Abstract
Admittedly, tourism stakeholders become more aware of the negative impacts of tourism, and it has become increasingly important to brand and position destinations towards sustainability. The main concern is emphasizing economic, social, and environmental awareness and implementation at the destination level regarding planning and development. This paper identifies the importance of sustainable place branding as part of destination social responsibility in the current global context. The main focus is identifying visitors’ responses as part of sustainable destination marketing. The study conducts a systematic literature review by rigorously selecting 26 related articles from the 106 search results for further analysis. The study results highlight the emergence of sustainable place branding concepts in academic literature, especially after the post-pandemic period. The themes identified in the literature analysis revolve around sustainable place branding in creating unique tourism experiences and engagement that resonates with the visitors’ self-perceptions and expectations of a destination. Sustainable place branding positively impacts destination image, trust, value, and loyalty. Moreover, it can create positive visitor outcomes, such as an intention to revisit because of positive word of mouth. The article concludes with suggestions for future research, emphasizing the need to explore further sustainable place branding and its influence on visitors’ responses in the evolving landscape of global tourism.
1. Introduction
Collated studies in tourism have acknowledged the importance of the place as the destination branding in terms of tourism [1,2], especially in the post-pandemic era, which alters the tourism trajectory by providing more eco- and socially friendly-practices in tourism development [3,4]. In particular, place branding is the reputation built through an amalgamation of geographical settings, cultural heritage, modern superstructures, and infrastructure, habits, and rituals [5,6,7]. In a competitive tourism environment, places must be marketed and provide a concept that can attract attention and become a product to use or, better yet, to live and experience temporarily [8]. The branded image of the place has evolved and encapsulated the concept of sustainability. Sustainability is the current development of a place that provides all positive trajectories that do not alter the social, natural, and economic environment [9].
The study aims to fill the gap through an extensive systematic literature review (SLR) by shedding light on the relationship between place branding and sustainability. Destinations have long been investing in building strong brands that focus on sustainability, as stronger brands tend to increase the attention that a particular destination receives from stakeholders [10]. However, these efforts are known to be very challenging due to the lack of visibility [11], which in turn impacts the actual visitors’ behavior and attitude towards these places. While studies identify that sustainable branding efforts can build stronger destination brands and better place promotion, further research is required to understand the actual visitors’ response [12]. Zouganeli, Trihas, Antonaki, and Kladou [13] argue that a stronger destination brand can enhance positive experiences and induce repeated visits and positive word-of-mouth. Therefore, the study will examine and explore the terms, according to the visitors’ responses, their perceptions of how sustainable branded destinations are socially responsible, and how they are perceived and experienced. Identifying the perception and attitude of the visitors will provide new insight that will enable the destination’s branded image to have a sustainable approach. SLR enables clustering keywords, terms, topics, and authors related to the topics of investigation. SLR is a popular research method that can identify the literature’s dearth and lead to valuable conclusions [3,14]. The study’s results will provide insights into generating new ideas for future research by suggesting new practices for socially sustainable destinations based on the visitors’ responses. By filling in these research gaps, one can gain an improved awareness of the intricate relationships that exist between place branding and sustainability [15]. This will help researchers, policymakers, destination managers, and marketers develop and implement strategies that will make destinations resilient, inclusive, and sustainable.
The study will explore the following questions:
- What are the current trends in sustainable destination branding and social destination responsibility?
- What is the trajectory of research findings based on the most relevant papers, research, and authors in the Web of Science database?
- What are the consequences of global research networks and partnerships, and how do co-authorship patterns among nations represent collaborations in sustainable place branding and visitor responses?
- What are the critical methodologies and approaches used in sustainable place branding and visitors’ response research?
- Based on the most common keywords, what are the main research clusters and theme topics, and how do these clusters further add knowledge on place branding sustainability and visitors’ responses?
The structure of the paper is as follows: In Section 2 is an overview of the literature. Section 3 explains the research methods used for this study, including the sample, data collection, and analytical techniques. In Section 4 the study’s results are presented, including its main conclusions and findings. Section 5, the study’s implications for academics, professionals, and industry decision-makers in sustainable place branding and destination social responsibility regarding visitors are discussed.
2. Literature Review
Admittedly, place branding is an intentional marketing technique used as a promotional tool to attract attention [16,17]. Since perceptions vary in describing a place and the value retrieved, branding aims to frame how a place attribute is perceived, lived, and experienced [5,18,19]. In particular, ‘the brand of a place is not created in the design of a logo but rather in people’s encounters with the place and all its diverse aspects’ [20]. At the same time, the community plays a vital role in framing the place’s characteristics and positioning the expression of the local culture through habits, behaviors, rituals, and traits [18,21]. Various tenets of research studies approached place brandings, such as its representation of national identity and national stereotypes [5,6,19,22] and as part of national diplomacy. That is because it involves the efforts of various actors who have the power to administer the place and attract attention by portraying it as a commodity, either national or commercial [2]. Additionally, place branding is synonymous with place personality and place image, considering various characteristics and encapsulating unique assets [23,24,25]. Thus, a place is branded by formulating an aspect of defining a geographical area and providing use as a way of living in terms of its natural setting, national identities, commercial activities, and urban planning [26,27].
Alarming negative impacts on the environment, social life, and the economy are calling for a framework for geographical place development with consideration for the people who reside and live in those areas. Sustainability involves the development that positively impacts the social, economic, and environmental aspects of living [20,28,29]. Additionally, sustainability is the approach of planning a place in terms of re-development and re-branding [21]. The goal of sustainable tourism is to reduce the detrimental consequences of travel on the environment, society, and economy while maximizing the beneficial advantages [4,8,30]. It entails ethical tourism activities that support the sustainability of destinations over the long term and ensure that resources are handled effectively to meet the needs of generations to come.
Conceptually, destination branding is associated with the image visitors perceive as the stimulus that motivates them to visit a place [2]. Thus, sustainability is basically an approach that can brand a destination and provide all positive procedures of administration and management. Examining the benefits of environmental, social, and economic sustainability is undoubtedly an adequate development path for places to be positioned in tourism as competitive and niche, offering dynamic experiences [31]. An example is social life as the ingredient that provides the ethical essence and identity, as well as the human aspects that make the place authentic and unique in terms of tourism [27]. An additional concept aligned with place branding and sustainability is destination social responsibility (hereafter DSR) [9,32]. DSR refers to ethical conduct associated with socially and environmentally responsible actions towards tourism destinations [33,34,35,36]. In particular, the pursuit is to reduce negative social impacts that can directly affect local communities. Additionally, a place/destination advertised as sustainable and socially responsible can be used as a promotional technique to intrigue potential visitors [37]. Admittedly, it is considered an established concept for responsible tourists, described as sensitive to environmental issues and socially responsible practices in tourism destinations [38]. Moreover, a destination that can be socially responsible must attest to an umbrella of interlinked procedures that can benefit the local community.
Residents’ attitudes as ambassadors of the destination must be committed to socially responsible behavior as part of the mentality building in the place [4,25,32]. However, there is a distinction between the perceptions of residents and visitors, whereas, in the case of residents, it is the place. In the case of visitors, it is the destination [2]. Visitors’ responses are deemed positive in places that promote an environmentally friendly approach. Consequently, there is positive word of mouth, and visitors’ experiences reflect a destination image [29]. Forming place branding is associated with visitors’ satisfaction and identification with positive place behavior [2,14]. Visitors generally have a positive attitude towards destinations that practice sustainability and engage in more culturally and environmentally driven development. Also, collective processes to brand a place revolve around sustainability as the remedy for vanishing negative impacts. Therefore, interconnected activities provide an understanding of the efforts toward sustainability as the primary identity for branding a place [28].
