Investigation of Flexibility Enhancement Mechanisms and Microstructural Characteristics in Emulsified Asphalt and Latex-Modified Cement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Cement
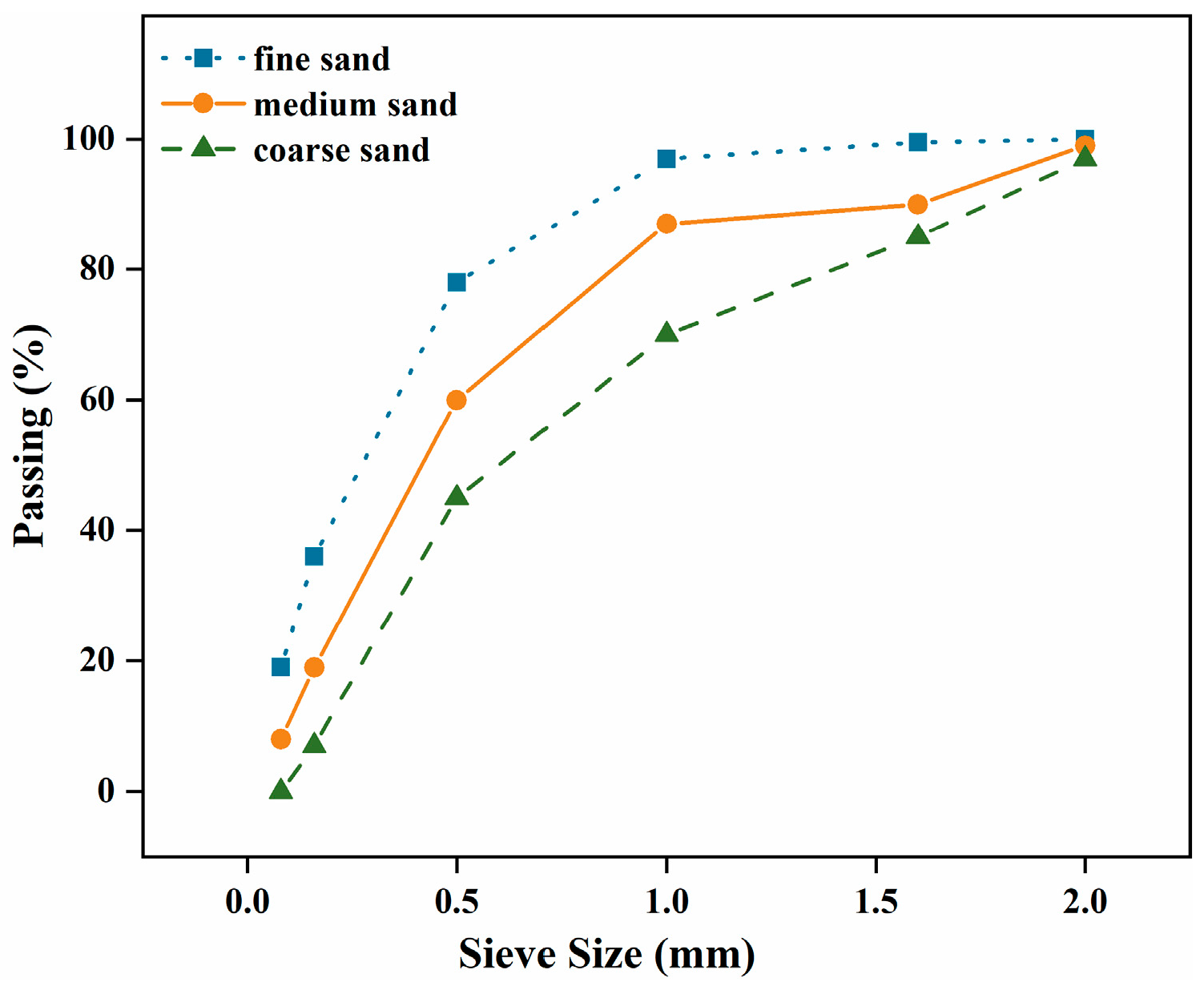
2.2. Aggregate and Water for Sample Preparation
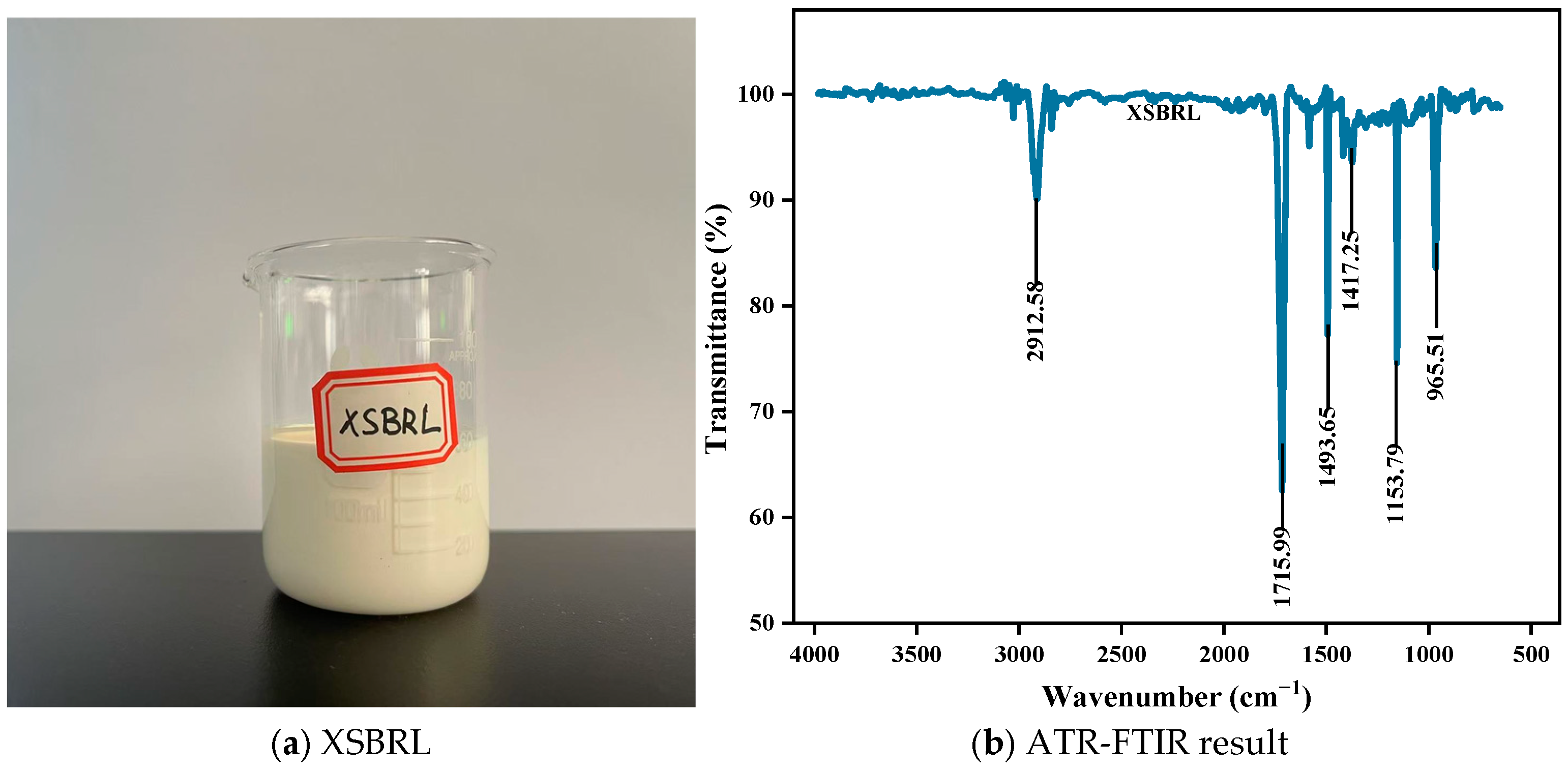
2.3. Emulsified Asphalt and Latex
