Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils in a Typical Mining and Smelting Industrial Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
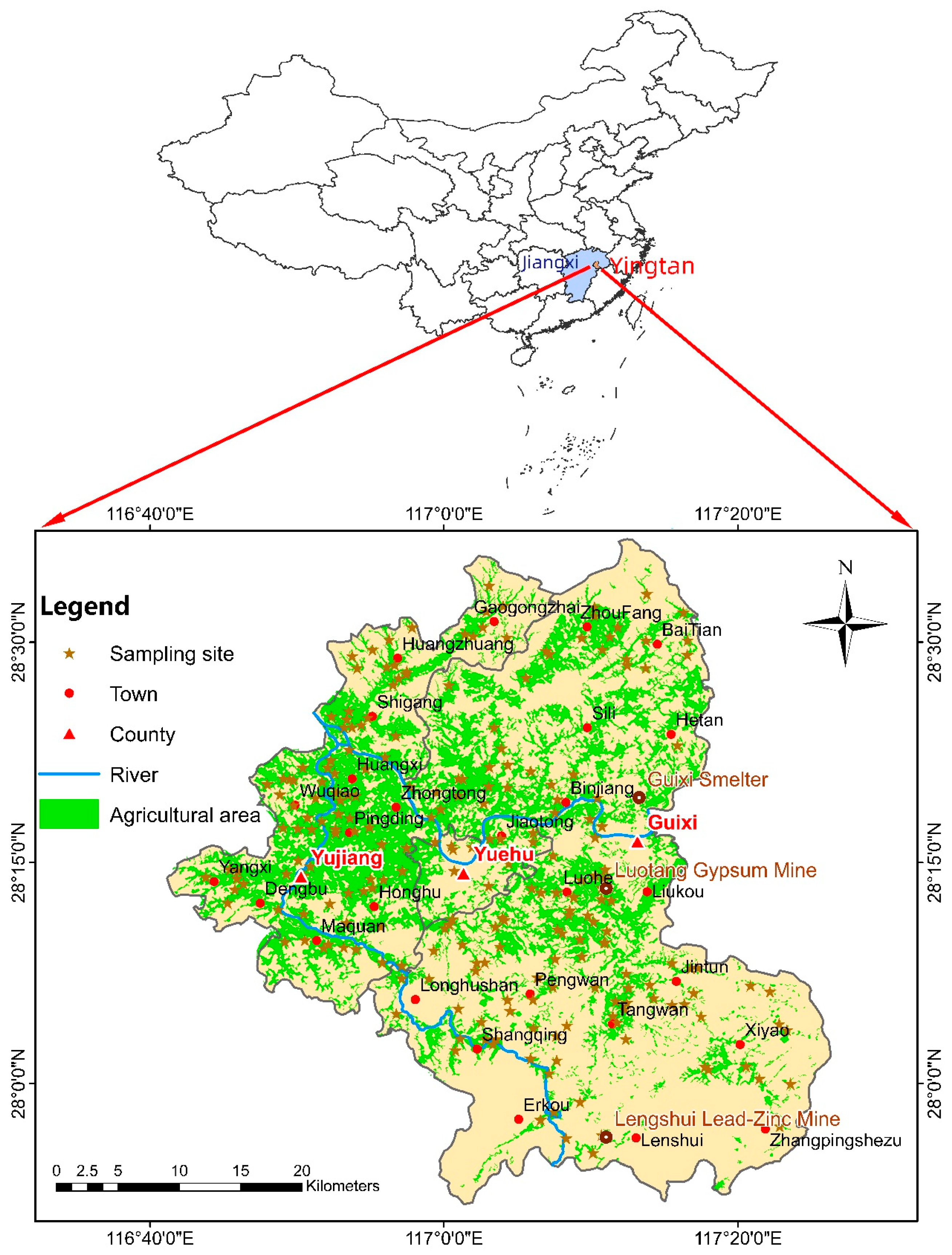
2.1. Sample Collection, Preparation, and Chemical Analysis
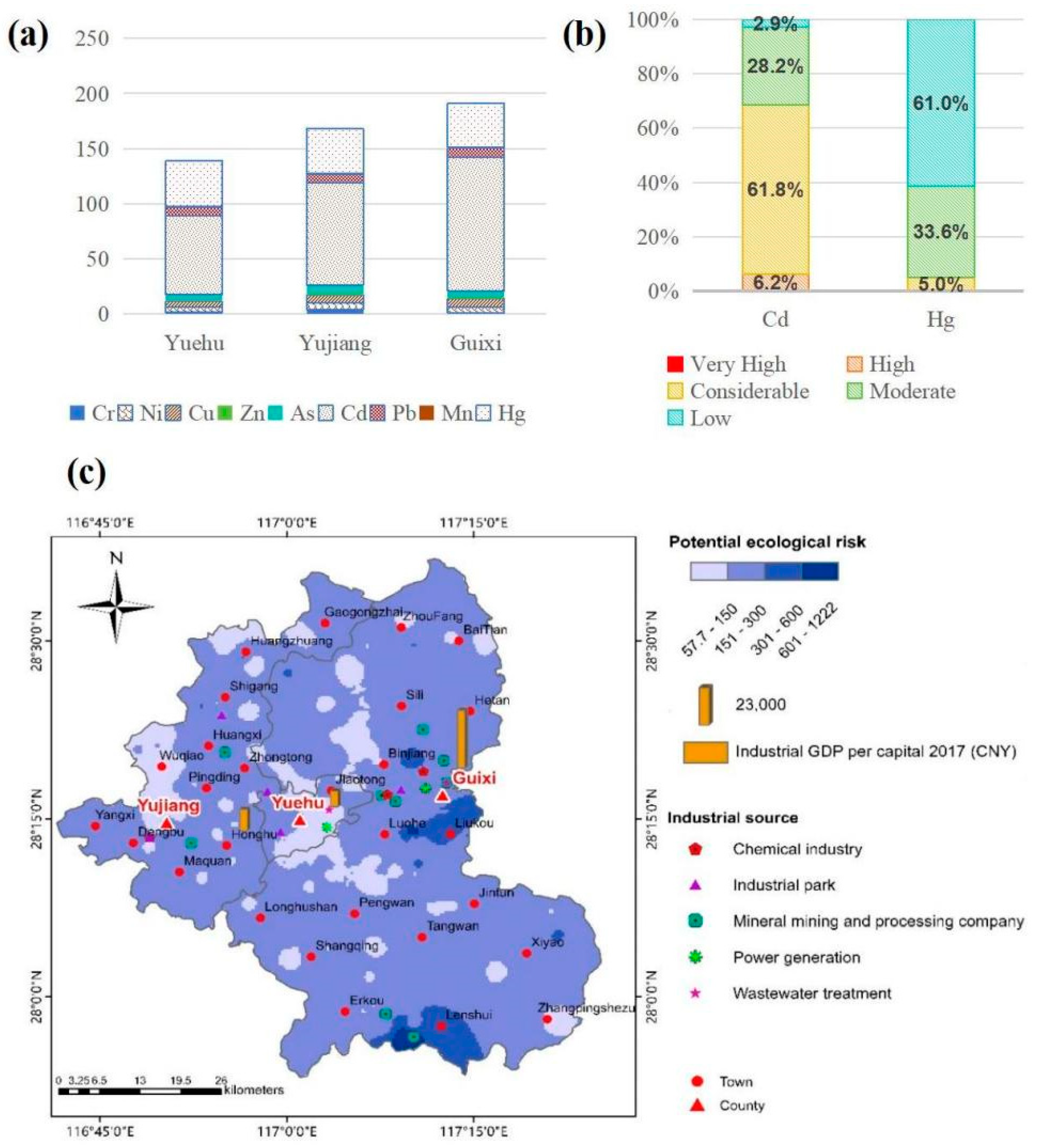
2.2. Ecological Risk Assessment
2.3. Source Identification and Apportionment
2.3.1. Multivariate Analysis Methods
2.3.2. APCS-MLR Receptor Model
2.4. Source-Specific Risk Assessment
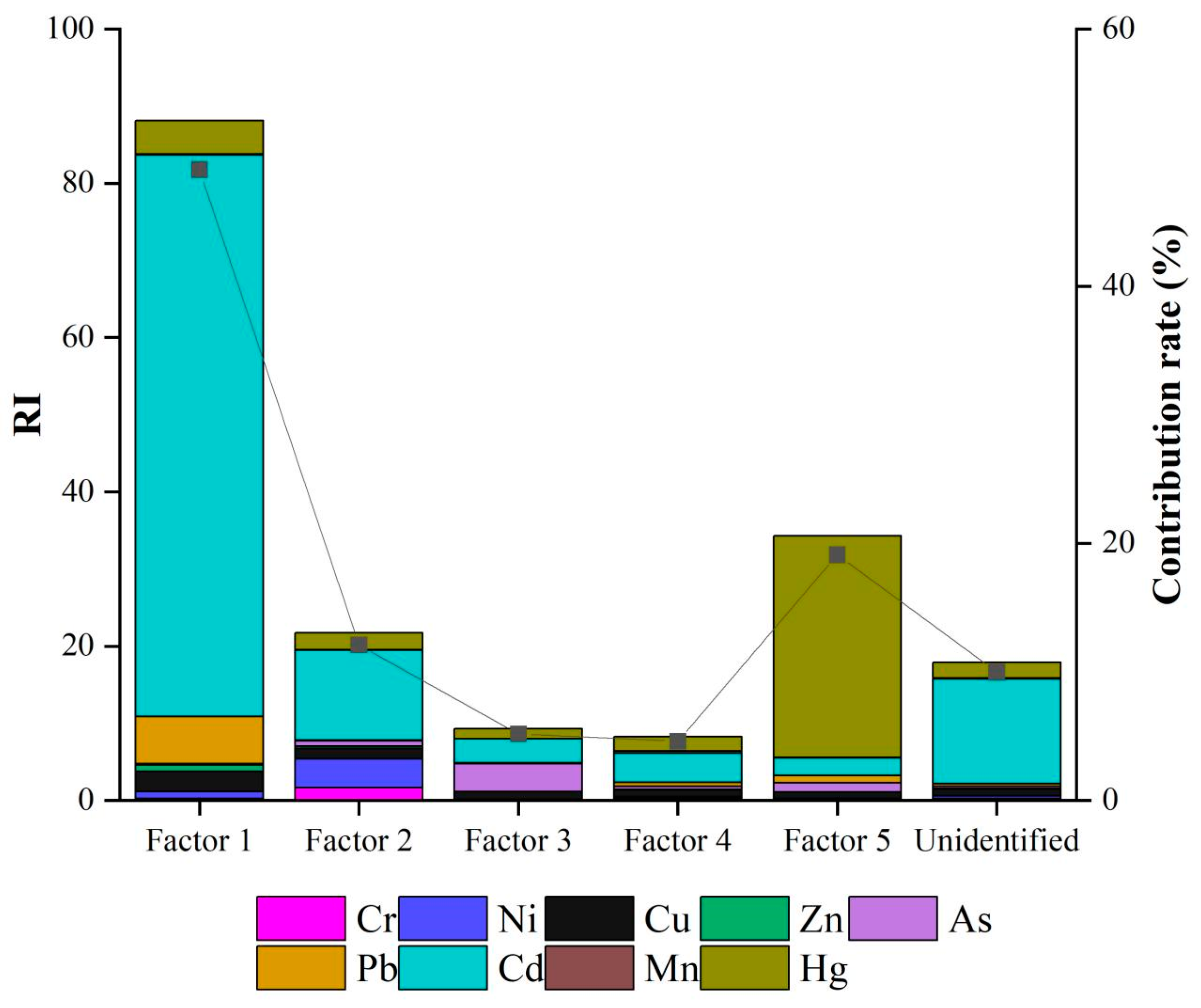
2.4.1. Ecological Risk Apportioned from Different Sources
2.4.2. Health Risk Apportioned from Different Sources
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soil
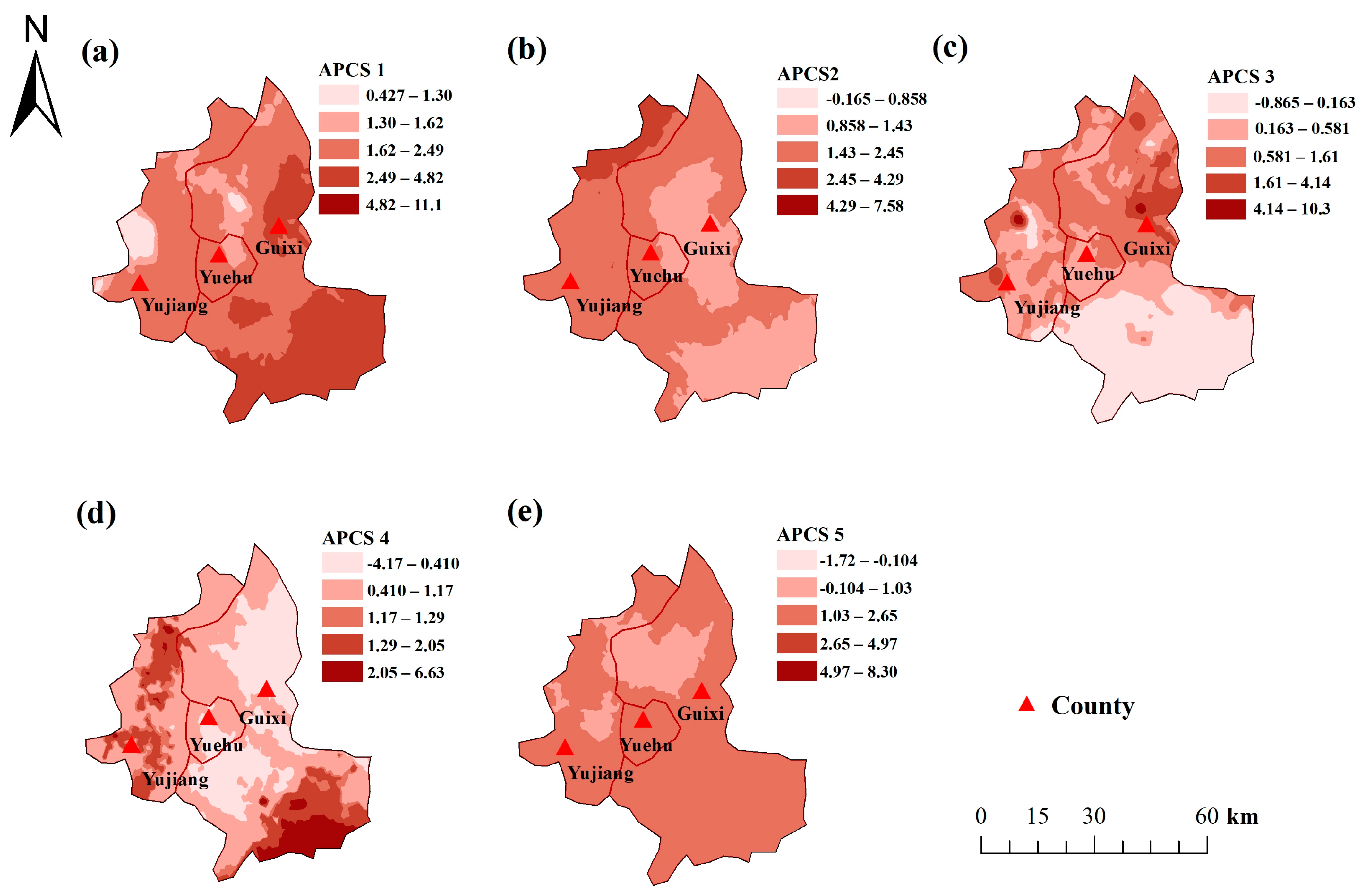
3.2. Source Identification and Apportionment
3.2.1. Source Identification and Apportionment
3.2.2. Quantitative Source Apportionment Using APCS-MLR
3.3. Source-Specific Risk Apportionment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, Y.J.; Lin, M.; Liu, Q.M.; Zhang, Z.H.; Fei, X.F.; Xiao, R.; Lv, X.N. Contamination assessment, health risk evaluation, and source identification of heavy metals in the soil-rice system of typical agricultural regions on the southeast coast of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 12870–12880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Q.; Li, Z.Y.; Lu, X.N.; Duan, Q.N.; Huang, L.; Bi, J. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from industrial and agricultural regions in China: Pollution and risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 690–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Chon, H.T. Characterization of cadmium biosorption by Exiguobacterium sp. isolated from farmland soil near Cu-Pb-Zn mine. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 11814–11822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.Y.; Wang, W.J.; Li, T.Q.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E. Current status of agricultural soil pollution by heavy metals in China: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3034–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.F.; Meng, Z.R.; Zerizghi, T.; Luo, J.; Guo, Q.J. A comprehensive method of source apportionment and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals: A case study in Qingyuan city, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.G.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y. Leaching of heavy metals from lead-zinc mine tailings and the subsequent migration and transformation characteristics in paddy soil. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Li, J.; Teng, Y.G.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, Y.Y. A partition computing-based positive matrix factorization (PC-PMF) approach for the source apportionment of agricultural soil heavy metal contents and associated health risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 388, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.P.; Cao, X.D.; Hu, Y.A.; Cheng, H.F. Pollution, Risk and Transfer of Heavy Metals in Soil and Rice: A Case Study in a Typical Industrialized Region in South China. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.H.; Wang, Y.T.; Zhang, D.G.; Lei, M. Source-specific ecological and health risks of potentially toxic elements in agricultural soils in Southern Yunnan Province and associated uncertainty analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 417, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Y.K.; Shah, M.H. Fractionation, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of selected metals in the soil of public parks of Lahore, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2023, 82, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-y.; Zhao, Y.-y.; Chen, D.-l.; Huang, H.-t.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.-j. Ecological risk assessment and early warning of heavy metal cumulation in the soils near the Luanchuan molybdenum polymetallic mine concentration area, Henan Province, central China. China Geol. 2023, 6, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.H.; Wu, H.H.; Wei, W.X.; Xu, C.B.; Tan, X.; Wen, Y.; Lin, A.J. Health risk assessment of heavy metal(loid)s in the farmland of megalopolis in China by using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor models: Taking Huairou District of Beijing as an example. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 835, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.C.; Tai, L.Y.; Qiao, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wang, Z.; Fu, K.X.; Chen, G.Y. Contamination source apportionment and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil around municipal solid waste incinerator: A case study in North China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proshad, R.; Uddin, M.; Idris, A.M.; Al, M.A. Receptor model-oriented sources and risks evaluation of metals in sediments of an industrial affected riverine system in Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, M.X.; Hu, W.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Tian, K.; Huang, B.A. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal risk in soil-crop systems along the Yangtze River in Nanjing, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Hu, K.L.; An, Y.; Chen, C.; Li, G.D. Spatial distribution and source apportionment of the heavy metals in the agricultural soil in a regional scale. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wan, Y.Y.; Wu, R.J.; Feng, D.K.; Li, K. Source identification and comprehensive apportionment of the accumulation of soil heavy metals by integrating pollution landscapes, pathways, and receptors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naccarato, A.; Tassone, A.; Cavaliere, F.; Elliani, R.; Pirrone, N.; Sprovieri, F.; Tagarelli, A.; Giglio, A. Agrochemical treatments as a source of heavy metals and rare earth elements in agricultural soils and bioaccumulation in ground beetles. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 749, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noulas, C.; Tziouvalekas, M.; Karyotis, T. Zinc in soils, water and food crops. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2018, 49, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.S.; Yan, Y.; Yu, R.L.; Hu, G.R.; Cheng, Y.F.; Huang, H.B. Source apportionment and health risks of the bioavailable and residual fractions of heavy metals in the park soils in a coastal city of China using a receptor model combined with Pb isotopes. Catena 2020, 194, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, S.; Sobiecka, E.; Contini, S.; Locoro, G.; Free, G.; Gawlik, B.M. The application of positive matrix factorization in the analysis, characterisation and detection of contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2007, 69, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.S. Multivariate receptor models and robust geostatistics to estimate source apportionment of heavy metals in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Peng, Z.H.; Zeng, J.Q.; Li, C.X.; Tang, L.; Jiang, J.; Luo, X.H.; Gao, W.Y.; Guo, J.K.; Shao, B.B.; et al. Source apportionment and quantitative risk assessment of heavy metals at an abandoned zinc smelting site based on GIS and PMF models. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.Y.; Jin, G.Q.; Khan, M.A.; Zhu, Y.W.; Duan, L.L.; Luo, W.X.; Jia, J.W.; Zhong, B.; Ma, J.W.; Ye, Z.Q.; et al. The quantitative source apportionment of heavy metals in peri-urban agricultural soils with UNMIX and input fluxes analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 21, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widiana, D.R.; You, S.J.; Yang, H.H.; Tsai, J.H.; Wang, Y.F. Source Apportionment of Air Pollution and Characteristics of Volatile Organic Compounds in a Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant, North Taiwan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 2878–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cheng, S.Q.; Li, H.F.; Fu, K.; Xu, Y. Groundwater pollution source identification and apportionment using PMF and PCA-APCA-MLR receptor models in a typical mixed land-use area in Southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.Y.; Zhao, R.; Pan, N.H.; Wang, F.F.; Yang, Y.Y.; Luo, H.P. Source apportionment of heavy metals in farmland soil of Wuwei, China: Comparison of three receptor models. J. Clean Prod. 2019, 237, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Christakos, G.; Guo, M.W.; Xiao, L.; Huang, W. Space-time quantitative source apportionment of soil heavy metal concentration increments. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- USEPA. EPA Method 3015A: Microwave Assisted Acid Digestion of Aqueous Samples and Extracts; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Hu, Y.N.; He, K.L.; Sun, Z.H.; Chen, G.; Cheng, H.F. Quantitative source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in the agricultural soils of an industrializing region and associated model uncertainty. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.F.; Yue, Q.L.; Jiang, X.X.