Abstract
Bamboo is a natural material having a fast reproduction and high mechanical strengths. However, when a bio-based material in general, and bamboo in particular are expected to be a construction material, their sensitivity to moisture and their durability are usually questionable. Indeed, it is well known that these materials do not possess the same performance in the long-term, when compared to industrial materials. Sustainable solutions for the bamboo treatment still need to be investigated. The present study explores the oil-heated treatment with different types of oils, like flax or sunflower oils. The present investigation concentrates on mechanical properties and durability of treated bamboos to assess the effectiveness of these kinds of treatment. First, bamboo specimens were treated to decrease their sensitivity to moisture and improve their durability. Different conditions of treatment were tested: treatment at 100 °C or 180 °C; with flax oil, sunflower oil, or without oil; treatment durations of 1 h, 2 h, or 3 h; and, different cooling methods and cooling durations. Then, mechanical and durability tests were carried out on untreated and treated bamboos: uniaxial compression tests, 3 points bending tests, water immersion tests, and humidity tests. The results showed that some tested treatment methods could increase both the durability and the compressive strength of treated specimens, compared to untreated bamboo. The best results were observed on specimens treated at 180 °C during 1 h or 2 h without oil, and then cooled in 20 °C sunflower oil.
1. Introduction
Bamboo is a wood-like plant that is a part of the grass family, consisting of a cylindrical hollow shoot, or culm. This culm is covered with a waxy surface, which prevents moisture from escaping. At intervals, the culm has raised ridges called nodes, from which branches will offshoot. The general physical features of bamboo are shown in Figure 1. The plant grows up from a throng of underground stems and roots, called rhizomes. Some species can grow to a height of up to 30.5 m, with a diameter as great as 305 mm [1]. Bamboo is a natural resource with very rapid renewability. Indeed, bamboo can have a very high growth rate, with some species growing up to 600 mm per day. However, it still takes four to five years for the bast fibers, or so-called wood fibers to mature. Thanks to these properties, bamboo can be used in environmentally friendly constructions as structural elements (Figure 2), or as a substitute for steel reinforcement rebars in low-cost buildings (see [1] for an excellent review and investigation on this topic). However, like timber or the most of bio-based materials, bamboo is sensitive to water and moisture; it can absorb or release water/moisture depending on its environment. Previous studies have shown that bamboo could absorb water up to 100% of its dry weight [2], or other sources reporting extreme values of up to 300% [3]. The moisture absorption tends to be quite high initially (after about 20–24 h [4,5]), which causes the material to swell until it reaches its fibers saturation point.
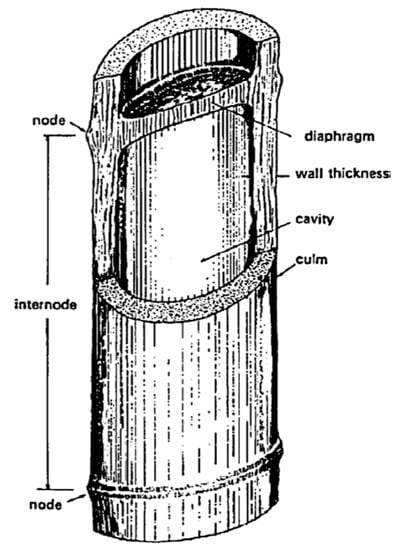
Figure 1.
General features of a bamboo culm [2].

Figure 2.
Bamboo used as structural elements in Vietnam (Architect: T.-N. Vo).
The sensitivity to moisture can cause swellings and shrinkages, which decrease the bonding between bamboo and concrete or mortar in the case where bamboo is used as reinforcement [1]. On the other hand, bamboo may also be attacked and destroyed by biodegradation factors [6]. There are several existing procedures to reduce bamboo’s moisture absorption, and improve the durability; but in several cases, chemical treatments were used [7,8,9,10], which may make the treated bamboo material less environmental friendly [11,12] and more expensive [5].
