Radiometric Microwave Indices for Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Relationships between Microwave Emission and Land Surface Parameters
2.1. Non Vegetated Land Surfaces
2.2. Vegetation
2.3. Snow
3. Model Simulations
3.1. Soil and Vegetation
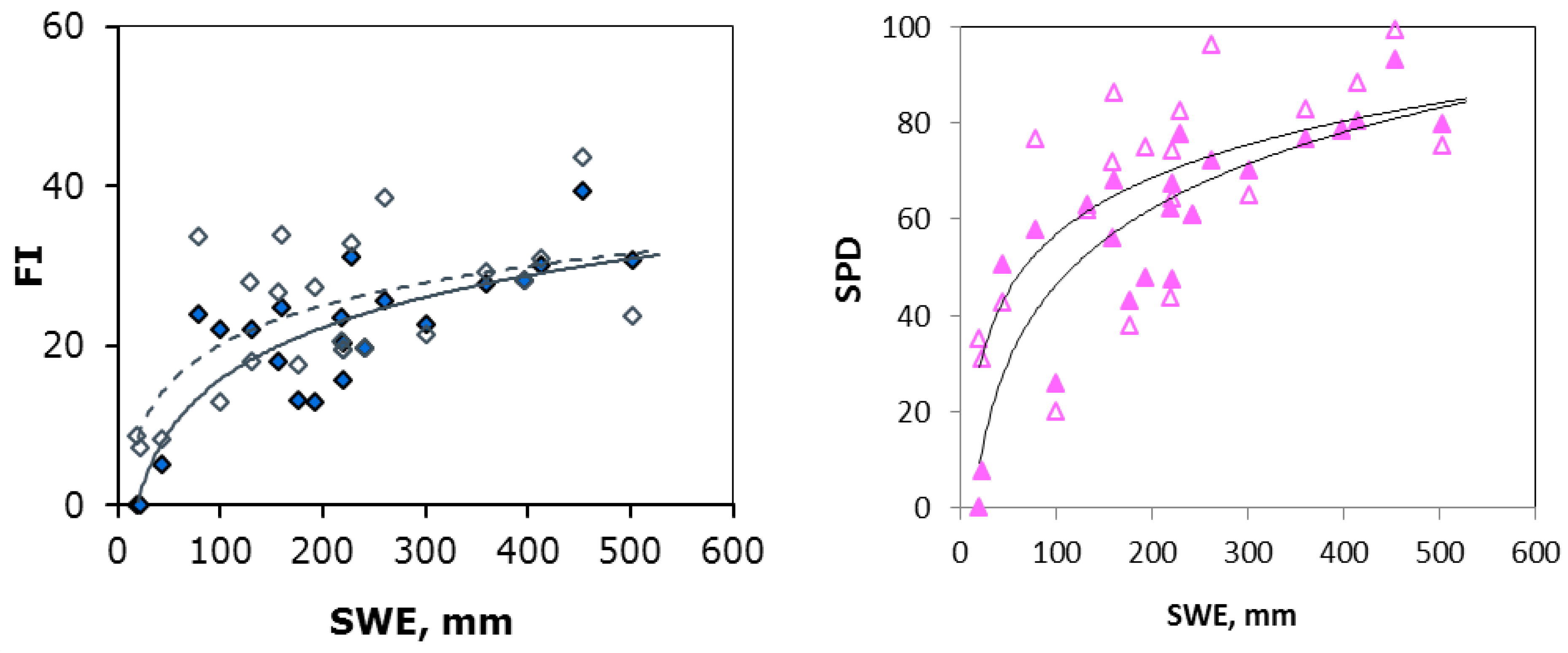
3.2. Snow
4. Observation from Satellite
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hollinger, J.; Lo, R.; Poe, G.; Savage, R.; Pierce, J. Special Sensor Microwave/Imager User’s Guide; Naval Res. Lab: Washington, DC, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive; Addison-Wesley: Reading, MA, USA, 1982; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Ulaby, F.T.; Moore, R.K.; Fung, A.K. Microwave Remote Sensing: Active and Passive. Vol III; Artech House: Nordwood, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P. Microwave Polarization Index for Monitoring Vegetation Growth. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1988, 26, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.J. Monitoring global land surface using Nimbus-7 37 GHz. Theory and examples. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 1579–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Choudhury, B. Remote sensing of soil moisture content over bare fields at 1.4 GHz frequency. J. Geophys. Res. 1981, 86, 5277–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirdiashev, K.P.; Chukhlantsev, A.A.; Shutko, A.M. Microwave radiation of the Earth’s surface in the presence of vegetation cover. Radio Eng. Electron. Phys. Engl. Transl. 1979, 24, 256–264. [Google Scholar]
