How Local Intermediaries Improve the Effectiveness of Public Payment for Ecosystem Services Programs: The Role of Networks and Agri-Environmental Assistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Case Study Research
- (Q1)
- Do local LCAs (a) provide for social networks (both between conflicting interest groups—i.e., bonding social capital; and towards individual farmers—i.e., bridging social capital) and (b) provide for agri-environmental information and assistance to farmers?
- (Q2)
- Do local LCAs assess their own work (a) as influencing farmers’ participation rates in AEMs and (b) as improving the spatial targeting of measures?
- (Q3)
- Can LCAs’ stated relative levels of social networks and their provision of agri-environmental information and assistance be related to their stated influence on farmers’ participation in and the spatial targeting of AEMs? In other words, can we find a relationship between LCAs’ stated involvement in the context of AEM implementation and their stated influence on the effectiveness of AEMs?
2.2. Analytical Framework
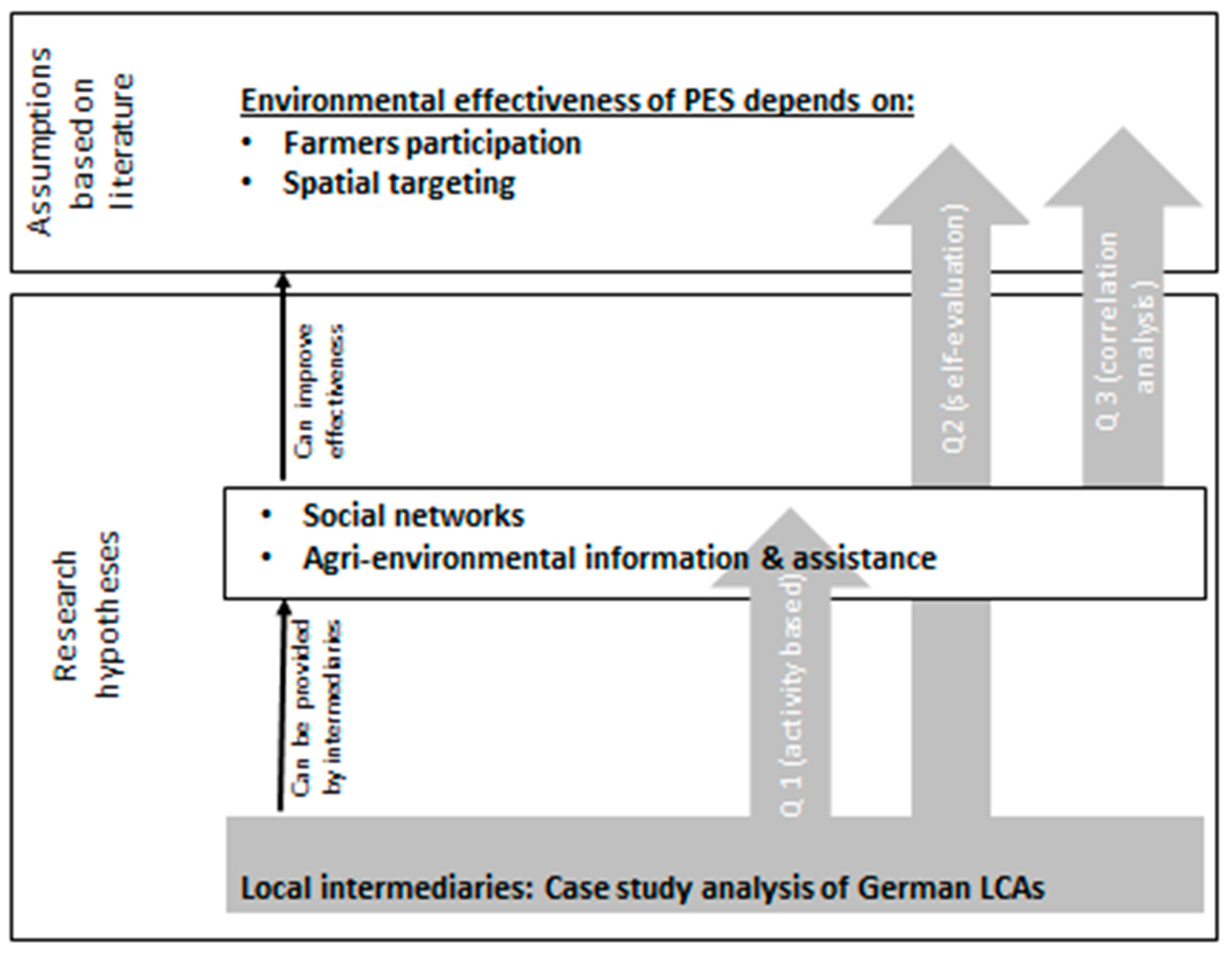
2.3. Data Collection
| Federal State | Existing LCAs | Invited LCAs | Participating LCAs | Participation Rate per Federal State |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bavaria | 55 | 52 | 19 | 36.5% |
| Baden-Wuerttemberg | 25 | 25 | 10 | 40.0% |
| North Rhine-Westphalia | 15 | 14 | 5 | 35.7% |
| Saxony | 15 | 14 | 2 | 14.3% |
| Brandenburg | 10 | 10 | 3 | 30.0% |
| Saxony-Anhalt | 9 | 9 | 3 | 33.3% |
| Mecklenburg-Hither Pomerania | 7 | 7 | 2 | 28.6% |
| Thuringa | 7 | 7 | 4 | 57.1% |
| Hesse | 6 | 5 | 2 | 40.0% |
| Schleswig-Holstein | 5 | 4 | 2 | 50.0% |
| Lower Saxony | 3 | 3 | 2 | 66.7% |
| Rhineland-Palatinate | 2 | 2 | 1 | 50.0% |
| Total Germany | 159 | 152 | 55 | 36.2% |
2.4. Questionnaire
2.4.1. Framing of Survey Questions and Limitations of the Data
2.4.2. Indicators to Operationalize Our Research Questions
Q1(a) Provision of Social Networks
Q1(b) Provision of Agri-Environmental Information and Assistance
Q2(a) Influence on Farmers’ Participation
Q2(b) Involvement in Spatial Targeting
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Provision of Social Networks
3.1.1. Practice-based Networks between Stakeholder Groups
3.1.2. Networks between LCAs and Farmers


3.2. Provision of Agri-Environmental Information and Assistance

| Variable | Yes | We could Provide Services in the Future | No | Not Applicable/Don’t know | No Response | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Info&assistance AEMs | 50.9% | 18.2% | 3.6% | 7.3% | 20% | 55 |
| (n = 28) | (n = 10) | (n = 2) | (n = 4) | (n = 11) | ||
| Info&assistance eco | 69.1% | 16.4% | 1.8% | 5.4% | 7.3% | 55 |
| (n = 38) | (n = 9) | (n = 1) | (n = 3) | (n = 4) | ||
| Info&assistance content | 56.5% | 23.6% | 3.6% | 7.3% | 7.3% | 55 |
| (n = 31) | (n = 13) | (n = 2) | (n = 4) | (n = 5) | ||
| Info&assistance effort | 58.2% | 16.4% | 9.1% | 9.1% | 7.3% | 55 |
| (n = 32) | (n = 9) | (n = 5) | (n = 5) | (n = 4) | ||
| Info&assistance fields | 60.0% | 21.8% | 9.1% | 3.6% | 5.5% | 55 |
| (n = 33) | (n = 12) | (n = 5) | (n = 2) | (n = 3) | ||
| Info&assistance forms | 40.0% | 18.2% | 25.5% | 9.1% | 7.3% | 55 |
| (n = 22) | (n = 10) | (n = 14) | (n = 5) | (n = 4) | ||
| Info&assistance info | 52.7% | 12.7% | 18.2% | 7.4% | 9.1% | 55 |
| (n = 29) | (n = 7) | (n = 10) | (n = 4) | (n = 5) | ||
| Info&assistance docu | 40.0% | 16.4% | 29.1% | 7.2% | 7.3% | 55 |
| (n = 22) | (n = 9) | (n = 16) | (n = 4) | (n = 4) |
3.3. Influence on Farmers’ Participation
3.3.1. Indirect Factors

3.3.2. Direct Factors

3.4. Involvement in Spatial Targeting
