What Drives Firms to Go Green in China? The Role of Digitalization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Basis and Hypotheses Development
2.1. The Resource-Based View and Digital Resources
2.2. Digital Resources and CSR
2.3. CSR and Environmental Performance
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Sample and Data Collection
3.2. Variables and Measurement
4. Empirical Testing and Results
4.1. Reliability and Validity Testing
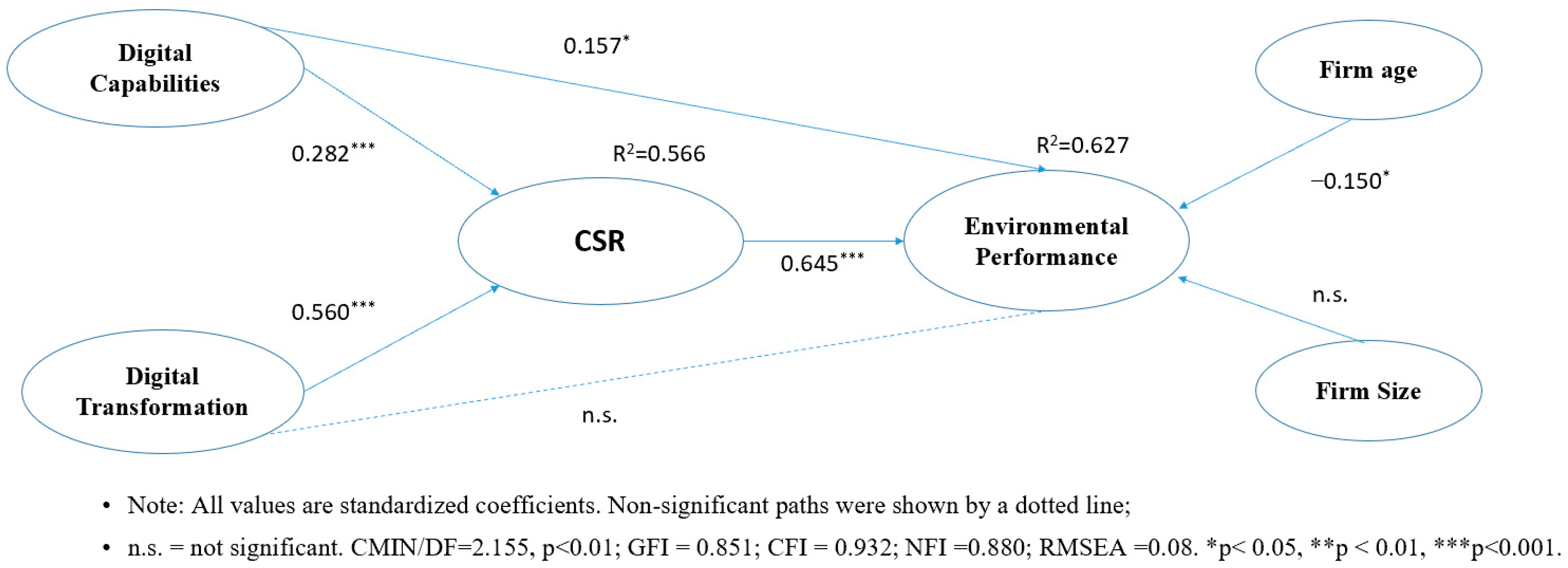
4.2. Hypothesis Testing
5. Conclusions and Implications
5.1. Discussion and Conclusions
5.2. Theoretical Contributions
5.3. Practical Implications
6. Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huma, S.; Junaid, A.; Ishtiaq, M.I. Achieving business competitiveness through corporate social responsibility and dynamic capabilities: An empirical evidence from emerging economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 386, 135820. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.; Renneboog, L. On the foundations of corporate social responsibility. J. Financ. 2017, 72, 853–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, R.; Liang, H.; Ng, L. Socially responsible corporate customers. J. Financ. Econ. 2021, 142, 598–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantalo, C.; Priem, R.L. Value creation through stakeholder synergy. Strateg. Manag. J. 2016, 37, 314–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, S.L.; Sharma, S. Engaging fringe stakeholders for competitive imagination. Acad. Manag. Exec. 2004, 18, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- Padgett, R.C.; Galán, J.I. The effect of R&D intensity on corporate social responsibility. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 93, 407–418. [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden, A.B.; Crittenden, V.L.; Crittenden, W.F. The digitalization triumvirate: How incumbents survive. Bus. Horiz. 2019, 62, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbik, Z.; Zozuľaková, V. Corporate social and digital responsibility. Manag. Syst. Prod. Eng. 2019, 27, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.Y.; Hao, Y.Y. Digital transformation and corporate environmental performance: The moderating role of board characteristics. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2022, 29, 1757–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, P.; Chen, X.Y.; Ke, Y. Does corporate integrity culture matter to corporate social responsibility? Evidence from China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 259, 120877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.Y.; Zeng, S.X.; Tam, C.M.; Ying, H.T.; Zou, H.L. Stakeholders’ influences on corporate green innovation strategy: A case study of manufacturing firms in China. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2013, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes, R.; Cowton, C.J. The maturing of socially responsible investment: A review of the developing link with corporate social responsibility. J. Bus. Ethics 2004, 52, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barney, J. Firm resources and sustained competitive advantage. J. Manag. 1991, 17, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.F.; Lew, Y.K.; Park, B.I. International new product development performance, entrepreneurial capability, and network in high-tech ventures. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 124, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Chou, T.C. Resource fit in digital transformation: Lessons learned from the CBC Bank Global E-banking project. Manag. Decis. 2011, 49, 1728–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, K.S.; Wäger, M. Building dynamic capabilities for digital transformation: An ongoing process of strategic renewal. Long Range Plan. 2019, 52, 326–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.Z.; Yim, K.; Chi, Y. The effects of strategic orientations on technology- and market-based breakthrough innovations. J. Mark. 2005, 69, 42–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatignon, H.; Xuereb, J.M. Strategic orientation of the firm and new product performance. J. Mark. Res. 1997, 34, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.J.; Parra-Requena, G.; Rodrigo-Alarcon, J.; Garcia-Villaverde, P.M. Environmental dynamism and entrepreneurial orientation: The moderating role of firm’s capabilities. J. Organ. Chang. Manag. 