Retrieval of the Fine-Mode Aerosol Optical Depth over East China Using a Grouped Residual Error Sorting (GRES) Method from Multi-Angle and Polarized Satellite Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. The Shortcomings in Current AODf Retrieval Algorithm
2.2. Improvement of Aerosol Model Determination Method
2.3. Data Processing
3. Results and Validation
3.1. Case study over East China
3.2. Validation of the Retrieved AODf against AERONET
4. Discussion
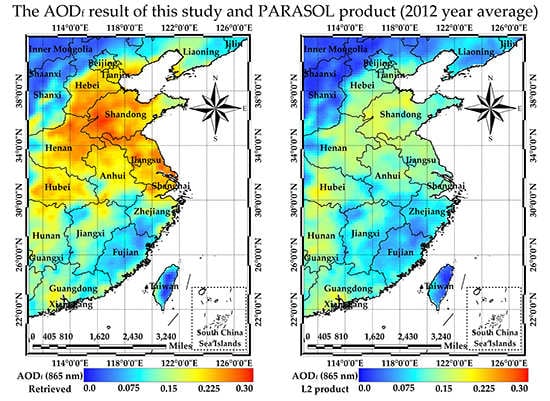
4.1. Comparison with PARASOL Level 2 Product
4.2. Application of the GRES Method for AODt Retrieval
5. Summary
- The GRES method is able to obtain comparable AODf retrieval results with AERONET ground-based data, the r at the Beijing, Xianghe, Taihu and Hong_Kong_PolyU sites are 0.900, 0.933, 0.957 and 0.968, respectively, which shows a high correlation.
- The AODf retrieval results using the GRES method have a better accuracy than PARASOL AODf product. For the high aerosol loading days, the comparisons with the AERONET AODf of the two results show an r of 0.851 versus 0.641, RMSE of 0.068 versus 0.126, Gfrac of 74.00% versus 34.00% and MAE of 0.054 versus 0.104.
- The comparison of the 2012 year-mean AODf from the GRES method and PARAOSL product shows some qualitative and quantitative differences in North China, Jiangsu, Shanghai, Hunan and Guangdong, the maximum quantitative difference at 865 nm is ±0.1.
- The application of the GRES method for total AOD retrieval using EOFs shows that the GRES method has a favorable expandability for the multi-angle aerosol retrieval and good performance for the optimal aerosol model determination.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tollefson, J. Asian pollution delays inevitable warming. Nature 2010, 463, 860–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Li, Z.; Kim, Y.J.; Kokhanovsky, A. Atmospheric Aerosol Monitoring from Satellite Observations: A History of Three Decades. In Atmospheric and Biological Environmental Monitoring; Kim, Y.J., Platt, U., Gu, M.B., Iwahashi, H., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 13–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Wald, A.E.; Remer, L.A.; Gao, B.C. The modis 2.1-μm channel-correlation with visible reflectance for use in remote sensing of aerosol. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. The second-generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from inversion of modis spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The collection 6 modis aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L. Modis 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kleidman, R.G.; Mattoo, S. Global evaluation of the collection 5 modis dark-target aerosol products over land. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 10399–10420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Validation of modis aerosol optical depth retrieval over mountains in central china based on a sun-sky radiometer site of sonet. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Lin, H.C.; Schwartz, C.S.; Lee, Y.H.; Wang, T. Three-dimensional variational assimilation of modis aerosol optical depth: Implementation and application to a dust storm over east Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, H.C.; Mckeen, S.A. Simultaneous three-dimensional variational assimilation of surface fine particulate matter and modis aerosol optical depth. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saide, P.E.; Carmichael, G.R.; Liu, Z.; Schwartz, C.S.; Lin, H.C.; Silva, A.M.D.; Hyer, E. Aerosol optical depth assimilation for a size-resolved sectional model: Impacts of observationally constrained, multi-wavelength and fine mode retrievals on regional scale analyses and forecasts. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10425–10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, C.S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, H.C.; Cetola, J.D. Assimilating aerosol observations with a “hybrid” variational-ensemble data assimilation system. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4043–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Gu, X.; Yu, T.; Cheng, T.; Chen, H. Trend Analysis of the Aerosol Optical Depth from Fusion of Misr and Modis Retrievals over China; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2014; pp. 682–691. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.; Van, D.A.; Martin, R.V.; Burnett, R.; Rainham, D.G.; Birkett, N.J.; Krewski, D. Estimates of global mortality attributable to particulate air pollution using satellite imagery. Environ. Res. 2013, 120, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Lau, A.K.H.; Li, C.; Fung, J.C.H. Using satellite remote sensing data to estimate the high-resolution distribution of ground-level PM2.5. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 156, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Franklin, M.; Kahn, R.; Koutrakis, P. Using aerosol optical thickness to predict ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the St. Louis area: A comparison between Misr and Modis. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, L. Satellite-based estimation of regional particulate matter (PM) in Beijing using vertical-and-rh correcting method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyouk, N.; Léon, J.F.; Delbarre, H.; Podvin, T.; Deroo, C. Impact of the mixing boundary layer on the relationship between PM2.5 and aerosol optical thickness. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Remote sensing of atmospheric fine particulate matter (PM2.5) mass concentration near the ground from satellite observation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Shao, J.; Li, B.; Hong, J.; Liu, D.; Li, D.; Wei, P.; Li, W.; Li, L.; et al. Remote sensing of atmospheric particulate mass of dry PM2.5 near the ground: Method validation using ground-based measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 173, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleidman, R.G.; O’Neill, N.T.; Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Tanré, D.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N. Comparison of moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (modis) and aerosol robotic network (aeronet) remote-sensing retrievals of aerosol fine mode fraction over ocean. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 3127–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Core Writing Team, Pachauri, R.K., Meyer, l.A., Eds.; IPCC: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014; p. 151. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Boucher, O.; Tanré, D.; Chin, M.; Remer, L.A.; Takemura, T. Aerosol anthropogenic component estimated from satellite data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Gu, X.; Xie, D.; Li, Z.; Yu, T.; Chen, H. Aerosol optical depth and fine-mode fraction retrieval over east Asia using multi-angular total and polarized remote sensing. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Z. Retrieval of aerosol size distribution from multi-angle polarized measurements assisted by intensity measurements over east China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 124, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waquet, F.; Peers, F.; Goloub, P.; Ducos, F.; Thieuleux, F.; Derimian, Y.; Riedi, J.; Chami, M.; Tanré, D. Retrieval of the eyjafjallajökull volcanic aerosol optical and microphysical properties from polder/parasol measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 1755–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokhanovsky, A.A.; Davis, A.B.; Cairns, B.; Dubovik, O.; Hasekamp, O.P.; Sano, I.; Mukai, S.; Rozanov, V.V.; Litvinov, P.; Lapyonok, T.; et al. Space-based remote sensing of atmospheric aerosols: The multi-angle spectro-polarimetric frontier. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 145, 85–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fang, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W. Retrieval of aerosol properties for fine/coarse mode aerosol mixtures over Beijing from parasol measurements. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9311–9324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Qie, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Hou, W.; Li, K.; Li, D.; Xu, H. Retrieval of aerosol fine-mode fraction from intensity and polarization measurements by parasol over east Asia. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Chen, H.; Lin, L.; Han, Z.; Goloub, P. Retrieval of aerosol optical properties over the Beijing area using polder/parasol satellite polarization measurements. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 1099–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Cheng, T.; Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Li, X.; Gong, H. Aerosol type over east Asian retrieval using total and polarized remote sensing. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 129, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qie, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Sun, B.; Li, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Hou, W.; et al. Improving remote sensing of aerosol optical depth over land by polarimetric measurements at 1640 nm: Airborne test in north China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 6240–6256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhengqiang, L.I.; Hou, W.; Donghui, L.I.; Zhang, Y. Dynamic model in retrieving aerosol optical depth from polarimetric measurements of parasol. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 19, 25–33. [Google Scholar]