There are also some eco-friendly methods to improve the durability, which use thermal and natural products like vegetable oils (palm, sunflower, or soy bean) [6,13,14]. Some of the studies in the literature investigated influences of the oil-treatment on the bamboo mechanical strength. Wahab et al. [14] studied tropical bamboo treated in palm oil at 140, 180, and 220 °C, during 30, 60, and 90 min. The results showed that the treatment decreased the mechanical properties (bending, compressive, and shear strengths). When the treatment duration increases, the mechanical strengths could decrease from 15 to 58% of the initial strength, depending on each treatment procedure and each mechanical property. On the other hand, the treatments usually lead to the color changes [8], [15,16,17] which is an undesirable effect. The present paper also investigates the oil-heated treatment, but with other kinds of oils, such as flax oil and sunflower oil. Furthermore, besides the durability aspect, influences of the treatment on mechanical properties of bamboo culms are also studied.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Treatments
The bamboo used in the present study was planted in the Savoy region, France. The bamboo is from the Phyllostachys family, which is present in Europe from the early nineteenth century. This bamboo was chosen due to its availability for the investigation. The diameters of the bamboo culms tested were about 5 cm. Different treatment processes were investigated; the main differences coming from the heating methods, oils used, and the cooling processes. For heating treatment, two ways were tried: specimens were put in an oven, or in hot oil. Different heating times and two types of oil were tested (flax oil and sunflower oil). The flax and sunflower oils were chosen in this study thanks to its availability and the reasonable price in France. Finally, specimens were cooled in oil, also with flax oil or sunflower oil. While specimens were cooled in oil, their weights were measured at different moments: 1 h, 12 h, 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h. Eleven different sets of bamboo (including the untreated set) were studied for different treatments and tests (Table 1). Each set had also several subsets, and each subset had five specimens. After the treatment, bamboo specimens were weighed and stored in ambient air for two weeks and then tested by mechanical tests.

Table 1.
Different methods of treatment and cooling.
In order to assess the oil-absorption of bamboo specimens, there were also the referent specimens, which were only treated by oven heating and then cooled in a desiccator. Then, the weight of these specimens were determined and compared with that of the specimens treated in oil. The specimens intended for uniaxial compression tests had 6 cm of length; the specimens intended for bending tests had 20 cm of length; and, for the durability tests, the specimen length was not important, so available specimens with different lengths were used.
2.2. Mechanical Tests
The mean compressive strength fcm, and the Young’s modulus E of specimens were characterized. The compressive strength was measured by uniaxial compression tests [18] on 6-cm height specimens; the diameter was the actual bamboo diameter (Figure 3). Therefore, the slenderness ratio (height/outer diameter) was about 1.2. For specimens tested under compression tests, they were cut by a circular saw to have two plane and parallel surfaces.
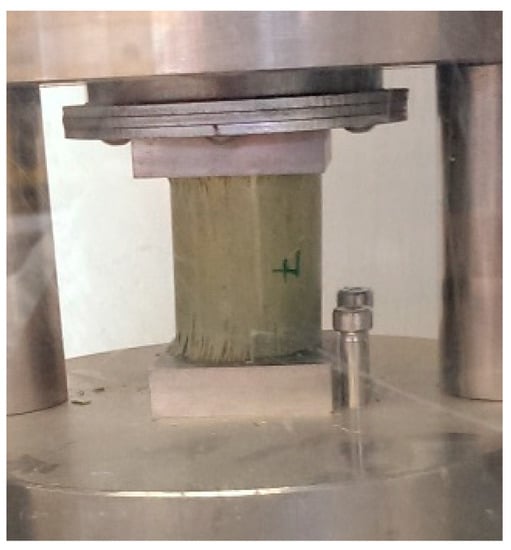

Figure 3.
A bamboo specimen during the uniaxial compression test.
The compressive strength σ was determined following [18], by taking into account the effective cross-sectional area A of bamboo specimens (having internal hollow core, Figure 1):
where F is the maximum force during the uniaxial compression test. A = π [D2 − (D − 2t)2]/4, with D and t are the means of the outer diameter and the wall thickness of the bamboo culm, respectively.
σ = F/A
Three-points bending tests were also performed on 20 cm-length specimens (Figure 4) to characterize the tensile strength and the Young’s modulus. However, only the Young’s modulus was determined, the tensile strength was not determined because specimens were not broken under the three-point bending testing device used, due to the high ductile property of bamboo.
