Detection, Localization and Classification of Multiple Mechanized Ocean Vessels over Continental-Shelf Scale Regions with Passive Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Experiment
2.2. Hydrophone Array
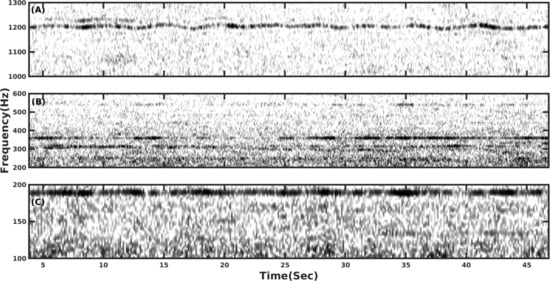
2.3. Signal Detection and Clustering
2.4. Localization
3. Results
3.1. Simultaneous Passive Acoustic Detection and Localization of Multiple Ocean Vessels on 23 February off Lofoten Archipelago
3.1.1. Commercial Ships Identified by GPS
3.1.2. Vessels Unidentified by GPS
3.2. Simultaneous Passive Acoustic Detection and Localization of Multiple Ocean Vessels on 26 February off Northern Finnmark
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Time-Frequency Characteristics of Dominant Narrowband Signal Detections from the Tow Ship, RV Knorr


| Forward Endfire | 45 from Forward Endfire | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Center Frequency (Hz) | Bandwidth (Hz) | Center Frequency (Hz) | Bandwidth (Hz) |
| 115.9 | 5.3 ± 0.6 | 214.6 | 8.5 ± 1.4 |
| 360.6 | 9.9 ± 0.5 | 360.5 | 10.0 ± 0.3 |
| 151.0 | 4.5 ± 1.3 | 450.3 | 5.6 ± 1.1 |
| 450.4 | 6.5 ± 2.0 | 540.3 | 7.2 ± 1.7 |
| 540.1 | 7.8 ± 2.1 | 721.1 | 6.6 ± 1.2 |
| 721.2 | 8.7 ± 1.4 | 809.9 | 6.0 ± 1.4 |
| 810.1 | 7.8 ± 1.9 | 1081.6 | 9.8 ± 1.5 |
| 1081.8 | 9.8 ± 1.1 | 1178.8 | 10.4 ± 2.1 |
| 1350.6 | 10.2 ± 1.4 | 1350.5 | 10.0 ± 2.2 |
| 1442.3 | 9.7 ± 1.2 | 1442.1 | 9.6 ± 1.1 |
| 1619.8 | 10.4 ± 1.6 | 1768.6 | 9.8 ± 1.7 |
| 1768.5 | 10.4 ± 1.1 | 1803.1 | 9.4 ± 1.0 |
| 1803.0 | 10.1 ± 1.4 | 1890.8 | 9.6 ± 1.3 |
| 1891.0 | 10.3 ± 1.2 | ||
References
- Garcia, H.A.; Zhu, C.; Schinault, M.E.; Kaplan, A.I.; Handegard, N.O.; Godø, O.R.; Ahonen, H.; Makris, N.C.; Wang, D.; Huang, W.; et al. Temporal–spatial, spectral, and source level distributions of fin whale vocalizations in the Norwegian Sea observed with a coherent hydrophone array. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2018, fsy127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, D.; Garcia, H.; Godø, O.R.; Ratilal, P. Continental Shelf-Scale Passive Acoustic Detection and Characterization of Diesel-Electric Ships Using a Coherent Hydrophone Array. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Garcia, H.; Huang, W.; Tran, D.D.; Jain, A.D.; Yi, D.H.; Gong, Z.; Jech, J.M.; Godø, O.R.; Makris, N.C.; et al. Vast assembly of vocal marine mammals from diverse species on fish spawning ground. Nature 2016, 531, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Huang, W.; Garcia, H.; Ratilal, P. Vocalization source level distributions and pulse compression gains of diverse baleen whale species in the Gulf of Maine. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, D.; Ratilal, P. Diel and Spatial Dependence of Humpback Song and Non-Song Vocalizations in Fish Spawning Ground. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Jain, A.D.; Tran, D.; Yi, D.H.; Wu, F.; Zorn, A.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Ecosystem scale acoustic sensing reveals humpback whale behavior synchronous with herring spawning processes and re-evaluation finds no effect of sonar on humpback song occurrence in the Gulf of Maine in Fall 2006. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.D.; Huang, W.; Bohn, A.C.; Wang, D.; Gong, Z.; Makris, N.C.; Ratilal, P. Using a coherent hydrophone array for observing sperm whale range, classification, and shallow-water dive profiles. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 135, 3352–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gong, Z.; Tran, D.D.; Ratilal, P. Comparing passive source localization and tracking approaches with a towed horizontal receiver array in an ocean waveguide. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 3705–3720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hildebrand, J.A. Anthropogenic and natural sources of ambient noise in the ocean. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2009, 395, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stojanovic, M. Underwater acoustic communications. In Proceedings of the Electro/95 International, Boston, MA, USA, 21–23 June 1995; pp. 435–440. [Google Scholar]
