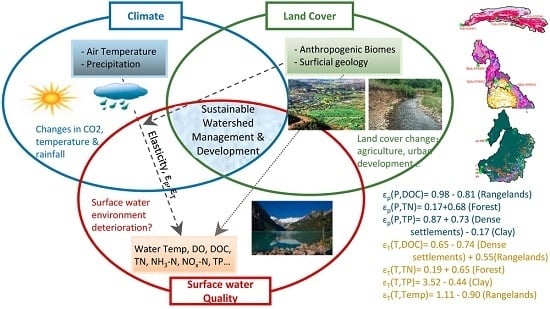
How Do Terrestrial Determinants Impact the Response of Water Quality to Climate Drivers?—An Elasticity Perspective on the Water–Land–Climate Nexus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
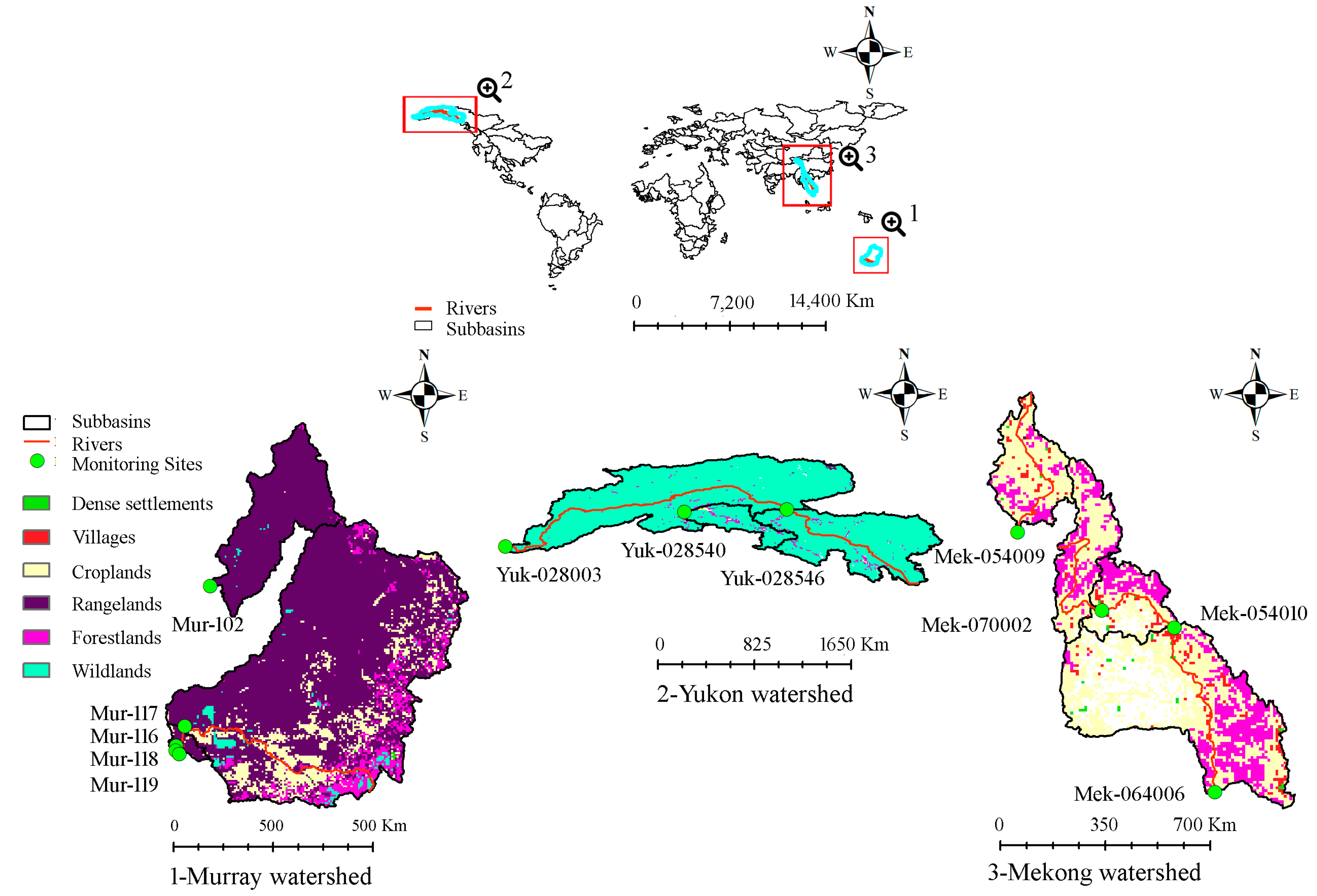
2. Study Area and Methods
2.1. Watersheds Description
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Water Quality Data
2.2.2. Climate Data
2.2.3. DEM and Terrestrial Determinants Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Climate Elasticity of Water Quality
2.3.2. Statistical Approaches
2.3.3. Sub-Watershed Delineation
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Trends Analysis of Water Quality Parameters and Climatic Drivers
3.2. Response Pattern of Water Quality to Climatic Drivers in the Three Basins
3.2.1. Order Pattern of εP and εT
3.2.2. Spatial Pattern of Precipitation Elasticity
3.2.3. Spatial Pattern of Temperature Elasticity
3.3. Impacts of Terrestrial Determinants on CEWQ
3.3.1. Relationship between Anthropogenic Biomes and CEWQ
Sensitivity of Precipitation Elasticity to Anthropogenic Biomes
Sensitivity of Temperature Elasticity to Anthropogenic Biomes
3.3.2. Relationship between Surficial Geology and CEWQ
3.3.3. Physical Insights to the Relationship
3.4. Linear Models of Terrestrial Determinants and CEWQ
3.5. Ecological and Management Implications
3.6. Limitations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Mata, L.J.; Arnell, N.; Doll, P.; Kabat, P.; Jimenez, B.; Miller, K.; Oki, T.; Zekai, S.; Shiklomanov, I. Freshwater Resources and Their Management; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change: Geneva, Switzerland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z.; Mata, L.; Arnell, N.W.; Döll, P.; Jimenez, B.; Miller, K.; Oki, T.; Şen, Z.; Shiklomanov, I. The implications of projected climate change for freshwater resources and their management. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehead, P.G.; Wilby, R.L.; Battarbee, R.W.; Kernan, M.; Wade, A.J. A review of the potential impacts of climate change on surface water quality. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 101–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricker, O.P.; Jones, B.F. Main factors affecting the composition of natural waters. In Trace Elements in Natural Waters; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Bierman, P.; Lewis, M.; Ostendorf, B.; Tanner, J. A review of methods for analysing spatial and temporal patterns in coastal water quality. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pińskwar, I. Projections of Changes in Precipitation Extremes in Poland; Monografie Komitetu Gospodarki Wodnej PAN: Warsaw, Poland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Krysanova, V. Climate change and stream water quality in the multi-factor context. Clim. Chang. 2010, 103, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, E.C.; Ramankutty, N. Putting people in the map: Anthropogenic biomes of the world. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2008, 6, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reimann, C.; Finne, T.E.; Nordgulen, Ø.; Sæther, O.M.; Arnoldussen, A.; Banks, D. The influence of geology and land-use on inorganic stream water quality in the Oslo region, Norway. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 1862–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, M.A.; Menking, K.M.; Gillikin, D.P.; Smith, K.C.; Freimuth, C.P.; Belli, S.L.; Pregnall, A.M.; Schlessman, M.A.; Batur, P. Influence of open space on water quality in an urban stream. Phys. Geogr. 