| Variable | Yes | We could Provide Services in the Future | No | Not Applicable/Don’t Know | No Response | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| We broker AEMs to relevant areas | 61.8% | 12.7% | 9.1% | 1.8% | 14.5% | 55 |
| (n = 34) | (n = 7) | (n = 5) | (n = 1) | (n = 8) | ||
| We broker AEMs towards most relevant farmers | 41.8% | 21.8% | 18.2% | 3.6% | 14.5% | 55 |
| (n = 23) | (n = 12) | (n = 10) | (n = 2) | (n = 8) | ||
| We broker AEMs towards relevant farmers to overcome single farm approach | 40.0% | 25.4% | 12.4% | 9.1% | 12.4% | 55 |
| (n = 22) | (n = 14) | (n = 7) | (n = 5) | (n = 7) |
3.5. The Relation between LCAs’ Involvement and Environmental Effectiveness
3.5.1. The relations between Social Networks and Participation
3.5.2. The Relations between Agri-Environmental Information and Assistance and Participation
| Participation (Indirect and Direct Influence Factors) | Targeting | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Farmers’ Perception Nature Conservation | Farmers’ Attitudes Nature Conservation Measures | Farmers’ willingness AEMs | Complex AEMs Contracts | Simple AEMs Contracts | Targeting Areas | Targeting Actors | Targeting Habitat Fragmentation | |
| Social Networks | Networks between stakeholder | 0.118 | −0.033 | 0.025 | 0.024 | 0.192 | 0.205 | −0.052 | 0.000 |
| (n = 50) | (n = 52) | (n = 52) | (n = 31) | (n = 32) | (n = 45) | (n = 44) | (n = 42) | ||
| Network LCA & farmer | 0.150 | 0.188 | 0.428 *** | 0.351 ** | 0.487 *** | 0.295 ** | 0.195 | 0.104 | |
| (n = 52) | (n = 53) | (n = 53) | (n = 32) | (n = 33) | (n = 46) | (n = 45) | (n = 43) | ||
| Network LCA & farmer for AEMs | 0.133 | 0.187 | 0.458 *** | 0.425 *** | 0.456 *** | 0.131 | 0.012 | −0.097 | |
| (n = 53) | (n = 53) | (n = 53) | (n = 32) | (n = 33) | (n = 46) | (n = 45) | (n = 43) | ||
| Network LCA & farmer for concerns on nature conservation | 0.212 | 0.152 | 0.477 *** | 0.337 ** | 0.343 ** | 0.378 ** | 0.154 | 0.114 | |
| (n = 53) | (n = 53) | (n = 53) | (n = 32) | (n = 33) | (n = 46) | (n = 45) | (n = 43) | ||
| Agri−environmental information and advice | Info & assistance AEMs | 0.011 | 0.116 | 0.038 | −0.025 | 0.250 | −0.047 | 0.086 | 0.072 |
| (n = 39) | (n = 38) | (n = 38) | (n = 23) | (n = 23) | (n = 33) | (n = 33) | (n = 31) | ||
| Info & assistance eco | −0.119 | 0.298 * | 0.294 ** | 0.063 | 0.066 | 0.497 *** | 0.228 | 0.175 | |
| (n = 45) | (n = 47) | (n = 47) | (n = 30) | (n = 31) | (n = 41) | (n = 41) | (n = 39) | ||
| Info & assistance content | −0.088 | 0.033 | 0.268 * | 0.206 | 0.168 | 0.345 ** | 0.348 ** | 0.198 | |
| (n = 45) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 29) | (n = 30) | (n = 41) | (n = 41) | (n = 39) | ||
| Info & assistance effort | −0.092 | 0.126 | 0.371 *** | 0.118 | 0.161 | 0.582 *** | 0.378 ** | 0.231 | |
| (n = 45) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 28) | (n = 29) | (n = 42) | (n = 42) | (n = 40) | ||
| Info & assistance fields | 0.004 | −0.037 | 0.247 * | 0.276 * | 0.310 * | 0.636 *** | 0.554 *** | 0.418 *** | |
| (n = 49) | (n = 50) | (n = 50) | (n = 30) | (n = 31) | (n = 44) | (n = 43) | (n = 41) | ||
| Info & assistance forms | −0.077 | 0.074 | 0.329 ** | 0.121 | 0.158 | 0.422 *** | 0.396 ** | 0.250 | |
| (n = 45) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 30) | (n = 30) | (n = 42) | (n = 43) | (n = 40) | ||
| Info & assistance info | 0.083 | 0.132 | 0.173 | 0.049 | 0.082 | 0.686 *** | 0.437 *** | 0.340 ** | |
| (n = 45) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 29) | (n = 30) | (n = 42) | (n = 41) | (n = 39) | ||
| Info & assistance docu | −0.198 | −0.224 | 0.059 | 0.092 | 0.067 | 0.333 ** | 0.402 *** | 0.275 * | |