- Stojanovic, M.; Preisig, J. Underwater acoustic communication channels: Propagation models and statistical characterization. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2009, 47, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dambra, R.; Firenze, E. Underwater Radiated Noise of a Small Vessel. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Congress on Sound and Vibration, Florence, Italy, 12–16 July 2015; pp. 12–16. [Google Scholar]
- Merchant, N.D.; Witt, M.J.; Blondel, P.; Godley, B.J.; Smith, G.H. Assessing sound exposure from shipping in coastal waters using a single hydrophone and Automatic Identification System (AIS) data. Mari. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, R.O.; Amorim, M.C.P.; Ladich, F. Effects of ship noise on the detectability of communication signals in the Lusitanian toadfish. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 2104–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Codarin, A.; Wysocki, L.E.; Ladich, F.; Picciulin, M. Effects of ambient and boat noise on hearing and communication in three fish species living in a marine protected area (Miramare, Italy). Mari. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1880–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ona, E.; Godø, O.R.; Handegard, N.O.; Hjellvik, V.; Patel, R.; Pedersen, G. Silent research vessels are not quiet. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2007, 121, EL145–EL150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitson, R. Underwater noise radiated by research vessels. ICES Mar. Sci. Symp. 1993, 196, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Mitson, R.B.; Knudsen, H.P. Causes and effects of underwater noise on fish abundance estimation. Aquat. Living Resour. 2003, 16, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, L.; Clark, C.; Merrick, R.; Van Parijs, S.; Ponirakis, D.; Schwehr, K.; Thompson, M.; Wiley, D. Characterizing the relative contributions of large vessels to total ocean noise fields: A Case study using the Gerry E. Studds Stellwagen Bank National Marine Sanctuary. Environ. Manag. 2008, 42, 735–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veirs, S.; Veirs, V.; Wood, J.D. Ship noise extends to frequencies used for echolocation by endangered killer whales. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittekind, D.K. A simple model for the underwater noise source level of ships. J. Ship Prod. Des. 2014, 30, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbe, C.; McCauley, R.; Gavrilov, A. Characterizing marine soundscapes. In The Effects of Noise on Aquatic Life II; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 265–271. [Google Scholar]
- Miksis-Olds, J.L.; Martin, B.; Tyack, P.L. Exploring the Ocean Through Soundscapes. Acoust. Today 2018, 14, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, M.; Henderson, L. Global ocean soundscapes. In Proceedings of the Meetings on Acoustics ICA2013, Montreal, QC, Canada, 2–7 June 2013; Volume 19, p. 010050. [Google Scholar]
