Characteristics of Ecosystem Services in Megacities Within the Yellow River Basin, Analyzed Through a Resilience Perspective: A Case Study of Xi’an and Jinan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Assessment of Ecosystem Services
2.3.1. Carbon Storage (CS)
2.3.2. Habitat Quality (HQ)
2.3.3. Food Production (FP)
2.3.4. Soil Conservation (SC)
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Bivariate Spatial Autocorrelations
2.4.2. Spearman Correlation Analysis
2.5. Geographic Detector
3. Results
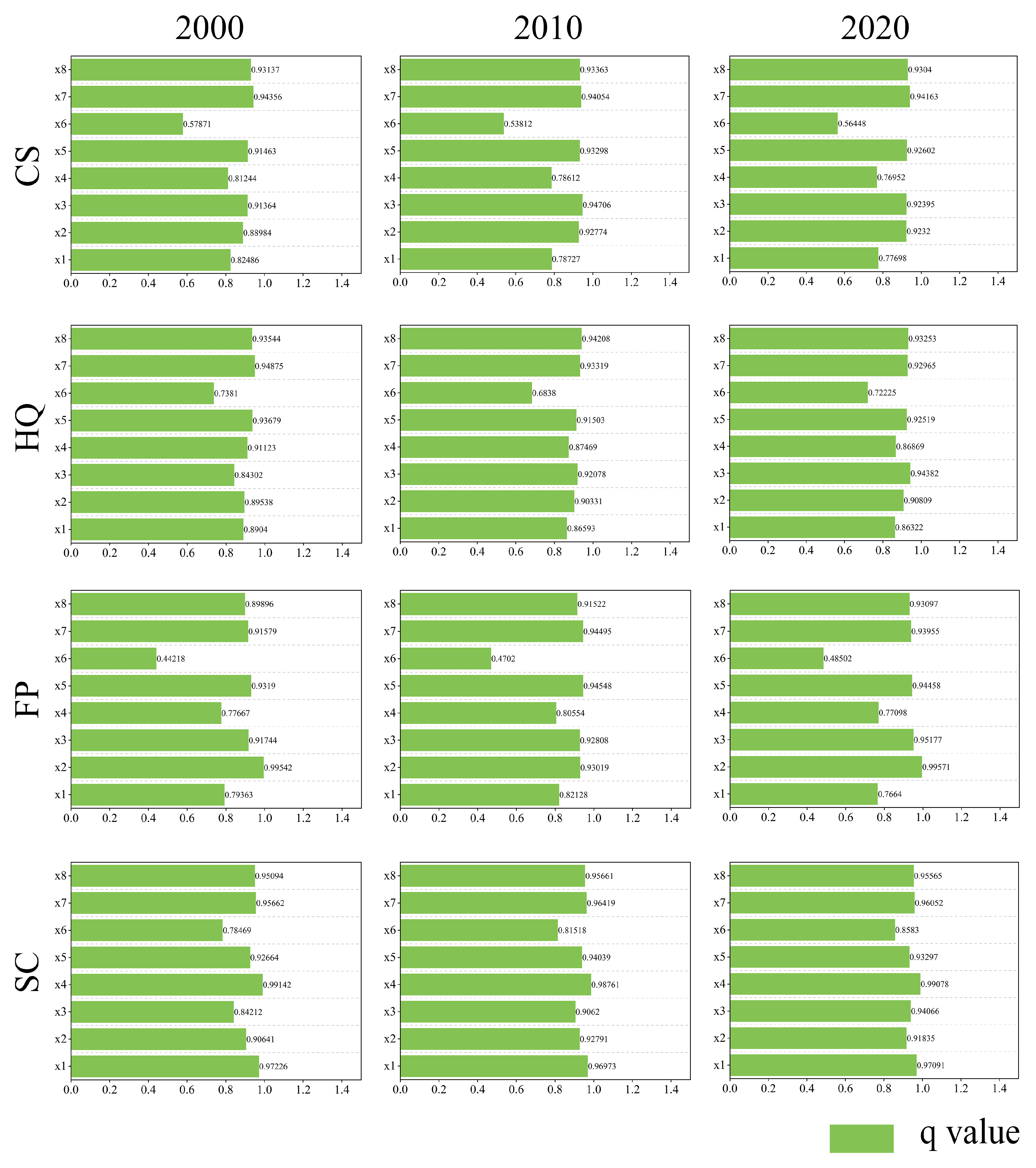
3.1. ES Calculation Parameter Analysis
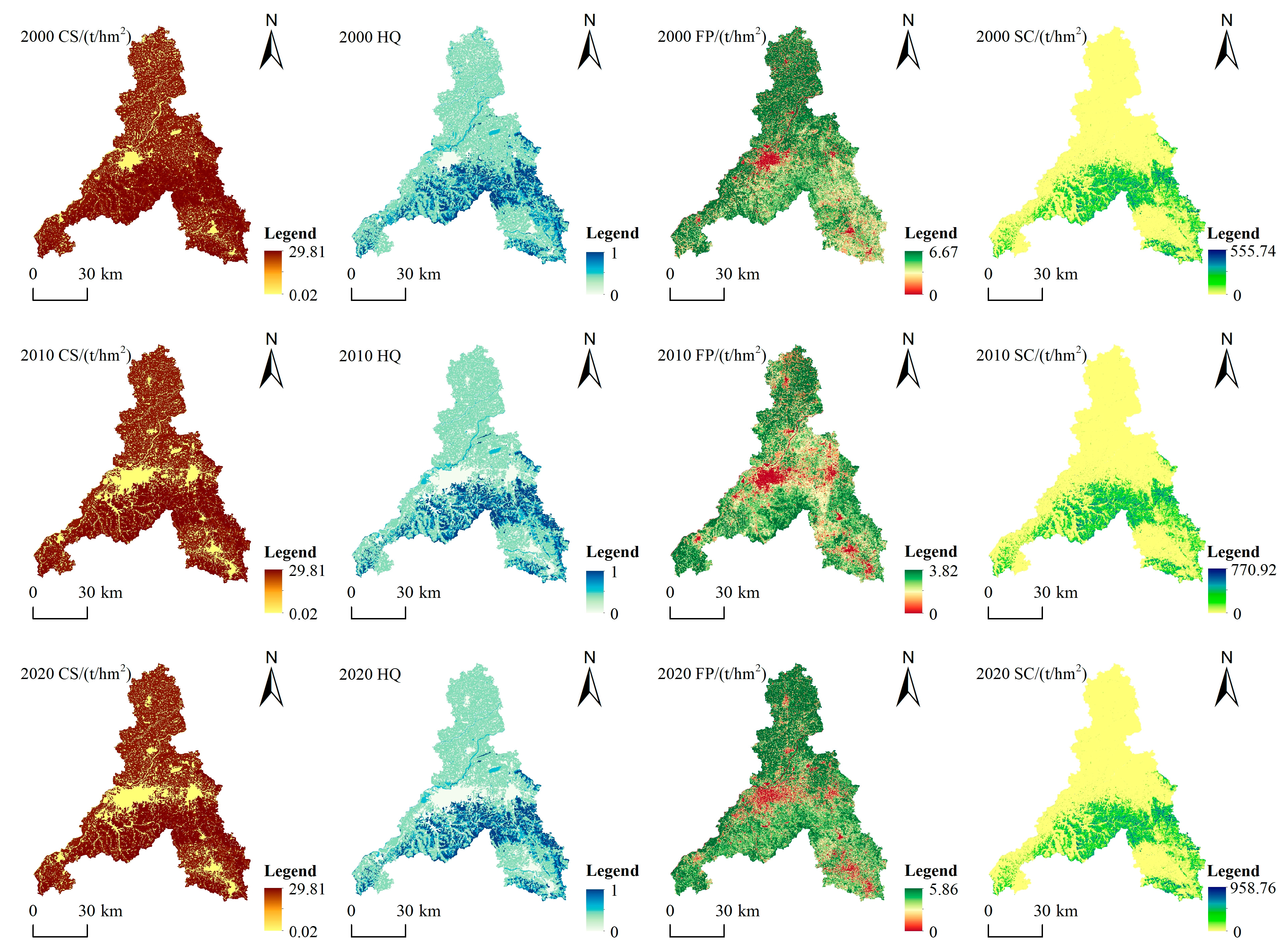
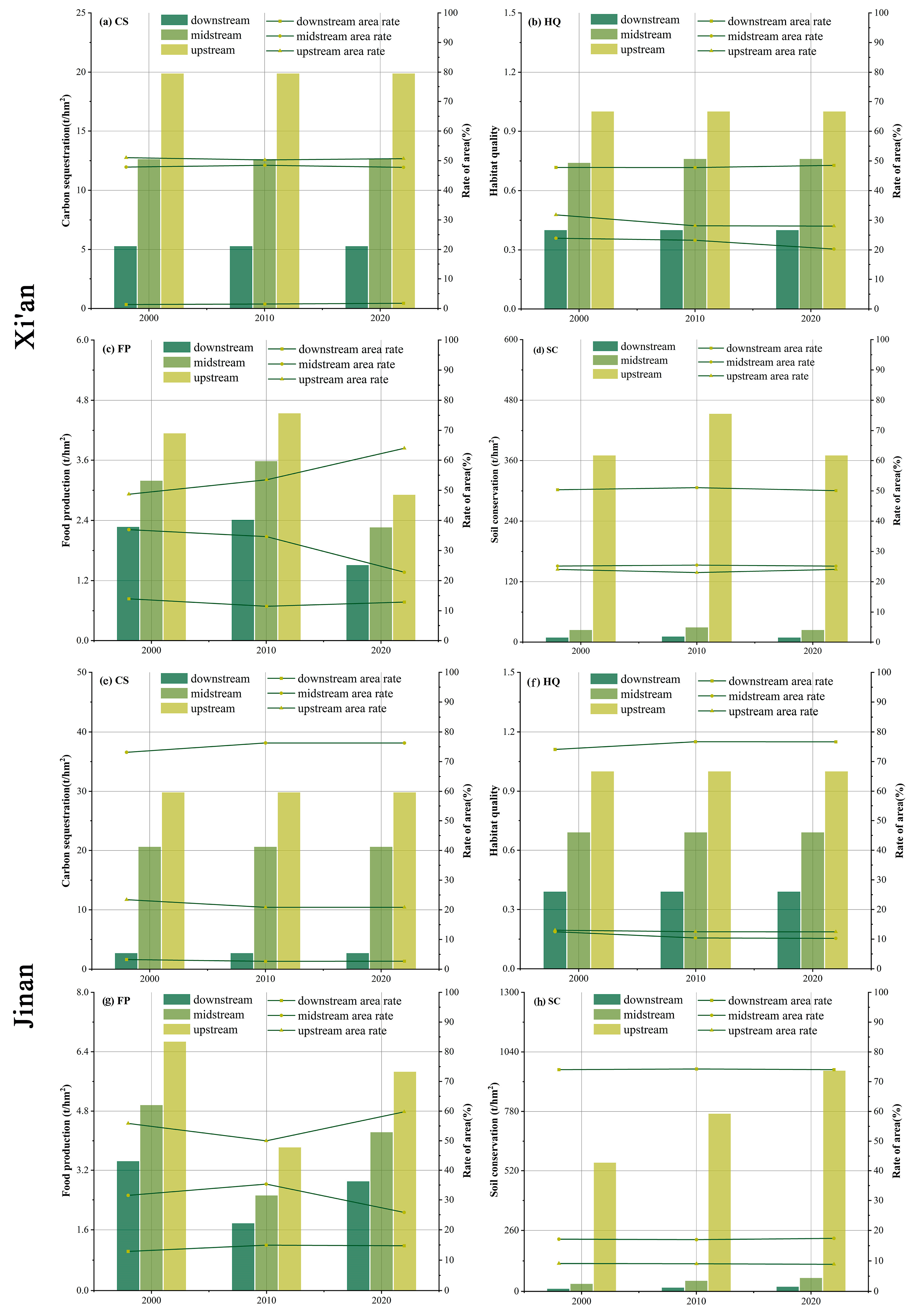
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations of ESs
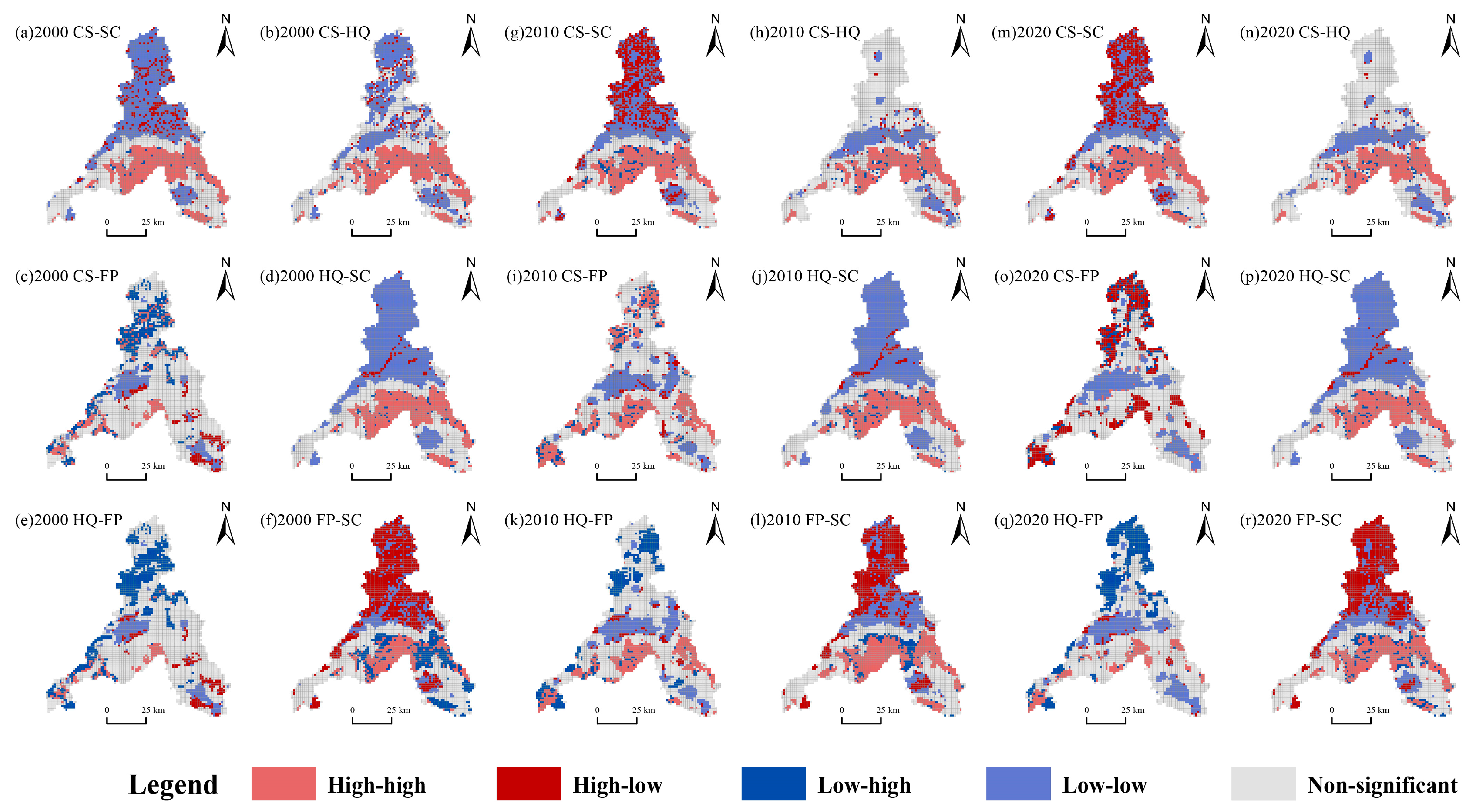
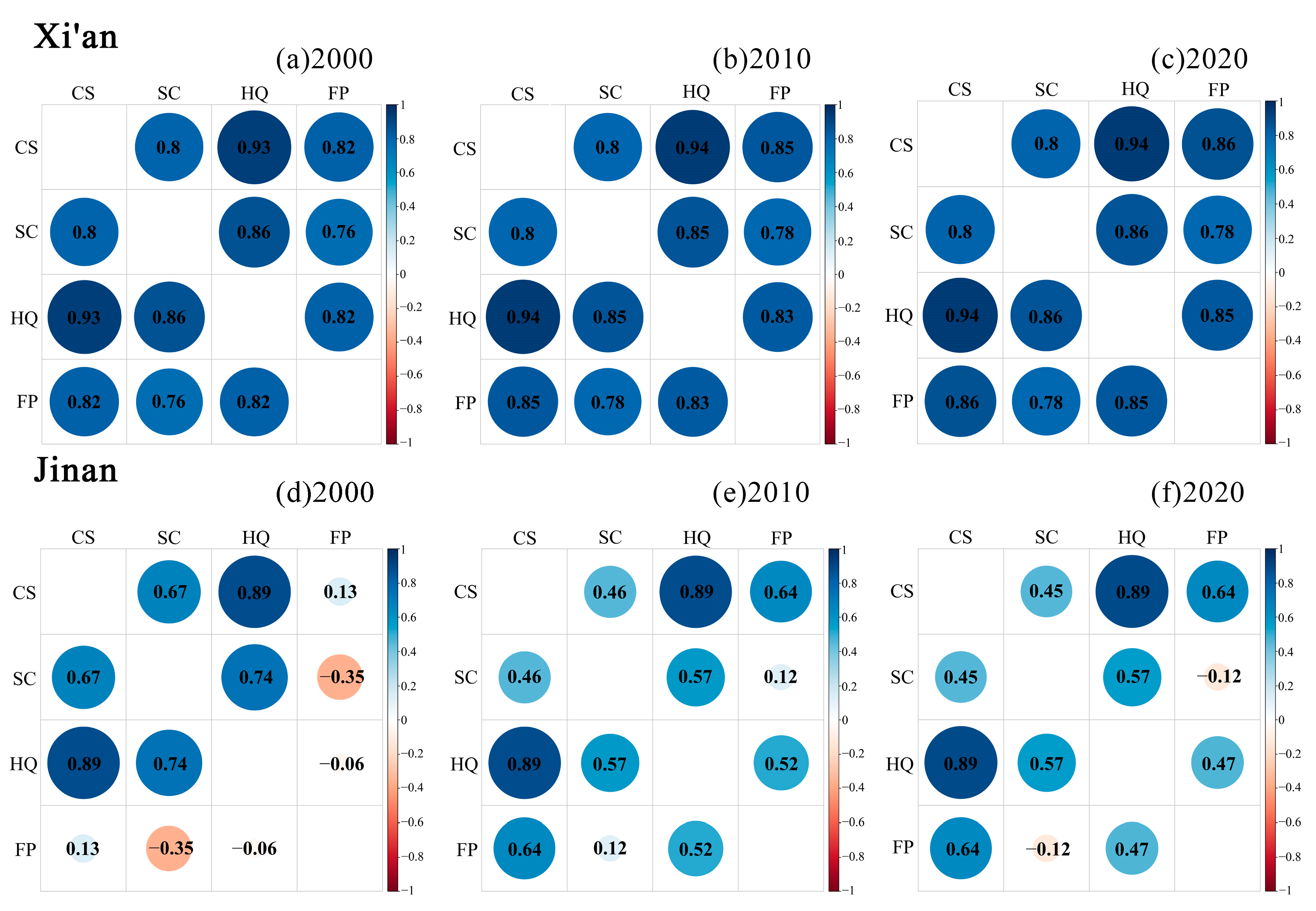
3.3. Changes in the Trade-Offs and Synergies of ESs
3.4. Influence of Driving Factors on ESs
3.4.1. Influence of Single Influencing Factors on ESs
3.4.2. The Influence of Factor Interaction
4. Discussion
4.1. Heterogeneity of ESs in Megacities from the Perspective of Resilience
4.2. What Is the Relationship Between ESs? What Are the Key Characteristics Affecting ESs?
4.3. Implications of Comparative Analysis of ESs Among Megacities
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- ESs are higher in the south and lower in the north of Xi’an. With the change in time, the low-value regions except SC increased. There is no clear boundary between ESs in Jinan. HQ and SC were higher in the central region and lower in the north central region. With the change in time, the low-value area increased.
- (2)
- Xi’an exhibited strong coordination effects among most ESs, except for CS-FP and HQ-FP. In Jinan, CS-SC, CS-HQ, and HQ-SC exhibited strong coordination, while HQ-FP and FP-SC displayed weak trade-off effects, gradually transitioning to a coordinated relationship over time.
- (3)
- Edge density, patch density, and NDVI significantly impacted CS in both Xi’an and Jinan. For HQ, DEM, slope, and patch density were most significant in Xi’an, while temperature, edge density, and patch density were most significant in Jinan. NDVI and temperature were key drivers of FP in both cities, whereas DEM and slope had a strong influence on SC.
- (1)
- This study focused on megacities in the middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River Basin, excluding cities in the upstream region. Therefore, future research should include representative cities in the entire Yellow River Basin for a more comprehensive comparison.
- (2)
- The study’s time span extends only to 2020. Future studies could incorporate simulation and scenario predictions to assess future ES conditions and influencing factors, providing a theoretical basis for ecosystem security and sustainable urban development.
- (3)