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.L.; Li, H.B.; Gu, X.H.; Zhang, S.Q.; Liu, J.F. A reusable and sensitive biosensor for total mercury in canned fish based on fluorescence polarization. Talanta 2013, 117, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Ni, S.J.; Tuo, X.; Zhang, C.J. Calculation of heavy metals’ toxicity coefficient in the evaluation of potential ecological risk index. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 31, 112–115. [Google Scholar]
- Doabi, S.A.; Afyuni, M.; Karami, M. Multivariate statistical analysis of heavy metals contamination in atmospheric dust of Kermanshah province, western Iran, during the spring and summer 2013. J. Geochem. Explor. 2017, 180, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokalioglu, S.; Kartal, S. Multivariate analysis of the data and speciation of heavy metals in street dust samples from the Organized Industrial District in Kayseri (Turkey). Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 2797–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.M.; Du, P.X.; Cao, J.J.; Posmentier, E.S. Multivariate analysis of heavy metal contamination in urban dusts of Xi’an, Central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 355, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facchinelli, A.; Sacchi, E.; Mallen, L. Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Su, Y.; Pei, L.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, D.M.; Wang, X.X. Ecological risk evaluation and source apportionment of heavy metals in park playgrounds: A case study in Xi’an, Shaanxi Province, a northwest city of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 24400–24412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shen, Z.J.; Wang, S.L.; Deng, L.; Sun, J.; Liu, P.; She, Z.L. Source apportionment of heavy metals in soils around a coal gangue heap with the APCS-MLR and PMF receptor models in Chongqing, southwest China. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Shan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, X. Source-oriented ecological and resistome risks associated with geochemical enrichment of heavy metals in river sediments. Chemosphere 2023, 336, 139119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USEPA. Exposure Factors Handbook, 2011 ed.; U.S. Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- Xu, J.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Dong, S.H.; Chen, Z.M.; He, L. Source identification and health risk assessment of heavy metals with mineralogy: The case of soils from a Chinese industrial and mining city. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 7255–7274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China National Environmental Monitoring Center. The Background Concentrations of Soil Elements of China; China Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- GB15618-2018; Ministry of Ecology and Environment. Soil Environmental Quality. Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.; Reddi, L. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, H.C.; Li, Y.T.