- Chukhlantsev, A.A. Microwave Radiometry of Vegetation Canopies; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Neale, C.M.U.; Farland, M.J.M.; Chang, K. Land surface type classification using microwave brightness temperatures from the SMM/I. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1990, 28, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P. Microwave Vegetation Indexes for detecting biomass and water conditions of agricultural crops. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 40, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Jackson, T.; Tao, J.; Du, J.; Bindlish, R.; Lu, L.; Chen, K.S. Microwave vegetation indices for short vegetation covers from satellite passive microwave sensor AMSR-E. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 4285–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallikainen, M.T.; Jolma, P.A. Comparison of algorithms for retrieval of snow water equivalent from Nimbus-7 SMMR data in Finland. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallikainen, M.T. Retrieval of snow water equivalent from Nimbus-7 SMMR data: Effect of land-cover categories and weather conditions. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1984, 9, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Chang, A.T.C. Development of a passive microwave global snow depth retrieval algorithm for Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) and Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-EOS (AMSR-E) data. Radio Sci. 2003, 38, 8076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.C.; Foster, J.L.; Hall, D.K.; Rango, A.; Hartline, B.K. Snow water equivalent estimation by microwave radiometry. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 1982, 5, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.L.; Chang, A.T.C.; Hall, D.K. Comparison of snow mass estimates from a prototype passive microwave snow algorithm, a revised algorithm and a snow depth climatology. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschbacher, J. Microwave Signatures from Land surface Radiometry. In Proceedings of the 10th Annual International Symposium on Geoscience and Remote Sensing IGARSS 1990, College Park, MD, USA, 20–24 May 1990; pp. 1149–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Tsutsui, H.; Koike, T. Development of Snow Retrieval Algorithm Using AMSR-E for the BJ Ground-Based Station on Seasonally Frozen Ground at Low Altitude on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 2012, 90, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P.; Chiarantini, L.; Coppo, P.; Gagliani, S.; Luzi, G. Multifrequency passive microwave remote sensing of soil moisture and roughness. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, B.J.; Schmugge, T.J.; Chang, A.; Newton, R.W. Effect of Surface Roughness on the Microwave Emission from Soils. J. Geophys. Res. 1979, 84, 5699–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppo, P.; Luzi, G.; Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P. Effect of soil roughness on microwave emission: Comparison between experimental data and model. In Proceedings of the Remote Sensing: Global Monitoring for Earth Management, IGARSS ’91, Espoo, Finland, 3–6 June 1991; pp. 1167–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmuller, U.; Maetzler, C. Rough bare soil reflectivity model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1999, 37, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Weng, F. Modeling Land Surface Roughness Effect on Soil Microwave Emission in Community Surface Emissivity Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, T.; Choudhury, B.J.; Schmugge, T.J.; Wang, J.R.; Jackson, T.J. A model for microwave emission from vegetation-covered fields. J. Geophys. Res. 1982, 87, 11229–11237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrazzoli, P.; Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P.; Schiavon, G.; Solimini, D.; Coppo, P. Sensitivity of Microwave Measurements to Vegetation Biomass and Soil Moisture Content: A Case Study. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloscia, S. Microwave emission from vegetation. In Passive Microwave Remote Sensing of Land-Atmosphere Interactions; Choudhury, B., Njoku, E., Kerr, Y., Pampaloni, P., Eds.; VSP Press: Zeist, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 358–374. [Google Scholar]
- Santi, E.; Pettinato, S.; Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P.; Macelloni, G.; Brogioni, M. An algorithm for generating soil moisture and snow depth maps from microwave spaceborne radiometers: HydroAlgo. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 3659–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P.; Pettinato, S.; Tomoyuki, N.; Seki, M.; Sekiya, K.; Maeda, T. Vegetation Water Content Retrieval by Means of Multifrequency Microwave Acquisitions from AMSR2. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2017, 10, 3861–3873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunzi, K.F.; Fisher, A.D.; Staelin, D.H.; Waters, J.W. Snow and ice surfaces measured by the Nimbus 5 microwave spectrometer. J. Geophys Res. 1976, 81, 4965–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofer, R.; Mätzler, C. Investigation of snow parameters by radiometry in the 3- to 60-mm wavelength region. J. Geophys. Res. 1980, 85, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.Q.; Kong, J.A. Strong fluctuation theory of electromagnetic wave scattering by a layer of random discrete scatterers. J. Appl. Phys. 1984, 55, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Walker, J.P.; Houser, P.R. Factors affecting remotely sensed snow water equivalent uncertainty. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markus, T.; Powell, D.C.; Wang, J.R. Sensitivity of passive microwave snow depth retrievals to weather effects and snow evolution. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, A.; Royer, A.; Derksen, C.; Montpetit, B.; Dupont, F.; Goïta, K. Coupling the snow thermodynamic model SNOWPACK with the microwave emission model of layered snowpacks for subarctic and arctic snow water equivalent retrievals. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanda, E.; Matzler, C.; Kunzi, K. Microwave remote sensing of snow cover. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1982, 4, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takala, M.; Luojus, K.; Pulliainen, J.; Derksen, C.; Lemmetyinen, J.; Kärnä, J.P.; Koskinen, J.; Bojkov, B. Estimating northern hemisphere snow water equivalent for climate research through assimilation of space-borne radiometer data and ground-based measurements. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3517–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tait, A.B. Estimation of Snow Water Equivalent Using Passive Microwave Radiation Data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1988, 64, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P.; Pettinato, S.; Brogioni, M.; Xiong, C.; Crepaz, A. Analysis of Microwave Emission and Related Indices Over Snow using Experimental Data and a Multilayer Electromagnetic Model. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 99, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rott, H.; Aschbacher, J. On the use of satellite microwave radiometers for large-scale hydrology. In Proceedings of the IAHS 3rd International Assembly on Remote Sensing and Large-Scale Global Processes, Baltimore, MD, USA, 10–19 May 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Chukhlantsev, A.A. Microwave Emission from Vegetation Canopies. Ph.D. Thesis, The Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology (State University), Moscow, Russia, 1981. (In Russian). [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, T.J.; Schmugge, T.J.; Wang, J.R. Passive microwave sensing of soil moisture under vegetation canopies. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pampaloni, P.; Paloscia, S. Microwave emission and plant water content: A comparison between field measurement and theory. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1986, 24, 900–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukhlantsev, A.A.; Golovachev, S.P.; Shutko, A.M. Experimental study of vegetable canopy microwave emission. Adv. Space Res. 1989, 9, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, L.; Pan, J.; Liang, D.; Li, Z.X.; Cline, D.; Tan, Y.H. Modeling active microwave remote sensing of snow using dense media radiative transfer (DMRT) theory with multiple scattering effects. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 990–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.D.; Chen, K.S. A Reappraisal of the Validity of the IEM Model for Backscattering from Rough Surfaces. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 743–753. [Google Scholar]
- Macelloni, G.; Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P.; Santi, E. Global scale monitoring of soil and vegetation using active and passive sensors. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2409–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, E.; Paloscia, S.; Pettinato, S.; Brocca, L.; Ciabatta, L. Robust Assessment of an Operational Algorithm for the Retrieval of Soil Moisture from AMSR-E Data in Central Italy. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 9, 2478–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

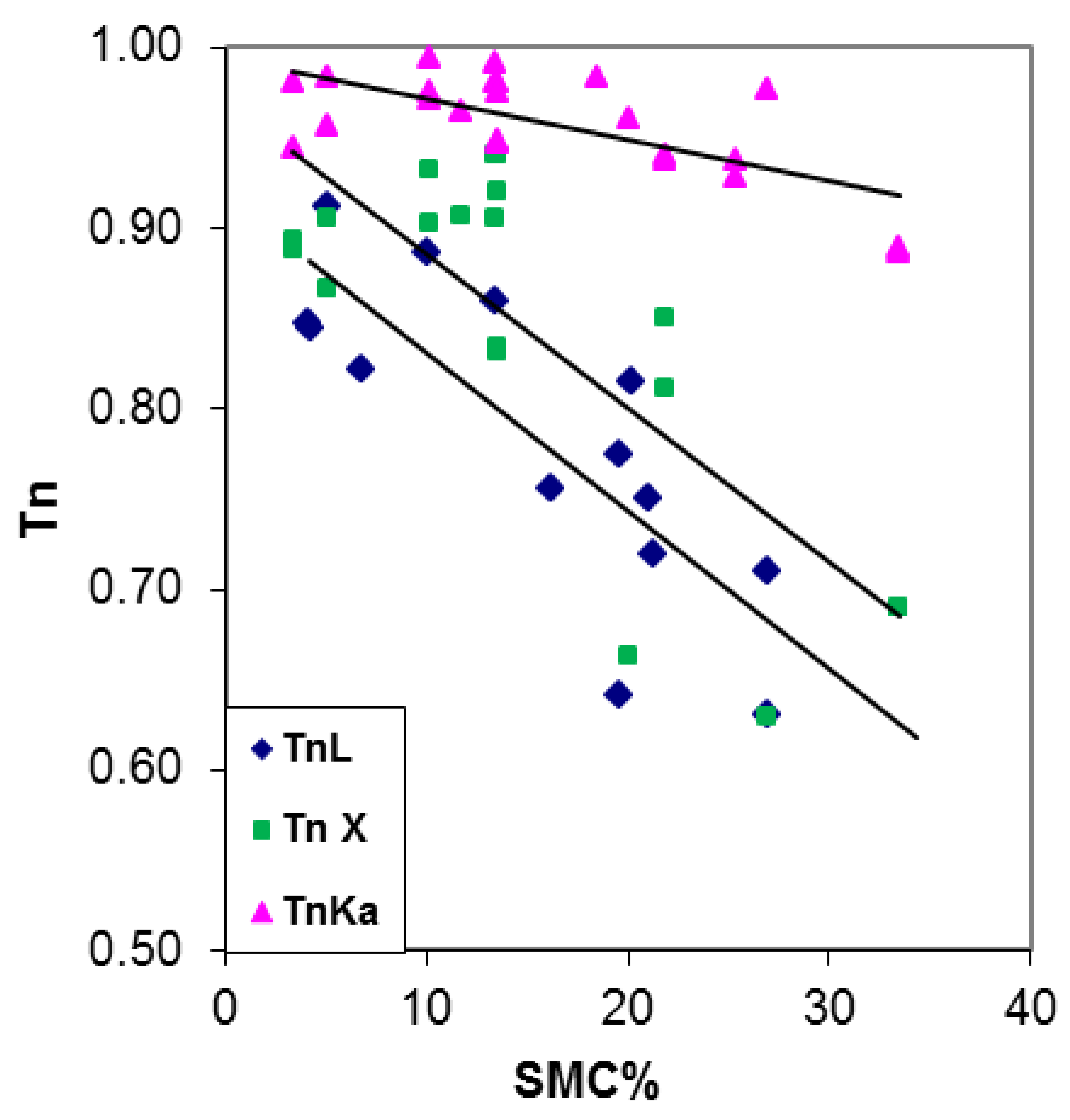
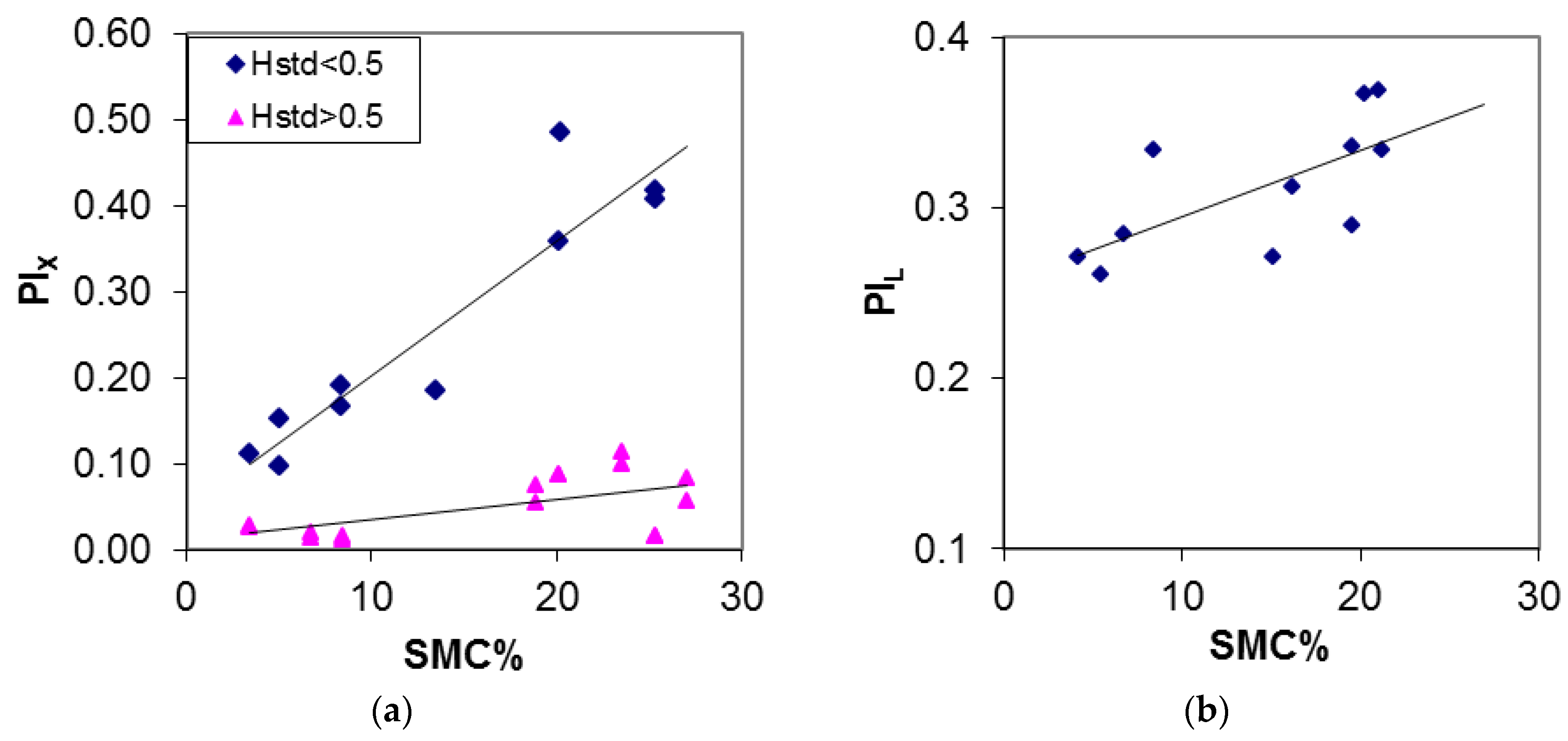
