State-Of-The-Art Review of Geosynthetic Clay Liners
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Configuration of Geosynthetic Clay Liners
3. Properties of GCLs
3.1. Hydraulic Conductivity and Chemical Compatibility
3.2. Self-Healing Capacity
3.3. Diffusion
3.4. Gas Migration
3.5. Mechanical Behaviour
3.5.1. Internal Shear Strength
3.5.2. Interface Shear Strength
4. Recent Advancement of GCL and Perspectives
4.1. Polymer-Treated GCL
4.2. Perspectives for Further Study
5. Conclusions
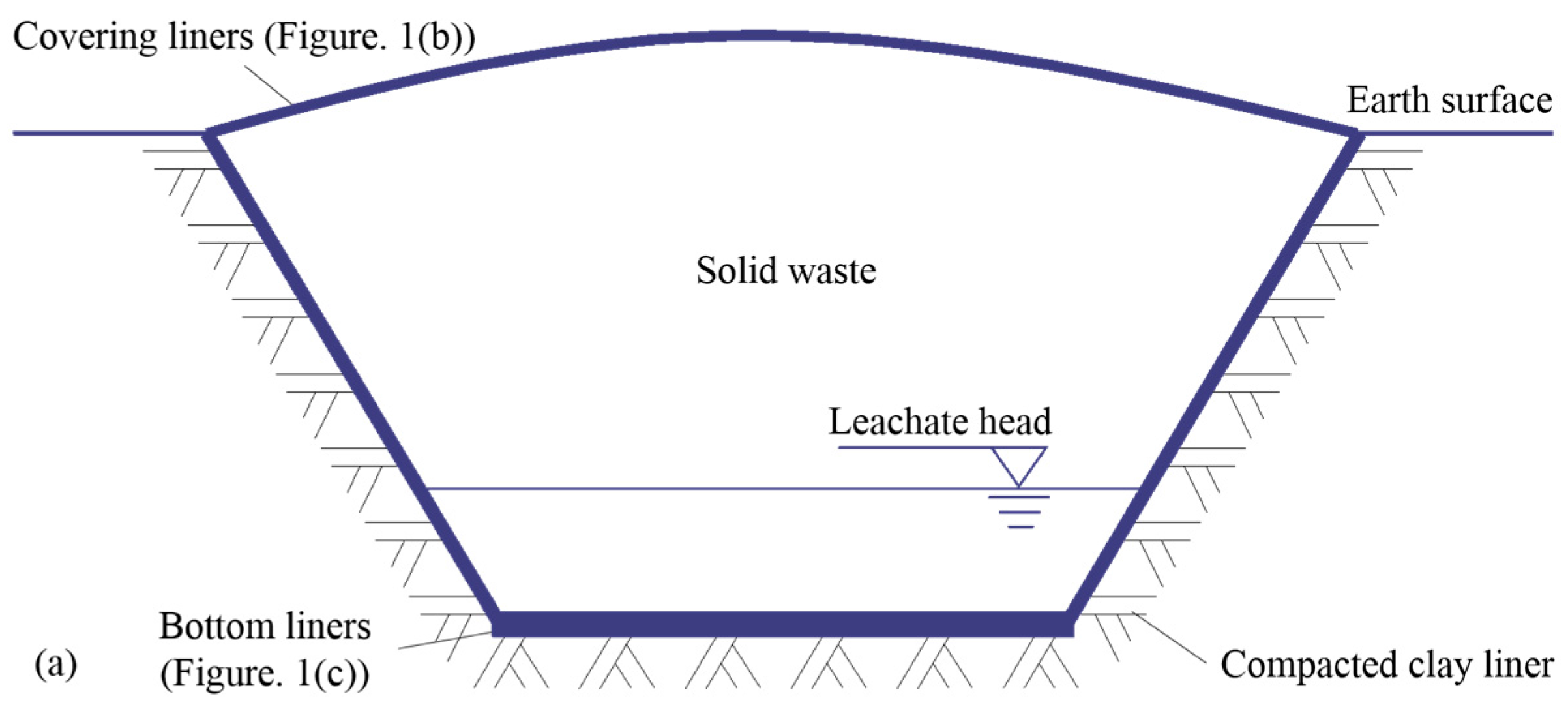
- (a)
- Research on geosynthetic clay liners has experienced rapid growth over the past few decades. Numerous laboratory investigations and field tests have been undertaken to examine the performance of geosynthetic clay liners, such as their hydraulic conductivity and chemical compatibility, water-swelling and self-healing capacity, diffusion, gas migration, and shear strength. These properties are found to be affected by a variety of factors, e.g., structural types, permeant solution, hydration condition, confining pressure, environmental factors (temperature, hydraulic head, etc.), which can vary from case to case. It is of great importance to assess the properties of GCL on a site-specific basis.
