Managing Uncertainty in Urban Road Traffic Emissions Associated with Vehicle Fleet Composition: From the Perspective of Spatiotemporal Sampling Coverage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Area and Data Sources
2.2. Emission Quantification Method
2.3. Uncertainty Quantification Method
2.4. Method for Constructing the Requirement Model for the Spatiotemporal Sampling Coverage of Fleet Composition
3. Results and Discussion
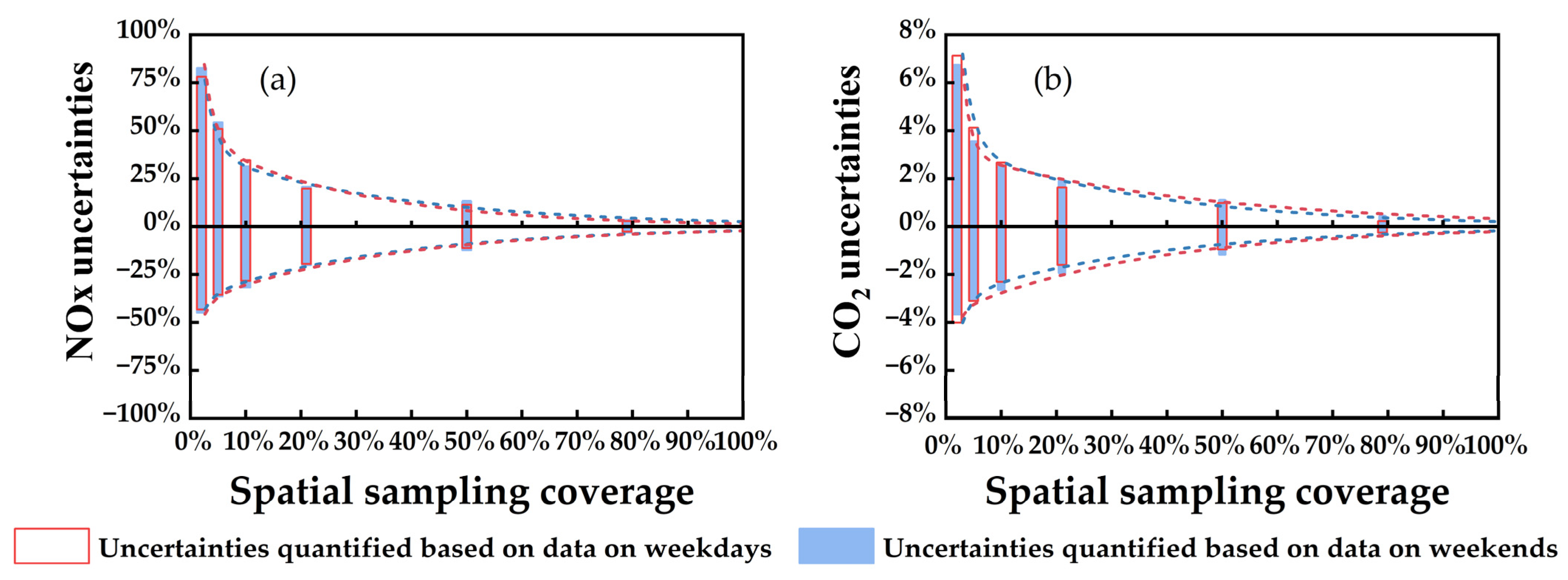
3.1. Variation Patterns in Regional Daily Road Traffic Emission Uncertainties with Changes in Spatial Sampling Coverage
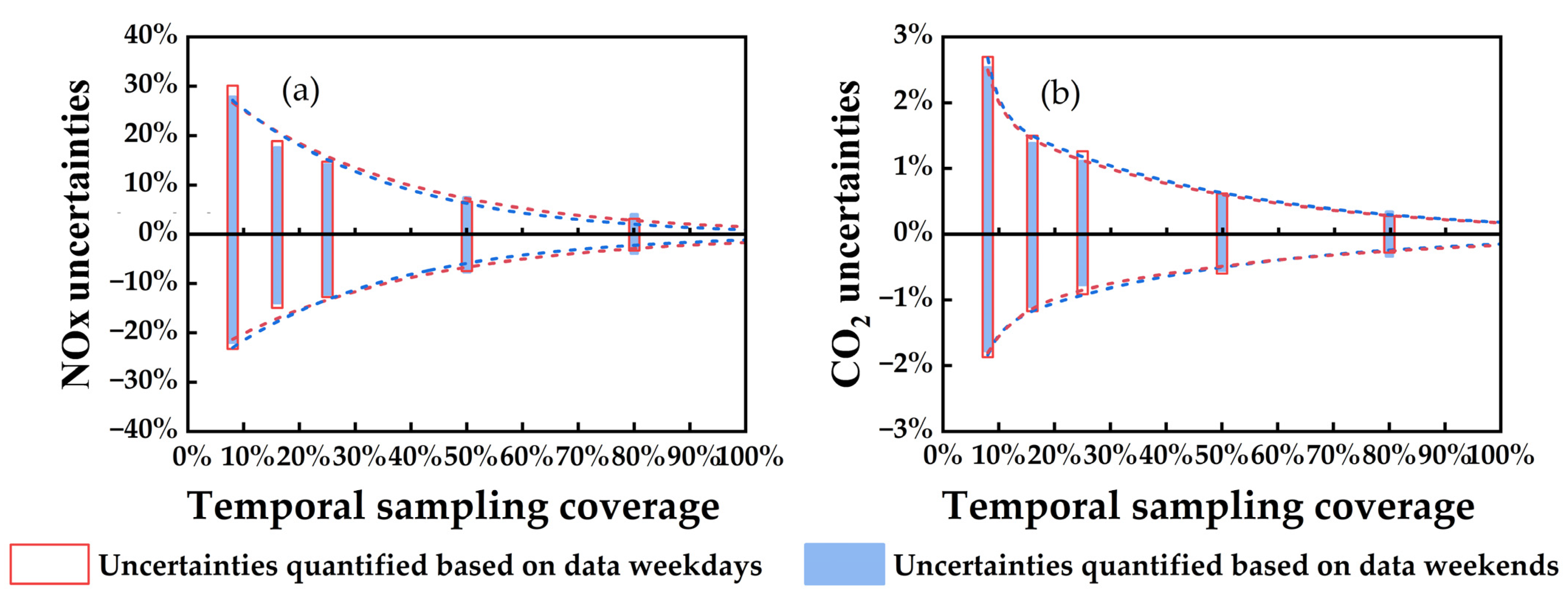
3.2. Variation Patterns in Regional Daily Road Traffic Emission Uncertainties with Changes in Temporal Sampling Coverage
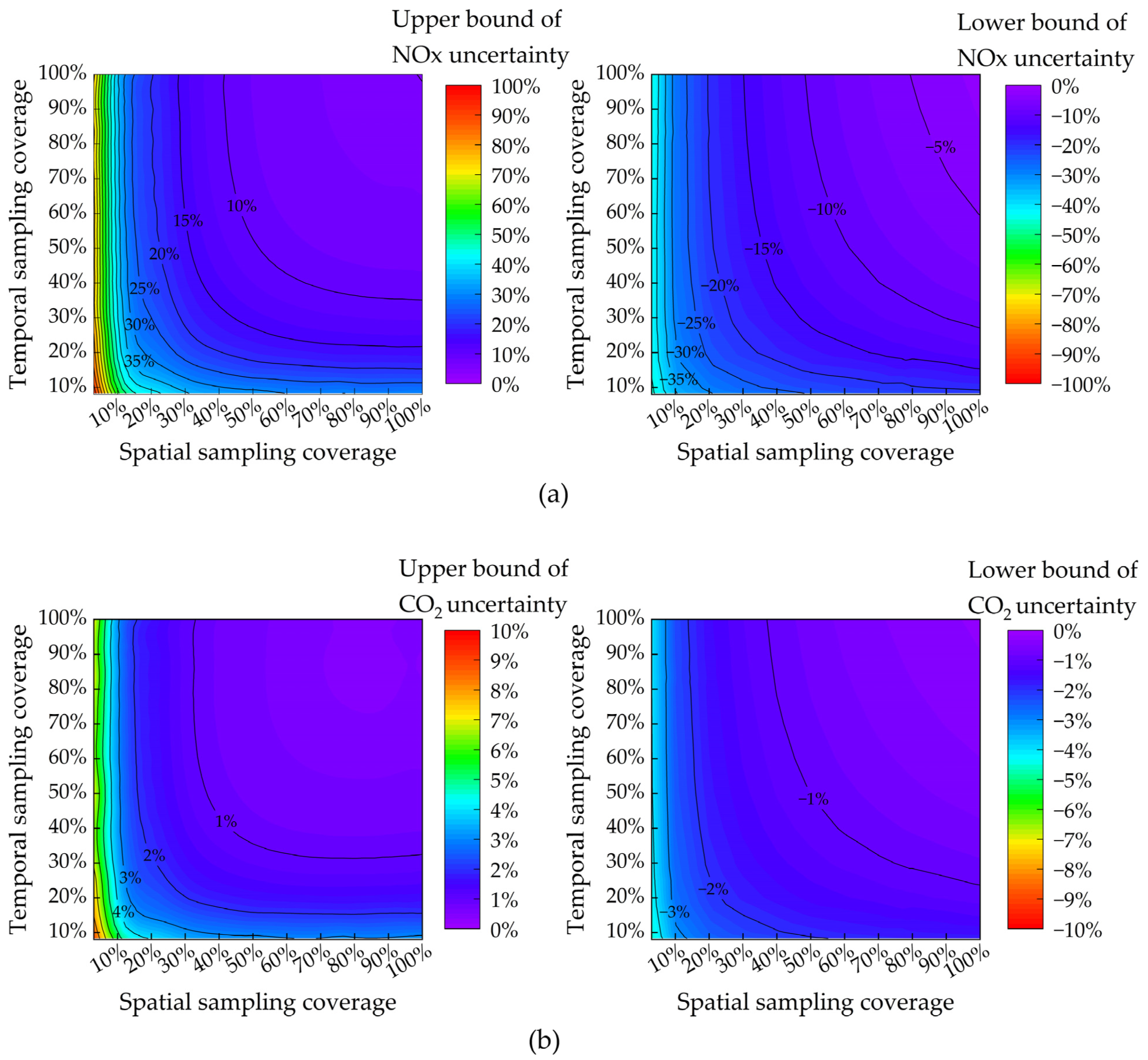
3.3. Construction of a Requirement Model for the Spatiotemporal Sampling Coverage of Fleet Composition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALPR | Automatic License Plate Recognition |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
| CO | Carbon Monoxide |
| CO2 | Carbon Dioxide |
| GDP | Gross Regional Product |
| HC | Hydrocarbons |
| ISSRC | International Sustainable Systems Research Center |
| IVE | International Vehicle Emissions |
| MSE | Normalized Mean Squared Error |
| MOVES | Motor Vehicle Emission Simulator |
| NOx | Nitrogen Oxides |
| PM | Particulate Matter |
| R2 | Correlation Coefficient |
| SO2 | Sulfur Dioxide |
| UCR | University of California, Riverside |
| VOC | Volatile Organic Compounds |
| VKT | Vehicle Kilometres Travelled |
| F value | F-statistic Value |
| p value | Probability Value |
References
- Gao, C.; Gao, C.; Song, K.; Xing, Y.; Chen, W. Vehicle emissions inventory in high spatial–temporal resolution and emission reduction strategy in Harbin-Changchun Megalopolis. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2020, 138, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, D.; Gurney, K.R.; Geethakumar, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Zhou, Y.; Razlivanov, I. Implications of uncertainty on regional CO2 mitigation policies for the U.S. onroad sector based on a high-resolution emissions estimate. Energy Policy 2013, 55, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazini, L.; Kalajahi, M.J.; Blond, N. An analysis of emission reduction strategy for light and heavy-duty vehicles pollutions in high spatial–temporal resolution and emission. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 29, 23419–23435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Jiang, L.; Xia, Y.; Wang, L.; Ye, J.; Hou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Song, Z.; et al. Quantifying on-road vehicle emissions during traffic congestion using updated emission factors of light-duty gasoline vehicles and real-world traffic monitoring big data. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 847, 157581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gately, C.K.; Hutyra, L.R. Large uncertainties in urban-scale carbon emissions. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2017, 122, 11242–11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viteri, R.; Borge, R.; Paredes, M.; Pérez, M.A. A high resolution vehicular emissions inventory for Ecuador using the IVE modelling system. Chemosphere 2023, 315, 137634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropkins, K.; Beebe, J.; Li, H.; Daham, B.; Tate, J.; Bell, M.; Andrews, G. Real-world vehicle exhaust emissions monitoring: Review and critical discussion. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 79–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, X.; Chen, X.; Jia, W.; Ye, J. Evaluating urban bus emission characteristics based on localized MOVES using sparse GPS data in Shanghai, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Xie, S.D. Determination of emission factors from motor vehicles under different emission standards in China. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2010, 46, 319–326. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboa, J.R.; Pachón, J.E.; Leuro, O.M.C.; González, S.F. A new database of on-road vehicle emission factors for Colombia: A case study of Bogotá. CTyF Cienc. Tecnol. Futuro 2019, 9, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Reng, P.P.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Mao, H.; Andre, M. Research on vehicle activity characteristics of typical roads in Tianjin. Environ. Pollut. Control 2018, 40, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, F.; González, C.M.; Trejos, E.M.; López, L.D.; Sandoval, F.J.; Cuellar, O.A.; Mangones, S.C.; Rojas, N.Y.; Aristizábal, B.H. Comparison of top-down and bottom-up road transport emissions through high-resolution air quality modeling in a city of complex orography. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Yang, F.; Liu, Z.; Shang, P.; Wang, H. Effect of taxis on emissions and fuel consumption in a city based on license plate recognition data: A case study in Nanning, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 215, 913–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Yang, L.; Xu, F.; Han, X.; Liu, B.; Zheng, N.; Li, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, J. Vehicle emission changes in China under different control measures over past two decades. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, D.; Amorim, J.H.; Sá, E.; Borrego, C.; Fontes, T.; Fernandes, P.; Pereira, S.R.; Bandeira, J.; Coelho, M.C.; Tchepel, O. Assessing the importance of transportation activity data for urban emission inventories. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Yin, S.; Gu, X.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, R. Refined 2013-based vehicle emission inventory and its spatial and temporal characteristics in Zhengzhou, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2017, 599, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, K.; Shen, S. Analyzing spatiotemporal traffic line source emissions based on massive didi online car-hailing service data. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2018, 62, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Zhang, K.; Pang, K.; Xiang, X. Characterization of spatio-temporal distribution of vehicle emissions using web-based real-time traffic data. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 709, 136227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lopes, D.; Mok, K.M.; Miranda, A.I.; Yuen, K.V.; Hoi, K.I. Development of a road traffic emission inventory with high spatial–temporal resolution in the world’s most densely populated region—Macau. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Gao, C.; Ba, Q.; You, H.; Zhang, X. Towards sustainable transport: Quantifying and mitigating pollutant emissions from heavy-duty diesel trucks in Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 119518–119531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, D.; Goyal, P. Estimation of vehicular emissions using dynamic emission factors: A case study of Delhi, India. Atmospheric Environ. 2014, 98, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafabakhsh, G.; Taghizadeh, S.A.; Kooshki, S.M. Investigation and sensitivity analysis of air pollution caused by road transportation at signalized intersections using IVE model in Iran. Eur. Transp. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Qi, W.; Jin, H. Urban sprawl among Chinese cities of different population sizes. Habitat Int. 2018, 79, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Central Committee of the Communist Party of China. State Council. Outline of Regional Integration Development Plan for the Yangtze River Delta. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2019-12/01/content_5457442.htm (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- National Bureau of Statistics, P.R.C. China Statistical Yearbook 2019; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Jin, J.; Xia, M.; Liu, Y.; Gao, M.; Zou, C.; Wang, T.; Lin, Y.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; et al. Vehicle emissions in a middle-sized city of China: Current status and future trends. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.X.; Huang, Z.H.; Wang, X.; Tang, W.X.; He, W.N.; Ji, L.; Wang, Y.J.; Ni, H. Emission inventory of motor vehicle based on traffic flow for Yangquan City in 2017. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2021, 11, 226–233. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.H.; Ma, J.L.; Li, L.; Lin, X.-F.; Xu, W.-J.; Ding, H. A high temporal-spatial vehicle emission inventory based on detailed hourly traffic data in a medium-sized city of China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 236, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, K.; Zou, B.; He, J. Quantification and management of urban traffic emissions based on individual vehicle data. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffarpasand, O.; Talaie, M.R.; Ahmadikia, H.; Khozani, A.T.; Shalamzari, M.D. A high-resolution spatial and temporal on-road vehicle emission inventory in an Iranian metropolitan area, Isfahan, based on detailed hourly traffic data. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 11, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadiha, A.; Malakooti, H.; Esfahanian, V. Development of reduction scenarios for criteria air pollutants emission in Tehran Traffic Sector, Iran. Sci. Total. Environ. 2018, 622, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, B.