Optimizing Biochar Application Rates to Improve Soil Properties and Crop Growth in Saline–Alkali Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Pot Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Property Measurements
2.4. Calculations
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil Properties and Nutrients
3.1.1. Effects of Biochar Application on SWC, pH, and SOC
3.1.2. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil Salt
3.1.3. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil N, P, and K
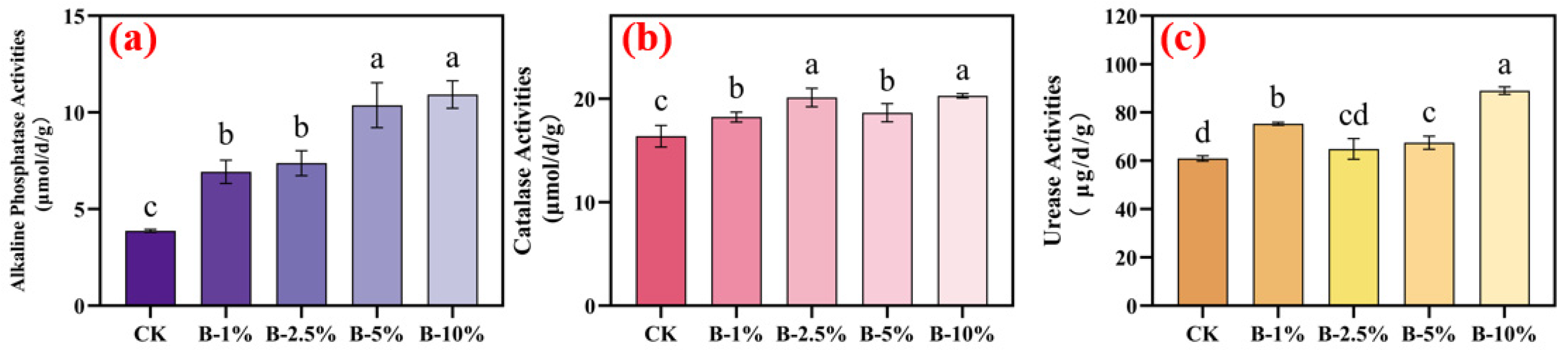
3.2. Effects of Biochar Application on Soil Enzyme Activities
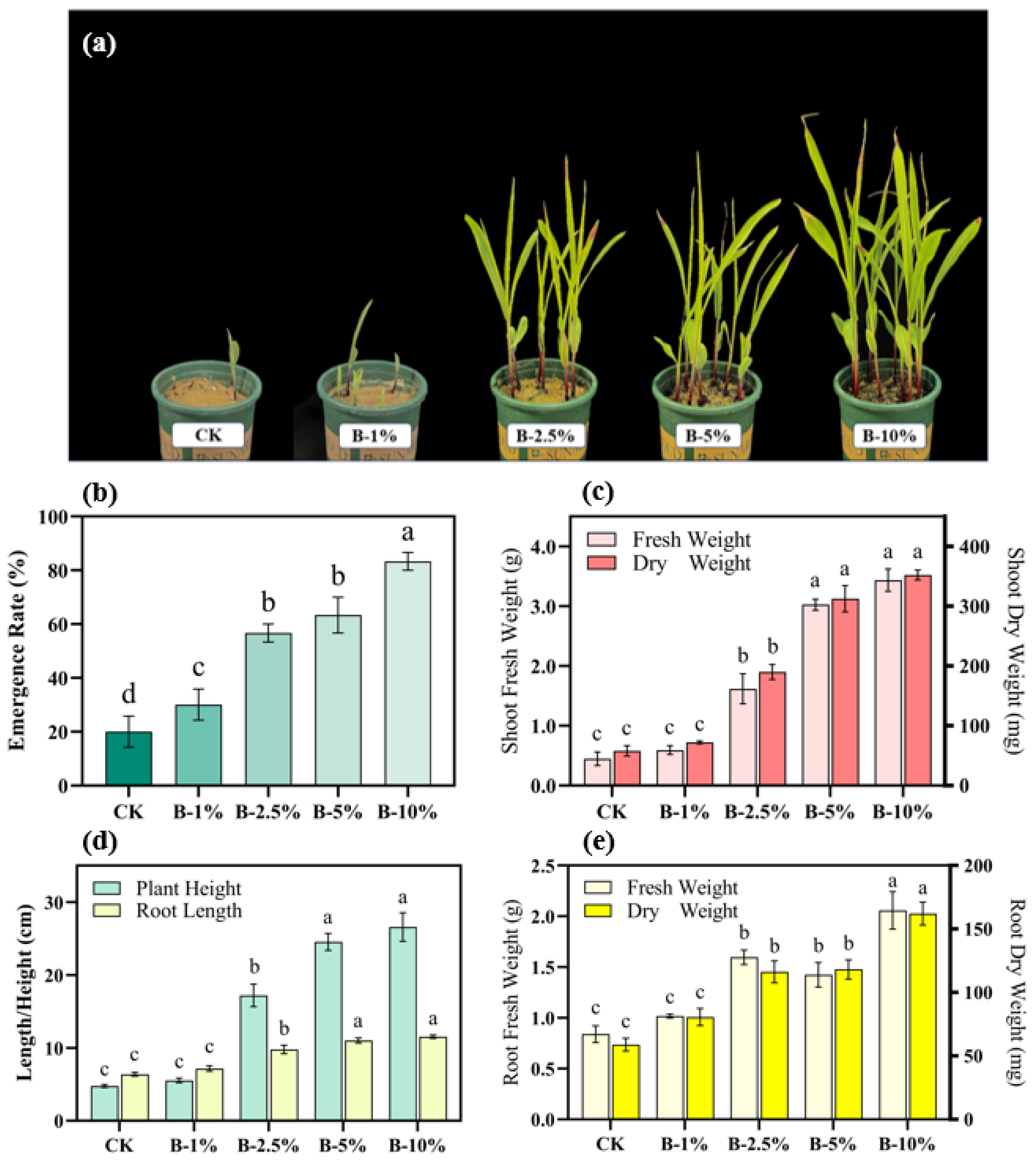
3.3. Effects of Biochar Application on Crop Growth
3.4. The Most Optimal Biochar Application Rate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abiala, M.A.; Abdelrahman, M.; Burritt, D.J.; Tran, L.S.P. Salt stress tolerance mechanisms and potential applications of legumes for sustainable reclamation of salt-degraded soils. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 3812–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, H. Current states and challenges of salt-affected soil remediation by cyanobacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 669, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.; Setia, R.; Barman, A.; Guo, Y.; Basak, N. Carbon Dynamics in Salt-affected Soils. In Research Developments in Saline Agriculture; Dagar, J.C., Yadav, R.K., Sharma, P.C., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 369–389. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, H.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, F.; Li, X.; et al. Biochar as a sustainable tool for improving the health of salt-affected soils. Soil. Environ. Health 2023, 1, 100033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yao, R.; Wang, X.; Xie, W. Research on ecological management and ecological industry development model of saline-alkali land in the Hetao Plain, China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2016, 36, 7059–7063. [Google Scholar]
- Collas, L.; Sourd, R.C.D.; Finch, T.; Green, R.; Hanley, N.; Balmford, A. The costs of delivering environmental outcomes with land sharing and land sparing. People Nat. 2023, 5, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Joseph, S. Biochar for Environmental Management: Science, Technology and Implementation, 2nd ed.; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Aborisade, M.A.; Feng, A.; Oba, B.T.; Kumar, A.; Battamo, A.Y.; Huang, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhao, L. Pyrolytic synthesis and performance efficacy comparison of biochar-supported nanoscale zero-valent iron on soil polluted with toxic metals. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2023, 69, 2249–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanutel, M.; Garré, S.; Sanglier, P.; Bielders, C. Biochar modifies soil physical properties mostly through changes in soil structure rather than through its internal porosity. Vadose Zone J. 2024, 23, e20301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aborisade, M.A.; Oba, B.T.; Kumar, A.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Okimiji, O.P.; Zhao, L. Remediation of metal toxicity and alleviation of toxic metals-induced oxidative stress in Brassica chinensis L using biochar-iron nanocomposites. Plant Soil. 2023, 493, 629–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Ding, Z.L.; Ali, E.F.; Kheir, A.M.S.; Eissa, M.A.; Ibrahim, O.H.M. Biochar and compost enhance soil quality and growth of roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L.) under saline conditions. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Zheng, H.; Yin, S.; Zhang, X.; You, X.; Wu, H.; Suo, F.; Han, K.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; et al. Comparative study of pyrochar and hydrochar on peanut seedling growth in a coastal salt-affected soil of Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, M.S.; Ye, Y.X.; Ji, H.S.; Li, L.Q.; Kibue, G.W.; Lu, H.F.; Zheng, J.F.; Pan, G.X. Biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution alleviated salt stress and improved leaf bioactivity of maize in a saline soil from central China: A 2-year field experiment. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Yuan, G.; Feng, L.; Bi, D.; Wei, J. Soil properties and the growth of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and maize (Zea mays L.) in response to reed (phragmites communis) biochar use in a salt-affected soil in the Yellow River Delta. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 303, 107124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qu, J.; Li, H.; La, S.; Tian, Y.; Gao, L. Biochar addition combined with daily fertigation improves overall soil quality and enhances water-fertilizer productivity of cucumber in alkaline soils of a semi-arid region. Geoderma 2020, 363, 114170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Liu, G.; Xia, Y.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Wang, Z. Use of biochar-compost to improve properties and productivity of the degraded coastal soil in the Yellow River Delta, China. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 780–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, P.; Ren, J. Biochar and organic fertilizer changed the ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea community structure of saline–alkali soil in the North China Plain. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; He, G.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Kong, Y.; Zhou, G.; Hu, R. Biochar amendment ameliorates soil properties and promotes Miscanthus growth in a coastal saline-alkali soil. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2020, 155, 103674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Crohn, D.M.; Šimůnek, J. Leaching and reclamation of a biochar and compost amended saline–sodic soil with moderate SAR reclaimed water. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 158, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, S.; Sun, H.; Lü, F.; He, P. Three-year rice grain yield responses to coastal mudflat soil properties amended with straw biochar. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 239, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saifullah; Dahlawi, S.; Naeem, A.; Rengel, Z.; Naidu, R. Biochar application for the remediation of salt-affected soils: Challenges and opportunities. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 625, 320–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Zhu, L.-x.; Shen, Y.-f.; Li, S.-q. Sensitivity of soil water retention and availability to biochar addition in rainfed semi-arid farmland during a three-year field experiment. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Cui, L.; Lin, Q.; Li, G.; Zhao, X. Efficiency of sewage sludge biochar in improving urban soil properties and promoting grass growth. Chemosphere 2017, 173, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yang, R.; Li, W.; Pan, Y.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, Z. Effect of biochar amendment on water infiltration in a coastal saline soil. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 3271–3279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebrun, M.; Miard, F.; Nandillon, R.; Hattab-Hambli, N.; Scippa, G.S.; Bourgerie, S.; Morabito, D. Eco-restoration of a mine technosol according to biochar particle size and dose application: Study of soil physico-chemical properties and phytostabilization capacities of Salix viminalis. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2188–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vochozka, M.; Maroušková, A.; Váchal, J.; Straková, J. Biochar pricing hampers biochar farming. Clean. Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Resources Conservation Service; Agriculture Department. Keys to Soil Taxonomy; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Luo, R.; Zhang, B.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Yu, X. Climate change impacts on corn production as evidenced by a model and historical yields in Inner Mongolia, China. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 976–983. [Google Scholar]
