Agricultural Productivity of Solar Pump and Water Harvesting Irrigation Technologies and Their Impacts on Smallholder Farmers’ Income and Food Security: Evidence from Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Description
2.2. Sampling and Data Collection
2.3. Variables of the Study
2.4. Econometric Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
3.2. Productivity, Net Water Value, Benefit–Cost, and Adequacy of Water for Solar Pump Irrigation Systems
3.2.1. Source of Irrigation Water and Extent of Irrigated Crops Using Solar Pumps
3.2.2. Water and Land Productivity
3.2.3. Net Value of Irrigation Water
3.2.4. Benefit–Cost Analysis by Crops and Financing Scheme
3.2.5. Benefit–Cost and Net Water Value per Technology Bundles
3.2.6. Adequacy of Water Supplies
3.3. Productivity, Adequacy, and Economic Indicators of Irrigation Using Water Harvesting Ponds
3.3.1. Adequacy and Productivity of Irrigation Water Supplies from Ponds
3.3.2. Net Water Value (NWV)
3.3.3. Benefit–Cost Analysis
3.4. Factors Influencing the Adoption of Solar Pump and Water Harvesting Pond-Based Irrigation
3.5. Welfare Impacts of Solar Pump and Water Harvesting Pond Irrigation
3.6. Challenges and Interventions for Solar Pump and Water Harvesting Pond-Based Irrigation Systems
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Otoo, M.; Lefore, N.; Schmitter, P.; Barron, J.; Gebregziabher, G. Business Model Scenarios and Suitability: Smallholder Solar Pump-Based Irrigation in Ethiopia. Agricultural Water Management–Making a Business Case for Smallholders; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2018; Volume 172. [Google Scholar]
- Haile, G.G.; Kasa, A.K. Irrigation in Ethiopia: A review. Acad. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 3, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awulachew, S.B. Irrigation potential in Ethiopia: Constraints and opportunities for enhancing the system. IWMI Gates Open Res. 2019, 3, 22. Available online: https://gatesopenresearch.org/documents/3-22/pdf (accessed on 10 March 2024).
- Gebul, M.A. Trend, status, and challenges of irrigation development in Ethiopia—A review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondimagegnhu, B.A.; Bogale, B.A. Small-scale irrigation and its effect on food security of rural households in North-West Ethiopia: A comparative analysis. Ethiop. J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 13, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizi, A.P.; Ashrafzadeh, A.; Ramezani, A. A financial comparative study of solar and regular irrigation pumps: Case studies in eastern and southern Iran. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Closas, A.; Rap, E. Solar-based groundwater pumping for irrigation: Sustainability, policies, and limitations. Energy Policy 2017, 104, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qoaider, L.; Steinbrecht, D. Photovoltaic systems: A cost competitive option to supply energy to off-grid agricultural communities in arid regions. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazed, S.M.; Hughes, B.R.; O’Connor, D.; Calautit, J.K. A review of sustainable solar irrigation systems for Sub-Saharan Africa. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1206–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamine, D.I.O.P. Technical and economic feasibility of solar irrigation pumping system: A review. Knowl.-Based Eng. Sci. 2020, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Falchetta, G.; Semeria, F.; Tuninetti, M.; Giordano, V.; Pachauri, S.; Byers, E. Solar irrigation in sub-Saharan Africa: Economic feasibility and development potential. Environ. Res. Lett. 2023, 18, 094044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Ringler, C.; Mondal, M.A.H. Solar or diesel: A comparison of costs for groundwater-fed irrigation in sub-Saharan Africa under two energy solutions. Earth’s Future 2021, 9, e2020EF001611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefore, N.; Closas, A.; Schmitter, P. Solar for all: A framework to deliver inclusive and environmentally sustainable solar irrigation for smallholder agriculture. Energy Policy 2021, 154, 112313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebregziabher, G. Water lifting irrigation technology adoption in Ethiopia: Challenges and opportunities. Gates Open Res. 2019, 3, 952. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems: A clean-energy, low-emission option for irrigation development and modernization. In Practice Brief Climate-Smart Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Burney, J.; Woltering, L.; Burke, M.; Naylor, R.; Pasternak, D. Solar-powered drip irrigation enhances food security in the Sudano–Sahel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1848–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendes, D.M.; Paglietti, L.; Jackson, D.; Chizhuka, F. Zambia: Irrigation Market Brief; Country Highlights, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Magrath, J. Transforming Lives in Zimbabwe: Rural Sustainable Energy Development Project; Oxfam Case Study; Oxfam GB: Oxford, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nigussie, L.; Lefore, N.; Schmitter, P.S.; Nicol, A. Gender and Water Technologies: Water Lifting for Irrigation and Multiple Purposes in Ethiopia; International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI): Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2017; Available online: https://cgspace.cgiar.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/7cd69a53-2d4a-415d-a0e6-d03af8615a36/content (accessed on 12 May 2024).
