State-of-the-Art Review on Sustainable Design and Construction of Quieter Pavements—Part 1: Traffic Noise Measurement and Abatement Techniques
Abstract
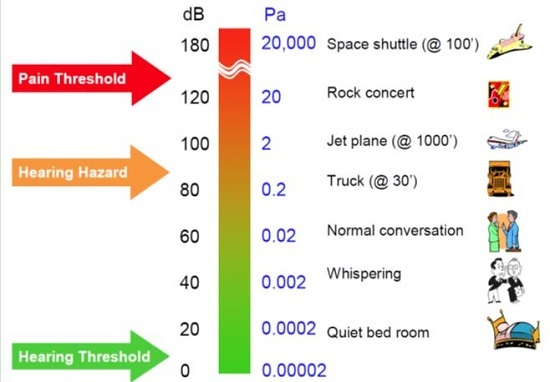
:1. Introduction
2. Noise Regulation Policy
3. Tire-Pavement Noise Generation Mechanisms
3.1. Sound Generation Mechanism
3.1.1. Tread Impact
3.1.2. Air Pumping
3.1.3. Stick-Slip
3.1.4. Stick-Snap
3.2. Sound Enhancement Mechanism
3.2.1. Horn Effect
3.2.2. Helmholtz Resonance
3.2.3. Pipe Resonance
3.2.4. Cavity Resonance
3.2.5. Carcass Vibration
4. Noise Measurement Methods
4.1. Wayside Noise Measurement
4.1.1. Statistical Pass-by Methods
4.1.2. Controlled Pass-by (CPB) Method
4.1.3. Continuous Flow Traffic Time Integrated Method (CTIM)
4.2. Noise Measurement at Source
4.2.1. CPX (Trailer) Method
4.2.2. OBSI Method
4.3. Laboratory Drum Method
4.4. Relationship between Source and Wayside Noise Measurements
5. Noise Abatement Techniques
5.1. Noise Barrier Wall
5.2. Vegetation Technique
5.3. Private Fencing
5.4. Buffer Zone
5.5. Using Insulating Materials
5.6. Traffic Management
5.7. Modifying Surface or Mixture Properties
5.7.1. Porous Asphalt Surface/Mixture
5.7.2. Double Layer Porous Surface
5.7.3. Thin Asphalt Layer
5.7.4. Stone Mastic Asphalt (SMA)
5.7.5. Asphalt Rubber Friction Course (ARFC)
5.7.6. Diamond Grinding Concrete
5.7.7. Exposed Aggregate Cement Concrete (EACC)
5.7.8. Poroelastic Road Surface (PERS)
5.7.9. Enhanced Porosity Concrete (EPC)
6. Conclusions
- Tire-pavement noise is generated due to a combination of noise generation and amplification mechanisms. Different combinations of generation and amplification mechanisms of noise may be dominant for different surfaces and conditions. Therefore, it is difficult to develop one single strategy which can be used to reduce the tire-pavement noise efficiently. Furthermore, some of these mechanisms are directly related to the safety, durability, and cost of pavement, which adds further challenges in mitigating noise.
- Tire-pavement noise measurement systems are reported widely in literature. Currently, there are three general methods used throughout the world, which include Pass-by methods, the CPX method, and the OBSI method. However, researchers encourage the use of the OBSI because of its efficient and precise monitoring of pavement noise. Noise prediction of quieter pavement can be performed by using OBSI when combined with TNM.
- There are a number of noise abatement techniques adopted by various transport authorities all over the world. Of them, noise barrier wall is used frequently by various highway agencies due to its effectiveness of initial noise reduction and acoustic performance over time. However, noise barrier wall is only a local solution and cannot be extended to the entire length of the road due to its high construction cost.
- European transport authorities recognize that modifying the pavement surface type has the potential to be a cost effective and practically viable noise abatement technique. However, FHWA is still reluctant to accept modifying pavement surface type as a noise abatement technique because the issues with cost, durability, maintenance and sustainability of noise benefit of these surfaces.