3. Experimental Design and Methods
3.1. Design of Experiments and Specimen Preparation
3.2. Cement Mortar Fluidity Test
3.3. Flexibility Test for Modified Cement Mortar
3.4. Materials Characterization
4. Results and Analysis
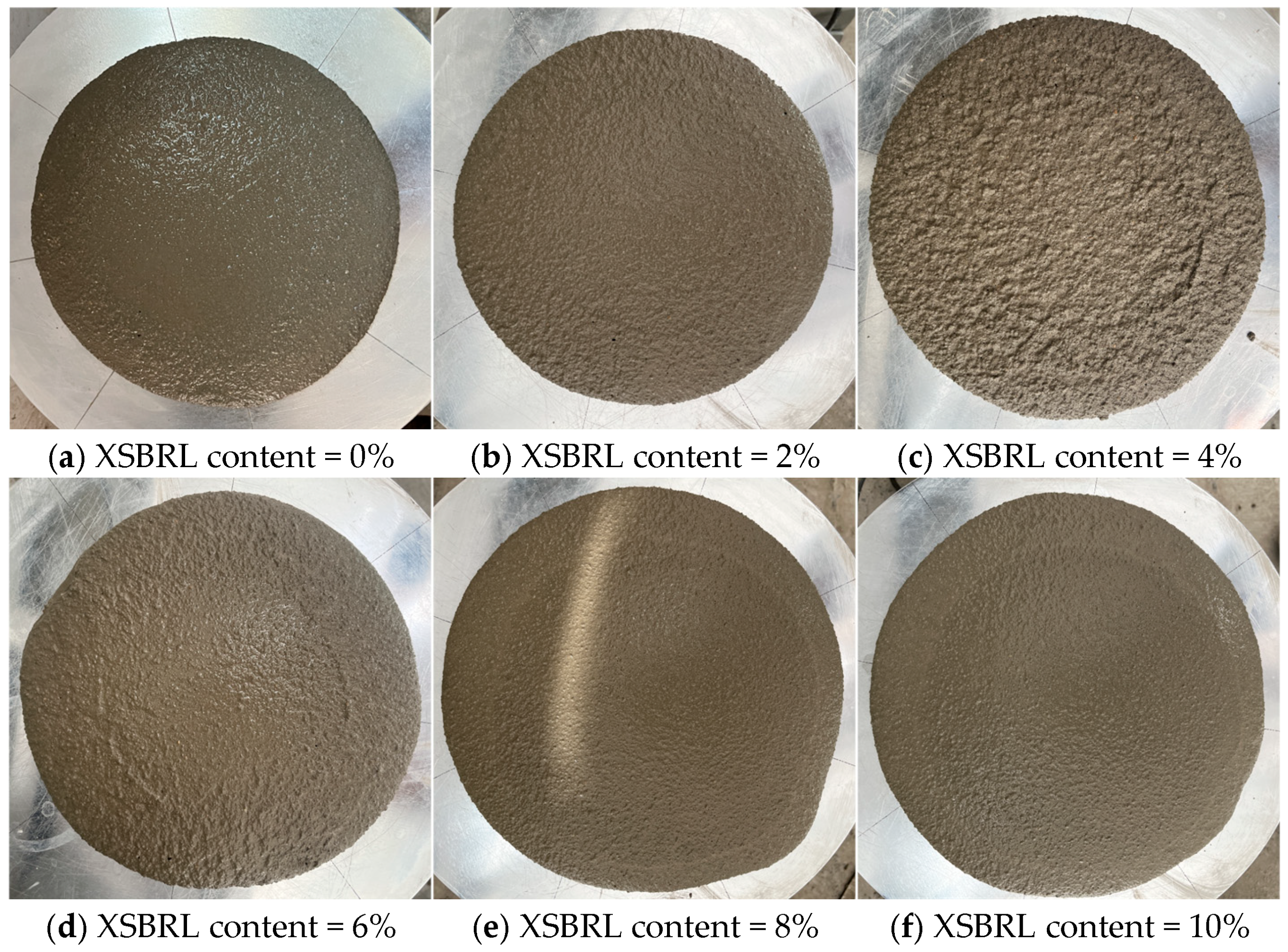
4.1. Fluidity Analysis
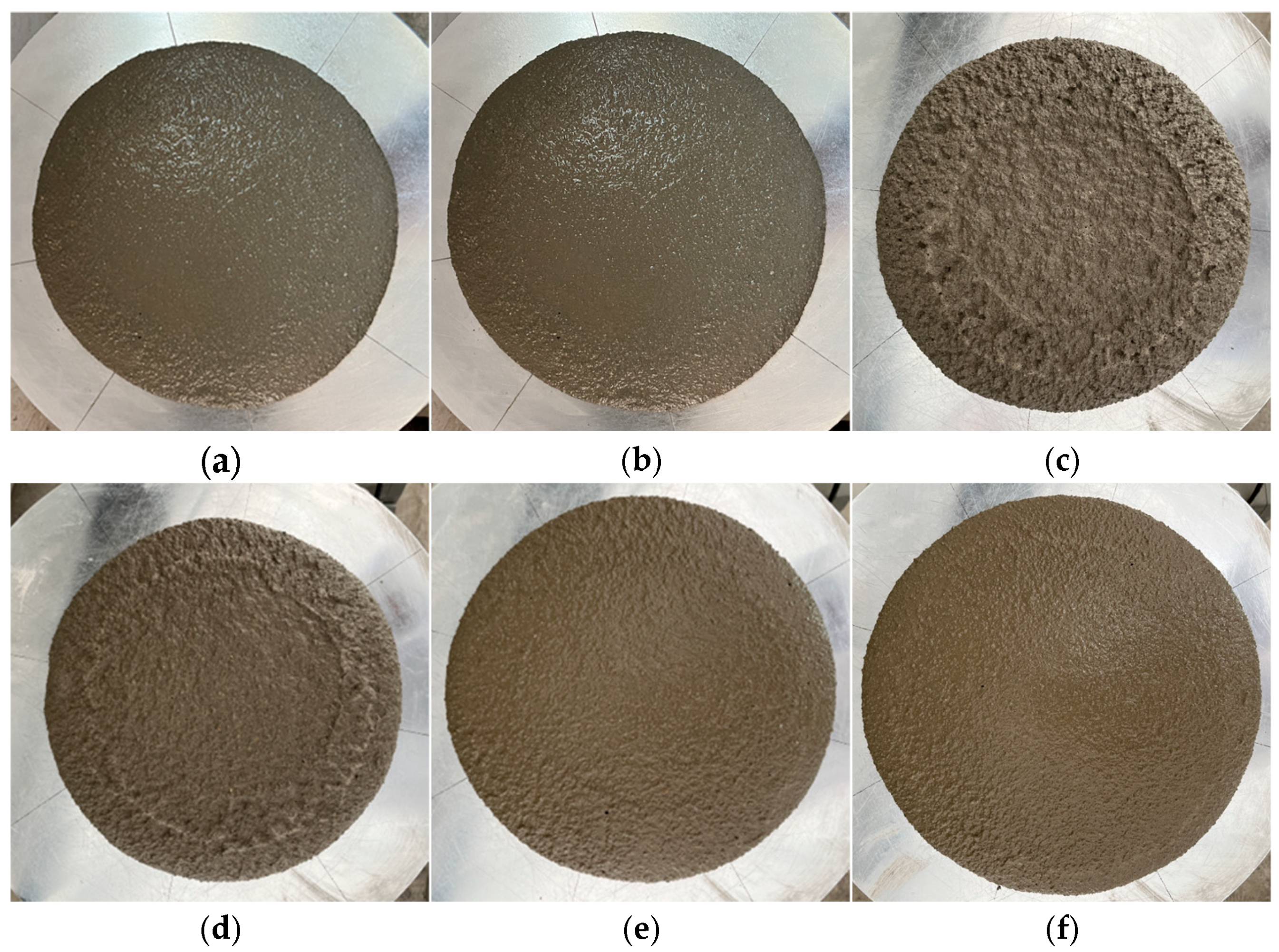
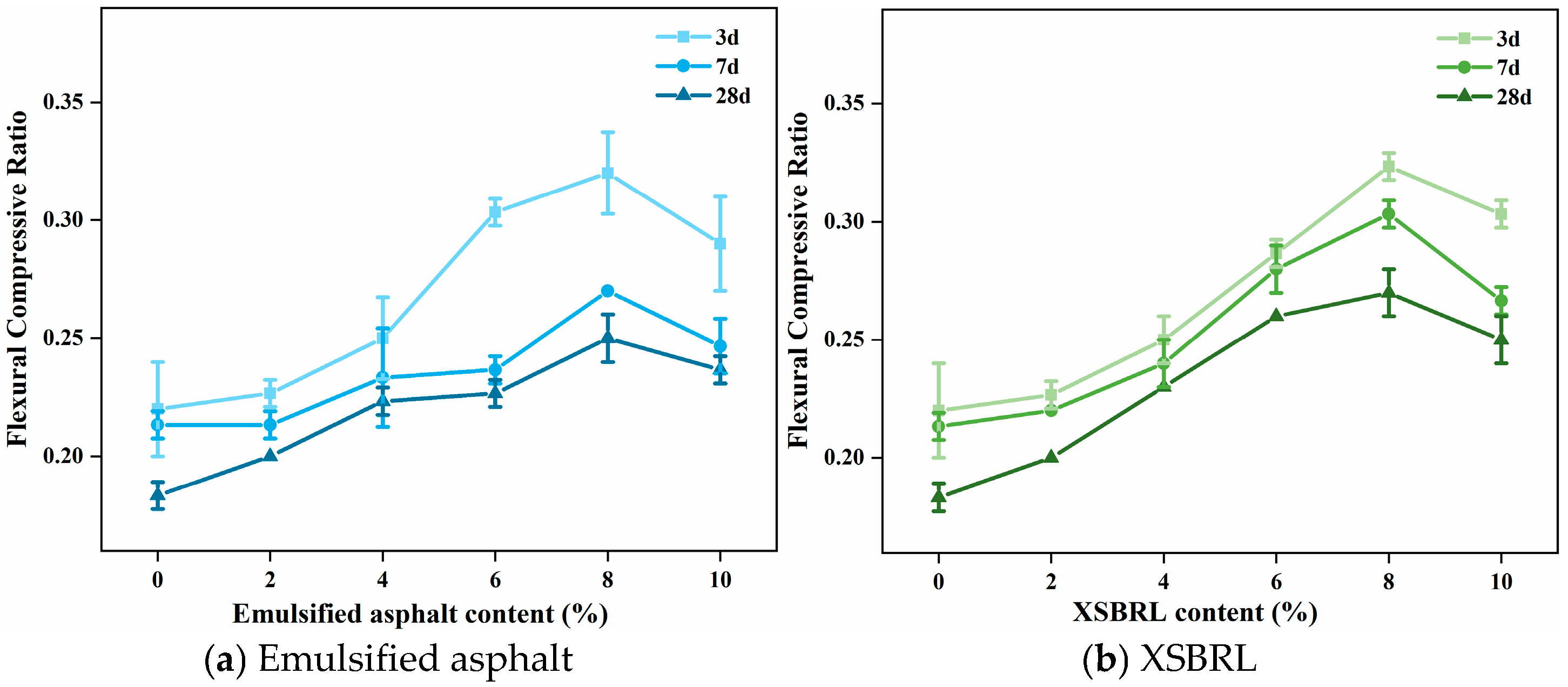