- Berhanu, H.; Bogalea, F.; Abebe, A.; Manaye, M. An Economic Feasibility Study of Solar and Diesel Water Pumping Systems for Irrigation in Ethiopia: A Case Study of Kombolcha, Wollo. Abyssinia J. Eng. Comput. 2022, 2, 28–41. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitter, P.; Kibret, K.S.; Lefore, N.; Barron, J. Suitability mapping framework for solar photovoltaic pumps for smallholder farmers in sub-Saharan Africa. Appl. Geogr. 2018, 94, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maru, H.; Haileslassie, A.; Zeleke, T. Impacts of small-scale irrigation on farmers’ livelihood: Evidence from the drought prone areas of upper Awash sub-basin, Ethiopia. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haile, B.; Mekonnen, D.; Choufani, J.; Ringler, C.; Bryan, E. Hierarchical modelling of small-scale irrigation: Constraints and opportunities for adoption in Sub-Saharan Africa. Water Econ. Policy 2022, 8, 2250005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amede, T. Technical and institutional attributes constraining the performance of small-scale irrigation in Ethiopia. Water Resour. Rural. Dev. 2015, 6, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowing, J.; Walker, D.; Parkin, G.; Forsythe, N.; Haile, A.T.; Ayenew, D.A. Can shallow groundwater sustain small-scale irrigated agriculture in sub-Saharan Africa? Evidence from NW Ethiopia. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2020, 10, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, A. Solar Irrigation Can Improve Food Security and Prosperity, Says UN Agency; Climate Action: Rome, Italy, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Amha, R.; Gebremedhin, B.; ILRI, A.A. Impact Assessment of Rainwater Harvesting Ponds: The Case of Alaba Woreda, Ethiopia; IWMI: Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2008; Available online: https://publications.iwmi.org/pdf/H044078.pdf (accessed on 3 May 2024).
- Teshome, A.; Adgo, E.; Mati, B. Impact of water harvesting ponds on household incomes and rural livelihoods in Minjar Shenkora district of Ethiopia. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2010, 10, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengsdijk, H.; Van Driel, J.; Haile, A.; Argaw, M.; Jansen, H. Competing Claims for Water in the Central Rift Valley of Ethiopia: Global Drivers and Local Opportunities. 2010. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Competing-claims-for-water-in-the-Central-Rift-of-Hengsdijk-Driel/e1bab16c3f561772f1af4094270edc2fe45b7ffd (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Hunde, N.F. Opportunity, problems and production status of vegetables in Ethiopia: A review. J. Plant Sci. Res. 2017, 4, 172. [Google Scholar]
- Debelie, H.D.; Clouting, H. Case Analysis of Public Participation in Environmental Impact Assessment of Irrigation Water Use in Central Rift Valley, Ethiopia. 2014. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329416633_Case_analysis_of_public_participation_in_environmental_impact_assessment_of_irrigation_water_use_in_Central_Rift_Valley_Ethiopia (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Ullah, I.; Khan, N.; Dai, Y.; Hamza, A. Does Solar-Powered Irrigation System Usage Increase the Technical Efficiency of Crop Production? New Insights from Rural Areas. Energie 2023, 16, 6641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getaneh, Y.; Alemu, A.; Ganewo, Z.; Haile, A. Food security status and determinants in North-Eastern rift valley of Ethiopia. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 8, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adem, M.; Cochrane, L.; Miceikienė, A.; Skominas, R.; Azadi, H. The dynamics of multidimensional food security in rural Ethiopia. Glob. Food Secur. 2023, 39, 100725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, J.L.; Ruel, M.; Frongillo, E.A.; Harris, J.; Ballard, T.J. Measuring the Food Access Dimension of Food Security: A Critical Review and Mapping of Indicators. Food Nutr. Bull. 2015, 36, 167–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habtewold, T.M. Impact of climate-smart agricultural technology on multidimensional poverty in rural Ethiopia. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1021–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INDDEP Project. Data4Diets: Building Blocks for Diet-Related Food Security Analysis; Tufts University: Boston, MA, USA, 2020; Available online: https://inddex.nutrition.tufts.edu/data4diets (accessed on 19 September 2020).