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Gong, S.; He, J.; Zou, C.; Song, G.; Li, X.; Wu, Z. Development of a vehicle emission inventory with high temporal–spatial resolution based on NRT traffic data and its impact on air pollution in Beijing—Part 1: Development and evaluation of vehicle emission inventory. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2016, 16, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of China. Bulletin of the Second National Pollution Source Census. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2020-06/10/content_5518391.htm (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Li, Y.; Bao, L.; Li, W.; Deng, H. Inventory and policy reduction potential of greenhouse gas and pollutant emissions of road transportation industry in China. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Technical regulation on Ambient Air Quality Index (AQI) (Trial). Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/jcffbz/201203/W020120410332725219541.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- State General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine, Ministry of Environmental Protection. Ambient Air Quality Standard. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/ywgz/fgbz/bz/bzwb/dqhjbh/dqhjzlbz/201203/W020120410330232398521.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- IPCC. 2006 IPCC Guidelines for National Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Chapter 3 Uncertainties; Institute for Global Environmental Strategies (IGES): Hayama, Japan, 2006; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Muthén, L.K.; Muthén, B.O. How to use a monte carlo study to decide on sample size and determine power. Struct. Equ. Model. A Multidiscip. J. 2002, 9, 599–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Song, G.; Zhai, Z.; Li, C.; Wu, Y. How many trajectories are needed to develop facility- and speed-specific vehicle-specific power distributions for emission estimation? Case study in Beijing. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2019, 2673, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Borken-Kleefeld, J. When is enough? Minimum sample sizes for on-road measurements of car emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13284–13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beasley, W.H.; Rodgers, J.L. Bootstrapping and Monte Carlo methods. In APA Handbook of Research Methods in Psychology; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; Volume 2, pp. 407–425. [Google Scholar]
- Qumsiyeh, M. Using the bootstrap for estimating the sample size in statistical experiments. J. Mod. Appl. Stat. Methods 2013, 12, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISSRC. IVE Model User’s Manual Version 2.0. Available online: https://manualzilla.com/doc/5821819/ive-model-users-manual-international-sustainable-systems (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Zhang, K.; Li, W.; Han, Y.; Geng, Z.; Chu, C. Production capacity identification and analysis using novel multivariate nonlinear regression: Application to resource optimization of industrial processes. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 282, 124469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkelä, M. Experimental design and response surface methodology in energy applications: A tutorial review. Energy Convers. Manag. 2017, 151, 630–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Record Number | Detector Location ID | Licence Plate Number (Anonymized) | Detection Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | HK-84 | 964352155 | 2018/5/8 07:00:05 |