2010, 31, 336–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, C.P.; Bode, R.W.; Smith, A.J.; Kleppel, G.S. Land-use proximity as a basis for assessing stream water quality in New York State (USA). Ecol. Indic. 2010, 10, 727–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utz, R.M.; Eshleman, K.N.; Hilderbrand, R.H. Variation in physicochemical responses to urbanization in streams between two Mid-Atlantic physiographic regions. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 402–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yin, Z.-Y. Using GIS to assess the relationship between land use and water quality at a watershed level. Environ. Int. 1997, 23, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, M.J.; Meyer, J.L. Streams in the urban landscape. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2001, 32, 333–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsegaye, T.; Sheppard, D.; Islam, K.; Tadesse, W.; Atalay, A.; Marzen, L. Development of chemical index as a measure of in-stream water quality in response to land-use and land cover changes. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2006, 174, 161–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-W.; Hwang, S.-J.; Lee, S.-B.; Hwang, H.-S.; Sung, H.-C. Landscape ecological approach to the relationships of land use patterns in watersheds to water quality characteristics. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeilhofer, P.; Lima, E.B.N.R.; Lima, G.A.R. Land use effects on water quality in the urban agglomeration of Cuiabá and Várzea Grande, Mato Grosso State, central Brazil. Urban Water J. 2010, 7, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehaffey, M.; Nash, M.; Wade, T.; Ebert, D.; Jones, K.; Rager, A. Linking land cover and water quality in New York city’s water supply watersheds. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 107, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Versace, V.; Ierodiaconou, D.; Stagnitti, F.; Hamilton, A.; Walter, M.; Mitchell, B.; Boland, A.-M. Regional-scale models for relating land cover to basin surface-water quality using remotely sensed data in a GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 142, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heathwaite, A. Multiple stressors on water availability at global to catchment scales: Understanding human impact on nutrient cycles to protect water quality and water availability in the long term. Freshw. Biol. 2010, 55, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miserendino, M.L.; Casaux, R.; Archangelsky, M.; Di Prinzio, C.Y.; Brand, C.; Kutschker, A.M. Assessing land-use effects on water quality, in-stream habitat, riparian ecosystems and biodiversity in Patagonian Northwest streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, S.; Qiu, Z. Understanding the relationship of land uses and water quality in twenty first century: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 173, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Jia, P.; Qi, C.; Ding, F. A review of surface water quality models. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 231768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathumratana, L.; Sthiannopkao, S.; Kim, K.W. The relationship of climatic and hydrological parameters to surface water quality in the Lower Mekong river. Environ. Int. 2008, 34, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Ozaki, N.; Kaminishi, H.; Harasawa, H.; Matsushige, K. Forecasting the changes in lake water quality in response to climate changes, using past relationships between meteorological conditions and water quality. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Sharma, A.; Sivakumar, B.; Wang, P. A global assessment of climate–water quality relationships in large rivers: An elasticity perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankarasubramanian, A.; Vogel, R.M.; Limbrunner, J.F. Climate elasticity of streamflow in the United States. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1771–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiew, F.H. Estimation of rainfall elasticity of streamflow in Australia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Jiang, J.; Wang, P.; Zheng, Y. Influences of topographic and socio-economic attributes on the climate sensitivity of global river water quality. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, F.; Kottek, M. Observed and projected climate shifts 1901–2100 depicted by world maps of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Meteorol. Z. 2010, 19, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP/GEMS. United Nations Environment Programme (Unep)/Global Water Quality Data and Statistics (Gems). Available online: www.gemstat.org (accessed on 16 November 2017).
- GEMSwater. Environmental Analytical Techniques Used for Water Quality Analyses. Available online: http://www.unep.org/gemswater/TechnicalResources/AnalyticalMethodsforEnvironmentalWaterQuality/tabid/78547/Default.aspx (accessed on 16 January 2013).
- EPA. South Australia Environmental Protection Agency. Available online: http://www.epa.sa.gov.au (accessed on 16 November 2017).
- NOAA. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Available online: http://www.esrl.noaa.gov/psd/data/ (accessed on 16 November 2017).
- DEM. Shuttle Radar Topography Mission Digital Elevation Model Imagery. Available online: http://www.webgis.com/srtm30.html (accessed on 16 November 2017).
- Ellis, E.C.; Ramankutty, N. Anthropogenic Biomes of the World, Version 1; NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2008.
- Ellis, E.C.; Goldewijk, K.K.; Siebert, S.; Lightman, D.; Ramankutty, N. Anthropogenic Biomes of the World, Version 2: 1700; NASA Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center (SEDAC): Palisades, NY, USA, 2013.
- Nachtergaele, F.; van Velthuizen, H.; Verelst, L.; Batjes, N.; Dijkshoorn, J.; van Engelen, V.; Fischer, G.; Jones, A.; Montanarella, L.; Petri, M. Harmonized World Soil Database (Version 1.0); Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN (FAO): Rome, Italy; International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA): Laxenburg, Austria; ISRIC-World Soil Information: Wageningen, The Netherlands; Inst of Soil Science-Chinese Acad of Sciences (ISS-CAS): Beijing, China; EC-Joint Research Centre (JRC): Ispra, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, Q. Response of streamflow to climate changes in the Yellow river basin, China. J. Hydrometeorol. 2011, 12, 1113–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheskin, D.J. Handbook of Parametric and Nonparametric Statistical Procedures; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Antonopoulos, V.Z.; Papamichail, D.M.; Mitsiou, K.A. Statistical and trend analysis of water quality and quantity data for the Strymon river in Greece. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2001, 5, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, V.; Papamichail, D. Trend analysis of water quality parameters for two transboundary rivers in Northern Greece. In Proceedings of the International Conference Protection and Restoration of the Environment VI, Skiathos, Greece, 1–5 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Helsel, D.R.; Hirsch, R.M. Statistical Methods in Water Resources; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2002; Volume 323.