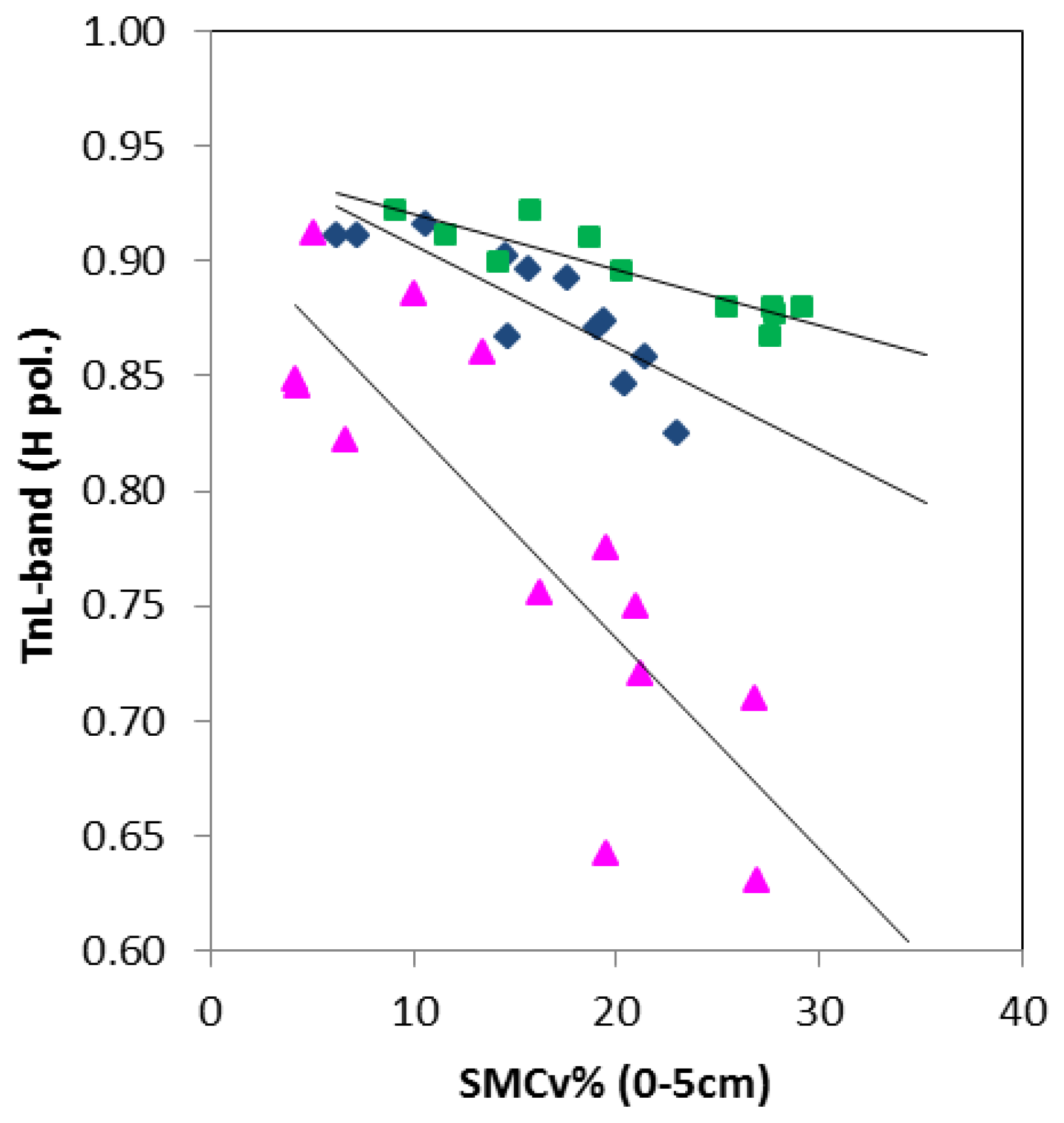
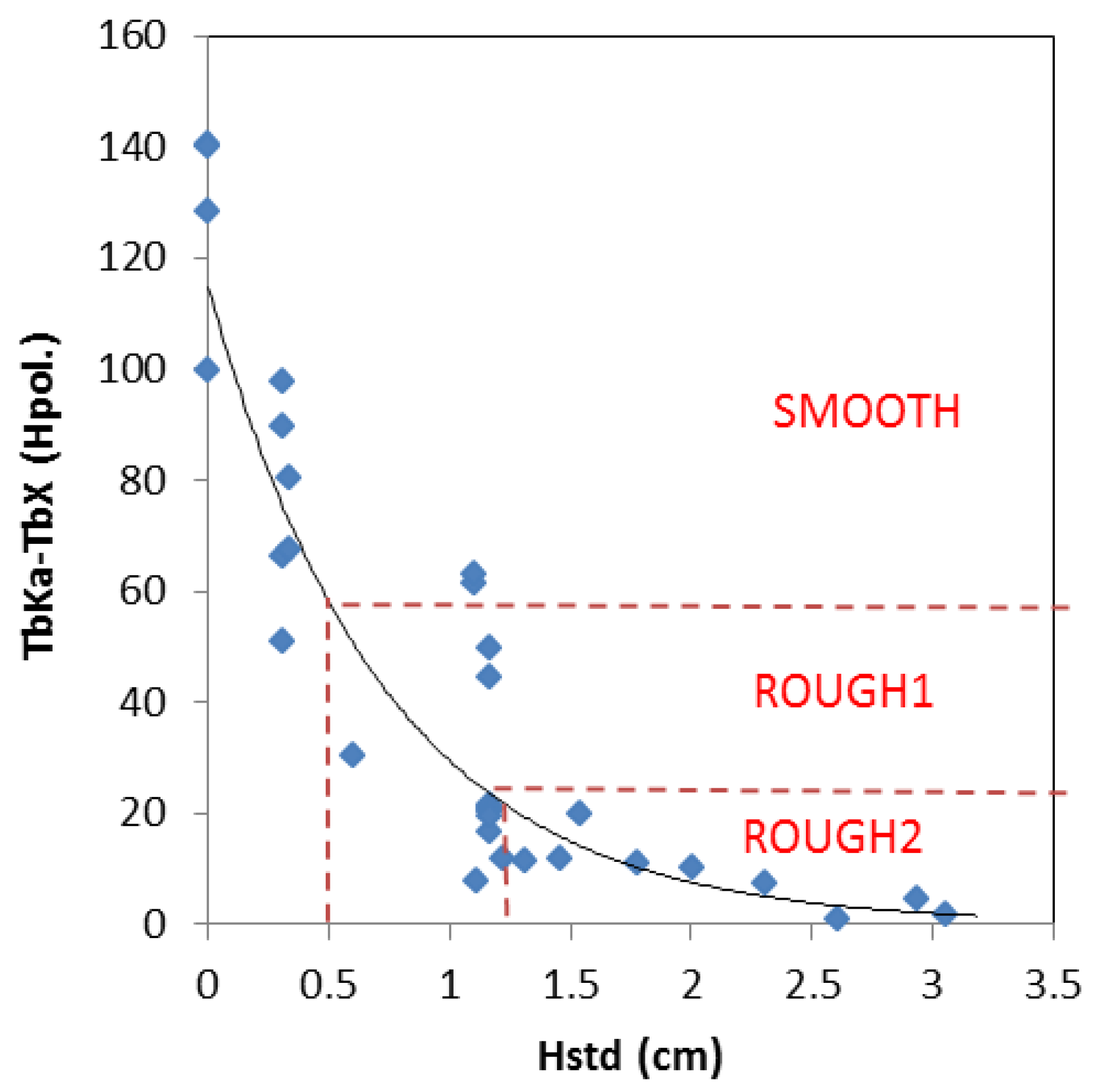
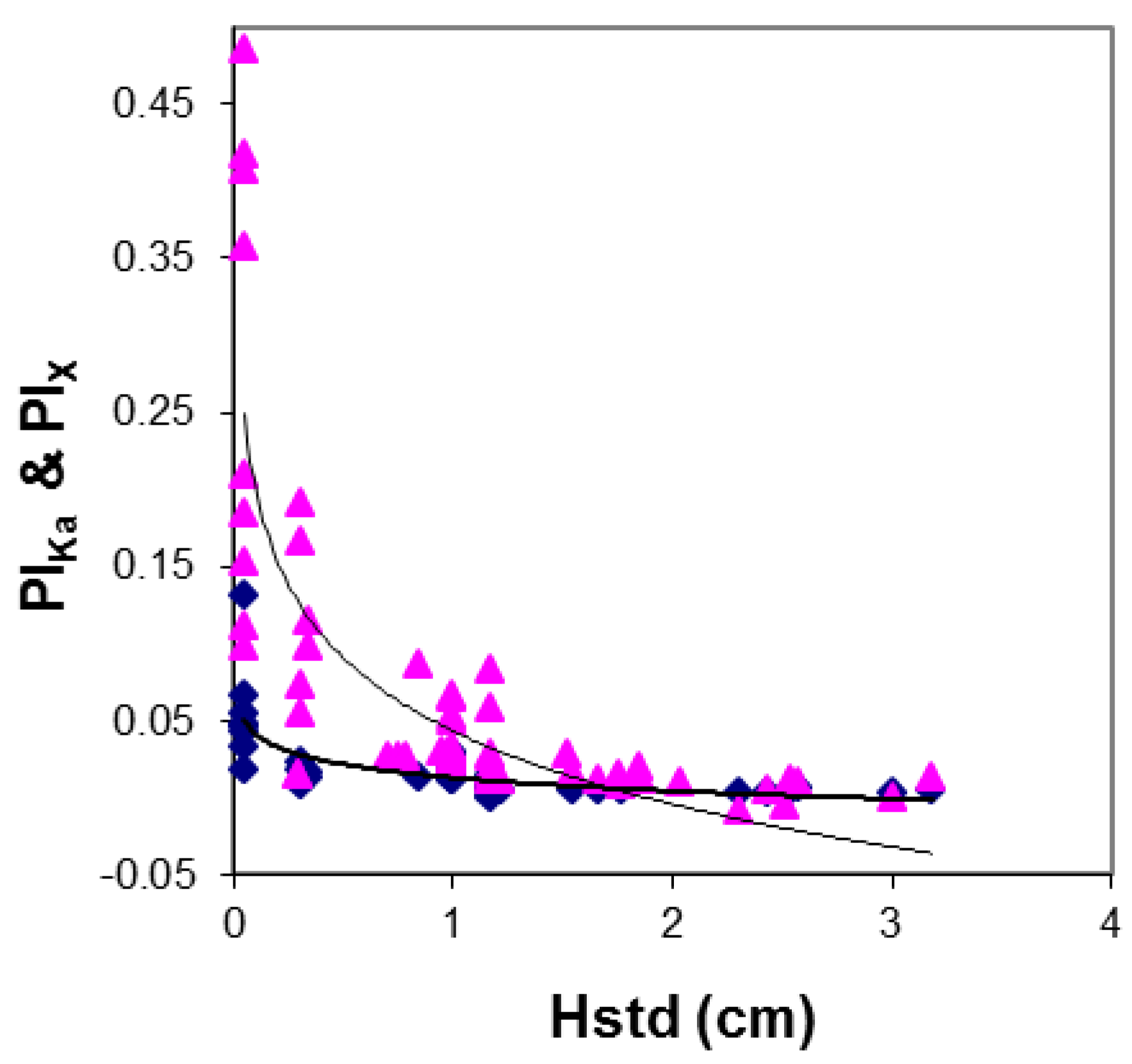
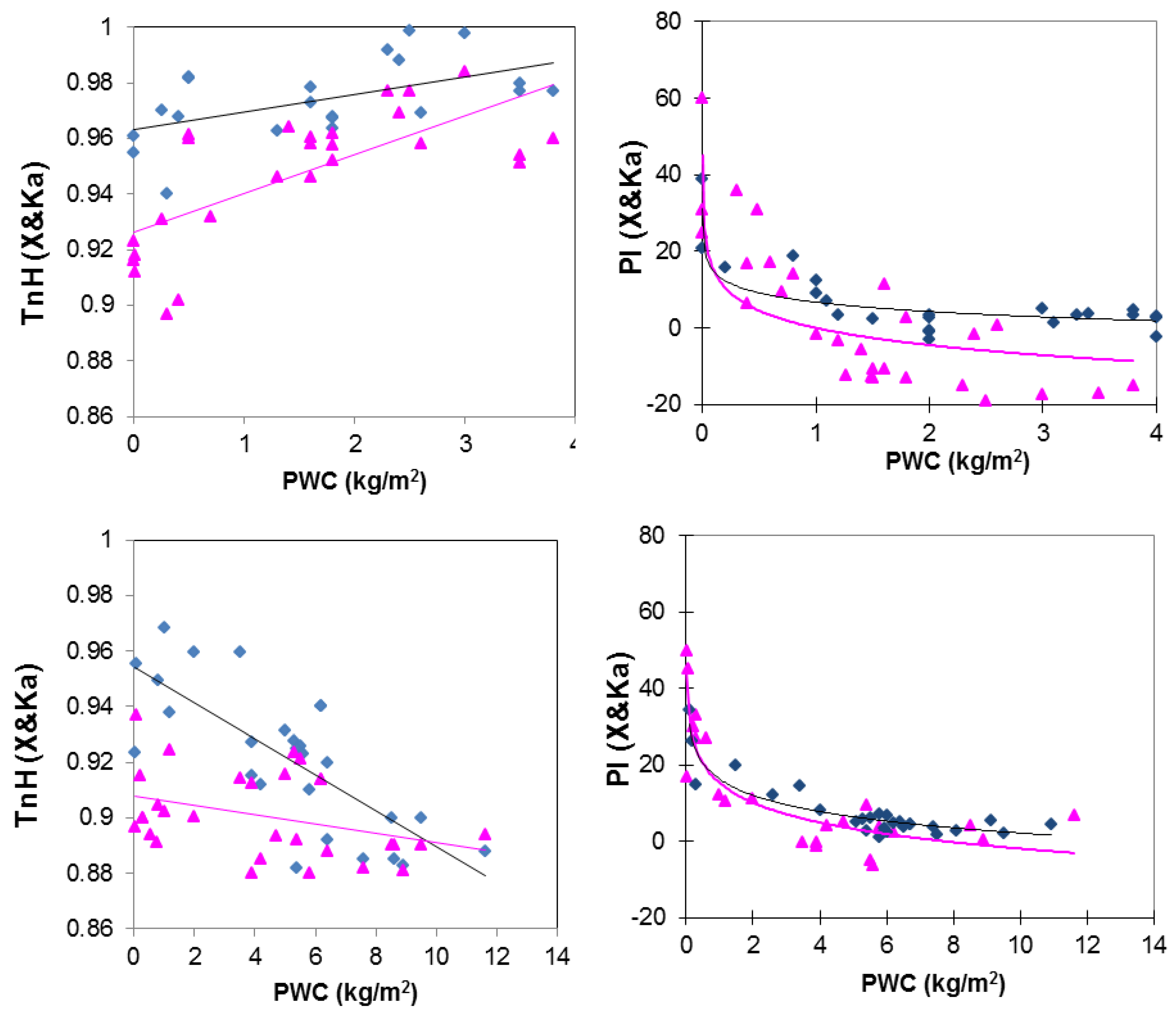
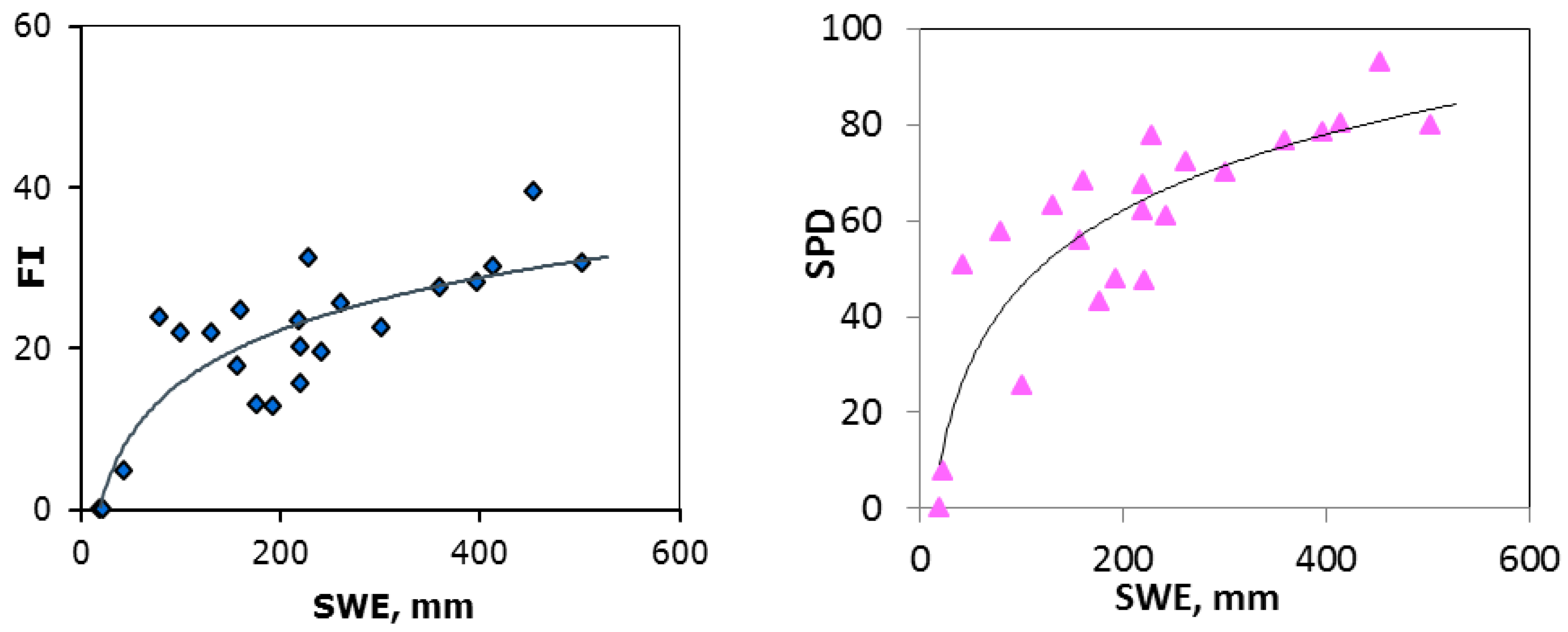

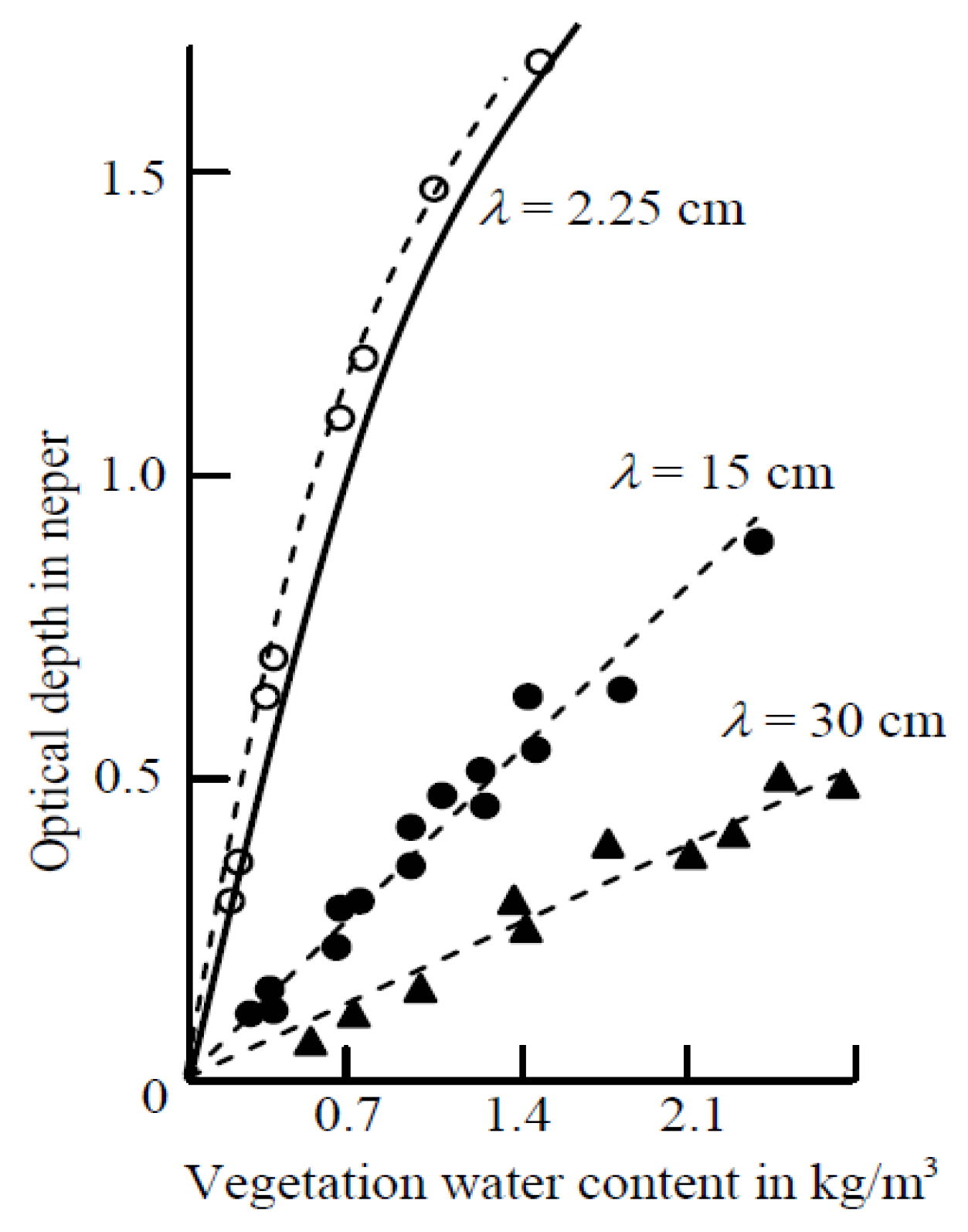

| Crop Type | Tn Regression Lines | R2 | PI Regression Lines | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narrow-leaf | TnX = 0.014PWC + 0.93 | 0.5 | PIX = −0.5ln(PWC) + 0.077 | 0.6 |
| Narrow-leaf | TnKa = 0.0063PWC + 0.96 | 0.3 | PIKa = −3.52ln(PWC) + 6.77 | 0.74 |
| Broad-leaf | TnX = −0.002PWC + 0.91 | 0.13 | PIX = −7.51ln(PWC) + 15.35 | 0.79 |
| Broad-leaf | TnKa = −0.0065PWC + 0.95 | 0.57 | PIKa = −6.17ln(PWC) + 16.34 | 0.85 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paloscia, S.; Pampaloni, P.; Santi, E. Radiometric Microwave Indices for Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121859
Paloscia S, Pampaloni P, Santi E. Radiometric Microwave Indices for Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces. Remote Sensing. 2018; 10(12):1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121859
Chicago/Turabian StylePaloscia, Simonetta, Paolo Pampaloni, and Emanuele Santi. 2018. "Radiometric Microwave Indices for Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces" Remote Sensing 10, no. 12: 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121859
APA StylePaloscia, S., Pampaloni, P., & Santi, E. (2018). Radiometric Microwave Indices for Remote Sensing of Land Surfaces. Remote Sensing, 10(12), 1859. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10121859