- Bhaduri, D.; Saha, A.; Desai, D.; Meena, H.N. Restoration of carbon and microbial activity in salt-induced soil by application of peanut shell biochar during short-term incubation study. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; De Souza, M.F.; Wang, X.; Ok, Y.S.; Meers, E. Influence of biochar addition and plant management (cutting and time) on ryegrass growth and migration of As and Pb during phytostabilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zeng, G.; Chen, Y.; Yu, M.; Yu, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, Y.; Huang, H. Effects of physico-chemical parameters on the bacterial and fungal communities during agricultural waste composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 2950–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Analytical Methods of Soil Agrochemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 1999; pp. 85–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kalembasa, S.J.; Jenkinson, D.S. A comparative study of titrimetric and gravimetric methods for the determination of organic carbon in soil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1973, 24, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; Sposito, G.; Smith, C.J.; Oster, J.D. Reassessing irrigation water quality guidelines for sodicity hazard. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 255, 107054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.W.; Adams, A.F.R. Studies on soil organic matter: I. Influence of phosphorus content of parent materials on accumulations of carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, and organic phosphorus in grassland soils. Soil. Sci. 1958, 85, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Sarkar, B.; Shaheen, S.M.; Gielen, G.; Bolan, N.; Guo, J.; Che, L.; Sun, H.; et al. Animal carcass- and wood-derived biochars improved nutrient bioavailability, enzyme activity, and plant growth in metal-phthalic acid ester co-contaminated soils: A trial for reclamation and improvement of degraded soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 261, 110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Opoku-Kwanowaa, Y.; Li, J.; Wu, J. Application of Organic Wastes to Primary Saline-alkali Soil in Northeast China: Effects on Soil Available Nutrients and Salt Ions. Commun. Soil. Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 1238–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; He, F.; Shao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, G. Effects of biochar application on Suaeda salsa growth and saline soil properties. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Shao, P. Biochar and effective microorganisms promote Sesbania cannabina growth and soil quality in the coastal saline-alkali soil of the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Wabel, M.I.; Hussain, Q.; Usman, A.R.A.; Ahmad, M.; Abduljabbar, A.; Sallam, A.S.; Ok, Y.S. Impact of biochar properties on soil conditions and agricultural sustainability: A review. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2124–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tittonell, P.; Rufino, M.C.; Janssen, B.H.; Giller, K.E. Carbon and nutrient losses during manure storage under traditional and improved practices in smallholder crop-livestock systems-evidence from Kenya. Plant Soil. 2010, 328, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhiya, A.K.; Anand, A.; Kaushal, P. Production, activation, and applications of biochar in recent times. Biochar 2020, 2, 253–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Ran, Q.; Li, F.; Shaheen, S.M.; Wang, H.; Rinklebe, J.; Liu, C.; Fang, L. Carbon-based strategy enables sustainable remediation of paddy soils in harmony with carbon neutrality. Carbon. Research 2022, 1, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, K.-R.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S.; Owens, G.; Nehls, T.; Wessolek, G.; Kim, K.-H. Effect of biochar on reclaimed tidal land soil properties and maize (Zea mays L.) response. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Yang, R.; Zhu, J.; Pan, Y.