Drainage Practice of Rice Paddies as a Sustainable Agronomic Management for Mitigating the Emission of Two Carbon-Based Greenhouse Gases (CO2 and CH4): Field Pilot Study in South Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Settings
2.1.1. Rice Pot Design
2.1.2. Soil Characterization
2.1.3. Farming Method
2.2. Measurement and Data Collection
2.2.1. Greenhouse Gas Emission
2.2.2. Chemical Analysis of Paddy Water and Paddy Soil
2.2.3. Rice Grain and Biomass
2.3. Data Analysis
2.3.1. GWP, Cumulative GHGs Emissions, and GHGI Estimates
2.3.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Characteristics
3.2. Weather Conditions of Experimental Site
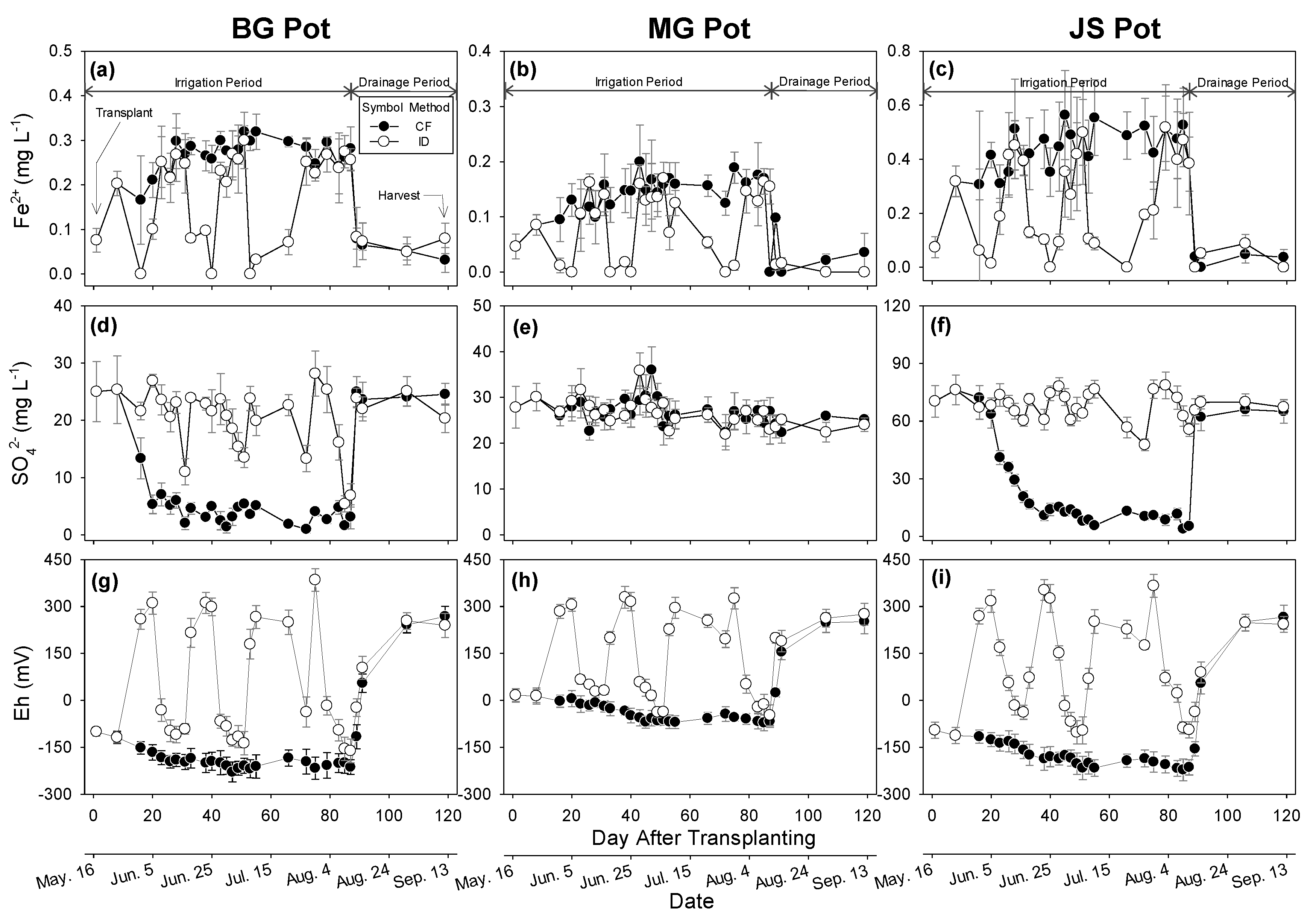
3.3. Impact of Irrigation Methods on Paddy Water
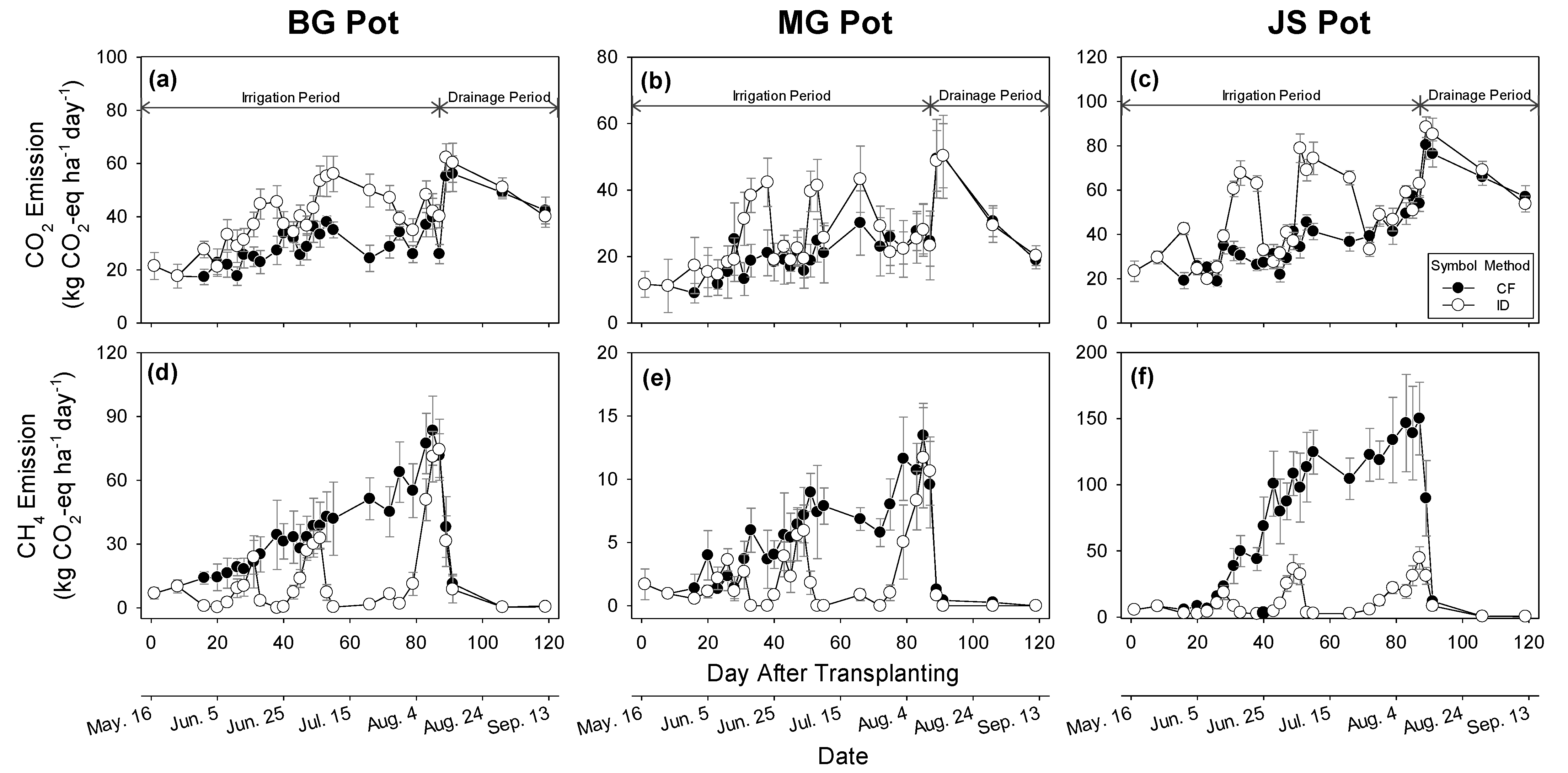
3.4. Impact of Irrigation Methods on GHGs Emission
3.4.1. Carbon Dioxide Emissions
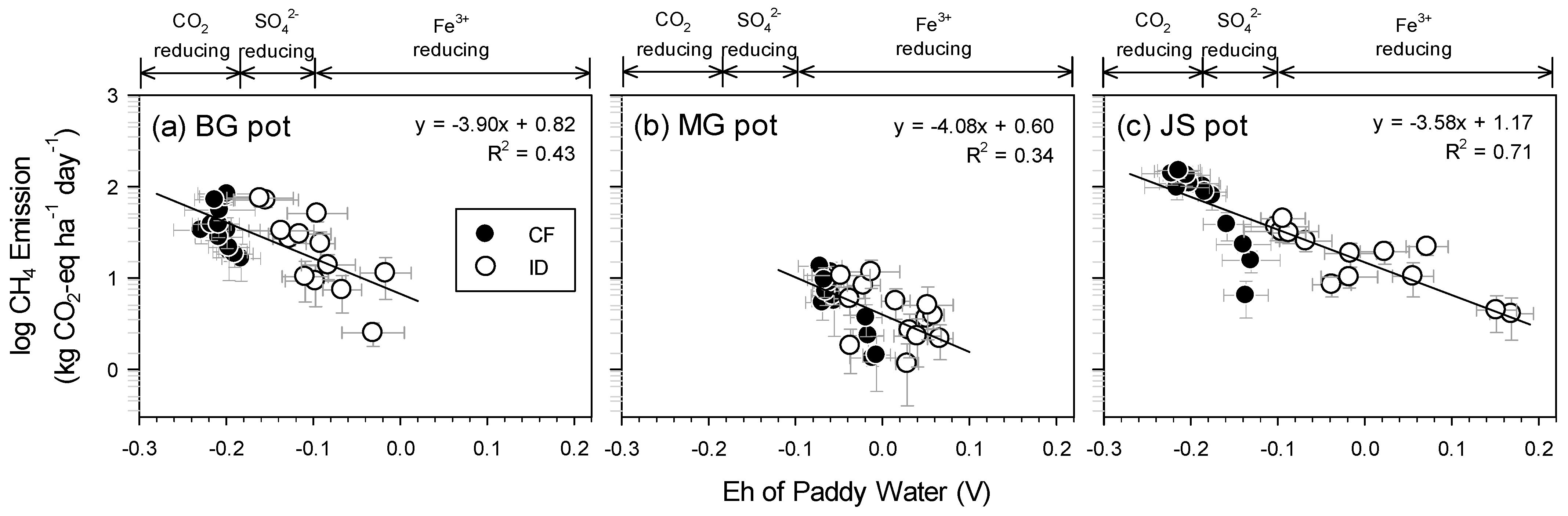
3.4.2. Methane Emissions
3.5. Rice Yield
3.6. Efficiency of Intermittent Drainage on GHGs Reduction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change). Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- KOSIS (Korean Statistical Information Service). Census of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries. Daejeon, Korea. Available online: http://kostat.go.kr/ansk/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- GIR (Greenhouse Gas Inventory Report). National Greenhouse Gas Inventory Report of Korea. Seoul, Korea. Available online: https://www.gir.go.kr/home/index.do?menuId=20 (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Fageria, N.K.; Carvalho, G.D.; Santos, A.B.; Ferreira, E.P.B.; Knupp, A.M. Chemistry of lowland rice soils and nutrient availability. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 1913–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Mer, J.; Roger, P. Production, oxidation, emission and consumption of methane by soils: A review. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2001, 37, 25–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.M.; Kim, G.W.; Kim, P.J.; Kim, S.Y. Comparison of net global warming potential between continuous flooding and midseason drainage in monsoon region paddy during rice cropping. Field Crops Res. 2016, 193, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Pan, G. Effect of mid-season drainage on CH4 and N2O emission and grain yield in rice ecosystem: A meta-nalysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; McDaniel, M.D.; Sun, L.; Su, W.; Fan, X.; Liu, S.; Xiao, X. Water-saving irrigation is a ‘win-win’ management strategy in rice paddies–With both reduced greenhouse gas emissions and enhanced water use efficiency. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Ge, J.; Tian, S.; Li, S.; Nguy-Robertson, A.L.; Zhan, M.; Cao, C. Effects of water-saving irrigation practices and drought resistant rice variety on greenhouse gas emissions from a no-till paddy in the central lowlands of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kögel-Knabner, I.; Amelung, W.; Cao, Z.H.; Fiedler, S.; Frenzel, P.; Jahn, R.; Kalbitz, K.; Kölbl, A.; Schloter, M. Biogeochemistry of paddy soils. Geoderma 2010, 157, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manono, B.O. Carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and methane emissions from the Waimate District (New Zealand) pasture soils as influenced by irrigation, effluent dispersal and earthworms. Cogent Environ. Sci. 2016, 2, 1256564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achtnich, C.; Bak, F.; Conrad, R. Competition for electron donors among nitrate reducers, ferric iron reducers, sulfate reducers, and methanogens in anoxic paddy soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1995, 19, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Kang, Y.G.; Sohn, K.M.; Kim, P.J.; Galgo, S.J.C. Creating new value of blast furnace slag as soil amendment to mitigate methane emission and improve rice cropping environments. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Romani, M.; Wang, J.; Planer-Friedrich, B.; Pausch, J.; Dorodnikov, M. Alternating Wet–Dry Cycles Rather than Sulfate Fertilization Control Pathways of Methanogenesis and Methane Turnover in Rice Straw-Amended Paddy Soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12075–12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soils; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Benard, P.; Kroener, E.; Vontobel, P.; Kaestner, A.; Carminati, A. Water percolation through the root-soil interface. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 95, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, K.; Minami, K.; Ogawa, Y. Effects of water percolation on methane emission from rice paddies: A lysimeter experiment. Plant Soil 1998, 198, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosier, A.R.; Halvorson, A.D.; Reule, C.A.; Liu, X.J. Net global warming potential and greenhouse gas intensity in irrigated cropping systems in northeastern Colorado. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1584–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.; Kim, C.; Cho, K.; Hyun, S. Characteristics of greenhouse gas emissions from rice paddy fields in South Korea under climate change scenario RCP-8.5 using the DNDC model. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute, A. Methods of Soil Analysis: Physical and Mineralogical Methods, Part 1; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Sparks, D.L. Methods of Soil Analysis: Chemical Methods, Part 3; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Degen, T.; Sadki, M.; Bron, E.; König, U.; Nénert, G. The highscore suite. Powder Diffr. 2014, 29 (Suppl. S2), S13–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkin, T.B.; Venterea, R.T. Chapter 3. Chamber-based trace gas flux measurements. In GRACEnet Sampling Protocols; Follett, R.F., Ed.; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Beltsville, MD, USA, 2010; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, W.; Park, M.; Cho, K.; Kim, J.-G.; Hyun, S. Mitigation of CO2 and N2O Emission from Cabbage Fields in Korea by Optimizing Tillage Depth and N-Fertilizer Level: DNDC Model Simulation under RCP 8.5 Scenario. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckman, K.; Lawrence, C.R.; Harden, J.W. A sequential selective dissolution method to quantify storage and stability of organic carbon associated with Al and Fe hydroxide phases. Geoderma 2018, 312, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, W.L. Chemical Equilibria in Soils; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Azadi, A.; Baghernejad, M.; Gholami, A.; Shakeri, S. Forms and distribution pattern of soil Fe (Iron) and Mn (Manganese) oxides due to long-term rice cultivation in fast Province Southern Iran. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2021, 52, 1894–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeppli, M.; Kaegi, R.; Kretzschmar, R.; Voegelin, A.; Hofstetter, T.B.; Sander, M. Electrochemical analysis of changes in iron oxide reducibility during abiotic ferrihydrite transformation into goethite and magnetite. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 3568–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Ashenberg, D. The aqueous geochemistry of the Berkeley pit, Butte, Montana, USA. Appl. Geochem. 