- More research is required for the sustainability of the modified surface before using as noise mitigation technique. However, these surfaces can be used as a noise mitigation technique with additional maintenance in accordance with conventional pavement maintenance scheduling. This may lead to overall cost of pavement construction and maintenance but it is still a viable option as noise benefit can be provided to the entire length of highway.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rasmussen, R.; Bernhard, R.; Sandberg, U.; Mun, E. The Little Book of Quieter Pavements; Report No. FHWA-IF-08-004; Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2007.
- Bernhard, R.; Wayson, R. An Introduction to Tire-Pavement Noise; Final Research Report SQDH 2005-1; Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg, U.; Ejsmont, J. Tire-Road Noise Reference Book; Informex: Kisa, Sweden, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Federal Highway Administration (FHWA). Highway Traffic Noise: Analysis and Abatement Guidance; Report No. FHWA-HEP-10-025; Federal Highway Administration, US DOT: Washington, DC, USA, 2011.
- World Health Organization (WHO). Night Noise Guidelines for Europe; Regional Office for Europe: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2009; Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0017/43316/E92845.pdf (accessed on 12 May 2016).
- Jabben, J.; Potma, J.; Swart, J. Continuous monitoring of noise emission from roadways. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2001, The Hague, The Netherlands, 27–30 August 2001.
- Babisch, W. Transportation noise and cardiovascular risk: Updated review and synthesis of epidemiological studies indicate that the evidence has increased. J. Noise Health 2006, 8, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, H.; Andersen, B. Thin Noise Reducing Pavements-Experiences; Report No. 145; Road Directorate, Danish Road Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, H.; Andersen, B. Noise-reducing pavements for highways and urban roads-state of the art in Denmark. In Proceedings of the Association of Asphalt Paving Technologists Technical Sessions, Long Beach, CA, USA, 7–9 March 2005.
- Donavan, P. Reducing traffic noise with quieter pavements. In Proceedings of the Noise-Con 2005, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 15–17 October 2005.
- Hanson, I.; James, S.; NeSmith, C. Tire-Pavement Noise Study; National Center for Asphalt Technology: Auburn, AL, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kragh, J.; Bendtsen, H.; Hildebrand, G. Noise classification for tendering quiet asphalt wearing courses. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2012, 48, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, J.; Read, D. Noise benefits of asphalt pavements—Trends at ages up to 52 months. J. Noise Control Eng. 2009, 57, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochat, J.; Hastings, A.; Read, D.; Lau, M. FHWA Traffic Noise Model (TNM) Pavement Effects Implementation Study: Progress Report 1; Research Report No. DOTVNTSC-FHWA-12-01; U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2012.
- Trevino, M.; Dossey, T. A Research Plan for Measuring Noise Levels in Highway Pavements in Texas; Report No. FHWA/TX-07/0-5185-1; Center for Transportation Research, The University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, G.; Morgan, A.; McKell, B. A Review of Current Research on Road Surface Noise Reduction Techniques; Project Record: TRL/001/08; Transportation Research Laboratory: Wokingham, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Dare, T.; McDaniel, R.; Shah, A.; Bernhard, R. Hot Mix Asphalt Surface Characteristics Related to Ride, Texture, Friction, Noise and Durability; Report No. MN/RC 2014-07; Minnesota Department of Transportation: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Schafer, R. The Soundscape; Destiny Books: Rochester, VT, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kephalopoulos, S.; Paviotti, M.; Lédée, F. Common Noise Assessment Methods in Europe (CNOSSOS-EU); Report EUR 25379 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Ispra, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterveld, K. The diabolic symphony of the mechanical age: Technology and symbolism of sound in European and North American noise abatement campaigns, 1900-40. J. Soc. Stud. Sci. 2001, 31, 37–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, J.; Sandberg, U. Tire-Pavement Noise; Where Does It Come from? Report No. 240, TR News; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhala, J. A study of Tire-Pavement Noise Using Near-Field Acoustical Holography. Ph.D. Thesis, Pennsylvania State University, State College, PA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg, U. Tire-road noise-myths and realities. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise, The Hague, The Netherlands, 27–30 August 2001.
- Nilsson, N.; Bennerhult, O.; Soederqvist, S. External tire-road noise: Its generation and reduction. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 1980, Miami, FL, USA, 8–10 December 1980; p. 245.