2013, 26, 475–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khin, S.; Ho, T.C. Digital technology, digital capability and organizational performance: A mediating role of digital innovation. Int. J. Innov. Sci. 2019, 11, 177–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levallet, N.; Chan, Y.E. Role of digital capabilities in unleashing the power of managerial improvisation. MIS Q. Exec. 2018, 17, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Bharadwaj, A.; El Sawy, O.A.; Pavlou, P.A.; Venkatraman, N.V. Digital business strategy: Toward a next generation of insights. MIS Q. 2013, 37, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teece, D.J. The foundations of enterprise performance: Dynamic and ordinary capabilities in an (economic) theory of firms. Acad. Manag. Perspect. 2014, 28, 328–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matarazzo, M.; Penco, L.; Profumo, G.; Quaglia, R. Digital transformation and customer value creation in made in Italy SMEs. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 123, 642–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanka, C.; Krumay, B.; Rueckel, D. The interplay of digital transformation and employee competency: A design science approach. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 178, 121575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadstock, D.C.; Matousek, R.; Meyer, M.; Tzeremes, N.G. Does corporate social responsibility impact firms’ innovation capacity? The indirect link between environmental & social governance implementation and innovation performance. J. Bus. Res. 2020, 119, 99–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.M.; Park, S.-Y.; Lee, H.J. Employee perception of CSR activities: Its antecedents and consequences. J. Bus. Res. 2013, 66, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Ramos, M.I.; Donate, M.J.; Guadamillas, F. Technological posture and corporate social responsibility: Effects on innovation performance. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, M.M. Does corporate social responsibility fuel firm performance? Evidence from the Asian automotive sector. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, A.; Siegel, D. Corporate social responsibility: A theory of the firm perspective. Acad. Manag. Rev. 2001, 26, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.S.; Lai, S.B.; Wen, C.T. The influence of green innovation performance on corporate advantage in Taiwan. J. Bus. Ethics 2006, 67, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehe, D.M.; Barin-Cruz, L. Corporate social responsibility, product differentiation strategy and export performance. J. Bus. Ethics 2010, 91, 325–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.W. Corporate social responsibility in China: Window dressing or structural change. Berkeley J. Int. Law 2010, 28, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson, P.M.; Li, Y.; Richardson, G.D.; Vasvari, F.P. Revisiting the relation between environmental performance and environmental disclosure: An empirical analysis. Account. Organ. Soc. 2008, 33, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossholder, K.W.; Bennett, N.; Kemery, E.R. Relationships between bases of power and work reactions: The mediational role of procedural justice. J. Manag. 1998, 24, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.K.; (Ram) Ramamurthy, K. Understanding the link between information technology capability and organizational agility: An empirical examination. MIS Q. 2011, 35, 931–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, S.J. Digital transformation: Opportunities to create new business models. Strategy Leadersh. 2012, 40, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.G.; Mendes, G.H.; Ayala, N.F.; Ghezzi, A. Servitization and industry 4.0 convergence in the digital transformation of product firms: A business model innovation perspective. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2019, 141, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasiri, M.; Ukko, J.; Saunila, M.; Rantala, T. Managing the digital supply chain: The role of smart technologies. Technovation 2020, 96, 102121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.F.; Pu, Y.; Zhu, Y.X.; Tang, C.Y. Revision and credit validity test of the CSR scale in the Chinese context. Soft Sci. 2010, 12, 106–110. [Google Scholar]
- Turker, D. Measuring corporate social responsibility: A scale development study. J. Bus. Ethics 2009, 85, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.G. New products: The factors that drive success. J. Int. Mark. 1994, 11, 60–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.; Freitas, I.M.B.; Fontana, R. Strategic orientation, innovation performance and the moderating influence of marketing management. J. Bus. Res. 1991, 97, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortinha, P.; Lages, C.; Lages, L.F. The trade-off between customer and technology orientations: Impact on innovation capabilities and export performance. J. Int. Mark. 2011, 19, 36–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, R.; Szulanski, G. Stickiness and the adaptation of organizational practices in cross-border knowledge transfers. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2004, 35, 508–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gefen, D.; Straub, D. A practical guide to factorial validity using pls-graph: Tutorial and annotated example. Commun. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2005, 16, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equations models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhang, Y.J.; Qiang, W. Does technological innovation benefit energy firms’ environmental performance? The moderating effect of government subsidies and media coverage. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2022, 180, 121728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Li, G.; Sun, P.; Peng, D. Inefficient investment and digital transformation: What is the role of financing constraints? Financ. Res. Lett. 2023, 51, 103429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Du, C.; Du, P.; Liu, G.; Zhou, G. Digital transformation and corporate environmental performance: Evidence from Chinese listed companies. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2024, 201, 123159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.; Bu, W. The Usage of Robots and Enterprises’ Pollution Emissions in China. J. Quant. Econ. Technol. Econ. 2022, 39, 157–176. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.J.; Jia, F.; Steward, M.D.; Schoenherr, T. The role of technology in enabling circular supply chain management. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2022, 106, A1–A6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Zhen, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X. Blockchain implementation for circular supply chain management: Evaluating critical success factors. Ind. Mark. Manag. 2022, 102, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Raza, S.A.; Huo, Z.; Shahzad, U.; Zhao, X. Does enterprise digital transformation contribute to the carbon emission reduction? Micro-level evidence from China. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2023, 86, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, A.; Roome, N. Toward an integrated model of leadership for corporate responsibility and sustainable development: A process model of corporate responsibility beyond management innovation. Corp. Gov. 2009, 9, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guadamillas, F.; Donate, M.J. Ethics and corporate social responsibility integrated into knowledge management and innovation technology: A case study. J. Manag. Dev. 2011, 30, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Year | Main Contributions | Application Area/Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barney | 1991 | Proposed the Resource-Based View (RBV), explaining differences in firm performance. | Firm Resources and Capabilities |
| Gatignon and Xuereb | 1997 | Defined the strategic direction of technology-oriented firms, emphasizing the importance of technological innovation. | Technology Development and Innovation |
| Zhou et al. | 2005 | Explored the relationship between strategic orientation and corporate culture, emphasizing its guiding role in enterprise development. | Organizational Culture and Strategic Orientation |
| Liu et al. | 2011 | Analyzed the impact of emerging resources on firm performance, emphasizing the importance of technological development. | Rapid Technological Development |
| Ruiz-Ortega et al. | 2013 | Analyzed the impact of technology investment on firm performance, emphasizing the enhancement of technological capabilities. | Technology Investment and Performance |
| Levallet and Chan | 2018 | Described the composition of a firm’s digital capabilities, emphasizing technical support and creative abilities. | Information Technology Infrastructure and Technical Support |
| Khin and Ho | 2019 | Introduced the concept of digital capability, emphasizing the importance of information technology infrastructure. | Digital Transformation and Digital Capabilities |
| Xiao et al. | 2021 | Synthesized perspectives on digital business strategy, emphasizing the integration of technological orientation and digital capabilities. | Digital Business Strategy |
| N | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Firm age | ||
| Below 10 | 57 | 32.8 |
| 11–30 | 97 | 56.3 |
| Over 30 | 19 | 10.9 |
| Firm type | ||
| State-owned enterprises | 11 | 6.3 |
| Private enterprises | 108 | 62.1 |
| Foreign-owned enterprises | 38 | 21.8 |
| Joint ventures | 5 | 2.9 |
| Others | 12 | 6.9 |
| Firm size | ||
| Below 300 | 117 | 67.2 |
| 301–2000 | 40 | 23.0 |
| Over 2000 | 17 | 9.8 |
| Average annual turnover (millions of CNY) | ||
| Below 3 | 12 | 6.9 |
| 3.1–20 | 43 | 24.7 |