All main stakeholders should be engaged and form synergistic relationships by considering destination development and planning toward sustainability and social responsibility that will positively affect branding [39]. The main arguments arise from the contagious effects of the negative impacts caused when a place develops for commercial use but still has a branded image and reputation. Conflicts of interest hinder rational development, and there is a gap between the rhetorical aspect of sustainability and its implementation [29]. Bringing together sustainability in a branded place indicates a commitment to social responsibility, environmental preservation, inclusive practices, and economic viability. In conclusion, place branding and sustainability are related ideas that can support one another. By encouraging ethical tourism, protecting cultural and natural resources, improving community well-being, and guaranteeing long-term economic prosperity and competitiveness, these ideas can add value to destinations.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Approach to the Literature Review
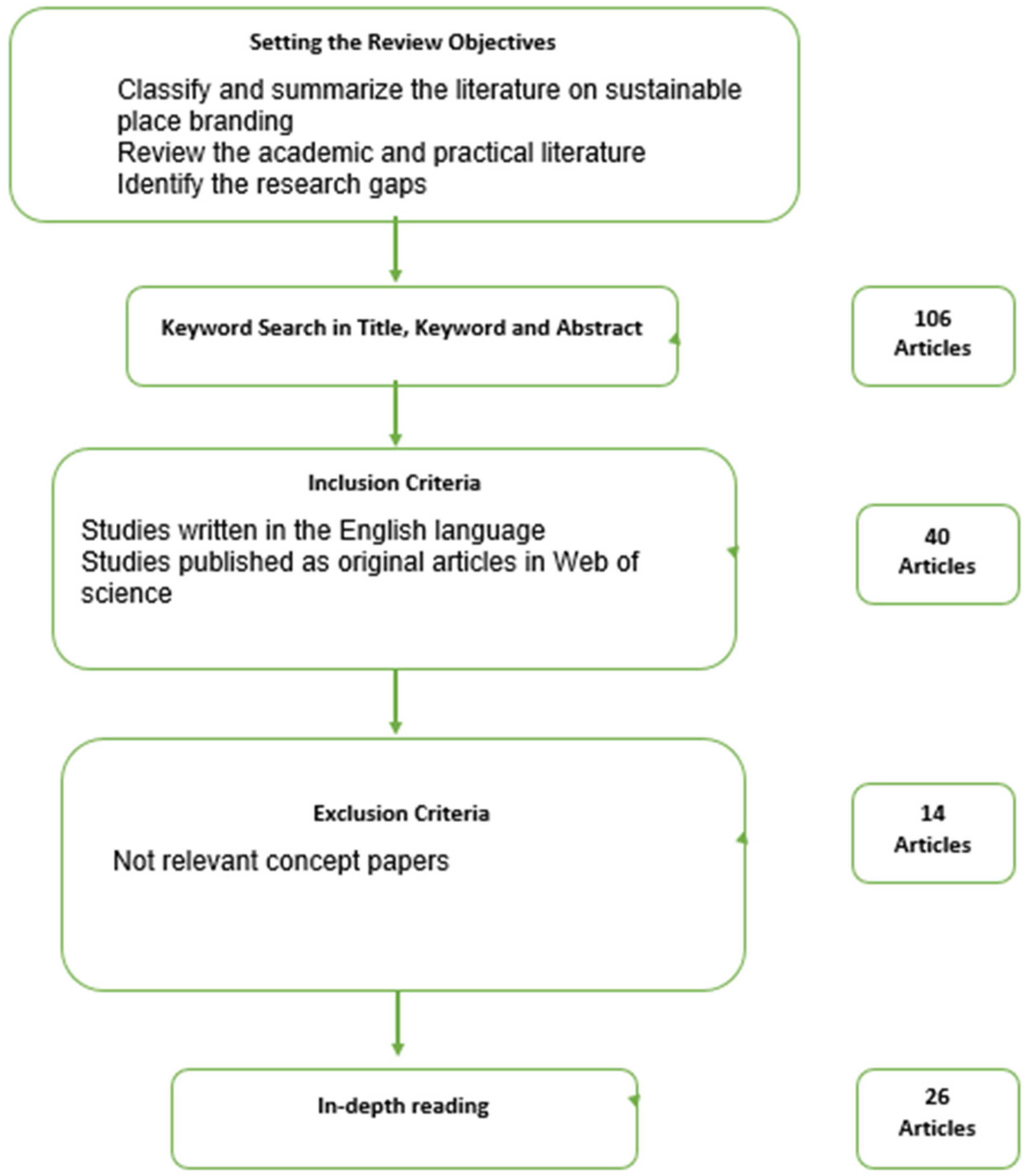
Using the PRISMA guidelines (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) as outlined by [40], a Systematic Literature Review (SLR) was conducted. The PRISMA framework facilitates the selection and identification of high-quality, impactful scientific articles through a structured process that includes four key steps: (1) identification, (2) screening, (3) assessing eligibility, and (4) including studies. The framework is shown in Figure 1. The PRISMA 2020 checklist can be found in Supplementary Materials, Table S1.
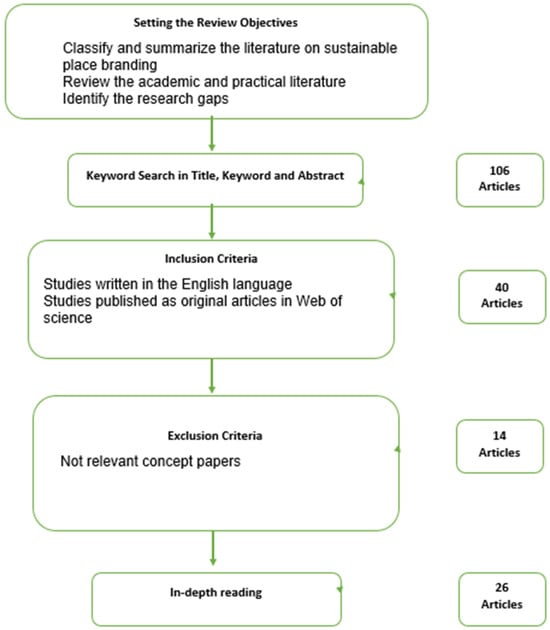
Figure 1.
PRISMA framework for systematic literature review.
The initial search commenced with the keyword “sustainable place branding”. The search terms were refined to recognize the need to narrow down to more specific studies and address the research gap identified. Acknowledging the varied terminology used in academic studies to describe sustainability and place branding concepts, a comprehensive list of synonyms was incorporated. The keywords “sustainable”, “green”, “eco-friendly”, “socially responsible”, “environmentally responsible”, and “ethical” were used interchangeably to capture the broad spectrum of sustainability. In the sustainable marketing literature, the continuum and development of these concepts over decades, as well as their interchangeable nature, have been identified and discussed for a long time [41]. Similarly, “place” and “destination”, as well as “visitor”, “tourist”, and “guest”, were recognized as interchangeable terms, reflecting the diverse lexicon in the field.
Furthermore, it was also identified that the keyword “sustainable” often has synonyms used, for example, “green”, “eco-friendly”, “socially responsible”, “environmentally responsible”, and “ethical”. In academic studies, “place” and “destination”, as well as “visitor”, “tourist”, and “guest”, are also used simultaneously. Therefore, during the research process, it was also decided to include closely related terms. A similar methodology was applied in the study of [39], which also identified several closely related terms used in the branding literature that were further used as synonyms to identify the relevant academic studies.
3.2. Validity of the Research Instrument, Search Strategy, Inclusion, and Exclusion Criteria
To ensure the validity of the SLR as a research instrument, several steps and precautions were taken. First, it is strongly recommended that the search process starts with clearly formulated research objectives and study concepts, followed by phrase searching using Boolean operators [42]. Once the search results were generated, robust inclusion and exclusion criteria were adopted to select the most relevant studies to be included in the literature review.
The refined keywords were combined using Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT) to construct a broad search string, enabling a comprehensive search. In the next step, the selected keywords were used to form a search string using Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), as suggested by [43]. The broad search string was as follows: (“sustainable” OR “green” OR “eco-friendly” OR “ethical” OR “socially responsible” OR “environmentally responsible”) AND (“place” OR “destination”) AND “brand” AND (“visitor” OR “tourist” OR “guest”).
The search was conducted through the Web of Science Core Collection, a database renowned for publishing research in tourism and destination management. This choice was informed by its use in previous research, ensuring consistency and relevance. Executed in January 2024, the search yielded a total of 106 results. An important aspect of the validity of the research instrument is the data quality, which was ensured by strictly defining that only the highest quality, peer-reviewed articles are selected for the study [44].
Several inclusion criteria were applied to refine the search results. Only academic, peer-reviewed journal articles written in English were considered, excluding books, reviews, conference papers, and other non-empirical materials. The focus was on empirical studies that measured visitors’ perceptions, directly aligning with the research gap. There was no restriction on the year of publication, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of the topic. Based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria, studies that were not empirical and studies that did not measure the link between sustainable place branding and visitors’ responses were excluded.
Applying the inclusion criteria reduced the pool to 40 articles. A review of abstracts led to further exclusions based on language and relevance of the study’s concepts to defined research objectives and gaps, ultimately selecting 26 studies for in-depth analysis. The number of final articles included in the study is aligned with the previously published studies. For example, ref. [45] study performed SLR on the relationship between the theory of planned behavior and the theory of reasoned action in the context of sustainable conservation of built heritage, and a rigorous literature search yielded a collection of 30 studies to be included in the further analysis. Furthermore, a SLR study on sustainable development in smart cities was conducted by selecting the 25 most relevant studies to the proposed search terms and research objectives [46].