- Descornet, G.; Sandberg, U. Road surface influence on tire/road noise-part II. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 1980, Miami, FL, USA, 8–10 December 1980.
- Nilsson, N. Principles in the control of external tire/road noise. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 1982, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–19 May 1982; p. 123.
- Fujikawa, T.; Koike, H.; Oshino, Y.; Tachibana, H. Road texture for abating truck tire noise generation. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2006, Honolulu, HI, USA, 3–6 December 2006.
- Plotkin, K.; Montroll, L.; Fuller, R. The generation of tire noise by air pumping and carcass vibration. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 1980, Miami, FL, USA, 8–10 December 1980; p. 273.
- Kim, S.; Jeong, W.; Park, Y.; Lee, S. Prediction method for tire air-pumping noise using a hybrid technique. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2006, 119, 3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, R.; Taryma, S. Investigations in tire/road noise in longitudinal slip conditions. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2004, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–24 August 2004; p. 2300.
- Wozniak, R. Measurement of tire/road noise in longitudinal slip conditions. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2001, The Hague, The Netherlands, 27–30 August 2001; p. 556.
- Kroger, M.; Lindner, M.; Popp, K. Influence of friction on noise and vibrations of tires. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2004, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–24 August 2004; p. 1457.
- Schaaf, K.; Ronneberger, D. Noise radiation from rolling tires-sound amplification by the “horn-effect”. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 1982, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–19 May 1982; p. 131.
- Iwai, S.; Miura, Y.; Hidetomo, K.; Levy, G. Influence of porous asphalt pavement characteristics on the horn amplification of tire-road contact noise. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 1994, Yokohama, Japan, 29–31 August 1994; p. 431.
- Lui, W.; Li, K. A theoretical study for the propagation of rolling noise over a porous road pavement. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2004, 116, 313. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsler, E.; Frey, R.; Coppens, B.; Sanders, V. Fundamentals of Acoustics, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ruhala, J.; Burroughs, B. Separation of leading edge, trailing edge, and sidewall noise sources from rolling tires. In Proceedings of the Noise-Con, Ypsilanti, MI, USA, 5–8 April 1998; p. 109.
- Fujii, T.; Iwai, S.; Kuroki, M. Behavior of tire tread groove relating to generation of tire-road noise at the contact patch. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2003, Jeju, Korea, 25–28 August 2003; p. 885.
- Koiki, H.; Fujikawa, T.; Oshino, Y.; Tachibana, H. Generation mechanism of tire-road noise. Part 2: Pipe resonance in tread groove of tire. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 1999, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 6–9 December 1999; p. 199.
- International Standard ISO 11819-1. Acoustics-Method for Measuring the Influence of Road Surfaces on Traffic Noise. Part 1: The Statistical Pass-by Method; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Fleming, G. Measurement of Highway-Related Noise; Report FHWA-PD-96-046; Federal Highway Administration, US DOT: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- AASHTO TP 98-13. Standard Method of Test for Determining the Influence of Road Surfaces on Vehicle Noise Using the Statistical Isolated Pass-by (SIP) Method; American Association of State and Highway Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Reyff, J. REMEL database developed for different PCC pavement surfaces. In Proceedings of the Noise-Con, Reno, Nevada, 22–24 October 2007.
- Fleming, G.; Rapoza, A.; Lee, C. Development of National Reference Energy Mean Emission Levels for the FHWA Traffic Noise Model (FHWA TNM®); Report No. DOT-VNTSC-FHWA-96-2, Version 1.0; U.S. Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA; Volpe National Transportation Systems Center: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Kuemmel, D.; Sonntag, R.; Crovetti, J.; Becker, Y.; Jaeckel, J.; Satanovsky, A. Noise and Texture on PCC Pavements-Results of a Multi-State Study; Report No. WI/SPR-08-99; Wisconsin Department of Transportation: Madison, WI, USA, 2000.
- AASHTO TP 99-13. Standard Method of Test for Determining the Influence of Road Surfaces on Traffic Noise Using the Continuous-Flow Traffic Time-Integrated Method (CTIM); American Association of State and Highway Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dumbacher, S.; Blough, J.; Hallman, D.; Wang, P. Source identification using acoustic array techniques. In Proceedings of the Society of Automotive Engineers Noise and Vibration (SAE Paper 951360), Traverse City, MI, USA, 15–18 May 1995.