- (b)
- With the wide use of GCLs in landfills and other geotechnical applications, more problems concerned with complicated environments, such as moisture-cycles, freeze-thaw cycles, thermal cycles, long-term exposure to solar radiation, GCL-lined slopes, can be encountered. Such particular environments may significantly influence the long-term hydraulic performance and durability of GCLs. Although primary studies on the impact of these factors can be found in some publications, the mechanism by which complicated conditions influence the physical and chemical properties of GCL components needs to be further investigated.
- (c)
- Polymer-treated technology has shown great potential for future GCL applications. The expansion capacity of bentonite in GCLs decreases when permeating aggressive leakages with high cation concentration. The addition of superabsorbent polymers, which have much higher resistance to aggressive leakages, can make up for the deficiency of bentonite and greatly improve hydraulic performance and self-healing capacity. Research on polymer-treated GCLs is still in its preliminary stages. Further study needs to be conducted on the microstructure of polymer–bentonite composite created by using the technology of free radical polymerization as well as on the macro behaviors of polymer–bentonite composites (e.g., hydraulic conductivity, water-swelling capacity, chemical compatibility, diffusion, gas migration, and shear strength).
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, S.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Kim, Y.H. Jet-Grouting with a newly developed technology: The Twin-Jet Method. Eng. Geol. 2013, 152, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Sun, W.J.; Wang, L.B.; Horpibulsuk, S. A field trial of horizontal jet grouting using the composite-pipe method in the soft deposit of Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2013, 35, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Ma, L.; Xu, Y.S.; Yin, Z.Y. Interpretation of increased deformation rate in aquifer IV due to groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Shen, S.L.; Xu, Y.S.; Yin, Z.Y. Characteristics of groundwater seepage with cutoff wall in gravel aquifer. I: Field observations. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Shen, S.L.; Yin, Z.Y.; Xu, Y.S. Characteristics of groundwater seepage with cutoff wall in gravel aquifer. II: Numerical analysis. Can. Geotech. J. 2015, 52, 1539–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.S.; Ma, L.; Shen, S.L.; Sun, W.J. Evaluation of land subsidence by considering underground structures penetrated into aquifers in Shanghai. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 1623–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.S.; Shen, S.L.; Ma, L.; Sun, W.J.; Yin, Z.Y. Evaluation of the blocking effect of retaining walls on groundwater seepage in aquifers with different insertion depths. Eng. Geol. 2014, 183, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xu, Y.S.; Shen, S.L.; Sun, W.J. Evaluation of the hydraulic conductivity of aquifer with piles. Hydrogeol. J. 2014, 22, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Cheng, W.C. Estimation of lateral displacement induced by jet grouting in clayey soils. Geotechnique 2017, 67, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Wu, Y.X.; Misra, A. Calculation of head difference at two sides of a cut-off barrier during excavation dewatering. Comput. Geotech. 2017, 91, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, D.E. Geotechnical Practice for Waste Disposal; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.J.; Hayashi, S. A study on sorption properties of Cd2+ on Ariake clay for evaluating its potential use as a landfill barrier material. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 32, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, C.D.; Meier, A.; Sample-Lord, K. Limiting membrane and diffusion behavior of a geosynthetic clay liner. Geotext. Geomembr. 2016, 44, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Bouazza, A.; Gates, W.P.; Rowe, R.K. Hydraulic performance of geosynthetic clay liners to sulfuric acid solutions. Geotext. Geomembr. 2015, 43, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Wang, Z.F.; Yang, J.; Ho, C.E. Generalized approach for prediction of jet grout column diameter. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2013, 139, 2060–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Wu, H.N.; Cui, Y.J.; Yin, Z.Y. Long-term settlement behavior of the metro tunnel in Shanghai. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 40, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Lu, Y. Forensic diagnosis of a leaking accident during excavation. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. ASCE 2017, 31, 4017061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Lu, Y. Why excavation of a small air shaft caused excessively large displacements: Forensic investigation. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. ASCE 2017, 31, 4016083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.N.; Shen, S.L.; Liao, S.M.; Yin, Z.Y. Longitudinal structural modelling of shield tunnels considering shearing dislocation between segmental rings. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2015, 50, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.N.; Shen, S.L.; Yang, J. Identification of tunnel settlement caused by land subsidence in soft deposit of Shanghai. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. ASCE 2017, 31, 4017092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Xu, Y.S. Numerical evaluation of land subsidence induced by groundwater pumping in Shanghai. Can. Geotech. J. 2011, 48, 1378–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, C.D.; Benson, C.H.; Katsumi, T.; Edil, T.B.; Lin, L. Evaluating the hydraulic conductivity of GCLs permeated with non-standard liquids. Geotext. Geomembr. 2000, 18, 133–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, C.B.; Rowe, R.K. Volatile organic compound diffusion and sorption coefficients for a needle-punched GCL. Geosynth. Int. 2004, 11, 257–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazza, A.; Vangpaisal, T.; Jefferis, S. Effect of wet-dry cycles and cation exchange on gas permeability of geosynthetic clay liners. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2006, 132, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.J.; Ross, J.D. Relationship between NP GCL internal and HDPE GMX/NP GCL interface shear strengths. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.C.; Sari, K.; Shen, S.L.; Cai, Y.Q. Predicting self-healing ratio of GCL with a damage hole. Geotext. Geomembr. 2016, 44, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Shen, S.L.; Wu, H.N.; Chai, J.C. Evaluation of effect of basal geotextile reinforcement under embankment loading on soft marine deposits. Geotext. Geomembr. 2015, 43, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Hayashi, S.; Shen, S.L. Contaminant mitigating performance of Chinese standard municipal solid waste landfill liner systems. Geotext. Geomembr. 2009, 27, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Xu, Q.; Yu, C. Elastic-Viscoplastic modeling for natural soft clays considering nonlinear creep. Int. J. Geomech. 2014, 14, A6014001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Du, Y.J.; Fan, R.D. SHMP amended calcium bentonite for slurry trench cutoff walls: Workability and microstructure characteristics. Can. Geotech. J. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Du, Y.J.; Fan, R.D. Short-term hydraulic conductivity and consolidation properties of soil-bentonite backfills exposed to CCR-impacted groundwater. ASCE J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2017. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.J.; Wei, M.L.; Reddy, K.R.; Liu, Z.P.; Jin, F. Effect of acid rain pH on leaching behavior of cement stabilized lead-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estornell, P.; Daniel, D.E. Hydraulic Conductivity of Three Geosynthetic Clay Liners. J. Geotech. Eng. 1992, 118, 1592–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, R.M. Designing with Geosynthetics, 5th ed.; Prentice Hall Book Co.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Chang, C.S.; Karstunen, M.; Hicher, P.Y. An anisotropic elastic viscoplastic model for soft clays. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Hattab, M.; Hicher, P.Y. Multiscale modeling of a sensitive marine clay. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2011, 35, 1682–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Xu, Q.; Hicher, P.Y. A simple critical state based double-yield-surface model for clay behavior under complex loading. Acta Geotech. 2013, 8, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Zhao, J.; Hicher, P.Y. A micromechanics-based model for sand-silt mixtures. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2014, 51, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Yin, J.H.; Huang, H.W. Rate-dependent and long-term yield stress and strength of soft Wenzhou marine clay: Experiments and modeling. Mar. Georesour. Geotechnol. 2015, 33, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.F.; Yin, Z.Y.; Shen, S.L.; Hicher, P.Y. Selection of sand models and identification of parameters using an enhanced genetic algorithm. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 2016, 40, 1219–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.F.; Yin, Z.Y.; Shen, S.L.; Hicher, P.Y. Investigation into MOGA for identifying parameters of a critical-state-based sand model and parameters correlation by factor analysis. Acta Geotech. 2016, 11, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.F.; Wu, Z.X.; Yin, Z.Y.; Shen, J.S. Estimation of critical state-related formula in advanced constitutive modeling of granular material. Acta Geotech. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Fan, R.D.; Liu, S.Y.; Reddy, K.R.; Jin, F. Workability, compressibility and hydraulic conductivity of zeolite-amended clayey soil/calcium-bentonite backfills for slurry-trench cutoff walls. Eng. Geol. 2015, 195, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Fan, R.D.; Reddy, K.R.; Liu, S.Y.; Yang, Y.L. Impacts of presence of lead contamination in clayey soil-calcium bentonite cutoff wall backfills. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 108, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Du, Y.J.; Reddy, K.R.; Fan, R.D. Phosphate-amended sand/Ca-bentonite mixtures as slurry trench wall backfills: Assessment of workability, compressibility and hydraulic conductivity. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 142, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Cui, Q.L.; Ho, E.C.; Xu, Y.S. Ground response to multiple parallel microtunneling operations in cemented silty clay and sand. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2016, 142, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Montmorillonite (accessed on 9 November 2017).