1989, 4, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girkin, N.T.; Turner, B.L.; Ostle, N.; Craigon, J.; Sjögersten, S. Root exudate analogues accelerate CO2 and CH4 production in tropical peat. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 117, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Qu, Y. Effects of irrigation regime and nitrogen fertilizer management on CH4, N2O and CO2 emissions from saline–alkaline paddy fields in Northeast China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, T.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, P.; Li, T.; Dai, C. The inhibitory effect of a water-saving irrigation regime on CH4 emission in Mollisols under straw incorporation for 5 consecutive years. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 278, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; He, Y.; Qi, Z.; Jiang, Q. Drainage in paddy systems maintains rice yield and reduces total greenhouse gas emissions on the global scale. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 370, 133515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinengo, S.; Schiavon, M.; Santoro, V.; Said-Pullicino, D.; Romani, M.; Miniotti, E.F.; Miniotti, F.; Celi, L.; Martin, M. Assessing phosphorus availability in paddy soils: The importance of integrating soil tests and plant responses. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, D.L. Environmental Soil Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sapkota, A.; Haghverdi, A.; Avila, C.C.E.; Ying, S.C. Irrigation and greenhouse gas emissions: A review of field-based studies. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Properties | Soils a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| BG | MG | JS | |
| Order/Subgroup b | Ultisols/Typic Fragiudults | Inceptisols/Anthraquic Eutrudepts | Alfisols/Typic Endoaqualfs |
| pH c | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 6.8 ± 0.1 | 7.0 ± 0.1 |
| Sand d | 27.4 ± 2.1 | 54.5 ± 0.3 | 41.4 ± 0.5 |
| Clay d | 33.9 ± 0.4 | 18.6 ± 1.0 | 24.8 ± 0.3 |
| Percolation rate e | 2.84 ± 0.53 | 8.51 ± 1.06 | 3.90 ± 0.55 |
| TOC f | 14.4 ± 0.40 | 14.9 ± 0.39 | 21.2 ± 0.46 |
| Labile C g | 8.42 ± 0.44 | 5.48 ± 0.55 | 10.6 ± 1.27 |
| Soluble ferric h | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 0.11 ± 0.03 | 0.15 ± 0.02 |
| Soluble sulfate i | 25.6 ± 0.3 | 22.7 ± 0.6 | 66.5 ± 2.7 |
| DCB-Fe j | 38.7 ± 0.33 | 32.3 ± 0.73 | 29.3 ± 0.22 |
| Ox-Fe k | 6.62 ± 0.26 | 5.84 ± 0.05 | 12.8 ± 0.32 |