In the final step, the full texts of these articles were retrieved, ensuring a thorough examination of their contributions to the understanding of sustainable place branding and its impact on visitor perceptions.
4. Results
In this section, we present the literature synthesis. After the articles were selected for the study, all articles were classified and grouped according to predetermined criteria (year of publishing, country from where data is collected, journal of publication, methods used in the study). Further, the keywords were used to generate the word cloud, and critical themes in the selected literature were identified.
4.1. Results from the Literature Analysis
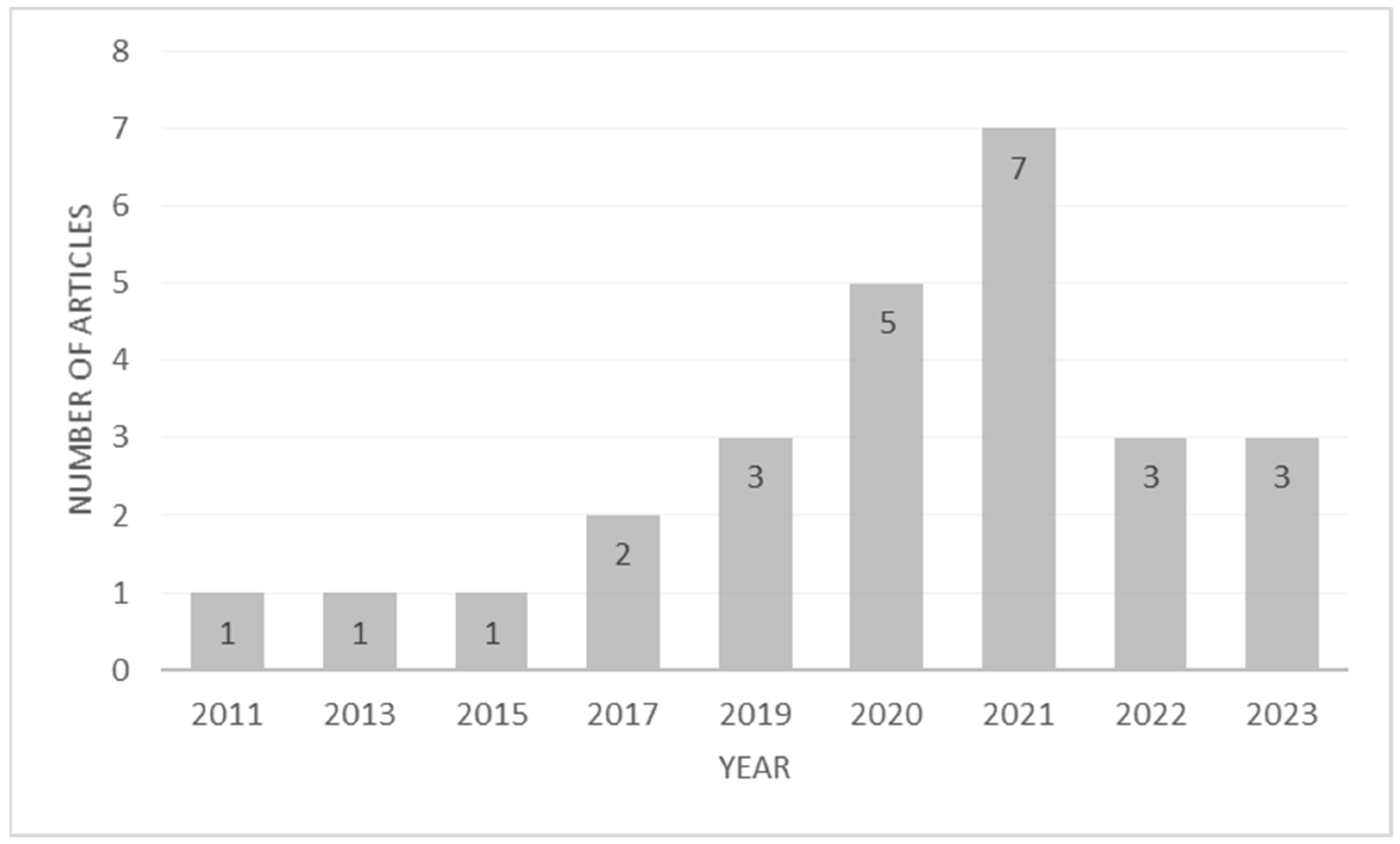
The systematic literature review begins by analyzing the time frame of the articles published on the given selection criteria. The time frame limitation was not set as an article selection criterion, as sustainable place branding is newly emerging in the academic literature. From the search results, it can be concluded that the earliest study on these concepts dates back to 2011, with pioneering research by Chen et al. on “The destination competitiveness of Kinmen’s tourism industry: exploring the interrelationships between tourist perceptions, service performance, customer satisfaction, and sustainable tourism” [47] in Journal of Sustainable Tourism. The study concepts have gained popularity since 2019, with most of the studies published in 2021, as shown in Figure 2. One of the major reasons for the spike in publications on sustainable place branding and the visitors’ responses can be attributed to increasing attention and investments in sustainable tourism destinations around the world [32]. These destinations still have to remain competitive, sustaining high visitor satisfaction and willingness to visit. In this context, academics and practitioners, including destination marketing and management organizations, are increasingly interested in understanding visitors’ interest and motivation to visit sustainable destinations, which has resulted in an increased number of studies on these concepts.
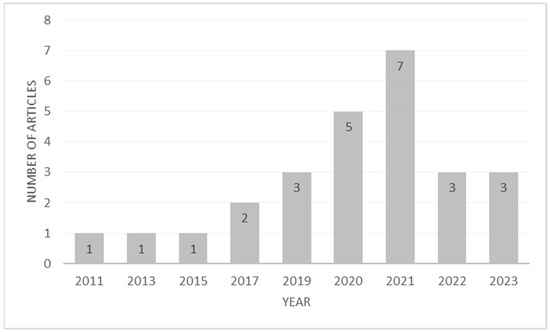
Figure 2.
Article distribution by year of publication.
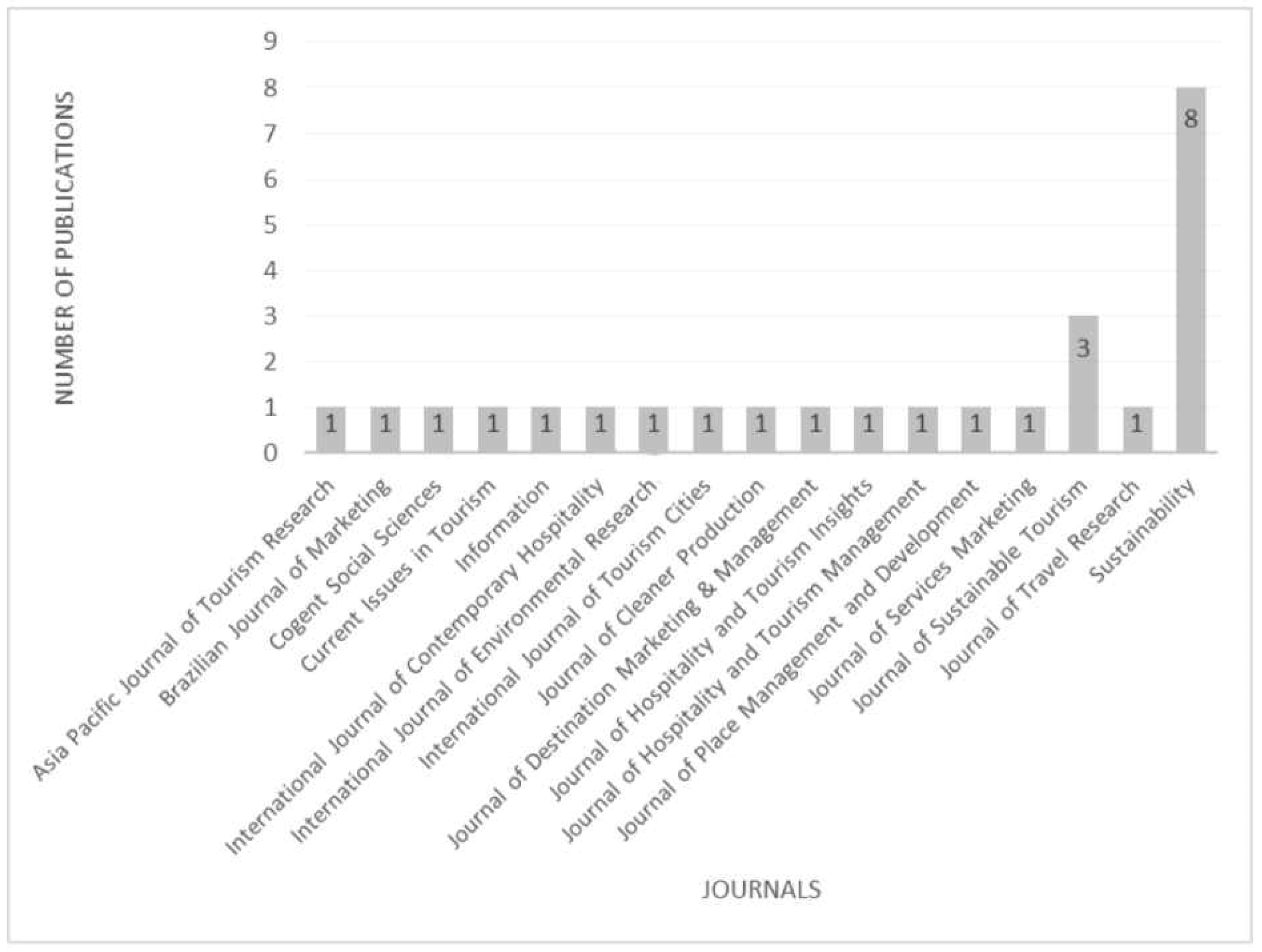
While the concepts of sustainable destination branding and visitors’ responses can be viewed from a multidisciplinary lens, as expected, majority of the articles are published in tourism and management journals, with articles published in the Journal of Sustainable Tourism (12% of the articles) and Sustainability (31% of the articles), as shown in Figure 3.