- Ruedrich, J.; Bartelsen, T.; Dohrmann, R.; Siegesmund, S. Moisture expansion as a deterioration factor for sandstone used in buildings. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.K. Fundamentals of Soil Behavior, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.J.; Jiang, N.J.; Liu, S.Y.; Jin, F.; Singh, D.N.; Pulppara, A. Engineering properties and microstructural characteristics of cement solidified zinc-contaminated kaolin clay. Can. Geotech. J. 2014, 51, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Wei, M.L.; Martin, L. Modeling compression behavior of cement treated zinc contaminated clayey soils. Soils Found. 2014, 54, 1018–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, G.H. Physico-Chemical Analysis of the Compressibility of Pure Clays. Géotechnique 1956, 6, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.Y.; Katsumi, T.; Benson, C.H.; Edil, T.B. Hydraulic Conductivity and Swelling of Nonprehydrated GCLs Permeated with Single-Species Salt Solutions. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2001, 127, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazza, A. Geosynthetic clay liners. Geotext. Geomembr. 2002, 20, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, C.H. Impact of subgrade water content on cation exchange and hydraulic conductivity of geosynthetic clay liners in composite barriers. In Coupled Phenomena in Environmental Geotechnics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.K.; Brachman, R.W.I.; Take, W.A.; Rentz, A.; Ashe, L.E. Field and laboratory observations of down-slope bentonite migration in exposed composite liners. Geotext. Geomembr. 2016, 44, 686–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, C.H.; Thorstad, P.A.; Jo, H.Y.; Rock, S.A. Hydraulic performance of geosynthetic clay liners in a landfill final cover. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2007, 133, 814–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, C.H.; Kucukkirca, I.E.; Scalia, J. Properties of geosynthetics exhumed from a final cover at a solid waste landfill. Geotext. Geomembr. 2010, 28, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egloffstein, T.A. Natural bentonites-influence of the ion exchange and partial desiccation on permeability and self-healing capacity of bentonites used in GCLs. Geotext. Geomembr. 2001, 19, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setz, M.C.; Tian, K.; Benson, C.H.; Bradshaw, S.L. Effect of ammonium on the hydraulic conductivity of geosynthetic clay liners. Geotext. Geomembr. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shackelford, C.D.; Sevick, G.W.; Eykholt, G.R. Hydraulic conductivity of geosynthetic clay liners to tailings impoundment solutions. Geotext. Geomembr. 2010, 28, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.Y.; Benson, C.H.; Shackelford, C.D.; Lee, J.-M.; Edil, T.B. Long-Term Hydraulic Conductivity of a Geosynthetic Clay Liner Permeated with Inorganic Salt Solutions. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2005, 131, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasko, S.; Jo, H.; Benson, C.; Edil, T.; Kataumi, T. Hydraulic conductivity of partially prehydrated geosynthetic clay liners permeated with aqueous calcium chlorides solution. In Proceedings of the Geosynthetics Conference, Oregon, OR, USA, 12–14 February 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Rosin-Paumier, S.; Touze-Foltz, N. Hydraulic and chemical evolution of GCLs during filter press and oedopermeametric tests performed with real leachate. Geotext. Geomembr. 2012, 33, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.L.; Wang, J.P.; Wu, H.N.; Xu, Y.S.; Ye, G.L.; Yin, Z.Y. Evaluation of hydraulic conductivity for both marine and deltaic deposit based on piezocone test. Ocean Eng. 2015, 110, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazza, A.; Singh, R.M.; Rowe, R.K.; Gassner, F. Heat and moisture migration in a geomembrane-GCL composite liner subjected to high temperatures and low vertical stresses. Geotext. Geomembr. 2014, 42, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazza, A.; Gates, W.P. Overview of performance compatibility issues of GCLs with respect to leachates of extreme chemistry. Geosynth. Int. 2014, 21, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornsey, W.P.; Scheirs, J.; Gates, W.P.; Bouazza, A. The impact of mining solutions/liquors on geosynthetics. Geotext. Geomembr. 