- Our study focused on four ESs due to data constraints. Future research should explore additional ES types to provide a more detailed understanding of ES dynamics in the Yellow River Basin and the primary factors influencing them.
- (4)
- Future research could investigate the impacts of various landscape patterns, such as fragmentation, connectivity, and stability, on ES functions and conduct more in-depth mechanistic studies.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chang, H.; Pallathadka, A.; Sauer, J.; Grimm, N.B.; Zimmerman, R.; Cheng, C.; Iwaniec, D.M.; Kim, Y.; Lloyd, R.; McPhearson, T.; et al. Assessment of Urban Flood Vulnerability Using the Social-Ecological-Technological Systems Framework in Six US Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 68, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Zhang, P.; Yu, F.; Zhu, X. A Review on Resilient Cities Research from the Perspective of Territorial Spatial Planning: A Bibliometric Analysis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1300764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folke, C.; Carpenter, S.; Elmqvist, T.; Gunderson, L.; Walker, B. Resilience: Now More than Ever: This Article Belongs to Ambio’s 50th Anniversary Collection. Theme: Anthropocene. Ambio 2021, 50, 1774–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mofrad, F.; Ignatieva, M.; Vernon, C. The Discourses, Opportunities, and Constraints in Canberra’s Green Infrastructure Planning. Urban For. Urban Green. 2022, 74, 127628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Grünewald, F. Disaster Preparedness in a Complex Urban System: The Case of Kathmandu Valley, Nepal. Disasters 2016, 40, 411–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumma, M.; Mohammad, I.; Nedumaran, S.; Whitbread, A.; Lagerkvist, C. Urban Sprawl and Adverse Impacts on Agricultural Land: A Case Study on Hyderabad, India. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Gong, J.; Li, J.; Chen, Q. Characteristics of Urban Expansion in Megacities and Its Impact on Water-Related Ecosystem Services: A Comparative Study of Chengdu and Wuhan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baklanov, A.; Molina, L.T.; Gauss, M. Megacities, Air Quality and Climate. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 126, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Shahtahmassebi, A.; Gan, M.; Deng, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, K. Characterizing Spatial Patterns and Driving Forces of Expansion and Regeneration of Industrial Regions in the Hangzhou Megacity, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 119959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlucci, M.; Salvati, L. Assessing Path-Dependent Urban Growth with Geographically Weighted Regressions. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Zeng, J. Impact of Urbanization on Ecosystem Health in Chinese Urban Agglomerations. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Azizi, P.; Moghadasi, M. Land Use Change, Urbanization, and Change in Landscape Pattern in a Metropolitan Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Jiang, L.; Shen, G.Q.P. Embodied Pasture Land Use Change in China 2000-2015: From the Perspective of Globalization. Land Use Policy 2019, 82, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Han, Q.; Vries, B.D. Urbanization Effects on the Food-Water-Energy Nexus within Ecosystem Services: A Case Study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration in China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Chen, C.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Prediction of Habitat Quality Based on Land Use and Cover Change in Jiangsu, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y.; No Ol, L.; Yoo, Y.-J.; Cho, H.J.; Sun, Z.; Jeon, S. Analysis of the Effect of Environmental Protected Areas on Land-Use and Carbon Storage in a Megalopolis. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, W.; Jiang, K.; Shao, X. The Impact of Big Data Pilot Zones on Urban Ecological Resilience: Evidence from a Machine Learning Approach. Sustainability 2025, 17, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; He, Q.; Gu, Y.; Wang, K.; Shen, Z. Urban Flood Resilience Assessment of Prefecture-Level Cities in Yangtze River Delta. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2025, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’Neill, R.V.; Raskin, R.G.; Sutton, P. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yuan, X.; An, J.; Su, Q.; Chen, B. Drivers of Ecosystem Services and Their Trade-Offs and Synergies in Different Land Use Policy Zones of Shaanxi Province, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Yan, K.; Shi, Y.; Lv, T.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X. Decrypting Resilience: The Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Ecological Resilience in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 106, 107540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Long, Y.; Yang, L.; Ding, X.; Sun, X.; Chen, T. Impacts of Urbanization on the Spatiotemporal Evolution of Ecological Resilience in the Plateau Lake Area in Central Yunnan, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huo, X.; Hong, Y.; Yu, C.; De Jong, M.; Cheng, B. How Urban Greening Policy Affects Urban Ecological Resilience: Quasi-Natural Experimental Evidence from Three Megacity Clusters in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 452, 142233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finisdore, J.; Rhodes, C.; Haines-Young, R.; Maynard, S.; Wielgus, J.; Dvarskas, A.; Houdet, J.; Quétier, F.; Lamothe, K.A.; Ding, H.; et al. The 18 Benefits of Using Ecosystem Services Classification Systems. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 45, 101160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, N.; Jutras-Perreault, M.-C.; Gobakken, T.; Ole Ørka, H.; Vacik, H. Systematic Review for a Set of Indicators Supporting the Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z. Exploring the Classification of China’s Ecosystem Service Networks and Their Driving Factors Based on Current Status and Evolutionary Trends. Appl. Geogr. 2024, 168, 103321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yang, X. Interrelationships between Urbanization and Ecosystem Services in the Urban Agglomeration around Poyang Lake and Its Zoning Management at an Integrated Multi-Scale. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Meng, X.; Liu, B. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services in the Upper Fenhe Watershed, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xue, D.; Miao, P. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Supply and Demand Bundles: A Case Study in the Sichuan-Yunnan Ecological Buffer Area, China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Sun, S.; Wen, Y.; Chen, H. Study on the Driving Factors of Ecosystem Service Value under the Dual Influence of Natural Environment and Human Activities. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qiao, J.; Li, M.; Huang, M. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of Ecosystem Service Interactions and Their Drivers at Different Spatial Scales in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zuo, Q.; Li, Q.; He, N. Spatiotemporal Analysis and Multi-Scenario Prediction of Ecosystem Services Based on Land Use/Cover Change in a Mountain-Watershed Region, China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aniah, P. Determinants of Adaptation Strategies to Offset Decreasing Provisioning Ecosystem Services in the Savannah Ecological Zone of Ghana. Environ. Chall. 2024, 14, 100856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Ecosystem Services and the Response to Urbanization: Evidence Based on Shandong Province of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Li, B.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Weng, A.; Jin, Y.; Cai, G.; Lin, Y.; Chen, B. Exploring the Evolution of Coupled Natural-Cultural Ecosystem Services and Their Geographically Scaled Driven Modeling in a Coastal City of Southeast China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 361, 121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Zhang, S.; Yung, E.H.K.; Chan, E.H.W.; Luan, B.; Chen, Y. On the Urban Compactness to Ecosystem Services in a Rapidly Urbanising Metropolitan Area: Highlighting Scale Effects and Spatial Non–Stationary. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 98, 106975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; An, J. Spatio-Temporal Interaction and Constraint Effects between Ecosystem Services and Human Activity Intensity in Shaanxi Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Identifying the Relationships among Multiple Ecosystem Services. J. Arid Environ. 