- Eicher-Miller, H.A.; Graves, L.; McGowan, B.; Mayfield, B.J.; Connolly, B.A.; Stevens, W.; Abbott, A. A Scoping Review of Household Factors Contributing to Dietary Quality and Food Security in Low-Income Households with School-Age Children in the United States. Adv. Nutr. 2023, 14, 914–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jateno, W.; Alemu, B.A.; Shete, M. Household dietary diversity across regions in Ethiopia: Evidence from Ethiopian socio-economic survey data. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.; Oweis, T.; Steduto, P.; Bindraban, P.; Hanjra, M.A.; Kijne, J. Improving agricultural water productivity: Between optimism and caution. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M. CROPWAT: A Computer Program for Irrigation Planning and Management; FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper No. 46; Food & Agriculture Org: Rome, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, D.; Smith, M.; El-Askari, K. CropWat for Windows: User Guide; Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Adetoro, A.A.; Ngidi, M.S.C.; Danso-Abbeam, G.; Ojo, T.O.; Ogundeji, A.A. Impact of irrigation on welfare and vulnerability to poverty in South African farming households. Sci. Afr. 2022, 16, e01177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setsoafia, E.D.; Ma, W.; Renwick, A. Effects of sustainable agricultural practices on farm income and food security in northern Ghana. Agric. Food Econ. 2022, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, W.; Tirivayi, N. The impacts of postharvest storage innovations on food security and welfare in Ethiopia. Food Policy 2018, 75, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjin, K.C.; Goundan, A.; Henning, C.H.; Sarr, S. Estimating the Impact of Agricultural Cooperatives in Senegal: Propensity Score Matching and Endogenous Switching Regression Analysis; Working Papers of Agricultural Policy, No. WP2020-10; Kiel University, Department of Agricultural Economics, Chair of Agricultural Policy: Kiel, Germany, 2020; Available online: https://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:gbv:8:3-2021-00299-3 (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Brown, H. Marriage, BMI, and Wages: A Double Selection. Scott. J. Polit. Econ. 2011, 58, 347–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, W.H. Econometric Analysis, 8th ed.; Pearson Education Inc.: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Teklewold, H.; Kassie, M.; Shiferaw, B.; Köhlin, G. Cropping system diversification, conservation tillage and modern seed adoption in Ethiopia: Impacts on household income, agrochemical use and demand for labor. Ecol. Econ. 2013, 93, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wekesa, B.M.; Ayuya, O.I.; Lagat, J.K. Effect of climate-smart agricultural practices on household food security in smallholder production systems: Micro-level evidence from Kenya. Agric. Food Secur. 2018, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Tagle, A.F.; Gómez-Tagle, A.; Fuerte-Velázquez, D.J.; Barajas-Alcalá, A.G.; Quiroz-Rivera, F.; Alarcón-Chaires, P.E.; Guerrero-García-Rojas, H. Blue and Green Water Footprint of Agro-Industrial Avocado Production in Central Mexico. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Dash, P.K.; Das, D.; Das, S. Growth, yield and water productivity of tomato as influenced by deficit irrigation water management. Environ. Process. 2023, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.; Gholami, M. Review of crop water productivity values for tomato, potato, melon, watermelon and cantaloupe in Iran. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2008, 10, 432–436. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Said, F.A.; Ashfaq, M.; Al-Barhi, M.; Hanjra, M.A.; Khan, I.A. Water productivity of vegetables under modern irrigation methods in Oman. Irrig. Drain. 2012, 61, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hama-Aziz, Z.Q.; Mustafa, R.A.; Neima, H.A. Farm-scale water productivity for tomato with mulched drip irrigation. Passer J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shideed, K.; Oweis, T.; Gabr, M.; Osman, M. Assessing On-Farm Water-Use Efficiency: A New Approach; ICARDA: Aleppo, Syria, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Asfaw, D.M. Analysis of technical efficiency of smallholder tomato producers in Asaita district, Afar National Regional State, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfay, T.; Gebremariam, M.; Gebretsadik, K.; Hagazi, M.; Girmay, S. Tomato yield and economic performance under vermicompost and mineral fertilizer applications. Open Agric. J. 2018, 12, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fi, M.; Ramírez, J.F.; Rubí, M.; Antonio, X.; Lara, A.V.; Acosta, A.D.; Rivera, R.; Ávila, A.L. Modelling the spatial behavior of Frankliniella occidentalis (thysanoptera: Thripidae) in growing avocado. Phyton 2017, 86, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, D.F.; Villa, F.; da Silva, G.J. Climate Change Implications on Cultivation of Avocado (Persea americana Mill.). In Cultivation for Climate Change Resilience; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 164–190. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, J. Water value in agriculture. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedra, H.; Mesa-Jurado, M.A.; López-Morales, C.A.; Castillo, M.M. Economic valuation of irrigation water in south-eastern Mexico. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2016, 32, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo, S.; Graterol, E.; Pulver, E. Sustainable transformation of rainfed to irrigated agriculture through water harvesting and smart crop management practices. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 437086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haileslassie, A.; Agide, Z.; Erkossa, T.; Hoekstra, D.; Schmitter, P.; Langan, S. On-Farm Smallholder Irrigation Performance in Ethiopia: From Water Use Efficiency to Equity and Sustainability; LIVES Working Paper 19; International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI): Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bazarfshan, O.; Yahyazadeh, M.; Jamshidi, S.; Zamani, H. Spatial prioritization of tomato cultivation based on water footprint, land productivity, and economic indices. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 71, 1363–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.D.; Rajvanshi, S.; Dash, S.K. Social Costs and Benefits of Micro Irrigation System Adoption in Canal Commands: A Study from IGNP Command Area of Bikaner in Rajasthan. 2008. Available online: https://ageconsearch.umn.edu/record/245273/?v=pdf (accessed on 23 January 2025).