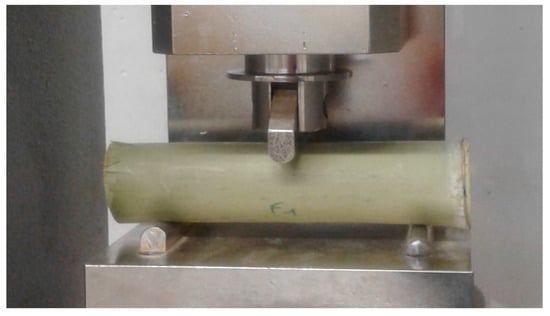
Figure 4.
A three-point bending test on a bamboo specimen.
The Young’s modulus was used to compare the mechanical characteristics of the tested bamboo with that presented in the literature. Effects of the studied treatments on the mechanical characteristics were assessed by uniquely basing on the compressive strength.
2.3. Tests under High Humidity
In order to test the resistance of treated bamboo against fungi development, specimens of each set were placed in boxes which contained 100% relative humidity (RH). Five untreated bamboo specimens were also tested for the comparison.
Before being tested under 100% RH, specimens were conditioned at a relative humidity level of 57%, and a temperature of 25 °C for seven days (until the equilibrium at 57% RH was obtained). These conditions were chosen in order to test all samples in the same conditions, allowing for further comparisons between the different treatments. The 57% RH value is a usual recommended value for durability tests because this value is often observed in service buildings [19].
To obtain a relative humidity level of 100%, a small quantity of water was put in a hermetic plastic box. The specimens were deposited on a shelf inside the box but above the water. The same procedure was used for 57% RH, but the humidity level was obtained with a saturated salt solution (NaBr). The specimens were put in 100% RH boxes, which were set at 30 °C. The RH and temperature in the box were monitored by the sensors installed in the box, which could measure both the RH and the temperature. The bamboo specimens were surveyed in the 100% HR box and weighed regularly until all specimens had fungus symptoms.
The adsorbed water vapor amount is calculated as following:
where: m100% = weight of the sample after an exposure time t to a relative humidity level of 100%, and m57% = weight of the sample after equilibrium at a humidity level of 57%.
(m100% − m57%)/m57%
2.4. Water Immersion Test
Another accelerated test for the durability of bamboo is the water immersion test. Before the tests, specimens were also conditioned at 57% RH for seven days. Then the specimens were immersed in water for 10 weeks. At the end of the test, specimens were taken out from the water, weighed and visible changes were investigated.
2.5. Aging Test
An accelerated aging test following the Japanese Industrial Standard (“JIS-A treatment” method) is also carried out in this investigation [20]. The specimens were immersed in the 70 °C hot water for 9 h, then, they were weighed and visually investigated. This acceleration treatment is equivalent to an outdoor exposure of bamboo during a 1 year period [21].
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Oils-Treatments on the Bamboo Appearance and Weight
Several specimens that had been treated in oil at a high temperature (180 °C) during 3 h and then immediately cooled in oil (at 20 °C) were cracked due to a sudden change of temperature (Figure 5). This observation is clearest for specimens treated in 180 °C sunflower oil for three hours. For specimens treated during 1 or 2 h, the cracking was not observed. So it is suggested that a long treatment (more than 2 h) at a high temperature (180 °C) may have deteriorated the microstructure of bamboo.

Figure 5.
Specimen cracked due to sudden change of temperature.
Results from the specimens treated by heating without oil and cooled into the desiccator, showed that a loss in the specimens’ weight occurred. This result could come from the moisture content evaporation, and the destruction of some organic components (such as carbohydrates) during the heating [22]. During the treatment, a weight decrease occurred due to the organic matter loss, whereas oil-absorption led to a weight increase. The organic matter loss is determined during the treatment in an oven without oil, but it is not really the same as during the oil treatment. That was why the absorbed oil amount for oil-treated specimens could not be precisely determined. However, it was observed that the weight loss during the treatment without oil (in oven) was higher for the treatment at 180 °C (22%) than for treatment at 100 °C (16%). So, it is suggested that the amount of destroyed organic components is more important at 180 °C than at 100 °C, because the moisture content is escaped also at both 180 °C and 100 °C.