2020, 183, 104265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Xu, H. Study on Ecosystem Service Values of Urban Green Space Systems in Suzhou City Based on the Extreme Gradient Boosting Geographically Weighted Regression Method: Spatiotemporal Changes, Driving Factors, and Influencing Mechanisms. Land 2025, 14, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; He, H.; Chen, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y. Diagnosing Degradation Risks of Ecosystem Services in Wuhan, China from the Perspective of Land Development: Identification, Measurement and Regulation. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xia, L. Assessment Impacts of Weather and Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) Change on Urban Vegetation Net Primary Productivity (NPP): A Case Study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4125–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Huang, Q.; He, C.; Zhao, X. Projecting the Impacts of Urban Expansion on Simultaneous Losses of Ecosystem Services: A Case Study in Beijing, China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 84, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamgir Hossen Bhuiyan, M.; Inostroza, L.; Nihei, T.; Sultana, M.; Louw, A.S.; Supe, H.; Chen, X.; Alsulamy, S.; Avtar, R. The Differential Impacts of the Spatiotemporal Vertical and Horizontal Expansion of Megacity Dhaka on Ecosystem Services. Curr. Res. Environ. Sustain. 2024, 7, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Cui, S.; Xu, L.; Ding, S.; Nie, W. Linking Land-Use Change, Landscape Patterns, and Ecosystem Services in a Coastal Watershed of Southeastern China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Singha, P.; Lepcha, K.; Debanshi, S.; Talukdar, S.; Saha, T.K. Proposing Multicriteria Decision Based Valuation of Ecosystem Services for Fragmented Landscape in Mountainous Environment. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 21, 100454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Li, R.; Liu, D.; Wu, Y. Dynamic Characteristics and Responses of Ecosystem Services under Land Use/Land Cover Change Scenarios in the Huangshui River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Ma, X.; Cao, L. Exploring the Response of Ecosystem Service Value to Land Use Changes under Multiple Scenarios Coupling a Mixed-Cell Cellular Automata Model and System Dynamics Model in Xi’an, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, Y.; Jia, W. Land Use Optimization Research Based on FLUS Model and Ecosystem Services–Setting Jinan City as an Example. Urban Clim. 2021, 40, 100984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wu, B. Spatial and Temporal Changes and Development Predictions of Urban Green Spaces in Jinan City, Shandong, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 152, 110373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, M.G.; Zawadzka, J.; Scott, A.J. Ecosystem Service Multifunctionality and Trade-Offs in English Green Belt Peri-Urban Planning. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 67, 101620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Gong, Y.; Xi, X.; Liu, C.; Qian, C.; Ye, B. The Study on the Spatiotemporal Changes in Tradeoffs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Response to Land Use/Land Cover Changes in the Region around Taihu Lake. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.; Chen, B.; Chen, W.; Xu, S.; He, X.; Yao, J.; Huang, Y. Analysis of Trade-off and Synergy of Ecosystem Services and Driving Forces in Urban Agglomerations in Northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 165, 112210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Hou, Y.; Andersen, P.S.; Xin, R.; Rong, Y.; Skov-Petersen, H. An Ecological Perspective for Understanding Regional Integration Based on Ecosystem Service Budgets, Bundles, and Flows: A Case Study of the Jinan Metropolitan Area in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Ling, Y.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, R.; Wang, Y. How Do Different Processes of Habitat Fragmentation Affect Habitat Quality?—Evidence from China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Hu, X.; Qiu, S.; Hu, Y.; Meersmans, J.; Liu, Y. Multifunctional Landscapes Identification and Associated Development Zoning in Mountainous Area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavidez, R.; Jackson, B.; Maxwell, D.; Norton, K. A Review of the (Revised) Universal Soil Loss Equation ((R)USLE): With a View to Increasing Its Global Applicability and Improving Soil Loss Estimates. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6059–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, X. Spatio-Temporal Variations of Habitat Quality and Its Driving Factors in the Yangtze River Delta Region of China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2024, 52, e02978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Yang, J.; Wu, F.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.; Li, X. Response Characteristics and Influencing Factors of Carbon Emissions and Land Surface Temperature in Guangdong Province, China. Urban Clim. 2022, 46, 101330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, G.; He, N.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wen, D.; Li, S.; Niu, S.; Ge, J. Carbon Storage in China’s Terrestrial Ecosystems: A Synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal Differentiation and Geographic Detection Mechanism of Ecological Security in Chongqing, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 35, e02072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, G.; Sengupta, A.; Alfaisal, F.M.; Alam, S.; Alharbi, R.S.; Jeon, B.