- Samshunnahar, M.; Khanum, R.; Islam, M.S. Profitability of small-scale tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) production in some selected areas in Bangladesh. Agriculturists 2016, 14, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molden, D.J.; Gates, T.K. Performance measures for evaluation of irrigation-water-delivery systems. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1990, 116, 804–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejen, Z.A.; Schultz, B.; Hayde, L. Water delivery performance at Metahara large-scale irrigation scheme, Ethiopia. Irrig. Drain. 2015, 64, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agide, Z.; Haileslassie, A.; Sally, H.; Erkossa, T.; Schmitter, P.; Langan, S.; Hoekstra, D. Analysis of Water Delivery Performance of Smallholder Irrigation Schemes in Ethiopia: Diversity and Lessons Across Schemes, Typologies and Reaches; LIVES Working Paper 15; International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI): Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oweis, T.; Hachum, A. Water harvesting and supplemental irrigation for improved water productivity of dry farming systems in West Asia and North Africa. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 80, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, S.; Biazin, B.; Muluneh, A.; Yimer, F.; Haileslassie, A. Rainwater harvesting for supplemental irrigation of onions in the southern dry lands of Ethiopia. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 178, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemeze, F.H. Economic valuation of supplemental irrigation via small-scale water harvesting. Water Resour. Econ. 2020, 31, 100160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simane, B.; Tulu, T.; Lantideru, A.; Dawit, D. Fostering the use of rainwater for off-season small-scale irrigation in arid and semi-arid areas of Ethiopia. In Rainwater-Smart Agriculture in Arid and Semi-Arid Areas: Fostering the Use of Rainwater for Food Security, Poverty Alleviation, Landscape Restoration and Climate Resilience; Springer International Publishing AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 147–158. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Ramilan, T.; Ramarao, C.A.; Rao, C.S.; Whitbread, A. Farm level rainwater harvesting across different agro climatic regions of India: Assessing performance and its determinants. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.R.; Rao, K.V.; Raju, B.M.K.; Samuel, J.; Dupdal, R.; Osman, M.; Kumar, R.N. Levels and determinants of economic viability of rainwater harvesting farm ponds. Indian J. Agric. Econ. 2019, 74, 539–551. [Google Scholar]
- Shita, A.; Kumar, N.; Singh, S. Agricultural Technology Adoption and Its Determinants in Ethiopia: A Reviewed Paper. Asia Pac. J. Res. I(LVV) 2018, 1, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Feyisa, B.W.; Yildiz, F. Determinants of agricultural technology adoption in Ethiopia: A meta-analysis. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1855817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.J.