| (n = 47) | (n = 47) | (n = 47) | (n = 29) | (n = 30) | (n = 43) | (n = 43) | (n = 41) | ||
3.5.3. The relations between Social Networks and Spatial Targeting
3.5.4. The Relations between Agri-Environmental Information and Assistance and Spatial Targeting
4. Discussion
4.1. Provision of Social Networks and Agri-Environmental Assistance
4.2. The Influence on Participation and Targeting
4.3. The Importance of Providing Social Networks and Agri-Environmental Information and Assistance for Participation and Targeting
4.3.1. The Importance of Agri-Environmental Information and Assistance
4.3.2. The Importance of Social Networks
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
| Indicator | Survey Questions | Response Categories | Value (Correlation Analysis) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social networks and perceived competency | |||
| Practice-based networks between stakeholders | “Do you provide a regular and practical local exchange on the ground and between the diverse stakeholder groups?” … and “if so, how often do you foster such an exchange annually?” | yes, no open answer | 0, 1 |
| Network LCA & farmer | “How often do farmers contact you on own initiative?” … and “why?” | always, very often, sometimes, rarely, never, not specified nature conservation, AEM, payment programs apart from AEM, others | Always = 4 |
| Very often = 3 | |||
| Sometimes = 2 | |||
| Rarely = 1 | |||
| Never = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| LCAs’ perceived competency for nature conservation | “Whom do farmers in your region commonly contact with concerns on nature conservation?” | public administration, LCA, farmer association, other farmers, neighbours, | LCAs mentioned = 1 |
| Otherwise = 0 | |||
| LCAs’ perceived competency for AEM | “Whom do farmers in your region commonly contact with concerns on AEM and why?” | public administration, LCA, farmer association, other farmers, neighbours, | LCAs mentioned = 1 |
| Otherwise = 0 | |||
| Components of agri-environmental information and assistance | |||
| Info & assistance AEM | “We inform farmers on the existence of AEM including availability of funds” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Info & assistance eco | “We inform farmers on the pursued ecological goal and explain why measures are important” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Info & assistance content | “We advise farmers on the content of the measures and explain how measures need to be implemented on own farm” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Info & assistance effort | “We advise farmers on the expected effort and time needed to implement measures” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Info & assistance fields | “We assist in identifying and selecting the most suitable plots and fields that shall be managed in accordance with AEMs on a single farm level” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Info & assistance forms | “We assist in completing and filling-in the AEM application forms, in particular if these are long and complex” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Info & assistance info | “We provide to and obtain for farmers additional and required information throughout the application and implementation process” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Info & assistance docu | “We assist farmers with the required documentation and recording of AEM implementation activities”. | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Participation | |||