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, D.J.; Xu, M.; Zhang, H.; Lu, P.L. An integrated approach to identify the source apportionment of potentially toxic metals in shale gas exploitation area soil, and the associated ecological and human health risks. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, B. Contents and relationship of elements in human hair for a non-industrialised population in Poland. Sci. Total Environ. 1998, 209, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-B.; Kong, S.-F.; Wang, W.; Yan, Q. Emission Inventory of Heavy Metals in Fine Particles Emitted from Residential Coal Burning in China. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2016, 37, 2823–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Hou, D.Y.; O’Connor, D.; Shen, Z.T.; Shi, P.L.; Ok, Y.S.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Wen, Y.; Luo, M.N. Lead contamination in Chinese surface soils: Source identification, spatial-temporal distribution and associated health risks. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 1386–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.N.; Liu, X.P.; Bai, J.M.; Shih, K.M.; Zeng, E.Y.; Cheng, H.F. Assessing heavy metal pollution in the surface soils of a region that had undergone three decades of intense industrialization and urbanization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 6150–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yingtan District People’s Government. Economic Structure of Yujiang. Available online: http://www.yujiang.gov.cn/art/2014/11/15/art_3556_799374.html (accessed on 15 November 2014).
- Morrison, J.M.; Goldhaber, M.B.; Lee, L.; Holloway, J.M.; Wanty, R.B.; Wolf, R.E.; Ranville, J.F. A regional-scale study of chromium and nickel in soils of northern California, USA. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1500–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachwal, M.; Wawer, M.; Magiera, T.; Steinnes, E. Integration of soil magnetometry and geochemistry for assessment of human health risk from metallurgical slag dumps. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 26410–26423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manta, D.S.; Angelone, M.; Bellanca, A.; Neri, R.; Sprovieri, M. Heavy metals in urban soils: A case study from the city of Palermo (Sicily), Italy. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 300, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.F.; Wen, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yuan, L.M.; Liu, L.L. Source apportionment and health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in soil from mining areas in northwestern China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhang, R.Z.; Gan, Y.D.; Cai, L.Q.; Freidenreich, A.; Wang, K.P.; Guo, T.W.; Wang, H.B. Multiple methods for the identification of heavy metal sources in cropland soils from a resource-based region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 3127–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.S.