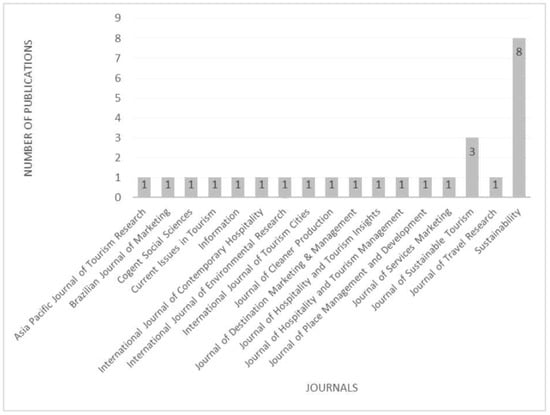
Figure 3.
Article distribution by journal of publishing.
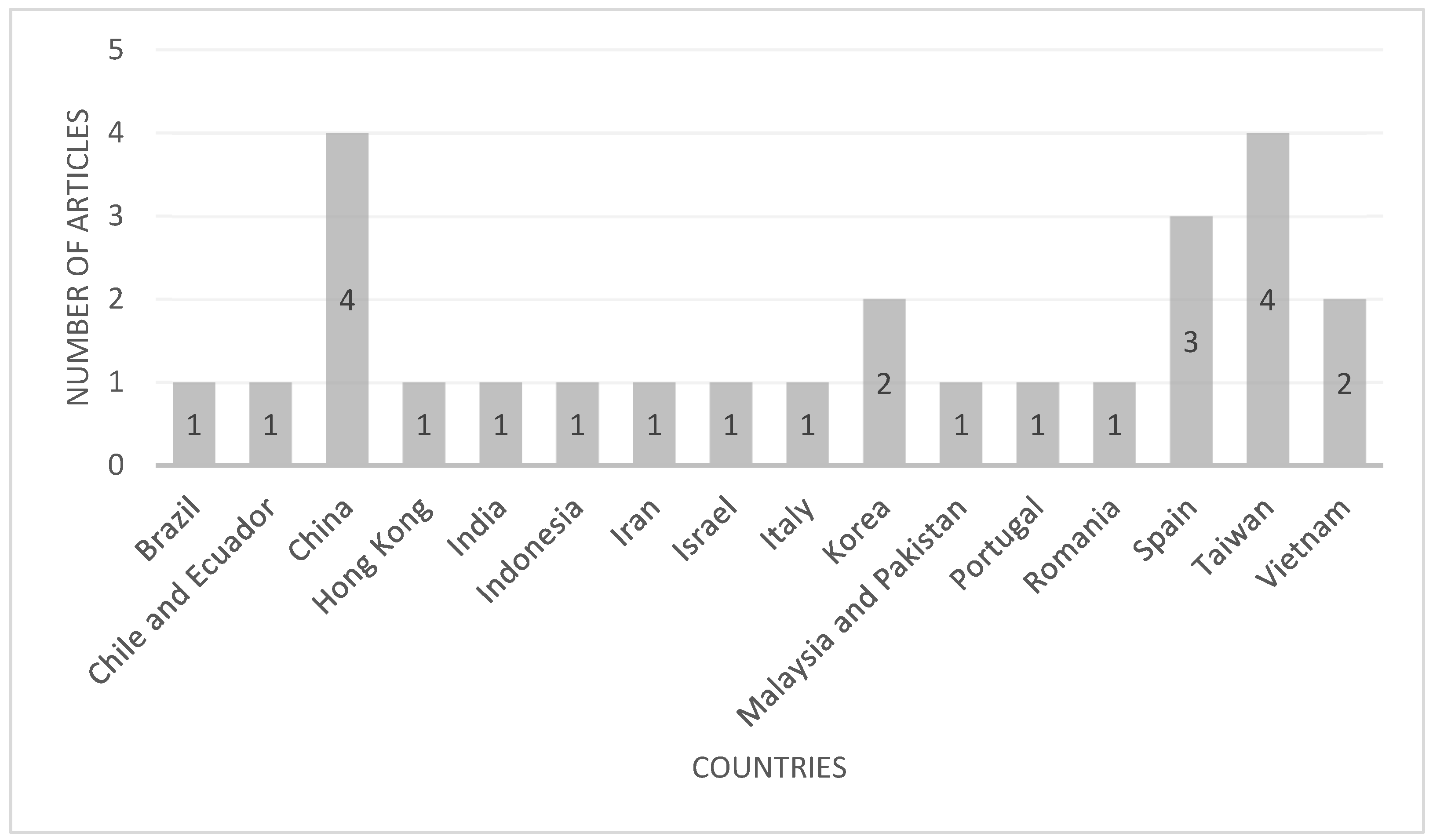
The literature analysis revealed that the majority of the articles on sustainable destination branding and visitors’ responses originated from China (15% of the articles), Taiwan (15% of the articles), and Spain (12% of the articles), among other South American, Asian, Middle-East and European countries (Figure 4). It is known that sustainable tourism and, therefore, research on sustainable destinations does not have a geographical scope; instead, a wide range of countries from various social, economic, and socio-ecological backgrounds [9] engage in sustainable tourism activities, also reflected in the distribution of the sourced articles for this study.
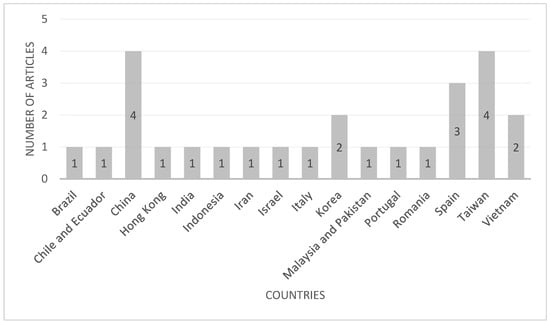
Figure 4.
Article distribution by country.