- Crocker, S.E.; Nielsen, P.L.; Miller, J.H.; Siderius, M. Geoacoustic inversion of ship radiated noise in shallow water using data from a single hydrophone. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2014, 136, EL362–EL368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallett, M.A. Characteristics of merchant ship acoustic signatures during port entry/exit. In Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the Australian Acoustical Society, Gold Coast, Australia, 3–5 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bruno, M.; Chung, K.W.; Salloum, H.; Sedunov, A.; Sedunov, N.; Sutin, A.; Graber, H.; Mallas, P. Concurrent use of satellite imaging and passive acoustics for maritime domain awareness. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Waterside Security Conference (WSS), Carrara, Italy, 3–5 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, K.W.; Sutin, A.; Sedunov, A.; Bruno, M. DEMON acoustic ship signature measurements in an urban harbor. Adv. Acoust. Vib. 2011, 2011, 952798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutin, A.; Bunin, B.; Sedunov, A.; Sedunov, N.; Fillinger, L.; Tsionskiy, M.; Bruno, M. Stevens passive acoustic system for underwater surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Waterside Security Conference (WSS), Carrara, Italy, 3–5 November 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Nejedl, V.; Stoltenberg, A.; Schulz, J. Free-field measurements of the radiated and structure borne sound of RV “Planet”. In Proceedings of the Meetings on Acoustics ECUA2012, Edinburgh, UK, 2–6 July 2012; Volume 17, p. 070061. [Google Scholar]
- McKenna, M.F.; Ross, D.; Wiggins, S.M.; Hildebrand, J.A. Underwater radiated noise from modern commercial ships. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 131, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urick, R.J. Principles of Underwater Sound; Peninsula Publishing: Los Altos Hills, CA, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Mitson, R. Underwater Noise of Research Vessels; ICES Co-Operative Research Report; ICES: Oxford, UK, 1995; Volume 61. [Google Scholar]
- Fréchou, D.; Dugué, C.; Briançon-Marjollet, L.; Fournier, P.; Darquier, M.; Descotte, L.; Merle, L. Marine Propulsor Noise Investigations in the Hydroacoustic Water Tunnel “GTH”. In Twenty-Third Symposium on Naval Hydrodynamics; Office of Naval Research Bassin d’Essais des CarenesNational Research Council: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bush, V.; Conant, J.B.; Tate, J.T. Principles and Applications of Underwater Sound; Technical Report; Office of Scientific Research and Development: Washington, DC, USA, 1946; Volume 7. [Google Scholar]
- Norwood, C. An introduction to ship radiated noise. Acoust. Aust. 2002, 30, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Ojak, W. Vibrations and waterborne noise on fishery vessels. J. Ship Res. 1988, 32, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, L.M.; Greeley, D.S. Source level model for propeller blade rate radiation for the world’s merchant fleet. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1980, 67, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelowska, G.; Kozaczka, E.; Kozaczka, S.; Szymczak, W. Underwater noise generated by a small ship in the shallow sea. Arch. Acoust. 2013, 38, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Preston, J. The ONR five octave research array (FORA) at Penn State. In Proceedings of the IEEE OCEANS 2003, San Diego, CA, USA, 22–26 September 2003; Volume 5, pp. 2607–2610. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, D.H.; Dudgeon, D.E. Array Signal Processing: Concepts and Techniques; Simon & Schuster: New York, NY, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheim, A.V.; Willsky, A.S.; Nawab, S.H. Signals and Systems; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1983; Volume 6, p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Ratilal, P. Angular Resolution Enhancement Provided by Nonuniformly-Spaced Linear Hydrophone Arrays in Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, N.C.; Avelino, L.Z.; Menis, R. Deterministic reverberation from ocean ridges. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1995, 97, 3547–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratilal, P.; Lai, Y.; Symonds, D.T.; Ruhlmann, L.A.; Preston, J.R.; Scheer, E.K.; Garr, M.T.; Holland, C.W.; Goff, J.A.; Makris, N.C. Long range acoustic imaging of the continental shelf environment: The Acoustic Clutter Reconnaissance Experiment 2001. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2005, 117, 1977–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.D. Instantaneous Continental-Shelf Scale Sensing of Cod With Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing (OAWRS). Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sezan, M.I. A peak detection algorithm and its application to histogram-based image data reduction. Comput. Vis. Gr. Image Process. 1990, 49, 36–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.; Andrews, M.; Ratilal, P. Probability distribution for energy of saturated broadband ocean acoustic transmission: Results from Gulf of Maine 2006 experiment. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2012, 132, 3659–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makris, N.C. The effect of saturated transmission scintillation on ocean acoustic intensity measurements. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1996, 100, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.D.; Wang, C. A versatile pitch tracking algorithm: From human speech to killer whale vocalizations. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, M.F.; Mussoline, S.E. A generalized baleen whale call detection and classification system. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 129, 2889–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanungo, T.; Mount, D.M.; Netanyahu, N.S.; Piatko, C.D.; Silverman, R.; Wu, A.Y. An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: Analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2002, 24, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duda, R.O.; Hart, P.E.; Stork, D.G. Pattern Classification; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Ratilal, P.; Makris, N.C. Simultaneous localization of multiple broadband non-impulsive acoustic sources in an ocean waveguide using the array invariant. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2015, 138, 2649–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Urick, R. Principles of Underwater Acoustics; McGraw-Hili Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Kinsler, L.E.; Frey, A.R.; Coppens, A.B.; Sanders, J.V. Fundamentals of acoustics. In Fundamentals of Acoustics, 4th ed.; Kinsler, L.E., Frey, A.R., Coppens, A.B., Sanders, J.V., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: New York, NY, USA, 1999; p. 560. ISBN 0-471-84789-5. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, F.B.; Kuperman, W.A.; Porter, M.B.; Schmidt, H. Computational Ocean Acoustics; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Fonseca, J.M.; Moura-Pires, F. Ship noise evaluation based on segmented decision trees. In Proceedings of the 1992 lEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Raleigh, NC, USA, 7–10 July 1992; Volume 3, pp. 1823–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, H.; Tang, S.; Sun, J. A SOM-based probabilistic neural network for classification of ship noises. In Proceedings of the IEEE 2002 International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems and West Sino Expositions, Chengdu, China, 29 June–1 July 2002; Volume 2, pp. 1209–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Farrokhrooz, M.; Karimi, M. Ship noise classification using probabilistic neural network and AR model coefficients. In Proceedings of the IEEE Oceans 2005-Europe, Brest, France, 20–23 June 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1107–1110. [Google Scholar]
