Monitoring Bare Soil Freeze–Thaw Process Using GPS-Interferometric Reflectometry: Simulation and Validation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
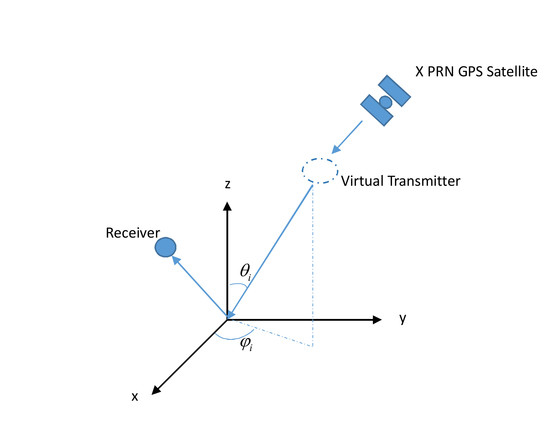
2. Theory and Method
3. Simulation Results and Analysis
3.1. Simulations of the Freeze/Thaw Soil Permittivity
3.2. Simulations of GPS Multipath Observables
3.2.1. Effects of Soil Temperature on GPS Multipath Observables
3.2.2. Multi-Frequencies Effects on GPS Multipath Observables
4. In-Situ Measurements Validation and Discussion
4.1. Virtual Temporary Bistatic Radar
4.2. Analytical Data Selection and Preparation
4.3. In-Situ Measurement Validation
5. Discussion
5.1. Influencing Factors
5.2. GNSS-R Polarimetry
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Soil Permittivity Models
Appendix A.2. Coherent Scattering Properties
Appendix A.3. Forward Multipath Simulators
References
- Judge, J.; Galantowicz, J.F.; England, A.W.; Dahl, P. Freeze/thaw classification for prairie soils using SSM/I radio brightness. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Armstrong, R.L.; Smith, J. Investigation of the near-surface soil freeze-thaw cycle in the contiguous United States: Algorithm development and validation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive. In Advanced Book Program/World Science Divison; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Jagdhuber, T.; Stockamp, J.; Hajnsek, I.; Ludwig, R. Identification of Soil Freezing and Thawing States Using SAR Polarimetry at C-Band. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2008–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Armstrong, R.L. Soil freeze/thaw cycles over snow-free land detected by passive microwave remote sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardellach, E.; Fabra, F.; Nogués-Correig, O.; Oliveras, S.; Ribó, S.; Rius, A. GNSS-R ground-based and airborne campaigns for ocean, land, ice, and snow techniques: Application to the GOLD-RTR data sets. Radio Sci. 2011, 46, 3604–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Komjathy, A. GNSS reflectometry and remote sensing: New objectives and results. Adv. Space Res. 2010, 46, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Gleason, S.; Cardellach, E.; Camps, A. Tutorial on remote sensing using GNSS bistatic radar of opportunity. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2014, 2, 8–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.U.; Voronovich, A.G. Scattering of GPS signals from the ocean with wind remote sensing application. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2000, 38, 951–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, E.; Camps, A.; Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Park, H. Using GNSS-R imaging of the ocean surface for oil slick detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.G.; Rizos, C. Feasibility of air target detection using GPS as a bistatic radar. J. Glob. Position Syst. 2006, 5, 119–126. [Google Scholar]
- Katzberg, S.J.; Torres, O.; Grant, M.S.; Masters, D. Utilizing calibrated GPS reflected signals to estimate soil reflectivity and dielectric constant: Results from SMEX02. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavorotny, V.; Masters, D.; Gasiewski, A.; Bartram, B. Seasonal polarimetric measurements of soil moisture using tower-based GPS bistatic radar. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 781–783. [Google Scholar]
- Egido, A.; Caparrini, M.; Guerriero, L.; Pierdicca, N.; Paloscia, S.; Santi, E.; Brogioni, M. LEiMON Land Monitoring with Navigation Signals; Final Report; ESA Contract 22117/08/NL/AF; ESA/ESTEC: Noordwijk, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Pierdicca, N.; Guerriero, L.; Giusto, R.; Brogioni, M.; Egido, A. Savers: A simulator of GNSS reflections from bare and vegetated soils. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 6542–6554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Alvarez, N.; Camps, A.; Vall-Llossera, M.; Bosch-Lluis, X. Land geophysical parameters retrieval using the interference pattern GNSS-R technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Arroyo, A.; Camps, A.; Aguasca, A.; Forte, G. Improving the accuracy of soil moisture retrievals using the phase difference of the dual-polarization GNSS-R interference patterns. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 11, 2090–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Small, E.E.; Gutmann, E.D.; Bilich, A.L.; Braun, J.J.; Zavorotny, V.U. Use of GPS receivers as a soil moisture network for water cycle studies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E.; Larson, K.M.; Zavorotny, V.U. Effects of near-surface soil moisture on GPS SNR data: Development of a retrieval algorithm for soil moisture. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.E.; Larson, K.M.; Braun, J.J. Sensing vegetation growth with reflected GPS signals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 245–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, C.C.; Small, E.E.; Larson, K.M.; Zavorotny, V.U. Vegetation sensing using GPS-interferometric reflectometry: Theoretical effects of canopy parameters on signal-to-noise ratio data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 2755–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Gutmann, E.D.; Zavorotny, V.U.; Braun, J.J.; Williams, M.W.; Nievinski, F.G. Can we measure snow depth with GPS receivers? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccreight, J.L.; Small, E.E.; Larson, K.M. Snow depth, density, and SWE estimates derived from GPS reflection data: Validation in the Western U.S. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 50, 6892–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Najibi, N. Sensing snow height and surface temperature variations in Greenland from GPS reflected signals. Adv. Space Res. 2014, 53, 1623–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boniface, K.; Braun, J.J.; Mccreight, J.L.; Nievinski, F.G. Comparison of snow data assimilation system with gps reflectometry snow depth in the western United States. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.G.; Qian, X.D.; Kutoglu, H. Snow depth variations estimated from GPS-Reflectometry: A case study in Alaska from L2P SNR data. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, K.M.; Lofgren, J.S.; Haas, R. Coastal sea level measurements using a single geodetic GPS receiver. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 51, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfgren, J.S.; Haas, R.; Johansson, J.M. Monitoring coastal sea level using reflected GNSS signals. Adv. Space Res. 2011, 47, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofgren, J.S.; Haas, R.; Scherneck, H.G. Sea level time series and ocean tide analysis from multipath signals at five GPS sites in different parts of the world. J. Geodyn. 2014, 80, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jin, S. Can we monitor the bare soil freeze-thaw process using GNSS-R? A simulation study. In Proceedings of the SPIE Asia-Pacific Remote Sensing, Beijing, China, 13–17 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hallikainen, M.T.; Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C.; El-Rayes, M.A. Microwave dielectric behavior of wet soil-part I: Empirical models and experimental observations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 1, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, M.C.; Ulaby, F.T.; Hallikainen, M.T.; El-Rayes, M.A. Microwave dielectric behavior of wet soil-part II: Dielectric mixing models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1985, 1, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracaglia, M.; Ferrazzoli, P.; Guerriero, L. A fully polarimetric multiple scattering model for crops. Remote Sens. Environ. 1995, 54, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.S.; Wu, T.D.; Tsang, L.; Li, Q.; Shi, J.; Fung, A.K. Emission of rough surfaces calculated by the integral equation method with comparison to three-dimensional moment method simulations. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peplinski, N.R.; Ulaby, F.T.; Dobson, M.C. Dielectric properties of soils in the 0.3–1.3-GHz range. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1995, 33, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, K. The estimation of dielectric constant of frozen soil-water mixture at microwave bands. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; pp. 2903–2905. [Google Scholar]
- Nievinski, F.G.; Larson, K.M. An open source GPS multipath simulator in Matlab/Octave. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nievinski, F.G.; Larson, K.M. Forward modeling of GPS multipath for near-surface reflectometry and positioning applications. GPS Solut. 2014, 18, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibi, S.; Nievinski, F.G.; Dam, T.V.; Monico, J.F.G. Assessment of modernized GPS L5 SNR for ground-based multipath reflectometry applications. Adv. Space Res. 2015, 55, 1104–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plate Boundary Observatory. Available online: http://pbo.unavco.org (accessed on 9 October 2017).
- Serreze, M.C.; Clark, M.P.; Armstrong, R.L.; McGinnis, D.A.; Pulwarty, R.S. Characteristics of the Western United States snowpack from snowpack telemetry (SNOTEL) data. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 2145–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Ts (°C) | L1 Carrier Frequency | L2 Carrier Frequency | L5 Carrier Frequency | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Real Part | Imaginary Part | Real Part | Imaginary Part | Real Part | Imaginary Part | |
| −1 | 8.67 | 1.03 | 8.71 | 1.17 | 8.71 | 1.20 |
| +1 | 21.11 | 3.54 | 21.28 | 3.50 | 21.30 | 3.51 |
| Date | SM (pct) | SD (cm) | ST (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2011, DOY 318 | 15.2 | 20 | 0.2 |
| 2011, DOY 319 | 15 | 20 | 0.1 |
| 2011, DOY 320 | 15 | 20 | 0 |
| 2011, DOY 321 | 15 | 20 | −0.1 |
| 2011, DOY 322 | 14.1 | 20 | −0.1 |
| 2011, DOY 323 | 13.5 | 20 | −0.2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Jin, S.; Chang, L. Monitoring Bare Soil Freeze–Thaw Process Using GPS-Interferometric Reflectometry: Simulation and Validation. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010014
Wu X, Jin S, Chang L. Monitoring Bare Soil Freeze–Thaw Process Using GPS-Interferometric Reflectometry: Simulation and Validation. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xuerui, Shuanggen Jin, and Liang Chang. 2018. "Monitoring Bare Soil Freeze–Thaw Process Using GPS-Interferometric Reflectometry: Simulation and Validation" Remote Sensing 10, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010014
APA StyleWu, X., Jin, S., & Chang, L. (2018). Monitoring Bare Soil Freeze–Thaw Process Using GPS-Interferometric Reflectometry: Simulation and Validation. Remote Sensing, 10(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10010014