- International Standard ISO-11819-2. Acoustics-Measurement of the Influence of Road Surfaces on Traffic Noise. Part 2: Close-Proximity Method; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bennert, T.; Hanson, D.; Maher, A.; Vitillo, N. Influence of pavement surface type on tire-pavement generated noise. J. Test. Eval. 2005, 33, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, D.; Mun, S. Study to analyze the effect of vehicles and pavement surface types on noise. J. Appl. Acoust. 2008, 69, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punnamee, S.; Dai, L. Road and tire noise emission assessment with closed proximity method on an asphalt rubber concrete pavement. In Proceedings of the Transportation Association of Canada Fall Meeting, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 14–17 October 2007.
- Scofield, L.; Donavan, P. Development of Arizona’s Quiet Pavement Research Program; Arizona Department of Transportation: Chandler, AZ, USA, 2004.
- Oswald, L.; Donavan, P. Acoustic Intensity Measurements in Low Mach Number Flows of Moderate Turbulence Levels; Research Publication GMR-3269; General Motors Research Laboratories: Warren, MI, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- GM North American Engineering Standards. Road Tire Noise Evaluation Procedure -GMN-7079TP; General Motors Corporation: Detroit, MI, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, R. Pin-point noise sources on vehicles during pass-by using intensity technique. In Proceedings of the International Tire-Road Noise Conference, Gothenberg, Sweden, 8–10 August 1990.
- AASHTO TP 76-15. Standard Method of Test for Measurement of Tire-Pavement Noise Using the on-Board Sound Intensity (OBSI) Method; American Association of State and Highway Transportation Officials: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalski, K. Influence of Mixture Composition on the Noise and Frictional Characteristics of Flexible Pavements. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wulf, T.; Dare, T.; Bernhard, R. The effect of grinding and grooving on the noise generation of Portland cement concrete pavement. In Proceedings of the Acoustics ’08 Paris Conference, Paris, France, 29 June–4 July 2008.
- Abbott, P.; Watts, G. The relationship between coast-by and close-proximity car tire noise levels for different road surfaces. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2004, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–25 August 2004.
- Hanson, D. Long-term noise characteristics of HMA. In Proceedings of the Noise-Con, Baltimore, MD, USA, 12–14 July 2004.
- Lédée, F. Modeling the local propagation effects of tire-load noise: Propagation filter between CPX and CPB measurements. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2004, Prague, Czech Republic, 22–25 August 2004.
- Sandberg, U.; Ejsmont, J. Tire-road noise: Trailer measurements in practice. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 1985, Munich, Germany, 18–20 September 1985.
- Donavan, P. Tire-pavement interaction noise measurement under vehicle operating conditions of cruise and acceleration. In Proceedings of the Society of Automotive Engineers Noise and Vibration (SAE Paper 931276), Traverse City, MI, USA, 10–13 May 1993.
- Donavan, P.; Rymer, B. Assessment of highway pavements for tire-road noise generation. In Proceedings of the Society of Automotive Engineers Noise and Vibration, Grand Traverse, MI, USA, 3 May 2003.
- Rasmussen, R.; Sohaney, C. Tire-Pavement and Environmental Traffic Noise Research Study; The Transtec Group, Inc.: Austin, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wayson, R.; MacDonald, M.; Martin, A. Modelling of Quieter Pavement in Florida—Phase I; John A. Volpe National Transportation Systems Center: Cambridge, MA, USA; Florida Department of Transportation: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wayson, R.; MacDonald, M.; Martin, A. On-Board Sound Intensity (OBSI) Study—Phase II; John A. Volpe National Transportation Systems Center: Cambridge, MA, USA; Florida Department of Transportation: Tallahassee, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Donavan, P. The effects of porous pavements on tire-pavement noise source levels and pass-by measurements. In Proceedings of the Noise-Con, Portland, OR, USA, 25–27 July 2011.