- Xi-ying, H.; Jin-fang, C.; Guang-jin, H.; Nan, L. Application of BP neural network and higher order spectrum for ship-radiated noise classification. In Proceedings of the 2010 2nd International Conference on Future Computer and Communication (ICFCC), Wuhan, China, 21–24 May 2010; Volume 1, pp. V1–712. [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis, A.; Handegard, N.O. Fish avoidance of research vessels and the efficacy of noise-reduced vessels: A Review. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2012, 70, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














| Ship Name | Center Frequency (Hz) | Bandwidth (Hz) | True Range (km) | True Speed (Knots) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WILSON | 49.6 | 4.2 ± 1.0 | 39.1 ± 5.7 | 6.8 ± 0.6 |
| ALGECIRAS, CG (M1) | 65.6 | 4.4 ± 1.1 | (28.6–46.0) | (5.6–7.6) |
| 82.6 | 4.6 ± 1.0 | |||
| 98.8 | 4.5 ± 1.2 | |||
| 339.2 | 6.6 ± 1.7 | |||
| 1019.5 | 10.7 ± 2.0 | |||
| 1357.5 | 10.6 ± 2.0 | |||
| 1700.7 | 11.2 ± 2.0 | |||
| BUEFJORD, F (M13) | 49.9 | 4.2 ± 1.0 | 13.6 ± 3.2 | 2.0 ± 2.1 |
| 102.0 | 4.1 ± 1.4 | |||
| 166.7 | 4.8 ± 1.7 | (5.5–16.0) | (0.6–8.3) | |
| 276.5 | 7.7 ± 1.4 | |||
| 553.2 | 6.7 ± 1.9 | |||
| 831.2 | 6.8 ± 1.8 | |||
| 1404.8 | 10.9 ± 2.0 | |||
| 1783.7 | 11.0 ± 1.9 | |||
| EROS, F (M14) | 1081.4 | 10.0 ± 1.2 | 22.2 ± 2.7 | 7.5 ± 0.5 |
| (18.2–25.9) | (6.8–8.2) | |||
| FORTUNA, F (M11) | 180.9 | 5.0 ± 0.4 | 17.7 ± 0.8 | 3.3 ± 1.7 |
| 256.3 | 8.2 ± 2.1 | (16.6–19.1) | (1.6–7.7) | |
| 446.0 | 6.8 ± 1.3 | |||
| 533.4 | 7.9 ± 1.4 | |||
| 1198.8 | 10.4 ± 1.3 | |||
| FUGLOYHAV, F (M5) | 74.7 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 10.8 ± 2.4 | 4.6 ± 2.3 |
| 112.7 | 4.0 ± 1.1 | (7.1–16) | (0.2–8.4) | |
| 421.6 | 7.6 ± 1.6 | |||
| 737.2 | 8.0 ± 2.3 | |||
| 1317.1 | 11.2 ± 1.9 | |||
| 1372.1 | 8.9 ± 2.1 | |||
| 1875.0 | 10.0 ± 2.2 |
| Ship Name | Center Frequency (Hz) | Bandwidth (Hz) | Mean Estimated Range (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown vessel U2 | 101.7 | 4.1 ± 0.7 | 5.0 |
| 489.6 | 7.7 ± 2.0 | ||
| 560.5 | 7.4 ± 1.6 | ||
| 1123.2 | 9.9 ± 1.8 | ||
| 1477.6 | 9.3 ± 2.1 | ||
| Unknown vessel U3 | 167.3 | 5.7 ± 0.9 | 201.8 |
| 238.1 | 8.6 ± 1.3 | ||
| Unknown vessel U4 | 486.5 | 7 ± 1.5 | 188.7 |
| 1264.9 | 9.7 ± 1.8 | ||
| 1463.9 | 9.4 ± 2 | ||
| Unknown vessel U6 | 257.8 | 7.8 ± 1.9 | 15.6 |
| 830.3 | 7.8 ± 1.7 | ||
| 1106.3 | 10.0 ± 2.2 | ||
| 1935.6 | 10.5 ± 2.1 | ||
| Unkown vessel U7 | 82.6 | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 19.5 |
| Unkown vessel U8 | 166.8 | 9.7 ± 1.5 | 23.1 |
| 470.3 | 6.9 ± 2.6 | ||
| 1049.0 | 8.4 ± 2.1 | ||
| Unkown vessel U9 | 360.7 | 10.0 ± 0.4 | 18.7 |
| 721.4 | 6.8 ± 1.6 | ||
| Unkown vessel U10 | 167.4 | 9.8 ± 0.8 | 7.8 |
| Unkown vessel U12 | 129.1 | 4.1 ± 1.3 | 173.4 |
| 166.2 | 3.9 ± 1.8 |
| Ship Name | Center Frequency (Hz) | Bandwidth (Hz) | True Range (km) | True Speed (knots) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Esvagt Castor, SAR (M1) | 170.9 | 4.4 ± 1.0 | 148.5 ± 5.4 | 1.2 ± 2.1 |
| (140.3–185.1) | (0.2–6.6) | |||
| Federal Rhine, CG (M2) | 95.5 | 4.7 ± 1.6 | 50.6 ± 2.8 | 13.3 ± 0.3 |
| 290.4 | 10.6 ± 1.5 | (48.8–57.2) | (12.7–13.7) | |
| 1121.2 | 10.7 ± 2 | |||
| 1533.6 | 10.3 ± 2.1 | |||
| 1609.7 | 10.1 ± 2.2 | |||
| Henriksen Jr, F (M3) | 1523.9 | 8.6 ± 1.3 | 23.5 ± 1.7 | 6.6 ± 0.7 |
| 1590.3 | 5.7 ± 0.9 | (21.6–26.3) | (5.4–7.5) | |
| Holmfoss, RCG (M4) | 609.2 | 7.2 ± 1.6 | 36.6 ± 4.4 | 15.4 ± 0.2 |
| 894.7 | 9.4 ± 1.7 | (31.8–44.4) | (15–15.7) | |
| 1791.1 | 11.0 ± 1.7 | |||
| Kapitan Durachenko, F (M5) | 840.9 | 8 ± 1.2 | 82.8 ± 1.3 | 3.9 ± 0.2 |