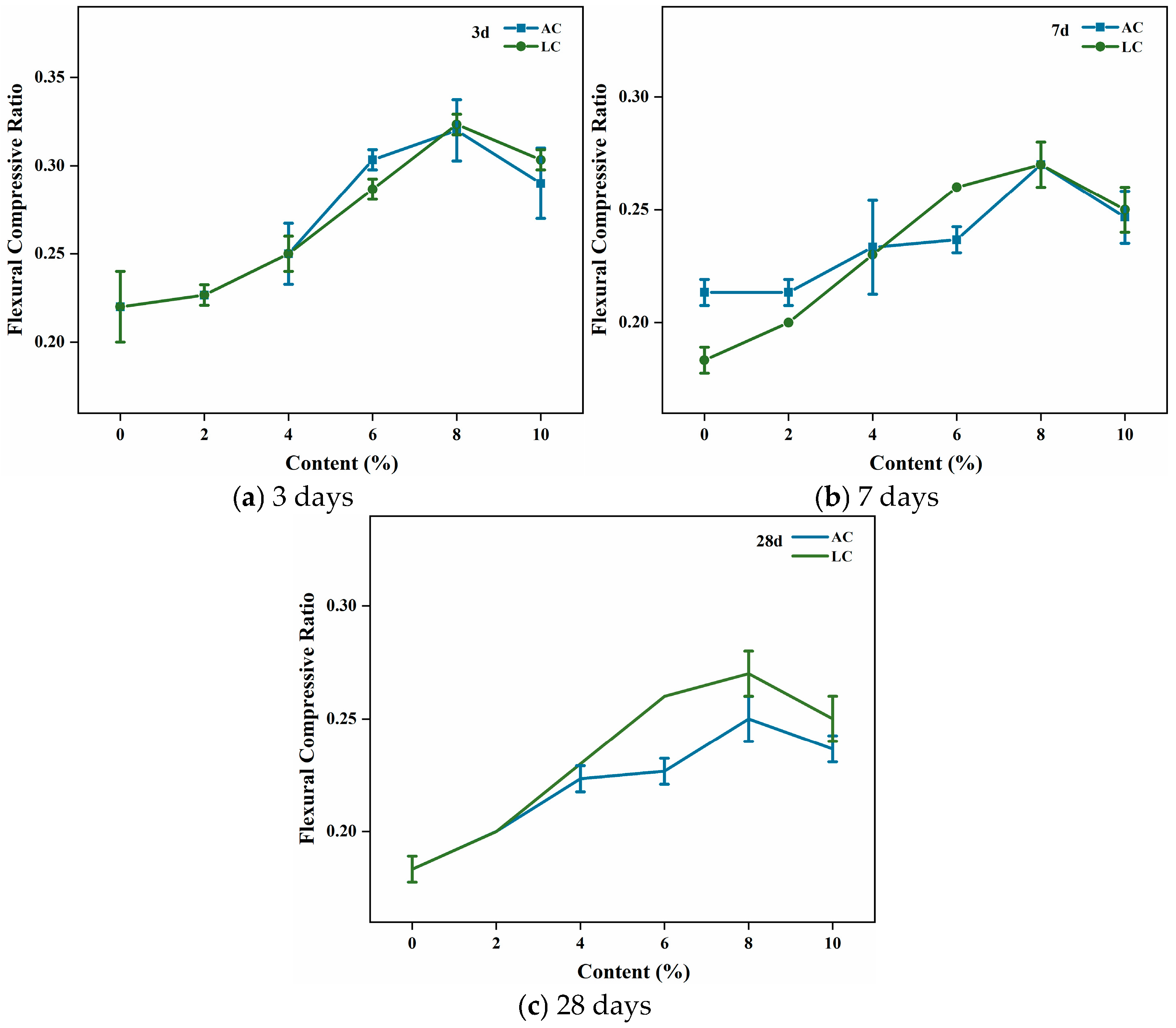
4.2. Flexibility Analysis
4.3. Physical Composition and Morphology Analysis
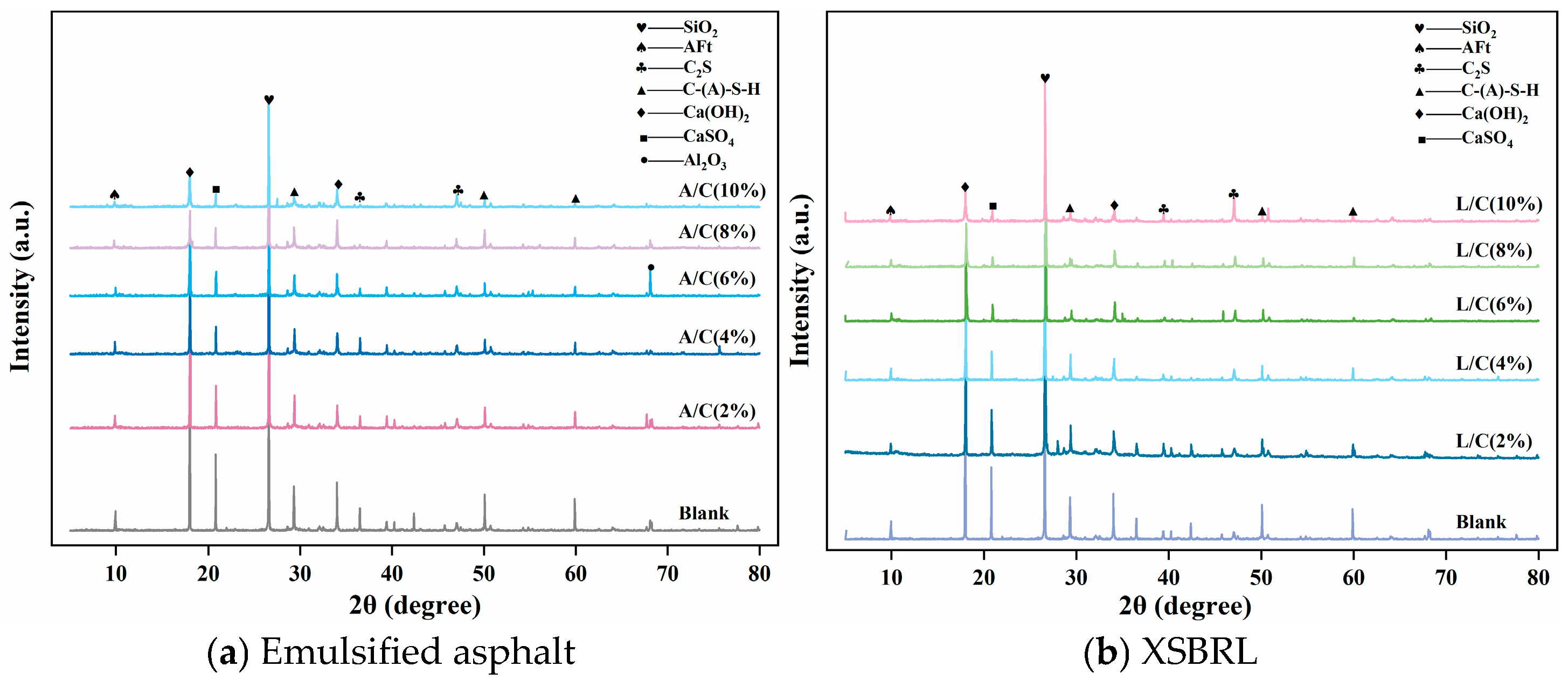
4.3.1. XRD Analysis
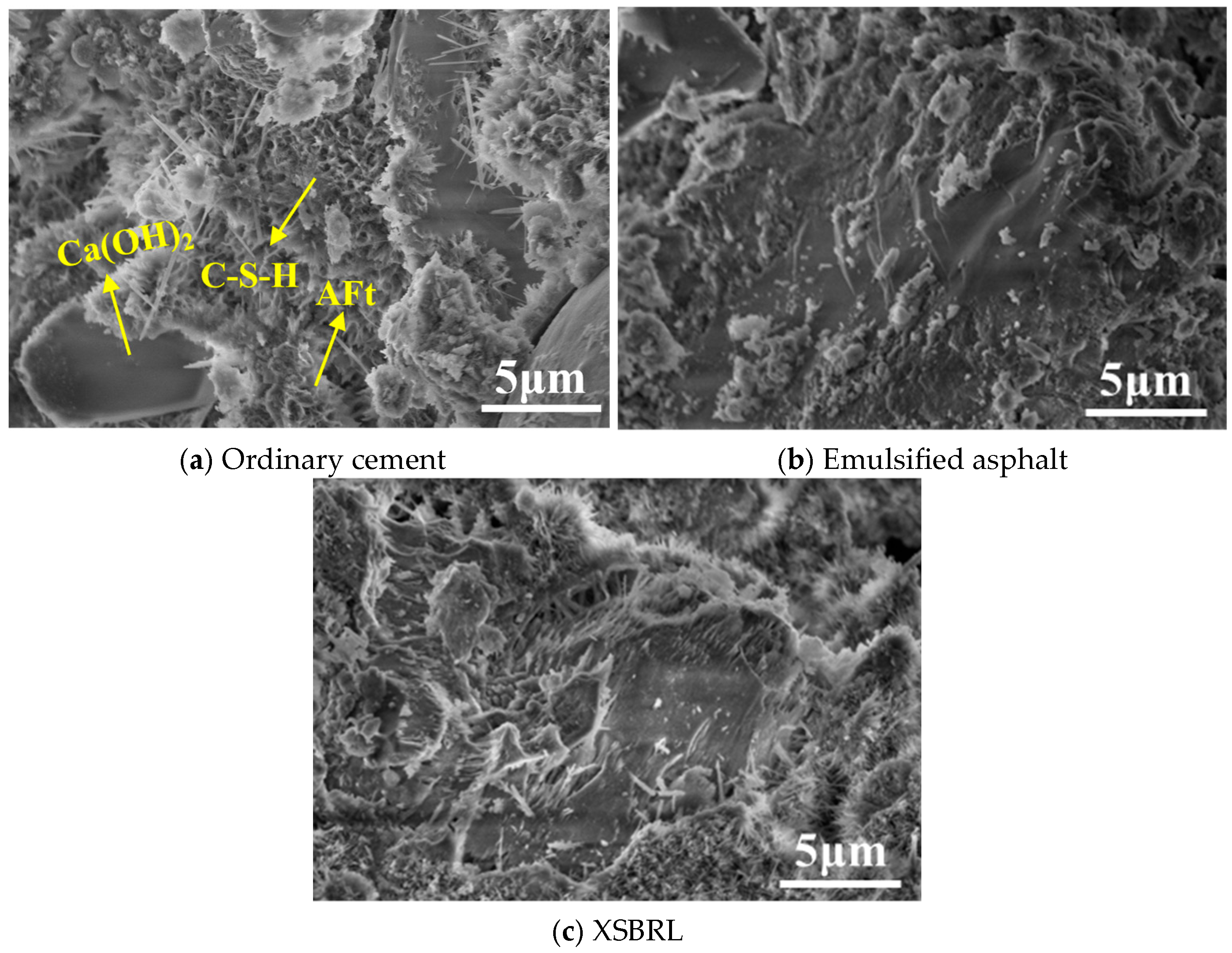
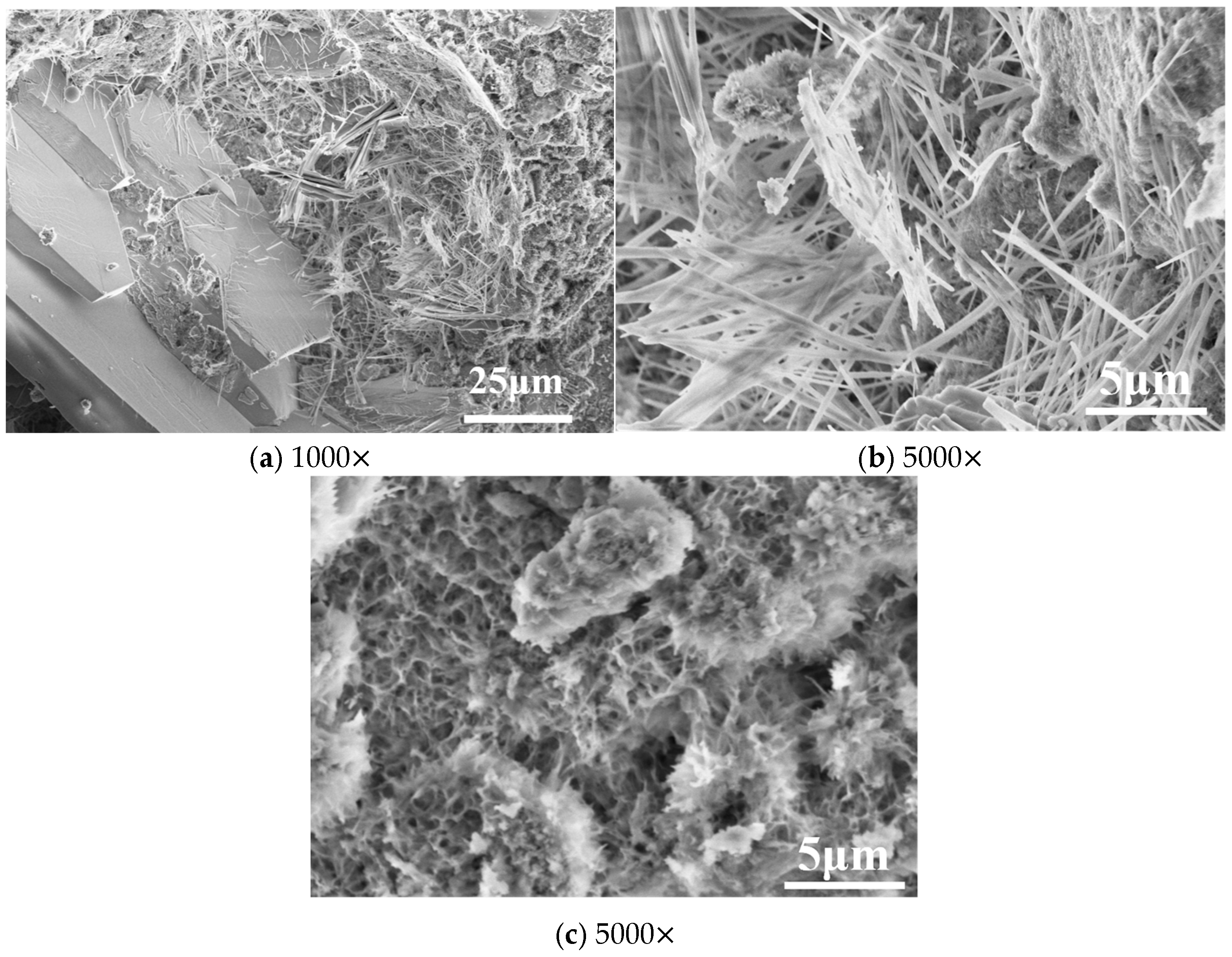
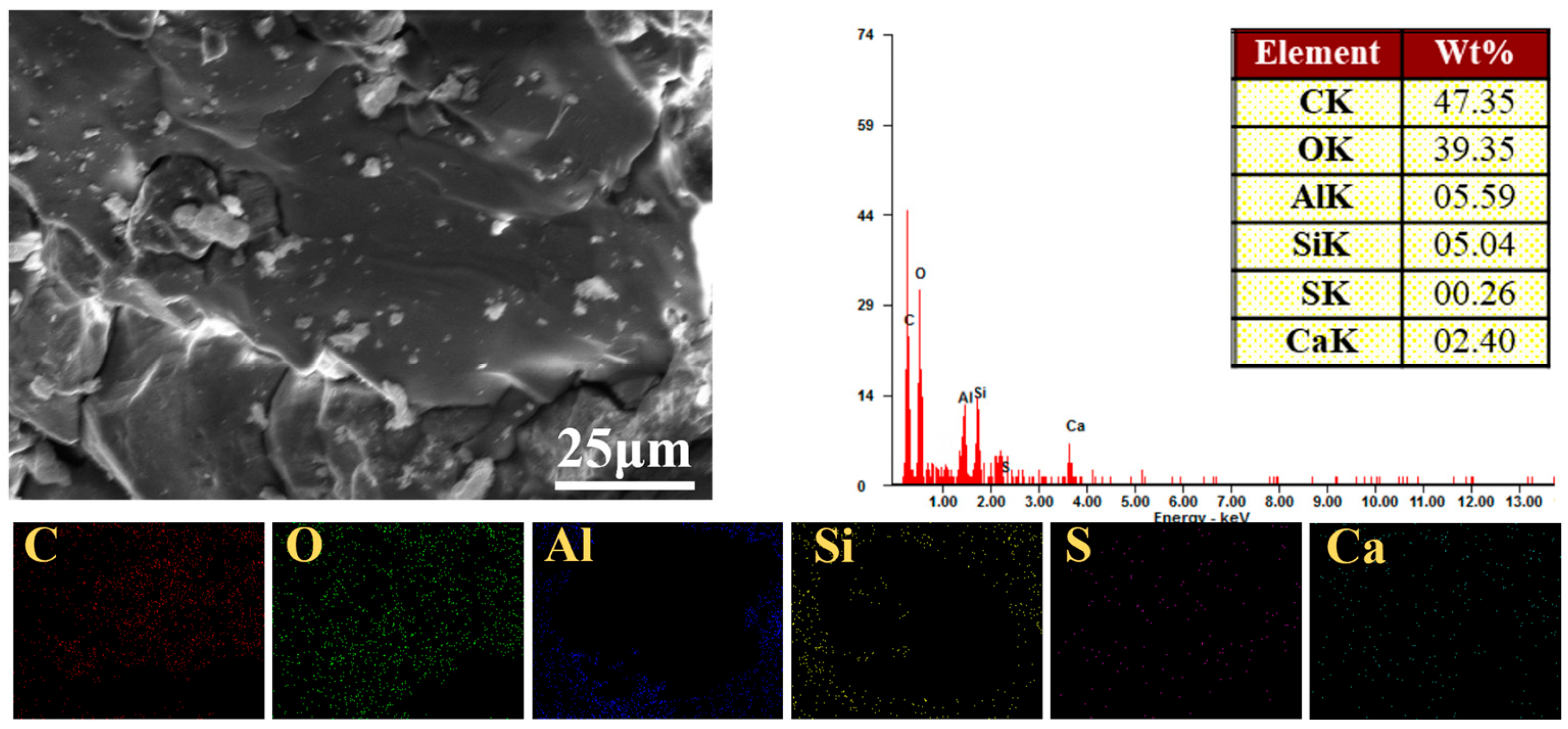
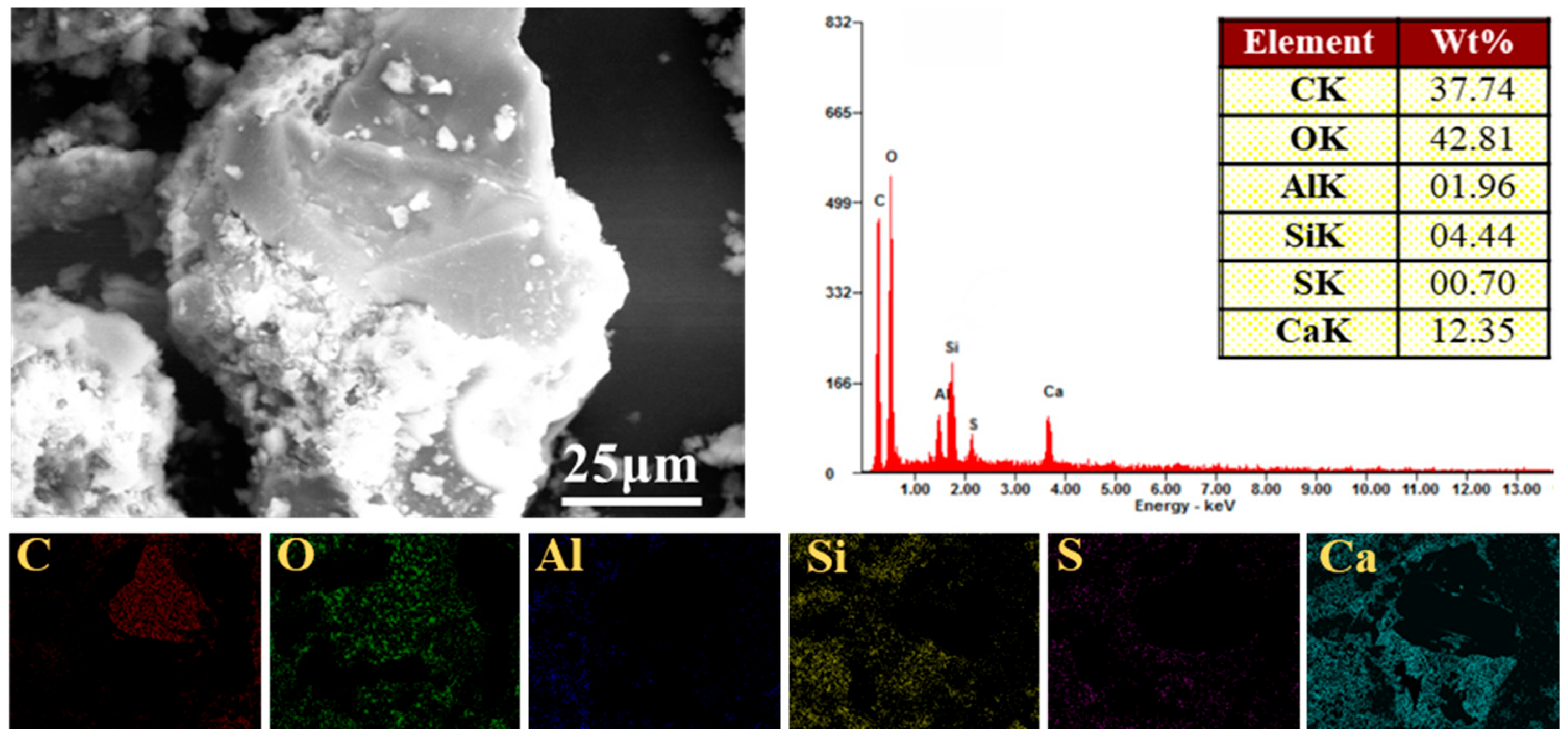
4.3.2. SEM Analysis