- Donavan, P.; Scofield, L. Near field tire noise measurements of similar pavements of different ages. In Proceedings of the Noise-Con, Baltimore, MD, USA, 12–14 July 2004.
- Donavan, P. Overview of the Arizona quiet pavement program. In Proceedings of the Noise-Con, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 17–19 October 2005.
- Donavan, P.; Lodico, D. Measuring Tire-Pavement Noise at the Source; National Cooperative Highway Research Program, NCHRP Project: 1-44, Report No. 630; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Donavan, P.; Pierce, L.; Lodico, D.; Rochat, J.; Knauer, H. Evaluating Pavement Strategies and Barriers for Noise Mitigation; National Cooperative Research Program, NCHRP Report No. 738; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso, S.; Graziano, A.; Kerali, H.; Odoki, J. Multicriteria analysis method for pavement maintenance management. J. Transp. Res. Rec. 2002, 1816, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Machí, C.; Chamorro, A.; Pellicer, E.; Yepes, V.; Videla, C. Sustainable pavement management: Integrating economic, technical, and environmental aspects in decision making. Transp. Res. Rec. 2015, 2523, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, V.; Torres-Machí, C.; Chamorro, A.; Pellicer, E. Optimal pavement maintenance programs based on a hybrid greedy randomized adaptive search procedure algorithm. J. Civ. Eng. Manag. 2016, 22, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellicer, E.; Sierra, A.; Yepes, V. Appraisal of infrastructure sustainability by graduate students using an active-learning method. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 113, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowlby, W.; Pratt, G.; Williamson, R.; Knauer, H.; Kaliski, K. Noise Barrier Acceptance Criteria: Analysis; FHWA Publication No. FHWA-HEP-16-017; Federal Highway Administration, US Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2016.
- Bendtsen, H. Noise Barrier Design: Danish and Some European Examples; Report: UCPRC-RP-2010-04; Road Directorate, Danish Road Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Smith, G.; Shores, R. Pavement noise investigation on North Carolina highways: An on-board sound intensity approach. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2012, 39, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, V.; Martí, J.V.; García-Segura, T. Cost and CO2 emission optimization of precast-prestressed concrete U-beam road bridges by a hybrid glowworm swarm algorithm. Autom. Constr. 2015, 49, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K. Propagation of sound and related shadow zones: The reality of field measurements versus modeled studies. Wall J. 2000, 41, 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, C.; Tom, K.; Norasit, T. Crumb rubber blends in noise absorption study. J. Mater. Struct. 2008, 41, 383–390. [Google Scholar]
- Lau, M.; Lee, C.; Rochat, J.; Boeker, E.; Fleming, G. FHWA Traffic Noise Model User’s Guide (Version 2.5 Addendum); U.S. Department of Transportation, Federal Highway Administration, Office of Natural and Human Environment: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Anderson, G.; Cynthia, Y.; Lee, G.; Menge, W. FHWA Traffic Noise Model, Version 1.0: User’s Guide; Report No. FHWA-PD-96-009 and DOT-VNTSC-FHWA-98-1; U.S. Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA; John A. Volpe National Transportation Systems Center: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg, U.; Mioduszewski, P. Reduction of noise and rolling resistance by horizontal grinding of asphalt pavements. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2015, San Francisco, CA, USA, 9–12 August 2015.
- Crocker, M.; Hanson, D.; Li, Z.; Karjatkar, R.; Vissamraju, K. Measurement of acoustical and mechanical properties of porous road surfaces and tire and road noise. J. Transp. Res. Board 2004, 1891, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Asphalt Pavement Association (EAPA). Abatement of Traffic Noise—The Arguments for Asphalt; EAPA: Brussels, Belgium, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hanson, D.; Waller, B. 2005 Colorado DOT Tire-Pavement Noise Study; Report No. CDOT-2006-18; Colorado Department of Transportation: Denver, CO, USA, 2006.
- Sandberg, U. The Global Experience in Using Low-Noise Road Surfaces: A Benchmark Report; Report Made in Response to ‘Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department’ Project No. AN 06-004; Hong Kong Environmental Protection Department: Hong Kong, China, 2009.
- Bendtsen, H. Drainage asphalt and noise reduction over a long period. In Proceedings of the Euro-Noise 1998, Munich, Germany, 4–7 October 1998.