| Farmers’ perception nature conservation | “Farmers’ perception towards nature conservation commonly improves when cooperating with LCAs” | strongly agree, slightly agree, neutral, slightly disagree, strongly disagree | Strongly agree = 2 |
| Slightly agree = 1 | |||
| Neutral = 0 | |||
| Slightly disagree = −1 | |||
| Strongly disagree = −2 | |||
| Farmers’ attitudes nature conservation measures | “Farmers’ attitudes towards nature conservation measures commonly improve when cooperating with LCAs” | strongly agree, slightly agree, neutral, slightly disagree, strongly disagree | Strongly agree = 2 |
| Slightly agree = 1 | |||
| Neutral = 0 | |||
| Slightly disagree = −1 | |||
| Strongly disagree = −2 | |||
| Farmers’ willingness AEM | “Farmers’ willingness to implement AEM on their fields commonly improves when cooperating with LCAs” | strongly agree, slightly agree, neutral, slightly disagree, strongly disagree | Strongly agree = 2 |
| Slightly agree = 1 | |||
| Neutral = 0 | |||
| Slightly disagree = −1 | |||
| Strongly disagree = −2 | |||
| Complex AEM contracts | “LCAs’ involvement has increased the number of complex, challenging, and cost-intensive AEM contracts signed” | strongly agree, slightly agree, neutral, slightly disagree, strongly disagree | Strongly agree = 2 |
| Slightly agree = 1 | |||
| Neutral = 0 | |||
| Slightly disagree = −1 | |||
| Strongly disagree = −2 | |||
| Simple AEM contracts | “LCAs’ involvement has increased the number contacts signed of those AEMs that are relatively easy to implement” | strongly agree, slightly agree, neutral, slightly disagree, strongly disagree | Strongly agree = 2 |
| Slightly agree = 1 | |||
| Neutral = 0 | |||
| Slightly disagree = −1 | |||
| Strongly disagree = −2 | |||
| Spatial Targeting | |||
| Targeting areas | “We broker AEMs in particular to very relevant areas” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Targeting actors | “We broker AEMs in particular towards the most relevant actors” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Targeting habitat fragmentation | “We broker AEMs in particular towards the most relevant actors to overcome a single-farm approach in order to e.g., alleviate habitat fragmentation or to ensure AEM implementation” | yes, we could provide service in the future, no, not applicable/don’t know | Yes = 1 |
| In future or no = 0 | |||
| Others not included in correlation analysis | |||
| Social Networks | Provision of Agri-environmental Information & Advice | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network between stake-holder | Network LCA & farmer | LCAs’ competen. nature conservation | LCAs’ competen. AEM | Info & assis. AEM | Info & assis. eco | Info & assis. content | Info & assis effort | Info & assis. fields | Info & assis. forms | Info & assis. info | Info & assis. docu. | |
| Network between stakeholder | 0.309 ** | 0.250 * | ||||||||||
| (n = 52) | (n = 52) | |||||||||||
| Networks LCA & farmer | 0.309 ** | 0.510 *** | 0.507 *** | 0.254 * | 0.268 * | 0.310 ** | 0.475 *** | 0.238 * | 0.237 * | |||
| (n = 52) | (n = 54) | (n = 54) | (n = 47) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 47) | ||||
| LCAs’ competency nature conservation | 0.250 * | 0.510 *** | 0.628 *** | 0.360 ** | 0.305 ** | |||||||
| (n = 52) | (n = 54) | (n = 55) | (n = 46) | (n = 50) | ||||||||
| LCAs’ competency AEM | 0.507 *** | 0.628 *** | 0.324 ** | 0.293 ** | 0.342 ** | 0.401 *** | 0.328 ** | 0.354 ** | ||||
| (n = 54) | (n = 55) | (n = 47) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 46) | (n = 50) | |||||
References