4.4. Mechanistic Study of Modified Cement Mortar
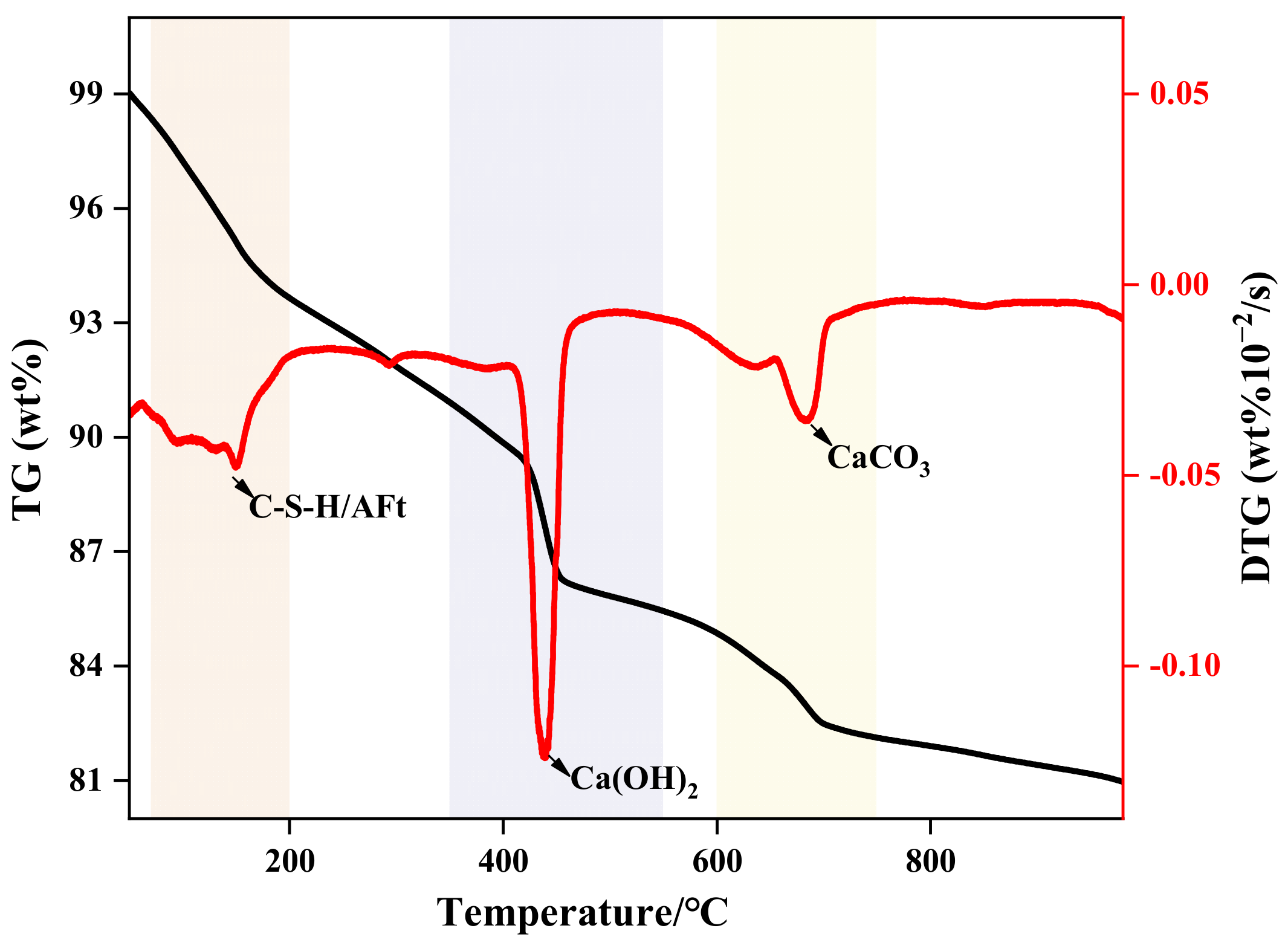
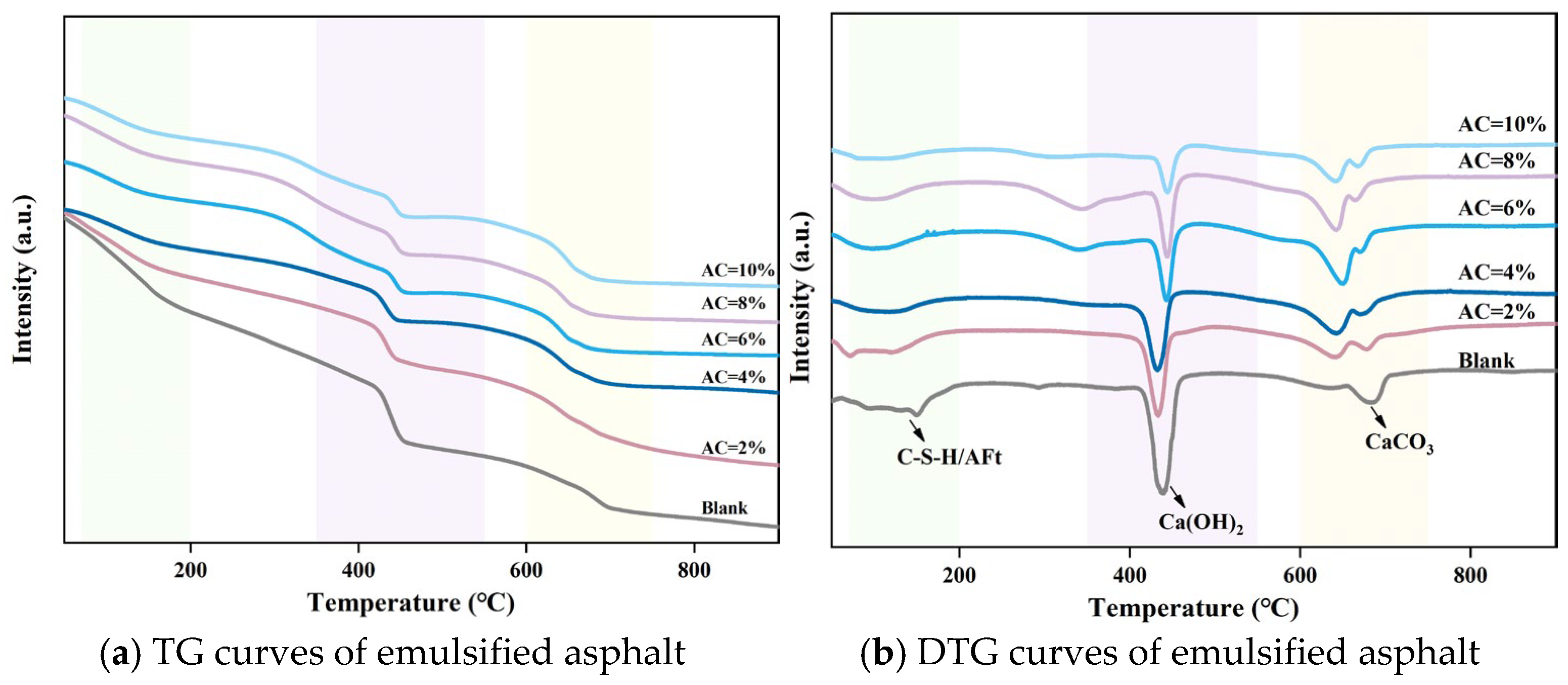
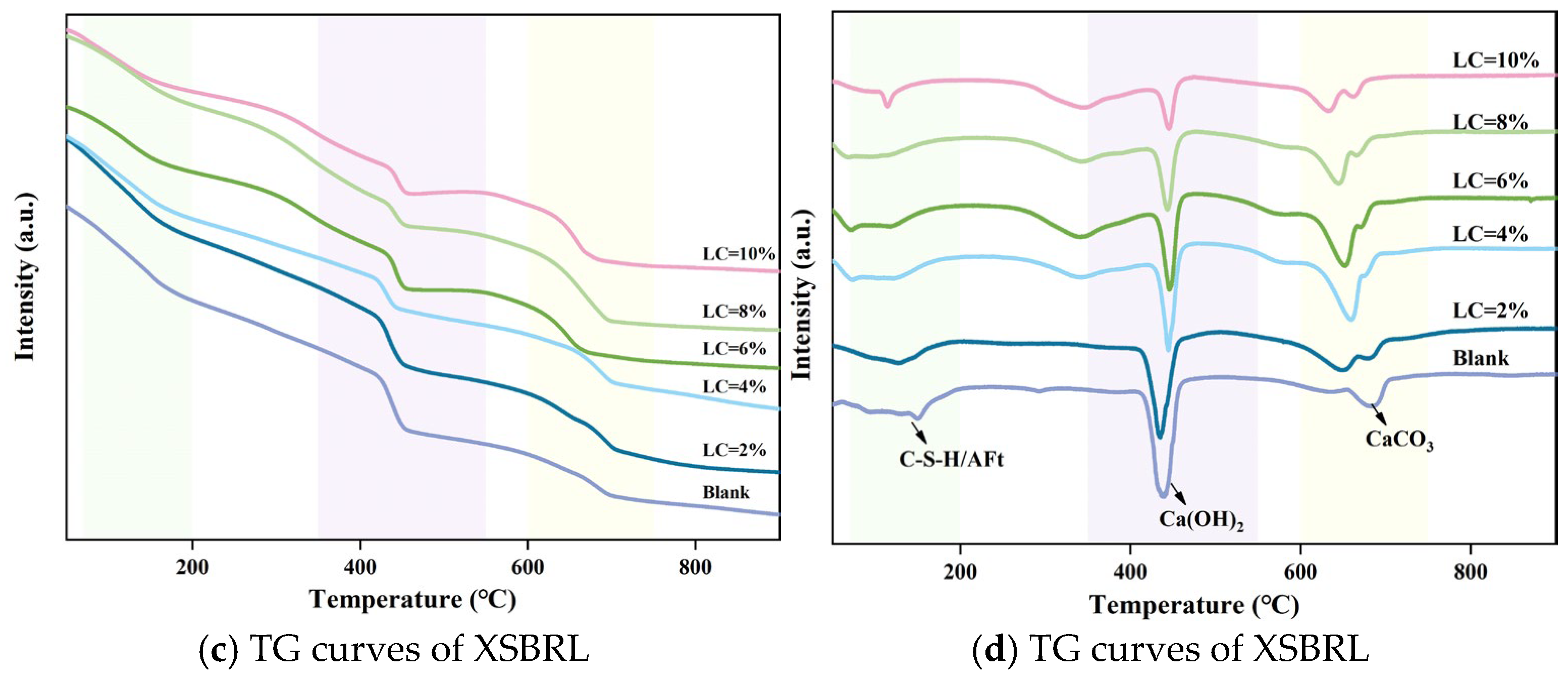
4.4.1. TG-DTG Analysis
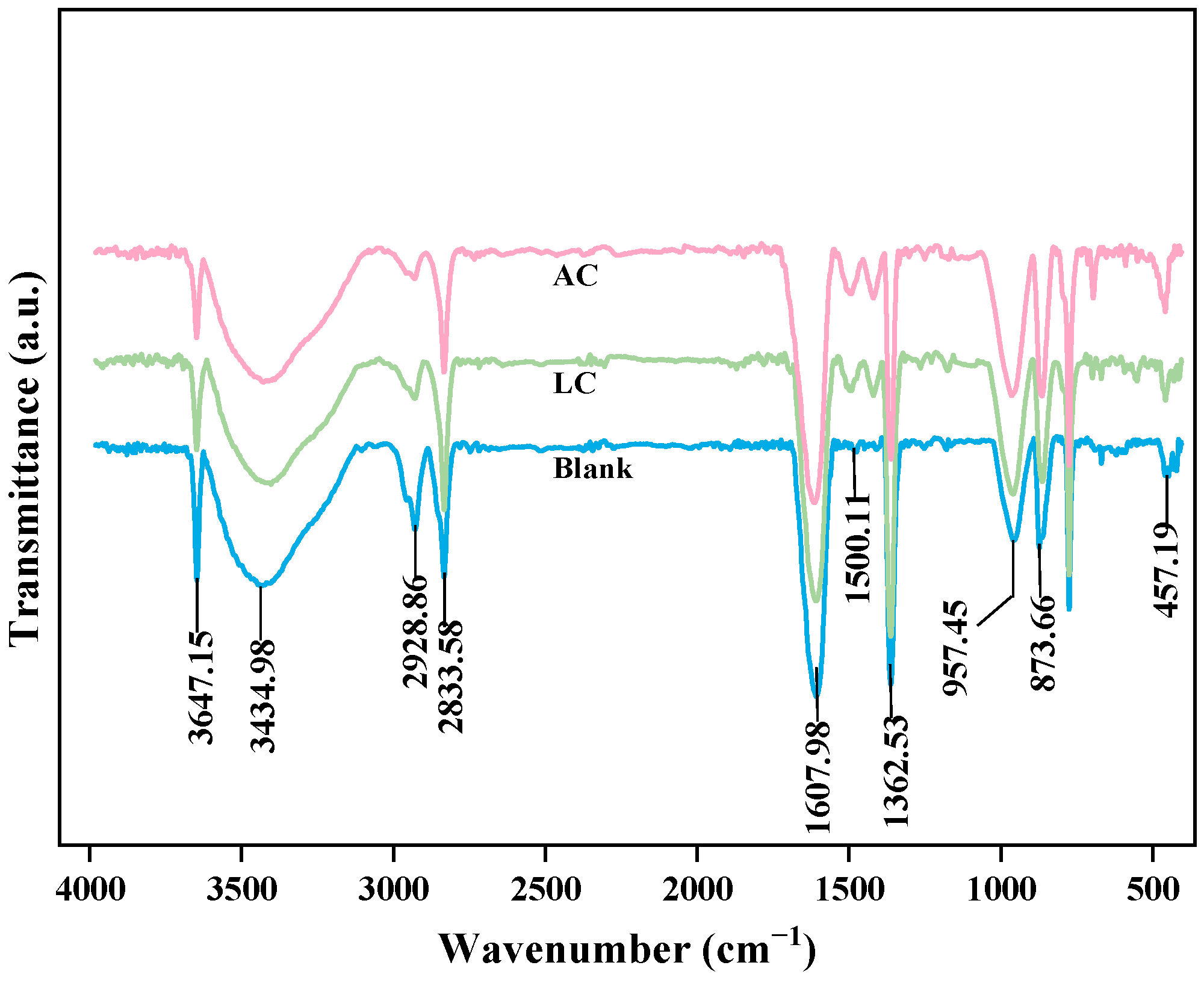
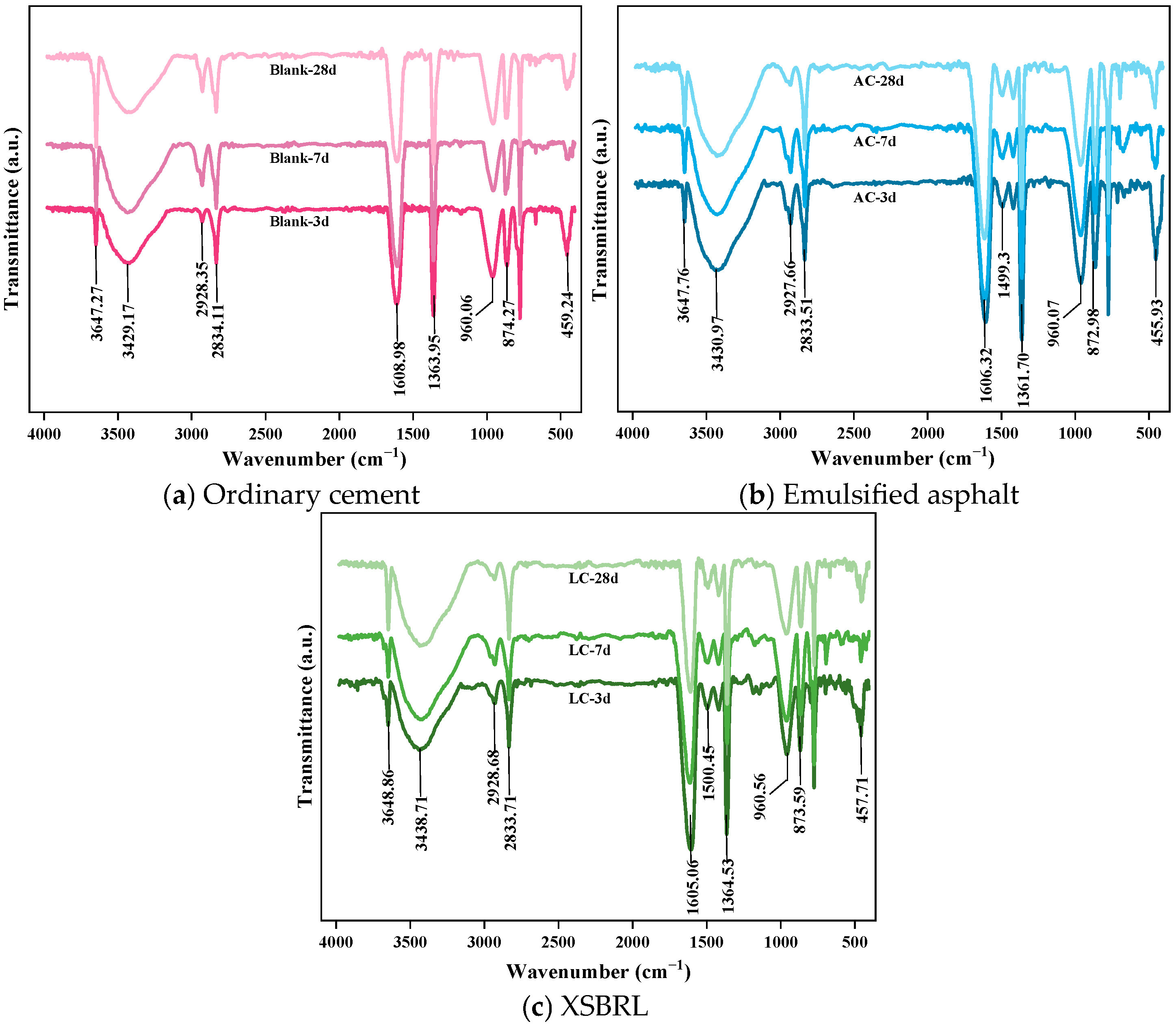
4.4.2. FTIR Modification Mechanism Analysis
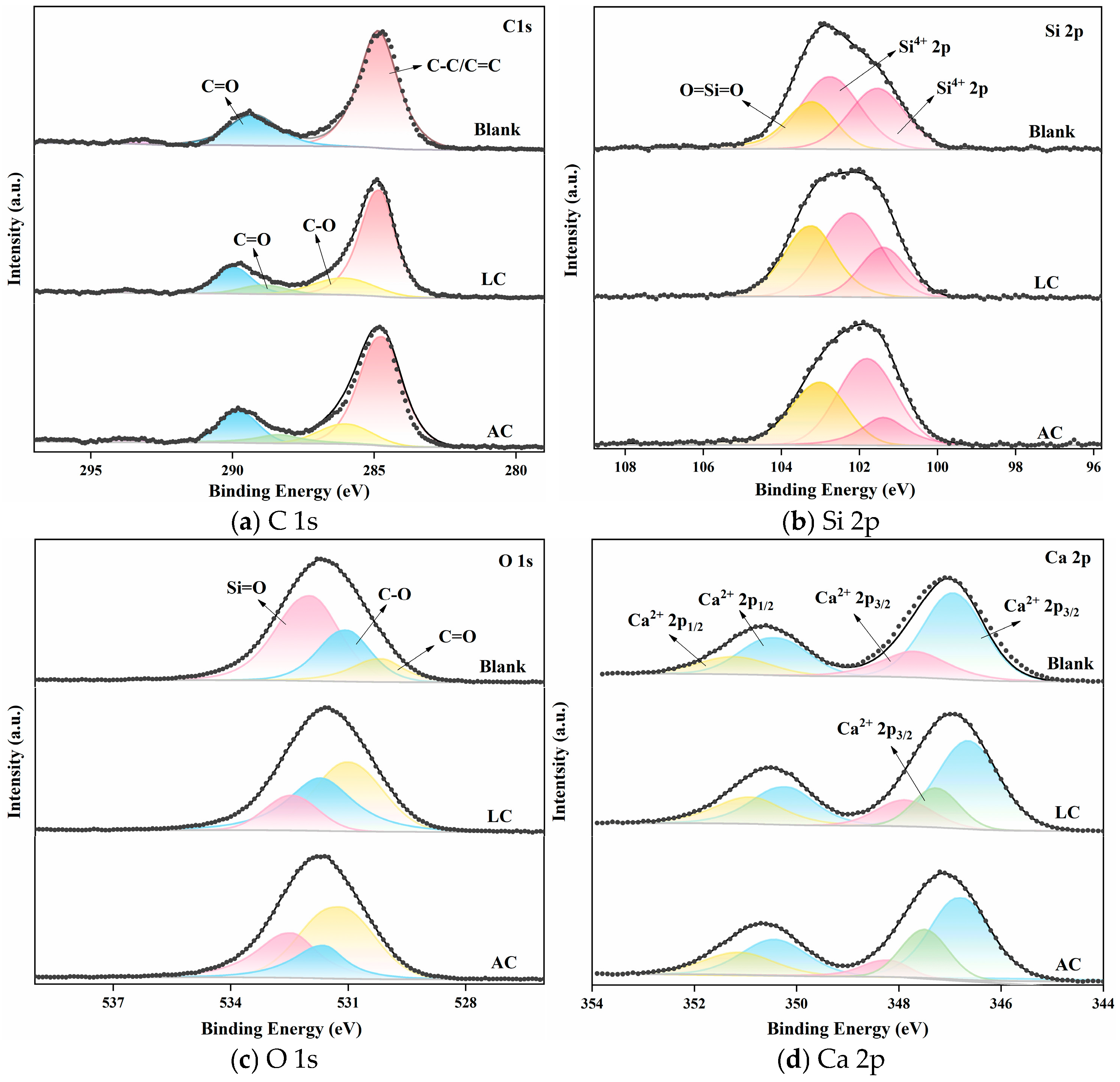
4.4.3. XPS Microscopic Interface Analysis
4.5. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The emulsified asphalt and XSBRL significantly enhance the flexibility of cement mortar through a novel modification strategy. The optimal flexibility was achieved at an 8% dosage of emulsified asphalt and XSBRL, exhibiting 38.9% and 50% improvements in performance compared to the ordinary cement mortar, respectively. The inclusion of emulsified asphalt and XSBRL in ordinary cement mortar significantly extends service life by enhancing crack resistance. Consequently, this minimizes the need for frequent repairs and replacements, thereby reducing overall lifecycle pollution, which encompasses energy consumption in production and waste generation during disposal.
- (2)
- Multi-technique analyses (including XRD, SEM, TG-DTG, FTIR, and XPS) revealed that excessive dosages of emulsified asphalt and XSBRL form polymer films on the surface of cement particles. These three-dimensional reticulated structures effectively mitigate the effects of external compressive and tensile stresses, thereby enhancing the flexibility of the modified mortar.