3.2. Humidity Test
After humidity tests, several specimens were attacked by fungus. On specimens treated at 100 °C, as well as on untreated specimens, fungi appeared at nearly the same time (2 or 3 days, Figure 6a). No difference had been seen between the two oils at the same temperature (100 °C). The untreated sample and those treated at 100 °C have adsorbed a water vapor amount of 9 ± 2% when the fungi appeared. This means that a temperature of 100 °C is not efficient enough to improve the durability of bamboo. Specimens which had been treated at 180 °C (Figure 6b,c) were less attacked by fungi than specimens treated at 100 °C. All the bamboos treated at 180 °C (in oil or in air) had the same resistance to fungi apparition. Fungi appeared after 5 days of exposure to the humidity level of 100% RH, and the adsorbed water vapor amount was about 12 ± 2%. The difference in fungi resistance between the specimens treated at 100 °C and 180 °C is suggested due to the less amount of carbohydrates in the bamboos treated at 180 °C. Fungus developed similarly whatever the cooling way had been. So, it can be suggested that the temperature of treatment is the predominant factor for the fungi resistance. It is worth noting also that at 180 °C, there are significant changes in the color of the specimens, which is not desirable in some cases if the constructor wishes to have the original appearance of the bamboo [8].
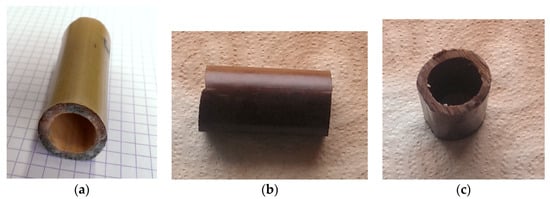
Figure 6.
After 3 days of exposure in 100% Relative Humidity (RH): (a) a specimen treated at 100 °C attacked by fungi (white parts on the cross-section); and (b,c) specimens treated at 180 °C, no fungi attack observed.
3.3. Water Immersion Test
After 10 weeks immersed in water, the untreated specimens had a weight increase of 50.1% (Table 2), but there was no swelling. The treated bamboos did not visibly manifest any significant changes on the form; only the specimens’ weights were increased by a maximum of 45%. This shows a small improvement of the treated specimens for the water absorption due to the absorbed oil, when compared to untreated specimens.

Table 2.
Weight increases of the specimens after the water immersion and ageing tests.
3.4. Aging Test
The water immersion at 70 °C was not severe enough to visibly deteriorate the treated and untreated specimens. Similar to the case of 20 °C water immersion, only weight changes were noted. While the untreated specimens’ weight increased by 59.2% in weight (Table 2), the 100 °C treated specimens’ weight increased by a maximum of 58%, whereas that of the 180 °C treated specimens increased by only 48% at maximum. This result shows also a significant improvement of the 180 °C treated specimens, compared to untreated specimens. This behavior may be due to the less amount of hydrophilic component in the 180 °C treated specimens.
3.5. Mechanical Tests
The Young’s moduli were determined from the force-displacement curves obtained from the three-points bending tests. Indeed, the bamboo specimens were considered as a hollow circular beam; and, the internal and external diameters of the cross-section were the average values of three measurements. Following the basic theory from the strength of materials, the Young’s modulus measured for the studied bamboo range from 8.8 to 9.6 GPa. The variation is due to the quality of different parts on a bamboo tree (bottom part or top part). These values are in the usual interval noted in the literature (from 7 to 20 GPa, [23]).