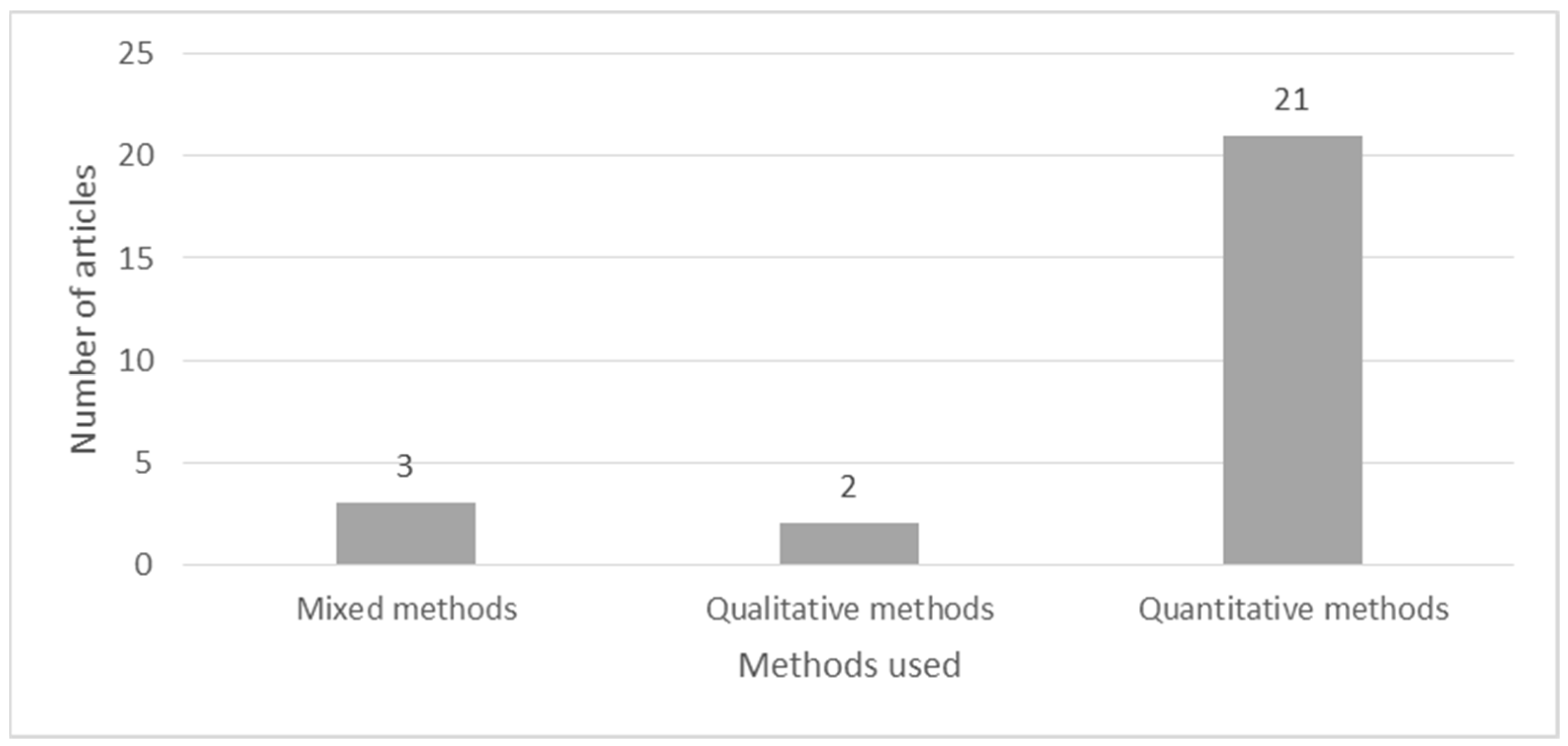
Further analysis in Figure 5 summarizes the article distribution by the methods that are used in the articles. All articles have engaged in primary data collection. A total of 8% of the articles collected only qualitative data with the help of interviews and case study analysis. Further, 12% of articles used mixed methods research combined qualitative and quantitative research methods. Finally, the majority of the research (80%) have collected primary data with the help of survey questionnaires. Consequently, the most commonly used data analysis methods are PLS-SEM with SmartPLS (19% of the studies), SEM with AMOS or LISREL (54% of the studies), and descriptive analysis and statistics (12% of the studies). Other data analysis techniques used in these studies are content analysis, factor analysis, sentiment analysis, cumulative logit model, and case study analysis.
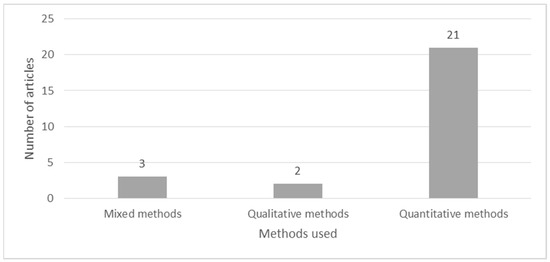
Figure 5.
Article distribution by research methods.
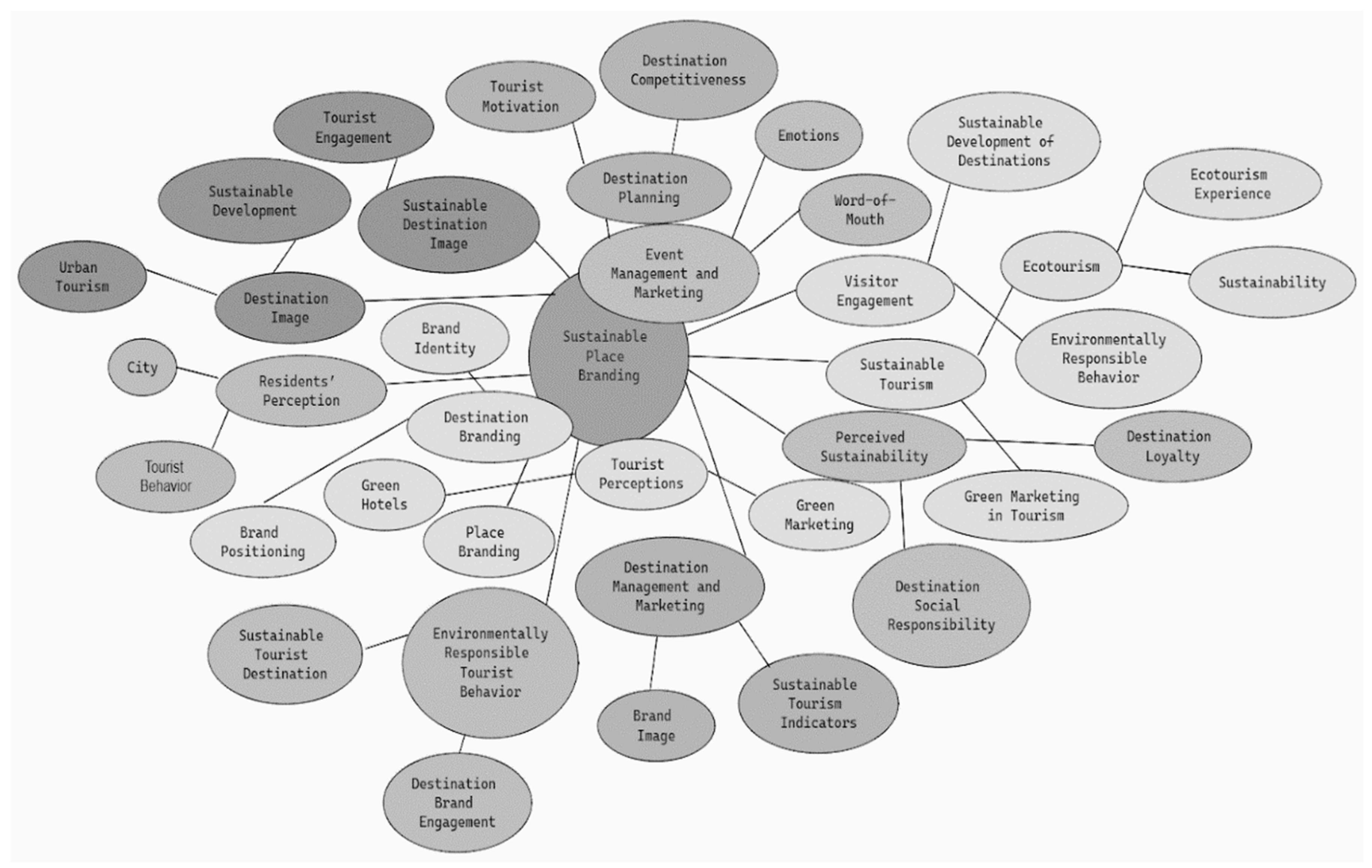
The keyword map explores the multifaceted domain of sustainable place branding, articulating a framework that weaves together strategic, perceptual, emotive, and operational dimensions vital to the enduring health of tourist destinations (Figure 6).
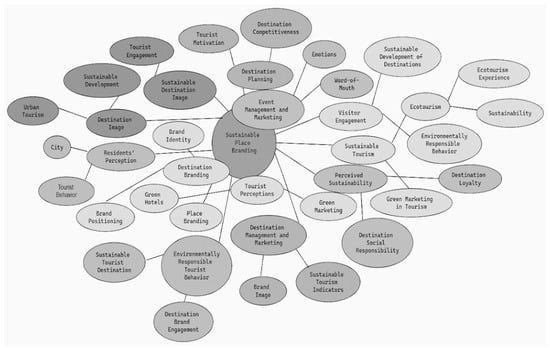
Figure 6.