- (3)
- Both emulsified asphalt and XSBRL form asphalt film and latex film that weaken the inorganic ion stacking effect. The carbonyl groups in emulsified asphalt coordinate with Ca2+ in the cement hydration system, while the carboxyl groups in XSBRL chemically form flexible linkages with Ca(OH)2. This mechanism prevents the formation of brittle hydrates and weak chemical bonds.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Umar, H.A.; Zeng, X.; Lan, X.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H. A review on cement asphalt emulsion mortar composites, structural development, and performance. Materials 2021, 14, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ye, C.; Tan, H.; Liu, X. Potential application of Portland cement-sulfoaluminate cement system in precast concrete cured under ambient temperature. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 251, 118869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Chen, Y.; Pu, H.; Ju, F.; Zhang, K.; Li, Q.; Wu, P. Dynamic properties and fragmentation mechanism of cemented tailings backfill with various particle size distributions of aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130084. [Google Scholar]
- Narimane, Z.; Zedira, H.; Castro-Gomez, J.; Bezzazi, B.; Talah, A.; Benbouras, M.A. Evolution of durability and mechanical properties of ordinary portland cement concretes in sulphates attack. Eng. Rev. 2020, 40, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, Y.-K. Adhesion in tension of polymer cement mortar by curing conditions using polymer dispersions as cement modifier. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 242, 118134. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Hu, S.; Cao, S.; Wang, F. Enhancing the mechanical behaviour of concretes through polymer modification of the aggregate-cement paste interface. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 54, 104605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, R.; Lu, Q. Influence of polymer latex on the setting time, mechanical properties and durability of calcium sulfoaluminate cement mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 911–922. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Du, M.; Fang, H.; Shi, M.; Zhang, C.; Wang, F. Polymer-modified cement mortars: Their enhanced properties, applications, prospects, and challenges. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 124290. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Liu, G. Factors influencing the performance of cement emulsified asphalt mortar—A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 279, 122479. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, X.; Jiang, T.; Shimada, H.; Sasaoka, T.; Hamanaka, A. Influence of CO2 nano-bubble water concentration and curing time on the macroscopic and microscopic mechanical properties of cemented backfill materials. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111099. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, J.; Jiang, W.; Yuan, D.; Sha, A.; Huang, Y. Effect of styrene–butadiene rubber latex on the properties of modified porous cement-stabilised aggregate. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2018, 19, 1702–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Ma, G.; Li, Y. Preparation and Performance Improvement Mechanism Investigation of High-Performance Cementitious Grout Material for Semi-Flexible Pavement. Polymers 2023, 15, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Qiao, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, D. A review of grouting materials for pouring semi-flexible pavement: Materials, design and performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 379, 131235. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, M.S.; Sharma, S.K. A review of mechanical and durability properties and microstructure of semi-flexible pavement. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2024, 9, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Shen, S.; Goodwin, R.D.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J. Performance characterization of semi-flexible composite mixture. Materials 2020, 13, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xiong, H.; Ren, Q.; Zheng, X.; Wu, L. Experimental study and performance characterization of semi-flexible pavements. Coatings 2022, 12, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Songqiang, C.; Jian, Z.; Xi, W.; Zining, C. Research on innovative preparation and performance of semi flexible pavement materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03050. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Wang, H. Analysis of the grouting fullness and road performance of hot-recycled semi-flexible pavement materials. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02755. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, J.; Hong, J. Investigation on reinforcing mechanisms of semi-flexible pavement material through micromechanical model. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 198, 732–741. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.; Li, X.-G.; Wang, P.-M. Influence of polymer on cement hydration in SBR-modified cement pastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1744–1751. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Wang, S.; Zeng, L.; Peng, X. Effect of styrene-butadiene rubber latex on the rheological behavior and pore structure of cement paste. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 163, 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Ilango, N.K.; Gujar, P.; Nagesh, A.K.; Alex, A.; Ghosh, P. Interfacial adhesion mechanism between organic polymer coating and hydrating cement paste. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 115, 103856. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, R.; Yao, H.; Farhan, S.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Z.; Du, C.; Jiang, H. Research on the mechanism of polymer latex modified cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 111, 710–718. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Yang, L.; Gong, H.; Zhou, Q.; He, L.; Chen, Q.; Cen, C.; Zhou, M. Investigating on the composite modification process and pavement performance of emulsified asphalt by styrene-butadiene latex/waterborne epoxy resin. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 487, 142134. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, S.M.; Ransinchung, G.D.R.N. Strength and permeation characteristics of cement mortar with Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement Aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 700–706. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Hong, B.; Lu, G.; Li, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, D. Carboxylated styrene-butadiene latex (XSB) in asphalt modification towards cleaner production and enhanced performance of pavement in cold regions. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 372, 133653. [Google Scholar]
- Nasir, H.; Kaur, M.; Faheem, S. A statistical Review on the Usage of Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement waste as a recyclable material. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1327, 012021. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, M.; Tran, N.Q.; Suddeepong, A.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Mobkrathok, M.; Chinkulkijniwat, A.; Arulrajah, A. Improved fatigue properties of cement-stabilized recycled materials–Lateritic soil using natural rubber latex for sustainable pavement applications. Transp. Geotech. 2023, 40, 100959. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 17671-2021; Method of Testing Cements—Determinationof Strength. China Building Materials Federation: Beijing, China, 2021. Available online: https://std.samr.gov.cn/gb/search/gbDetailed?id=71F772D798CCD3A7E05397BE0A0AB82A (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- GB/T 14684-2022; Sand for Construction. China Building Materials Federation: Beijing, China, 2022. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=BFD788F1742125DC8E9922E38F6167BD (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- GB/T 2419-2005; Test Method for Fluidity of Cement Mortar. China Building Materials Federation: Beijing, China, 2005. Available online: https://openstd.samr.gov.cn/bzgk/gb/newGbInfo?hcno=596BCFED07711DA50BEE68692C2F6819 (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Hua, L.; Liu, Z.; Mao, Z.; Hong, J. Influence of cationic asphalt emulsion on the water transportation behavior and durability of cement mortar. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2022, 17, e01548. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Morlor, C.S.; Leung, C.; Wang, H. Mechanical properties and fractal analysis of cement mortar incorporating styrene-butadiene rubber latex and carboxylated MWCNTs. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125175. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Yao, H.; Zhong, F.; Jiang, M. Hardened properties and microstructure change of sulphoaluminate cement modified with different doses of styrene-butadiene rubber latex. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 400, 132618. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.; Zhu, S.; Quan, X.; Peng, Y. Effect of phenyl functional group on the demulsification process of dodecyl anion emulsified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 354, 129196. [Google Scholar]
- Gastaldi, D.; Paul, G.; Marchese, L.; Irico, S.; Boccaleri, E.; Mutke, S.; Buzzi, L.; Canonico, F. Hydration products in sulfoaluminate cements: Evaluation of amorphous phases by XRD/solid-state NMR. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 90, 162–173. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, H.; Radlińska, A. Quantitative analysis of phase assemblage and chemical shrinkage of alkali-activated slag. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2016, 14, 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Mao, Z.; Xu, G.; Chang, H.; Hong, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z. Study on the early cement hydration process in the presence of cationic asphalt emulsion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 261, 120025. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Zheng, M.; Fan, X.; Li, H.; Wang, F.; Lin, X. Properties and mechanism of waterborne epoxy resin-SBR composite modified emulsified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 122059. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, L.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Que, Y. Interaction between cement and asphalt emulsion and its influences on asphalt emulsion demulsification, cement hydration and rheology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 329, 127220. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Mi, T.; Ding, X.; Liu, W.; Dong, B.; Dong, Z.; Tang, L.; Xing, F. Assessment of compositional changes of carbonated cement pastes subjected to high temperatures using in-situ Raman mapping and XPS. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103454. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Dalbehera, M.M.; Rawat, A.; Sharma, P. Carbonation study and determination of cement to sand ratio in hardened cement mortar by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Surf. Interface Anal. 2020, 52, 603–610. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, J.; Tong, X.; Cheng, Y. High-performance semi-flexible pavement coating material with the microscopic interface Optimization. Coatings 2020, 10, 268. [Google Scholar]










| Composition | SiO2 | Al2O3 | CaO | Fe2O3 | MgO | K2O | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content | 25.70 | 4.88 | 60.41 | 3.74 | 0.61 | 0.78 | 3.10 |
| Fluidity/mm | Flexural Strength/MPa | Compressive Strength/MPa | Setting Time/min | Soundness | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Days | 28 Days | 3 Days | 28 Days | Initial | Final | ||
| 199.5 | 5.3 | 9.0 | 28.5 | 50.2 | 158 | 201 | Qualified |
| Emulsified Asphalt | Evaporated Residue of Emulsified Asphalt | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viscosity/s | Residual content/% | Solubility/% | Needle penetration/DMM | Ductility/cm |
| 8–20 | 50 | 97.5 | 45–150 | 40 |
| Viscosity /MPa·s | Solid Content /% | pH | Density/ (g/cm3) | Mean Grain size/nm | Glass State Temperature/°C | Surface Tension/ (mN/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35–150 | 50–52 | 7.8–10 | 1.01 | 150 | 13 | 30–48 |
| Cement Content (%) | Cement Quality (g) | Water (g) | Emulsified Asphalt or XSBRL Content (%) | Emulsified Asphalt or XSBRL Quality (g) | Standard Sand (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 33 | 450 | 225 | 0 | 0 | 1350 |
| 2 | 4.5 | ||||
| 4 | 9 | ||||
| 6 | 11.25 | ||||
| 8 | 13.5 | ||||
| 10 | 18 |
| Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p-Value | F Crit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intergroup | 0.026317 | 5 | 0.005263 | 21.53182 | 0.00 | 3.105875 |
| Within a group | 0.002933 | 12 | 0.000244 | |||
| Total | 0.02925 | 17 |
| Source of Variation | SS | df | MS | F | p-Value | F Crit |
| Intergroup | 0.026983 | 5 | 0.005396 | 51.126315 | 0.00 | 3.105875 |
| Within a group | 0.001266 | 12 | 0.000105 | |||
| Total | 0.02825 | 17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, W.; Huang, Y.; He, Y.; Wei, H.; Bai, R.; Li, H.; Cui, Q.; Li, S. Investigation of Flexibility Enhancement Mechanisms and Microstructural Characteristics in Emulsified Asphalt and Latex-Modified Cement. Sustainability 2025, 17, 6317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146317
Liu W, Huang Y, He Y, Wei H, Bai R, Li H, Cui Q, Li S. Investigation of Flexibility Enhancement Mechanisms and Microstructural Characteristics in Emulsified Asphalt and Latex-Modified Cement. Sustainability. 2025; 17(14):6317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146317
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Wen, Yong Huang, Yulin He, Hanyu Wei, Ruyun Bai, Huan Li, Qiushuang Cui, and Sining Li. 2025. "Investigation of Flexibility Enhancement Mechanisms and Microstructural Characteristics in Emulsified Asphalt and Latex-Modified Cement" Sustainability 17, no. 14: 6317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146317
APA StyleLiu, W., Huang, Y., He, Y., Wei, H., Bai, R., Li, H., Cui, Q., & Li, S. (2025). Investigation of Flexibility Enhancement Mechanisms and Microstructural Characteristics in Emulsified Asphalt and Latex-Modified Cement. Sustainability, 17(14), 6317. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17146317