| 20.1–400 | 79 | 45.4 |
| Over 400 | 40 | 23.0 |
| Product category | ||
| Consumer durables | 14 | 8.0 |
| Consumer non-durables | 7 | 4.0 |
| Complete industrial products | 32 | 18.4 |
| Raw materials/component industrial goods | 50 | 28.7 |
| Others | 71 | 40.8 |
| Construct and Indicators | Mean | SD | SFL |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital Transformation (AVE = 0.750, alpha = 0.922, CR = 0.923) | |||
| Businesses are committed to digital transformation, covering everything that can be digitized | 5.138 | 1.274 | 0.857 |
| Companies collect a lot of data from different sources | 5.115 | 1.267 | 0.908 |
| The corporate goal is to utilize digital resources to create closer connections between different business processes | 5.421 | 1.139 | 0.834 |
| The corporate goal is to enhance efficient customer interfaces through digitization | 5.218 | 1.239 | 0.863 |
| Digital Capabilities (AVE = 0.860, alpha = 0.980, CR = 0.980) | |||
| Communication technology and network infrastructure for enterprise support of connectivity to various digital platforms, etc. | 5.086 | 1.253 | 0.861 |
| Enterprise support for digital platforms, extended applications, etc. | 5.207 | 1.264 | 0.866 |
| Enterprises can plan business activities between business sectors supported by information (digital) technology | 5.092 | 1.269 | 0.939 |
| Enterprises can develop programs for the application of information systems in business cooperation | 5.109 | 1.261 | 0.936 |
| Enterprises are able to utilize information (digital) technology resources to establish effective cooperation mechanisms | 5.132 | 1.235 | 0.967 |
| Companies can develop new markets with partners through information (digital) technology | 5.029 | 1.237 | 0.952 |
| Enterprises are better able to take advantage of Internet-based business opportunities | 5.167 | 1.203 | 0.939 |
| Enterprises can enhance information sharing and respond faster to the market through information (digital) technologies | 5.195 | 1.205 | 0.954 |
| CSR (AVE = 0.781, alpha = 0.910, CR = 0.947) | |||
| Employee rights and benefits | 5.611 | 1.079 | 0.900 |
| Product quality and safety | 6.081 | 0.929 | 0.890 |
| Business integrity and fair competition | 6.044 | 0.975 | 0.893 |
| Social security | 5.573 | 1.128 | 0.873 |
| Environmental sustainability | 5.831 | 1.083 | 0.864 |
| Environmental Performance (AVE = 0.831, alpha = 0.985, CR = 0.951) | |||
| Wastewater is reduced in business operations | 5.741 | 0.972 | 0.912 |
| Reduced emissions from business operations | 5.729 | 0.986 | 0.907 |
| Solid pollution from business operations has been reduced | 5.729 | 0.969 | 0.927 |
| Pollutants have been reduced during the production phase of the enterprise | 5.713 | 0.955 | 0.899 |
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 1. Digital transformation | 0.866 | |||
| 2. Digital capabilities | 0.547 *** | 0.927 | ||
| 3. CSR | 0.714 *** | 0.613 *** | 0.884 | |
| 4. Environmental performance | 0.605 *** | 0.568 *** | 0.779 *** | 0.912 |
| Variables | Estimate | Coefficients | Bias-Corrected 95% CI | Percentile 95% CI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SE | Z | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | ||
| Total Effects | |||||||
| Digital transformation → Environmental performance | 0.358 | 0.083 | 4.313 | 0.214 | 0.538 | 0.190 | 0.519 |
| Digital capabilities → Environmental performance | 0.293 | 0.086 | 3.407 | 0.129 | 0.456 | 0.143 | 0.476 |
| Indirect Effects | |||||||
| Digital transformation → Environmental performance | 0.309 | 0.069 | 4.478 | 0.201 | 0.485 | 0.175 | 0.446 |
| Digital capabilities → Environmental performance | 0.157 | 0.055 | 2.855 | 0.074 | 0.300 | 0.063 | 0.280 |
| Direct Effects | |||||||
| Digital transformation → Environmental performance | 0.049 | 0.084 | 0.583 | −0.110 | 0.222 | −0.102 | 0.232 |
| Digital capabilities → Environmental performance | 0.136 | 0.069 | 1.971 | 0.006 | 0.278 | 0.017 | 0.299 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, X.; Xiao, S. What Drives Firms to Go Green in China? The Role of Digitalization. Sustainability 2025, 17, 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010234
Pan X, Xiao S. What Drives Firms to Go Green in China? The Role of Digitalization. Sustainability. 2025; 17(1):234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010234
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Xiaoyan, and Shufeng Xiao. 2025. "What Drives Firms to Go Green in China? The Role of Digitalization" Sustainability 17, no. 1: 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010234
APA StylePan, X., & Xiao, S. (2025). What Drives Firms to Go Green in China? The Role of Digitalization. Sustainability, 17(1), 234. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17010234