Keyword Map of Sustainable Place Branding Literature.
At the center of the word cloud is “Sustainable Place Branding”, which acts as the cornerstone, unifying various tourism elements into a coherent methodology focused on maintaining the unique allure of destinations while promoting economic vitality. This principal concept is pivotal, underscoring its indispensable role in harmonizing the elements within the tourism landscape. Delving deeper, the framework encapsulates several sub-themes that reveal the composite nature of sustainable tourism:
Strategic Destination Management: This sub-theme comprises “Destination Planning” and “Destination Management and Marketing”, underscoring the necessity for a calculated, strategic approach to sustainable tourism development. Integral to this strategy is “Event Management and Marketing”, which is indicative of a comprehensive approach to destination evolution.
Marketing and Branding Dynamics: The map delineates the importance of “Destination Branding”, “Green Marketing in Tourism”, “Brand Image”, and “Place Branding”. This constellation of concepts highlights the imperative of framing destinations within a sustainability narrative, aligning with the escalating consumer trend towards eco-friendly travel.
Perceptual Constructs and Experiential Dimensions: Featuring “Tourist Perceptions”, “Visitor Engagement”, “Ecotourism Experience”, and “Residents’ Perception”, this thematic area accentuates the subjective and perceived image of destinations as experienced by tourists and local communities.
Sustainability and Environmental Stewardship: Focusing on the environmental aspects of sustainability, the framework includes “Sustainable Development of Destinations”, “Perceived Sustainability”, and “Environmentally Responsible Behavior”, reflecting a strong commitment to ecological conservation and sustainable practices.
Competitive Advantage: Concepts such as “Destination Competitiveness” and “Sustainable Destination Image” reflect an orientation toward enhancing the distinctiveness of destinations in a market increasingly valuing sustainability.
Feedback and Loyalty Mechanisms: Including “Word-of-Mouth” and “Destination Loyalty”, the framework identifies reputation management and consumer loyalty as critical to the sustainable growth of tourist locales.
Diverse Tourism Practices: The map identifies “Ecotourism” and “Urban Tourism” as distinct kinds of sustainable tourism, emphasizing the adaptation of sustainability efforts to various environments and tourism styles.
Stakeholder Involvement: Highlighting “Tourist Engagement” and “Sustainable Tourist Destination”, the framework points to the necessity of active stakeholder participation in achieving sustainable tourism goals.
Socio-Economic Metrics: The map brings to light “Destination Social Responsibility” and “Sustainable Tourism Indicators” as essential metrics for assessing tourism’s social and economic impacts, thereby supporting the overarching goal of sustainable development.
The keyword map thus serves as an integrative representation of the critical elements for fostering sustainable tourism. It encapsulates the complex interdependencies between economic, environmental, and social factors and the marketing strategies essential to crafting sustainable tourism destinations. The interwoven nature of these concepts within the map calls for an inclusive, stakeholder-engaged model of sustainable tourism development.
4.2. Thematic Content Analysis
In this section, we will look at the three main themes identified carefully and independently by each author, analyzing the studies selected for systematic literature review.
4.2.1. Sustainable Place Branding Creating Tourism Experiences and Engagement
Nowadays, almost every country and region engages in tourism activities, as it has the potential to create economic gains and social and environmental benefits. Tourism accounts for about 9% of the world’s GDP and is one of the fastest-growing industries [48]. However, the tourism industry has experienced some major shifts in recent years, one of which is a shift away from standardized mass tourism [49] to more specialized alternative tourism. The studies selected for the analysis show that sustainable tourism is one of the tools that allows destination managers to build more innovative and attractive tourism products [50], for example, by emphasizing sustainability through local businesses, local food, and local culture. Further analysis [51] reveals that in today’s tourism landscape, visitors are interested in activities, accommodation, local food, and unique surroundings, which all form the green image of the destination.
When destination managers and stakeholders create and offer more sustainable tourism experiences, it creates visitors’ emotional responses like connection, attraction, and involvement [52,53]. The study [52] emphasizes that when visitors engage with sustainable destinations, they build a positive relationship with the destination, which also leads to better satisfaction with the destination. Overall, it promotes environmentally responsible behavior of the visitors’ where visitors now become advocates of the destination and protect and promote sustainable practices. However, it is also argued [53] that perceptions of the environment quality, first impressions, and awareness of the sustainability and pro-environmental behavior of the destination play a role. In this context, a study [54] argues that one’s engagement and environmentally responsible behavior will largely depend on one’s personal characteristics and fit with the characteristics of the sustainable destination. Positive outcomes can be created when a visitor feels compatible with the destination and there is a fit between visitors’ individual characteristics and motives and the destination. Overall, it can be concluded that the engagement with the sustainable destination among each visitor will largely depend on the complex individual, behavioral, emotional, and cognitive characteristics and how these characteristics align with those within the sustainable destination.
4.2.2. Sustainable Place Creating Positive Brand Outcomes
The second theme identified in the selected studies reveals that sustainable place branding efforts tend to lead to positive brand outcomes that ensure that a sustainable place brand is unique and memorable. Some studies take a rather general approach, discussing the general attributes of sustainable place branding, suggesting that communication and information technologies [55] and UNESCO Natural and Cultural Heritage designation [56] are significant components of building a sustainable brand. Further, studies argue that all economic, environmental, legal, ethical, and philanthropic responsibility activities performed by the stakeholders in the particular destination can build a strong destination image that differentiates the destination from others for visitors [57,58,59] and residents [30]. These efforts also form positive brand attitudes [43] and increase the perceived functional, convenience, emotional, social, and epistemic value of the destination [60] by identifying traits in the destination that tourists greatly value. Studies also demonstrate that sustainable destination branding not only enhances brand love and engagement [58] but also fosters trust in the destination brand and its offerings [61,62], ultimately reinforcing the destination’s reputation for trustworthiness [2]. In turn, it serves as a compelling incentive for potential visitors to choose the destination for their travels.
Studies [63,64] also propose a concept of green brand equity that explains the overall “destination’s greening practices” [63] and “consumer’s subjective appraisal of organizational efforts that involve creating service exchanges and producing, promoting, packaging and reclaiming products in a manner that is sensitive or responsive to ecological concerns”. According to these studies [63,64], green equity strongly predicts value and brand equity. In the same vein, studies also confirm that positive brand impressions and outcomes can further enhance the destinations’ brand equity [59,65], a crucial factor for destinations’ differentiation, and summarize the competitive strengths that sustainable place branding can provide.
4.2.3. Impact on Intention Visitors’ Loyalty and Positive Word of Mouth
Finally, the last theme identified in the studies shows a strong link between sustainable place branding and the behavioral outcomes of the visitors’. Pro-environmental branding and labeling efforts lead to the intention to consume eco-tourism products [66] and visit sustainable destinations [62]. Furthermore, sustainable and green actions at the destination level can also promote willingness to revisit a destination in the post-travel stage [57,62,67,68]. Studies [57] credit destinations’ efforts to build a sustainable brand image that involves all stakeholders with favorable results. Also, personal factors, such as perceptions, awareness, and concerns for environmental protection [67,68], are identified as significant determinants for revisit intention.
Positive word-of-mouth (WOM) in both physical and electronic environments significantly impacts future visitors. Visitors who are overall satisfied with their experiences at the destination [30,69,70] are willing to promote the destination to their close contacts through informal communication [59] and eWOM (blogs, microblogs, review sites, social network sites, media-sharing sites, etc.) platforms [57,59,67,70].
Finally, a large body of literature shows sustainable place branding efforts create loyalty [57,61,63,64,69,71]. Visitors tend to see sustainable and green initiatives as a marketing program that fosters loyalty alongside other promotional efforts [64]. The human-place relationship is formed through positive self and place image match [71] and is also guided by unconscious beliefs [63] and satisfaction with tourism offerings and images [69]. However, study findings also emphasize differences in achieving these outcomes, mainly due to cultural differences, for example, among Asian and Western tourists [57].
5. Discussion and Conclusions
5.1. Summary of the Research Findings
This systematic literature review meticulously examined the nexus between sustainable place branding and its influence on visitor perceptions, engagement, and behaviors, highlighting the significant role these elements play in shaping the future of tourism destinations.