| 1041.6 | 9.7 ± 1.9 | (81.9–86.5) | (3.6–4.2) | |
| 1147.0 | 10.8 ± 1.6 | |||
| 1469.7 | 9.4 ± 1.2 | |||
| Kepromar, F (M6) | 49.4 | 5.4 ± 0.5 | 25.1 ± 12.0 | 9.9 ± 0.5 |
| 73.9 | 5 ± 0.7 | (12.5–51.6) | (9.2–10.7) | |
| 312.7 | 8.9 ± 1.6 | |||
| 1011.7 | 10.9 ± 1.6 | |||
| 1990.1 | 11.0 ± 2.1 | |||
| Nordlys, P (M7) | 492.7 | 9.3 ± 1.2 | 24.7 ± 1.9 | 14.4 ± 0.3 |
| 737.9 | 10.2 ± 1.5 | (23.1–27.9) | (14.1–14.9) | |
| 767.2 | 9.6 ± 1.3 | |||
| 1545.3 | 10.0 ± 2.7 | |||
| 1600.9 | 9.6 ± 2.8 | |||
| Nordstrand, F (M8) | 765.6 | 11.3 ± 2.2 | 61.0 ± 8.4 | 0.3 ± 0.2 |
| 893.4 | 10.8 ± 2.5 | (43.5–72.1) | (0–0.7) | |
| Persey-4, F (M9) | 652.4 | 9.4 ± 1.8 | 46.3 ± 19.5 | 4.5 ± 0.5 |
| 988.2 | 10.6 ± 1.3 | (16.3–80.3) | (3–5.9) | |
| 1458.6 | 9.8 ± 1.7 | |||
| RN Murmansk, T (M10) | 66.1 | 4.7 ± 0.4 | 48.2 ± 5.5 | 12.9 ± 0.3 |
| 420.4 | 9 ± 1.8 | (41.7–58.6) | (12.2–13.4) | |
| Troma, T (M11) | 510.7 | 7.7 ± 1.4 | 34.9 ± 0.6 | 11.8 ± 0.4 |
| 560.7 | 7.3 ± 1.7 | (34.2–36.1) | (10.8–12.3) | |
| 764.3 | 10.0 ± 2.0 | |||
| 1008.3 | 10.2 ± 1.7 | |||
| 1757.6 | 9.8 ± 1.8 | |||
| United Fortune, CG (M12) | 394.9 | 11.3 ± 1.1 | 47.6 ± 2.0 | 11.7 ± 0.2 |
| 438.7 | 9.9 ± 1.1 | (44.9–50.0) | (11.6–12.0) | |
| 1152.6 | 11.2 ± 1.7 | |||
| Variant, F (M13) | 459.0 | 9.8 ± 1.42 | 15.0 ± 0.6 | 3.0 ± 0.3 |
| 541.0 | 9.5 ± 1.2 | (14.3–15.5) | (2.4–3.3) | |
| 824.3 | 10.3 ± 1.5 | |||
| 1531.2 | 11.5 ± 1.8 | |||
| Wilson Husum, CG (M14) | 538.6 | 8.7 ± 1.6 | 23.4 ± 1.9 | 11.4 ± 0.3 |
| 950.8 | 8.7 ± 1.5 | (21.6–27.5) | (11–11.9) | |
| 1023.6 | 9.6 ± 1.8 | |||
| 1123.1 | 10.4 ± 1.1 | |||
| Wolgastern, T (M15) | 118.6 | 5.3 ± 0.8 | 150.0 ± 10.1 | 11.9 ± 0.5 |
| 561.7 | 9.2 ± 1.4 | (38.9–70.0) | (11–12.9) | |
| 1106.7 | 10.6 ± 1.8 |
| Ship Name | Center Frequency (Hz) | Bandwidth (Hz) | Estimated Range (km) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unknown vessel (U16) | 1043.6 | 10.2 ± 1.8 | 21.6 |
| Ship Name | 09:30:00–10:50:32 | 10:50:32–12:00:00 | 12:00:00–13:00:00 | 13:00:00–15:15:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WILSON ALGECIRAS (M1) | 9.53% | |||
| FUGLOYHAV (M5) | 32.43% | 44.49% | 14.17% | 5.27% |
| FORTUNA (M11) | 7.16% | 4.62% | ||
| BUEFJORD (M13) | 32.18% | 9.06% | 8.13% | |
| EROS (M14) | 22.93% | 12.40% |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, C.; Garcia, H.; Kaplan, A.; Schinault, M.; Handegard, N.O.; Godø, O.R.; Huang, W.; Ratilal, P. Detection, Localization and Classification of Multiple Mechanized Ocean Vessels over Continental-Shelf Scale Regions with Passive Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111699
Zhu C, Garcia H, Kaplan A, Schinault M, Handegard NO, Godø OR, Huang W, Ratilal P. Detection, Localization and Classification of Multiple Mechanized Ocean Vessels over Continental-Shelf Scale Regions with Passive Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(11):1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111699
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Chenyang, Heriberto Garcia, Anna Kaplan, Matthew Schinault, Nils Olav Handegard, Olav Rune Godø, Wei Huang, and Purnima Ratilal. 2018. "Detection, Localization and Classification of Multiple Mechanized Ocean Vessels over Continental-Shelf Scale Regions with Passive Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 10, no. 11: 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111699
APA StyleZhu, C., Garcia, H., Kaplan, A., Schinault, M., Handegard, N. O., Godø, O. R., Huang, W., & Ratilal, P. (2018). Detection, Localization and Classification of Multiple Mechanized Ocean Vessels over Continental-Shelf Scale Regions with Passive Ocean Acoustic Waveguide Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 10(11), 1699. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111699