views | 2578 | 65 | ||
| Number of likes | 5042 | 82 |
| Classes | Data Recording | Maximum Time (h) | Average Time (h) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental class | Watch the video | 191.9 | 189.5 |
| Watch the text | 124.5 | 122.5 | |
| Length of study | 144.7 | 140 | |
| Length of time logged on | 189.9 | 175.9 | |
| Control class | Watch the video | 189.5 | 67.6 |
| Watch the text | 109 | 77 | |
| Length of study | 126.8 | 98 | |
| Length of time logged on | 105.5 | 68 |
| Classes | N | Data Validation | Average | Standard Deviation | Standard Error of the Mean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental class | 150 | 53.47 | 6.248 | 0.911 | |
| T | 0.008 | 0.004 | 0.001 | ||
| P | 0.007 | 0.002 | 0.001 | ||
| Control class | 150 | 47.38 | 5.648 | 0.701 | |
| T | 0.025 | 0.018 | 0.05 | ||
| P | 0.048 | 0.016 | 0.05 |
| Years of Graduation | Experimental Class | Control Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Academic Development | Career Development (Employment Rate) | Academic Development | Career Development (Employment Rate) | |
| 1 | 3.8 | 75% | 3.2 | 65% |
| 2 | 3.9 | 80% | 3.4 | 70% |
| 3 | 4.1 | 85% | 3.5 | 75% |
| 4 | 4.2 | 90% | 3.6 | 80% |
| 5 | 4.5 | 95% | 3.8 | 81% |
| 6 | 4.8 | 98% | 4.0 | 85% |
| 7 | 5.0 | 100% | 4.1 | 90% |
| 8 | 5.0 | 100% | 4.2 | 92% |
| 9 | 5.0 | 100% | 4.4 | 94% |
| 10 | 5.0 | 100% | 4.5 | 95% |
| Number of Practices | Experimental Class | Control Class | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degree of Difficulty | Practicality | Degree of Difficulty | Practicality | |
| 1 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 7 |
| 2 | 7.5 | 8.5 | 6.5 | 7.5 |
| 3 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 8 |
| 4 | 8.5 | 9.5 | 7.5 | 8.5 |
| 5 | 9 | 10 | 8 | 9 |
| 6 | 9.5 | 10 | 8.5 | 9.5 |
| 7 | 9.8 | 10 | 9 | 9.8 |
| 8 | 10 | 10 | 9.2 | 9.9 |
| 9 | 10 | 10 | 9.5 | 9.9 |
| 10 | 10 | 10 | 9.8 | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Yang, S. Constructing and Testing AI International Legal Education Coupling-Enabling Model. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041524
Wang Y, Yang S. Constructing and Testing AI International Legal Education Coupling-Enabling Model. Sustainability. 2024; 16(4):1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041524
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yunyao, and Shudong Yang. 2024. "Constructing and Testing AI International Legal Education Coupling-Enabling Model" Sustainability 16, no. 4: 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041524
APA StyleWang, Y., & Yang, S. (2024). Constructing and Testing AI International Legal Education Coupling-Enabling Model. Sustainability, 16(4), 1524. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041524