The analysis of 26 articles rigorously selected from 106 highlights a notable shift in academic literature toward recognizing sustainable place branding as a critical driver for creating differentiated and memorable tourism experiences. These experiences resonate deeply with tourists’ evolving expectations for sustainability, resulting in enhanced destination image, increased trust, and higher perceived value and loyalty among visitors. Key findings suggest that effectively communicated sustainable branding efforts significantly boost visitor engagement and satisfaction, fostering environmentally responsible behaviors and encouraging positive word-of-mouth recommendations. Moreover, the review identifies a strategic imperative for destination marketers and policymakers: to integrate sustainability into the core of destination branding strategies, thereby meeting the growing demand for responsible travel experiences and ensuring the long-term competitiveness and appeal of tourism destinations. The synthesis of these insights not only contributes to academic discourse but also offers practical guidance for developing sustainable, resilient, and inclusive tourist destinations, paving the way for future research to explore the long-term effectiveness of sustainable branding across different cultural and geographical contexts.
5.2. Conclusions
This systematic literature review has rigorously examined the nexus between sustainable place branding, sustainability, and social responsibility, highlighting these elements’ critical role in shaping tourism destinations. The review, which successfully identified and synthesized studies from the Web of Science database, has provided a nuanced understanding of how sustainable branding practices affect visitor perceptions, engagement, and, ultimately, the sustainability of tourism destinations.
Our findings underscore the importance of sustainable place branding in creating memorable and engaging tourism experiences that align with visitors’ values and expectations towards sustainability and social responsibility. The thematic analysis revealed that sustainable tourism practices enhance destination competitiveness and contribute to environmental preservation, social equity, and economic viability. Visitors’ engagement with sustainable destinations fosters a positive relationship, improving satisfaction and promoting environmentally responsible behavior.
Furthermore, the review highlighted the evolving nature of tourism, where destinations increasingly leverage sustainability as a strategic branding element to differentiate themselves and meet the growing demand for responsible travel experiences. The literature synthesis points to a shift from mass tourism to more personalized, sustainable tourism experiences, underscoring the need for destinations to integrate sustainability deeply into their branding and operational strategies.
5.3. Discussion
5.3.1. Implications for Practice
The findings of this review have several implications for tourism practitioners and policymakers. Firstly, there is a clear indication that destinations should prioritize sustainability and social responsibility in their branding efforts. This includes marketing sustainable practices and implementing concrete actions that contribute to the preservation of the environment, the well-being of local communities, and the provision of economic benefits to a wide range of stakeholders.
Secondly, the positive outcomes associated with sustainable place branding—such as enhanced brand equity, visitor loyalty, and positive word-of-mouth—emphasize the strategic advantage of embedding sustainability into the core of destination branding strategies. Tourism managers and marketers can leverage these insights to design and promote tourism experiences that resonate with the values of responsible travelers.
Thirdly, encourage destinations to pursue sustainability certifications from recognized organizations. Detail how these certifications can serve as a marketing tool, enhancing a destination’s reputation and appealing to eco-conscious travelers. Discuss the process and benefits of obtaining such certifications.
Fourth, expand on the importance of engaging local communities in the implementation and planning stages of sustainable tourism initiatives. Offer examples of community-led tourism projects and how they contribute to a stronger, more authentic place brand.
Fifth, highlight the role of public-private partnerships in leveraging resources, expertise, and networks for sustainable place branding. Discuss successful case studies where such collaborations have led to innovative sustainability projects and enhanced destination branding.
Finally, visitor education initiatives indicate that destinations must promote sustainable behaviors among tourists. These initiatives can include informational campaigns, sustainability tours, and interactive experiences that educate visitors on preserving the destination’s natural and cultural assets.
5.3.2. Directions for Future Research
While this review has contributed valuable insights into the relationship between sustainable place branding, sustainability, and social responsibility, it also identifies areas for further investigation. Future research could explore the long-term impacts of sustainable branding on destination competitiveness and sustainability. Additionally, studies could examine the role of emerging technologies and digital platforms in facilitating sustainable tourism practices and enhancing visitor engagement. We recommend that future studies employ quantitative and qualitative research methods to deepen the understanding of sustainable place branding’s impact on visitor perceptions and behaviors. This mixed-methods approach can unveil nuanced insights into the effectiveness of various sustainable branding strategies.
Future research could examine how global events (such as pandemics, economic crises, or climate change events) affect sustainable place branding strategies and visitor perceptions. This line of inquiry could provide insights into resilience and adaptability in place branding.
Moreover, there is a need for more comparative studies that investigate the effectiveness of different sustainable place branding strategies across various cultural and geographical contexts. Research could provide deeper insights into how sustainability can be tailored and communicated effectively to diverse audiences.
5.4. Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, this systematic literature review has highlighted the pivotal role of sustainable place branding in promoting tourism destinations as environmentally responsible, socially equitable, and economically viable. By embracing sustainability and social responsibility, destinations can enhance their appeal to visitors and contribute to the broader goals of sustainable development. As the tourism industry continues to evolve, integrating sustainability into place branding strategies will remain a critical factor in shaping the future of tourism.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/su16083312/s1, Table S1: The PRISMA 2020 checklist. Ref. [72] is cited in Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.G., S.I. and S.L.; methodology, S.I.; validation, Z.G., S.I. and S.L.; formal analysis, S.I. and S.L.; resources, S.L.; data curation, Z.G.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.G., S.I. and S.L.; writing—review and editing, S.I.; visualization, Z.G.; supervision, Z.G., S.I. and S.L.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Qu, H.; Kim, L.H.; Im, H.H. A model of destination branding: Integrating the concepts of the branding and destination image. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenker, S.; Braun, E.; Petersen, S. Branding the destination versus the place: The effects of brand complexity and identification for residents and visitors. Tour. Manag. 2017, 58, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.; Jebarajakirthy, C.; Sharma, B.K.; Maseeh, H.I.; Agrawal, A.; Shah, J.; Saha, R. Place Branding: A Systematic Literature Review and Future Research Agenda. J. Travel Res. 2023, 63, 535–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krabokoukis, T. Exploring the State of Research on Tourism Sustainability: A Bibliometric Analysis in the Post-COVID Era. Highlights Sustain. 2023, 2, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotler, P.; Gertner, D. Country as brand, product, and beyond: A place marketing and brand management perspective. J. Brand Manag. 2002, 9, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anholt, S. Places; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Govers, R.; Go, F. Place Branding; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Seabra, C.; Bhatt, K. Tourism Sustainability and COVID-19 Pandemic: Is There a Positive Side? Sustainability 2022, 14, 8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourlon, F.; Gale, T.; Adiego, A.; Álvarez-Barra, V.; Salazar, A. Grounding Sustainable Tourism in Science—A Geographic Approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markina, I.; Drogomyretska, M. The role of branding in the sustainable development of tourist destination. J. Res. Trade Manag. Econ. Dev. 2014, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Therkelsen, A.; James, L.; Halkier, H. Place branding for sustainable development: The role of tourism in sustainable place branding strategies. In Marketing Countries, Places, and Place-Associated Brands; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northampton, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 319–336. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, V.; Vandewalle, I.; Bamber, D. Place branding’s role in sustainable development. J. Place Manag. Dev. 2011, 4, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouganeli, S.; Trihas, N.; Antonaki, M.; Kladou, S. Aspects of sustainability in the destination branding process: A bottom-up approach. J. Hosp. Mark. Manag. 2012, 21, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí-Amortegui, L.; Clemente-Almendros, J.A.; Medina, R.; Gala, M.G. Sustainability and Competitiveness in the Tourism Industry and Tourist Destinations: A Bibliometric Study. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florek, M.; Hereźniak, M.; Augustyn, A. Measuring the effectiveness of city brand strategy. In search for a universal evaluative framework. Cities 2021, 110, 103079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertner, D.; Kotler, P. How can a place correct a negative image? Place Brand. 2004, 1, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.; Rahman, Z. Place branding research: A thematic review and future research agenda. Int. Rev. Public Nonprofit Mark. 2016, 13, 289–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, E.; Kavaratzis, M.; Zenker, S. My city–my brand: The different roles of residents in place branding. J. Place Manag. Dev. 2013, 6, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briciu, V.A.; Briciu, A. Defining Place Branding through Local and National Identity and National Stereotypes. In Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov. Series VII: Social Sciences • Law; Transilvania University of Braşov: Brașov, Romania, 2023; pp. 