2010, 28, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.J.; Triplett, E.J.; Kim, R.H.; Olsta, J.T. Field Study of Installation Damage for Geosynthetic Clay Liners. Geosynth. Int. 1998, 5, 491–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, K.; Chai, J.C. Self-healing capacity of geosynthetic clay liners and influencing factors. Geotext. Geomembr. 2013, 41, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Orsini, C. Effect of GCL and subgrade type on internal erosion in GCLs under high gradients. Geotext. Geomembr. 2003, 21, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Take, W.A.; Brachman, R.W.I.; Rowe, R.K. Observations of bentonite erosion from solar-driven moisture migration in GCLs covered only by a black geomembrane. Geosynth. Int. 2015, 22, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camillis, M.D.; Emidio, G.D.; Bezuijen, A.; Verástegui-Flores, R.D. Hydraulic conductivity and swelling ability of a polymer modified bentonite subjected to wet-dry cycles in seawater. Geotext. Geomembr. 2016, 44, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzieri, F.; Pasqualini, E. Permeability of Damaged Geosynthetic Clay Liners. Geosynth. Int. 2000, 7, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, G.L.S.; Sporer, H.; Zanzinger, H.; Gartung, E. Self-healing properties of geosynthetic clay liners. Geosynth. Int. 2001, 8, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, S.; Daniel, D.E. Results of laboratory tests on a geotextile/bentonite liner material. In Proceedings of the Geosynthetics Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 26–28 February 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.K.; Lake, C.B. Geosynthetic clay liner research, design and applications. In Proceedings of the 7th International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, Cagliari, Italy, 4–8 October 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Koerner, R.M. Design with Geosynthetics, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.K.; Li, T.A. Preliminary study of the bentonite self-healing of slits in a GCL upon full hydration. In Proceedings of the Geo-Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–18 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ören, A.H.; Akar, R.Ç. Swelling and hydraulic conductivity of bentonites permeated with landfill leachates. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 142, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastar, F.; Hejazi, S.M.; Sheikhzadeh, M.; Alirezazadeh, A. A parametric study on hydraulic conductivity and self-healing properties of geotextile clay liners used in landfills. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 202 (Pt 1), 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.X.; Shen, S.L.; Yuan, D.J. Characteristics of dewatering induced drawdown curve under barrier effect of retaining wall in aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2016, 539, 554–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Shen, J.S.; Cheng, W.C.; Hino, T. Semi-analytical solution to pumping test data with barrier, wellbore storage, and partial penetration effects. Eng. Geol. 2017, 226, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, G.; Al Nassar, M.; Plagne, V.; Cazaux, C. Evaluation of Self-healing ability of geosynthetic clay liners. In Proceedings of the ISRM International Symposium, Melbourne, Australia, 19–24 November 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.L.; Du, Y.J.; Reddy, K.R.; Fan, R.D. Compatibility of Phosphate-Amended Ca-Bentonite Soil Backfill with Groundwater Impacted by Coal Ash Leachate. Geotech. Spec. Publ. 2017, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, C.B.; Rowe, R.K. Diffusion of sodium and chloride through geosynthetic clay liners. Geotext. Geomembr. 2000, 18, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fick, A. Ueber diffusion. Ann. Der Phys. 1855, 170, 59–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, R.K.; Lake, C.B.; Petrov, R.J. Apparatus and procedures for accessing inorganic diffusion coefficient for geosynthetic clay liners. Geotech. Test. J. 2000, 23, 206–214. [Google Scholar]