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Oliver, M.M.H.; Akhi, K. Influencing factors of adopting solar irrigation technology and its impact on farmers’ livelihood. A case study in Bangladesh. Future Food J. Food Agric. Soc. 2021, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunny, F.A.; Fu, L.; Rahman, M.S.; Huang, Z. Determinants and Impact of Solar Irrigation Facility (SIF) Adoption: A Case Study in Northern Bangladesh. Energies 2022, 15, 2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okello, D.; Mayega, R.W.; Muhumuza, C.; Amuge, P.O.; Kakamagi, E.; Amollo, M.; Amuku, I.; Kayiwa, R.; Bazeyo, W. Gender and Innovation for Climate-Smart Agriculture: Assessment of Gender Responsiveness of RAN’s Agricultural-Focused Innovations; CCAFS Working Paper No. 260; CGIAR Research Program on Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS): Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2018; Available online: https://ccafs.cgiar.org/ (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Abegunde, V.O.; Sibanda, M.; Obi, A. Determinants of the Adoption of Climate-Smart Agricultural Practices by Small-Scale Farming Households in King Cetshwayo District Municipality, South Africa. Sustainability 2020, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, J.P.; Rahut, D.B.; Maharjan, S.; Erenstein, O. Factors affecting the adoption of multiple climate-smart agricultural practices in the Indo-Gangetic Plains of India. Nat. Resour. Forum 2018, 42, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurgat, B.K.; Lamanna, C.; Kimaro, A.; Namoi, N.; Manda, L.; Rosenstock, T.S. Adoption of Climate-Smart Agriculture Technologies in Tanzania. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 4, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekuria, Z.K.; Amede, A.K.; Mekonnen, E.E. Adoption of rainwater harvesting and its impact on smallholder farmer livelihoods in Kutaber district, South Wollo Zone, Ethiopia. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1834910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serote, B.; Mokgehle, S.; Du Plooy, C.; Mpandeli, S.; Nhamo, L.; Senyolo, G. Factors Influencing the Adoption of Climate-Smart Irrigation Technologies for Sustainable Crop Productivity by Smallholder Farmers in Arid Areas of South Africa. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgessa, T. The Determinants of Agricultural Productivity and Rural Household Income in Ethiopia. Ethiop. J. Econ. 2015, 24, 63–91. [Google Scholar]
- Bizimana, J.-C.; Yalew, B.B.; Assefa, T.T.; Belay, S.A.; Degu, Y.M.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Reyes, M.R.; Vara Prasad, P.V.; Tilahun, S.A. Simulating Potential Impacts of Solar MajiPump on the Economy and Nutrition of Smallholder Farmers in Sub-Humid Ethiopia. Water 2023, 15, 4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, E. The impact of solar water pumps on energy-water-food nexus: Evidence from Rajasthan, India. Energy Policy 2019, 129, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durga, N.; Schmitter, P.; Ringler, C.; Mishra, S.; Magombeyi, M.S.; Ofosu, A.; Pavelic, P.; Hagos, F.; Melaku, D.; Verma, S.; et al. Barriers to the uptake of solar-powered irrigation by smallholder farmers in Sub-Saharan Africa: A review. Energy Strategy Rev. 2024, 51, 101294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Syan, A.S.; Kaur, A.; Hundal, B.S. Determinants of farmers’ decision to adopt solar powered pumps. Int. J. Energy Sect. Manag. 2020, 14, 707–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beshir, S. Review on estimation of crop water requirement, irrigation frequency and water use efficiency of cabbage production. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2017, 5, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regasa, M.G.; Negash, R.; Bekele, A.E.; Nemera, D.B. Smallholder market participation and its associated factors: Evidence from Ethiopian vegetable producers. Cogent Food Agric. 2020, 6, 1783173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyi, I.; Faris, A.; Ayele, A.; Oljirra, A.; Bayessa, M. Profitability and market performance of smallholder vegetable production: Evidence from Ethiopia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, B.; Tilahun, Y.; Bekele, T.; Mekonen, G. Assessment of challenges of crop production and marketing in Bench-Sheko, Kaffa, Sheka, and West-Omo zones of southwest Ethiopia. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabidi, H.A.; Goh, H.W.; Chang, C.K.; Chan, N.W.; Zakaria, N.A. A Review of Roof and Pond Rainwater Harvesting Systems for Water Security: The Design, Performance and Way Forward. Water 2020, 12, 3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hone, M.; Lindi, S.; Eticha, B. Determination of Different Lining Materials for Reducing Seepage Loss in Water Harvesting Structures at Arsi Zone, Ethiopia. Glob. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2024, 2, 19–24. [Google Scholar]

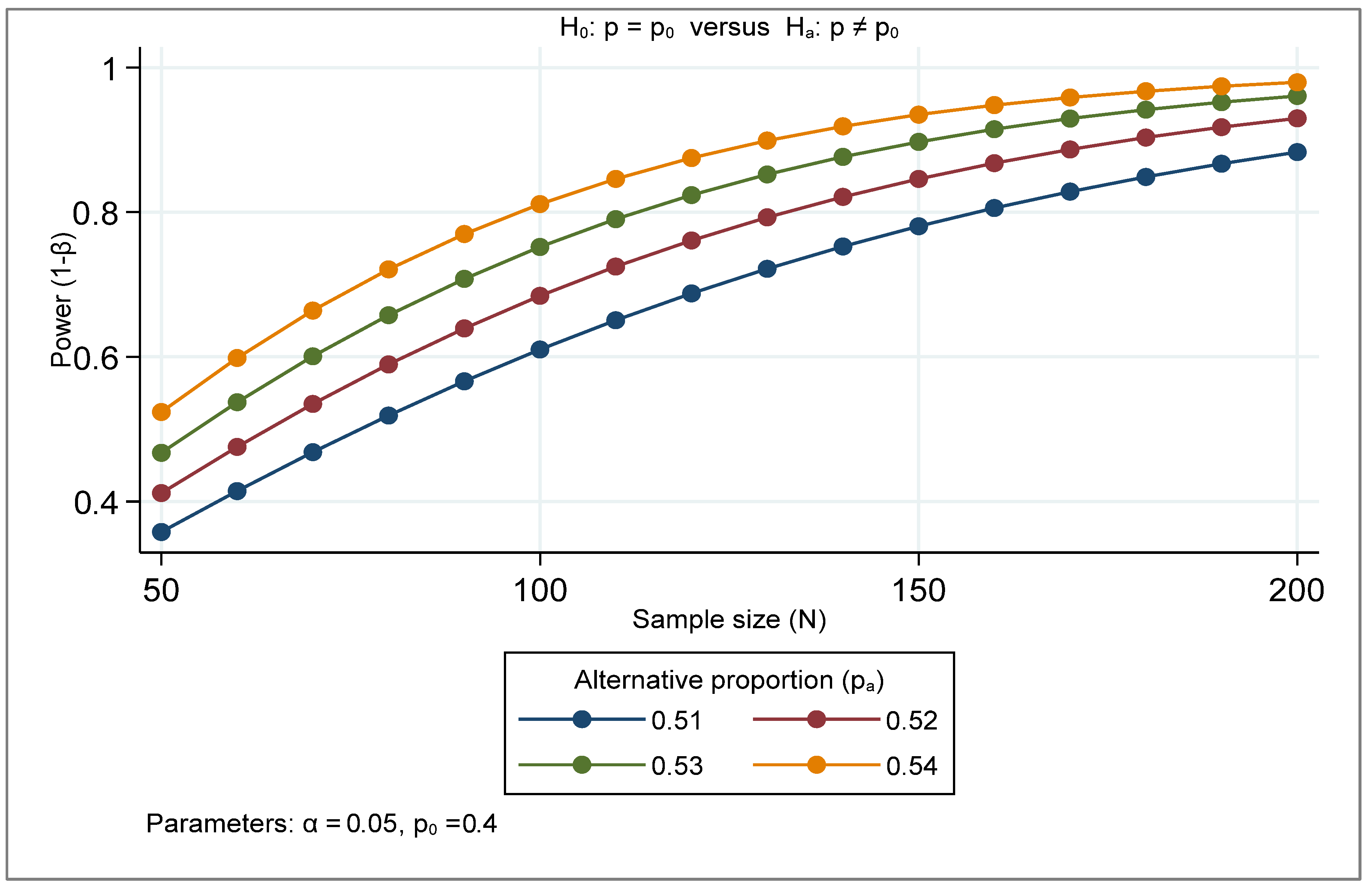

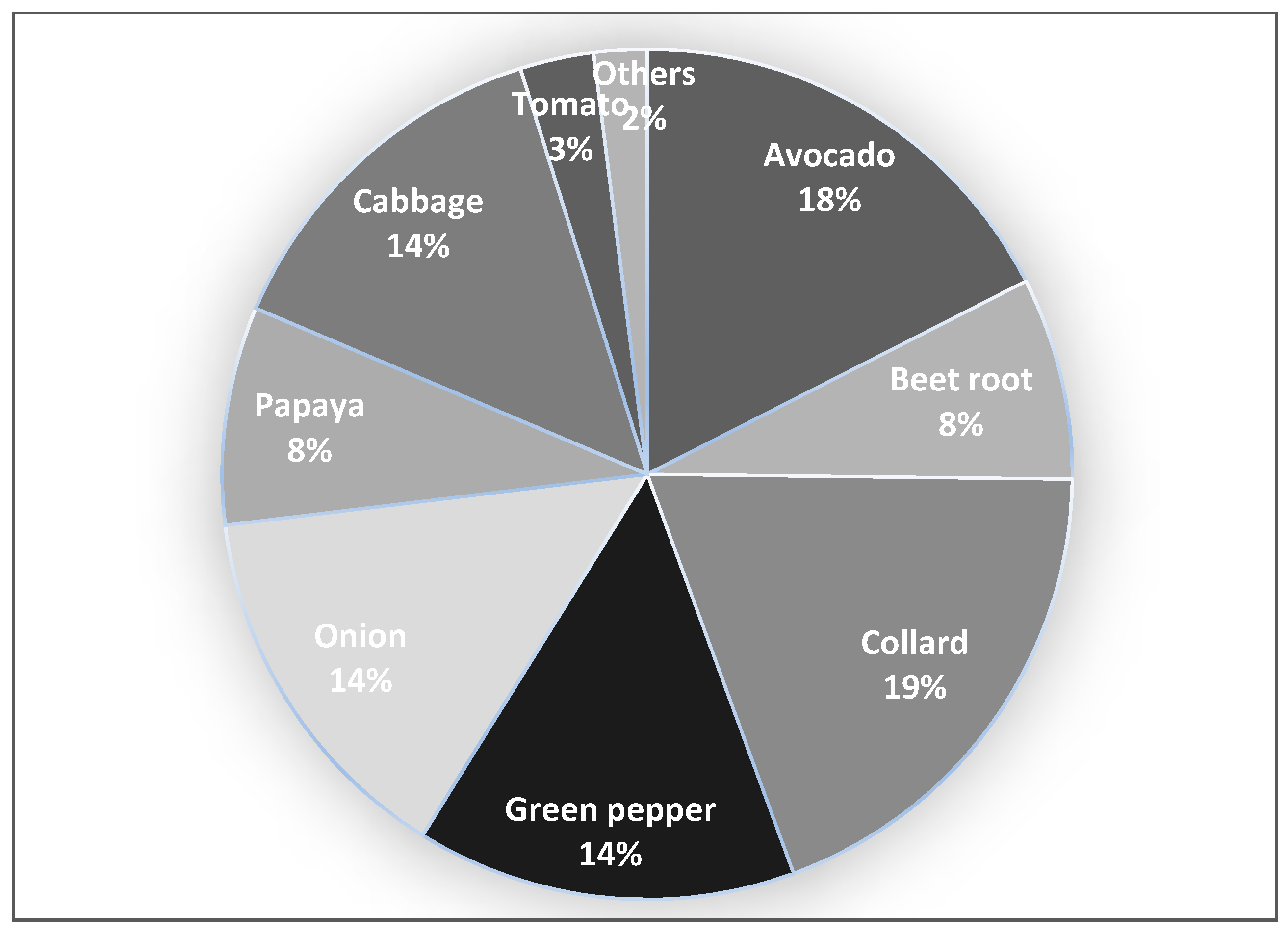





| Variables | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (dummy) | 0.86 | 0.34 | 0 | 1 |
| Age (in years) | 45.18 | 11.13 | 22 | 76 |
| Years of schooling (in years) | 5.05 | 4.00 | 0 | 17 |
| Household size (in number) | 6.84 | 2.29 | 2 | 15 |
| Family labor (in number) | 4.82 | 2.26 | 1 | 15 |
| Total land (in hectare) | 1.18 | 0.87 | 0.125 | 6 |
| Irrigable land (in hectare) | 0.31 | 0.47 | 0 | 3 |
| Land irrigated with solar pump (in hectare) | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.00 | 0.63 |
| Land irrigated with water harvesting pond (in hectare) | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.75 |
| Non-irrigable land (in hectare) | 0.85 | 0.68 | 0 | 5 |
| Experience of crop farming (in years) | 27.23 | 10.99 | 5 | 57 |
| Experience of irrigation (in years) | 4.91 | 6.84 | 0 | 33 |
| Household crop income (in USD) | 1214.09 | 1774.27 | 0 | 9164.12 |
| HFCS (ranges from 0 to 112) | 59.53 | 18.58 | 21.5 | 112 |
| HDDS (ranges from 0 to 12) | 7.27 | 1.59 | 4 | 11 |
| Crop | LP (in kg/ha) | WP (in kg/m3) |
|---|---|---|
| Avocado | 10,421 | 1.26 |
| Beet Root | 5690 | 0.72 |
| Carrot | 4375 | 0.31 |
| Collard | 9014 | 0.01 |
| Green Pepper | 3378 | 0.38 |
| Onion | 9214 | 2.34 |
| Papaya | 8758 | 0.75 |
| Lettuce | 1224 | 0.07 |
| Cabbage | 10,123 | 1.46 |
| Tomato | 17,333 | 13.24 |
| Crop | Gross Water Value, USD/m3 | Net Water Value, USD/m3 |
|---|---|---|
| Avocado | 0.65 | 0.21 |
| Green Pepper | 0.99 | 0.21 |
| Onion | 1.04 | 0.28 |
| Cabbage | 1.08 | 0.22 |
| Tomato | 4.02 | 1.53 |
| Financing Scheme | Average Net Annual Benefit per Household (in USD) | Average Annual Water Volume Delivered per Household (in m3) | Overall Average Net Water Value (in USD/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NGO-supported | 513.18 | 2237.4 | 0.23 |
| Government-supported | −58.61 | 3181.7 | −0.02 |
| Private purchase | 146.93 | 2260.6 | 0.06 |
| Crop | BCR |
|---|---|
| Avocado | 2.45 |
| Beet Root | 0.45 |