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntounis, N.; Kavaratzis, M. Re-branding the High Street: The place branding process and reflections from three UK towns. J. Place Manag. Dev. 2017, 10, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.; Rowley, J.; Keegan, B. Place and Destination Branding: A Review and Conceptual Mapping of the Domain. Eur. Manag. Rev. 2020, 18, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, N.G.; Cleveland, M. Marketing Countries, Places, and Place-Associated Brands: Identity and Image; Edward Elgar Publishing: Northampton, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ekinci, Y.; Hosany, S. Destination personality: An application of brand personality to tourism destinations. J. Travel Res. 2006, 45, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulou, A.; Papadimitriou, D. The role of destination personality in predicting tourist behaviour: Implications for branding mid-sized urban destinations. Curr. Issues Tour. 2015, 18, 1132–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, C.; Mehmood, A.; Marsden, T. Co-created visual narratives and inclusive place branding: A socially responsible approach to residents’ participation and engagement. Sustain. Sci. 2019, 15, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govers, R. From place marketing to place branding and back. Place Brand. Public Dipl. 2011, 7, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y. 2010 Branding the nation: Towards a better understanding. Place Brand. Public Dipl. 2010, 6, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruyn, C.; Said, F.B.; Meyer, N.; Soliman, M. Research in tourism sustainability: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis from 1990 to 2022. Heliyon 2023, 9, e18874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liasidou, S.; Fella, K.; Stylianou, C. A sustainable destination is an accessible destination: Examining the relationship as a remedy to seasonality. Worldw. Hosp. Tour. Themes 2022, 14, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.C.; De la Cruz, E.R.R.; Vázquez, F.J.C. Sustainable tourism and residents’ perception towards the brand: The case of Malaga (Spain). Sustainability 2019, 11, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, V.; Sousa, M.J.; Costa, C.; Au-Yong-Oliveira, M. Tourism towards Sustainability and Innovation: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streimikiene, D.; Svagzdiene, B.; Jasinskas, E.; Simanavicius, A. Sustainable tourism development and com-petitiveness: The systematic literature review. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 29, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Swanson, S.R. The effect of destination social responsibility on tourist environmentally responsible be-havior: Compared analysis of first-time and repeat tourists. Tour. Manag. 2017, 60, 308–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Gong, Q.; Huang, Y. How do destination social responsibility strategies affect tourists’ intention to visit? An attribution theory perspective. J. Retail. Consum. Serv. 2020, 54, 102023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Lian, Q.; Huang, Y. How do tourists’ attribution of destination social responsibility motives impact trust and intention to visit? The moderating role of destination reputation. Tour. Manag. 2020, 77, 103970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florek, M. Search of a Place Brand Identity Model; Edward Elgar Publishing eBooks: Northampton, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannakis, G.E.; Vlachos, P.A.; Koritos, C.D.; Kassinis, G.I. Are publicly traded tourism and hospitality providers greenwashing? Tour. Manag. 2024, 103, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agapito, D.; Kronenburg, R.; Pinto, P. A review on destination social responsibility: Towards a research agenda. Curr. Issues Tour. 2022, 26, 554–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Jebarajakirthy, C.; Maseeh, H.I.; Dhanda, K.; Saha, R.; Dahiya, R. Two decades of brand hate research: A review and research agenda. Mark. Intell. Plan. 2023, 41, 763–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katrandjiev, H. Ecological marketing, green marketing, sustainable marketing: Synonyms or an evolution of ideas. Econ. Altern. 2016, 1, 71–82. [Google Scholar]
- Shaheen, N.; Shaheen, A.; Ramadan, A.; Hefnawy, M.T.; Ramadan, A.; Ibrahim, I.A.; Hassanein, M.E.; Ashour, M.E.; Flouty, O. Appraising systematic reviews: A comprehensive guide to ensuring validity and reliability. Front. Res. Metr. Anal. 2023, 8, 1268045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, L.Z.; Andrea, C. How to carry out a literature search for a systematic review: A practical guide. BJPsych Adv. 2018, 24, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caiado, R.G.G.; de Freitas Dias, R.; Mattos, L.V.; Quelhas, O.L.G.; Leal Filho, W. Towards sustainable development through the perspective of eco-efficiency-A systematic literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 890–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, J.; Mateus, R.; Silvestre, J.D.; Roders, A.P. Going beyond good intentions for the sustainable conservation of built heritage: A systematic literature review. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trindade, E.P.; Hinnig, M.P.F.; da Costa, E.M.; Marques, J.S.; Bastos, R.C.; Yigitcanlar, T. Sustainable development of smart cities: A systematic review of the literature. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2017, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.M.; Chen, S.H.; Lee, H.T. The destination competitiveness of Kinmen’s tourism industry: Exploring the interrelationships between tourist perceptions, service performance, customer satisfaction and sustainable tourism. J. Sustain. Tour. 2011, 19, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardievna, S.G.; Qizi, A.M.A. The Role of Tourism in the Development of the Country’s Economy. Cent. Asian J. Innov. Tour. Manag. Financ. 2024, 5, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bunghez, C.L. The emerging trend of niche tourism: Impact analysis. J. Mark. Res. Case Stud. 2021, 2021, 134710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelbman, A. Tourist experience and innovative hospitality management in different cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistoreanu, P.; Aluculesei, A.C.; Avram, D. Is green marketing a label for ecotourism? The Romanian experience. Information 2020, 11, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Tang, C.; Lv, X.; Xing, B. Visitor engagement, relationship quality, and environmentally responsible behavior. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourhossein, M.; Baker, B.J.; Dousti, M.; Behnam, M.; Tabesh, S. Embarking on the trail of sustainable harmony: Exploring the nexus of visitor environmental engagement, awareness, and destination social responsibility in natural parks. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2023, 30, 100821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.A.; Li, J.; Afzal, H. Protect for affinity? The role of destination brand engagement in forming environmentally responsible tourist behaviours. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 1344–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.S.; Peters, M.; Pikkemaat, B. Investigating visitors’ perception of smart city dimensions for city branding in Hong Kong. Int. J. Tour. Cities 2019, 5, 620–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, M.M.; Guizzardi, A. Does designation as a UNESCO world heritage site influence tourist evaluation of a local destination? J. Travel Res. 2020, 59, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Hwang, Y.S. Do the social responsibility efforts of the destination affect the loyalty of tourists? Sustainability 2019, 11, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, P.; Borges, A.P.; Vieira, E.P. Corporate social responsibility image and emotions for the competitiveness of tourism destinations. J. Place Manag. Dev. 2021, 14, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Suárez, M.; Yagüe, M.J. Making sense from experience: How a sustainable multi-sensory event spurs word-of-mouth recommendation of a destination brand. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polo Pena, A.I.; Frias Jamilena, D.M.; Rodriguez Molina, M.A. The effect of a destination branding strategy for rural tourism on the perceived value of the conservation of the indigenous resources of the rural tourism destination: The case of Spain. Curr. Issues Tour. 2013, 16, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Iyer, R.; Lee, Y.K. Why Do Local Foodscapes Matter in Building Tourist Trust and Loyalty? Sustainability 2022, 14, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y. Sustainable Tourism Development Based upon Visitors’ Brand Trust: A Case of “100 Religious Attractions”. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, I.A.; Ruan, W.J.; Cai, X.; Huang, G.I. Green-Induced tourist equity: The cross-level effect of regional environmental performance. J. Sustain. Tour. 2021, 29, 1043–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, M.S.; Wong, I.A. Green marketing programs as strategic initiatives in hospitality. J. Serv. Mark. 2015, 29, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.C.; Chang, Y.R.; Liu, D.J. Sustainable development of an organic agriculture village to explore the influential effect of brand equity from the perspective of landscape resources. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, N.T.K. Understanding the effects of eco-label, eco-brand, and social media on green consumption intention in ecotourism destinations. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 128995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Thapa, B.; Kim, H. International Tourists’ Perceived Sustainability of Jeju Island, South Korea. Sustainability 2017, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.C.; Liu, C.H.S. Moderating and mediating roles of environmental concern and ecotourism experience for revisit intention. Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 29, 1854–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Xue, K. A model of destination loyalty: Integrating destination image and sustainable tourism. Asia Pac. J. Tour. Res. 2020, 25, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nukhu, R.; Singh, S. Is satisfaction a moderator? The effect of sensory experience on perceived environmental sustainability and WOM: A study on the world’s first organic state–Sikkim, India. J. Hosp. Tour. Insights 2024, 7, 479–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakiah, S.; Winarno, A.; Hermana, D. Examination of consumer engagement for loyalty in sustainable destination image. Cogent Soc. Sci. 2023, 9, 2269680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).