- Faure, B.; Hamet, J.F.; Kestemont, X.; Luminari, M.; Quaresma, L.; Sandulli, D. Traffic Noise and Road Surfaces: State of the Art; Belgian Road Research Centre: Brussels, Belgium, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Goubert, L.; Hooghwerff, J.; The, B.; Hofman, R. Two-layer porous asphalt: An international survey in the frame of the Noise Innovation Programme (IPG). In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2005, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 7–10 August 2005.
- Bendtsen, H.; Larsen, E. Two-layer porous pavements and noise reductions in Denmark. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise, The Hague, The Netherlands, 27–30 August 2001.
- Sandberg, U.; Kragh, J.; Goubert, L.; Bendtsen, H.; Bergiers, A.; Biligiri, K.; Karlsson, R.; Nielsen, E.; Olesen, E.; Vansteenkiste, S. Optimization of Thin Asphalt Layers—State of the Art Review; Project: ERA-NET ROAD; European National Road Administrations: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, H.; Raaberg, J. Safety and Noise Reduction, Thin Layers; Technical Note 52; Road Directorate, Danish Road Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Vuye, C.; Bergiers, A.; Vanhooreweder, B. The acoustical durability of thin noise reducing asphalt layers. Coatings 2016, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendtsen, H.; Lu, Q.; Kohler, E. Acoustic Aging of Asphalt Pavements: A Californian/Danish Comparison; Report No. UCPRC-RP-2010-0; California Department of Transportation: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2010.
- Kragh, J. Road Surfacing—Noise Reduction Time History; Report 161; Road Directorate, Danish Road Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kragh, J.; Nielsen, E.; Olesen, E.; Goubert, L.; Vansteenkiste, S.; Visscher, J.; Sandberg, U.; Karlsson, R. Optimization of Thin Asphalt Layers; Project: ERA-NET ROAD, Project No. VV 2009/40520; European National Road Administrations: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen, S.; Bendtsen, H.; Andersen, B. Optimized Thin Layers—Urban Roads, the Kastrupvej Experiment; Technical Note 66; Road Directorate, Danish Road Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, H.; Raaberg, J. French Experiences on Noise Reducing Thin Layers; Technical Note 28; Road Directorate, Danish Road Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- European Asphalt Pavement Association (EAPA). Heavy Duty Surfaces: The Arguments for SMA; EAPA: Brussels, Belgium, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Valtonen, J.; Hyyppä, I.; Sainio, P. Noise reduction vs. wearing properties. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Asphalt Pavements, Copenhagen, Denmark, 17–22 August 2002.
- Aspro; Silence in Arizona. Official Journal of the Institute of Asphalt Technology; Institute of Asphalt Technology: Bathgate, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Bendtsen, H.; Nielson, E. DRI-DWW Thin Layer Project—Final Report; DRI Report 159; Road Directorate, Danish Road Institute: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sotil, A.; Biligiri, K.; Kalousch, E.; Golden, S. The Dynamic Complex Modulus (E*) Test as a Potential Indicator for an Asphalt Mixture’s Tire- Road Noise Characteristics; TRB Paper 06-3088; Transportation Research Board: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ripke, O.; Andersen, B.; Bendtsen, H.; Sandberg, U. Silence—Report of Promising New Road Surfaces for Testing; Silence Report F.D4; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tehrani, F. Noise abatement of hot mix asphalt: A brief review. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2014, 8, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen, R.; Garber, S.; Fick, G.; Ferragut, T.; Wiegand, P. How to Reduce Tire-Pavement Noise: Interim Better Practices for Constructing and Texturing Concrete Pavement Surface; Research Report Pooled Fund TPF-5(139); National Concrete Pavement Technology Center: Ames, IA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Litzka, J.; Haberl, J. Evaluation of Near Field Noise Emissions on Austria Pavements; Final Project Report; BMVIT: Vienna, Austria, 2005; unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- SILVIA. Guidance Manual for the Implementation of Low-Noise Road Surfaces; FEHRL Report 2006/02; FEHRL Secretariat: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg, U.; Goubert, L. Poroelastic Road Surface (PERS): A review of 30 years of R&D work. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2011, Osaka, Japan, 4–7 September 2011.