| 2 | HK-91 | 964352146 | 2018/5/8 07:30:55 |
| 3 | HK-136 | 964352158 | 2018/5/8 08:20:50 |
| Vehicle Technical Attribute Parameters in the IVE Model | Example of Vehicle Technical Attribute Parameters in the IVE Model | Corresponding Parameters in the Xuancheng Registration Database | Example of Xuancheng Registration Database |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight | <2268 kg | Mass | 2000 kg |
| Description | <1.5 L | Displacement | 1 L |
| Fuel | Petrol | Fuel | Petrol |
| Exhaust | EURO I | Exhaust | China 1 1 |
| Age | <79 × 106 m | Registration date, vehicle type and function | For detailed vehicle age estimation methods, please refer to Yu et al. [29] |
| Air/Fuel Control | Multi-Pt FI | - | Determined based on the vehicle’s Description and Exhaust |
| Evaporative | PCV/Tank | - | Determined based on the vehicle’s Description and Exhaust |
| f(x1,x2) | Coefficient | R2 | MSE | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | d | e | f | |||
| Upper bound of NOx uncertainty | −0.026 | −0.024 | 0.281 | 0.194 | −0.049 | 0.049 | 0.993 | 4.8 × 10−4 |
| Lower bound of NOx uncertainty | 0.215 | 0.078 | −0.037 | −0.085 | 0.102 | −0.028 | 0.985 | 2.7 × 10−4 |
| Upper bound of CO2 uncertainty | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.030 | 0.025 | −0.005 | 0.005 | 0.986 | 8.4 × 10−6 |
| Lower bound of CO2 uncertainty | 0.013 | 0.008 | −0.007 | −0.005 | 0.005 | −0.003 | 0.987 | 2.1 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Zeng, X.; Li, W.; He, S.; Feng, Z.; Tan, Z. Managing Uncertainty in Urban Road Traffic Emissions Associated with Vehicle Fleet Composition: From the Perspective of Spatiotemporal Sampling Coverage. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083504
Cai Y, Zeng X, Li W, He S, Feng Z, Tan Z. Managing Uncertainty in Urban Road Traffic Emissions Associated with Vehicle Fleet Composition: From the Perspective of Spatiotemporal Sampling Coverage. Sustainability. 2024; 16(8):3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083504
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yufeng, Xuelan Zeng, Weichi Li, Song He, Zedong Feng, and Zihang Tan. 2024. "Managing Uncertainty in Urban Road Traffic Emissions Associated with Vehicle Fleet Composition: From the Perspective of Spatiotemporal Sampling Coverage" Sustainability 16, no. 8: 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083504
APA StyleCai, Y., Zeng, X., Li, W., He, S., Feng, Z., & Tan, Z. (2024). Managing Uncertainty in Urban Road Traffic Emissions Associated with Vehicle Fleet Composition: From the Perspective of Spatiotemporal Sampling Coverage. Sustainability, 16(8), 3504. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16083504