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Cang, L.; Xu, B.; Ding, J. Source identification and apportionment of heavy metals in urban soil profiles. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, Q.E.; Lu, M.H.; Huang, Z.J.; Yuan, Z.B.; Jia, G.L.; Xiao, X.; Wu, Y.Q.; Zhang, Z.W.; Li, C.; Zhong, Z.M.; et al. Anthropogenic atmospheric toxic metals emission inventory and its spatial characteristics in Guangdong province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.A.; Cheng, H.F.; Tao, S.; Schnoor, J.L. China’s Ban on Phenylarsonic Feed Additives, A Major Step toward Reducing the Human and Ecosystem Health Risk from Arsenic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 12177–12187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, D.K.; Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.J.; Yuan, F.Q.; Zhu, G.H. Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. Catena 2019, 175, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtarzadeh, Z.; Keshavarzi, B.; Moore, F.; Marsan, F.A.; Padoan, E. Potentially toxic elements in the Middle East oldest oil refinery zone soils: Source apportionment, speciation, bioaccessibility and human health risk assessment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 40573–40591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.P.; Lu, W.X.; Long, Y.Q.; Bao, X.H.; Yang, Q.C. Assessment of heavy metals contamination in urban topsoil from Changchun City, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2011, 108, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Guan, Q.Y.; Shao, W.Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.R.; Li, H.C.; Sun, Y.F. A joint method to quantify source contributions of heavy metals to ecological and human health risks in oasis farmland soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 1600–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Tian, Y.Q.; Shi, H.D.; Fei, Y.; Qi, J.X.; Mo, L. Research on health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil based on multi-factor source apportionment: A case study in Guangdong Province, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.C.; Yuan, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Martín, J.D. An integrated approach for quantifying source apportionment and source-oriented health risk of heavy metals in soils near an old industrial area. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; He, M.J.; Zhi, Y.Y.; Chang, S.X.; Gu, B.J.; Liu, X.M.; Xu, J.M. An integrated analysis on source-exposure risk of heavy metals in agricultural soils near intense electronic waste recycling activities. Environ. Int. 2019, 133, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.H.; Hu, Y.N.; Cheng, H.F. Public health risk of toxic metal(loid) pollution to the population living near an abandoned small-scale polymetallic mine. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujre, N.; Mitra, S.; Soni, A.; Agnihotri, R.; Rangan, L.; Rene, E.R.; Sharma, M.P. Speciation, contamination, ecological and human health risks assessment of heavy metals in soils dumped with municipal solid wastes. Chemosphere 2021, 262, 128013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Metal | Concentration (mg/kg) | B.V. a (mg/kg) | % of Samples > B.V. | S.V. b (mg/kg) | % of Samples > S.V. | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | S.D. | Min | P5 | Q1 | Median | Q3 | P95 | Max | pH ≤ 5.5 | 5.5 < pH ≤ 6.5 | 6.5 < pH ≤ 7.5 | ||||