-H. Evaluating the Effects of Landscape Fragmentation on Ecosystem Services: A Three-Decade Perspective. Ecol. Inform. 2023, 77, 102283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Zheng, G.; Liang, T. The Impact of Land Use and Land Cover Changes on the Landscape Pattern and Ecosystem Service Value in Sanjiangyuan Region of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Gu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Pan, S. Spatially Non-Stationary Relationships between Landscape Fragmentation and Soil Conservation Services in China, 2000–2018. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Zhuang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, J. Optimization of Land Use Patterns in a Typical Coal Resource-Based City Based on the Ecosystem Service Relationships of ‘Food–Carbon–Recreation’. Land 2025, 14, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Wang, B. Identification of Ecological Functional Areas and Scenario Simulation Analysis of the Wanjiang Urban Belt from a Trade-Off/Synergy Perspective. Land 2025, 14, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, L.; Fan, H.; Zhang, F.; Chen, W.; Xia, Y.; Yan, B. The Dominant Role of Human Activity Intensity in Spatial Pattern of Ecosystem Health in the Poyang Lake Ecological Economic Zone. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Chen, F.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, G. Effects of Land Utilization Transformation on Ecosystem Services in Urban Agglomeration on the Northern Slope of the Tianshan Mountains, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 162, 112046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Huang, C.; Li, X.; Song, M. The Spatial–Temporal Evolution and Influencing Factors of the Coupling Coordination of New-Type Urbanization and Ecosystem Services Value in the Yellow River Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Gu, T.; Fang, C.; Pan, S.; Zeng, J.; Wu, J. Simulating the Impact of Urban Expansion on Ecosystem Services in Chinese Urban Agglomerations: A Multi-Scenario Perspective. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, G.; Xue, B.; A, Y. Changes in Vegetation Cover and Its Influencing Factors in the Inner Mongolia Reach of the Yellow River Basin from 2001 to 2018. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Land Use Type | Carbon Density (t/hm2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aboveground Biomass Carbon Density | Subsurface Biomass Carbon Density | Soil Carbon Density | Carbon Density of Dead Organic Matter | |
| Cropland | 4.94 | 42.83 | 77.26 | 3.34 |
| Forest | 39.95 | 58.89 | 103.38 | 18.68 |
| Grassland | 3.97 | 40.58 | 83.28 | 12.56 |