- Dahmen, E.; Hall, M.J. Screening of Hydrological Data: Tests for Stationarity and Relative Consistency; ILRI: Nairobi, Kenya, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Naddafi, K.; Honari, H.; Ahmadi, M. Water quality trend analysis for the Karoon river in Iran. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 134, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.Y.; Lee, K.-L.; Im, T.H.; Lee, I.J.; Kim, S.; Han, K.-Y.; Ahn, J.M. Evaluation of water quality for the Nakdong river watershed using multivariate analysis. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2016, 5, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Multi-scale analysis of relationship between landscape pattern and urban river water quality in different seasons. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheu, A.; Poff, N.; St-Hilaire, A. A classification of stream water temperature regimes in the conterminous USA. River Res. Appl. 2015, 32, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, R.A.; Hawkins, C.P.; Carlisle, D.M. Predicting thermal reference conditions for USA streams and rivers. Freshw. Sci. 2012, 32, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, M.T.; Franssen, W.H.; Yearsley, J.R.; Ludwig, F.; Haddeland, I.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Kabat, P. Global river discharge and water temperature under climate change. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2013, 23, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putro, B.; Kjeldsen, T.; Hutchins, M.G.; Miller, J. An empirical investigation of climate and land-use effects on water quantity and quality in two urbanising catchments in the Southern United Kingdom. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roa-Espinosa, A.; Wilson, T.; Norman, J.; Johnson, K. Predicting the impact of urban development on stream temperature using a thermal urban runoff model (turm). In Proceedings of the National Conference on Urban Stormwater: Enhancing Programs at the Local Level, Chicago, IL, USA, 17–20 February 2003; pp. 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead, P.; Wilby, R.; Butterfield, D.; Wade, A. Impacts of climate change on in-stream nitrogen in a lowland chalk stream: An appraisal of adaptation strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 365, 260–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arheimer, B.; Andréasson, J.; Fogelberg, S.; Johnsson, H.; Pers, C.B.; Persson, K. Climate change impact on water quality: Model results from Southern Sweden. AMBIO J. Hum. Environ. 2005, 34, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahearn, D.S.; Sheibley, R.W.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Anderson, M.; Johnson, J.; Tate, K.W. Land use and land cover influence on water quality in the last free-flowing river draining the Western Sierra Nevada, California. J. Hydrol. 2005, 313, 234–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbraith, L.M.; Burns, C.W. Linking land-use, water body type and water quality in Southern New Zealand. Landsc. Ecol. 2007, 22, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haidary, A.; Amiri, B.J.; Adamowski, J.; Fohrer, N.; Nakane, K. Assessing the impacts of four land use types on the water quality of wetlands in Japan. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 2217–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G. Influences of watershed landscape composition and configuration on lake—Water quality in the Yangtze river basin of China. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. Spatially varying relationships between land use and water quality across an urbanization gradient explored by geographically weighted regression. Appl. Geogr. 2011, 31, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J. Spatial variations in the relationships between land use and water quality across an urbanization gradient in the watersheds of Northern Georgia, USA. Environ. Manag. 2013, 51, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, R.; Cai, S.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Li, Z.; Nie, X. Inferring land use and land cover impact on stream water quality using a Bayesian hierarchical modeling approach in the Xitiaoxi river watershed, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2014, 133, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H. Water quality impacts of climate and land use changes in Southeastern Pennsylvania. Prof. Geogr. 2004, 56, 240–257. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, J.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Q.; Kang, M. Impacts of land use on surface water quality in a subtropical river basin: A case study of the Dongjiang river basin, Southeastern China. Water 2015, 7, 4427–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.S.; Baker, M.E.; Whigham, D.F.; Weller, D.E.; Jordan, T.E.; Kazyak, P.F.; Hurd, M.K. Spatial considerations for linking watershed land cover to ecological indicators in streams. Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 137–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unwin, M.; Snelder, T.; Booker, D.; Ballantine, D.; Lessard, J. Predicting Water Quality in New Zealand Rivers from Catchment-Scale Physical, Hydrological and Land Cover Descriptors Using Random Forest Models; National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research: Christchurch, New Zealand, 2010.