| Cr | 56.4 | 45.4 | 5.80 | 12.0 | 22.2 | 37.4 | 77.8 | 155 | 261 | 45.9 | 43.6 | 250 | 250 | 300 | 0.41 |
| Ni | 21 | 10.2 | 3.59 | 8.47 | 13.5 | 18.6 | 27.3 | 40.8 | 84.1 | 18.9 | 48.5 | 60 | 70 | 100 | 0.41 |
| Cu | 30.7 | 23.0 | 8.00 | 13.6 | 20.6 | 26.7 | 34.9 | 50.8 | 304 | 20.3 | 75.9 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 6.22 |
| Zn | 87.2 | 34.6 | 15.3 | 34.6 | 63.4 | 86.4 | 105 | 138 | 278 | 69.4 | 71.4 | 200 | 200 | 250 | 1.24 |
| As | 9.41 | 10.8 | 1.38 | 2.46 | 4.90 | 7.35 | 11.0 | 19.2 | 133 | 14.9 | 10.4 | 30 | 30 | 25 | 1.66 |
| Cd | 0.386 | 0.361 | 0.0725 | 0.164 | 0.260 | 0.353 | 0.430 | 0.667 | 4.04 | 0.108 | 98.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 63.9 |
| Pb | 47.3 | 20.1 | 9.20 | 21.0 | 34.5 | 44.4 | 58.2 | 77.9 | 208 | 29.1 | 85.1 | 80 | 100 | 140 | 3.22 |
| Mn | 186 | 137 | 26.3 | 50.2 | 91.1 | 152 | 238 | 412 | 1120 | 328 | 10.4 | - | - | - | - |
| Hg | 0.0850 | 0.0499 | 0.00468 | 0.0247 | 0.0547 | 0.0758 | 0.109 | 0.174 | 0.455 | 0.084 | 39 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0 |
| Metal | Cr | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | Mn | Hg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | 1 | ||||||||
| Ni | 0.558 ** | 1 | |||||||
| Cu | 0.141 * | 0.258 * | 1 | ||||||
| Zn | 0.170 * | 0.443 * | 0.502 ** | 1 | |||||
| As | 0.208 * | 0.148 * | 0.247 * | 0.131 * | 1 | ||||
| Cd | −0.0787 | 0.0623 | 0.182 * | 0.437 * | 0.113 | 1 | |||
| Pb | 0.00576 | 0.166 * | 0.167 * | 0.696 ** | 0.0963 | 0.507 ** | 1 | ||
| Mn | 0.184 * | 0.00994 | 0.0603 | 0.128 * | 0.0101 | 0.120 | 0.211 * | 1 | |
| Hg | 0.0395 | 0.152 * | 0.108 | 0.190 * | 0.147 * | 0.0552 | 0.209 * | −0.0508 | 1 |
| Metal | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC4 | PC5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cr | −0.125 | 0.842 | 0.16 | 0.24 | −0.016 |
| Ni | 0.178 | 0.868 | 0.005 | −0.136 | 0.071 |
| Cu | 0.418 | 0.256 | 0.495 | −0.383 | −0.221 |
| Zn | 0.842 | 0.349 | 0.072 | −0.111 | 0.03 |
| As | 0.013 | 0.065 | 0.924 | 0.078 | 0.147 |
| Cd | 0.747 | −0.172 | 0.108 | 0.1 | −0.04 |
| Pb | 0.846 | 0.016 | −0.053 | 0.179 | 0.201 |
| Mn | 0.171 | 0.083 | 0.037 | 0.885 | −0.126 |
| Hg | 0.108 | 0.05 | 0.099 | −0.107 | 0.939 |
| Metal | R2 | Contribution (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Factor 1 | Factor 2 | Factor 3 | Factor 4 | Factor 5 | Unknown | ||
| Cr | 0.808 | 9.63 | 66.6 | 4.24 | 9.00 | 0.863 | 9.63 |
| Ni | 0.809 | 16.6 | 68.0 | 0.136 | 4.91 | 4.38 | 5.96 |
| Cu | 0.682 | 34.3 | 17.7 | 13.3 | 11.6 | 10.9 | 12.1 |
| Zn | 0.850 | 67.2 | 22.8 | 1.66 | 3.57 | 1.58 | 3.27 |