- Rowe, R.K.; Asce, F.; Mukunoki, T.; Sangam, H.P. BTEX diffusion and sorption for a geosynthetic clay liner at two temperatures. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2005, 131, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paumier, S.; Touzefoltz, N.; Mazeas, L.; Guenne, A. Quantification of volatile organic compounds diffusion for virgin geosynthetic clay liners and for a GCL after contact with a synthetic leachate. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2011, 137, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, K.; Rowe, R.K.; Jamieson, H. Diffusion of metals in geosynthetic clay liners. Geosynth. Int. 2009, 16, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, M.J.A.; Touze-Foltz, N.; Gardoni, M.; Ahari, M.; Mazeas, L. Quantification of diffusion of phenolic compounds in virgin GCL and in GCL after contact with a synthetic leachate. Geotext. Geomembr. 2013, 38, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanzinger, H.; Koerner, R.M.; Gartung, E. Clay Geosynthetic Barriers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Vangpaisal, T.; Bouazza, A. Gas permeability of partially hydrated geosynthetic clay liners. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazza, A.; Vangpaisal, T. An apparatus to measure gas permeability of geosynthetic clay liners. Geotext. Geomembr. 2003, 21, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, G.; Bouazza, A.; Cazaux, D. Gas permeability of geosynthetic clay liners. Geotext. Geomembr. 2000, 18, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubertin, M.; Aachib, M.; Authier, K. Evaluation of diffusive gas flux through covers with a GCL. Geotext. Geomembr. 2000, 18, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouf, M.A.; Bouazza, A.; Rao, M.S.; Gates, W.P.; Rowe, R.K. Gas flow unified measurement system for sequential measurement of gas diffusion and gas permeability of partially hydrated geosynthetic clay liners. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 53, 1000–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazza, A.; Rahman, F. Oxygen diffusion through partially hydrated geosynthetic clay liners. Géotechnique 2007, 57, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouazza, A.; Vangpaisal, T. Gas advective flux of partially saturated geosynthetic clay liners. In Proceedings of the Geo-Denver, Denver, CO, USA, 5–8 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bouazza, A.; Vangpaisal, T. Gas permeability of GCLs, effect of poor distribution of needle-punched fibers. Geosynth. Int. 2007, 14, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.B.; Fernandez, F.; Horsfield, D.W. Shear strength of reinforced geosynthetic clay liner. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. 1996, 122, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.B.; Scranton, H.B.; Daniel, D.E. Shear strength testing for geosynthetic clay liners. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Testing and Acceptance Criteria for Geosynthetic Clay Liners, Atlanta, GA, USA, 29 January 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, P.J.; Chiu, P. Internal and interface shear strengths of unreinforced and needle-punched geosynthetic clay liners. Geosynth. Int. 2004, 11, 176–199. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, P.J.; Rowland, M.G.; Scheithe, J.R. Internal shear strength of three geosynthetic clay liners. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 1998, 124, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zornberg, J.G.; Mccartney, J.S. Analysis of a large database of GCL internal shear strength results. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2005, 131, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, H.T.; Stark, T.D. Shear Behavior of an Unreinforced Geosynthetic Clay Liner. Geosynth. Int. 1997, 4, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.Y.; Chang, C.S.; Hicher, P.Y. Micromechanical modelling for effect of inherent anisotropy on cyclic behaviour of sand. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2010, 47, 1933–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, T.D.; Eid, H.T. Shear behavior of reinforced geosynthetic clay liners. Geosynth. Int. 1996, 3, 771–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triplett, E.J.; Fox, P.J. Shear strength of HDPE geomembrane/geosynthetic clay liner interfaces. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2001, 127, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergado, D.T.; Ramana, G.V.; Sia, H.I.; Varun, V. Evaluation of interface shear strength of composite liner system and stability analysis for a landfill lining system in Thailand. Geotext. Geomembr. 2006, 24, 371–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.J.; Kim, R.H. Effect of progressive failure on measured shear strength of geomembrane/GCL interface. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2008, 134, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccartney, J.S.; Zornberg, J.G. Analysis of a Large Database of GCL-Geomembrane Interface Shear Strength Results. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2009, 135, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, R.J. Design issues with strain-softening interfaces in landfill liners. In Proceedings of the Waste Technology, Charleston, SC, USA, 3–5 October 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Vukelić, A.; Szavits-Nossan, A.; Kvasnička, P. The influence of bentonite extrusion on shear strength of GCL/geomembrane interface. Geotext. Geomembr. 2008, 26, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Lin, W.A.; Zhan, T.L.T. Investigation of mechanisms of bentonite extrusion from GCL and related effects on the shear strength of GCL/GM interfaces. Geotext. Geomembr. 2010, 28, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehervari, A.; Gates, W.P.; Patti, A.F.; Turney, T.W.; Bouazza, A.; Rowe, R.K. Potential hydraulic barrier performance of cyclic organic carbonate modified bentonite complexes against hyper-salinity. Geotext. Geomembr. 2016, 44, 748–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohnhoff, G.L.; Shackelford, C.; Malusis, M.; Scalia, J.; Bension, C.; Edil, T.; Di Emidio, G.; Katsumi, T.; Mazzieri, F. Novel bentonites for containment barrier applications. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, Pairs, France, 2–6 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Mazzieri, F.; Emidio, G.D.; Fratalocchi, E.; Sante, M.D.; Pasqualini, E. Permeation of two GCLs with an acidic metal-rich synthetic leachate. Geotext. Geomembr. 2013, 40, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, V.S.; Stott, D.E.; Norton, L.D.; Graveel, J.G. Polyacrylamide molecular weight and charge effects on infiltration under simulated rainfall. SSSAJ 2000, 64, 1786–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Dixon, J.B.; White, G.N.; Loeppert, R.H.; Juo, A.S.R. Bonding between polyacrylamide and smectite. Colloid Surface A 2006, 281, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razakamanantsoa, A.R.; Barast, G.; Djeran-Maigre, I.; Couradin, A.; Didier, G. Hydraulic performance of bentonite soil mixture reinforced by polymer in contact of different fluids. In Proceedings of the Journées Nationales de Géotechnique et de Géologiedel’Ingénieur, Nantes, France, 18–20 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Didier, G.; Comeaga, L. Influence of initial hydration conditions on GCL leachate permeability. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Testing and Acceptance Criteria for Geosynthetic Clay Liners, Atlanta, GA, USA, 29 January 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Elhajji, D.; Ashmawy, A.K.; Darlington, J.; Sotelo, N. Effect of inorganic leachate on polymer treated GCL material. In Proceedings of the Geosynthetics, Portland, OR, USA, 12–14 January 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ashmawy, A.K.; Elhajji, D.; Sotelo, N.; Muhammad, N. Hydraulic performance of untreated and polymer-treated bentonite in inorganic landfill leachates. Clays Clay Miner. 2002, 50, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razakamanantsoa, A.R.; Barast, G.; Djeran-Maigre, I. Hydraulic performance of activated calcium bentonite treated by polyionic charged polymer. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 59–60, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalia, J.; Benson, C.H.; Bohnhoff, G.L.; Edil, T.B. Long-Term Hydraulic Conductivity of a Bentonite-Polymer Composite Permeated with Aggressive Inorganic Solutions. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2014, 140, 4013025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujida, A. Evaluation of the Behavior of Newly Developed Water Absorption Debio-Materials; Report of National Institute of Technology; Tomakomai College: Tomakomai, Japan, 2014; Available online: http://www.tomakomai-ct.ac.jp (accessed on 6 November 2017). (In Japanese)












© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kong, D.-J.; Wu, H.-N.; Chai, J.-C.; Arulrajah, A. State-Of-The-Art Review of Geosynthetic Clay Liners. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112110
Kong D-J, Wu H-N, Chai J-C, Arulrajah A. State-Of-The-Art Review of Geosynthetic Clay Liners. Sustainability. 2017; 9(11):2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112110
Chicago/Turabian StyleKong, De-Jun, Huai-Na Wu, Jin-Chun Chai, and Arul Arulrajah. 2017. "State-Of-The-Art Review of Geosynthetic Clay Liners" Sustainability 9, no. 11: 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112110
APA StyleKong, D.-J., Wu, H.-N., Chai, J.-C., & Arulrajah, A. (2017). State-Of-The-Art Review of Geosynthetic Clay Liners. Sustainability, 9(11), 2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112110