- Morgan, A. IPG Research Report-Innovative Mitigation Measures for Road Traffic Noise; Report DVS-2008-018; Road and Hydraulic Engineering Division of Rijkswaterstaat: Delft, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Neithalath, N.; Weiss, J.; Olek, J. Reducing the Noise Generated in Concrete Pavements through Modification of the Surface Characteristics; PCA R&D Serial No. 2878; Portland Cement Association: Skokie, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Neithalath, N.; Marlof, A.; Weiss, J.; Olek, J. Modeling the influence of pore structure on the acoustics absorption of enhanced porosity concrete. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2005, 3, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descornet, G. Low noise road surface techniques and materials. In Proceedings of the Inter-Noise 2000, Nice, France, 27–30 August 2000.



















| Reference Used | Reference Pavement | Pavement | Maximum Aggregate Size (mm) of TAL | Air Void (%) | Noise Test Reference Condition | Noise Reduction Compared to Reference Pavement (dB) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passenger Car | Multi-Axle Trucks | ||||||
| Vuye et al. [96] | SMA-10
| Test Section 2 | 4 | 25 |
| 6.9 | 3.6 |
| Test Section 3 | 4 | 25 | 5.9 | 3.2 | |||
| Test Section 4 | 6.3 | 11 | 5.7 | 2.7 | |||
| Test Section 6 | 6.3 | 15 | 5.8 | 4.2 | |||
| Test Section 7 | 6.3 | 11 | 4.6 | 3.5 | |||
| Test Section 8 | 6.3 | 11 | 3.7 | 3.0 | |||
| Test Section 9 | 6.3 | 11 | 3.3 | 2.5 | |||
| Test Section 10 | 8 | 14 | 1.3 | 1.3 | |||
| Thompson et al. [100] | DAC
| OGAC 6 | 6 | - |
| 4.3 | - |
| SMA-a-6 * | 6 * | 3.4 | 1.3 | - | |||
| SMA-b-6 * | 6 * | 5.7 | 0.9 | - | |||
| SMA-6 | 6 | 15.3 | 3.2 | - | |||
| SMA-4 | 4 | 8.8 | 1.6 | - | |||
| SMA-4 * | 4 * | 10.2 | 3.0 | - | |||
| SMA-6 * (opt) | 6 * | 13.9 | 3.7 | - | |||
| Bendtsen and Raaberg [101] | AC
| Type-1 | 6 | - |
For multi-axle trucks—80 km/h | 2.7 | 1.9 |
| Type-2 | 6 | Higher air void than type-1 | 3.7 | 3.1 | |||
| Bendtsen and Raaberg [101] | AC
| Type-1 | 6 | - |
For multi-axle trucks—80 km/h | 4.2 | 3.0 |
| Type-2 | 6 | Higher air void than type-1 | 5.2 | 4.2 | |||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ohiduzzaman, M.; Sirin, O.; Kassem, E.; Rochat, J.L. State-of-the-Art Review on Sustainable Design and Construction of Quieter Pavements—Part 1: Traffic Noise Measurement and Abatement Techniques. Sustainability 2016, 8, 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080742
Ohiduzzaman M, Sirin O, Kassem E, Rochat JL. State-of-the-Art Review on Sustainable Design and Construction of Quieter Pavements—Part 1: Traffic Noise Measurement and Abatement Techniques. Sustainability. 2016; 8(8):742. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080742
Chicago/Turabian StyleOhiduzzaman, MD, Okan Sirin, Emad Kassem, and Judith L. Rochat. 2016. "State-of-the-Art Review on Sustainable Design and Construction of Quieter Pavements—Part 1: Traffic Noise Measurement and Abatement Techniques" Sustainability 8, no. 8: 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080742
APA StyleOhiduzzaman, M., Sirin, O., Kassem, E., & Rochat, J. L. (2016). State-of-the-Art Review on Sustainable Design and Construction of Quieter Pavements—Part 1: Traffic Noise Measurement and Abatement Techniques. Sustainability, 8(8), 742. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8080742