- Deuzé, J.L.; Bréon, F.M.; Devaux, C.; Goloub, P.; Herman, M.; Lafrance, B.; Maignan, F.; Marchand, A.; Nadal, F.; Perry, G.; et al. Remote sensing of aerosols over land surfaces from polder-adeos-1 polarized measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 4913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanré, D.; Bréon, F.M.; Deuzé, J.L.; Dubovik, O.; Ducos, F.; François, P.; Goloub, P.; Herman, M.; Lifermann, A.; Waquet, F. Remote sensing of aerosols by using polarized, directional and spectral measurements within the a-train: The parasol mission. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M.; Deuzé, J.L.; Devaux, C.; Goloub, P.; Bréon, F.M.; Tanré, D. Remote sensing of aerosols over land surfaces including polarization measurements and application to polder measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bréon, F.-M.; Vermeulen, A.; Descloitres, J. An evaluation of satellite aerosol products against sunphotometer measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3102–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cheng, T.; Gu, X.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y. Evaluation of polarized remote sensing of aerosol optical thickness retrieval over China. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13711–13728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Herman, M.; Holdak, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.L.; Ducos, F.; Sinyuk, A.; Lopatin, A. Statistically optimized inversion algorithm for enhanced retrieval of aerosol properties from spectral multi-angle polarimetric satellite observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2011, 4, 975–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 673–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanré, D.; Deuzé, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcette, J.J. Second simulation of the satellite signal in the solar spectrum, 6s: An overview. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotchenova, S.Y.; Vermote, E.F.; Raffaella, M.; Klemm, F.J. Validation of a vector version of the 6s radiative transfer code for atmospheric correction of satellite data. Part I: Path radiance. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 6762–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotchenova, S.Y.; Vermote, E.F. Validation of a vector version of the 6s radiative transfer code for atmospheric correction of satellite data. Part II. Homogeneous lambertian and anisotropic surfaces. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 6762–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadal, F.; Bréon, F.M. Parameterization of surface polarized reflectance derived from polder spaceborne measurements. Geosci. Remote Sens. IEEE Trans. 1999, 37, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maignan, F.; Bréon, F.-M.; Fédèle, E.; Bouvier, M. Polarized reflectances of natural surfaces: Spaceborne measurements and analytical modeling. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 2642–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martonchik, J.V. Determination of aerosol optical depth and land surface directional reflectances using multiangle imagery. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 17015–17022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martonchik, J.V.; Diner, D.J.; Kahn, R.A.; Ackerman, T.P.; Verstraete, M.M.; Pinty, B.; Gordon, H.R. Techniques for the retrieval of aerosol properties over land and ocean using multi-angle imaging. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 1212–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, M. Aerosol remote sensing from polder/adeos over the ocean: Improved retrieval using a nonspherical particle model. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanré, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, D.; Li, K.; Xu, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.; Xie, Y.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Li, W. Sun-sky radiometer observation network with the extension of multi-wavelength polarization measurements. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 19, 495–519. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Aerosol optical and microphysical properties of four typical sites of sonet in China based on remote sensing measurements. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9928–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Li, L.; Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, K.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y. Ground-based polarimetric remote sensing of dust aerosol properties in Chinese deserts near Hexi corridor. Adv. Meteorol. 2014, 2014, 240452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T. Aeronet—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from aerosol robotic network (aeronet) sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, N.T.; Dubovik, O.; Eck, T.F. Modified angström exponent for the characterization of submicrometer aerosols. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 2368–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, N.T.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Smirnov, A.; Dubovik, O.; Royer, A. Bimodal size distribution influences on the variation of angstrom derivatives in spectral and optical depth space. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2001, 106, 9787–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, N.T.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Thulasiraman, S. Spectral discrimination of coarse and fine mode optical depth. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Kahn, R.A.; Pinty, B.; Gobron, N.; Nelson, D.L.; Holben, B.N. Using angular and spectral shape similarity constraints to improve Misr aerosol and surface retrievals over land. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Qie, L.; Hou, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, H. Retrieval of aerosol optical depth using the empirical orthogonal functions (Eofs) based on Parasol multi-angle intensity data. Remote Sens. 2017, 2017, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Hou, W.; Hong, J.; Zheng, F.; Luo, D.; Wang, J.; Gu, X.; Qiao, Y. Directional polarimetric camera (DPC): Monitoring aerosol spectral optical properties over land from satellite observation. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2018, 218, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China, S.; Scarnato, B.; Owen, R.C.; Zhang, B.; Ampadu, M.T.; Kumar, S.; Dzepina, K.; Dziobak, M.P.; Fialho, P.; Perlinger, J.A. Morphology and mixing state of aged soot particles at a remote marine free troposphere site: Implications for optical properties. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; He, C.; Bi, L.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Z.; Li, W. Fractal dimensions and mixing structures of soot particles during atmospheric processing. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2017, 4, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Gu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H.; Yu, T. The optical properties of absorbing aerosols with fractal soot aggregates: Implications for aerosol remote sensing. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2013, 125, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liou, K.N.; Takano, Y.; Zhang, R.; Levy Zamora, M.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Leung, L.R. Variation of the radiative properties during black carbon aging: Theoretical and experimental intercomparison. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11967–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J. Evaluation of modis aerosol retrieval algorithms over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during low to very high pollution events. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 7941–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Variable | Number | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | 2 | 670 nm, 865 nm |
| Solar zenith angle | 15 | 0°–84°, interval 6° |
| View zenith angle | 15 | 0°–84°, interval 6° |
| Relative azimuth angle | 16 | 0°–180°, interval 12° |
| AODf at 550 nm | 6 | 0.01, 0.25, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0 |
| Aerosol model | 25 | Presented in Section 2.3 |
| Class | r0 (μm) | σ0 | mr | mi |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.05 to 0.20, interval 0.01 | 0.40 | 1.47 | 0.010 |
| 2 | 0.12 to 0.16, interval 0.01 | 0.51 | 1.49 | 0.011 |
| 3 | 0.10 to 0.13, interval 0.01 | 0.52 | 1.50 | 0.012 |
| Parameter | AERONET mean | Retrieved mean | Retrieved MAE | PARASOL mean | PARASOL MAE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AODf | 0.109 | 0.107 | 0.030 | 0.079 | 0.043 |
| AODf > 0.15 | 0.283 | 0.269 | 0.054 | 0.192 | 0.104 |
| AODf < 0.15 | 0.055 | 0.057 | 0.023 | 0.044 | 0.024 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Qie, L.; Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Wang, Y.; Ye, Z. Retrieval of the Fine-Mode Aerosol Optical Depth over East China Using a Grouped Residual Error Sorting (GRES) Method from Multi-Angle and Polarized Satellite Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111838
Zhang Y, Li Z, Liu Z, Zhang J, Qie L, Xie Y, Hou W, Wang Y, Ye Z. Retrieval of the Fine-Mode Aerosol Optical Depth over East China Using a Grouped Residual Error Sorting (GRES) Method from Multi-Angle and Polarized Satellite Data. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(11):1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111838
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yang, Zhengqiang Li, Zhihong Liu, Juan Zhang, Lili Qie, Yisong Xie, Weizhen Hou, Yongqian Wang, and Zhixiang Ye. 2018. "Retrieval of the Fine-Mode Aerosol Optical Depth over East China Using a Grouped Residual Error Sorting (GRES) Method from Multi-Angle and Polarized Satellite Data" Remote Sensing 10, no. 11: 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111838
APA StyleZhang, Y., Li, Z., Liu, Z., Zhang, J., Qie, L., Xie, Y., Hou, W., Wang, Y., & Ye, Z. (2018). Retrieval of the Fine-Mode Aerosol Optical Depth over East China Using a Grouped Residual Error Sorting (GRES) Method from Multi-Angle and Polarized Satellite Data. Remote Sensing, 10(11), 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10111838