Uniaxial compressive tests were also used to determine the ultimate compressive strength. Observations during the tests confirmed the ductile behavior of bamboo culms. When the specimen reached the maximal stress, only a vertical crack appeared (Figure 7), and the specimen did not present a brittle failure. The obtained ultimate compressive strengths are illustrated in Figure 8. It is important to note that, due to a low slenderness ratio (of 1.2), the presented compressive strengths were obtained by multiplying the ultimate compressive stresses by a ratio of 0.85, to take into account influences of the frictions between the specimens’ surfaces and the loading press plates. These frictions prevent the lateral extensions (due to the Poisson’s effect) at the two ends of the specimen tested. Therefore, the stresses in these zones are not homogeneous and the compressive strength obtained on low slenderness ratio specimens are higher than that obtained on specimens with a reasonable slenderness ratio (about 2 [18]). When the slenderness ratio increases, the ultimate stress obtained decreases because when the slenderness ratio is high, the specimen is in failure due to the buckling phenomenon. This phenomenon is well known in mechanical tests and the corrector factor is recommended by regulations (Eurocode [24], for example). However, the scope of the present study is to compare the influences of different treatment methods on the compressive strength, so the application or not of the corrector factor does not have consequences on the conclusions.

Figure 7.
Specimens after compression tests.
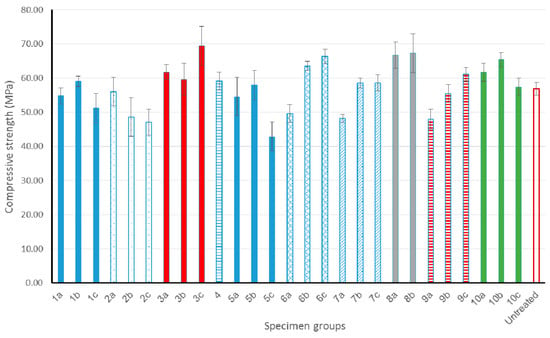
Figure 8.
Compressive strengths obtained.
4. Discussion
From Figure 8, the obtained compressive strength of the untreated specimens was about 57 MPa, which is in the same interval of the usual values reported in the literature (38–130 MPa [22,23]). For treated specimens, the compressive strengths of several specimens decreased or remained equal to the untreated sample. Only a few specimens presented a significant increase of compressive strength (sets 3c; 6b 6c; 8a, 8b; and, 10a, 10b). The results obtained for the set 3 are strange and doubtful because the only difference between specimens of 3a, 3b, and 3c was the cooling duration. So, this result could come from the inhomogeneity of a natural material as bamboo. The sets 6 and 8 corresponded to a treatment in oven without oil (100 °C for set 6, and 180 °C for set 8), whereas the set 10 corresponded to a treatment in oil at 180 °C. Several results reported in the literature showed that the mechanical properties decreased when the oil-treatment duration increased. For example, Wahab et al. [14] reported that all compressive strengths decreased when the specimens were treated after 1 h, 2 h, and 3 h, respectively. However, in the present study, this trend was not observed for all oil-treated specimens. Only sets 1, 2, 5, and 10 followed the trend reported previously, and more especially for the 3 h duration. For other sets, the compressive strengths did not decrease when the treatment-duration increased.
The main difference between the sets 1, 2, 3, and 4 is the duration of the cooling. From the results presented in Figure 8, a general rule about influence of cooling duration on the compressive strength was not obvious because in several cases longer cooling durations provided higher results, but in other cases, the results were lower. Therefore, it is suggested that the cooling duration does not have a real influence on the durability and on the compressive strength.
It is noted in the literature that when a relatively high temperature (about 100 °C) treatment is applied, moisture in the bamboo begins to be removed, which can lead to the increase in strength [22]. However, at a higher temperature (above 125 °C), the compressive strength decreased with temperature, primarily due to the decomposition of macromolecules [25]. The hemicelluloses degrade at temperatures between 150 °C and 200 °C, while lignin decomposes at temperatures between 220 °C and 250 °C [3]. This may be the reason why the set 3c (bamboo treated in flax oil at 100 °C during 3 h and then cooled in flax oil) and set 6c (treated at 100 °C in oven and cooled in flax oil) had remarkable strength increases. However, as mentioned above, these sets did not provide satisfying results in durability tests (apparition of fungus). The best compromise was the sets 8, where specimens were treated by heat without oil, at 180 °C (during 1 h or 2 h), and then cooled in sunflower oil. This method of treatment improves the compressive strength of about 10% and gives a satisfying behavior under durability tests.