- Pirard, R.; Lapeyre, R. Classifying market-based instruments for ecosystem services: A guide to the literature jungle. Ecosyst. Serv. 2014, 9, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomers, S.; Matzdorf, B. Payments for ecosystem services: A review and comparison of developing and industrialized countries. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 6, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baylis, K.; Peplow, S.; Rausser, G.; Simon, L. Agri-environmental policies in the EU and the United States: A comparison. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 65, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherr, S.; Milder, J.; Inbar, M. Paying farmers for stewardship. In Farming with Nature. The Science and Practice of Ecoagricultre; Scherr, S., McNeely, J.A., Eds.; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007; pp. 378–399. [Google Scholar]
- Prager, K.; Freese, J. Stakeholder involvement in agri-environmental policy making—Learning from a local- and a state-level approach in Germany. J. Env. Manag. 2009, 90, 1154–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, N.; Whitby, M.; Simpson, I. Assessing the success of agri-environmental policy in the UK. Land Use Policy 1999, 16, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettepenningen, E.; Verspecht, A.; van Huylenbroeck, G. Measuring private transaction costs of European agri-environmental schemes. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2009, 52, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthes, S.; Matzdorf, B. Studies on agri-environmental measures: A survey of the literature. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deumlich, D.; Kiesel, J.; Thiere, J.; Reuter, H.I.; Volker, L.; Funk, R. Application of the SIte COmparison Method (SICOM) to assess the potential erosion risk—A basis for the evaluation of spatial equivalence of agri-environmental measures. Catena 2006, 68, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijn, D.; Berendse, F.; Smit, R.; Gilissen, N.; Smit, J.; Brak, B.; Groeneveld, R. Ecological effectiveness of agri-environment schemes in different agricultural landscapes in The Netherlands. Conserv. Biol. 2004, 18, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijn, D.; Sutherland, W.J. How effective are agri-environment schemes in conserving and promoting biodiversity. J. Appl. Ecol. 2003, 40, 947–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matzdorf, B.; Kaiser, T.; Rohner, M.-S. Developing biodiversity indicator to design efficient agri-environmental schemes for extensively used grassland. Ecol. Indic. 2008, 8, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wünscher, T.; Engel, S.; Wunder, S. Spatial targeting of payments for environmental services. A tool for boosting conservation benefits. Ecol. Econ. 2008, 65, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Horst, D. Assessing the efficiency gains of improved spatial targeting of policy interventions; the example of an agri-environmental scheme. J. Environ. Manag. 2007, 85, 1976–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smallshire, D.; Robertson, P.; Thompson, P. Policy into practice: The development and delivery of agri-environment schemes and supporting advice in England. Ibis 2004, 146, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uthes, S.; Matzdorf, B.; Müller, K.; Kaechele, H. Spatial targeting of agri-environmental measures: Cost-effectiveness and distributional consequences. Environ. Manag. 2010, 46, 494–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matzdorf, B.; Biedermann, C.; Meyer, C.; Nicolaus, K.; Sattler, C.; Schomers, S. Was kostet die Welt? Payments for Ecosystem Services in der Praxis. Erfolgreiche PES-Beispiele aus Deutschland, Großbritannien und den USA; Oekom-Verlag: München, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Matzdorf, B.; Biedermann, C.; Meyer, C.; Nicolaus, K.; Sattler, C.; Schomers, S. Paying for Green? Payments for Ecosystem Services in Practice. Successful examples of PES from Germany, the United Kingdom and the United States. Available online: http://www.civiland-zalf.org/download/PayingforGreen_PESinpractice.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2015).