| Carrot | 0.45 |
| Collard | 0.77 |
| Green Pepper | 1.91 |
| Onion | 2.77 |
| Papaya | 1.02 |
| Lettuce | 0.21 |
| Cabbage | 2.53 |
| Tomato | 2.99 |
| Crops | Seasonal Water Delivery from Ponds, m3/ha | Total Seasonal Irrigation Demand, m3/ha | Adequacy | Net WP of Irrigation Water, kg/m3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beet root | 673.9 | 2985 | 0.23 | 0.66 |
| Collard | 214.9 | 2985 | 0.07 | 0.39 |
| Carrot | 488.1 | 2985 | 0.16 | 2.04 |
| Onion | 481.4 | 2985 | 0.16 | 1.51 |
| Potato | 386.9 | 3800 | 0.10 | 0.63 |
| Cabbage | 370.3 | 3514.0 | 0.11 | 0.40 |
| Total | 2615.4 | 19,254.0 | 0.14 |
| Pond Type | Total Costs, USD | Total Benefits, USD | BCR |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small | 21,682.77 | 12,202.26 | 0.67 |
| Large | 25,711.20 | 18,862.00 | 0.95 |
| Technology Bundle | TC (in USD) | TB (in USD) | BCR |
|---|---|---|---|
| PRF | 305.17 | 285.71 | 0.94 |
| PRIF | 379.18 | 206.39 | 0.54 |
| PRIFA | 437.45 | 360.12 | 0.82 |
| PRIFO | 390.56 | 427.18 | 1.09 |
| PRIFOA | 524.11 | 636.88 | 1.22 |
| PRIO | 448.33 | 160.71 | 0.36 |
| PRO | 625.10 | 184.15 | 0.29 |
| Variables | Solar Pump Irrigation Adoption | Water Harvesting Pond Irrigation | Adoption of Both Irrigation Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | −0.887 ** (0.409) | 1.054 (0.804) | −0.427 (0.331) |
| Age of household head | 0.029* (0.016) | −0.081 ** (0.032) | −0.002 (0.013) |
| Years of schooling | 0.131 *** (0.041) | −0.090 (0.057) | 0.061 * (0.034) |
| Dependency ratio | −0.216 (0.174) | −0.060 (0.300) | −0.304 * (0.171) |
| Family labor | −0.021 (0.080) | 0.318 ** (0.128) | 0.112 (0.069) |
| Irrigable land size | 1.539 ** (0.680) | 1.848 ** (0.885) | 2.789 *** (1.066) |
| Irrigation experience | 0.159 ** (0.068) | 0.221 ** (0.092) | 0.202 ** (0.087) |
| Oromia dummy | 2.500 *** (0.914) | − | 3.227 ** (1.312) |
| Central Ethiopia dummy | 2.752 *** (0.940) | − | 3.238 ** (1.317) |
| Altitude | −0.006 *** (0.001) | 0.001 ** (0.000) | 0.000 (0.000) |
| Constant | 5.331 *** (2.503) | −2.967 * (1.677) | −3.904 ** (1.561) |
| Pseudo R2 | 0.55 | 0.66 | 0.59 |
| Wald Chi2 | 43.53 | 33.11 | 29.29 |
| Prob > Chi2 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.001 |
| Irrigation Technology | Welfare Indicators | Mean | Mean Difference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Adopters | Adopters | |||
| Solar irrigation | Crop income (in USD) | 613.65 | 2115.70 | −1502.06 *** |
| HFCS | 52.26 | 65.67 | −13.41 *** | |
| HDDS | 6.67 | 8 | −1.33 *** | |
| Water harvesting pond irrigation | Crop income (in USD) | 613.65 | 1166.37 | −552.72 ** |
| HFCS | 52.26 | 72.58 | −20.32 *** | |
| HDDS | 6.67 | 7.7 | −1.033 *** | |
| Solar and water harvesting pond irrigation | Crop income (in USD) | 613.65 | 1869.12 | −1255.48 *** |
| HFCS | 52.26 | 67.46 | −15.21 *** | |
| HDDS | 6.67 | 7.92 | −1.26 *** | |
| Finance Scheme for Solar Panels | Mean of Welfare Indicators | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Crop Income (in USD) | HFCS | HDDS | |
| Self-purchase | 1319.53 | 63.93 | 7.8 |
| Government support | 1942.97 | 58.71 | 7.47 |
| NGO support | 2710.87 | 71.44 | 8.48 |
| Agricultural Technology Bundles | Number of Technologies in the Bundle | Rate of Adoption | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Purchase | Government Support | NGO Support | ||
| CPRIFOA | 7 | 16.67 | 16.67 | 66.67 |