Other sets giving acceptable results for all tests were sets 5a, 5b (180 °C in oven during 1 or 2 h, then cooled by flax oil), and set 10 (treated at sunflower oil 180 °C during 1 or 2 h, then cooled by sunflower oil), but their compressive strength was slightly lower than that of the sets 3c, 6c, and 8 as mentioned above. For practice and economic reasons, sets 5a, 5b and 8a, 8b seem preferable than set 10, because oil is only used for the cooling and not needed for the treatments. From the good results observed on sets 5a, 5b, 8a, and 8b, it is suggested that the treatment at a high temperature (180 °C), during a reasonable time (1 or 2 h) can destroy sugar, starch, and protein which are highly susceptible to attack by fungi [26,27]; then the less-sensitive material was covered by oil during the cooling, which led the material to have a better durability. A longer treatment (from 3 h) at 180 °C can destroy more elements in the micro-structure of bamboo, which leads to the cracking presented in the previous section.
During the immersion tests in water, the bamboo weight increased due to water absorption but no fungi nor swelling were observed after ten weeks of treatment. However, when specimens were exposed to 100% RH, fungi appeared after only 5 days for the most resistant. So it is deduced that bamboo is more resistant to water than to moisture. Therefore, it is not surprising that in some cases, peoples immerse bamboo in water for the bamboo preservation [26].
5. Conclusions
The present study investigated different methods of treatment for bamboo: different oils (flax oil, sunflower oil, and without oil); different temperatures (100 °C or 180 °C); different treatment durations (1 h, 2 h, or 3 h); and, different cooling methods (oven, flax oil, sunflower oil) and cooling durations. Results showed that the treatment duration influenced properties of treated bamboos. Three hours at 180 °C was a too long treatment for the bamboo endurance, leading to cracks during cooling and to the degradation of the bamboo. One hour or two hours are more convenient for treatment at 180 °C. The results also showed that some studied treatment methods could increase both the durability and the compressive strength of treated specimens, when compared to untreated bamboo. As a conclusion of all these experiments, the best compressive strength was obtained for the samples treated without oil (oil was used only for cooling), and the best resistance to fungi and to water sorption were for specimens treated at 180 °C. Thus, among the procedures tested, the best compromise was set 8, where specimens were treated by heat without oil, at 180 °C (during 1 h or 2 h) and then cooled in sunflower oil. This is an interesting result because oil is only needed for cooling, which simplifies the treatment. It will be important to verify this result on other bamboo types.
Author Contributions
Anne-Cécile Grillet conceived, analyzed the experiments for the treatment methods; Quoc-Bao Bui piloted the mechanical experiments; and, Hoang-Duy Tran performed the experiments and analyzed the data. Quoc-Bao Bui wrote and Anne-Cécile Grillet revised the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Moroz, J.G.; Lissel, S.L.; Hagel, M.D. Performance of bamboo reinforced concrete masonry shear walls. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 61, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, B.V. Bamboo Reinforcement for Cement Matrices in New Reinforced Concrete; Surrey University Press: Guildford, UK, 1984; pp. 141–194. [Google Scholar]
- Mehra, S.R.; Uppal, H.L.; Chadda, L.R. Some preliminary investigations in the use of bamboo for reinforcing concrete. Indian Concr. 1951, 25, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Júnior, A.S.S.; Junior, J.L.A.; Torres, S.M.; Barros, S.; Ortiz, S.R.; Barbosa, N.P. Bamboo PH and absorption in different liquids. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Non-conventional Materials and Technologies (NOCMAT 2009), Bath, UK, 6–9 September 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ghavami, K. Bamboo as reinforcement in structural concrete elements. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2005, 27, 637–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulaiman, O.; Hashim, R.; Wahab, R.; Ismail, Z.A.; Samsi, H.W.; Mohamed, A. Evaluation of shear strength of oil treated laminated bamboo. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 2466–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, U.M.K.; Paridah, M.T.; Hamdan, H.; Sapuan, S.M.; Bakar, E.S. Effect of curing time on physical and mechanical properties of phenolic-treated bamboo strips. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 29, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.T.; Yeh, T.F.; Wu, J.H. Mechanisms for the surface colour protection of bamboo treated with chromated phosphate. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 74, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.J.; Wu, J.H.; Chang, S.T. Green colour protection of makino bamboo (Phyllostachys makinoi) treated with ammoniacal copper quaternary and copper azole preservatives. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, C.; Nguyen, T.; Stanley, D.; Persily, A.; Corsi, R.L. Effect of ozonation on fungal resistance of bamboo and oak flooring materials. Build. Environ. 2014, 81, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, M.J.; Cheng, S.S.; Lee, C.J.; Chang, S.T. Novel environmentally-benign methods for green-colour protection of bamboo culms and leaves. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2011, 96, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamlouk, M.S.; Zaniewski, J.P. Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers, 3rd ed.; Pearson Educational International: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Cheng, D.; Wålinder, M.E.P.; Zhou, D. Wettability of oil heat-treated bamboo and bonding strength of laminated bamboo board. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, R.; Samsi, H.W.; Sudin, M.; Moktar, J. Strength and durability of bamboo treated through an oil-curing process. J. Biol. Sci. 2004, 4, 658–663. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Wagenführ, A.; Phuong, L.X.; Dai, V.H.; Bremer, M.; Fischer, S. The Effects of Thermal Modification on the Properties of two Vietnamese Bamboo Species, Part I: Effects on physical properties. BioResources 2012, 7, 5355–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelosi, C.; Agresti, G.; Calienno, L.; Lo Monaco, A.; Picchio, R.; Santamaria, U.; Vinciguerra, V. Application of spectroscopic techniques for the study of the surface changes in poplar wood and possible implications in conservation of wooden artefacts. In Proceedings of the SPIE Optics for Arts, Architecture, and Archaeology IV, Monaco, Germany, 13 May 2013; Volume 8790, p. 879014/1-14. [Google Scholar]
- Candelier, K.; Thevenon, M.-F.; Petrissans, A.; Dumarcay, S.; Gerardin, P.; Petrissans, M. Control of wood thermal treatment and its effects on decay resistance: A review. Ann. For. Sci. 2016, 73, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO. ISO 22157-1: Bamboo—Determination of Physical and Mechanical Properties—Part I: Requirements; International Standards Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Glass, S.V.; TenWolde, A. Review of In-Service Moisture and Temperature Conditions in Wood-Frame Buildings; United States Department of Agriculture: Quilcene, WA, USA, 2007; 57p.
- Japanese Standards Association. Japanese Industrial Standards, JIS A-5905: 2003 Fberboards; Japanese Standards Association: Tokyo, Japan, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Norita, H.; Kojima, Y.; Suzuki, S. The aging effects of water immersion treatments in wet-bending for standardized testing of wood panels. J. Wood Sci. 2008, 54, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Ren, H.-Q.; Jiang, Z.-H. Effects of Temperature on the Compressive Strength Parallel to the Grain of Bamboo Scrimbe. Materials 2016, 9, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abang, A.; Aband, A. Utilization of bamboo as a low cost structural material. In Appropriate Building Materials for Low Cost Housing: African Region, Proceedings of a Symposium, Nairobi, Kenya, 7–14 November 2013; E. & F.N. Spoon: London, UK, 1983; pp. 177–182. [Google Scholar]
- The European Union. Eurocode 5, EN 1995-1-1:2004, Design of Timber Structures—Part 1-1: General—Common Rules and Rules for Buildings; European Committee for Standardization: Bruxelles, Belgium, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer, E.L. Effect of pyrolytic temperatures on the longitudinal strength of dry douglas fir. J. Test Eval. 1973, 1, 319–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Shukla, K.S.; Dev, T; Dobriyal, P.B. Bamboo Preservatlon Technlques: A Review; International Network for Bamboo and Rattan and Indian Council of Forestry Research Education (INBAR and ICFRE): Dehra Dun, India, 1994; 64p. [Google Scholar]
- Tomak, E.D.; Topaloglu, E.; Gumuskaya, E.; Yildiz, U.C.; Ay, N. An FT-IR study of the changes in chemical composition of bamboo degraded by brown-rot fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 85, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).