- Bosselmann, A.S.; Lund, J.F. Do intermediary institutions promote inclusiveness in PES programs? The case of Costa Rica. Geoforum 2013, 49, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber-Stearns, H.R.; Goldstein, J.H.; Duke, E.A. Intermediary roles and payments for ecosystem services: A typology and program feasibility application in Panama. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 6, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, C.; Trampnau, S.; Schomers, S.; Meyer, C.; Matzdorf, B. Multi-classification of payments for ecosystem services: How do classification characteristics relate to overall PES success? Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 6, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farley, J.; Costanza, R. Payments for ecosystem services: From local to global. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 2060–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schomers, S.; Sattler, C.; Matzdorf, B. An analytical framework for assessing the potential of intermediaries to improve the performance of payments for ecosystem services. Land Use Policy 2015, 42, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, E.; Beeton, R.J.S. An accidental outcome: Social capital and its implication for Landcare and the “status quo”. J. Rural Stud. 2012, 28, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.S. Foundations of Social Theory; The Belknap Press of Havard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA; London, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Adler, P.; Kwon, S. Social capital: The good, the bad, the ugly. In Knowledge and Social Capital: Foundations and Applications; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2000; pp. 89–115. [Google Scholar]
- Woolcock, M. Social capital and economic development: Toward a theoretical synthesis and policy framework. Theory Soc. 1998, 27, 151–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuyama, F. Trust: The Social Virtues and the Creation of Prosperity; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Portes, A.; Sensenbrenner, J. Embeddedness and immigration: Notes on the social determinants of economic action. Am. J. Soc. 1993, 98, 1320–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, J.; Rahn, W. Individual-level evidence for the causes and consequences of social capital. Am. J. Pol. Sci. 1997, 41, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanyi, J.C. Individualistic and functionalistic explanations in the light of game theory: The example of the social status. Stud. Logic Found. Math. 1968, 49, 305–348. [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara, H.; Pascual, U. Social capital in community level environmental governance: A critique. Ecol. Econ. 2009, 68, 1549–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granovetter, M. Economic action and social structure: The problem of embeddedness. Am. J. Soc. 1985, 91, 481–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasib, A.B.A.; Jordan, J.L. Are friendly farmers environmentally friendly? Environmental awareness as a social capital outcome. In Proceedings of the Annual Meetings, Southern Agricultural Economic Associations, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 February 2006.