| CPRIOA, CPRFOA, PRIFOA | 6 | 18.75 | 31.25 | 50 |
| PRIFA, PRIFO, PRIOA, PRFOA, CPRFA | 5 | 29.41 | 29.41 | 41.18 |
| PRIO, PROA, CPIO, PRFA, PRIF, CPOA, CPRI | 4 | 10 | 40 | 50 |
| PFO, PIO, PRA, PRF, CPF | 3 | 60 | 40 | - |
| PO, CO | 2 | 66.67 | 33.33 | - |
| Technology Bundle | SP | WHP | Crop Income (in USD) | HFCS | HDDS | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP | WHP | SP | WHP | SP | WHP | |||
| CPRIFOA | ✓ | 4124.93 | - | 78.58 | - | 8.83 | - | |
| PRIFOA | ✓ | ✓ | 2749.97 | 847.03 | 66.68 | 86.33 | 8.29 | 8.33 |
| CPRIFO | ✓ | - | 767.40 | - | 68.5 | - | 7.5 | |
| PRIFO | ✓ | ✓ | 2270.36 | 1504.68 | 75.33 | 69.35 | 9.33 | 7.6 |
| PRIOA | ✓ | ✓ | 1343.10 | 177.23 | 71 | 71 | 9.33 | 7 |
| PRIFA | ✓ | 829.25 | - | 77.71 | - | 8.43 | - | |
| PRFOA | ✓ | 1123.33 | 60.67 | - | 7 | - | ||
| PRFO | ✓ | - | 531.69 | - | 72.5 | - | 8 | |
| PRIO | ✓ | 2481.50 | - | 50.67 | - | 7.33 | - | |
| CPIO | ✓ | 2130.28 | - | 68.5 | - | 8 | - | |
| PRA | ✓ | ✓ | 205.76 | 354.46 | 34 | 51 | 6 | 7 |
| Type of Irrigation System | Welfare Indicators | Adopting (1) | Non-Adopting (2) | ATT = (1)–(2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Solar pump irrigation | Crop income (in USD) | 2115.70 (147.19) | 1035.03 (33.60) | 1080.67 *** (150.98) |
| HFCS | 65.67 (1.21) | 66.08 (1.01) | −0.41 (1.57) | |
| HDDS | 8 (0.09) | 7.56 (0.08) | 0.44 *** (0.12) | |
| Water harvesting pond irrigation | Crop income (in USD) | 1166.37 (164.28) | 229.56 (66.88) | 936.80 *** (177.38) |
| HFCS | 72.58 (2.51) | 46.84 (3.12) | 25.74 *** (4.01) | |
| HDDS | 7.7 (0.164) | 7.09 (0.159) | 0.61 ** (0.228) | |
| Solar pump and water harvesting irrigation | Crop income (in USD) | 1869.12 (112.66) | 524.08 (40.65) | 1345.04 *** (119.76) |
| HFCS | 67.46 (0.90) | 64.80 (1.50) | 2.66 (1.75) | |
| HDDS | 7.92 (0.05) | 7.71 (0.10) | 0.21 ** (0.11) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Negera, M.; Dejen, Z.A.; Melaku, D.; Tegegne, D.; Adamseged, M.E.; Haileslassie, A. Agricultural Productivity of Solar Pump and Water Harvesting Irrigation Technologies and Their Impacts on Smallholder Farmers’ Income and Food Security: Evidence from Ethiopia. Sustainability 2025, 17, 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041486
Negera M, Dejen ZA, Melaku D, Tegegne D, Adamseged ME, Haileslassie A. Agricultural Productivity of Solar Pump and Water Harvesting Irrigation Technologies and Their Impacts on Smallholder Farmers’ Income and Food Security: Evidence from Ethiopia. Sustainability. 2025; 17(4):1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041486
Chicago/Turabian StyleNegera, Mebratu, Zeleke Agide Dejen, Dagmawi Melaku, Desalegn Tegegne, Muluken Elias Adamseged, and Amare Haileslassie. 2025. "Agricultural Productivity of Solar Pump and Water Harvesting Irrigation Technologies and Their Impacts on Smallholder Farmers’ Income and Food Security: Evidence from Ethiopia" Sustainability 17, no. 4: 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041486
APA StyleNegera, M., Dejen, Z. A., Melaku, D., Tegegne, D., Adamseged, M. E., & Haileslassie, A. (2025). Agricultural Productivity of Solar Pump and Water Harvesting Irrigation Technologies and Their Impacts on Smallholder Farmers’ Income and Food Security: Evidence from Ethiopia. Sustainability, 17(4), 1486. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17041486