- Tong, S.T.; Chen, W. Modeling the relationship between land use and surface water quality. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 66, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D.L.; Jordan, T.E.; Weller, D.E. Effects of precipitation and air temperature on nitrogen discharges from Rhode river watersheds. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1999, 115, 547–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateni, F.; Fakheran, S.; Soffianian, A. Assessment of land cover changes & water quality changes in the Zayandehroud river basin between 1997–2008. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 10511–10519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olness, A.; Smith, S.; Rhoades, E.; Menzel, R. Nutrient and sediment discharge from agricultural watersheds in Oklahoma. J. Environ. Qual. 1975, 4, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, R.; Rhoades, E.; Olness, A.; Smith, S. Variability of annual nutrient and sediment discharges in runoff from Oklahoma cropland and rangeland. J. Environ. Qual. 1978, 7, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, W.F. Water quality of agricultural coastal plain watersheds. Agric. Wastes 1986, 16, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Gu, S.; Tan, X.; Zhang, Q. Water quality in the Upper Han river basin, China: The impacts of land use/land cover in riparian buffer zone. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 165, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, L.; Yang, K.; Liu, Q.; Qian, G. Influences of land use on water quality in a reticular river network area: A case study in Shanghai, China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2015, 137, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliva, L.; Williams, D.D. Buffer zone versus whole catchment approaches to studying land use impact on river water quality. Water Res. 2001, 35, 3462–3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeder, M.; Chang, H. Multi-scale analysis of oxygen demand trends in an urbanizing Oregon watershed, USA. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, H.; Chen, Q.; Wu, H. Study of landscape patterns of variation and optimization based on non-point source pollution control in an estuary. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 87, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchman, D.L.; Suzuki, Y.; Garside, C.; Ducklow, H.W. High turnover rates of dissolved organic carbon during a spring phytoplankton bloom. Nature 1991, 352, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futter, M.; Butterfield, D.; Cosby, B.; Dillon, P.; Wade, A.; Whitehead, P. Modeling the mechanisms that control in—Stream dissolved organic carbon dynamics in upland and forested catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, G. The impact of climate change on European lakes. In The Impact of Climate Change on European Lakes; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, J. Effects of grassland conversion to cropland and forest on soil organic carbon and dissolved organic carbon in the farming-pastoral ecotone of Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2009, 29, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkley, D.; Fisher, R. Ecology and Management of Forest Soils; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han river basin, South Korea. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3285–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, J.; Van Leeuwen, J.; Abate, D.; Pichler, M.; Bestland, E.; Chittleborough, D.J.; Fleming, N.; Cohen, J.; Liffner, J.; Drikas, M. The effect of vegetation and soil texture on the nature of organics in runoff from a catchment supplying water for domestic consumption. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 529, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.P. Effect of Urban Stormwater BMPs on Runoff Temperature in Trout Sensitive Regions. 2008. Available online: https://repository.lib.ncsu.edu/handle/1840.16/4980 (accessed on 16 November 2017).