- Baumgart-Getz, A.; Prokopy, L.S.; Floress, K. Why farmers adopt best management practice in the United States: A meta-analysis of the adoption literature. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 96, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettepenningen, E.; Vandermeulen, V.; Delaet, K.; Van Huylenbroeck, G.; Wailes, E.J. Investigating the influence of the institutional organisation of agri-environmental schemes on scheme adoption. Land Use Policy 2013, 33, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattler, C.; Nagel, U.J. Factors affecting farmer’s acceptance of conservation measures—A case study from north-eastern Germany. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducos, G.; Dupraz, P.; Bonnieux, F. Agri-environment contract adoption under fixed and variable compliance costs. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2009, 52, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defrancesco, E.; Gatto, P.; Runge, F.; Trestini, S. Factors affecting farmers’ participation in agri-environmental measures: A Northern Italian perspective. J. Agric. Econ. 2008, 59, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falconer, K. Farm level constraints on agri-environmental scheme participation: A transactional perspective. J. Rural Stud. 2000, 16, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, R.; Gregg, D. Farmers’ intrinsic motivations, barriers to the adoption of conservation practices and effectiveness of policy instruments: Empirical evidence from northern Australia. Land Use Policy 2011, 28, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, K.; Posthumus, H. Socio-economic factors influencing farmers’ adoption of soil conservation practices in Europe. In Human Dimensions of Soil and Water Conservation, A Global Perspective; Nova Science Publisher: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 203–223. [Google Scholar]
- Metzner, J.; Keller, P.; Kretschmar, C.; Krettinger, B.; Liebig, N.; Mäck, U.; Orlich, I. Kooperativer Naturschutz in der Praxis: Umsetzungsbeispiele der Landschaftspflegeverbände und ihre Bewertung. Naturschutz Landschaftsplanung 2013, 45, 315–321. [Google Scholar]
- Prager, K. Agri-environmental collaboratives as bridging organisations in landscape management. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 161, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzner, J. Landschaftspflegeverbände—Markenzeichen des kooperativen Naturschutzes in Deutschland: Struktur, Arbeitsweise und Potential. Naturschutz Landschaftsplanung 2013, 45, 299–305. [Google Scholar]
- Prager, K.; Vanclay, F. Landcare in Australia and Germany: comparing structures and policies for community engagement in natural resource management. Ecol. Manag. Restor. 2010, 11, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, L.-A.; Mills, A.; Ingram, J.; Burton, R.J.F.; Dwyer, J.; Blackstock, K. Considering the source: Commercialisation and trust in agri-environmental information and advisory services in England. J. Environ. Manag. 2013, 118, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prager, K. Agri-environmental collaboratives for landscape management in Europe. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2015, 12, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prager, K.; Reed, M.; Scott, A. Encouraging collaboration for the provision of ecosystem services at a landscape scale—Rethinking agri-environmental payments. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metzner, J.; Kaerlein, M. Hinweise zur Gründung eines kooperativen Landschaftspflegeverbandes. Naturschutz und Landschaftsplanung 2013, 45, 305–306. [Google Scholar]
- Ingram, J. Agronomist-farmers knowledge encounters: An analysis of knowledge exchange in the context of best management practices in England. Agric. Hum. Values 2008, 25, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polman, N.B.P.; Slangen, L.H.G. Institutional design of agri-environmental contracts in te European Union: The role of trust and social capital. NJAS Wagening. J. Life Sci. 2008, 55, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garforth, C.; Angell, B.; Archer, J.; Green, K. Fragmentation or creative diversity? Options in the provision of land management advisory services. Land Use Policy 2003, 20, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.; Morris, C. The knowledge challenge within the transition towards sustainable soil management: An analysis of agricultural advisors in England. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 100–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettepenningen, E.; van Huylenbroeck, G. Factors influencing private transaction costs related to Agri-environmental Schemes in Europe. In Multifunctional Rural Land Management: Economics and Policies; Routledge: London, UK, 2009; pp. 145–168. [Google Scholar]
- Garbach, K.; Lubell, M.; DeClerck, F.A.J. Payment for Ecosystem Services: The roles of positive incentives and information sharing in stimulating adoption of silvopastoral conservation practices. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 156, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) No 1305/2013 of the European Parliament and the Council of 17 December 2013 on support for rural development by the European Agricultural Fund for Rural Developmen (EAFRD) and repealing Council Regulation (EC) No 1698/2005. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2013:347:0487:0548:EN:PDF (accessed on 2 October 2015).