| Water | 0.73 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Construction | 0.09 | 0 | 58.67 | 0 |
| Unused | 0.38 | 0 | 31.92 | 3.42 |
| Land Use Type | Carbon Density (t/hm2) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aboveground Biomass Carbon Density | Subsurface Biomass Carbon Density | Soil Carbon Density | Carbon Density of Dead Organic Matter | |
| Cropland | 17.14 | 80.72 | 108.43 | 9.82 |
| Forest | 42.4 | 115.98 | 158.83 | 14.11 |
| Grassland | 35.3 | 86.54 | 99.94 | 7.28 |
| Water | 0.31 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Construction | 2.53 | 27.67 | 0 | 0 |
| Unused | 1.32 | 0 | 21.65 | 0 |
| Xi’an | Jinan | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use Type | Habitat Suitability | Threats | Habitat Suitability | Threats | ||||
| Cropland | Construction | Unused | Cropland | Construction | Unused | |||
| Cropland | 0.3 | 0 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| Forest | 1 | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| Grassland | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| Water | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| Construction | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Unused | 0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 | 0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0 |
| Xi’an | Jinan | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Threat Factors | Influence Distance (km) | Weight | Spatial Decay Type | Influence Distance (km) | Weight | Spatial Decay Type |
| Cropland | 4 | 0.6 | linear | 8 | 0.6 | linear |
| Construction | 8 | 0.8 | linear | 12 | 1 | linear |
| Unused | 4 | 0.5 | linear | 5 | 0.4 | linear |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, B.; Tang, X.; Cui, J.; Cai, L. Characteristics of Ecosystem Services in Megacities Within the Yellow River Basin, Analyzed Through a Resilience Perspective: A Case Study of Xi’an and Jinan. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083371
Zhang B, Tang X, Cui J, Cai L. Characteristics of Ecosystem Services in Megacities Within the Yellow River Basin, Analyzed Through a Resilience Perspective: A Case Study of Xi’an and Jinan. Sustainability. 2025; 17(8):3371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083371
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Bowen, Xianglong Tang, Jiexin Cui, and Leshan Cai. 2025. "Characteristics of Ecosystem Services in Megacities Within the Yellow River Basin, Analyzed Through a Resilience Perspective: A Case Study of Xi’an and Jinan" Sustainability 17, no. 8: 3371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083371
APA StyleZhang, B., Tang, X., Cui, J., & Cai, L. (2025). Characteristics of Ecosystem Services in Megacities Within the Yellow River Basin, Analyzed Through a Resilience Perspective: A Case Study of Xi’an and Jinan. Sustainability, 17(8), 3371. https://doi.org/10.3390/su17083371


_Su.png)