- Morrill, J.C.; Bales, R.C.; Conklin, M.H. Estimating stream temperature from air temperature: Implications for future water quality. J. Environ. Eng. 2005, 131, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, M.L.; O’Connor, G.A. Temperature effects on phosphorus release from a biosolids-amended soil. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2013, 2013, 981715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulliette, A.D.; Noble, R.T. Impacts of rainfall on the water quality of the Newport river estuary (Eastern North Carolina, USA). J. Water Health 2008, 6, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Pairs | Negative Ranks | Positive Ranks | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| |εT (T, DO)|−|εP (P, DO)| | 7 | 4 | 0.328 |
| |εT (T, Turb)|−|εP (P, Turb)| | 2 | 6 | 0.674 |
| |εT (T, DOC)|−|εP (P, DOC)| | 3 | 4 | 0.176 |
| |εT (T, TN-UF)|−|εP (P, TN-UF)| | 0 | 9 | 0.008 |
| |εT (T, NH4-F)|−|εP (P, NH4-F)| | 4 | 2 | 0.116 |
| |εT (T, NO2-F)|−|εP (P, NO2-F)| | 1 | 2 | 0.285 |
| |εT (T, NOX-F)|−|εP (P, NOX-F)| | 2 | 10 | 0.136 |
| |εT (T, P-F)|−|εP (P, P-F)| | 5 | 7 | 0.209 |
| |εT (T, P-UF)|−|εP (P, P-UF)| | 5 | 6 | 0.929 |
| |εT (T, PO4-F)|−|εP (P, PO4-F)| | 2 | 0 | 0.180 |
| |εT (T, PO4-UF)|−|εP (P, PO4-UF)| | 1 | 3 | 0.715 |
| |εT (T, Temp)|−|εP (P, Temp)| | 0 | 10 | 0.005 |
| CEWQ | DOC | TN-UF | NH4-F | NOX-F | P-F | P-UF | Temp | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthro-Pogenic Biomes | 0/+ | + | S | 0/+ | 0/+ | 0/+ | + | Sign of εP [26] | |
| S | + | - | - | + | + | + | Sign of εT [26] | ||
| Dense settlements | 0.603 * | 0.611 * | Precipitation Elasticity, εP | ||||||
| Croplands | 0.591 * | 0.585 * | |||||||
| Rangelands | −0.851 ** | −0.637 * | |||||||
| Forested | 0.649 * | 0.612 * | |||||||
| Dense settlements | −0.714 * | Temperature Elasticity, εT | |||||||
| Croplands | −0.580 * | ||||||||
| Rangelands | −0.578 * | −0.767 ** | |||||||
| Forested | 0.623 * | ||||||||
| Surficial Geology | CEWQ | Elasticity Type | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DOC | NH4-F | P-F | P-UF | Temp | ||
| Gravel | −0.599 | 0.580 | Precipitation Elasticity εP | |||
| Silt | 0.615 | |||||
| Clay | −0.601 | |||||
| Gravel | −0.576 | Temperature Elasticity, εT | ||||
| Clay | −0.665 | |||||
| Elasticity Type | WQ Parameters | Regression Model | R | R2 | ΔR2 | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Elasticity | DOC | 1.041 − 0.915 (Dense settlements) | 0.714 | 0.509 | 9.348 | 0.014 | |
| 0.646 − 0.735 (Dense settlements) + 0.545 (Rangelands) | 0.851 | 0.725 | 0.215 | 10.533 | 0.006 | ||
| TN-UF | 0.185 + 0.654 (Forest) | 0.623 | 0.388 | 5.705 | 0.041 | ||
| P-UF | 3.523 − 0.438 (Clay) | 0.665 | 0.443 | 7.144 | 0.026 | ||
| Temp | 1.107 − 0.898 (Rangelands) | 0.767 | 0.589 | 12.876 | 0.006 | ||
| Precipitation Elasticity | DOC | 0.979 − 0.813 (Rangelands) | 0.851 | 0.725 | 23.680 | 0.001 | |
| 1.4 − 0.705 (Rangelands) − 0.014 (Gravel) | 0.924 | 0.854 | 0.130 | 23.478 | 0.000 | ||
| TN-UF | 0.17 + 0.681 (Forest) | 0.649 | 0.421 | 6.557 | 0.031 | ||
| NOX-F | 0.321 − 0.653 (Rangelands) | 0.637 | 0.405 | 6.133 | 0.035 | ||
| 0.153 − 0.589(Rangelands) + 0.005 (Croplands) | 0.817 | 0.667 | 0.262 | 8.014 | 0.012 | ||
| P-F | −0.411 − 0.798 (Dense settlements) | 0.611 | 0.373 | 5.360 | 0.046 | ||
| 0.872 + 0.730 (Dense settlements) − 0.169 (Clay) | 0.818 | 0.670 | 0.297 | 8.117 | 0.012 | ||
| Temp | −0.231 − 0.014 (Silt) | 0.615 | 0.378 | 5.475 | 0.044 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khan, A.U.; Jiang, J.; Sharma, A.; Wang, P.; Khan, J. How Do Terrestrial Determinants Impact the Response of Water Quality to Climate Drivers?—An Elasticity Perspective on the Water–Land–Climate Nexus. Sustainability 2017, 9, 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112118
Khan AU, Jiang J, Sharma A, Wang P, Khan J. How Do Terrestrial Determinants Impact the Response of Water Quality to Climate Drivers?—An Elasticity Perspective on the Water–Land–Climate Nexus. Sustainability. 2017; 9(11):2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112118
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhan, Afed U., Jiping Jiang, Ashish Sharma, Peng Wang, and Jehanzeb Khan. 2017. "How Do Terrestrial Determinants Impact the Response of Water Quality to Climate Drivers?—An Elasticity Perspective on the Water–Land–Climate Nexus" Sustainability 9, no. 11: 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112118
APA StyleKhan, A. U., Jiang, J., Sharma, A., Wang, P., & Khan, J. (2017). How Do Terrestrial Determinants Impact the Response of Water Quality to Climate Drivers?—An Elasticity Perspective on the Water–Land–Climate Nexus. Sustainability, 9(11), 2118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su9112118