| Major Minerals | Quartz (SiO2), Magnesioferrite (MgFe2O4), Magnetite (Fe2O4) | Quartz (SiO2), Gupeiite (SiFe3), Magnetite (Fe2O4) | Quartz (SiO2), Ferrihydrite (Fe2O3·0.5H2O), Langite (Cu4(SO4)(OH)6·2H2O) |
| Paddy Pot | Irrigation Method b | GHGs Emission (t CO2-eq ha−1) | Rice Production (t ha−1) | GHGI d (t CO2-eq t grain−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | CH4 | Σ GWP c | Grain | Aboveground Biomass | |||
| BG | CF | 3.87 ± 0.12 | 3.24 ± 0.22 | 7.11 ± 0.25 | 7.09 ± 1.08 | 15.35 ± 2.06 | 1.00 ± 0.19 |
| ID | 4.94 ± 0.15 (+28%) | 1.16 ± 0.09 (−64%) | 6.10 ± 0.17 (−14%) | 6.23 ± 0.96 (NS) e | 13.42 ± 2.35 (NS) | 0.98 ± 0.18 (NS) | |
| MG | CF | 2.77 ± 0.21 | 0.48 ± 0.03 | 3.26 ± 0.21 | 5.82 ± 0.86 | 12.68 ± 1.78 | 0.56 ± 0.12 |
| ID | 3.25 ± 0.19 (+17%) | 0.19 ± 0.02 (−61%) | 3.44 ± 0.19 (NS) | 5.10 ± 0.79 (NS) | 12.35 ± 1.87 (NS) | 0.67 ± 0.14 (NS) | |
| JS | CF | 5.05 ± 0.12 | 6.62 ± 0.33 | 11.67 ± 0.35 | 7.79 ± 0.55 | 16.04 ± 1.55 | 1.50 ± 0.15 |
| ID | 6.30 ± 0.13 (+25%) | 1.02 ± 0.06 (−85%) | 7.32 ± 0.14 (−37%) | 6.98 ± 1.19 (NS) | 14.68 ± 2.17 (NS) | 1.05 ± 0.20 (−30%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, W.; Park, M.; Cho, K.; Hyun, S. Drainage Practice of Rice Paddies as a Sustainable Agronomic Management for Mitigating the Emission of Two Carbon-Based Greenhouse Gases (CO2 and CH4): Field Pilot Study in South Korea. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072802
Hwang W, Park M, Cho K, Hyun S. Drainage Practice of Rice Paddies as a Sustainable Agronomic Management for Mitigating the Emission of Two Carbon-Based Greenhouse Gases (CO2 and CH4): Field Pilot Study in South Korea. Sustainability. 2024; 16(7):2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072802
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Wonjae, Minseok Park, Kijong Cho, and Seunghun Hyun. 2024. "Drainage Practice of Rice Paddies as a Sustainable Agronomic Management for Mitigating the Emission of Two Carbon-Based Greenhouse Gases (CO2 and CH4): Field Pilot Study in South Korea" Sustainability 16, no. 7: 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072802
APA StyleHwang, W., Park, M., Cho, K., & Hyun, S. (2024). Drainage Practice of Rice Paddies as a Sustainable Agronomic Management for Mitigating the Emission of Two Carbon-Based Greenhouse Gases (CO2 and CH4): Field Pilot Study in South Korea. Sustainability, 16(7), 2802. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16072802