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Z. Can the increase of irrigation frequency improve the rate of water and salt migration in biochar-amended saline soil? J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 4021–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Guo, W.N.; Lin, Q.M.; Li, G.T.; Zhao, X.R. Improving salt leaching in a simulated saline soil column by three biochars derived from rice straw (Oryza sativa L.), sunflower straw (Helianthus annuus), and cow manure. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2016, 71, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raison, R.J. Modification of the soil environment by vegetation fires, with particular reference to nitrogen transformations - review. Plant Soil. 1979, 51, 73–108. [Google Scholar]
- Abebe, N.; Endalkachew, K.; Mastawesha, M.; Gebremedhin, A. Effect of Biochar Application on Soil Properties and Nutrient Uptake of Lettuces (Lactuca sativa) Grown in Chromium Polluted Soils. Am. Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2011, 12, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoud, E.; El-Beshbeshy, T.; El-Kader, N.A.; El Shal, R.; Khalafallah, N. Impacts of biochar application on soil fertility, plant nutrients uptake and maize (Zea mays L.) yield in saline sodic soil. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Bing, X.; Jiao, L.; Xiao, H.; Li, B.; Sun, H. Amelioration effects of coastal saline-alkali soil by ball-milled red phosphorus-loaded biochar. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Liu, G.; Zhou, B.; Chen, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Li, Z. Effects of modified biochar on water and salt distribution and water-stable macro-aggregates in saline-alkaline soil. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, K.D. Use of biochar for alleviating negative impact of salinity stress in corn grown in arid soil. Can. J. Soil. Sci. 2022, 102, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, G.; Shao, H.B. Furfural and its biochar improve the general properties of a saline soil. Solid. Earth 2014, 5, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhdar, A.; Rabhi, M.; Ghnaya, T.; Montemurro, F.; Jedidi, N.; Abdelly, C. Effectiveness of compost use in salt-affected soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 171, 29–37. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, V.N.L.; Greene, R.S.B.; Dalal, R.C.; Murphy, B.W. Soil carbon dynamics in saline and sodic soils: A review. Soil. Use Manag. 2010, 26, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Zhang, W.; Gulaqa, A.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Weng, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, Q.; Jin, F. Effects of Peanut Shell Biochar on Soil Nutrients, Soil Enzyme Activity, and Rice Yield in Heavily Saline-Sodic Paddy Field. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; da Silva, J.P.; Steiner, C.; Nehls, T.; Zech, W.; Glaser, B. Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: Fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil. 2003, 249, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Long, A.; Fossum, B.; Kaiser, M. Effects of pyrolysis temperature and feedstock type on biochar characteristics pertinent to soil carbon and soil health: A meta-analysis. Soil. Use Manag. 2023, 39, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashari, M.S.; Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Pan, W.; Fu, J.; Pan, G.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X. Effects of amendment of biochar-manure compost in conjunction with pyroligneous solution on soil quality and wheat yield of a salt-stressed cropland from Central China Great Plain. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Meng, J.; Jiang, L.; Yang, X.; Lan, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, W. Rice husk biochar impacts soil phosphorous availability, phosphatase activities and bacterial community characteristics in three different soil types. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2017, 116, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, K.; Chen, X.; Ge, T.; Zhu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Su, Y. Effects of long-term fertilization on phoD-harboring bacterial community in Karst soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Sui, Y.; Wen, X. Effects of Biochar on Soil Moisture, Organic Carbon and Available Nutrient Contents in Manural Loessial Soils. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2013, 32, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Liu, Y.; Yan, J.; Hina, K.; Hussain, Q.; Qiu, T.; Zhu, J. Revitalizing coastal saline-alkali soil with biochar application for improved crop growth. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 179, 106594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premalatha, R.P.; Malarvizhi, P.; Parameswari, E. Effect of biochar doses under various levels of salt stress on soil nutrient availability, soil enzyme activities and plant growth in a marigold crop. Crop Pasture Sci. 2023, 74, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masto, R.E.; Kumar, S.; Rout, T.K.; Sarkar, P.; George, J.; Ram, L.C. Biochar from water hyacinth (Eichornia crassipes) and its impact on soil biological activity. CATENA 2013, 111, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Chen, C.; Marschner, P. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Liu, J.; McGrouther, K.; Huang, H.; Lu, K.; Guo, X.; He, L.; Lin, X.; Che, L.; Ye, Z.; et al. Effect of biochar on the extractability of heavy metals (Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn) and enzyme activity in soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demisie, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M. Effect of biochar on carbon fractions and enzyme activity of red soil. CATENA 2014, 121, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Camps-Arbestain, M.; Shen, Q.; Lehmann, J.; Singh, B.; Sabir, M. Biochar effects on crop yields with and without fertilizer: A meta-analysis of field studies using separate controls. Soil. Use Manag. 2020, 36, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Wong, J.T.F.; Hashimoto, Y.; Huang, L.; Rinklebe, J.; Chang, S.X.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S. Response of microbial communities to biochar-amended soils: A critical review. Biochar 2019, 1, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xiong, X.; Wang, L.; Hou, D.; Bolan, N.S.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Tsang, D.C.W. A critical review on performance indicators for evaluating soil biota and soil health of biochar-amended soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 414, 125378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, P.; Ma, Z.; Chang, S.X. Biochar increases soil microbial biomass with changes in extra- and intracellular enzyme activities: A global meta-analysis. Biochar 2020, 2, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.; Lee, S.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Farooq, M.; Song, H.; Sarmah, A.K.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Ahmad, M.; Shaheen, S.M.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar application to low fertility soils: A review of current status, and future prospects. Geoderma 2019, 337, 536–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimetu, J.M.; Lehmann, J. Stability and stabilisation of biochar and green manure in soil with different organic carbon contents. Aust. J. Soil. Res. 2010, 48, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducey, T.F.; Ippolito, J.A.; Cantrell, K.B.; Novak, J.M.; Lentz, R.D. Addition of activated switchgrass biochar to an aridic subsoil increases microbial nitrogen cycling gene abundances. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2013, 65, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Luo, X.; Xing, B. Enhanced growth of halophyte plants in biochar-amended coastal soil: Roles of nutrient availability and rhizosphere microbial modulation. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 41, 517–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhou, Q.; Tian, Z.; Cui, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. Apply biochar to ameliorate soda saline-alkali land, improve soil function and increase corn nutrient availability in the Songnen Plain. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiong, Y.; Qu, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, Q.; Huang, G. Impact of biochar addition on soil properties and water-fertilizer productivity of tomato in semi-arid region of Inner Mongolia, China. Geoderma 2018, 331, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Li, Y.; Si, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Bai, Y.; et al. Optimizing biochar application to improve soil physical and hydraulic properties in saline-alkali soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.; Ranjbar, F. Effects of sodic water on soil sodicity and nutrient leaching in poultry and sheep manure amended soils. Geoderma 2009, 153, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clare, A.; Shackley, S.; Joseph, S.; Hammond, J.; Pan, G.; Bloom, A. Competing uses for China’s straw: The economic and carbon abatement potential of biochar. GCB Bioenergy 2015, 7, 1272–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, N.R.; Mulder, J.; Hale, S.E.; Zimmerman, A.R.; Pandit, B.H.; Cornelissen, G. Multi-year double cropping biochar field trials in Nepal: Finding the optimal biochar dose through agronomic trials and cost-benefit analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 637–638, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Properties | Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar | Soil | |
| pH | 8.92 | 8.78 |
| C (%) | 52.52 | - |
| H (%) | 1.31 | - |
| O (%) | 7.49 | - |
| N (%) | 1.23 | - |
| C/N | 42.70 | - |
| Brunauer–Emmett–Teller (BET) Surface area (m2/g) | 96.44 | - |
| Salt content (g/kg) | - | 10.44 |
| EC (mS/cm) | - | 3.88 |
| SAR | - | 4.90 |
| Organic carbon (g/kg) | 401.58 | 5.47 |
| Total N (g/kg) | 8.73 | 0.60 |
| Total P (g/kg) | 2.37 | 0.66 |
| Total K (g/kg) | 29.06 | 10.07 |
| Available N (mg/kg) | 48.92 | 203.27 |
| Available P (mg/kg) | 239.13 | 94.25 |
| Available K (mg/kg) | 19,363.85 | 194.20 |
| Treatments | Soil Salt Ions (g/kg) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ | K+ | SO42− | Cl− | HCO3− | CO32− | |
| CK | 3.02 ± 0.20 a 1 | 0.21 ± 0.01 ab | 0.31 ± 0.01 a | 0.10 ± 0.01 e | 3.21 ± 0.04 a | 2.37 ± 0.02 ab | 0.21 ± 0.02 a | 0.01 a |
| B-1% | 2.95 ± 0.07 a | 0.20 ± 0.01 ab | 0.30 ± 0.01 a | 0.24 ± 0.00 d | 3.08 ± 0.09 a | 2.33 ± 0.09 b | 0.21 ± 0.01 a | 0.00 a |
| B-2.5% | 2.06 ± 0.27 b | 0.16 ± 0.02 b | 0.21 ± 0.03 b | 0.39 ± 0.04 c | 2.33 ± 0.14 c | 1.70 ± 0.12 c | 0.21 ± 0.02 a | 0.00 a |
| B-5% | 2.36 ± 0.07 b | 0.22 ± 0.03 a | 0.25 ± 0.02 b | 0.80 ± 0.04 b | 2.78 ± 0.21 b | 2.34 ± 0.11 ab | 0.24 ± 0.01 a | 0.00 a |
| B-10% | 2.06 ± 0.09 b | 0.25 ± 0.00 a | 0.25 ± 0.01 b | 1.31 ± 0.03 a | 3.26 ± 0.10 a | 2.57 ± 0.20 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 a | 0.00 a |
| Variable Y | Minimum Value of Response Variable (m + n) | Optimal Biochar Application Rate (μ, %) | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Salt content (Y1, g/kg) | 7.91 | 3.19 | 0.97 |
| EC (Y2, mS/cm) | 2.55 | 3.16 | 0.98 |
| Cl− content (Y3, g/kg) | 1.61 | 2.92 | 0.97 |
| SO42− content (Y4, g/kg) | 2.04 | 3.37 | 0.99 |
| Average value | - | 3.16 | 0.98 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Xu, H.; Shen, G.; Chen, Q. Optimizing Biochar Application Rates to Improve Soil Properties and Crop Growth in Saline–Alkali Soil. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062523
Chen X, Liu L, Yang Q, Xu H, Shen G, Chen Q. Optimizing Biochar Application Rates to Improve Soil Properties and Crop Growth in Saline–Alkali Soil. Sustainability. 2024; 16(6):2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062523
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xin, Li Liu, Qinyan Yang, Huanan Xu, Guoqing Shen, and Qincheng Chen. 2024. "Optimizing Biochar Application Rates to Improve Soil Properties and Crop Growth in Saline–Alkali Soil" Sustainability 16, no. 6: 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062523
APA StyleChen, X., Liu, L., Yang, Q., Xu, H., Shen, G., & Chen, Q. (2024). Optimizing Biochar Application Rates to Improve Soil Properties and Crop Growth in Saline–Alkali Soil. Sustainability, 16(6), 2523. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16062523