- Greiner, R. Motivations and attitudes influence farmers’ willingness to participate in biodiversity conservation contracts. Agric. Syst. 2015, 137, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebert, R.; Toogood, M.; Knierim, A. Factors affecting European farmers’ participation in biodiversity policies. Sociol. Ruralis 2006, 46, 318–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.W. The Australian Landcare movement: Towards ‘post-productivist’ rural governance? J. Rural Stud. 2004, 20, 461–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, A.; Lockwood, M. Landcare and catchment management in Australia: Lessons for state-sponsored community participation. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2000, 13, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, P.; Halpin, D. Landcare as a politically relevant new social movement? J. Rural Stud. 1998, 14, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ducos, G.; Dupraz, P. Private provision of environmental services and transaction costs: Agro-environmental contracts in France. In Proceedings of the Environmental and Resource Economists 3rd World Confress, Kyoto, Japan, 3–7 July 2006.
- Tamini, L.D. A nonparametric analysis of the impact of agri-environmental advisory activities on best management practice adoption: A case study of Quebec. Ecol. Econ. 2011, 70, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Page, G.; Bellotti, B. Farmers value on-farm ecosystem services as important, but what are the impediments to participation in PES schemes? Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 515–516, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, C.; Reutter, M.; Matzdorf, B.; Sattler, C.; Schomers, S. Design rules for successful governmental payments for ecosystem services: Taking agri-environmental measures in Germany as an example. J. Env. Manag. 2015, 157, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prager, K. Adaptives Management in Naturschutz und Landschaftspflege—Die Rolle von Gruppen und Verbänden in Europa. Nat. Landsch. 2011, 86, 343–349. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schomers, S.; Matzdorf, B.; Meyer, C.; Sattler, C. How Local Intermediaries Improve the Effectiveness of Public Payment for Ecosystem Services Programs: The Role of Networks and Agri-Environmental Assistance. Sustainability 2015, 7, 13856-13886. https://doi.org/10.3390/su71013856
Schomers S, Matzdorf B, Meyer C, Sattler C. How Local Intermediaries Improve the Effectiveness of Public Payment for Ecosystem Services Programs: The Role of Networks and Agri-Environmental Assistance. Sustainability. 2015; 7(10):13856-13886. https://doi.org/10.3390/su71013856
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchomers, Sarah, Bettina Matzdorf, Claas Meyer, and Claudia Sattler. 2015. "How Local Intermediaries Improve the Effectiveness of Public Payment for Ecosystem Services Programs: The Role of Networks and Agri-Environmental Assistance" Sustainability 7, no. 10: 13856-13886. https://doi.org/10.3390/su71013856
APA StyleSchomers, S., Matzdorf, B., Meyer, C., & Sattler, C. (2015). How Local Intermediaries Improve the Effectiveness of Public Payment for Ecosystem Services Programs: The Role of Networks and Agri-Environmental Assistance. Sustainability, 7(10), 13856-13886. https://doi.org/10.3390/su71013856