| As | 0.886 | 2.54 | 10.8 | 57.4 | 6.26 | 18.3 | 4.63 |
| Cd | 0.612 | 75.1 | 1.13 | 1.33 | 6.66 | 11.8 | 4.02 |
| Pb | 0.791 | 67.9 | 10.9 | 2.89 | 3.54 | 2.13 | 12.7 |
| Mn | 0.836 | 18.9 | 7.67 | 1.18 | 49.1 | 8.60 | 14.5 |
| Hg | 0.916 | 10.8 | 5.40 | 3.23 | 4.49 | 71.0 | 5.10 |
| Item | Source | As | Pb | Cd | TCRing | TCRinh | TCRdermal | TCR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adult | Factor 1 | 3.45 × 10−6 | 1.57 × 10−7 | 1.01 × 10−10 | 3.55 × 10−6 | 1.24 × 10−10 | 5.46 × 10−8 | 3.60 × 10−6 |
| Factor 2 | 1.47 × 10−5 | 2.38 × 10−9 | 1.63 × 10−11 | 1.45 × 10−5 | 1.11 × 10−10 | 2.33 × 10−7 | 1.47 × 10−5 | |
| Factor 3 | 7.79 × 10−5 | 2.78 × 10−9 | 4.32 × 10−12 | 7.67 × 10−5 | 5.05 × 10−10 | 1.23 × 10−6 | 7.79 × 10−5 | |
| Factor 4 | 8.50 × 10−6 | 1.40 × 10−8 | 5.29 × 10−12 | 8.38 × 10−6 | 5.99 × 10−11 | 1.35 × 10−7 | 8.51 × 10−6 | |
| Factor 5 | 2.49 × 10−5 | 2.47 × 10−8 | 3.18 × 10−12 | 2.45 × 10−5 | 1.63 × 10−10 | 3.95 × 10−7 | 2.49 × 10−5 | |
| Unknown | 6.29 × 10−6 | 8.44 × 10−9 | 1.90 × 10−11 | 6.19 × 10−6 | 5.94 × 10−11 | 9.96 × 10−8 | 6.29 × 10−6 | |
| Total | 1.36 × 10−4 | 2.09 × 10−7 | 1.49 × 10−10 | 1.34 × 10−4 | 1.02 × 10−9 | 2.15 × 10−6 | 1.36 × 10−4 | |
| Children | Factor 1 | 1.74 × 10−5 | 7.98 × 10−7 | 1.22 × 10−10 | 1.80 × 10−5 | 1.49 × 10−10 | 1.94 × 10−7 | 1.82 × 10−5 |
| Factor 2 | 7.41 × 10−5 | 1.21 × 10−8 | 1.96 × 10−11 | 7.33 × 10−5 | 1.33 × 10−10 | 8.29 × 10−7 | 7.42 × 10−5 | |
| Factor 3 | 3.93 × 10−4 | 1.41 × 10−8 | 5.21 × 10−12 | 3.89 × 10−4 | 6.08 × 10−10 | 4.39 × 10−6 | 3.93 × 10−4 | |
| Factor 4 | 4.29 × 10−5 | 7.08 × 10−8 | 6.36 × 10−12 | 4.25 × 10−5 | 7.21 × 10−11 | 4.79 × 10−7 | 4.29 × 10−5 | |
| Factor 5 | 1.26 × 10−4 | 1.25 × 10−7 | 3.83 × 10−12 | 1.24 × 10−4 | 1.97 × 10−10 | 1.40 × 10−6 | 1.26 × 10−4 | |
| Unknown | 3.17 × 10−5 | 4.28 × 10−8 | 2.28 × 10−11 | 3.14 × 10−5 | 7.15 × 10−11 | 3.54 × 10−7 | 3.18 × 10−5 | |
| Total | 6.85 × 10−4 | 1.06 × 10−6 | 1.80 × 10−10 | 6.78 × 10−4 | 1.23 × 10−9 | 7.65 × 10−6 | 6.86 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Cao, X.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils in a Typical Mining and Smelting Industrial Area. Sustainability 2024, 16, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041673
Li W, Cao X, Hu Y, Cheng H. Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils in a Typical Mining and Smelting Industrial Area. Sustainability. 2024; 16(4):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041673
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wei, Xudong Cao, Yuanan Hu, and Hefa Cheng. 2024. "Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils in a Typical Mining and Smelting Industrial Area" Sustainability 16, no. 4: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041673
APA StyleLi, W., Cao, X., Hu, Y., & Cheng, H. (2024). Source Apportionment and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Agricultural Soils in a Typical Mining and Smelting Industrial Area. Sustainability, 16(4), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16041673








